



生物多样性 ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (8): 25037. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025037 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2025037
吉晟男1,2, 韩佳蓉3, 任月恒1, 穆晓东2, 朱彦鹏1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-01-24
接受日期:2025-04-12
出版日期:2025-08-20
发布日期:2025-09-17
通讯作者:
*E-mail: zhuyp@craes.org.cn
基金资助:
Shengnan Ji1,2, Jiarong Han3, Yueheng Ren1, Xiaodong Mu2, Yanpeng Zhu1,*( )
)
Received:2025-01-24
Accepted:2025-04-12
Online:2025-08-20
Published:2025-09-17
Contact:
*E-mail: zhuyp@craes.org.cn
Supported by:摘要:
外来入侵植物对生态系统、生物多样性和人类社会构成了严重威胁。海南岛作为我国生物多样性最丰富的地区之一, 面临着外来入侵植物的潜在危害。为评估重点管理外来入侵物种在海南岛的潜在适生区及其入侵风险, 本研究基于农业农村部等六部委最新发布的《重点管理外来入侵物种名录》中的33种入侵植物, 利用最大熵(MaxEnt)模型与地理信息系统(GIS)技术, 对物种分布数据和环境因子进行了综合分析。结果显示, 共有25种入侵植物在海南岛具有不同程度的适生区, 其中假高粱(Sorghum halepense)、飞机草(Chromolaena odorata)、刺苋(Amaranthus spinosus)和马缨丹(Lantana camara) 4个物种的适生区面积均占海南岛总面积的50%以上, 风险等级最高。入侵热点主要集中在海南岛东北部低海拔平原和部分沿海区域, 人类活动强度、温度季节性、平均昼夜温差和最暖季降水量是影响其分布的主要因素。结合结果分析, 本研究建议加强对高风险区域和高风险物种的精准监测和综合防控, 同时将社会环境因素及生物互作机制纳入后续研究, 以进一步提升对外来入侵植物的预警能力并制定科学高效的防控策略。
吉晟男, 韩佳蓉, 任月恒, 穆晓东, 朱彦鹏 (2025) 基于MaxEnt模型预测海南岛重点管理外来入侵植物适生区及其入侵风险. 生物多样性, 33, 25037. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025037.
Shengnan Ji, Jiarong Han, Yueheng Ren, Xiaodong Mu, Yanpeng Zhu (2025) Prediction of suitable habitats and risk assessment for key invasive alien plant species on Hainan Island based on the MaxEnt model. Biodiversity Science, 33, 25037. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025037.
| 风险等级 Risk level | 物种 Species | 分布点数 Distribution point | 海南岛适生面积比例 Suitability area ratio on Hainan Island (AR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 高风险 High-risk (0.5 ≤ AR < 1.0) | 假高粱 Sorghum halepense | 244 | 0.8641 |
| 飞机草 Chromolaena odorata | 2,005 | 0.7521 | |
| 刺苋 Amaranthus spinosus | 789 | 0.5449 | |
| 马缨丹 Lantana camara | 3,874 | 0.5394 | |
| 中风险 Middle-risk (0.3 ≤ AR < 0.5) | 银胶菊 Parthenium hysterophorus | 1,370 | 0.4846 |
| 藿香蓟 Ageratum conyzoides | 44 | 0.4482 | |
| 五爪金龙 Ipomoea cairica | 4,071 | 0.4230 | |
| 凤眼蓝 Eichhornia crassipes | 995 | 0.4044 | |
| 假臭草 Praxelis clematidea | 1,167 | 0.3137 | |
| 低风险 Low-risk (0.1 ≤ AR < 0.3) | 大薸 Pistia stratiotes | 715 | 0.2981 |
| 小蓬草 Erigeron canadensis | 1,315 | 0.1734 | |
| 极低风险 Minimal-risk (0 ≤ AR < 0.1) | 三叶鬼针草 Bidens pilosa | 6,145 | 0.0739 |
| 空心莲子草 Alternanthera philoxeroides | 1,370 | 0.0647 | |
| 紫茎泽兰 Ageratina adenophora | 68 | 0.0615 | |
| 光荚含羞草 Mimosa bimucronata | 52 | 0.0486 | |
| 毒莴苣 Lactuca serriola | 25 | 0.0294 | |
| 垂序商陆 Phytolacca americana | 1,051 | 0.0276 | |
| 薇甘菊 Mikania micrantha | 4,726 | 0.0178 | |
| 互花米草 Spartina alterniflora | 47 | 0.0076 | |
| 野燕麦 Avena fatua | 176 | 0.0039 | |
| 落葵薯 Anredera cordifolia | 1,176 | 0.0018 | |
| 苏门白酒草 Erigeron sumatrensis | 2,882 | 0.0008 | |
| 水盾草 Cabomba caroliniana | 23 | 0.0000 | |
| 加拿大一枝黄花 Solidago canadensis | 149 | 0.0000 | |
| 豚草 Ambrosia artemisiifolia | 137 | 0.0000 |
表1 海南岛25种重点管理外来入侵植物适生区面积比例及风险分级
Table 1 Proportion of suitable habitat area and risk classification for 25 key invasive alien plant species on Hainan Island
| 风险等级 Risk level | 物种 Species | 分布点数 Distribution point | 海南岛适生面积比例 Suitability area ratio on Hainan Island (AR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 高风险 High-risk (0.5 ≤ AR < 1.0) | 假高粱 Sorghum halepense | 244 | 0.8641 |
| 飞机草 Chromolaena odorata | 2,005 | 0.7521 | |
| 刺苋 Amaranthus spinosus | 789 | 0.5449 | |
| 马缨丹 Lantana camara | 3,874 | 0.5394 | |
| 中风险 Middle-risk (0.3 ≤ AR < 0.5) | 银胶菊 Parthenium hysterophorus | 1,370 | 0.4846 |
| 藿香蓟 Ageratum conyzoides | 44 | 0.4482 | |
| 五爪金龙 Ipomoea cairica | 4,071 | 0.4230 | |
| 凤眼蓝 Eichhornia crassipes | 995 | 0.4044 | |
| 假臭草 Praxelis clematidea | 1,167 | 0.3137 | |
| 低风险 Low-risk (0.1 ≤ AR < 0.3) | 大薸 Pistia stratiotes | 715 | 0.2981 |
| 小蓬草 Erigeron canadensis | 1,315 | 0.1734 | |
| 极低风险 Minimal-risk (0 ≤ AR < 0.1) | 三叶鬼针草 Bidens pilosa | 6,145 | 0.0739 |
| 空心莲子草 Alternanthera philoxeroides | 1,370 | 0.0647 | |
| 紫茎泽兰 Ageratina adenophora | 68 | 0.0615 | |
| 光荚含羞草 Mimosa bimucronata | 52 | 0.0486 | |
| 毒莴苣 Lactuca serriola | 25 | 0.0294 | |
| 垂序商陆 Phytolacca americana | 1,051 | 0.0276 | |
| 薇甘菊 Mikania micrantha | 4,726 | 0.0178 | |
| 互花米草 Spartina alterniflora | 47 | 0.0076 | |
| 野燕麦 Avena fatua | 176 | 0.0039 | |
| 落葵薯 Anredera cordifolia | 1,176 | 0.0018 | |
| 苏门白酒草 Erigeron sumatrensis | 2,882 | 0.0008 | |
| 水盾草 Cabomba caroliniana | 23 | 0.0000 | |
| 加拿大一枝黄花 Solidago canadensis | 149 | 0.0000 | |
| 豚草 Ambrosia artemisiifolia | 137 | 0.0000 |
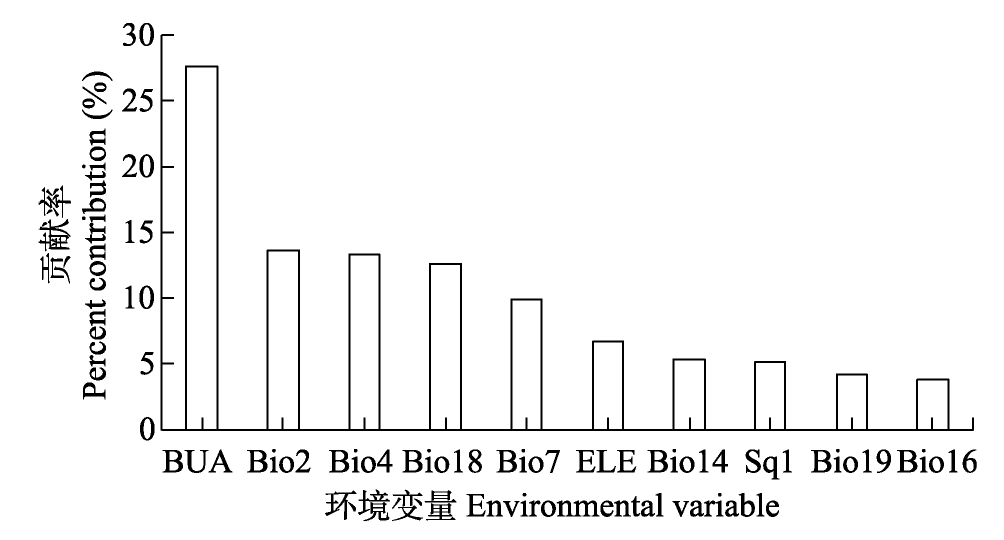
图3 环境变量对海南岛重点管理外来入侵植物潜在适生区的平均贡献率(只展示排名前10的环境变量)。BUA: 建设用地面积; ELE: 海拔; Sq1: 营养供应; Bio2: 平均昼夜温差; Bio4: 温度季节性; Bio7: 年温度变化范围; Bio14: 最干月降水量; Bio16: 最湿季降水量; Bio18: 最暖季降水量; Bio19: 最冷季降水量。
Fig. 3 Mean percentage contribution of environmental variables to potential suitable habitats of key invasive alien plant species on Hainan Island (only the top 10 contributing environmental variables shown). BUA, Built-up area; ELE, Elevation; Sq1, Nutrient availability; Bio2, Mean diurnal range; Bio4, Temperature seasonality; Bio7, Temperature annual range; Bio14, Precipitation of driest month; Bio16, Precipitation of wettest quarter; Bio18, Precipitation of warmest quarter; Bio19, Precipitation of coldest quarter.
| [1] |
Allouche O, Tsoar A, Kadmon R (2006) Assessing the accuracy of species distribution models: Prevalence, kappa and the true skill statistic (TSS). Journal of Applied Ecology, 43, 1223-1232.
DOI URL |
| [2] | Asif M, Ayub M, Tanveer A, Akhtar J (2017) Estimating yield losses and economic threshold level of Parthenium hysterophorus in forage sorghum. Planta Daninha, 35, e017164158. |
| [3] |
Atwater DZ, Barney JN (2021) Climatic niche shifts in 815 introduced plant species affect their predicted distributions. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 30, 1671-1684.
DOI URL |
| [4] | Chen J, Ma FZ, Zhang YJ, Wang CB, Xu HG (2021) Spatial distribution patterns of invasive alien species in China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 26, e01432. |
| [5] |
Chen YK, Yang XB, Li DH, Long WX (2016) Status of vascular plant species on Hainan Island. Biodiversity Science, 24, 948-956. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[陈玉凯, 杨小波, 李东海, 龙文兴 (2016) 海南岛维管植物物种多样性的现状. 生物多样性, 24, 948-956.]
DOI |
|
| [6] |
Chu QS, Liu YJ, Peng CY, Zhang YL, Cernava T, Qiong L, Zhou YH, Siddiqui AJ, Ghani MI, Wang QR, Liu Y, Chen XYL (2024) Invasive alien plants in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau (China): Current state and future predictions. Ecological Indicators, 166, 112488.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Cui S, Zhang H, Liu L, Lyu W, Xu L, Zhang Z, Han Y (2024) Hypervolume niche dynamics and global invasion risk of Phenacoccus solenopsis under climate change. Insects, 15, 250.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Dawson W, Moser D, van Kleunen M, Kreft H, Pergl J, Pyšek P, Weigelt P, Winter M, Lenzner BM, Blackburn TE, Dyer E, Cassey PL, Scrivens SP, Economo E, Guénard B, Capinha C, Seebens H, García-Díaz P, Nentwig W, García-Berthou E, Casal CE, Mandrak N, Fuller P, Meyer C, Essl F (2017) Global hotspots and correlates of alien species richness across taxonomic groups. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 1, 186. |
| [9] |
Dong BC, Dong R, Yang Q, Kinlock NL, Yu FH, van Kleunen M (2025) Predicting invasion success of naturalized cultivated plants in China. Journal of Applied Ecology, 62, 651-660.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Dong BC, Yang Q, Kinlock NL, Pouteau R, Pyšek P, Weigelt P, Yu FH, van Kleunen M (2024) Naturalization of introduced plants is driven by life-form-dependent cultivation biases. Diversity and Distributions, 30, 55-70.
DOI URL |
| [11] | Gaertner M, Den Breeyen A, Hui C, Richardson DM (2009) Impacts of alien plant invasions on species richness in Mediterranean-type ecosystems: A meta-analysis. Progress in Physical Geography, 33, 319-338. |
| [12] |
Guerra-Coss FA, Badano EI, Cedillo-Rodríguez IE, Ramírez-Albores JE, Flores J, Barragán-Torres F, Flores-Cano JA (2021) Modelling and validation of the spatial distribution of suitable habitats for the recruitment of invasive plants on climate change scenarios: An approach from the regeneration niche. Science of the Total Environment, 777, 146007.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Gong Z, Peng ZQ, Ma GC, Wan FH, Sun JH, Hu MJ, Fan ZW, Jin T, Wen HB (2022) Prevention and control of alien invasive species in Hainan under the background of free trade port. Plant Protection, 48, 221-231. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [龚治, 彭正强, 马光昌, 万方浩, 孙江华, 胡美姣, 范志伟, 金涛, 温海波 (2022) 自由贸易港背景下的海南外来入侵生物防控探讨. 植物保护, 48, 221-231.] | |
| [14] |
Harun I, Pushiri H, Amirul-Aiman AJ, Zulkeflee Z (2021) Invasive water hyacinth: Ecology, impacts, and prospects for the rural economy. Plants, 10, 1613.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Hong SH, Lee YH, Lee G, Lee DH, Adhikari P (2021) Predicting impacts of climate change on northward range expansion of invasive weeds in South Korea. Plants, 10, 1604.
DOI URL |
| [16] | Huang QQ, Shen YD, Li XX, Fan ZW (2016) Research progress on the mechanisms of invasion and spread of typical harmful plants in Hainan. Journal of Biosafety, 25(1), 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄乔乔, 沈奕德, 李晓霞, 范志伟 (2016) 海南典型有害植物的入侵扩散机理研究进展. 生物安全学报, 25(1), 1-6.] | |
| [17] | Iqbal U, Usman Z, Azam A, Abbas H, Mehmood A, Ahmad KS (2023) Invasive success of star weed (Parthenium hysterophorus L.) through alteration in structural and functional peculiarities. PeerJ, 11, e16609. |
| [18] | Jiang C, Jia JH, Yang Y, Sheng R, Ren LJ, Ji HH, Ye SF (2024) Forty years of Spartina alterniflora in China: Cognitive evolution and governance strategies. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 44, 8944-8956. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [江灿, 贾俊鹤, 杨颖, 盛蓉, 任璘婧, 纪焕红, 叶属峰 (2024) 互花米草在中国的40年: 认知演变与治理对策. 生态学报, 44, 8944-8956.] | |
| [19] |
Kaur A, Kaur S, Singh HP, Batish DR, Kohli RK (2019) Phenotypic variations alter the ecological impact of invasive alien species: Lessons from Parthenium hysterophorus. Journal of Environmental Management, 241, 187-197.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Li FF, Hao Q, Cui X, Ma JS (2024) Analysis and reflection of plant species in the Key Management List of Invasive Alien Species. Plant Science Journal, 42, 266-274. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李飞飞, 郝强, 崔夏, 马金双 (2024) 对《重点管理外来入侵物种名录》中植物物种的解析与思考. 植物科学学报, 42, 266-274.] | |
| [21] | Liao XJ, Ding SJ, Zhang BR, Feng YS (2003) A study on soil environmental geochemistry in the northeastern Hainan Province. Geology and Prospecting, 39(6), 68-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [廖香俊, 丁式江, 张本仁, 冯亚生 (2003) 海南省东北地区土壤环境地球化学研究. 地质与勘探, 39(6), 68-70.] | |
| [22] | Liu C, Wolter C, Xian W, Jeschke JM (2020) Most invasive species largely conserve their climatic niche. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 117, 23643-23651. |
| [23] |
Liu CR, White M, Newell G (2013) Selecting thresholds for the prediction of species occurrence with presence‐only data. Journal of Biogeography, 40, 778-789.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Luo WQ, Fu SH, Yang XB, Chen YK, Zhou W, Yang Q, Tao C, Zhou WS (2015) Distribution patterns of alien invasive plants and their influences on native plants of Hainan Island. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 39, 486-500. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[罗文启, 符少怀, 杨小波, 陈玉凯, 周威, 杨琦, 陶楚, 周文嵩 (2015) 海南岛入侵植物的分布特点及其对本地植物的影响. 植物生态学报, 39, 486-500.]
DOI |
|
| [25] | Lü JJ, Nong SQ (2020) Habitat characteristic and distribution of invasive plant Alternanthera philoxeroides in Hainan Province. Tropical Forestry, 48(4), 13-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吕洁杰, 农寿千 (2020) 海南省外来入侵植物空心莲子草的分布和生境特征. 热带林业, 48(4), 13-19.] | |
| [26] |
Marino C, Leclerc C, Bellard C (2022) Profiling insular vertebrates prone to biological invasions: What makes them vulnerable? Global Change Biology, 28, 1077-1090.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
McDowell WG, Byers JE (2019) High abundance of an invasive species gives it an outsized ecological role. Freshwater Biology, 64, 577-586.
DOI |
| [28] |
Merow C, Smith MJ, Silander JA Jr (2013) A practical guide to MaxEnt for modeling species’ distributions: What it does, and why inputs and settings matter. Ecography, 36, 1058-1069.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Muscarella R, Galante PJ, Soley-Guardia M, Boria RA, Kass JM, Uriarte M, Anderson RP (2014) ENMeval: An R package for conducting spatially independent evaluations and estimating optimal model complexity for MaxEnt ecological niche models. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 5, 1198-1205.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Nyasembe VO, Cheseto X, Kaplan F, Foster WA, Teal PEA, Tumlinson JH, Borgemeister C, Torto B (2015) The invasive American weed Parthenium hysterophorus can negatively impact malaria control in Africa. PLoS ONE, 10, e0137836. |
| [31] | Peng ZB, Wang CY, Jiang Y, Li JH, Mai QF, Jiang JS (2013) Alien invasion plants in Hainan Island and control measures. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 33(4), 52-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [彭宗波, 王春燕, 蒋英, 李建华, 麦全法, 蒋菊生 (2013) 海南岛外来植物入侵现状及防控策略研究. 热带农业科学, 33(4), 52-57.] | |
| [32] |
Phillips SJ, Anderson RP, Dudík M, Schapire RE, Blair ME (2017) Opening the black box: An open-source release of MaxEnt. Ecography, 40, 887-893.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Phillips SJ, Anderson RP, Schapire RE (2006) Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecological Modelling, 190, 231-259.
DOI URL |
| [34] | Poudel M, Adhikari P, Thapa K (2019) Biology and control methods of the alien invasive weed Mikania micrantha: A review. Environmental Contaminants Reviews, 2, 6-12. |
| [35] | Qin F, Han BC, Bussmann RW, Xue TT, Liang YF, Zhang WD, Liu Q, Chen TX, Yu SX (2024) Present status, future trends, and control strategies of invasive alien plants in China affected by human activities and climate change. Ecography, 2024, e06919. |
| [36] | Runghen R, Llopis-Belenguer C, McNeill MR, Dalla Riva GV, Stouffer DB (2023) Using network analysis to study and manage human-mediated dispersal of exotic species. Biological Invasions, 25, 3369-3389. |
| [37] |
Sardans J, Bartrons M, Margalef O, Gargallo-Garriga A, Janssens IA, Ciais P, Obersteiner M, Sigurdsson BD, Chen HYH, Peñuelas J (2017) Plant invasion is associated with higher plant-soil nutrient concentrations in nutrient‐poor environments. Global Change Biology, 23, 1282-1291.
DOI PMID |
| [38] |
Seebens H, Blackburn TM, Dyer EE, Genovesi P, Hulme PE, Jeschke JM, Pagad S, Pyšek P, Winter M, Arianoutsou M, Bacher S, Blasius B, Brundu G, Capinha C, Celesti-Grapow L, Dawson W, Dullinger S, Fuentes N, Jäger H, Kartesz J, Kenis M, Kreft H, Kühn I, Lenzner B, Liebhold A, Mosena A, Moser D, Nishino M, Pearman D, Pergl J, Rabitsch W, Rojas-Sandoval J, Roques A, Rorke S, Rossinelli S, Roy HE, Scalera R, Schindler S, Štajerova K, Tokarska-Guzik B, van Kleunen M, Walker K, Weigelt P, Yamanaka T, Essl F (2017) No saturation in the accumulation of alien species worldwide. Nature Communications, 8, 14435.
DOI PMID |
| [39] |
Takahashi D, Park YS (2020) Spatial heterogeneities of human-mediated dispersal vectors accelerate the range expansion of invaders with source-destination-mediated dispersal. Scientific Reports, 10, 21410.
DOI PMID |
| [40] | Tang SX, Zhao ZZ, Bi H, Xie GZ (2008) Analysis of characteristics and development of climate resources in Hainan. Journal of Hainan Normal University (Natural Science), 21, 343-346. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [唐少霞, 赵志忠, 毕华, 谢跟踪 (2008) 海南岛气候资源特征及其开发利用. 海南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 21, 343-346.] | |
| [41] |
Tu WQ, Xiong QL, Qiu XP, Zhang YM (2021) Dynamics of invasive alien plant species in China under climate change scenarios. Ecological Indicators, 129, 107919.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Vilà M, Espinar JL, Hejda M, Hulme PE, Jarošík V, Maron JL, Pergl J, Schaffner U, Sun Y, Pyšek P (2011) Ecological impacts of invasive alien plants: A meta-analysis of their effects on species, communities and ecosystems. Ecology Letters, 14, 702-708.
DOI PMID |
| [43] |
Walden-Schreiner C, Leung YF, Kuhn T, Newburger T, Tsai WL (2017) Environmental and managerial factors associated with pack stock distribution in high elevation meadows: Case study from Yosemite National Park. Journal of Environmental Management, 193, 52-63.
DOI PMID |
| [44] |
Wan FH, Guo JY, Wang DH (2002) Alien invasive species in China: Their damages and management strategies. Biodiversity Science, 10, 119-125. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[万方浩, 郭建英, 王德辉 (2002) 中国外来入侵生物的危害与管理对策. 生物多样性, 10, 119-125.]
DOI |
|
| [45] |
Wan JZ, Wang CJ, Tan JF, Yu FH (2017) Climatic niche divergence and habitat suitability of eight alien invasive weeds in China under climate change. Ecology and Evolution, 7, 1541-1552.
DOI URL |
| [46] | Wang BS, Zhang WY (2002) Groups and features of tropical forest vegetation of Hainan Island. Guihaia, 22, 107-115. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王伯荪, 张炜银 (2002) 海南岛热带森林植被的类群及其特征. 广西植物, 22, 107-115.] | |
| [47] | Wang Y (2002) Features of Hainan Island coastal environment. Marine Geology Letters, 18(3), 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王颖 (2002) 海南岛海岸环境特征. 海洋地质动态, 18(3), 1-9.] | |
| [48] |
Wang YS, Xie BY, Wan FH, Xiao QM, Dai LY (2007) Application of ROC curve analysis in evaluating the performance of alien species’ potential distribution models. Biodiversity Science, 15, 365-372. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[王运生, 谢丙炎, 万方浩, 肖启明, 戴良英 (2007) ROC曲线分析在评价入侵物种分布模型中的应用. 生物多样性, 15, 365-372.]
DOI |
|
| [49] |
Warren DL, Wright AN, Seifert SN, Shaffer HB (2014) Incorporating model complexity and spatial sampling bias into ecological niche models of climate change risks faced by 90 California vertebrate species of concern. Diversity and Distributions, 20, 334-343.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Wei B, Liu LS, Gu CJ, Yu HB, Zhang YL, Zhang BH, Cui BH, Gong DQ, Tu YL (2022) The climate niche is stable and the distribution area of Ageratina adenophora is predicted to expand in China. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21443. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[魏博, 刘林山, 谷昌军, 于海彬, 张镱锂, 张炳华, 崔伯豪, 宫殿清, 土艳丽 (2022) 紫茎泽兰在中国的气候生态位稳定且其分布范围仍有进一步扩展的趋势. 生物多样性, 30, 21443.]
DOI |
|
| [51] |
Xu HW, Liu Q, Wang SY, Yang GS, Xue S (2022) A global meta-analysis of the impacts of exotic plant species invasion on plant diversity and soil properties. Science of the Total Environment, 810, 152286.
DOI URL |
| [52] | Yang Y, Bian Z, Ren W, Wu J, Liu J, Shrestha N (2023) Spatial patterns and hotspots of plant invasion in China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 43, e02424. |
| [53] |
Zhang B, Hastings A, Grosholz ED, Zhai L (2023) The comparison of dispersal rate between invasive and native species varied by plant life form and functional traits. Movement Ecology, 11, 73.
DOI PMID |
| [54] | Zhang HS, Xu L, Lyu WW, Zhou Y, Wang WF, Gao RH, Cui SP, Zhang ZW (2023) Multidimensional climatic niche conservatism and invasion risk of Phenacoccus solenopsis. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 34, 1649-1658. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[张辉盛, 徐琳, 吕韦韦, 周昱, 王卫锋, 高瑞贺, 崔绍朋, 张志伟 (2023) 扶桑绵粉蚧多维气候生态位保守性与入侵风险. 应用生态学报, 34, 1649-1658.]
DOI |
|
| [55] |
Zhang HY, Goncalves P, Copeland E, Qi SS, Dai ZC, Li GL, Wang CY, Du DL, Thomas T (2020) Invasion by the weed Conyza canadensis alters soil nutrient supply and shifts microbiota structure. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 143, 107739.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Zhang JP, Miao L, Wu PL, Yang XT, Guo WY, Li SC, Feng G (2023) Effects of anthropogenic activities and climate factors on the distribution of invasive alien species in China. Scientia Sinica Vitae, 53, 543-550. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [张吉平, 苗露, 伍盘龙, 杨雪婷, 郭文永, 李士成, 冯刚 (2023) 人类活动和气候因子对中国外来入侵物种分布的影响. 中国科学: 生命科学, 53, 543-550.] |
| [1] | 周铝, 郭画, 姚世贸, 田成. 王朗国家级自然保护区红腹角雉时空分布模式[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(7): 24537-. |
| [2] | 王艳丽, 张英, 戚春林, 张昌达, 史佑海, 杜彦君, 丁琼. 海南热带雨林国家公园生物多样性热点与保护空缺区域识别: 基于大型真菌与植物视角[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24081-. |
| [3] | 董廷玮, 黄美玲, 韦旭, 马硕, 岳衢, 刘文丽, 郑佳鑫, 王刚, 马蕊, 丁由中, 薄顺奇, 王正寰. 上海地区金线侧褶蛙种群的潜在空间分布格局及其景观连通性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 22692-. |
| [4] | 刘伟, 王濡格, 范天巧, 娜依曼·阿不都力江, 宋新航, 肖书平, 郭宁, 帅凌鹰. 福建省明溪县黑冠鹃隼生境适宜性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22660-. |
| [5] | 鲍虞园, 李银康, 林吴颖, 周志琴, 肖晓波, 颉晓勇. 中国南海北部近海鲎资源调查及北部湾潮间带中华鲎幼鲎潜在栖息地评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22407-. |
| [6] | 肖俞, 李宇然, 段禾祥, 任正涛, 冯圣碧, 姜志诚, 李家华, 张品, 胡金明, 耿宇鹏. 高黎贡山外来植物入侵现状及管控建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 23011-. |
| [7] | 邓昶, 郝杰威, 高德, 任明迅, 张莉娜. 海南受威胁苔藓植物适生热点区域识别与保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22580-. |
| [8] | 崔夏, 刘全儒, 吴超然, 何宇飞, 马金双. 京津冀外来入侵植物[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 21497-. |
| [9] | 郭朝丹, 赵彩云, 李飞飞, 李俊生. 天然林和人工林外来入侵和本地植物对比研究: 以弄岗国家级自然保护区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21356-. |
| [10] | 赵琦, 蒋际宝, 张曾鲁, 金清, 李佳丽, 邱江平. 海南岛蚯蚓物种组成及其系统发育分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22224-. |
| [11] | 施雨含, 任宗昕, 王维嘉, 徐鑫, 刘杰, 赵延会, 王红. 中国-喜马拉雅三种黄耆属植物与其传粉熊蜂的空间分布预测[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(6): 759-769. |
| [12] | 郭朝丹, 朱金方, 柳晓燕, 赵彩云, 李俊生. 贵州典型自然保护区内外外来入侵草本植物的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 596-604. |
| [13] | 郝希阳, 贺姹, 楚克林, 申志新, 赵强, 高伟, 潘达, 孙红英. 海南岛淡水蟹类分布格局与多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 605-616. |
| [14] | 韩雪, 苏锦权, 姚娜娜, 陈宝明. 外来入侵植物的根系觅养行为研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(6): 727-733. |
| [15] | 邓亨宁, 鞠文彬, 高云东, 张君议, 李诗琦, 高信芬, 徐波. 新建川藏铁路(雅安-昌都段)沿线外来入侵植物种类及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(10): 1174-1181. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()