



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 22531. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022531 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022531
所属专题: 昆虫多样性与生态功能
江建平1,*( ), 杜诚2, 刘冰3,*(
), 杜诚2, 刘冰3,*( ), 王科4, 蔡磊4,*(
), 王科4, 蔡磊4,*( ), 李强5, 黄晓磊5,*(
), 李强5, 黄晓磊5,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-09-17
接受日期:2022-11-01
出版日期:2022-10-20
发布日期:2022-11-08
通讯作者:
江建平,刘冰,蔡磊,黄晓磊
作者简介:huangxl@fafu.edu.cn基金资助:
Jianping Jiang1,*( ), Cheng Du2, Bing Liu3,*(
), Cheng Du2, Bing Liu3,*( ), Ke Wang4, Lei Cai4,*(
), Ke Wang4, Lei Cai4,*( ), Qiang Li5, Xiaolei Huang5,*(
), Qiang Li5, Xiaolei Huang5,*( )
)
Received:2022-09-17
Accepted:2022-11-01
Online:2022-10-20
Published:2022-11-08
Contact:
Jianping Jiang,Bing Liu,Lei Cai,Xiaolei Huang
摘要:
发现并描述地球上的生物物种, 建立可靠的生物分类系统, 编制权威且具有时效性的生物物种名录, 实现生物物种多样性信息的数字化和共享, 对于生物多样性科学研究、资源管理、科学决策和社会经济发展都有重要意义。在全球和区域层面, 生物物种编目工作越来越被重视, 也取得了一些可喜的进展。为反映中国生物物种编目工作近些年取得的成绩, 本文联合各相关类群的专家, 分别总结了脊椎动物、昆虫和其他无脊椎动物、植物、菌物等主要类群的物种编目进展情况, 并就将来如何更好地促进生物编目工作的开展提出了展望。现有数据显示, 中国已记录哺乳动物698种, 鸟类1,450种, 爬行类586种, 两栖类611种, 淡水鱼类1,591种, 高等植物38,493种(其中维管植物35,379种), 菌物约27,900种, 但尚无全面的包括所有昆虫和无脊椎动物的物种名录。近10年, 中国新增维管植物5个新科、86个新属、2,090个新种、374个新记录; 新增菌物新物种4,679个, 隶属于36纲140目438科1,372属。
江建平, 杜诚, 刘冰, 王科, 蔡磊, 李强, 黄晓磊 (2022) 中国生物物种编目进展与展望. 生物多样性, 30, 22531. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022531.
Jianping Jiang, Cheng Du, Bing Liu, Ke Wang, Lei Cai, Qiang Li, Xiaolei Huang (2022) Bio-inventory in China: Progress and perspectives. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22531. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022531.
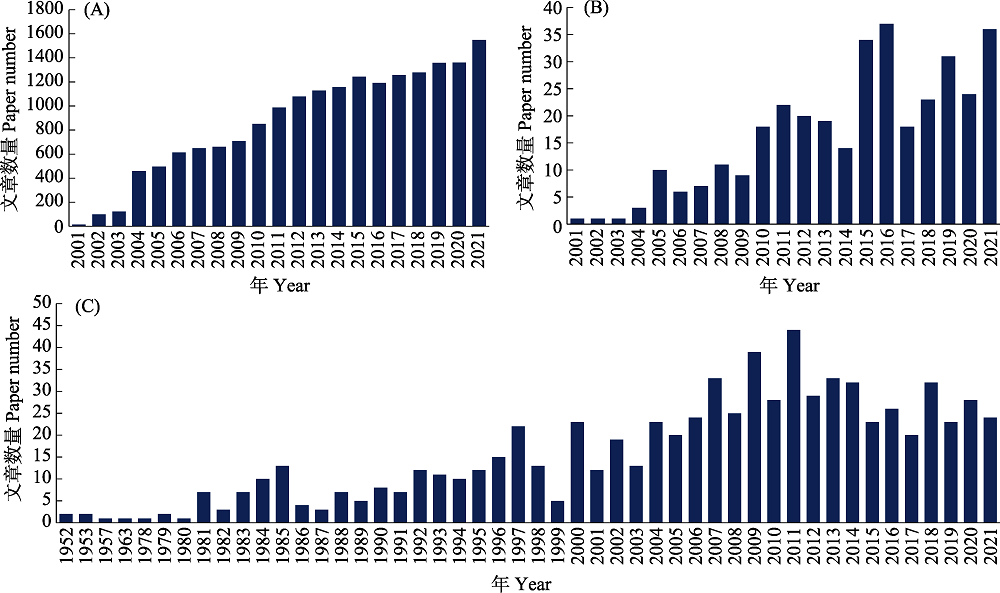
图3 昆虫和蜘蛛新物种及编目文章发表情况。(A)以检索式“(insect OR spider) AND China AND new species”在Web of Science检索的文章数量; (B)以检索式“(insect OR spider) AND China AND (catalogue OR inventory)”在Web of Science检索的文章数量; (C)以“昆虫 + 编目/名录”和“蜘蛛 + 编目/名录”为关键词在中国知网检索的文章数量。
Fig. 3 Trends of published papers on new species and inventory of insects and spiders. (A) The Web of Science retrieval results using terms (insect OR spider) AND China AND new species; (B) The Web of Science retrieval results using terms (insect OR spider) AND China AND (catalogue OR inventory); (C) The CNKI retrieval results using terms (insect OR spider) AND (catalogue OR inventory)
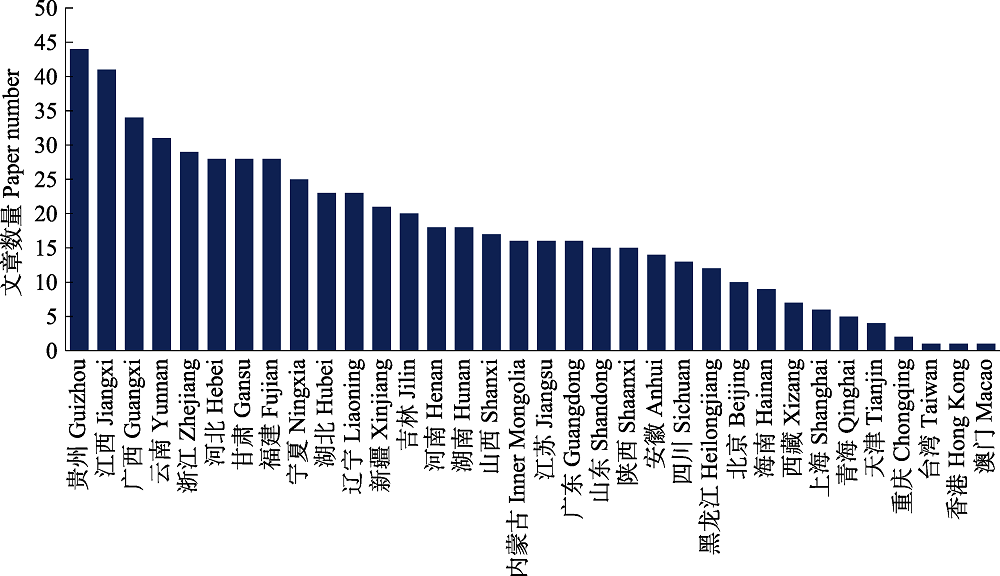
图4 以“昆虫 + 编目/名录”和“蜘蛛 + 编目/名录”为关键词在中国知网检索的文章在不同省区的分布(除去全国性名录)
Fig. 4 The geographical distribution of papers retrieved from CNKI using terms (insect OR spider) AND (catalogue OR inventory)
| 科名 Family | 新物种数量 New species number | 属名 Genus | 新物种数量 New species number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 兰科 Orchidaceae | 223 | 楼梯草属 Elatostema | 104 | |
| 苦苣苔科 Gesneriaceae | 218 | 报春苣苔属 Primulina | 86 | |
| 荨麻科 Urticaceae | 136 | 小檗属 Berberis | 70 | |
| 毛茛科 Ranunculaceae | 126 | 风毛菊属 Saussurea | 48 | |
| 菊科 Asteraceae | 122 | 秋海棠属 Begonia | 47 | |
| 小檗科 Berberidaceae | 77 | 蜘蛛抱蛋属 Aspidistra | 44 | |
| 禾本科 Poaceae | 75 | 凤仙花属 Impatiens | 44 | |
| 天门冬科 Asparagaceae | 64 | 耳蕨属 Polystichum | 44 | |
| 鳞毛蕨科 Dryopteridaceae | 58 | 马铃苣苔属 Oreocharis | 34 | |
| 豆科 Fabaceae | 54 | 翠雀属 Delphinium | 33 | |
| 其他121科 Other 121 families | 937 | 其他524属 Other 524 genera | 1,536 | |
表1 2012-2021年中国维管植物新种发表最多的10个科和属
Table 1 Top 10 families and genera in which new species of vascular plants from China were described from 2012 to 2021
| 科名 Family | 新物种数量 New species number | 属名 Genus | 新物种数量 New species number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 兰科 Orchidaceae | 223 | 楼梯草属 Elatostema | 104 | |
| 苦苣苔科 Gesneriaceae | 218 | 报春苣苔属 Primulina | 86 | |
| 荨麻科 Urticaceae | 136 | 小檗属 Berberis | 70 | |
| 毛茛科 Ranunculaceae | 126 | 风毛菊属 Saussurea | 48 | |
| 菊科 Asteraceae | 122 | 秋海棠属 Begonia | 47 | |
| 小檗科 Berberidaceae | 77 | 蜘蛛抱蛋属 Aspidistra | 44 | |
| 禾本科 Poaceae | 75 | 凤仙花属 Impatiens | 44 | |
| 天门冬科 Asparagaceae | 64 | 耳蕨属 Polystichum | 44 | |
| 鳞毛蕨科 Dryopteridaceae | 58 | 马铃苣苔属 Oreocharis | 34 | |
| 豆科 Fabaceae | 54 | 翠雀属 Delphinium | 33 | |
| 其他121科 Other 121 families | 937 | 其他524属 Other 524 genera | 1,536 | |
| 国家 Country | 大洲 Continent | 新物种数 Number of new species | 占全球 的比例 Percentage to the world (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 中国 China | 亚洲 Asia | 4,679 | 20.09 |
| 美国 USA | 北美洲 North America | 1,758 | 7.55 |
| 泰国 Thailand | 亚洲 Asia | 1,640 | 7.04 |
| 巴西 Brazil | 南美洲 South America | 1,485 | 6.38 |
| 澳大利亚 Australia | 大洋洲 Oceania | 1,409 | 6.05 |
| 印度 India | 亚洲 Asia | 909 | 3.90 |
| 意大利 Italy | 欧洲 Europe | 859 | 3.69 |
| 西班牙 Spain | 欧洲 Europe | 683 | 2.93 |
| 法国 France | 欧洲 Europe | 639 | 2.74 |
| 南非 South Africa | 非洲 Africa | 513 | 2.20 |
| 日本 Japan | 亚洲 Asia | 501 | 2.15 |
| 韩国 Korea | 亚洲 Asia | 409 | 1.76 |
| 德国 Germany | 欧洲 Europe | 399 | 1.71 |
| 新西兰 New Zealand | 大洋洲 Oceania | 396 | 1.70 |
| 俄罗斯 Russia | 欧洲 Europe | 362 | 1.55 |
| 加拿大 Canada | 北美洲 North America | 295 | 1.27 |
| 厄瓜多尔 Ecuador | 南美洲 South America | 267 | 1.15 |
| 墨西哥 Mexico | 北美洲 North America | 265 | 1.14 |
| 荷兰 The Netherlands | 欧洲 Europe | 257 | 1.10 |
| 英国 UK | 欧洲 Europe | 218 | 0.94 |
表2 近10年发现菌物新物种最多的20个国家
Table 2 Top 20 countries with most new fungal species discovered in the last decade
| 国家 Country | 大洲 Continent | 新物种数 Number of new species | 占全球 的比例 Percentage to the world (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 中国 China | 亚洲 Asia | 4,679 | 20.09 |
| 美国 USA | 北美洲 North America | 1,758 | 7.55 |
| 泰国 Thailand | 亚洲 Asia | 1,640 | 7.04 |
| 巴西 Brazil | 南美洲 South America | 1,485 | 6.38 |
| 澳大利亚 Australia | 大洋洲 Oceania | 1,409 | 6.05 |
| 印度 India | 亚洲 Asia | 909 | 3.90 |
| 意大利 Italy | 欧洲 Europe | 859 | 3.69 |
| 西班牙 Spain | 欧洲 Europe | 683 | 2.93 |
| 法国 France | 欧洲 Europe | 639 | 2.74 |
| 南非 South Africa | 非洲 Africa | 513 | 2.20 |
| 日本 Japan | 亚洲 Asia | 501 | 2.15 |
| 韩国 Korea | 亚洲 Asia | 409 | 1.76 |
| 德国 Germany | 欧洲 Europe | 399 | 1.71 |
| 新西兰 New Zealand | 大洋洲 Oceania | 396 | 1.70 |
| 俄罗斯 Russia | 欧洲 Europe | 362 | 1.55 |
| 加拿大 Canada | 北美洲 North America | 295 | 1.27 |
| 厄瓜多尔 Ecuador | 南美洲 South America | 267 | 1.15 |
| 墨西哥 Mexico | 北美洲 North America | 265 | 1.14 |
| 荷兰 The Netherlands | 欧洲 Europe | 257 | 1.10 |
| 英国 UK | 欧洲 Europe | 218 | 0.94 |
| [1] | Antonelli A, Fry C, Smith RJ, Simmonds MSJ, Kersey PJ, Pritchard HW, Abbo MS, Acedo C, Adams J, Ainsworth AM, and other 201 authors (2020) State of the World’s Plants and Fungi 2020. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, London. |
| [2] |
Cai B, Wang YZ, Chen GY, Li JT (2015) A revised taxonomy for Chinese reptiles. Biodiversity Science, 23, 365-382. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[蔡波, 王跃招, 陈跃英, 李家堂 (2015) 中国爬行纲动物分类厘定. 生物多样性, 23, 365-382.]
DOI |
|
| [3] |
Cao L, Zhang E, Zang CX, Cao WX (2016) Evaluating the status of China’s continental fish and analyzing their causes of endangerment through the red list assessment. Biodiversity Science, 24, 598-609. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[曹亮, 张鹗, 臧春鑫, 曹文宣 (2016) 通过红色名录评估研究中国内陆鱼类受威胁现状及其成因. 生物多样性, 24, 598-609.]
DOI |
|
| [4] | Chen SC, He YH (2008) Phasmatodea of China. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [陈树椿, 何允恒 (2008) 中国䗛目昆虫. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [5] | Cheng QT, Zheng BS (1987) Systematic Key to Fishes of China (I, II). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [成庆泰, 郑葆珊 (1987) 中国鱼类系统检索(上、下册). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [6] | Cheng TH (1964) Systematic Key to Birds of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [郑作新 (1964) 中国鸟类系统检索. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [7] | Cheng TH (1976) Checklist of Birds in China, 2nd edn. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [郑作新 (1976) 中国鸟类分布名录(第二版). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [8] | Cheng TH (1987) A Synopsis of the Avifauna of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [郑作新 (1987) 中国鸟类区系纲要. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [9] | Cheng TH (1994) A Complete Checklist of Species and Subspecies of the Chinese Birds. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [郑作新 (1994) 中国鸟类种和亚种分类名录大全. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [10] | Cheng TH (2000) A Complete Checklist of Species and Subspecies of the Chinese Birds, 2nd edn. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [郑作新 (2000) 中国鸟类种和亚种分类名录大全(第二版). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [11] |
Costello MJ, May RM, Stork NE (2013) Can we name Earth’s species before they go extinct? Science, 339, 413-416.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Du C, Liu J, Ye W, Liao S, Ge BJ, Liu B, Ma JS (2021) Annual report of new taxa and new names for Chinese plants in 2020. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1011-1020. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杜诚, 刘军, 叶文, 廖帅, 葛斌杰, 刘冰, 马金双 (2021) 中国植物新分类群、新名称2020年度报告. 生物多样性, 29, 1011-1020.] | |
| [13] | Eschmeyer MN, Fong JD (2019) Species of Fishes by Family/Subfamily. California Academy of Sciences, San Francisco. |
| [14] | Fang R, Kirk PM, Wei JC, Li Y, Cai L, Fan L, Wei TZ, Zhao RL, Wang K, Yang ZL, Li TH, Li Y, Phurbu-Dorji, Yao YJ (2018) Country focus: China. In: State of the World’s Fungi (ed. Willis KJ), pp. 48-55. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. |
| [15] | Fang ZG, Wu H (2001) A Checklist of Insects from Zhejiang. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [方志刚, 吴鸿 (2001) 浙江昆虫名录. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [16] | Fei L (1999) Atlas of Amphibians in China. Henan Science and Technology Press, Zhengzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [费梁 (1999) 中国两栖动物图鉴. 河南科学技术出版社, 郑州.] | |
| [17] | Fei L, Hu SQ, Ye CY, Huang YZ (2006) Fauna Sinica•Amphibia (1): General Accounts of Amphibia, Gymnophiona, Urodela. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [费梁, 胡淑琴, 叶昌媛, 黄永昭 (2006) 中国动物志•两栖纲(第一卷): 总论, 蚓螈目, 有尾目. 科学出版社, 北京..] | |
| [18] | Fei L, Hu SQ, Ye CY, Huang YZ (2009a) Fauna Sinica•Amphibia (2): Anura. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [费梁, 胡淑琴, 叶昌媛, 黄永昭 (2009a) 中国动物志•两栖纲(第二卷): 无尾目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [19] | Fei L, Hu SQ, Ye CY, Huang YZ (2009b) Fauna Sinica•Amphibia (3): Anura•Ranidae. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [费梁, 胡淑琴, 叶昌媛, 黄永昭 (2009b) 中国动物志•两栖纲(第三卷): 无尾目•蛙科. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [20] | Fei L, Ye CY, Huang YZ, Jiang JP, Xie F (2005) An Illustrated Key to Chinese Amphibians. Sichuan Publishing House of Science and Technology, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [费梁, 叶昌媛, 黄永昭, 江建平, 谢锋 (2005) 中国两栖动物检索及图解. 四川科学技术出版社, 成都.] | |
| [21] | Fei L, Ye CY, Huang YZ (1990) Key to Chinese Amphibia. Chongqing Branch, Science and Technology Literature Publishing House, Chongqing. (in Chinese) |
| [费梁, 叶昌媛, 黄永昭 (1990) 中国两栖动物检索. 科学技术文献出版社重庆分社, 重庆.] | |
| [22] | Fei L, Ye CY, Jiang JP (2012) Colored Atlas of Chinese Amphibians and Their Distributions. Sichuan Publishing House of Science and Technology, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [费梁, 叶昌媛, 江建平 (2012) 中国两栖动物及其分布彩色图鉴. 四川科学技术出版社, 成都.] | |
| [23] | Hu SQ, Ye CY, Fei L (1977) Systematic Key to Amphibians of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [胡淑琴, 叶昌媛, 费梁 (1977) 中国两栖动物系统检索. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [24] |
Jiang JP, Cai B, Wang B, Chen WT, Wen ZX, Zhang DZ (2022) New vertebrate forms discovered in China during 2021. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22225. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [江建平, 蔡波, 王斌, 陈蔚涛, 温知新, 张德志 (2022) 中国脊椎动物2021年度新增物种报告. 生物多样性, 30, 22225.] | |
| [25] | Jiang JP, Xie F, Li C, Wang B (2020) Species Catalogue of China (Vol. 2): Animals•Vertebrates (IV)•Amphibia. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [江建平, 谢锋, 李成, 王斌 (2020) 中国生物物种名录(第二卷): 动物•脊椎动物(IV)•两栖纲. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [26] |
Jiang ZG, Liu SY, Wu Y, Jiang XL, Zhou KY (2017) China’s mammal diversity (2nd edition). Biodiversity Science, 25, 886-895. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[蒋志刚, 刘少英, 吴毅, 蒋学龙, 周开亚 (2017) 中国哺乳动物多样性(第2版). 生物多样性, 25, 886-895.]
DOI |
|
| [27] |
Jiang ZG, Ma Y, Wu Y, Wang YX, Feng ZJ, Zhou KY, Liu SY, Luo ZH, Li CW (2015) China’s mammal diversity. Biodiversity Science, 23, 351-364. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[蒋志刚, 马勇, 吴毅, 王应祥, 冯祚建, 周开亚, 刘少英, 罗振华, 李春旺 (2015) 中国哺乳动物多样性. 生物多样性, 23, 351-364.]
DOI |
|
| [28] | Kirk PM, Norvell LL, Yao YJ (2021) Changes to the Code of Nomenclature in Melbourne. Journal of Fungal Research, 9, 125-128. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [Kirk PM, Norvell LL, 姚一建 (2021) 国际植物学墨尔本大会上命名法规的变化. 菌物研究, 9, 125-128.] | |
| [29] |
Li CX, Miao XY (2016) Notes on the rank of China in the world in terms of higher plant diversity. Biodiversity Science, 24, 725-727. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[李春香, 苗馨元 (2016) 浅议中国高等植物多样性在世界上的排名. 生物多样性, 24, 725-727.]
DOI |
|
| [30] | Li FS (2011) Psyllidomorpha of China (Insecta: Hemiptera). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李法圣 (2011) 中国木虱志. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [31] |
Li JJ, Huang XL (2022) Progress and perspectives on insect biogeography in China. Acta Geographica Sinica, 77, 133-149. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[李俊洁, 黄晓磊 (2022) 中国昆虫生物地理学进展与展望. 地理学报, 77, 133-149.]
DOI |
|
| [32] | Li SQ, Lin YC (2016) Species Catalogue of China (Vol. 2): Animals•Invertebrates (I)•Arachnida•Araneae. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [李枢强, 林玉成 (2016) 中国生物物种名录(第二卷): 动物•无脊椎动物(I)•蛛形纲•蜘蛛目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [33] | Li SZ (1981) A Synopsis of Freshwater Fishes of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李思忠 (1981) 中国淡水鱼类的分布区划. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [34] | Lin MY, Yang XK (2019) Catalogue of Chinese Coleoptera (Vol. 9 Chrysomeloidea): Vesperidae, Disteniidae, Cerambycidae. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [林美英, 杨星科 (2019) 中国甲虫名录(第9卷叶甲总科): 暗天牛科, 瘦天牛科, 天牛科. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [35] |
Liu B, Qin HN (2022) Recent advances in the national inventory of higher plant species in China. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22397. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [刘冰, 覃海宁 (2022) 中国高等植物多样性编目进展. 生物多样性, 30, 22397.] | |
| [36] |
Lücking R, Aime MC, Robbertse B, Miller AN, Aoki T, Ariyawansa HA, Cardinali G, Crous PW, Druzhinina IS, Geiser DM, Hawksworth DL, Hyde KD, Irinyi L, Jeewon R, Johnston PR, Kirk PM, Malosso E, May TW, Meyer W, Nilsson HR, Öpik M, Robert V, Stadler M, Thines M, Vu D, Yurkov AM, Zhang N, Schoch CL (2021) Fungal taxonomy and sequence-based nomenclature. Nature Microbiology, 6, 540-548.
DOI PMID |
| [37] | MacKinnon J, Phillipps K, He FQ (2000) A Field Guide to Birds of China. Hunan Education Publishing House, Changsha. (in Chinese) |
| [约翰·马敬能, 卡伦·菲利普斯, 何芬奇 (2000) 中国鸟类野外手册. 湖南教育出版社, 长沙.] | |
| [38] |
May RM (1988) How many species are there on earth? Science, 241, 1441-1449.
DOI PMID |
| [39] | McNeill J, Barrie FF, Buck WR, Demoulin V, Greuter W, Hawksworth DL, Herendeen PS, Knapp S, Marhold K, Prado J, Prud’homme Van Reine WF, Smith GF, Wiersema JH (2012) International Code of Nomenclature for Algae, Fungi, and Plants (Melbourne Code). Koeltz Scientific Books, Königstein, Germany. |
| [40] |
Mittelbach GG, Schemske DW, Cornell HV, Allen AP, Brown JM, Bush MB, Harrison SP, Hurlbert AH, Knowlton N, Lessios HA (2007) Evolution and the latitudinal diversity gradient: Speciation, extinction and biogeography. Ecology Letters, 10, 315-331.
PMID |
| [41] | Nowak RM (1999) Walker’s Mammals of the World, 6th edn. Johns Hopkins University Press, Washington, DC. |
| [42] | Pan QH, Wang YX, Yan K (2007) A Field Guide to the Mammals of China. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [潘清华, 王应祥, 岩崑 (2007) 中国哺乳动物彩色图鉴. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [43] |
Qian H, Zhang J, Zhao JC (2022) How many known vascular plant species are there in the world? An integration of multiple global plant databases. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22254 (in Chinese and in English)
DOI |
|
[钱宏, 张健, 赵静超 (2022) 世界上已知维管植物有多少种? 基于多个全球植物数据库的整合. 生物多样性, 30, 22254.]
DOI |
|
| [44] | Shaw TH (1962) Economic Fauna of China:Mammals. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [寿振黄 (1962) 中国经济动物志: 兽类. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [45] | Shen XC (1993) A Checklist of Insects from Henan. China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [申效诚 (1993) 河南昆虫名录. 中国农业科学技术出版社, 北京.] | |
| [46] | Smith A, Xie Y, Hoffmann RS, Lunde D, MacKinnon J, Wilson DE, Wozencraft WC, Gemma F (2009) A Guide to the Mammals of China. Hunan Education Publishing House, Changsha. (in Chinese) |
| [Smith A, 解焱, Hoffmann RS, Lunde D, MacKinnon J, Wilson DE, Wozencraft WC, Gemma F (2009) 中国兽类野外手册. 湖南教育出版社, 长沙.] | |
| [47] |
Stork NE (2018) How many species of insects and other terrestrial arthropods are there on earth. Annual Review of Entomology, 63, 31-45.
DOI URL |
| [48] | Tan BJ (1992) A Systematic List of the Mammals. China Medical Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [谭邦杰 (1992) 哺乳动物分类名录. 中国医药科技出版社, 北京.] | |
| [49] | The Biodiversity Committee of Chinese Academy of Sciences (2022) Catalogue of Life China: 2022 Annual Checklist. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [中国科学院生物多样性委员会 (2022) 中国生物物种名录. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [50] | Tian WS, Jiang YM (1986) Identification Manual of Chinese Amphibians and Reptiles. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [田婉淑, 江耀明 (1986) 中国两栖爬行动物鉴定手册. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [51] |
Wan X, Zhang LB (2021) Global new species of vascular plants published in 2020. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1003-1010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [万霞, 张丽兵 (2021) 2020年发表的全球维管植物新种. 生物多样性, 29, 1003-1010.] | |
| [52] |
Wan X, Zhang LB (2022) Global new taxa of vascular plants published in 2021. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22116. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [万霞, 张丽兵 (2022) 世界维管植物新分类群2021年度报告. 生物多样性, 30, 22116.] | |
| [53] |
Wang B, Cai B, Chen WT, Wen ZX, Zhang DZ, He SP, Lei FM, Yang QS, Jiang JP (2021) New vertebrate forms discovered in China in 2020. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1021-1025. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [王斌, 蔡波, 陈蔚涛, 温知新, 张德志, 何舜平, 雷富民, 杨奇森, 江建平 (2021) 中国脊椎动物2020年新增物种. 生物多样性, 29, 1021-1025.] | |
| [54] |
Wang K, Ren JL, Chen HM, Lü ZT, Guo XG, Jiang K, Chen JM, Li JT, Guo P, Wang YY, Che J (2020) The updated checklists of amphibians and reptiles of China. Biodiversity Science, 28, 189-218. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[王剀, 任金龙, 陈宏满, 吕植桐, 郭宪光, 蒋珂, 陈进民, 李家堂, 郭鹏, 王英永, 车静 (2020) 中国两栖、爬行动物更新名录. 生物多样性, 28, 189-218.]
DOI |
|
| [55] | Wang K, Zhao MJ, Su JH, Yang L, Deng H, Wang YH, Wu HJ, Li Y, Wu HM, Wei XD, Wei TZ, Cai L, Yao YJ (2020) The use of Checklist of Fungi in China database in the red list assessment of macrofungi in China. Biodiversity Science, 28, 74-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王科, 赵明君, 苏锦河, 杨柳, 邓红, 王永会, 吴海军, 李熠, 吴红梅, 卫晓丹, 魏铁铮, 蔡磊, 姚一建 (2020) 中国菌物名录数据库在大型真菌红色名录编制中的作用. 生物多样性, 28, 74-98.] | |
| [56] | Wang M, Fan XL (2002) Butterflies Fauna Sinica:Lycaenidae. Henan Science and Technology Press, Zhengzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [王敏, 范骁凌 (2002) 中国灰蝶志. 河南科学技术出版社, 郑州.] | |
| [57] | Wang XM, Ren GD, Liu RG (1992) An Annotated Checklist of Insects from Ningxia. Shaanxi Normal University Publishing House, Xi’an. (in Chinese) |
| [王希蒙, 任国栋, 刘荣光 (1992) 宁夏昆虫名录. 陕西师范大学出版社, 西安.] | |
| [58] | Wang YX (2003) A Complete Checklist of Mammal Species and Subspecies in China:A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [王应祥 (2003) 中国哺乳动物种和亚种分类名录与分布大全. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [59] | Wang YX, Zhang SY (1993) Checklist of Mammals in China. Wild Animals, (2), 12-17; (3), 6-13; (4), 11-16; (5), 10-11. (in Chinese) |
| [王玉玺, 张淑云 (1993) 中国兽类分布名录. 野生动物, (2), 12-17; (3), 6-13; (4), 11-16; (5), 10-11.] | |
| [60] | Wei FW, Yang QS, Wu Y, Jiang XL, Liu SY, Li BG, Yang G, Li M, Zhou J, Li S, Hu YB, Ge DY, Li S, Yu WH, Chen BY, Zhang ZJ, Zhou CQ, Wu SB, Zhang L, Chen ZZ, Chen SD, Deng HQ, Jiang TL, Zhang LB, Shi HY, Lu XL, Li Q, Liu Z, Cui YQ, Li YC (2021) Catalogue of mammals in China (2021). Acta Theriologica Sinica, 41, 487-501. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[魏辅文, 杨奇森, 吴毅, 蒋学龙, 刘少英, 李保国, 杨光, 李明, 周江, 李松, 胡义波, 葛德燕, 李晟, 余文华, 陈炳耀, 张泽钧, 周材权, 吴诗宝, 张立, 陈中正, 陈顺德, 邓怀庆, 江廷磊, 张礼标, 石红艳, 卢学理, 李权, 刘铸, 崔雅倩, 李玉春 (2021) 中国兽类名录(2021版). 兽类学报, 41, 487-501.]
DOI |
|
| [61] | Willis KJ (2017) The State of the World’s Plants Report: 2017. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, London. |
| [62] | Willis KJ, Bachman S (2016) The State of the World’s Plants Report: 2016. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, London. |
| [63] | Wu CF (1935- 1941) Catalogus insectorum Sinensium. Fan Memorial Institute of Biology, Beiping. |
| [64] |
Yao YJ, Wei JC, Zhuang WY, Cai L, Liu DM, Li JS, Wei TZ, Li Y, Wang K, Wu HJ (2020) Development of red list assessment of macrofungi in China. Biodiversity Science, 28, 4-10. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[姚一建, 魏江春, 庄文颖, 蔡蕾, 刘冬梅, 李俊生, 魏铁铮, 李熠, 王科, 吴海军 (2020) 中国大型真菌红色名录评估研究进展. 生物多样性, 28, 4-10.]
DOI |
|
| [65] | Zhang CG, Shao KT, Wu HL, Zhao YH (2020) Species Catalogue of China (Vol. 2): Animals•Vertebrates (V)• Fishes (I and II). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张春光, 邵广昭, 伍汉霖, 赵亚辉 (2020) 中国生物物种名录(第二卷): 动物•脊椎动物(V)•鱼类(上、下册). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [66] | Zhang E, Cao WX (2021) China’s Red List of Biodiversity•Vertebrates (Vol. V): Freshwater Fishes (I, II). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [张鹗, 曹文宣 (2021) 中国生物多样性红色名录•脊椎动物(第五卷): 淡水鱼类(上、下册). 科学出版社, 北京. ] | |
| [67] | Zhang MW, Zong Y, Ma JF (1998) Fauna Sinica•Reptilia (1): General Accounts, Testudoformes, Crocodiliformes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张孟闻, 宗愉, 马积藩 (1998) 中国动物志•爬行纲(第一卷): 总论, 龟鳖目, 鳄形目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [68] | Zhang YQ, You QJ, Pu TS, Lin RZ (1992) Insect Catalogue of Guangxi. Guangxi Science and Technology Press, Nanning. (in Chinese) |
| [张永强, 尤其儆, 蒲天胜, 林日钊 (1992) 广西昆虫名录. 广西科学技术出版社, 南宁.] | |
| [69] | Zhao EM, Jiang YM, Shen Y (1977) Systematic Key to Reptiles of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [赵尔宓, 江耀明, 沈杨 (1977) 中国爬行动物系统检索. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [70] | Zhao EM, Adler K (1993) Herpetology of China. Society for the Study of Amphibians and Reptiles, Oxford, Ohio. |
| [71] | Zhao EM, Huang MH, Zong Y (1998) Fauna Sinica•Reptilia (3): Squamata•Serpentes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [赵尔宓, 黄美华, 宗愉 (1998) 中国动物志•爬行纲(第三卷): 有鳞目•蛇亚目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [72] | Zhao EM, Zhao KT, Zhou KY (1999) Fauna Sinica•Reptilia (2): Squamata•Lacertilia. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [赵尔宓, 赵肯堂, 周开亚 (1999) 中国动物志•爬行纲(第二卷): 有鳞目•蜥蜴亚目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [73] | Zheng CL (1986) The number of mammalian species in China. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 6, 78-80. (in Chinese) |
| [郑昌林 (1986) 中国兽类之种数. 兽类学报, 6, 78-80.] | |
| [74] | Zheng GM (2005) A Checklist on the Classification and Distribution of the Birds of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [郑光美 (2005) 中国鸟类分类与分布名录. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [75] | Zheng GM (2011) A Checklist on the Classification and Distribution of the Birds of China, 2nd edn. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [郑光美 (2011) 中国鸟类分类与分布名录(第二版). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [76] | Zheng GM (2017) A Checklist on the Classification and Distribution of the Birds of China, 3rd edn. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [郑光美 (2017) 中国鸟类分类与分布名录(第三版). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [77] | Zhu SQ (1995) Key to Freshwater Fishes of China. Jiangsu Science and Technology Press, Nanjing. (in Chinese) |
| [朱松泉 (1995) 中国淡水鱼类检索. 江苏科学技术出版社, 南京.] |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 周璇, 张生芳, 刘宁, 鲁玉杰, 郑斯竹, 杨晓军, 路园园, 刘梅柯, 白明. 储藏物甲虫系统地位厘清及拉英汉名录更新[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24238-. |
| [10] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [11] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [12] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [13] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [14] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [15] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn