



生物多样性 ›› 2011, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (2): 243-257. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.09330 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2011.09330
所属专题: 中国的森林生物多样性监测
李亮1,2, 刘海丰1, 白帆1,2, 祝燕1, 李广起1,2, 李文超1, 桑卫国1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2010-12-29
接受日期:2011-03-14
出版日期:2011-03-20
发布日期:2011-06-01
通讯作者:
桑卫国
作者简介:*E-mail: swg@ibcas.ac.cn基金资助:
Liang Li1,2, Haifeng Liu1, Fan Bai1,2, Yan Zhu1, Guangqi Li1,2, Wenchao Li1, Weiguo Sang1,*( )
)
Received:2010-12-29
Accepted:2011-03-14
Online:2011-03-20
Published:2011-06-01
Contact:
Weiguo Sang
摘要:
植被的群落构成是决定森林演替方向的重要因素之一。辽东栎林(Quercus wutaishanica forest, QWF)、棘皮桦林(Betula dahurica forest, BDF)、胡桃楸林(Juglans mandshurica forest, JMF)与杂木林(mixed forest, MF)是东灵山地区4种典型的暖温带落叶阔叶次生林。为了更好地了解东灵山地区暖温带落叶阔叶次生林植被动态, 我们对该4种林型的物种组成与群落结构进行了综合分析。参照巴拿马(Barro Colorado Island, BCI) 50 ha热带雨林样地的技术规范, 于2009年在北京东灵山地区以上4个林型中各建立了一块1 ha样地, 对样地中所有胸径大于1 cm的木本个体进行了坐标定位和调查。结果表明, QWF样地有22种, 属于20科20属; BDF样地共22种, 属于16科18属; JMF样地30种, 隶属于21科23属; MF样地19种, 隶属于14科15属。从物种多度、平均胸径、胸高断面积和重要值等指标来看,各群落具有比较明显的优势种; 4个样地所有树种的径级分布均呈倒“J”型, 具有良好的更新层; 共有树种的径级分布在不同样地有所不同, 如辽东栎在QWF样地呈偏态分布, 在BDF样地则为倒“J”型分布, 而棘皮桦在QWF和BDF样地都呈正态分布, 但是径级分布有所差异, 表明径级结构与群落类型有密切关系。
李亮, 刘海丰, 白帆, 祝燕, 李广起, 李文超, 桑卫国 (2011) 东灵山4种落叶阔叶次生林的物种组成与群落结构. 生物多样性, 19, 243-257. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.09330.
Liang Li, Haifeng Liu, Fan Bai, Yan Zhu, Guangqi Li, Wenchao Li, Weiguo Sang (2011) Species composition and community structure of four deciduous broad- leaved secondary forest in Dongling Mountain. Biodiversity Science, 19, 243-257. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.09330.
| 分布区类型 Areal-types | 辽东栎林 QWF | 棘皮桦林 BDF | 胡桃楸林 JMF | 杂木林 MF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 属数 No. of genera (%) | 属数 No. of genera (%) | 属数 No. of genera (%) | 属数 No. of genera (%) | ||||
| 1 世界广布 Cosmopolitan | 0 (0.00) | 1 (5.56) | 1 (4.55) | 1 (6.67) | |||
| 8 北温带 North Temperate Zone | 15 (75.00) | 12 (66.67) | 16 (72.73) | 9 (60.00) | |||
| 9 东亚及北美间断 East Asia & North America disjuncted | 3 (15.00) | 2 (11.11) | 2 (9.09) | 2 (13.33) | |||
| 10 旧世界温带 Old World Temperate | 1 (5.00) | 2 (11.11) | 2 (9.09) | 2 (13.33) | |||
| 14 东亚 East Asia | 1 (5.00) | 1 (5.56) | 1 (4.55) | 1 (6.67) | |||
| 合计 Total | 20 (100.00) | 18 (100.00) | 22 (100.00) | 15 (100.00) | |||
表1 4种林型样地木本植物群落种子植物属的分布区类型
Table 1 Distribution types of spermatophyte in the four forest type plots
| 分布区类型 Areal-types | 辽东栎林 QWF | 棘皮桦林 BDF | 胡桃楸林 JMF | 杂木林 MF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 属数 No. of genera (%) | 属数 No. of genera (%) | 属数 No. of genera (%) | 属数 No. of genera (%) | ||||
| 1 世界广布 Cosmopolitan | 0 (0.00) | 1 (5.56) | 1 (4.55) | 1 (6.67) | |||
| 8 北温带 North Temperate Zone | 15 (75.00) | 12 (66.67) | 16 (72.73) | 9 (60.00) | |||
| 9 东亚及北美间断 East Asia & North America disjuncted | 3 (15.00) | 2 (11.11) | 2 (9.09) | 2 (13.33) | |||
| 10 旧世界温带 Old World Temperate | 1 (5.00) | 2 (11.11) | 2 (9.09) | 2 (13.33) | |||
| 14 东亚 East Asia | 1 (5.00) | 1 (5.56) | 1 (4.55) | 1 (6.67) | |||
| 合计 Total | 20 (100.00) | 18 (100.00) | 22 (100.00) | 15 (100.00) | |||
| 物种名 Species | 多度 Abundance | 平均胸径 Mean DBH (cm) | 胸高断面积 Basal area (m2/ha) | 重要值 Importance value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 辽东栎林 Quercus wutaishanica forest (QWF) 辽东栎 Quercus wutaishanica | 323 | 19.48 | 96,264.1 | 25.48 |
| 棘皮桦 Betula dahurica | 178 | 19.56 | 53,478.1 | 15.87 |
| 色木槭 Acer mono | 595 | 3.22 | 4,831.8 | 13.64 |
| 六道木 Abelia biflora | 153 | 3.65 | 1,598.4 | 5.64 |
| 照山白 Rhododendron micranthum | 293 | 3.00 | 2,064.1 | 7.50 |
| 山杨 Populus davidiana | 97 | 10.75 | 8,807.6 | 5.60 |
| 毛叶丁香 Syringa pubescens | 104 | 3.03 | 751.6 | 3.95 |
| 白桦 Betula platyphylla | 28 | 22.76 | 11,386.3 | 4.05 |
| 毛榛 Corylus mandshurica | 311 | 2.38 | 1,387.2 | 6.20 |
| 迎红杜鹃 Rhododendron mucronulatum | 43 | 2.39 | 193.5 | 2.29 |
| 大叶白蜡 Fraxinus rhynchophylla | 20 | 3.92 | 240.8 | 1.63 |
| 蒿柳 Salix viminalis | 10 | 15.18 | 1,808.5 | 1.44 |
| 沙梾 Swida bretschneideri | 15 | 2.55 | 76.8 | 1.04 |
| 榆树 Ulmus pumila | 8 | 26.14 | 4,292.2 | 1.53 |
| 总计 Total | 2,178 | 138.03 | 187,181.0 | 95.85 |
| 棘皮桦林 Betula dahurica forest (BDF) | ||||
| 辽东栎 Quercus wutaishanica | 910 | 10.18 | 74,063.5 | 23.15 |
| 棘皮桦 Betula dahurica | 627 | 12.84 | 81,156.4 | 22.02 |
| 大叶白蜡 Fraxinus rhynchophylla | 1,063 | 5.36 | 23,982.9 | 16.11 |
| 六道木 Abelia biflora | 427 | 3.08 | 3,179.1 | 7.36 |
| 色木槭 Acer mono | 274 | 5.30 | 6,043.7 | 6.59 |
| 照山白 Rhododendron micranthum | 237 | 2.48 | 1,147.4 | 4.78 |
| 北京丁香 Syringa pekinensis | 206 | 2.60 | 1,096.1 | 4.52 |
| 土庄绣线菊 Spiraea pubescens | 46 | 1.21 | 53.1 | 2.90 |
| 蒙椴 Tilia mongolica | 81 | 9.45 | 5,675.1 | 3.98 |
| 大果榆 Ulmus macrocarpa | 81 | 6.51 | 2,695.1 | 2.09 |
| 胡枝子 Lespedeza bicolor | 24 | 1.23 | 28.7 | 1.18 |
| 山桃 Amygdalus davidiana | 16 | 5.79 | 421.5 | 1.04 |
| 糠椴 Tilia mandshurica | 46 | 5.60 | 1,134.2 | 1.26 |
| 总计 Total | 4,038 | 71.65 | 200,676.8 | 96.97 |
| 胡桃楸林 Juglans mandshurica forest (JMF) | ||||
| 胡桃楸 Juglans mandshurica | 305 | 13.76 | 45,359.2 | 20.81 |
| 大叶白蜡 Fraxinus rhynchophylla | 598 | 5.83 | 15,949.4 | 16.90 |
| 北京丁香 Syringa pekinensis | 366 | 5.78 | 9,614.8 | 11.49 |
| 山杨 Populus davidiana | 58 | 18.52 | 15,611.6 | 6.41 |
| 土庄绣线菊 Spiraea pubescens | 195 | 1.33 | 271.8 | 5.85 |
| 辽东栎 Quercus wutaishanica | 88 | 9.36 | 6,046.3 | 4.72 |
| 蒙椴 Tilia mongolica | 77 | 9.04 | 4,944.0 | 4.49 |
| 六道木 Abelia biflora | 97 | 3.15 | 754.1 | 3.70 |
| 小花溲疏 Deutzia parviflora | 57 | 1.87 | 156.1 | 3.31 |
| 棘皮桦 Betula dahurica | 39 | 11.71 | 4,197.0 | 3.16 |
| 山桃 Amygdalus davidiana | 79 | 5.15 | 1,642.7 | 3.02 |
| 大果榆 Ulmus macrocarpa | 56 | 4.51 | 892.9 | 2.45 |
| 色木槭 Acer mono | 34 | 6.97 | 1,295.3 | 2.10 |
| 榆树 Ulmus pumila | 20 | 6.97 | 763.5 | 1.73 |
| 黄花柳 Salix caprea | 3 | 39.60 | 3,693.4 | 1.27 |
| 鼠李 Rhamnus davurica | 15 | 2.44 | 70.1 | 1.18 |
| 照山白 Rhododendron micranthum | 13 | 2.62 | 70.1 | 1.15 |
| 青杨 Populus cathayana | 10 | 8.04 | 507.1 | 1.10 |
| 糠椴 Tilia mandshurica | 18 | 6.12 | 529.0 | 1.10 |
| 大花溲疏 Deutzia grandiflora | 9 | 1.38 | 13.4 | 1.07 |
| 山杏 Armeniaca sibirica | 25 | 4.67 | 426.6 | 1.04 |
| 总计 Total | 2,162 | 168.80 | 112,808.4 | 98.05 |
| 杂木林 mixed forest (MF) | ||||
| 山桃 Amygdalus davidiana | 927 | 3.45 | 8,651.1 | 17.35 |
| 辽东栎 Quercus wutaishanica | 208 | 13.69 | 30,619.7 | 16.37 |
| 大果榆 Ulmus macrocarpa | 624 | 5.30 | 13,773.4 | 15.81 |
| 大叶白蜡 Fraxinus rhynchophylla | 313 | 6.76 | 11,212.1 | 11.32 |
| 北京丁香 Syringa pekinensis | 278 | 6.94 | 10,517.8 | 9.62 |
| 土庄绣线菊 Spiraea pubescens | 207 | 1.35 | 296.6 | 6.10 |
| 胡桃楸 Juglans mandshurica | 44 | 17.06 | 10,053.3 | 5.26 |
| 色木槭 Acer mono | 87 | 8.51 | 4,948 | 4.70 |
| 鼠李 Rhamnus davurica | 72 | 2.51 | 355.2 | 3.96 |
| 山荆子 Malus baccata | 28 | 7.76 | 1,324.1 | 1.84 |
| 棘皮桦 Betula dahurica | 9 | 18.18 | 2,334.4 | 1.38 |
| 胡枝子 Lespedeza bicolor | 13 | 2.27 | 52.7 | 1.37 |
| 小花溲疏 Deutzia parviflora | 33 | 1.48 | 56.6 | 1.30 |
| 圆叶鼠李 Rhamnus globosa | 14 | 1.94 | 41.2 | 1.23 |
| 总计 Total | 2,857 | 97.20 | 94,236.2 | 97.61 |
附表I 东灵山4个1 ha样地内重要值≥1的物种
Table 2 Table I Species with the importance value≥1 in the four 1-ha plots
| 物种名 Species | 多度 Abundance | 平均胸径 Mean DBH (cm) | 胸高断面积 Basal area (m2/ha) | 重要值 Importance value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 辽东栎林 Quercus wutaishanica forest (QWF) 辽东栎 Quercus wutaishanica | 323 | 19.48 | 96,264.1 | 25.48 |
| 棘皮桦 Betula dahurica | 178 | 19.56 | 53,478.1 | 15.87 |
| 色木槭 Acer mono | 595 | 3.22 | 4,831.8 | 13.64 |
| 六道木 Abelia biflora | 153 | 3.65 | 1,598.4 | 5.64 |
| 照山白 Rhododendron micranthum | 293 | 3.00 | 2,064.1 | 7.50 |
| 山杨 Populus davidiana | 97 | 10.75 | 8,807.6 | 5.60 |
| 毛叶丁香 Syringa pubescens | 104 | 3.03 | 751.6 | 3.95 |
| 白桦 Betula platyphylla | 28 | 22.76 | 11,386.3 | 4.05 |
| 毛榛 Corylus mandshurica | 311 | 2.38 | 1,387.2 | 6.20 |
| 迎红杜鹃 Rhododendron mucronulatum | 43 | 2.39 | 193.5 | 2.29 |
| 大叶白蜡 Fraxinus rhynchophylla | 20 | 3.92 | 240.8 | 1.63 |
| 蒿柳 Salix viminalis | 10 | 15.18 | 1,808.5 | 1.44 |
| 沙梾 Swida bretschneideri | 15 | 2.55 | 76.8 | 1.04 |
| 榆树 Ulmus pumila | 8 | 26.14 | 4,292.2 | 1.53 |
| 总计 Total | 2,178 | 138.03 | 187,181.0 | 95.85 |
| 棘皮桦林 Betula dahurica forest (BDF) | ||||
| 辽东栎 Quercus wutaishanica | 910 | 10.18 | 74,063.5 | 23.15 |
| 棘皮桦 Betula dahurica | 627 | 12.84 | 81,156.4 | 22.02 |
| 大叶白蜡 Fraxinus rhynchophylla | 1,063 | 5.36 | 23,982.9 | 16.11 |
| 六道木 Abelia biflora | 427 | 3.08 | 3,179.1 | 7.36 |
| 色木槭 Acer mono | 274 | 5.30 | 6,043.7 | 6.59 |
| 照山白 Rhododendron micranthum | 237 | 2.48 | 1,147.4 | 4.78 |
| 北京丁香 Syringa pekinensis | 206 | 2.60 | 1,096.1 | 4.52 |
| 土庄绣线菊 Spiraea pubescens | 46 | 1.21 | 53.1 | 2.90 |
| 蒙椴 Tilia mongolica | 81 | 9.45 | 5,675.1 | 3.98 |
| 大果榆 Ulmus macrocarpa | 81 | 6.51 | 2,695.1 | 2.09 |
| 胡枝子 Lespedeza bicolor | 24 | 1.23 | 28.7 | 1.18 |
| 山桃 Amygdalus davidiana | 16 | 5.79 | 421.5 | 1.04 |
| 糠椴 Tilia mandshurica | 46 | 5.60 | 1,134.2 | 1.26 |
| 总计 Total | 4,038 | 71.65 | 200,676.8 | 96.97 |
| 胡桃楸林 Juglans mandshurica forest (JMF) | ||||
| 胡桃楸 Juglans mandshurica | 305 | 13.76 | 45,359.2 | 20.81 |
| 大叶白蜡 Fraxinus rhynchophylla | 598 | 5.83 | 15,949.4 | 16.90 |
| 北京丁香 Syringa pekinensis | 366 | 5.78 | 9,614.8 | 11.49 |
| 山杨 Populus davidiana | 58 | 18.52 | 15,611.6 | 6.41 |
| 土庄绣线菊 Spiraea pubescens | 195 | 1.33 | 271.8 | 5.85 |
| 辽东栎 Quercus wutaishanica | 88 | 9.36 | 6,046.3 | 4.72 |
| 蒙椴 Tilia mongolica | 77 | 9.04 | 4,944.0 | 4.49 |
| 六道木 Abelia biflora | 97 | 3.15 | 754.1 | 3.70 |
| 小花溲疏 Deutzia parviflora | 57 | 1.87 | 156.1 | 3.31 |
| 棘皮桦 Betula dahurica | 39 | 11.71 | 4,197.0 | 3.16 |
| 山桃 Amygdalus davidiana | 79 | 5.15 | 1,642.7 | 3.02 |
| 大果榆 Ulmus macrocarpa | 56 | 4.51 | 892.9 | 2.45 |
| 色木槭 Acer mono | 34 | 6.97 | 1,295.3 | 2.10 |
| 榆树 Ulmus pumila | 20 | 6.97 | 763.5 | 1.73 |
| 黄花柳 Salix caprea | 3 | 39.60 | 3,693.4 | 1.27 |
| 鼠李 Rhamnus davurica | 15 | 2.44 | 70.1 | 1.18 |
| 照山白 Rhododendron micranthum | 13 | 2.62 | 70.1 | 1.15 |
| 青杨 Populus cathayana | 10 | 8.04 | 507.1 | 1.10 |
| 糠椴 Tilia mandshurica | 18 | 6.12 | 529.0 | 1.10 |
| 大花溲疏 Deutzia grandiflora | 9 | 1.38 | 13.4 | 1.07 |
| 山杏 Armeniaca sibirica | 25 | 4.67 | 426.6 | 1.04 |
| 总计 Total | 2,162 | 168.80 | 112,808.4 | 98.05 |
| 杂木林 mixed forest (MF) | ||||
| 山桃 Amygdalus davidiana | 927 | 3.45 | 8,651.1 | 17.35 |
| 辽东栎 Quercus wutaishanica | 208 | 13.69 | 30,619.7 | 16.37 |
| 大果榆 Ulmus macrocarpa | 624 | 5.30 | 13,773.4 | 15.81 |
| 大叶白蜡 Fraxinus rhynchophylla | 313 | 6.76 | 11,212.1 | 11.32 |
| 北京丁香 Syringa pekinensis | 278 | 6.94 | 10,517.8 | 9.62 |
| 土庄绣线菊 Spiraea pubescens | 207 | 1.35 | 296.6 | 6.10 |
| 胡桃楸 Juglans mandshurica | 44 | 17.06 | 10,053.3 | 5.26 |
| 色木槭 Acer mono | 87 | 8.51 | 4,948 | 4.70 |
| 鼠李 Rhamnus davurica | 72 | 2.51 | 355.2 | 3.96 |
| 山荆子 Malus baccata | 28 | 7.76 | 1,324.1 | 1.84 |
| 棘皮桦 Betula dahurica | 9 | 18.18 | 2,334.4 | 1.38 |
| 胡枝子 Lespedeza bicolor | 13 | 2.27 | 52.7 | 1.37 |
| 小花溲疏 Deutzia parviflora | 33 | 1.48 | 56.6 | 1.30 |
| 圆叶鼠李 Rhamnus globosa | 14 | 1.94 | 41.2 | 1.23 |
| 总计 Total | 2,857 | 97.20 | 94,236.2 | 97.61 |
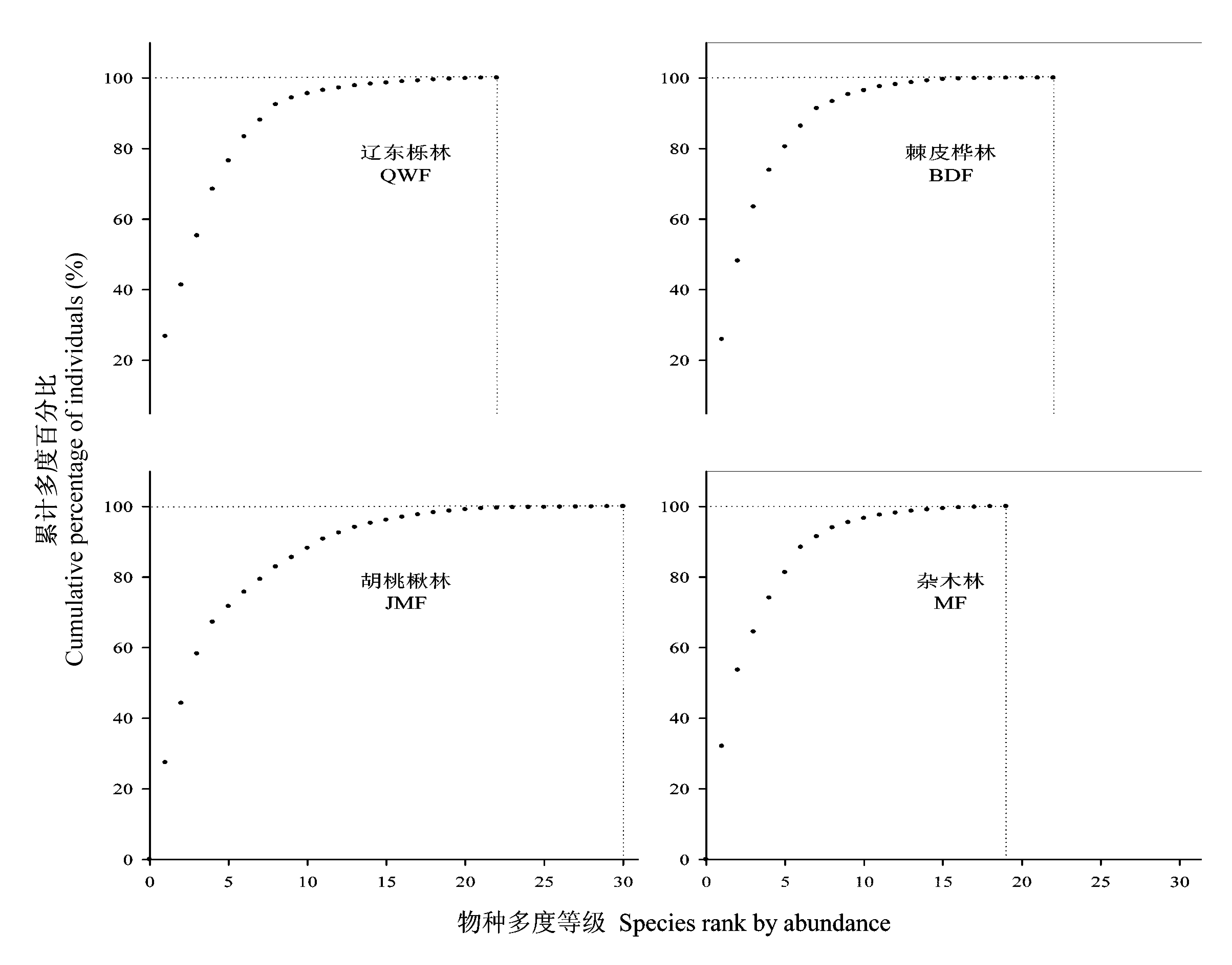
图1 物种多度的累计分布图
Fig. 1 Cumulative distribution curve of species abundance in the study plots. QWF, Quercus wutaishanica forest; BDF, Betula dahurica forest; JMF, Juglans mandshurica forest; MF, Mixed forest.
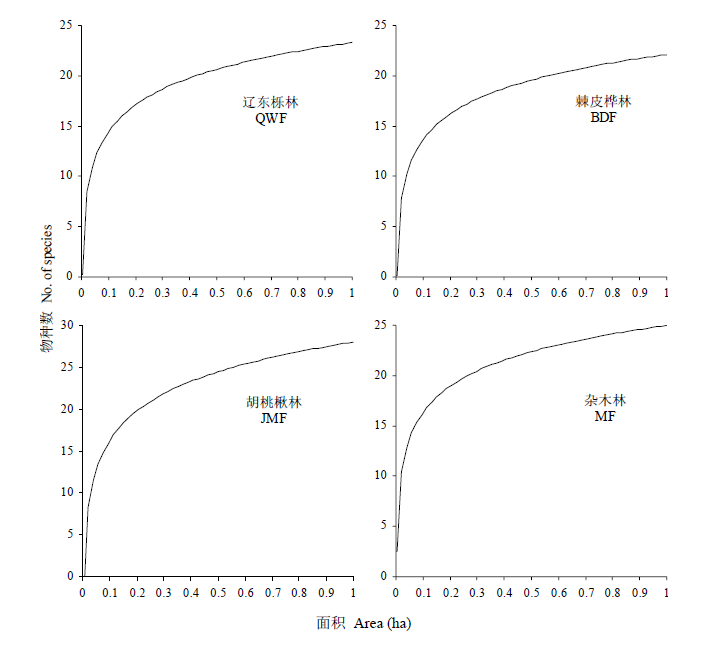
图2 研究样地的种-面积曲线
Fig. 2 Species-area curve in the study plots. QWF, Quercus wutaishanica forest; BDF, Betula dahurica forest; JMF, Juglans mandshurica forest; MF, Mixed forest.
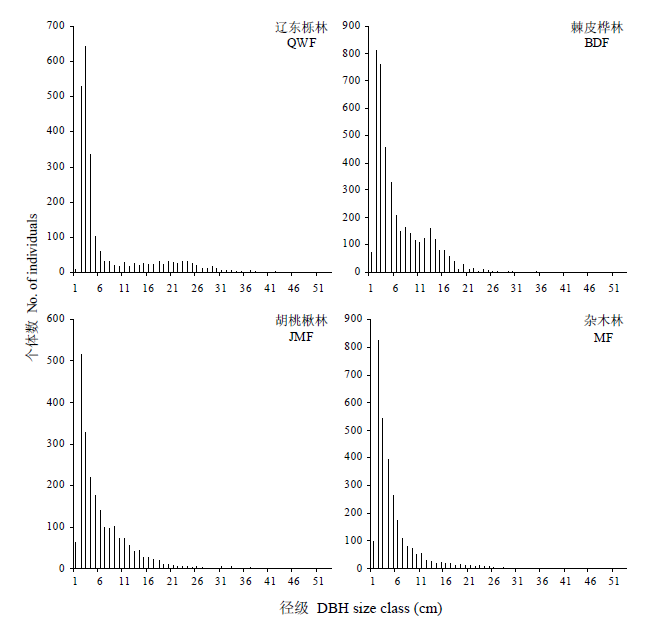
图3 所有物种的径级分布图
Fig. 3 Size-class distribution of all species in the study plots. QWF, Quercus wutaishanica forest; BDF, Betula dahurica forest; JMF, Juglans mandshurica forest; MF, Mixed forest.
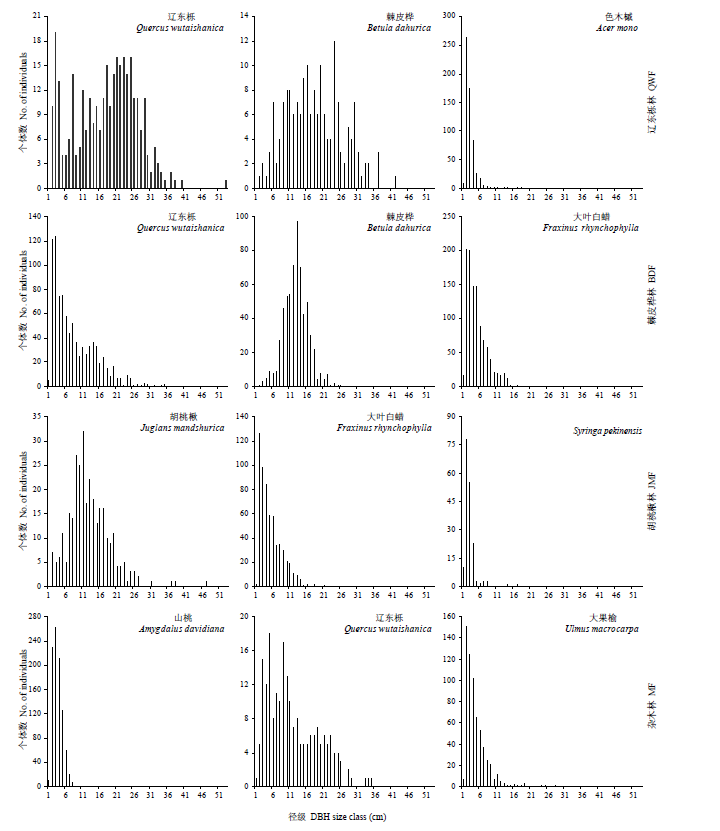
图4 每个样地重要值占前3位的物种的径级结构
Fig. 4 Species size-class distributions of the top three species ranked by importance value in each plot. QWF, Quercus wutaishanica forest; BDF, Betula dahurica forest; JMF, Juglans mandshurica forest; MF, Mixed forest.
| [1] | Chen DK (陈大珂), Zhou XF (周晓峰), Zhu N (祝宁) (1994) Natural Secondary Forest: Structure, Function, Dynamic and Management (天然次生林: 结构、功能、动态与经营). Northeast Forestry University Press, Harbin. (in Chinese) |
| [2] | Chen LZ (陈灵芝) (1997) The importance of Dongling Mountain region of warm temperate deciduous broad-leaved forest. In: The Study on Structure and Function of Forest in Warm Temperate Zone (暖温带森林生态系统结构与功能的研究) (ed. Chen LZ (陈灵芝)), pp. 1-9. Science Press, Beijing.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [3] |
Condit R (1995) Research in large, long-term tropical forest plots. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 18-23.
DOI URL PMID |
| [4] | Condit R (1998) Tropical Forest Census Plots: Methods and Results from Barro Colorado Island, Panama and a Comparison with Other Plots. Springer, Berlin. |
| [5] | Greig-Smith P (1983) Quantitative Plant Ecology, 3rd edn. Blackwell Scientific Publications, London. |
| [6] | Gao XM (高贤明), Wang W (王巍), Du XJ (杜晓军), Ma KP (马克平) (2001) Size structure, ecological significance and population origin of Quercus wutaishanica forest in Beijing mountainous area. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica (植物生态学报), 25, 673-678. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [7] | Hao ZQ (郝占庆), Li BH (李步杭), Zhang J (张健), Wang XG (王绪高), Ye J (叶吉), Yao XL (姚晓琳) (2008a) Broad- leaved Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) mixed forest plot in Changbaishan (CBS) of China: community composition and structure. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese version) (植物生态学报), 32, 238-250. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] | Hao ZQ (郝占庆), Zhang J (张健), Li BH (李步杭), Ye J (叶吉), Wang XG (王绪高), Yao XL (姚晓琳) (2008 b) Natural secondary poplar-birch forest in Changbai Mountain: species composition and community structure. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese version) (植物生态学报), 32, 251-261. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Hooper DU, Chapin FS III, Ewel JJ, Hector A, Inchausti P, Lavorel S, Lawton JH, Lodge DM, Loreau M, Naeem S, Schmid B, Setala H, Symstad AJ, Vandermeer J, Wardle DA (2005) Effects of biodiversity on ecosystem functioning: a consensus of current knowledge. Ecological Monographs, 75, 3-35. |
| [10] | Hou JH (侯继华), Huang JH (黄建辉), Ma KP (马克平) (2004) Eleven-year population growth dynamics of major species in a Quercus liaotungensis forest in the Dongling Mountains, northern China. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica (植物生态学报), 28, 609-615. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] | Huang ZL (黄忠良), Meng ML (蒙满林), Zhang YC (张佑昌) (1998) Climate of Dinghushan Biosphere Reserve. Tropical and Subtropical Forest Ecosystem (热带亚热带森林生态系统研究), 8, 134-139. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] | Hubbell SP (2001) The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [13] | Hubbell SP (2004) Two decades of research on the BCI Forest Dynamics Plot: where we have been and where we are going. In: Tropical Forest Diversity and Dynamism: Findings from a Large-scale Plot Network (eds Losos EC, Leigh EG Jr), pp. 8-30. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [14] | Hubbell SP, Foster RB (1986) Commonness and rarity in a neotropical forest: implications for tropical tree conservation. In: Conservation Biology: Science of Scarcity and Diversity (ed. Soulé M), pp.205-231. Sinauer Press, Sunderland. |
| [15] | Hussain MS, Sultana A, Khan JA, Khan A (2008) Species composition and community structure of forest stands in Kumaon Himalaya, Uttarakhand, India. Tropical Ecology, 49, 167-181. |
| [16] | Jiang YX (蒋有绪), Guo QS (郭泉水), Ma J (马娟) (1998) Classification and Community Characteristic of the Forests in China (中国森林群落分类及其群落学特征), Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [17] | Liu HF (刘海丰), Li L (李亮), Sang WG (桑卫国) (2011) Species composition and community structure of the Donglingshan forest dynamic plot in a warm temperate deciduous broad-leaved secondary forest, China. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 19, 232-242. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Loreau M, Naeem S, Inchausti P, Bengtsson J, Grime JP, Hector A, Hooper DU, Huston MA, Raffaelli D, Schmid B, Tilman D, Wardle DA (2001) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: current knowledge and future challenge. Science, 294, 804-808. |
| [19] | Lü SH (吕仕洪), Li XK (李先琨), Xiang WS (向悟生), Su ZM (苏宗明), Ou ZL (欧祖兰), Lu MX (陆茂新) (2004) The community structure characteristics and the population dynamics of Litsea dilleniifolia in Longgang of Guangxi. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment (植物资源与环境学报), 13(2), 25-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [20] | Ma KP (马克平), Chen LZ (陈灵芝), Yu SL (于顺利), Huang JH (黄建辉), Gao XM (高贤明), Liu CR (刘灿然) (1997) The major community types in Dongling Mountain region. In: Study on Structure and Function of Forests in Warm Temperate Zone (暖温带森林生态系统结构与功能的研究) (ed. Chen LZ (陈灵芝)), pp. 56-75. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [21] | Ma XD (马旭东), Zhang SJ (张苏峻), Su ZY (苏志尧), Ou YD (区余端), Liu G (刘刚) (2010) Community structure in relation to microtopography in a montane evergreen broadleaved forest in Chebaling National Nature Reserve. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 30, 5151-5160. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [22] | Olivero AM, Hix DM (1998) Influence of aspect and stand age on ground flora of southeastern Ohio forest ecosystems. Plant Ecology, 139, 177-187. |
| [23] | Ricklefs RE (2004) A comprehensive framework for global patterns in biodiversity. Ecology Letters, 7, 1-15. |
| [24] |
Tilman D, Reich PB, Knops JMH (2006) Biodiversity and ecosystem stability in a decade long grassland experiment. Nature, 441, 629-632.
URL PMID |
| [25] | Watkins AJ, Wilson JB (1994) Plant community structure, and its relation to the vertical complexity of communities: dominance/diversity and spatial rank consistency. Oikos, 70, 91-98. |
| [26] |
Wright SJ (2002) Plant diversity in tropical forests: a review of mechanisms of species coexistence. Oecologia, 130, 1-14.
URL PMID |
| [27] | Wu XP (吴晓莆), Wang ZH (王志恒), Cui HT (崔海亭), Fang JY (方精云) (2004) Community structures and species composition of oak forests in mountainous area of Beijing. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 12, 155-162. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] | Wu XP, Zheng Y, Ma KP (2002) Population distribution and dynamics of Quercus liaotungensis, Fraxinus rhynchophylla and Acer mono in Dongling Mountain, Beijing. Acta Botanica Sinica (植物学报), 44, 212-223. |
| [29] | Wu ZY (吴征镒) (1991) The areal-types of the world families of seed plants. Acta Botanica Yunnanica (云南植物研究), 4(Suppl.), 1-139. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [30] | Yang H (杨慧), Lou AR (娄安如), Gao YJ (高益军), Song HT (宋宏涛) (2007) Life history characteristics and spatial distribution of the Betula platyphylla population in the Dongling Mountain region, Beijing, China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese version) (植物生态学报), 31, 272-282. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [31] | Yang HX (阳含熙), Wu YG (伍业钢) (1988) Tree composition, age structure and regeneration strategy of the mixed broadleaf Korean pine forest in Changbaishan Biosphere Reserve, China. Scientia Silvae Sinicae (林业科学), 24, 18-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] | Ye WH (叶万辉), Cao HL (曹洪麟), Huang ZL (黄忠良), Lian JY (练琚愉), Wang ZG (王志高), Li L (李林), Wei SG (魏识广), Wang ZM (王章明) (2008) Community structure of a 20 ha lower subtropical evergreen broadleaved forest plot in Dinghushan, China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese version) (植物生态学报), 32, 274-286. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [33] | Yu XX (余新晓), Zhang XM (张晓明), Wang XB (王雄宾) (2008) Vegetation community features and succession law of natural shrubs in Beijing mountainous area. Journal of Beijing Forestry University (北京林业大学学报), 30(Suppl. 2.), 107-111. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [34] | Zhang JT (张金屯) (1995) Methods in Vegetation Quantitative Ecology (植被数量生态学方法). China Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [35] | Zhang M (张谧), Xiong GM (熊高明), Zhao CM (赵常明) Chen ZG (陈志刚), Xie ZQ (谢宗强) (2003) The structures and patterns of a Fagus engleriana-Cyclobalanopsis oxyodon community in Shennongjia area, Hubei Province. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica (植物生态学报), 27, 603-609. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [36] | Zhang YX (张育新), Ma KM (马克明), Qi J (祁建), Feng Y (冯云), Zhang JY (张洁瑜) (2009) Size structure and spatial pattern of Quercus liaotungensis population along elevation gradient in Dongling Mountain, Beijing. Acta Ecologica Sinica (生态学报), 29, 2789-2796. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [37] | Zhu Y (祝燕), Zhao GF (赵谷风), Zhang LW (张俪文), Shen GC (沈国春), Mi XC (米湘成), Ren HB (任海保), Yu MJ (于明坚), Chen JH (陈建华), Chen SW (陈声文), Fang T (方腾), Ma KP (马克平) (2008) Community composition and structure of Gutianshan forest dynamic plot in a mid-subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest, East China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese version) (植物生态学报), 32, 262-273. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 张明燡, 王晓梅, 郑言鑫, 吴楠, 李东浩, 樊恩源, 李娜, 单秀娟, 于涛, 赵春暖, 李波, 徐帅, 吴玉萍, 任利群. 黄河口典型牡蛎礁分布区资源状况和栖息地功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [2] | 仝淼, 王欢, 张文双, 王超, 宋建潇. 重金属污染土壤中细菌抗生素抗性基因分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [3] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [4] | 魏诗雨, 宋天骄, 罗佳宜, 张燕, 赵子萱, 茹靖雯, 易华, 林雁冰. 秦岭火地塘针叶林土壤细菌群落的海拔分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [5] | 时永强, 栾青杉, 单秀娟, 韦超, 赵永松, 孙策策, 金显仕. 长岛南部海域浮游动物多样性周年变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [6] | 倪艳梅, 陈莉, 董志远, 孙德斌, 李宝泉, 王绪敏, 陈琳琳. 黄河三角洲湿地生态修复区大型底栖动物群落结构与生态健康评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23303-. |
| [7] | 魏嘉欣, 姜治国, 杨林森, 熊欢欢, 金胶胶, 罗方林, 李杰华, 吴浩, 徐耀粘, 乔秀娟, 魏新增, 姚辉, 余辉亮, 杨敬元, 江明喜. 湖北神农架中亚热带山地落叶阔叶林25 ha动态监测样地群落物种组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23338-. |
| [8] | 刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇. 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [9] | 吴芳芳, 刘娜, 何春梅, 原作强, 郝占庆, 尹秋龙. 秦岭山地木本植物群落结构及多样性的海拔梯度格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24239-. |
| [10] | 单航, 雷祖培, 郑方东, 韦博良, 仲磊, 于明坚. 2013-2023年浙江乌岩岭次生常绿阔叶林群落动态变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24372-. |
| [11] | 冯嘉谊, 练琚愉, 冯瑜莙, 张东旭, 曹洪麟, 叶万辉. 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林群落垂直分层对群落结构及功能的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24306-. |
| [12] | 王兴煜, 孟京辉, 任思远, 祝燕. 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林群落生物多样性与地上生物量的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24230-. |
| [13] | 杜晴晴, 任思远, Nicole Tsz Shun Yuan, 祝燕. 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林幼树及成树生产力的影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24284-. |
| [14] | 黄骏涵, 余梵冬, 王裕祥, 黄哲, 张铭斯, 房苗, 舒璐, 徐猛, 韦慧, 汪学杰, 顾党恩, 罗思. 花地河中下游外来鱼类入侵现状及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24249-. |
| [15] | 杨舒涵, 王贺, 陈磊, 廖蓥飞, 严光, 伍一宁, 邹红菲. 松嫩平原异质生境对土壤线虫群落特征的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23295-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn