



生物多样性 ›› 2008, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (2): 156-165. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.07292 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2008.07292
廖信军1,3, 常洪3, 张桂香2,*( ), 王冬蕾3, 宋卫涛4, 韩旭2, 张自富5
), 王冬蕾3, 宋卫涛4, 韩旭2, 张自富5
收稿日期:2007-09-17
接受日期:2007-12-24
出版日期:2008-03-20
发布日期:2008-02-20
通讯作者:
张桂香
作者简介:*E-mail:gxzhang27@hotmail.com基金资助:
Xinjun Liao1,3, Hong Chang3, Guixiang Zhang2,*( ), Donglei Wang3, Weitao Song4, Xu Han2, Zifu Zhang5
), Donglei Wang3, Weitao Song4, Xu Han2, Zifu Zhang5
Received:2007-09-17
Accepted:2007-12-24
Online:2008-03-20
Published:2008-02-20
Contact:
Guixiang Zhang
摘要:
本文以大额牛(Bos frontalis)为外群, 应用16对微卫星DNA标记结合荧光-多重PCR技术, 评估了5个中国地方牦牛(Bos grunniens) (帕里牦牛、斯布牦牛、西藏高山牦牛、麦洼牦牛和九龙牦牛)品种内遗传变异和品种间遗传关系。6个群体的16个微卫星座位上共检测到159个等位基因, 其中有33个等位基因为5个牦牛品种所特有。6个群体的有效等位基因数(Ne)在2.2043-3.2754之间, 平均杂合度(H)在0.4858-0.6153之间, 平均多态信息含量(PIC)在0.4230-0.5711之间。5个牦牛品种的微卫星座位有丰富的遗传多样性; 而大额牛的遗传多样性相对较贫乏。5个牦牛群体间的遗传分化系数(Gst)为0.0527, 表明牦牛亚群体间遗传分化水平很低。采用邻近结合法构建聚类图和模糊聚类分析表明, 5个牦牛品种分为两大类, 其中斯布牦牛、西藏高山牦牛、帕里牦牛和麦洼牦牛为一大类, 九龙牦牛为一类。研究结果将为中国地方牦牛品种的保护和利用提供重要的理论依据。
廖信军, 常洪, 张桂香, 王冬蕾, 宋卫涛, 韩旭, 张自富 (2008) 中国5个地方牦牛品种遗传多样性的微卫星分析. 生物多样性, 16, 156-165. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.07292.
Xinjun Liao, Hong Chang, Guixiang Zhang, Donglei Wang, Weitao Song, Xu Han, Zifu Zhang (2008) Genetic diversity of five native Chinese yak breeds based on microsatellite DNA markers. Biodiversity Science, 16, 156-165. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.07292.
| 代号 Code | 品种 Breeds | 数量 Sample size | 采集地点 Collection location |
|---|---|---|---|
| PL | 帕里牦牛 Pali yak | 62 | 西藏自治区帕里镇 Pali Town, Tibet |
| SB | 斯布牦牛 Sibu yak | 57 | 西藏自治区斯布乡斯布牦牛场 Sibu Yak Farm of Sibu Town, Tibet |
| GS | 西藏高山牦牛 Tibetan High Mountainous yak | 61 | 西藏自治区那曲地区那曲县布巴镇 Buba Town, Naqu County, Tibet |
| JL | 九龙牦牛 Jiulong yak | 60 | 四川九龙县 Jiulong County, Sichuan |
| MW | 麦洼牦牛 Maiwa yak | 59 | 四川阿坝州畜牧局牦牛选育基地 Yak Breeding Center of Aba State Livestock Bureau, Sichuan |
| GY | 大额牛 Gayal | 20 | 云南泸水县老窝乡 Laowo Town, Lushui County, Yunnan |
表1 牦牛品种名称、数量和采集地点
Table 1 Name, sample size and collecting location of the studied yak breeds
| 代号 Code | 品种 Breeds | 数量 Sample size | 采集地点 Collection location |
|---|---|---|---|
| PL | 帕里牦牛 Pali yak | 62 | 西藏自治区帕里镇 Pali Town, Tibet |
| SB | 斯布牦牛 Sibu yak | 57 | 西藏自治区斯布乡斯布牦牛场 Sibu Yak Farm of Sibu Town, Tibet |
| GS | 西藏高山牦牛 Tibetan High Mountainous yak | 61 | 西藏自治区那曲地区那曲县布巴镇 Buba Town, Naqu County, Tibet |
| JL | 九龙牦牛 Jiulong yak | 60 | 四川九龙县 Jiulong County, Sichuan |
| MW | 麦洼牦牛 Maiwa yak | 59 | 四川阿坝州畜牧局牦牛选育基地 Yak Breeding Center of Aba State Livestock Bureau, Sichuan |
| GY | 大额牛 Gayal | 20 | 云南泸水县老窝乡 Laowo Town, Lushui County, Yunnan |
| 座位 Locus | 引物序列 (5’-3’) Primer sequence | 退火温度 Annealing temp.(℃) | 片段大小 Allele Size (bp) | 观察 等位基因数 Observed allele number | 荧光标记 Fluorescence | 所在染色体 Chromosome location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPS115 | F: AAAGTGACACAACAGCTTCTCCAG R: AACGAGTGTCCTAGTTTGGCTGTG | 55-60 | 234-258 | 11 | Vic | 15 |
| TGLA122 | F: CCCTCCTCCAGGTAAATCAGC R: AATCACATGGCAAATAAGTACATAC | 55-58 | 136-184 | 12 | Ned | 21 |
| TGLA53 | F: GCTTTCAGAAATAGTTTGCATTCA R: ATCTTCACATGATATTACAGCAGA | 55 | 143-191 | 13 | Pet | 16 |
| TGLA126 | F: CTAATTTAGAATGAGAGAGGCTTCT R: TTGGTCTCTATTCTCTGAATATTCC | 55-58 | 115-131 | 7 | Vic | 20 |
| TGLA227 | F: CGAATTCCAAATCTGTTAATTTGCT R: ACAGACAGAAACTCAATGAAAGCA | 55-56 | 75-105 | 10 | Pet | 18 |
| HEL13 | F: TAAGGACTTGAGATAAGGAG R: CCATCTACCTCCATCTTAAC | 51.6 | 165-191 | 11 | Pet | 11 |
| INRA005 | F: CAATCTGCATGAAGTATAAATAT R: CTTCAGGCATACCCTACACC | 55 | 120-160 | 10 | Ned | 12 |
| BM1824 | F: GAGCAAGGTGTTTTTCCAATC R: CATTCTCCAACTGCTTCCTTG | 57 | 180-200 | 7 | 6fam | 1 |
| HEL5 | F: GCAGGATCACTTGTTAGGGA R: AGACGTTAGTGTACATTAAC | 54 | 149-165 | 7 | Vic | 21 |
| BM2113 | F: GCTGCCTTCTACCAAATACCC R: CTTAGACAACAGGGGTTTGG | 55-60 | 116-146 | 13 | 6fam | 2 |
| TGLA57 | F: GCTTCCAAAACTTTACAATATGTAT R: GCTTTTTAATCCTCAGCTTGCTG | 55 | 77-99 | 9 | 6fam | 1 |
| ILSTS013 | F: ACACAAAATCAGATCAGTGG R: CTTGATCCTTATAGAACTGG | 58 | 121-135 | 11 | Vic | 9 |
| ILSTS050 | F: AAATCAGACACCCAGTTTCC R: GTTTTTCTACACGAGTTGGC | 55 | 161-183 | 13 | Pet | 21 |
| AGLA293 | F: GAAACTCAACCCAAGACAACTCAAG R: ATGACTTTATTCTCCACCTAGCAGA | 55 | 210-240 | 11 | 6fam | 5 |
| ILSTS008 | F: GAATCATGGATTTTCTGGGG R: TAGCAGTGAGTGAGGTTGGC | 58 | 175-187 | 7 | 6fam | 14 |
| TGLA73 | F: GAGAATCACCTAGAGAGAGGCA R: CTTTCTCTTTAAATTCTATATGGT | 55 | 111-143 | 14 | 6fam | 9 |
表2 16对微卫星引物的信息
Table 2 The information about sixteen microsatellite primers
| 座位 Locus | 引物序列 (5’-3’) Primer sequence | 退火温度 Annealing temp.(℃) | 片段大小 Allele Size (bp) | 观察 等位基因数 Observed allele number | 荧光标记 Fluorescence | 所在染色体 Chromosome location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPS115 | F: AAAGTGACACAACAGCTTCTCCAG R: AACGAGTGTCCTAGTTTGGCTGTG | 55-60 | 234-258 | 11 | Vic | 15 |
| TGLA122 | F: CCCTCCTCCAGGTAAATCAGC R: AATCACATGGCAAATAAGTACATAC | 55-58 | 136-184 | 12 | Ned | 21 |
| TGLA53 | F: GCTTTCAGAAATAGTTTGCATTCA R: ATCTTCACATGATATTACAGCAGA | 55 | 143-191 | 13 | Pet | 16 |
| TGLA126 | F: CTAATTTAGAATGAGAGAGGCTTCT R: TTGGTCTCTATTCTCTGAATATTCC | 55-58 | 115-131 | 7 | Vic | 20 |
| TGLA227 | F: CGAATTCCAAATCTGTTAATTTGCT R: ACAGACAGAAACTCAATGAAAGCA | 55-56 | 75-105 | 10 | Pet | 18 |
| HEL13 | F: TAAGGACTTGAGATAAGGAG R: CCATCTACCTCCATCTTAAC | 51.6 | 165-191 | 11 | Pet | 11 |
| INRA005 | F: CAATCTGCATGAAGTATAAATAT R: CTTCAGGCATACCCTACACC | 55 | 120-160 | 10 | Ned | 12 |
| BM1824 | F: GAGCAAGGTGTTTTTCCAATC R: CATTCTCCAACTGCTTCCTTG | 57 | 180-200 | 7 | 6fam | 1 |
| HEL5 | F: GCAGGATCACTTGTTAGGGA R: AGACGTTAGTGTACATTAAC | 54 | 149-165 | 7 | Vic | 21 |
| BM2113 | F: GCTGCCTTCTACCAAATACCC R: CTTAGACAACAGGGGTTTGG | 55-60 | 116-146 | 13 | 6fam | 2 |
| TGLA57 | F: GCTTCCAAAACTTTACAATATGTAT R: GCTTTTTAATCCTCAGCTTGCTG | 55 | 77-99 | 9 | 6fam | 1 |
| ILSTS013 | F: ACACAAAATCAGATCAGTGG R: CTTGATCCTTATAGAACTGG | 58 | 121-135 | 11 | Vic | 9 |
| ILSTS050 | F: AAATCAGACACCCAGTTTCC R: GTTTTTCTACACGAGTTGGC | 55 | 161-183 | 13 | Pet | 21 |
| AGLA293 | F: GAAACTCAACCCAAGACAACTCAAG R: ATGACTTTATTCTCCACCTAGCAGA | 55 | 210-240 | 11 | 6fam | 5 |
| ILSTS008 | F: GAATCATGGATTTTCTGGGG R: TAGCAGTGAGTGAGGTTGGC | 58 | 175-187 | 7 | 6fam | 14 |
| TGLA73 | F: GAGAATCACCTAGAGAGAGGCA R: CTTTCTCTTTAAATTCTATATGGT | 55 | 111-143 | 14 | 6fam | 9 |
| 座位 Locus | 帕里牦牛 Pali yak | 斯布牦牛 Sibu yak | 西藏高山牦牛 Tibetan High Mountainous yak | 九龙牦牛 Jiulong yak | 麦洼牦牛 Maiwa yak | 大额牛 Gayal | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM1824 | 192 (0.009) | ||||||||||||
| BM2113 | 116 (0.009) | 120 (0.632) | |||||||||||
| 138 (0.009) . | 132 (0.261) | ||||||||||||
| HEL5 | 149 (0.010) | 141 (0.010) | 155 (0.021) | ||||||||||
| INRA005 | 136 (0.026) | 132 (0.500) | |||||||||||
| 148 (0.009) | |||||||||||||
| TGLA126 | 127(0.009) | ||||||||||||
| TGLA53 | 161 (0.009) | 179 (0.009) | |||||||||||
| 175 (0.009) | |||||||||||||
| HEL13 | 83 (0.009) | 165 (0.009) | 191 (0.375) | ||||||||||
| 193 (0.096) | |||||||||||||
| SPS115 | 230 (0.018) | 256 (0.103) | |||||||||||
| TGLA122 | 138 (0.018) | 142 (0.008) | 166 (0.009) | ||||||||||
| 168 (0.017) | |||||||||||||
| TGLA227 | 87 (0.009) | 99 (0.010) | 101 (0.020) | 97 (0.009) | 81 (0.125) | ||||||||
| AGLA293 | 202 (0.009) | 238 (0.009) | 220 (0.017) | 234 (0.059) | |||||||||
| 242 (0.019) | |||||||||||||
| ILSTS013 | 105 (0.009) | 133(0.231) | |||||||||||
| 109 (0.009) | |||||||||||||
| ILSTS050 | 147 (0.184) 149 (0.105) 151 (0.316) | ||||||||||||
| 153 (0.316) 155 (0.079) | |||||||||||||
| TGLA57 | 31 (0.017) | 71 (0.008) | 97 (0.017) | ||||||||||
| TGLA73 | 193 (0.017) | ||||||||||||
表4 6个群体特有等位基因及频率(括号内为频率)
Table 4 Unique alleles and their frequencies in the six populations studied. Allele frequency in the parentheses.
| 座位 Locus | 帕里牦牛 Pali yak | 斯布牦牛 Sibu yak | 西藏高山牦牛 Tibetan High Mountainous yak | 九龙牦牛 Jiulong yak | 麦洼牦牛 Maiwa yak | 大额牛 Gayal | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM1824 | 192 (0.009) | ||||||||||||
| BM2113 | 116 (0.009) | 120 (0.632) | |||||||||||
| 138 (0.009) . | 132 (0.261) | ||||||||||||
| HEL5 | 149 (0.010) | 141 (0.010) | 155 (0.021) | ||||||||||
| INRA005 | 136 (0.026) | 132 (0.500) | |||||||||||
| 148 (0.009) | |||||||||||||
| TGLA126 | 127(0.009) | ||||||||||||
| TGLA53 | 161 (0.009) | 179 (0.009) | |||||||||||
| 175 (0.009) | |||||||||||||
| HEL13 | 83 (0.009) | 165 (0.009) | 191 (0.375) | ||||||||||
| 193 (0.096) | |||||||||||||
| SPS115 | 230 (0.018) | 256 (0.103) | |||||||||||
| TGLA122 | 138 (0.018) | 142 (0.008) | 166 (0.009) | ||||||||||
| 168 (0.017) | |||||||||||||
| TGLA227 | 87 (0.009) | 99 (0.010) | 101 (0.020) | 97 (0.009) | 81 (0.125) | ||||||||
| AGLA293 | 202 (0.009) | 238 (0.009) | 220 (0.017) | 234 (0.059) | |||||||||
| 242 (0.019) | |||||||||||||
| ILSTS013 | 105 (0.009) | 133(0.231) | |||||||||||
| 109 (0.009) | |||||||||||||
| ILSTS050 | 147 (0.184) 149 (0.105) 151 (0.316) | ||||||||||||
| 153 (0.316) 155 (0.079) | |||||||||||||
| TGLA57 | 31 (0.017) | 71 (0.008) | 97 (0.017) | ||||||||||
| TGLA73 | 193 (0.017) | ||||||||||||
| 座位 Locus | 帕里牦牛 Pali yak | 斯布牦牛 Sibu yak | 西藏高山牦牛 Tibetan High Mountainous yak | 九龙牦牛 Jiulong yak | 麦洼牦牛 Maiwa yak | 大额牛 Gayal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM1824 | 180 (0.562) | 186 (0.925) | ||||
| BM2113 | 128 (0.772) | 128 (0.583) | 128 (0.612) | 120 (0.632) | ||
| HEL5 | 137 (0.696) | 137 (0.962) | 137 (0.781) | 137 (0.894) | 137 (0.726) | |
| INRA005 | 134 (0.658) | 134 (0.543) | 132 (0.500), 134 (0.500) | |||
| TGLA126 | 117 (0.586) | 119 (0.700) | ||||
| TGLA53 | 153 (0.500) | 159 (0.500), 165 (0.500) | ||||
| HEL13 | 183 (0.644) | 183 (0.628) | 183 (0.603) | 197 (0.625) | ||
| SPS115 | 240 (0.465) | 250 (0.667) | ||||
| TGLA122 | 152 (0.388) | |||||
| TGLA227 | 75 (0.632) | 75 (0.573) | 73 (0.620) | 73 (0.561) | 73 (0.602) | 75 (0.850) |
| AGLA293 | 208 (0.860) | 208 (0.890) | 208 (0.833) | 208 (0.627) | 208 (0.737) | 226 (0.529) |
| ILSTS008 | 181 (0.553) | 181 (0.686) | 181 (0.647) | 171 (0.895) | ||
| ILSTS013 | 121 (0.593) | 121 (0.585) | 117 (0.410) | |||
| ILSTS050 | 169 (0.696) | 151 (0.316), 153 (0.316) | ||||
| TGLA57 | 73 (0.658) | 73 (0.746) | 73 (0.741) | 73 (0.636) | 73 (0.746) | 81 (0.450) |
| TGLA73 | 115 (0.246) | 125 (0.600) |
表5 6个群体优势等位基因及频率
Table 5 Dominant alleles and their frequencies in the six populations. Allele frequency in the parentheses.
| 座位 Locus | 帕里牦牛 Pali yak | 斯布牦牛 Sibu yak | 西藏高山牦牛 Tibetan High Mountainous yak | 九龙牦牛 Jiulong yak | 麦洼牦牛 Maiwa yak | 大额牛 Gayal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM1824 | 180 (0.562) | 186 (0.925) | ||||
| BM2113 | 128 (0.772) | 128 (0.583) | 128 (0.612) | 120 (0.632) | ||
| HEL5 | 137 (0.696) | 137 (0.962) | 137 (0.781) | 137 (0.894) | 137 (0.726) | |
| INRA005 | 134 (0.658) | 134 (0.543) | 132 (0.500), 134 (0.500) | |||
| TGLA126 | 117 (0.586) | 119 (0.700) | ||||
| TGLA53 | 153 (0.500) | 159 (0.500), 165 (0.500) | ||||
| HEL13 | 183 (0.644) | 183 (0.628) | 183 (0.603) | 197 (0.625) | ||
| SPS115 | 240 (0.465) | 250 (0.667) | ||||
| TGLA122 | 152 (0.388) | |||||
| TGLA227 | 75 (0.632) | 75 (0.573) | 73 (0.620) | 73 (0.561) | 73 (0.602) | 75 (0.850) |
| AGLA293 | 208 (0.860) | 208 (0.890) | 208 (0.833) | 208 (0.627) | 208 (0.737) | 226 (0.529) |
| ILSTS008 | 181 (0.553) | 181 (0.686) | 181 (0.647) | 171 (0.895) | ||
| ILSTS013 | 121 (0.593) | 121 (0.585) | 117 (0.410) | |||
| ILSTS050 | 169 (0.696) | 151 (0.316), 153 (0.316) | ||||
| TGLA57 | 73 (0.658) | 73 (0.746) | 73 (0.741) | 73 (0.636) | 73 (0.746) | 81 (0.450) |
| TGLA73 | 115 (0.246) | 125 (0.600) |
| 座位 Locus | 5个牦牛群体共有等位基因(bp) Common alleles in five yak populations | 6个品种共有等位基因(bp) Common alleles in six breeds | 5个牦牛群体特有等位基因数 No. of unique allele in five yak populations | 大额牛特有等位基因数 No. of unique allele in Gayal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM1824 | 178, 180, 186, 190 | 186 | 1 | 0 |
| BM2113 | 118, 124, 128, 134, 144 | 124, 128 | 2 | 2 |
| HEL5 | 137, 139 | 3 | 0 | |
| INRA005 | 134, 152 | 134 | 2 | 1 |
| TGLA126 | 109, 115, 117, 119 | 119 | 1 | 0 |
| TGLA53 | 153, 157, 159, 165, 169 | 165 | 3 | 0 |
| HEL13 | 183, 189, 197, 199 | 197 | 3 | 1 |
| SPS115 | 232, 238, 240, 242, 244, 246 | 1 | 1 | |
| TGLA122 | 140, 146, 148, 150, 152, 164 | 4 | 0 | |
| TGLA227 | 73, 75 | 75 | 4 | 1 |
| AGLA293 | 208, 214, 226 | 226 | 4 | 1 |
| ILSTS008 | 179, 181 | 0 | 0 | |
| ILSTS013 | 119, 121, 123, 125, 127 | 119 | 2 | 1 |
| ILSTS050 | 167, 169, 171 | 0 | 5 | |
| TGLA57 | 73, 77, 81, 83 | 77, 81 | 2 | 1 |
| TGLA73 | 115, 117, 119, 123, 125, 127, 129, 193 | 115, 117, 123, 125 | 1 | 0 |
表6 6个群体共有等位基因和特有等位基因数
Table 6 The common alleles and the number of unique alleles in the six populations
| 座位 Locus | 5个牦牛群体共有等位基因(bp) Common alleles in five yak populations | 6个品种共有等位基因(bp) Common alleles in six breeds | 5个牦牛群体特有等位基因数 No. of unique allele in five yak populations | 大额牛特有等位基因数 No. of unique allele in Gayal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM1824 | 178, 180, 186, 190 | 186 | 1 | 0 |
| BM2113 | 118, 124, 128, 134, 144 | 124, 128 | 2 | 2 |
| HEL5 | 137, 139 | 3 | 0 | |
| INRA005 | 134, 152 | 134 | 2 | 1 |
| TGLA126 | 109, 115, 117, 119 | 119 | 1 | 0 |
| TGLA53 | 153, 157, 159, 165, 169 | 165 | 3 | 0 |
| HEL13 | 183, 189, 197, 199 | 197 | 3 | 1 |
| SPS115 | 232, 238, 240, 242, 244, 246 | 1 | 1 | |
| TGLA122 | 140, 146, 148, 150, 152, 164 | 4 | 0 | |
| TGLA227 | 73, 75 | 75 | 4 | 1 |
| AGLA293 | 208, 214, 226 | 226 | 4 | 1 |
| ILSTS008 | 179, 181 | 0 | 0 | |
| ILSTS013 | 119, 121, 123, 125, 127 | 119 | 2 | 1 |
| ILSTS050 | 167, 169, 171 | 0 | 5 | |
| TGLA57 | 73, 77, 81, 83 | 77, 81 | 2 | 1 |
| TGLA73 | 115, 117, 119, 123, 125, 127, 129, 193 | 115, 117, 123, 125 | 1 | 0 |
| 品种 Breeds | 帕里牦牛 PL | 斯布牦牛 SB | 西藏高山牦牛 GS | 九龙牦牛 JL | 麦洼牦牛 MW | 大额牛 GY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 帕里牦牛 PL | 0.0861 | 0.0707 | 0.1266 | 0.0944 | 0.7136 | |
| 斯布牦牛 SB | 0.0793 | 0.0715 | 0.1071 | 0.0615 | 0.7052 | |
| 西藏高山牦牛 GS | 0.0827 | 0.0649 | 0.0970 | 0.0723 | 0.6955 | |
| 九龙牦牛 JL | 0.1632 | 0.1659 | 0.1168 | 0.0987 | 0.6515 | |
| 麦洼牦牛 MW | 0.0838 | 0.0738 | 0.0937 | 0.1239 | 0.6836 | |
| 大额牛 GY | 1.1508 | 1.4356 | 1.6049 | 1.2457 | 1.4628 |
表7 6个群体间的Nei’s遗传距离(DA)(对角线上方)和Nei’s标准遗传距离(DS)(对角线下方)。品种代号同表1
Table 7 Nei’s genetic distance (DA) (above diagonal) and Nei’s standard genetic distance (DS) (below diagonal) among the six studied populations. Breed codes see Table 1.
| 品种 Breeds | 帕里牦牛 PL | 斯布牦牛 SB | 西藏高山牦牛 GS | 九龙牦牛 JL | 麦洼牦牛 MW | 大额牛 GY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 帕里牦牛 PL | 0.0861 | 0.0707 | 0.1266 | 0.0944 | 0.7136 | |
| 斯布牦牛 SB | 0.0793 | 0.0715 | 0.1071 | 0.0615 | 0.7052 | |
| 西藏高山牦牛 GS | 0.0827 | 0.0649 | 0.0970 | 0.0723 | 0.6955 | |
| 九龙牦牛 JL | 0.1632 | 0.1659 | 0.1168 | 0.0987 | 0.6515 | |
| 麦洼牦牛 MW | 0.0838 | 0.0738 | 0.0937 | 0.1239 | 0.6836 | |
| 大额牛 GY | 1.1508 | 1.4356 | 1.6049 | 1.2457 | 1.4628 |
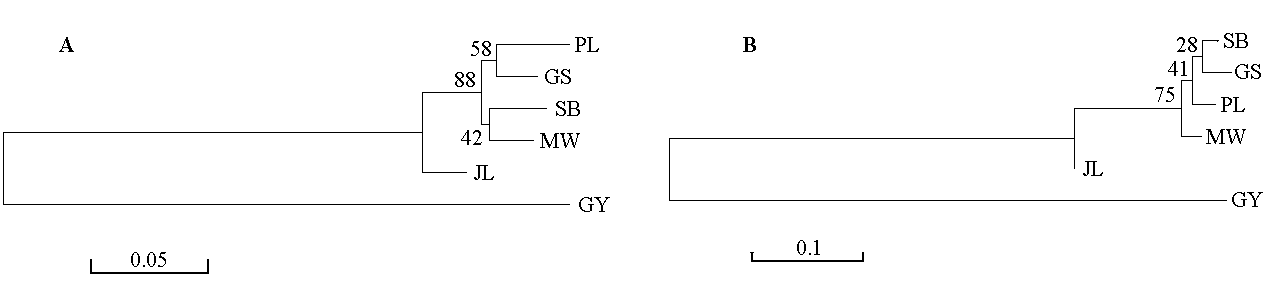
图1 基于Nei’s遗传距离(DA) (A)和Nei’s标准遗传距离(DS)(B)用NJ方法构建的6个群体的聚类图(品种代号同表1)
Fig. 1 Dendrograms of six populations based on Nei’s genetic distance (DA) (A) and Nei’s standard genetic distance (DS) (B) using neighbor-joining method. Breed codes see Table 1.
| 品种 Breeds | 帕里牦牛 PL | 斯布牦牛 SB | 西藏高山牦牛 GS | 九龙牦牛 JL | 麦洼牦牛 MW | 大额牛 GY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 帕里牦牛 PL | 1.0000 | 0.9530 | 0.9530 | 0.9340 | 0.9530 | 0.3450 |
| 斯布牦牛 SB | 0.9530 | 1.0000 | 0.9600 | 0.9340 | 0.9560 | 0.3450 |
| 西藏高山牦牛 GS | 0.9510 | 0.9600 | 1.0000 | 0.9340 | 0.9560 | 0.3450 |
| 九龙牦牛 JL | 0.9110 | 0.9100 | 0.9340 | 1.0000 | 0.9340 | 0.3450 |
| 麦洼牦牛 MW | 0.9510 | 0.9560 | 0.9460 | 0.9310 | 1.0000 | 0.3450 |
| 大额牛 GY | 0.2420 | 0.2500 | 0.1650 | 0.3450 | 0.2370 | 1.0000 |
表8 6个群体的模糊等价关系矩阵(上三角)和模糊相容关系矩阵(下三角)
Table 8 Fuzzy similarity relation matrix (above diagonal) and fuzzy containing relation matrix (below diagonal) among the six populations. Breed codes see Table 1.
| 品种 Breeds | 帕里牦牛 PL | 斯布牦牛 SB | 西藏高山牦牛 GS | 九龙牦牛 JL | 麦洼牦牛 MW | 大额牛 GY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 帕里牦牛 PL | 1.0000 | 0.9530 | 0.9530 | 0.9340 | 0.9530 | 0.3450 |
| 斯布牦牛 SB | 0.9530 | 1.0000 | 0.9600 | 0.9340 | 0.9560 | 0.3450 |
| 西藏高山牦牛 GS | 0.9510 | 0.9600 | 1.0000 | 0.9340 | 0.9560 | 0.3450 |
| 九龙牦牛 JL | 0.9110 | 0.9100 | 0.9340 | 1.0000 | 0.9340 | 0.3450 |
| 麦洼牦牛 MW | 0.9510 | 0.9560 | 0.9460 | 0.9310 | 1.0000 | 0.3450 |
| 大额牛 GY | 0.2420 | 0.2500 | 0.1650 | 0.3450 | 0.2370 | 1.0000 |
| [1] |
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, David RW (1980) Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. American Journal of Human Genetics, 32,314-331.
URL PMID |
| [2] | Cai L(蔡立) (1992) Chinese Yak (中国牦牛). China Agricultural Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [3] | Chang GB(常国斌) (2004) Study on the Level of Evolutionary Divergence Between Two Wild and Domestic Quail Species (两种野生鹌鹑与家鹑进化趋异水平的研究). PhD dissertation, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou. (in Chinese with English summary). |
| [4] | Chang H(常洪) (1995) Essentials of Livestock Genetic Resources (家畜遗传资源学纲要). China Agricultural Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [5] | Editorial Committee of Chinese Yak (中国牦牛学编委会) (1989) Chinese Yak (中国牦牛学). Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [6] |
Guo SC, Savolainen P, Su JP, Zhang Q, Qi DL, Zhou J, Zhong Y, Zhao XQ, Liu JQ (2006) Origin of mitochondrial DNA diversity of domestic yaks. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 6,73.
DOI URL PMID |
| [7] |
Hanotte O, Okomo M, Verjee Y, Regee E, Teale A (1997) A polymorphic Y chromosome microsatellite locus in cattle. Animal Genetics, 28,318-319.
URL PMID |
| [8] | Lai SJ(赖松家), Wang L(王玲), Liu YP(刘益平), Li XW(李学伟) (2005) Study on mitochondrial DNA genetic polymorphism of some yak breeds in China. Acta Genetica Sinica (遗传学报), 32,463-470. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] |
Lai SJ, Chen SY, Liu YP, Yao YG (2007) Mitochondrial DNA sequence diversity and origin of Chinese domestic yak. Animal Genetics, 38,77-80.
URL PMID |
| [10] | Li QF(李齐发), Li YX(李隐侠), Zhao XB(赵兴波), Liu ZS(刘振山), Zhang QB(张庆波), Song DW(宋大伟), Qu XG(屈旭光), Li N(李宁), Xie Z(谢庄) (2006) Sequencing cytochrome b gene of mitochondrial DNA in yak and researching its origin and taxonomic status . Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica (畜牧兽医学报), 37,1118-1123. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] | Lu SD(卢圣栋) (1993) Experimental Technique of Modern Molecular Biology (现代分子生物学实验技术). Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [12] | Luo YF(罗永发), Wang ZG(王志刚), Li JQ(李加琪), Zhang GX(张桂香), Chen YS(陈瑶生), Liang Y(梁勇), Yu FQ(于福清), Song WT(宋卫涛), Zhang ZF(张自富) (2006) Genetic variation and genetic relationship among 13 Chinese and introduced cattle breeds using microsatellite DNA markers. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 14,498-507. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] | Ma YH(马月辉), Chen YC(陈幼春), Feng WQ(冯维祺), Wang DY(王端云) (2002) Germplasm of Chinese domestic animals and their conservation. Review of China Agricultural Science and Technology (中国农业科技导报), 3,37-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Nei M (1972) Genetic distance between populations. The American Naturalist, 106,283-292. |
| [15] |
Nei M, Tajima F, Tateno Y (1983) Accuracy of estimated phylogenetic trees from molecular data. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 19,153-170.
URL PMID |
| [16] |
Nguyen TT, Genini S, Ménétrey F, Malek M, Vögeli P, Goe MR, Stranzinger G (2005) Application of bovine microsatellite markers for genetic diversity analysis of Swiss yak (Poephagus grunniens). Animal Genetics, 36,484-489.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] | Ota T (1993) DISPAN: Genetic Distance and Phylogenetic Analysis. Institute of Molecular Evolutionary Genetics, The Pennsylvania State University. |
| [18] | Qi XB (2004) Genetic Diversity, Differentiation, and Relationship of Domestic Yak Populations: A Microsatellite and Mitochondrial DNA Study. PhD dissertation, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou. |
| [19] |
Qi XB, Han JL, Lkhagva B, Chekarova I, Badamdorj D, Rege JEO, Hanotte O (2005) Genetic diversity and differentiation of Mongolian and Russian yak populations. Journal of Animal Breeding and Genetics, 122,117-126.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] | Qiu H(邱怀), Qin ZR(秦志锐), Chen YC(陈幼春), Wang DA(王东安), Wei WY(韦文雅), Li KL(李孔亮), Li RY(李忍益), Zou XQ(邹霞青), Guo JX(郭经恂), Tong BQ(童碧泉), Ji YL(冀一伦), Cai L(蔡立) (1986) Bovine Breeds in China (中国牛品种志). Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai. (in Chinese) |
| [21] | Raymond M, Rousset F (1995) Population genetics software for exact tests and ecumenicism. Journal of Heredity, 86,248-249. |
| [22] | Tu ZC(涂正超), Zhang YP(张亚平), Qiu H(邱怀) (1998) Mitochondrial DNA polymorphism and genetic diversity in Chinese yaks. Acta Genetica Sinica (遗传学报), 25,205-212. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [23] |
Tu ZC, Zhang YP, Qiu H (1997) Genetic diversity and divergence in Chinese yak ( Bos grunniens) populations inferred from blood protein electrophoresis . Biochemical Genetics, 35,13-16.
URL PMID |
| [24] | Wang DL(王冬蕾), Chang H(常洪), Yang JX(杨军香), Zhang GX(张桂香), Wang ZG(王志刚), Yu B(于波), Liao XJ(廖信军), Song WT(宋卫涛), Han X(韩旭) (2007) Analysis on the genetic structure of 8 Asia buffalo populations. Hereditas (Beijing) (遗传), 29,1103-1109. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [25] | Zhong JC(钟金城), Chen ZH(陈智华), Zi XD(字向东), Wen YL(文勇立), Ma L(马力) (2001) Cluster analysis of yak breeds. Journal of Southwest Nationalities College (National Science Edition) (西南民族学院学报(自然科学版)), 27,92-94. ( in Chinese with English abstract ). |
| [26] | Zhong JC(钟金城), Zhao SJ(赵素君), Chen ZH(陈智华), Ma ZJ(马志杰) (2006) Study on genetic diversity and classification of the yak. Scientia Agricultura Sinica (中国农业科学), 39,389-397. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 弋维, 艾鷖, 吴萌, 田黎明, 泽让东科. 青藏高原高寒草甸土壤古菌群落对不同放牧强度的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24339-. |
| [2] | 熊飞, 刘红艳, 翟东东, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 陈大庆. 基于基因组重测序的长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [3] | 陶克涛, 白东义, 图格琴, 赵若阳, 安塔娜, 铁木齐尔·阿尔腾齐米克, 宝音德力格尔, 哈斯, 芒来, 韩海格. 基于基因组SNPs对东亚家马不同群体遗传多样性的评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21031-. |
| [4] | 陶克涛, 韩海格, 赵若阳, 图格琴, 芒来, 白东义. 家马的驯化起源与遗传演化特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(6): 734-748. |
| [5] | 翁茁先, 黄佳琼, 张仕豪, 余锴纯, 钟福生, 黄勋和, 张彬. 利用线粒体COI基因揭示中国乌骨鸡遗传多样性和群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(6): 667-676. |
| [6] | 武星彤, 陈璐, 王敏求, 张原, 林雪莹, 李鑫玉, 周宏, 文亚峰. 丹霞梧桐群体遗传结构及其遗传分化[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(11): 1168-1179. |
| [7] | 刘青青, 董志军. 基于线粒体COI基因分析钩手水母的群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(11): 1204-1211. |
| [8] | 刘若愚, 孙忠民, 姚建亭, 胡自民, 段德麟. 中国近海重要生态建群红藻真江蓠的群体遗传多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(7): 781-790. |
| [9] | 周蓉, 李佳琦, 李铀, 刘迺发, 房峰杰, 施丽敏, 王莹. 基于线粒体DNA的大石鸡种群遗传变异[J]. 生物多样性, 2012, 20(4): 451-459. |
| [10] | 何晓红, 韩秀丽, 关伟军, 田可川, 张文彬, 马月辉. 采用微卫星标记分析10个双峰驼群体的遗传变异和群体间的遗传关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2012, 20(2): 199-206. |
| [11] | 张春光, 赵亚辉, 邢迎春, 郭瑞禄, 张清, 冯云, 樊恩源. 北京及其邻近地区野生鱼类物种多样性及其资源保育[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(5): 597-604. |
| [12] | 王丽侠, 程须珍, 王素华. 基于SSR标记分析小豆及其近缘植物的遗传关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(1): 17-23. |
| [13] | 陈碧云, 胡琼, Christina Dixelius, 李国庆, 伍晓明. 利用SRAP分析核盘菌遗传多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2010, 18(5): 509-515. |
| [14] | 张俊红, 黄华宏, 童再康, 程龙军, 梁跃龙, 陈奕良. 光皮桦6个南方天然群体的遗传多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2010, 18(3): 233-240. |
| [15] | 张根, 席贻龙, 薛颖昊, 胡忻, 项贤领, 温新利. 基于rDNA ITS序列探讨粉煤灰污染对萼花臂尾轮虫种群遗传多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2010, 18(3): 241-250. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()