



生物多样性 ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (1): 24339. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024339 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024339
弋维1, 艾鷖1, 吴萌1, 田黎明2, 泽让东科1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-07-29
接受日期:2024-09-12
出版日期:2025-01-20
发布日期:2024-12-09
通讯作者:
* E-mail: 基金资助:
Wei Yi1, Yi Ai1, Meng Wu1, Liming Tian2, Tserang Donko Mipam1,*( )
)
Received:2024-07-29
Accepted:2024-09-12
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2024-12-09
Contact:
* E-mail: Supported by:摘要:
古菌因其独特且多样化的遗传和代谢特征, 在全球碳氮循环等过程中发挥着关键作用。放牧家畜啃食、排泄和践踏等行为将影响土壤古菌群落, 但关于放牧对高寒草地古菌群落结构及其多样性的影响尚不明确。本研究在青藏高原的高寒草甸进行了为期两年的牦牛放牧试验, 设置了对照组(禁牧)、轻度放牧(1头牦牛/ha)、中度放牧(2头牦牛/ha)和重度放牧(3头牦牛/ha) 4个放牧强度, 每个强度设置3个重复。结果表明, 土壤古菌群落在各放牧强度之间的α多样性指数均无显著差异, 但轻度放牧均增加了土壤古菌群落多样性与丰富度; 随着放牧强度的增加, 泉古菌门呈现出先减少后增加的趋势, 广古菌门和小古菌门相对丰度在轻度放牧中最高, 对照组最低。与对照组相比, 放牧降低了土壤容重、增加了土壤含水率; 重度放牧使土壤全磷降低、有效磷增加; 泉古菌门与全磷和全钾呈显著负相关(P < 0.05), 广古菌门与全磷呈显著正相关(P < 0.05)而与全钾呈显著负相关(P < 0.05), 小古菌门与全磷呈显著正相关(P < 0.05)。综上所述, 轻度放牧有增加土壤古菌群落丰富度和多样性的趋势, 不同土壤古菌群落组成受土壤碳氮影响较大, 表明放牧可能通过改变土壤养分进而影响古菌群落结构。研究结果为正确评估放牧对高寒草地生态系统的影响提供了科学基础。
弋维, 艾鷖, 吴萌, 田黎明, 泽让东科 (2025) 青藏高原高寒草甸土壤古菌群落对不同放牧强度的响应. 生物多样性, 33, 24339. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024339.
Wei Yi, Yi Ai, Meng Wu, Liming Tian, Tserang Donko Mipam (2025) Soil archaeal community responses to different grazing intensities in the alpine meadows of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Biodiversity Science, 33, 24339. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024339.
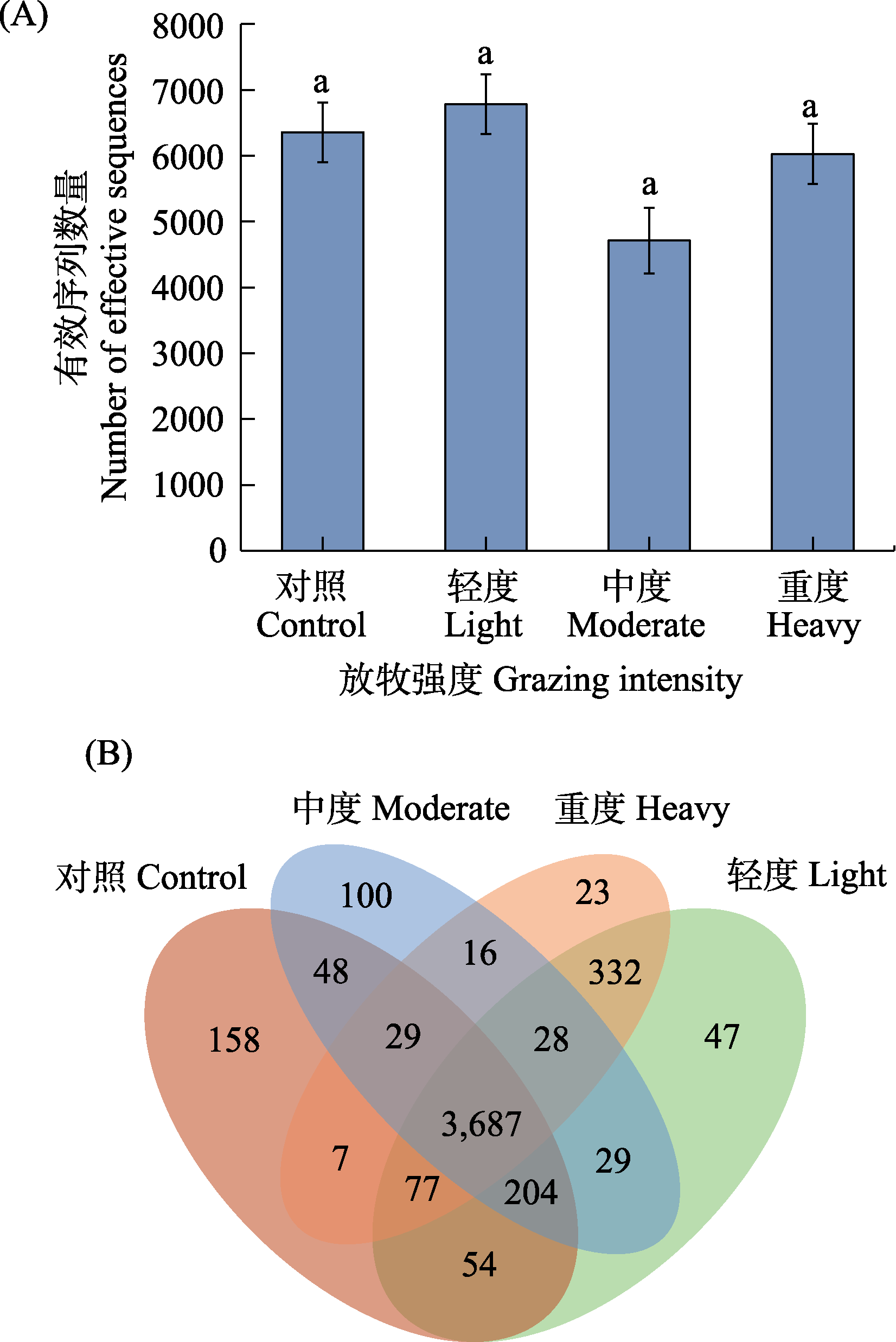
图1 不同放牧强度下土壤古菌有效序列数(A)和OTU数 (B)。不同字母表示差异显著(P < 0. 05)。
Fig. 1 Number of sequence (A) and OTU (B) of soil archaea under different grazing intensities. Different letters mean significant differences at P < 0. 05 level.
| 指数 Index | 对照组 Control | 轻度放牧 Light grazing | 中度放牧 Moderate grazing | 重度放牧 Heavy grazing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simpson指数 Simpson index | 0.83 ± 0.04a | 0.85 ± 0.03a | 0.82 ± 0.02a | 0.82 ± 0.081a |
| Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | 4.72 ± 0.47a | 4.96 ± 0.19a | 4.66 ± 0.057a | 4.57 ± 0.84a |
| Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 702.13 ± 97.38a | 766.28 ± 82.05a | 686.68 ± 61.40a | 595.72 ± 118.69a |
| ACE指数 ACE index | 746.69 ± 98.98a | 794.23 ± 59.16a | 724.66 ± 68.31a | 612.67 ± 133.73a |
表1 不同放牧强度的土壤古菌α多样性指数
Table 1 The α diversity index of soil archaea in different grazing intensities
| 指数 Index | 对照组 Control | 轻度放牧 Light grazing | 中度放牧 Moderate grazing | 重度放牧 Heavy grazing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simpson指数 Simpson index | 0.83 ± 0.04a | 0.85 ± 0.03a | 0.82 ± 0.02a | 0.82 ± 0.081a |
| Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | 4.72 ± 0.47a | 4.96 ± 0.19a | 4.66 ± 0.057a | 4.57 ± 0.84a |
| Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 702.13 ± 97.38a | 766.28 ± 82.05a | 686.68 ± 61.40a | 595.72 ± 118.69a |
| ACE指数 ACE index | 746.69 ± 98.98a | 794.23 ± 59.16a | 724.66 ± 68.31a | 612.67 ± 133.73a |
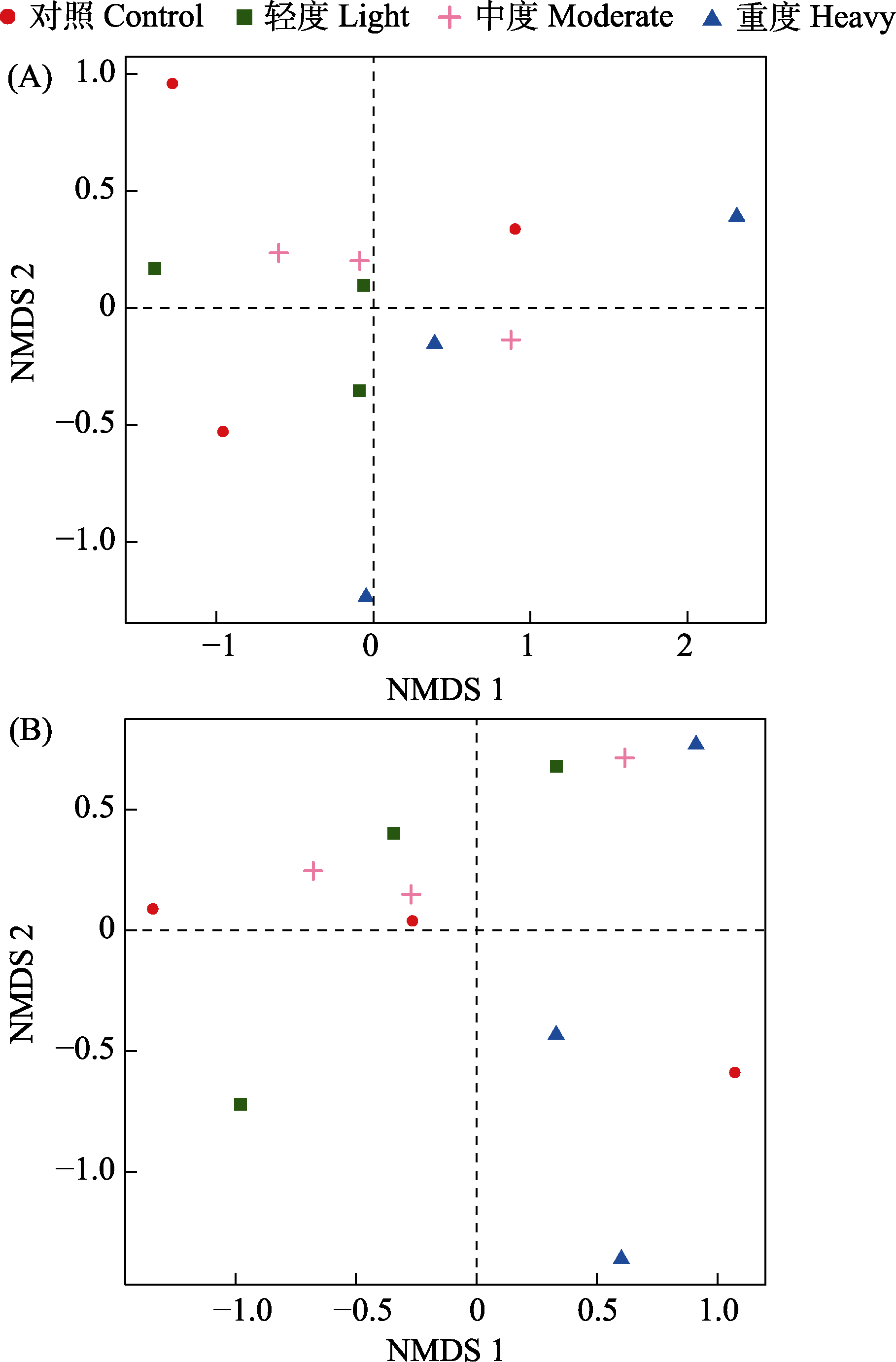
图4 不同放牧强度下土壤古菌群落非加权UniFrac NMDS (A)与加权UniFrac NMDS (B)分析
Fig. 4 Analysis of unweighted UniFrac NMDS (A) and weighted UniFrac NMDS (B) in soil archaeal communities under different grazing intensities
| 环境指标 Environmental indicators | 对照 Control | 轻度放牧 Light grazing | 中度放牧 Moderate grazing | 重度放牧 Heavy grazing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 物种丰富度 Species richness | 25.50 ± 0.50a | 25.92 ± 2.77a | 29.33 ± 2.50a | 26.67 ± 2.13a |
| Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index | 2.34 ± 0.11b | 2.39 ± 0.17ab | 2.53 ± 0.21a | 2.63 ± 0.06a |
| Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index | 0.69 ± 0.03b | 0.74 ± 0.04ab | 0.75 ± 0.05ab | 0.80 ± 0.01a |
| 地上净初级生产力 ANPP (g/cm2) | 299.52 ± 17.83b | 426.51 ± 88.17a | 448.47 ± 43.29a | 336.34 ± 62.99ab |
| 土壤含水率 SM (%) | 27.23 ± 5.69b | 33.02 ± 5.75a | 33.4 ± 4.10a | 32.72 ± 7.26a |
| 土壤容重 BD (g/cm3) | 1.26 ± 0.10a | 1.12 ± 0.13b | 1.18 ± 0.10ab | 1.11 ± 0.12b |
| 土壤全氮 TN (g/kg) | 2.96 ± 0.58a | 3.21 ± 0.57a | 3.19 ± 0.44a | 3.62 ± 1.15a |
| 土壤全磷 TP (g/kg) | 0.77 ± 0.08a | 0.89 ± 0.12a | 0.82 ± 0.11a | 0.81 ± 0.20a |
| 土壤全钾 TK (g/kg) | 16.97 ± 0.96a | 17.00 ± 1.21a | 16.4 ± 1.04a | 15.75 ± 0.68a |
| 土壤有效氮 AN (mg/kg) | 225.44 ± 43.20b | 272.34 ± 45.75a | 267.28 ± 39.58a | 273.44 ± 47.35a |
| 土壤有效磷 AP (mg/kg) | 3.96 ± 0.66b | 4.5 ± 1.70ab | 5.03 ± 1.46ab | 5.53 ± 1.53a |
| 土壤速效钾 AK (mg/kg) | 134.67 ± 61.63a | 161.6 ± 78.03a | 192.07 ± 72.27a | 165.05 ± 79.69a |
| 土壤pH Soil pH | 5.92 ± 0.30a | 5.83 ± 0.19ab | 5.69 ± 0.18b | 5.74 ± 0.18b |
| 土壤有机质 SOM (g/kg) | 66.88 ± 9.58a | 74.28 ± 5.72a | 65.42 ± 14.50a | 68.81 ± 21.77a |
表2 不同放牧强度对环境因子的影响
Table 2 Effects of different grazing intensities on environmental factor
| 环境指标 Environmental indicators | 对照 Control | 轻度放牧 Light grazing | 中度放牧 Moderate grazing | 重度放牧 Heavy grazing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 物种丰富度 Species richness | 25.50 ± 0.50a | 25.92 ± 2.77a | 29.33 ± 2.50a | 26.67 ± 2.13a |
| Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index | 2.34 ± 0.11b | 2.39 ± 0.17ab | 2.53 ± 0.21a | 2.63 ± 0.06a |
| Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index | 0.69 ± 0.03b | 0.74 ± 0.04ab | 0.75 ± 0.05ab | 0.80 ± 0.01a |
| 地上净初级生产力 ANPP (g/cm2) | 299.52 ± 17.83b | 426.51 ± 88.17a | 448.47 ± 43.29a | 336.34 ± 62.99ab |
| 土壤含水率 SM (%) | 27.23 ± 5.69b | 33.02 ± 5.75a | 33.4 ± 4.10a | 32.72 ± 7.26a |
| 土壤容重 BD (g/cm3) | 1.26 ± 0.10a | 1.12 ± 0.13b | 1.18 ± 0.10ab | 1.11 ± 0.12b |
| 土壤全氮 TN (g/kg) | 2.96 ± 0.58a | 3.21 ± 0.57a | 3.19 ± 0.44a | 3.62 ± 1.15a |
| 土壤全磷 TP (g/kg) | 0.77 ± 0.08a | 0.89 ± 0.12a | 0.82 ± 0.11a | 0.81 ± 0.20a |
| 土壤全钾 TK (g/kg) | 16.97 ± 0.96a | 17.00 ± 1.21a | 16.4 ± 1.04a | 15.75 ± 0.68a |
| 土壤有效氮 AN (mg/kg) | 225.44 ± 43.20b | 272.34 ± 45.75a | 267.28 ± 39.58a | 273.44 ± 47.35a |
| 土壤有效磷 AP (mg/kg) | 3.96 ± 0.66b | 4.5 ± 1.70ab | 5.03 ± 1.46ab | 5.53 ± 1.53a |
| 土壤速效钾 AK (mg/kg) | 134.67 ± 61.63a | 161.6 ± 78.03a | 192.07 ± 72.27a | 165.05 ± 79.69a |
| 土壤pH Soil pH | 5.92 ± 0.30a | 5.83 ± 0.19ab | 5.69 ± 0.18b | 5.74 ± 0.18b |
| 土壤有机质 SOM (g/kg) | 66.88 ± 9.58a | 74.28 ± 5.72a | 65.42 ± 14.50a | 68.81 ± 21.77a |
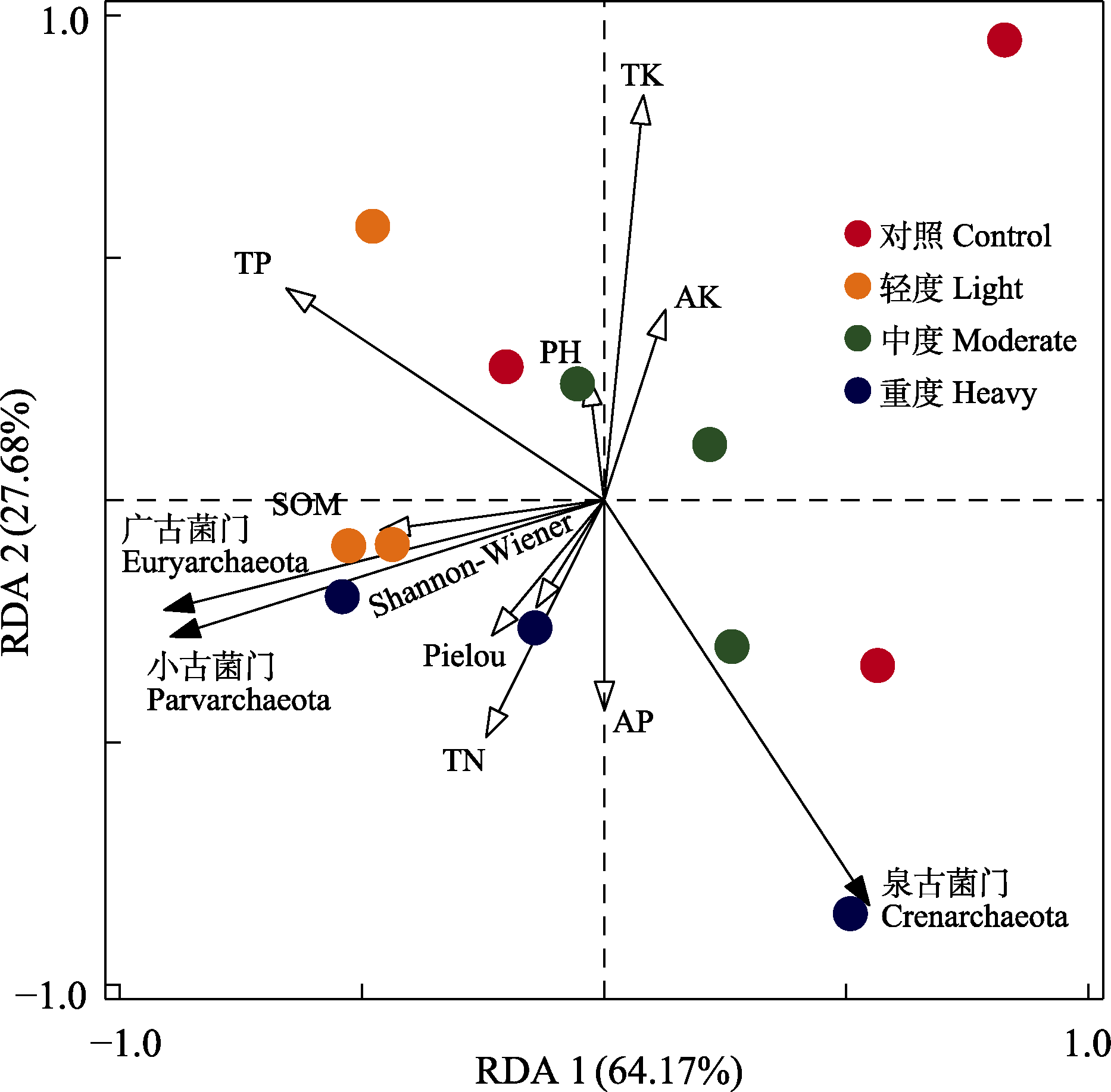
图5 不同古菌优势菌门相对丰度与环境因子的冗余分析(RDA)。TN: 土壤全氮; TP: 土壤全磷; SOM: 土壤有机质; TK: 土壤全钾; AP: 土壤有效磷; AK: 土壤速效钾。Shannon-Wiener: Shannon-Wiener多样性指数; Pielou: Pielou均匀度指数。
Fig. 5 Redundancy analysis (RDA) results of environmental factors and relative abundance of dominant different archaea phyla. TN, Soil total nitrogen; TP, Soil total phosphorus; SOM, Soil organic matter; TK, Soil total potassium; AP, Soil available phosphorus; AK, Soil available potassium. Shannon-Wiener: Shannon-Wiener diversity index; Pielou: Pielou evenness index.
| [1] |
Baker BJ, De Anda V, Seitz KW, Dombrowski N, Santoro AE, Lloyd KG (2020) Diversity, ecology and evolution of archaea. Nature Microbiology, 5, 887-900.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Bao SD (2000) Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis, 3rd edn. China Agricultural Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [鲍士旦 (2000) 土壤农化分析(第三版). 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [3] | Brown SP, Jumpponen A (2015) Phylogenetic diversity analyses reveal disparity between fungal and bacterial communities during microbial primary succession. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 89, 52-60. |
| [4] | Brussaard L, de Ruiter PC, Brown GG (2007) Soil biodiversity for agricultural sustainability. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 121, 233-244. |
| [5] |
Chen H, Jiang W (2014) Application of high-throughput sequencing in understanding human oral microbiome related with health and disease. Frontiers in Microbiology, 5, 508.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | Chen L, Zheng RB, Guo XL, Hou YW (2020) Effects of different grazing forms on ammonia-oxidizing microorganism communities in peat swamp soils of Northwest Yunnan. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40, 2321-2332. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈梨, 郑荣波, 郭雪莲, 侯亚文 (2020) 不同放牧对滇西北高原泥炭沼泽土壤氨氧化微生物群落的影响. 生态学报, 40, 2321-2332.] | |
| [7] | Chen MF, Zeng H, Wang J (2015) Research progress in the ecological characteristics of soil water in alpine grasslands on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 37(2), 94-101. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈玫妃, 曾辉, 王钧 (2015) 青藏高原高寒草地土壤水分生态特征研究现状. 中国草地学报, 37(2), 94-101.] | |
| [8] | Chen YL, Hu HW, Han HY, Du Y, Wan SQ, Xu ZW, Chen BD (2014) Abundance and community structure of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in response to fertilization and mowing in a temperate steppe in Inner Mongolia. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 89, 67-79. |
| [9] | da C Jesus E, Marsh TL, Tiedje JM, de S Moreira FM (2009) Changes in land use alter the structure of bacterial communities in Western Amazon soils. The ISME Journal, 3, 1004-1011. |
| [10] | Dong SK, Tang L, Zhang XF, Liu SL, Liu QR, Su XK, Zhang Y, Wu XY, Zhao ZZ, Li Y, Sha W (2017) Relationship between plant species diversity and functional diversity in alpine grassland. Acta Ecologica Sincia, 37, 1472-1483. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [董世魁, 汤琳, 张相锋, 刘世梁, 刘全儒, 苏旭坤, 张勇, 武晓宇, 赵珍珍, 李钰, 沙威 (2017) 高寒草地植物物种多样性与功能多样性的关系. 生态学报, 37, 1472-1483.] | |
| [11] |
Du YG, Shu K, Guo XW, Zhu PJ (2019) Moderate grazing promotes grassland nitrous oxide emission by increasing ammonia-oxidizing archaea abundance on the Tibetan Plateau. Current Microbiology, 76, 620-625.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics, 26, 2460-2461.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | Gao MH, Yu CY, Liu JY, Yu FL, Sun GJ (2022) High throughput analysis of soil archaeal community diversity in Hulunbuir meadow grassland. Feed Review, (5), 8-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [高明华, 于春艳, 刘金月, 于凤莅, 孙广霁 (2022) 呼伦贝尔草甸草原土壤古菌群落多样性高通量分析. 饲料博览, (5), 8-15.] | |
| [14] | Gao XF, Han GD (2011) Effects of grazing on soil nitrogen cycling in sheep grass steppe. Soil, 43, 161-166. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [高雪峰, 韩国栋 (2011) 放牧对羊草草原土壤氮素循环的影响. 土壤, 43, 161-166.] | |
| [15] | Gao YZ, Han XG, Wang SP (2004) The effects of grazing on grassland soils. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24, 790-797. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [高英志, 韩兴国, 汪诗平 (2004) 放牧对草原土壤的影响. 生态学报, 24, 790-797.] | |
| [16] | Guo XP, Yang Y, Niu ZS, Lu DP, Zhu CH, Feng JN, Wu JY, Chen YR, Tou FY, Liu M, Hou LJ (2019) Characteristics of microbial community indicate anthropogenic impact on the sediments along the Yangtze Estuary and its coastal area, China. Science of the Total Environment, 648, 306-314. |
| [17] | Hu HW, Zhang LM, Yuan CL, He JZ (2013) Contrasting Euryarchaeota communities between upland and paddy soils exhibited similar pH-impacted biogeographic patterns. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 64, 18-27. |
| [18] | Jeffery S, Harris JA, Rickson RJ, Ritz K (2009) The spectral quality of light influences the temporal development of the microbial phenotype at the arable soil surface. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 41, 553-560. |
| [19] | Le Roux X, Poly F, Currey P, Commeaux C, Hai B, Nicol GW, Prosser JI, Schloter M, Attard E, Klumpp K (2008) Effects of aboveground grazing on coupling among nitrifier activity, abundance and community structure. The ISME Journal, 2, 221-232. |
| [20] | Lecain DR, Morgan JA, Schuman GE, Reeder JD, Hart RH (2000) Carbon exchange rates in grazed and ungrazed pastures of Wyoming. Journal of Range Management, 53, 199. |
| [21] | Lei MT, Li Y, Zhang WL, Niu LH, Wang LF, Zhang HJ (2020) Identifying ecological processes driving vertical and horizontal archaeal community assemblages in a contaminated urban river. Chemosphere, 245, 125615. |
| [22] | Li GX, Ma KM (2018) Progress in the study of elevational patterns of soil microbial diversity. Acta Ecologica Sinicia, 38, 1521-1529. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [厉桂香, 马克明 (2018) 土壤微生物多样性海拔格局研究进展. 生态学报, 38, 1521-1529.] | |
| [23] | Li LN, Yang HT, Li YX, Xie JY, Huang XL, Li L, Li TL (2023) Succession characteristics of archaeal communities in wetland soils of the Fen River mainstream and their driving factors. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 43(8), 372-382. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李丽娜, 杨惠婷, 李云霄, 谢钧宇, 黄晓磊, 栗丽, 李廷亮 (2023) 汾河干流湿地土壤中古菌群落的演替特征及其驱动因素. 环境科学学报, 43(8), 372-382.] | |
| [24] | Liu XY, Mou YT (2012) Research progress in the ecosystem services function and value of grasslands. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 21(6), 286-295. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘兴元, 牟月亭 (2012) 草地生态系统服务功能及其价值评估研究进展. 草业学报, 21(6), 286-295.] | |
| [25] | Liu YX, Cao PX, Ma HM, Liu X (2019) Progress of research on soil microbial diversity and its influencing factors on the Tibetan Plateau. Environmental Ecology, 1(6), 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘怡萱, 曹鹏熙, 马红梅, 刘星 (2019) 青藏高原土壤微生物多样性及其影响因素研究进展. 环境生态学, 1(6), 1-7.] | |
| [26] |
Lozupone C, Knight R (2005) UniFrac: A new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71, 8228-8235.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | McNaughton SJ, Milchunas DG, Frank DA (1996) How can net primary productivity be measured in grazing ecosystems? Ecology, 77, 974-977. |
| [28] | Mipam TD, Chen SY, Liu JQ, Miehe G, Tian LM (2021) Short-term yak-grazing alters plant-soil stoichiometric relations in an alpine meadow on the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Plant and Soil, 458, 125-137. |
| [29] | Mipam TD, Zhong LL, Liu JQ, Miehe G, Tian LM (2019) Productive overcompensation of alpine meadows in response to yak grazing in the eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Frontiers in Plant Science, 10, 925. |
| [30] | Nacke H, Thürmer A, Wollherr A, Will C, Hodac L, Herold N, Schöning I, Schrumpf M, Daniel R (2011) Pyrosequencing- based assessment of bacterial community structure along different management types in German forest and grassland soils. PLoS ONE, 6, e17000. |
| [31] | Pan H, Xie KX, Zhang QC, Jia ZJ, Xu JM, Di HJ, Li Y (2018) Archaea and bacteria respectively dominate nitrification in lightly and heavily grazed soil in a grassland system. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 54, 41-54. |
| [32] | Qin YY, Zhang XF, Adamowski JF, Biswas A, Holden NM, Hu ZY (2021) Grassland grazing management altered soil properties and microbial β-diversity but not α-diversity on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Applied Soil Ecology, 167, 104032. |
| [33] |
Ramette A (2007) Multivariate analyses in microbial ecology. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 62, 142-160.
DOI PMID |
| [34] | Ren JZ (1998) Research Methods in Grassland Science. China Agricultural Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [任继周 (1998) 草业科学研究方法. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [35] |
Robertson CE, Harris JK, Spear JR, Pace NR (2005) Phylogenetic diversity and ecology of environmental Archaea. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 8, 638-642.
PMID |
| [36] | Rong YP, Han JG, Wang P, Mao PS (2001) The effects of grazing intensity on soil physics and chemical properties. Grassland of China, 23(4), 41-47. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [戎郁萍, 韩建国, 王培, 毛培胜 (2001) 放牧强度对草地土壤理化性质的影响. 中国草地, 23(4), 41-47.] | |
| [37] |
Shi Y, Adams JM, Ni YY, Yang T, Jing X, Chen LT, He JS, Chu HY (2016) The biogeography of soil archaeal communities on the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Scientific Reports, 6, 38893.
DOI PMID |
| [38] |
Song J, Wang FG, Wen L, Wang LX, Li JL, Wu SN, Xu ZC (2019) Effects of grazing on plant diversity and soil nutrients in typical temperate steppe. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 27, 1694-1701. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[宋洁, 王凤歌, 温璐, 王立新, 李金雷, 武胜男, 徐智超 (2019) 放牧对温带典型草原植物物种多样性及土壤养分的影响. 草地学报, 27, 1694-1701.]
DOI |
|
| [39] | Song ZQ, Wang L, Chen JQ, Zhou EM, Zhang CL, Li WJ (2013) Diversity of Crenarchaeota in terrestrial hot springs and their surrounding environments in Kamchatka, Russia. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 53, 569-576. (in Chinese) |
| [宋兆齐, 王莉, 陈金全, 周恩民, 张传伦, 李文均 (2013) 俄罗斯堪察加地区热泉及其周边生境的泉古菌多样性. 微生物学报, 53, 569-576.] | |
| [40] | Sun YF, Shen JP, Zhang CJ, Han GD, Hong M, Zhao B, He JZ (2018) Responses of soil ammonia oxidizers and denitrifiers to different grazing intensities. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 2874-2883. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙翼飞, 沈菊培, 张翠景, 韩国栋, 红梅, 赵巴音那木拉, 贺纪正 (2018) 不同放牧强度下土壤氨氧化和反硝化微生物的变化特征. 生态学报, 38, 2874-2883.] | |
| [41] | Wang YH, Tian LM, Ai Y, Chen SY, Mipam TD (2022) Effects of short-term yak grazing on soil fungal communities in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 31(10), 41-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[王永宏, 田黎明, 艾鷖, 陈仕勇, 泽让东科 (2022) 短期牦牛放牧对青藏高原高寒草地土壤真菌群落的影响. 草业学报, 31(10), 41-52.]
DOI |
|
| [42] | Yang Y, Jia LX, Qiao JR, Li MR, Zhang F, Chen DL, Zhang H, Zhao ML (2019) Effects of heavy grazing on soil nutrient and microbial diversity in desert grassland. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 41(4), 72-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨阳, 贾丽欣, 乔荠瑢, 李梦然, 张峰, 陈大岭, 张昊, 赵萌莉 (2019) 重度放牧对荒漠草原土壤养分及微生物多样性的影响. 中国草地学报, 41(4), 72-79.] | |
| [43] | Yang YF, Zhang XJ, Yu XY (2022) Characteristics of archaeal community structures in the different river reach sediments in the shiwuli river, Caohu Lake basin. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 53(1), 106-115. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨艳芳, 张秀娟, 于小彦 (2022) 巢湖十五里河不同河段沉积物古菌群落结构特征研究. 土壤通报, 53(1), 106-115.] | |
| [44] | Yuan HZ, Wu H, Ge TD, Li KL, Wu JS, Wang JR (2015) Effects of long-term fertilization on bacterial and archaeal diversity and community structure within subtropical red paddy soils. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 26, 1807-1813. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [袁红朝, 吴昊, 葛体达, 李科林, 吴金水, 王久荣 (2015) 长期施肥对稻田土壤细菌、古菌多样性和群落结构的影响. 应用生态学报, 26, 1807-1813.] | |
| [45] | Zhang CX, Nan ZB (2010) Research progress on effects of grazing on physical and chemical characteristics of grassland soil. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 19(4), 204-211. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张成霞, 南志标 (2010) 放牧对草地土壤理化特性影响的研究进展. 草业学报, 19(4), 204-211.] | |
| [46] | Zhang Q, Ma L, Zhang ZH, Xu WH, Zhou BR, Song MH, Qiao AH, Wang F, She YD, Yang XY, Guo J, Zhou HK (2019) Ecological restoration of degraded grassland in Qinghai-Tibet alpine region: Degradation status, restoration measures, effects and prospects. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39, 7441-7451. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张骞, 马丽, 张中华, 徐文华, 周秉荣, 宋明华, 乔安海, 王芳, 佘延娣, 杨晓渊, 郭婧, 周华坤 (2019) 青藏高寒区退化草地生态恢复: 退化现状、恢复措施、效应与展望. 生态学报, 39, 7441-7451.] | |
| [47] | Zhao FZ, Ren CJ, Shelton S, Wang ZT, Pang GW, Chen J, Wang J (2017) Grazing intensity influence soil microbial communities and their implications for soil respiration. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 249, 50-56. |
| [48] | Zhao J (1999) Effect of stocking rates on soil microbial number and biomass in steppe. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 7(3), 222-227. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵吉 (1999) 不同放牧率对冷蒿小禾草草原土壤微生物数量和生物量的影响. 草地学报, 7(3), 222-227.] | |
| [49] | Zheng YK, Wang XB, GU YF, Zhang XP (2014) Diversity of soil ammonia-oxidising archaea in the Ruoergai Plateau wetland. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 54, 1090-1096. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郑有坤, 王宪斌, 辜运富, 张小平 (2014) 若尔盖高原湿地土壤氨氧化古菌的多样性. 微生物学报, 54, 1090-1096.] | |
| [50] | Zhou FK, Zhou L, Zhao XQ, Yan ZL, Liu W, Shi Y (2002) Effects of grazing disturbance on alpine grassland. Grassland of China, (5), 53-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周华坤, 周立, 赵新全, 严作良, 刘伟, 师燕 (2002) 放牧干扰对高寒草场的影响. 中国草地, (5), 53-61.] |
| [1] | 周志华, 金效华, 罗颖, 李迪强, 岳建兵, 刘芳, 何拓, 李希, 董晖, 罗鹏. 中国林草部门落实《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》的机制、成效分析及建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24487-. |
| [2] | 田志奇, 苏杨. 环境相关国际公约的中国履约模式和在《生物多样性公约》中的应用: 从完成《昆蒙框架》目标和发挥国家公园作用的角度[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24593-. |
| [3] | 宋阳, 柳军, 何少林, 徐薇, 程琛, 刘博, 余绩庆. 我国能源企业生物多样性保护主流化管理路径[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24345-. |
| [4] | 耿江天, 王菲, 赵华斌. 城市化对中国蝙蝠影响的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24109-. |
| [5] | 孙怡欣, 侯春雨, 周磊, 魏雪, 马金豪, 薛娟, 李小涵, 吴鹏飞. 青藏高原盆栽一年生和多年生豆科牧草对土壤线虫群落的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24040-. |
| [6] | 李邦泽, 张树仁. 中国莎草科最新物种名录和分类纲要[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24106-. |
| [7] | 胡宗刚. 抗战胜利后中美曾筹划合编《中国植物志》[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24220-. |
| [8] | 姚祝, 魏雪, 马金豪, 任晓, 王玉英, 胡雷, 吴鹏飞. 气候暖湿化对高寒草甸土壤线虫群落的短期影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23483-. |
| [9] | 池玉杰, 张心甜, 田志炫, 关成帅, 谷新治, 刘智会, 王占斌, 王金杰. 东北亚地区白粉菌的物种多样性与寄主物种多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23443-. |
| [10] | 江建平, 蔡波, 王斌, 陈蔚涛, 温知新, 张德志, 隋璐璐, 马舜, 王伟波. 中国脊椎动物2023年度新增物种报告[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24327-. |
| [11] | 曹焕喜, 周青松, 罗阿蓉, 唐璞, 李廷景, 李泽建, 陈华燕, 牛泽清, 朱朝东. 2023年现生膜翅目新分类单元[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24319-. |
| [12] | 杜诚, 刘军, 叶文, 廖帅. 中国植物新分类群、新名称变化2023年度报告[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24253-. |
| [13] | 徐思远, 连琦琦, 张瑞欣, 赵嘉腾, 周璇, 周露, 陈芹, 白明. 2023年全球鞘翅目现生类群新分类单元[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24307-. |
| [14] | 努日耶·木合太尔, 张秀英, 苏比奴尔·艾力, 李后魂. 中国鳞翅目新物种2023年度报告[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24428-. |
| [15] | 林晨, 杨棋程, 吴艳玲, 侯鹏, 张冰, 杨定. 2023年中国双翅目新分类单元[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24328-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn