



生物多样性 ›› 2013, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (3): 359-363. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.05162 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2013.05162
陈丽1,2, 董洪进2, 彭华2,*
收稿日期:2012-08-27
接受日期:2013-03-07
出版日期:2013-05-20
发布日期:2013-06-05
通讯作者:
彭华
Li Chen1,2, Hongjin Dong2, Hua Peng2,*
Received:2012-08-27
Accepted:2013-03-07
Online:2013-05-20
Published:2013-06-05
Contact:
Peng Hua
摘要:
云南省为我国乃至世界生物多样性的热点区域之一。为深入认识和保护云南的植物多样性, 作者以《云南植物志》为基础, 对其中记载的各物种在云南的县级分布情况进行了统计。结果显示: 云南省高等植物多样性最丰富的为滇西北地区, 其中的玉龙县、贡山县、香格里拉县物种数分别高达4,358种、3,981种和3,874种, 其次为以西双版纳州为主体的南部热带边缘, 其中的勐腊、景洪的物种数也都在3,000种以上; 而以云南高原为主体的滇东和滇中地区植物多样性则较为贫乏, 作者认为这与人们的关注度和野外调查的强度直接相关。云南分布有4,008种特有物种, 4,509种狭域物种, 特有物种的分布规律与总物种相似; 含狭域物种最多的为贡山县(556种), 是唯一超过500种的县。云南省多数物种的分布范围极为狭窄, 64.1%的物种仅分布在1-5个县, 46.0%的特有物种只分布在1个县的范围内。通过以上分析, 作者指出由于此前对云南植物多样性的调查仍不完善, 结果并不能全面反映真实的地带性规律, 建议加大调查深度和标本采集量。如果条件许可, 一些极易沦为濒危种的狭域分布种也应得到优先关注。
陈丽, 董洪进, 彭华 (2013) 云南省高等植物多样性与分布状况. 生物多样性, 21, 359-363. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.05162.
Li Chen,Hongjin Dong,Hua Peng (2013) Diversity and distribution of higher plants in Yunnan, China. Biodiversity Science, 21, 359-363. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.05162.
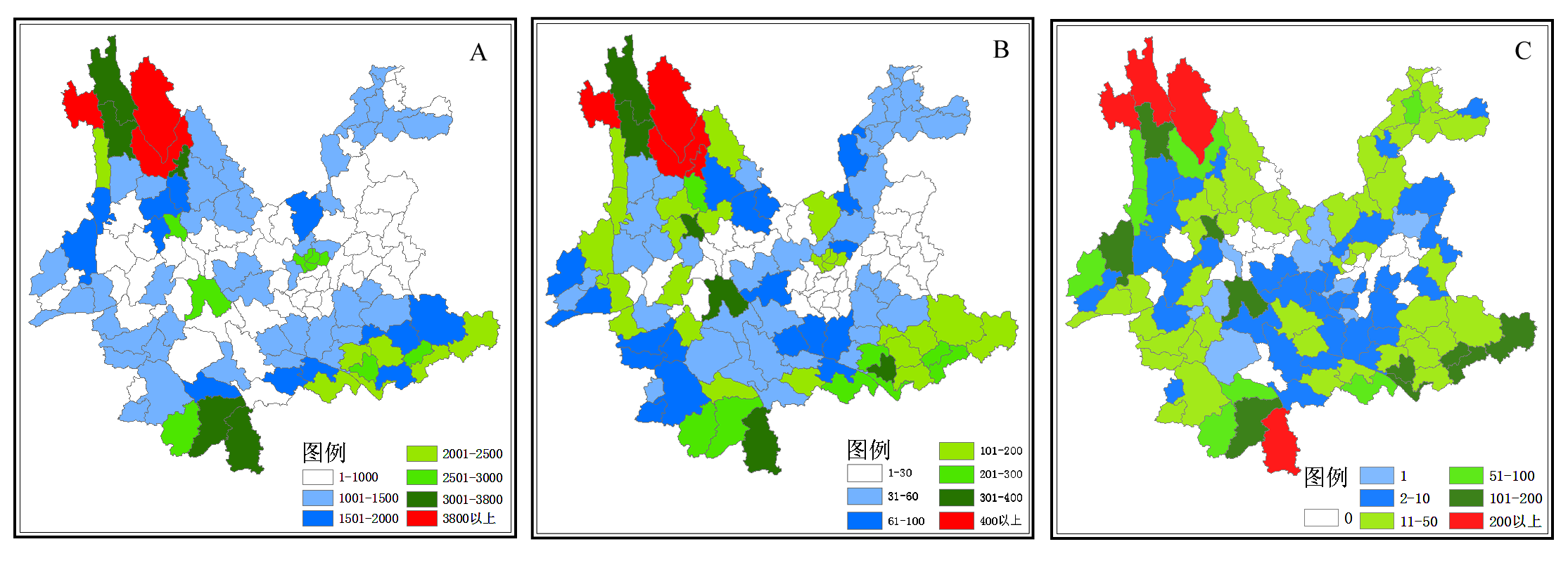
图1 云南省各县高等植物(A)、特有植物(B)和狭域分布物种(C)的多样性分布格局
Fig. 1 Distributional pattern of species diversity for overall higher plants (A), endemic species (B) and narrow-ranging species (C) at the county level in Yunnan Province
| 分布县数 No. of counties | 物种数 No. of species | 分布县数 No. of counties | 特有种数 No. of endemic species |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 169 | 0 | 14 |
| 1 | 4,509 | 1 | 1,845 |
| 2-5 | 7,257 | 2 | 699 |
| 6-10 | 3,016 | 3 | 456 |
| 11-20 | 1,801 | 4-5 | 455 |
| 21-30 | 543 | 6-10 | 347 |
| 31-40 | 201 | 11-20 | 114 |
| 41-50 | 111 | 21-30 | 53 |
| 51-60 | 53 | 31-40 | 14 |
| 61-80 | 51 | 41-50 | 6 |
| 81-100 | 14 | >50 | 5 |
| 101-120 | 54 | ||
| 121-129 | 534 |
表1 云南省高等植物物种数和特有物种数与其分布的县数之间的相关性
Table 1 Correlation between the number of overall species and endemic species and the amount of their distributional counties
| 分布县数 No. of counties | 物种数 No. of species | 分布县数 No. of counties | 特有种数 No. of endemic species |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 169 | 0 | 14 |
| 1 | 4,509 | 1 | 1,845 |
| 2-5 | 7,257 | 2 | 699 |
| 6-10 | 3,016 | 3 | 456 |
| 11-20 | 1,801 | 4-5 | 455 |
| 21-30 | 543 | 6-10 | 347 |
| 31-40 | 201 | 11-20 | 114 |
| 41-50 | 111 | 21-30 | 53 |
| 51-60 | 53 | 31-40 | 14 |
| 61-80 | 51 | 41-50 | 6 |
| 81-100 | 14 | >50 | 5 |
| 101-120 | 54 | ||
| 121-129 | 534 |
| 序号No. | 县 County | 苔藓植物Bryophytes | 蕨类植物Ferns | 裸子植物Gymnosperms | 被子植物Angiosperms | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种Species | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species | |||||
| 1 | 五华区 | 5/56 | 6/139 | 7/286 | 7/39 | 9/86 | 9/192 | 1/8 | 1/21 | 1/43 | 57/173 | 122/887 | 165/2194 | |||
| 2 | 盘龙区 | 5/56 | 6/143 | 7/292 | 7/39 | 9/86 | 9/193 | 1/8 | 1/21 | 1/43 | 57/177 | 121/895 | 166/2172 | |||
| 3 | 官渡区 | 5/56 | 6/139 | 7/286 | 7/39 | 9/86 | 9/193 | 1/8 | 1/21 | 1/43 | 56/174 | 120/884 | 162/2144 | |||
| 4 | 西山区 | 7/58 | 7/150 | 8/315 | 7/39 | 10/86 | 10/194 | 1/8 | 1/21 | 1/43 | 57/176 | 123/885 | 167/2150 | |||
| 5 | 东川区 | 1/20 | 1/30 | 1/37 | 0/25 | 0/29 | 0/44 | 1/9 | 1/20 | 1/33 | 39/157 | 62/616 | 88/1203 | |||
| 6 | 安宁市 | 2/34 | 2/70 | 2/108 | 1/27 | 1/40 | 1/65 | 0/5 | 0/11 | 0/16 | 19/147 | 22/520 | 23/846 | |||
| 7 | 富民县 | 1/21 | 1/32 | 1/37 | 0/26 | 0/41 | 0/66 | 0/6 | 0/11 | 0/15 | 40/154 | 49/591 | 52/1021 | |||
| 8 | 呈贡县 | 2/14 | 2/29 | 2/39 | 0/22 | 0/29 | 0/42 | 0/5 | 0/10 | 0/13 | 15/138 | 18/467 | 19/747 | |||
| 9 | 晋宁县 | 1/12 | 1/18 | 1/21 | 0/21 | 0/27 | 0/39 | 0/5 | 0/10 | 0/13 | 16/139 | 19/464 | 20/737 | |||
| 10 | 宜良县 | 1/20 | 1/28 | 1/31 | 2/26 | 2/38 | 2/57 | 0/5 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 21/145 | 25/499 | 27/813 | |||
| 11 | 石林县 | 1/19 | 1/33 | 1/43 | 2/26 | 2/37 | 2/59 | 0/5 | 0/10 | 0/14 | 23/146 | 29/513 | 31/820 | |||
| 12 | 嵩明县 | 1/35 | 1/67 | 1/103 | 2/29 | 2/53 | 2/95 | 0/5 | 0/13 | 0/17 | 44/160 | 66/621 | 78/1150 | |||
| 13 | 禄劝县 | 2/25 | 2/46 | 2/67 | 5/35 | 5/74 | 5/185 | 1/7 | 1/17 | 1/26 | 54/169 | 84/720 | 110/1440 | |||
| 14 | 寻甸县 | 2/26 | 2/39 | 2/62 | 0/22 | 0/26 | 0/37 | 0/5 | 0/11 | 0/14 | 24/144 | 30/505 | 32/827 | |||
| 15 | 麒麟区 | 0/13 | 0/15 | 0/16 | 0/23 | 0/27 | 0/33 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 7/127 | 8/418 | 9/621 | |||
| 16 | 马龙县 | 1/11 | 1/13 | 1/14 | 0/21 | 0/25 | 0/34 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 3/122 | 3/393 | 3/586 | |||
| 17 | 陆良县 | 0/12 | 0/15 | 0/16 | 0/20 | 0/24 | 0/33 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 3/118 | 3/395 | 3/597 | |||
| 18 | 师宗县 | 0/15 | 0/24 | 0/28 | 0/25 | 0/27 | 0/38 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 9/134 | 9/481 | 9/734 | |||
| 19 | 罗平县 | 0/14 | 0/16 | 0/17 | 2/28 | 2/42 | 2/62 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 7/131 | 9/482 | 9/734 | |||
| 20 | 富源县 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 0/14 | 0/21 | 0/26 | 0/35 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 5/120 | 5/400 | 5/604 | |||
| 21 | 宣威市 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 0/15 | 0/25 | 0/37 | 0/51 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 4/121 | 4/399 | 4/591 | |||
| 22 | 沾益县 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 0/14 | 0/20 | 0/29 | 0/38 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 4/123 | 4/398 | 4/597 | |||
| 23 | 会泽县 | 0/12 | 0/14 | 0/15 | 1/27 | 1/42 | 1/67 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/8 | 24/141 | 38/513 | 42/867 | |||
| 24 | 红塔区 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 0/14 | 0/21 | 0/28 | 0/41 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/5 | 15/134 | 16/461 | 16/701 | |||
| 25 | 江川县 | 0/10 | 0/13 | 0/15 | 0/21 | 0/27 | 0/36 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 7/129 | 8/452 | 8/713 | |||
| 26 | 澄江县 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 0/14 | 0/27 | 0/43 | 0/71 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 11/123 | 16/486 | 17/712 | |||
| 27 | 华宁县 | 0/11 | 0/14 | 0/13 | 0/21 | 0/27 | 0/36 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 4/118 | 4/410 | 4/601 | |||
| 28 | 通海县 | 0/19 | 0/18 | 0/20 | 0/24 | 0/36 | 0/51 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 8/127 | 8/414 | 8/622 | |||
| 29 | 峨山县 | 0/10 | 0/12 | 0/14 | 1/29 | 1/45 | 1/60 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 23/139 | 28/542 | 29/856 | |||
| 30 | 元江县 | 0/16 | 0/18 | 0/20 | 0/27 | 0/37 | 0/60 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 39/145 | 55/634 | 65/1066 | |||
| 31 | 新平县 | 0/18 | 0/25 | 0/25 | 7/39 | 12/90 | 14/209 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/5 | 29/139 | 33/503 | 37/756 | |||
| 32 | 易门县 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 0/14 | 1/29 | 1/50 | 1/78 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 19/132 | 24/480 | 27/756 | |||
| 33 | 昭阳区 | 0/30 | 0/43 | 0/53 | 0/21 | 0/31 | 0/45 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/7 | 30/144 | 36/553 | 48/963 | |||
| 34 | 鲁甸县 | 0/10 | 0/12 | 0/13 | 0/23 | 0/30 | 0/44 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 19/126 | 22/425 | 31/696 | |||
| 35 | 巧家县 | 0/22 | 0/33 | 0/38 | 4/31 | 4/59 | 4/134 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/5 | 32/145 | 48/566 | 74/1047 | |||
| 36 | 彝良县 | 0/46 | 0/76 | 0/125 | 1/25 | 1/75 | 1/75 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 26/151 | 33/561 | 47/1033 | |||
| 37 | 大关县 | 0/35 | 0/57 | 0/87 | 2/39 | 3/89 | 3/192 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 32/149 | 36/559 | 53/1020 | |||
| 38 | 永善县 | 0/24 | 0/35 | 0/45 | 2/29 | 2/51 | 2/100 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 25/136 | 29/488 | 45/861 | |||
| 39 | 绥江县 | 0/11 | 0/14 | 0/15 | 4/38 | 6/93 | 6/196 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 24/140 | 27/505 | 38/869 | |||
| 40 | 水富县 | 0/11 | 0/12 | 0/13 | 0/22 | 0/28 | 0/41 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 17/125 | 19/419 | 28/680 | |||
| 41 | 盐津县 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 0/14 | 0/22 | 0/29 | 0/42 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 28/144 | 34/515 | 52/898 | |||
| 42 | 威信县 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 0/14 | 0/24 | 0/33 | 0/54 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 0/8 | 23/134 | 26/455 | 35/762 | |||
| 43 | 镇雄县 | 0/21 | 0/27 | 0/32 | 1/27 | 1/41 | 1/78 | 0/7 | 0/7 | 0/10 | 36/151 | 41/581 | 58/1120 | |||
| 44 | 思茅区 | 0/23 | 0/31 | 0/39 | 2/31 | 2/49 | 2/73 | 0/6 | 0/7 | 0/11 | 66/174 | 120/836 | 161/1687 | |||
| 45 | 宁洱县 | 0/16 | 0/26 | 0/26 | 1/21 | 1/29 | 1/42 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 0/9 | 21/148 | 32/595 | 45/986 | |||
| 46 | 江城县 | 0/14 | 0/17 | 0/18 | 0/27 | 0/44 | 0/63 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 28/143 | 34/535 | 42/881 | |||
| 47 | 墨江县 | 0/15 | 0/18 | 0/19 | 0/28 | 0/45 | 0/69 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 23/141 | 31/528 | 39/872 | |||
| 48 | 镇沅县 | 0/15 | 0/18 | 0/19 | 2/28 | 2/45 | 2/69 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 22/141 | 28/528 | 38/872 | |||
| 49 | 景东县 | 1/42 | 1/79 | 1/135 | 10/46 | 18/103 | 23/256 | 1/8 | 1/11 | 2/18 | 87/186 | 172/981 | 292/2297 | |||
| 50 | 景谷县 | 0/13 | 0/16 | 0/17 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/42 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 22/141 | 31/536 | 42/878 | |||
| 51 | 澜沧县 | 0/15 | 0/19 | 0/22 | 2/28 | 2/47 | 2/71 | 2/5 | 2/7 | 4/11 | 47/156 | 67/677 | 89/1192 | |||
| 52 | 孟连县 | 0/12 | 0/14 | 0/15 | 2/32 | 2/61 | 2/95 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 35/164 | 53/685 | 67/1175 | |||
| 53 | 西盟县 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 0/14 | 3/31 | 3/55 | 3/91 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 23/142 | 30/539 | 38/876 | |||
| 54 | 临翔区 | 0/14 | 0/19 | 0/22 | 2/29 | 2/43 | 2/60 | 1/6 | 1/8 | 2/12 | 51/161 | 79/713 | 104/1332 | |||
| 55 | 云县 | 0/13 | 0/16 | 0/17 | 1/23 | 1/35 | 1/48 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 22/139 | 27/498 | 29/786 | |||
| 56 | 凤庆县 | 0/16 | 0/20 | 0/21 | 0/24 | 0/32 | 0/46 | 0/5 | 0/7 | 0/9 | 54/166 | 84/679 | 109/1260 | |||
| 57 | 永德县 | 0/12 | 0/18 | 0/23 | 5/37 | 5/77 | 6/149 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 26/135 | 33/498 | 39/810 | |||
| 58 | 镇康县 | 0/17 | 0/25 | 0/32 | 5/31 | 5/47 | 6/74 | 0/6 | 0/7 | 0/10 | 26/162 | 33/728 | 39/1348 | |||
| 59 | 耿马县 | 1/28 | 2/46 | 2/64 | 2/28 | 2/45 | 3/82 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/7 | 49/156 | 65/676 | 77/1185 | |||
| 60 | 双江县 | 0/11 | 0/16 | 0/17 | 0/25 | 0/40 | 0/56 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 39/152 | 50/624 | 61/1066 | |||
| 61 | 沧源县 | 2/29 | 2/57 | 2/102 | 3/34 | 3/68 | 3/127 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 46/156 | 64/660 | 83/1165 | |||
| 62 | 隆阳区 | 0/32 | 0/49 | 0/56 | 0/24 | 0/34 | 0/48 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 30/145 | 40/529 | 49/884 | |||
| 63 | 腾冲县 | 2/43 | 2/84 | 2/179 | 4/40 | 6/72 | 6/123 | 1/7 | 1/9 | 1/12 | 59/169 | 124/751 | 181/1534 | |||
| 64 | 龙陵县 | 0/12 | 0/14 | 0/15 | 1/26 | 2/35 | 2/50 | 1/6 | 1/7 | 2/11 | 55/152 | 78/587 | 100/1044 | |||
| 65 | 施甸县 | 0/10 | 0/13 | 0/14 | 0/20 | 0/27 | 0/36 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 12/125 | 18/412 | 20/644 | |||
| 66 | 昌宁县 | 0/12 | 0/15 | 0/17 | 0/23 | 0/30 | 0/39 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 14/125 | 20/422 | 22/657 | |||
| 67 | 古城区 | 8/64 | 11/174 | 11/414 | 4/33 | 5/69 | 9/197 | 2/9 | 2/20 | 3/38 | 80/179 | 191/919 | 440/3124 | |||
| 68 | 玉龙县 | 11/69 | 15/202 | 15/481 | 5/34 | 8/72 | 12/222 | 2/9 | 2/20 | 3/37 | 81/179 | 229/974 | 549/3618 | |||
| 69 | 永胜县 | 0/30 | 0/52 | 0/85 | 3/21 | 3/26 | 3/45 | 0/5 | 0/7 | 0/9 | 42/149 | 69/625 | 95/1232 | |||
| 70 | 华坪县 | 0/21 | 0/39 | 0/68 | 2/18 | 2/21 | 2/35 | 0/5 | 0/7 | 0/11 | 24/137 | 32/492 | 45/922 | |||
| 71 | 宁蒗县 | 1/26 | 1/43 | 1/73 | 1/20 | 1/26 | 1/42 | 0/7 | 0/10 | 0/14 | 47/153 | 73/590 | 103/1248 | |||
| 72 | 文山县 | 0/21 | 0/27 | 0/34 | 5/35 | 6/69 | 7/131 | 0/8 | 0/11 | 0/15 | 69/179 | 123/837 | 164/1821 | |||
| 73 | 砚山县 | 0/10 | 0/12 | 0/13 | 1/31 | 1/52 | 1/87 | 0/5 | 0/7 | 0/8 | 47/164 | 93/764 | 110/1483 | |||
| 74 | 丘北县 | 1/38 | 1/55 | 1/85 | 0/28 | 0/39 | 0/56 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 23/145 | 40/564 | 51/1002 | |||
| 75 | 广南县 | 0/12 | 0/14 | 0/15 | 4/42 | 5/103 | 6/239 | 0/7 | 0/8 | 0/13 | 48/164 | 82/711 | 109/1402 | |||
| 76 | 富宁县 | 0/12 | 0/15 | 0/16 | 0/28 | 0/43 | 0/74 | 0/8 | 0/10 | 0/17 | 67/178 | 119/892 | 141/1922 | |||
| 77 | 西畴县 | 0/18 | 0/23 | 0/27 | 14/45 | 19/111 | 23/271 | 3/9 | 3/13 | 4/21 | 81/183 | 175/916 | 259/2193 | |||
| 78 | 麻粟坡县 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 0/14 | 11/41 | 15/98 | 20/243 | 1/9 | 1/13 | 1/21 | 72/181 | 165/890 | 262/2057 | |||
| 79 | 马关县 | 0/16 | 0/18 | 0/23 | 10/42 | 14/104 | 19/261 | 0/8 | 0/9 | 0/13 | 53/169 | 95/739 | 140/1465 | |||
| 80 | 个旧市 | 0/12 | 0/15 | 0/17 | 0/26 | 0/40 | 0/53 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 20/142 | 39/555 | 52/993 | |||
| 81 | 蒙自县 | 0/13 | 0/18 | 0/19 | 6/33 | 8/62 | 8/123 | 0/6 | 0/8 | 0/11 | 72/169 | 163/907 | 210/1908 | |||
| 82 | 开远市 | 0/12 | 0/15 | 0/17 | 0/23 | 0/32 | 0/45 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 24/143 | 42/556 | 51/986 | |||
| 83 | 弥勒县 | 0/11 | 0/14 | 0/15 | 1/29 | 1/56 | 1/94 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 22/140 | 42/552 | 54/974 | |||
| 84 | 泸西县 | 0/10 | 0/12 | 0/13 | 0/21 | 0/30 | 0/42 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 17/137 | 35/537 | 44/960 | |||
| 85 | 金平县 | 0/24 | 0/35 | 0/46 | 14/49 | 23/122 | 28/351 | 1/6 | 1/7 | 2/13 | 75/189 | 151/907 | 226/2014 | |||
| 86 | 屏边县 | 0/27 | 0/45 | 0/80 | 13/44 | 15/98 | 18/225 | 1/9 | 1/11 | 2/19 | 91/195 | 208/1022 | 355/2565 | |||
| 87 | 建水县 | 0/12 | 0/14 | 0/15 | 0/23 | 0/33 | 0/46 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 30/144 | 56/603 | 69/1094 | |||
| 88 | 石屏县 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 0/14 | 0/24 | 0/38 | 0/53 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 31/146 | 53/606 | 67/1103 | |||
| 89 | 红河县 | 0/20 | 0/26 | 0/44 | 0/21 | 0/30 | 0/42 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/7 | 28/141 | 47/582 | 58/1047 | |||
| 90 | 元阳县 | 1/31 | 1/64 | 1/100 | 5/38 | 8/92 | 11/210 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 34/154 | 60/669 | 76/1241 | |||
| 91 | 绿春县 | 1/39 | 1/86 | 1/170 | 7/38 | 8/92 | 8/189 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 48/164 | 87/754 | 119/1482 | |||
| 92 | 河口县 | 0/43 | 0/79 | 0/131 | 11/44 | 14/91 | 21/252 | 1/5 | 1/5 | 1/9 | 67/183 | 135/937 | 182/1939 | |||
| 93 | 景洪市 | 0/61 | 0/128 | 0/239 | 7/48 | 10/95 | 12/228 | 1/8 | 1/9 | 2/16 | 82/197 | 195/1212 | 286/2931 | |||
| 94 | 勐腊县 | 2/59 | 2/135 | 2/286 | 8/44 | 9/90 | 11/205 | 0/7 | 0/8 | 0/13 | 86/199 | 194/1225 | 300/2952 | |||
| 95 | 勐海县 | 0/58 | 0/116 | 0/224 | 5/39 | 6/75 | 7/155 | 1/8 | 1/9 | 2/14 | 80/193 | 167/1131 | 233/2603 | |||
| 96 | 楚雄市 | 1/16 | 1/31 | 1/39 | 0/26 | 0/38 | 0/59 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 0/8 | 30/143 | 40/544 | 47/945 | |||
| 97 | 禄丰县 | 1/12 | 1/19 | 1/22 | 0/29 | 0/50 | 0/83 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 0/9 | 23/137 | 28/494 | 30/836 | |||
| 98 | 武定县 | 1/20 | 1/30 | 1/39 | 0/30 | 0/52 | 0/93 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 0/9 | 19/142 | 23/505 | 25/854 | |||
| 99 | 元谋县 | 1/13 | 1/21 | 1/24 | 5/24 | 8/30 | 11/48 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 0/8 | 34/139 | 60/520 | 76/880 | |||
| 100 | 永仁县 | 1/14 | 1/21 | 1/24 | 2/26 | 2/47 | 2/84 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/9 | 23/136 | 25/473 | 26/784 | |||
| 101 | 大姚县 | 3/20 | 3/32 | 3/39 | 4/32 | 4/60 | 4/125 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 0/8 | 38/153 | 57/583 | 73/1041 | |||
| 102 | 姚安县 | 1/13 | 1/20 | 1/23 | 0/21 | 0/26 | 0/38 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 0/8 | 17/132 | 18/453 | 19/753 | |||
| 103 | 牟定县 | 1/13 | 1/20 | 1/23 | 0/21 | 0/26 | 0/38 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 0/8 | 16/129 | 17/440 | 18/723 | |||
| 104 | 南华县 | 1/14 | 1/21 | 1/24 | 0/22 | 0/29 | 0/42 | 0/4 | 0/8 | 0/8 | 19/130 | 20/445 | 23/734 | |||
| 105 | 双柏县 | 1/14 | 1/21 | 1/24 | 5/38 | 8/79 | 9/150 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 0/10 | 44/150 | 52/561 | 61/983 | |||
| 106 | 大理市 | 3/41 | 3/119 | 3/211 | 8/33 | 9/72 | 10/177 | 1/6 | 1/11 | 1/16 | 67/177 | 158/860 | 313/2308 | |||
| 107 | 漾濞县 | 0/30 | 0/47 | 0/64 | 8/41 | 11/93 | 13/220 | 0/5 | 0/7 | 0/8 | 51/158 | 84/682 | 124/1378 | |||
| 108 | 祥云县 | 0/11 | 0/14 | 0/15 | 0/21 | 0/29 | 0/41 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 15/134 | 24/460 | 28/746 | |||
| 109 | 宾川县 | 0/27 | 0/66 | 0/95 | 3/28 | 3/56 | 3/107 | 0/5 | 0/7 | 0/8 | 50/157 | 80/633 | 117/1202 | |||
| 110 | 洱源县 | 0/14 | 0/17 | 0/20 | 4/27 | 5/41 | 5/93 | 0/5 | 0/8 | 0/9 | 49/164 | 110/716 | 170/1560 | |||
| 111 | 鹤庆县 | 0/21 | 0/28 | 0/35 | 2/29 | 2/50 | 2/122 | 0/8 | 0/11 | 0/17 | 53/161 | 122/757 | 210/1767 | |||
| 112 | 剑川县 | 0/17 | 0/21 | 0/25 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/46 | 0/5 | 0/8 | 0/9 | 34/154 | 45/554 | 60/1050 | |||
| 113 | 云龙县 | 0/13 | 0/17 | 0/19 | 1/22 | 1/32 | 1/56 | 0/7 | 0/9 | 0/13 | 21/142 | 31/473 | 36/791 | |||
| 114 | 永平县 | 0/19 | 0/27 | 0/38 | 1/23 | 1/33 | 1/47 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 21/142 | 29/492 | 33/799 | |||
| 115 | 巍山县 | 0/12 | 0/15 | 0/16 | 0/21 | 0/30 | 0/42 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 20/143 | 36/475 | 40/828 | |||
| 116 | 南涧县 | 0/14 | 0/17 | 0/19 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/43 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 16/135 | 23/461 | 25/736 | |||
| 117 | 弥渡县 | 0/15 | 0/15 | 0/15 | 0/24 | 0/33 | 0/47 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 14/133 | 22/455 | 26/737 | |||
| 118 | 潞西市 | 0/11 | 0/14 | 0/15 | 0/24 | 0/34 | 0/47 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 38/133 | 57/455 | 68/737 | |||
| 119 | 瑞丽市 | 1/29 | 1/54 | 1/78 | 1/30 | 1/50 | 1/76 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 2/6 | 36/160 | 55/625 | 69/1048 | |||
| 120 | 陇川县 | 0/12 | 0/15 | 0/16 | 0/24 | 0/32 | 0/42 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 28/138 | 37/513 | 41/834 | |||
| 121 | 盈江县 | 0/18 | 0/28 | 0/41 | 3/42 | 4/82 | 4/178 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 42/158 | 61/642 | 81/1125 | |||
| 122 | 梁河县 | 0/14 | 0/17 | 0/22 | 0/24 | 0/32 | 0/41 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 22/137 | 31/514 | 33/826 | |||
| 123 | 泸水县 | 2/38 | 2/64 | 2/87 | 9/41 | 13/100 | 18/241 | 1/5 | 1/6 | 2/8 | 53/156 | 86/673 | 126/1344 | |||
| 124 | 兰坪县 | 1/18 | 1/21 | 1/24 | 0/27 | 0/42 | 0/72 | 2/5 | 2/8 | 2/9 | 33/137 | 44/536 | 54/944 | |||
| 125 | 福贡县 | 3/50 | 3/121 | 3/258 | 6/39 | 9/84 | 11/209 | 1/5 | 1/9 | 2/13 | 54/156 | 111/690 | 180/1593 | |||
| 126 | 贡山县 | 10/78 | 12/253 | 12/724 | 12/46 | 28/124 | 49/412 | 2/7 | 2/14 | 3/23 | 82/177 | 189/873 | 419/2821 | |||
| 127 | 香格里拉县 | 4/51 | 4/155 | 4/316 | 3/29 | 4/54 | 5/166 | 2/7 | 2/14 | 3/31 | 70/169 | 188/893 | 453/3361 | |||
| 128 | 维西县 | 5/59 | 5/152 | 5/328 | 3/28 | 6/57 | 11/175 | 2/8 | 2/17 | 3/31 | 65/164 | 149/821 | 310/2480 | |||
| 129 | 德钦县 | 4/64 | 4/155 | 5/312 | 8/27 | 11/56 | 12/179 | 1/7 | 1/16 | 1/33 | 67/159 | 151/826 | 356/2988 | |||
附录I 云南省特有植物/高等植物分县统计
Appendix I An enumeration of endemic/higher plants in various counties of Yunnan Province
| 序号No. | 县 County | 苔藓植物Bryophytes | 蕨类植物Ferns | 裸子植物Gymnosperms | 被子植物Angiosperms | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种Species | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种 Species | |||||
| 1 | 五华区 | 5/56 | 6/139 | 7/286 | 7/39 | 9/86 | 9/192 | 1/8 | 1/21 | 1/43 | 57/173 | 122/887 | 165/2194 | |||
| 2 | 盘龙区 | 5/56 | 6/143 | 7/292 | 7/39 | 9/86 | 9/193 | 1/8 | 1/21 | 1/43 | 57/177 | 121/895 | 166/2172 | |||
| 3 | 官渡区 | 5/56 | 6/139 | 7/286 | 7/39 | 9/86 | 9/193 | 1/8 | 1/21 | 1/43 | 56/174 | 120/884 | 162/2144 | |||
| 4 | 西山区 | 7/58 | 7/150 | 8/315 | 7/39 | 10/86 | 10/194 | 1/8 | 1/21 | 1/43 | 57/176 | 123/885 | 167/2150 | |||
| 5 | 东川区 | 1/20 | 1/30 | 1/37 | 0/25 | 0/29 | 0/44 | 1/9 | 1/20 | 1/33 | 39/157 | 62/616 | 88/1203 | |||
| 6 | 安宁市 | 2/34 | 2/70 | 2/108 | 1/27 | 1/40 | 1/65 | 0/5 | 0/11 | 0/16 | 19/147 | 22/520 | 23/846 | |||
| 7 | 富民县 | 1/21 | 1/32 | 1/37 | 0/26 | 0/41 | 0/66 | 0/6 | 0/11 | 0/15 | 40/154 | 49/591 | 52/1021 | |||
| 8 | 呈贡县 | 2/14 | 2/29 | 2/39 | 0/22 | 0/29 | 0/42 | 0/5 | 0/10 | 0/13 | 15/138 | 18/467 | 19/747 | |||
| 9 | 晋宁县 | 1/12 | 1/18 | 1/21 | 0/21 | 0/27 | 0/39 | 0/5 | 0/10 | 0/13 | 16/139 | 19/464 | 20/737 | |||
| 10 | 宜良县 | 1/20 | 1/28 | 1/31 | 2/26 | 2/38 | 2/57 | 0/5 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 21/145 | 25/499 | 27/813 | |||
| 11 | 石林县 | 1/19 | 1/33 | 1/43 | 2/26 | 2/37 | 2/59 | 0/5 | 0/10 | 0/14 | 23/146 | 29/513 | 31/820 | |||
| 12 | 嵩明县 | 1/35 | 1/67 | 1/103 | 2/29 | 2/53 | 2/95 | 0/5 | 0/13 | 0/17 | 44/160 | 66/621 | 78/1150 | |||
| 13 | 禄劝县 | 2/25 | 2/46 | 2/67 | 5/35 | 5/74 | 5/185 | 1/7 | 1/17 | 1/26 | 54/169 | 84/720 | 110/1440 | |||
| 14 | 寻甸县 | 2/26 | 2/39 | 2/62 | 0/22 | 0/26 | 0/37 | 0/5 | 0/11 | 0/14 | 24/144 | 30/505 | 32/827 | |||
| 15 | 麒麟区 | 0/13 | 0/15 | 0/16 | 0/23 | 0/27 | 0/33 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 7/127 | 8/418 | 9/621 | |||
| 16 | 马龙县 | 1/11 | 1/13 | 1/14 | 0/21 | 0/25 | 0/34 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 3/122 | 3/393 | 3/586 | |||
| 17 | 陆良县 | 0/12 | 0/15 | 0/16 | 0/20 | 0/24 | 0/33 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 3/118 | 3/395 | 3/597 | |||
| 18 | 师宗县 | 0/15 | 0/24 | 0/28 | 0/25 | 0/27 | 0/38 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 9/134 | 9/481 | 9/734 | |||
| 19 | 罗平县 | 0/14 | 0/16 | 0/17 | 2/28 | 2/42 | 2/62 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 7/131 | 9/482 | 9/734 | |||
| 20 | 富源县 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 0/14 | 0/21 | 0/26 | 0/35 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 5/120 | 5/400 | 5/604 | |||
| 21 | 宣威市 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 0/15 | 0/25 | 0/37 | 0/51 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 4/121 | 4/399 | 4/591 | |||
| 22 | 沾益县 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 0/14 | 0/20 | 0/29 | 0/38 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 4/123 | 4/398 | 4/597 | |||
| 23 | 会泽县 | 0/12 | 0/14 | 0/15 | 1/27 | 1/42 | 1/67 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/8 | 24/141 | 38/513 | 42/867 | |||
| 24 | 红塔区 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 0/14 | 0/21 | 0/28 | 0/41 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/5 | 15/134 | 16/461 | 16/701 | |||
| 25 | 江川县 | 0/10 | 0/13 | 0/15 | 0/21 | 0/27 | 0/36 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 7/129 | 8/452 | 8/713 | |||
| 26 | 澄江县 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 0/14 | 0/27 | 0/43 | 0/71 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 11/123 | 16/486 | 17/712 | |||
| 27 | 华宁县 | 0/11 | 0/14 | 0/13 | 0/21 | 0/27 | 0/36 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 4/118 | 4/410 | 4/601 | |||
| 28 | 通海县 | 0/19 | 0/18 | 0/20 | 0/24 | 0/36 | 0/51 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 8/127 | 8/414 | 8/622 | |||
| 29 | 峨山县 | 0/10 | 0/12 | 0/14 | 1/29 | 1/45 | 1/60 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 23/139 | 28/542 | 29/856 | |||
| 30 | 元江县 | 0/16 | 0/18 | 0/20 | 0/27 | 0/37 | 0/60 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 39/145 | 55/634 | 65/1066 | |||
| 31 | 新平县 | 0/18 | 0/25 | 0/25 | 7/39 | 12/90 | 14/209 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/5 | 29/139 | 33/503 | 37/756 | |||
| 32 | 易门县 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 0/14 | 1/29 | 1/50 | 1/78 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 19/132 | 24/480 | 27/756 | |||
| 33 | 昭阳区 | 0/30 | 0/43 | 0/53 | 0/21 | 0/31 | 0/45 | 0/6 | 0/6 | 0/7 | 30/144 | 36/553 | 48/963 | |||
| 34 | 鲁甸县 | 0/10 | 0/12 | 0/13 | 0/23 | 0/30 | 0/44 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 19/126 | 22/425 | 31/696 | |||
| 35 | 巧家县 | 0/22 | 0/33 | 0/38 | 4/31 | 4/59 | 4/134 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/5 | 32/145 | 48/566 | 74/1047 | |||
| 36 | 彝良县 | 0/46 | 0/76 | 0/125 | 1/25 | 1/75 | 1/75 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 26/151 | 33/561 | 47/1033 | |||
| 37 | 大关县 | 0/35 | 0/57 | 0/87 | 2/39 | 3/89 | 3/192 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 32/149 | 36/559 | 53/1020 | |||
| 38 | 永善县 | 0/24 | 0/35 | 0/45 | 2/29 | 2/51 | 2/100 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 25/136 | 29/488 | 45/861 | |||
| 39 | 绥江县 | 0/11 | 0/14 | 0/15 | 4/38 | 6/93 | 6/196 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 24/140 | 27/505 | 38/869 | |||
| 40 | 水富县 | 0/11 | 0/12 | 0/13 | 0/22 | 0/28 | 0/41 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 17/125 | 19/419 | 28/680 | |||
| 41 | 盐津县 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 0/14 | 0/22 | 0/29 | 0/42 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 28/144 | 34/515 | 52/898 | |||
| 42 | 威信县 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 0/14 | 0/24 | 0/33 | 0/54 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 0/8 | 23/134 | 26/455 | 35/762 | |||
| 43 | 镇雄县 | 0/21 | 0/27 | 0/32 | 1/27 | 1/41 | 1/78 | 0/7 | 0/7 | 0/10 | 36/151 | 41/581 | 58/1120 | |||
| 44 | 思茅区 | 0/23 | 0/31 | 0/39 | 2/31 | 2/49 | 2/73 | 0/6 | 0/7 | 0/11 | 66/174 | 120/836 | 161/1687 | |||
| 45 | 宁洱县 | 0/16 | 0/26 | 0/26 | 1/21 | 1/29 | 1/42 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 0/9 | 21/148 | 32/595 | 45/986 | |||
| 46 | 江城县 | 0/14 | 0/17 | 0/18 | 0/27 | 0/44 | 0/63 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 28/143 | 34/535 | 42/881 | |||
| 47 | 墨江县 | 0/15 | 0/18 | 0/19 | 0/28 | 0/45 | 0/69 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 23/141 | 31/528 | 39/872 | |||
| 48 | 镇沅县 | 0/15 | 0/18 | 0/19 | 2/28 | 2/45 | 2/69 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 22/141 | 28/528 | 38/872 | |||
| 49 | 景东县 | 1/42 | 1/79 | 1/135 | 10/46 | 18/103 | 23/256 | 1/8 | 1/11 | 2/18 | 87/186 | 172/981 | 292/2297 | |||
| 50 | 景谷县 | 0/13 | 0/16 | 0/17 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/42 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 22/141 | 31/536 | 42/878 | |||
| 51 | 澜沧县 | 0/15 | 0/19 | 0/22 | 2/28 | 2/47 | 2/71 | 2/5 | 2/7 | 4/11 | 47/156 | 67/677 | 89/1192 | |||
| 52 | 孟连县 | 0/12 | 0/14 | 0/15 | 2/32 | 2/61 | 2/95 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 35/164 | 53/685 | 67/1175 | |||
| 53 | 西盟县 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 0/14 | 3/31 | 3/55 | 3/91 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 23/142 | 30/539 | 38/876 | |||
| 54 | 临翔区 | 0/14 | 0/19 | 0/22 | 2/29 | 2/43 | 2/60 | 1/6 | 1/8 | 2/12 | 51/161 | 79/713 | 104/1332 | |||
| 55 | 云县 | 0/13 | 0/16 | 0/17 | 1/23 | 1/35 | 1/48 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 22/139 | 27/498 | 29/786 | |||
| 56 | 凤庆县 | 0/16 | 0/20 | 0/21 | 0/24 | 0/32 | 0/46 | 0/5 | 0/7 | 0/9 | 54/166 | 84/679 | 109/1260 | |||
| 57 | 永德县 | 0/12 | 0/18 | 0/23 | 5/37 | 5/77 | 6/149 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 26/135 | 33/498 | 39/810 | |||
| 58 | 镇康县 | 0/17 | 0/25 | 0/32 | 5/31 | 5/47 | 6/74 | 0/6 | 0/7 | 0/10 | 26/162 | 33/728 | 39/1348 | |||
| 59 | 耿马县 | 1/28 | 2/46 | 2/64 | 2/28 | 2/45 | 3/82 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/7 | 49/156 | 65/676 | 77/1185 | |||
| 60 | 双江县 | 0/11 | 0/16 | 0/17 | 0/25 | 0/40 | 0/56 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 39/152 | 50/624 | 61/1066 | |||
| 61 | 沧源县 | 2/29 | 2/57 | 2/102 | 3/34 | 3/68 | 3/127 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 46/156 | 64/660 | 83/1165 | |||
| 62 | 隆阳区 | 0/32 | 0/49 | 0/56 | 0/24 | 0/34 | 0/48 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 30/145 | 40/529 | 49/884 | |||
| 63 | 腾冲县 | 2/43 | 2/84 | 2/179 | 4/40 | 6/72 | 6/123 | 1/7 | 1/9 | 1/12 | 59/169 | 124/751 | 181/1534 | |||
| 64 | 龙陵县 | 0/12 | 0/14 | 0/15 | 1/26 | 2/35 | 2/50 | 1/6 | 1/7 | 2/11 | 55/152 | 78/587 | 100/1044 | |||
| 65 | 施甸县 | 0/10 | 0/13 | 0/14 | 0/20 | 0/27 | 0/36 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 12/125 | 18/412 | 20/644 | |||
| 66 | 昌宁县 | 0/12 | 0/15 | 0/17 | 0/23 | 0/30 | 0/39 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 14/125 | 20/422 | 22/657 | |||
| 67 | 古城区 | 8/64 | 11/174 | 11/414 | 4/33 | 5/69 | 9/197 | 2/9 | 2/20 | 3/38 | 80/179 | 191/919 | 440/3124 | |||
| 68 | 玉龙县 | 11/69 | 15/202 | 15/481 | 5/34 | 8/72 | 12/222 | 2/9 | 2/20 | 3/37 | 81/179 | 229/974 | 549/3618 | |||
| 69 | 永胜县 | 0/30 | 0/52 | 0/85 | 3/21 | 3/26 | 3/45 | 0/5 | 0/7 | 0/9 | 42/149 | 69/625 | 95/1232 | |||
| 70 | 华坪县 | 0/21 | 0/39 | 0/68 | 2/18 | 2/21 | 2/35 | 0/5 | 0/7 | 0/11 | 24/137 | 32/492 | 45/922 | |||
| 71 | 宁蒗县 | 1/26 | 1/43 | 1/73 | 1/20 | 1/26 | 1/42 | 0/7 | 0/10 | 0/14 | 47/153 | 73/590 | 103/1248 | |||
| 72 | 文山县 | 0/21 | 0/27 | 0/34 | 5/35 | 6/69 | 7/131 | 0/8 | 0/11 | 0/15 | 69/179 | 123/837 | 164/1821 | |||
| 73 | 砚山县 | 0/10 | 0/12 | 0/13 | 1/31 | 1/52 | 1/87 | 0/5 | 0/7 | 0/8 | 47/164 | 93/764 | 110/1483 | |||
| 74 | 丘北县 | 1/38 | 1/55 | 1/85 | 0/28 | 0/39 | 0/56 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 23/145 | 40/564 | 51/1002 | |||
| 75 | 广南县 | 0/12 | 0/14 | 0/15 | 4/42 | 5/103 | 6/239 | 0/7 | 0/8 | 0/13 | 48/164 | 82/711 | 109/1402 | |||
| 76 | 富宁县 | 0/12 | 0/15 | 0/16 | 0/28 | 0/43 | 0/74 | 0/8 | 0/10 | 0/17 | 67/178 | 119/892 | 141/1922 | |||
| 77 | 西畴县 | 0/18 | 0/23 | 0/27 | 14/45 | 19/111 | 23/271 | 3/9 | 3/13 | 4/21 | 81/183 | 175/916 | 259/2193 | |||
| 78 | 麻粟坡县 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 0/14 | 11/41 | 15/98 | 20/243 | 1/9 | 1/13 | 1/21 | 72/181 | 165/890 | 262/2057 | |||
| 79 | 马关县 | 0/16 | 0/18 | 0/23 | 10/42 | 14/104 | 19/261 | 0/8 | 0/9 | 0/13 | 53/169 | 95/739 | 140/1465 | |||
| 80 | 个旧市 | 0/12 | 0/15 | 0/17 | 0/26 | 0/40 | 0/53 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 20/142 | 39/555 | 52/993 | |||
| 81 | 蒙自县 | 0/13 | 0/18 | 0/19 | 6/33 | 8/62 | 8/123 | 0/6 | 0/8 | 0/11 | 72/169 | 163/907 | 210/1908 | |||
| 82 | 开远市 | 0/12 | 0/15 | 0/17 | 0/23 | 0/32 | 0/45 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 24/143 | 42/556 | 51/986 | |||
| 83 | 弥勒县 | 0/11 | 0/14 | 0/15 | 1/29 | 1/56 | 1/94 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 22/140 | 42/552 | 54/974 | |||
| 84 | 泸西县 | 0/10 | 0/12 | 0/13 | 0/21 | 0/30 | 0/42 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 17/137 | 35/537 | 44/960 | |||
| 85 | 金平县 | 0/24 | 0/35 | 0/46 | 14/49 | 23/122 | 28/351 | 1/6 | 1/7 | 2/13 | 75/189 | 151/907 | 226/2014 | |||
| 86 | 屏边县 | 0/27 | 0/45 | 0/80 | 13/44 | 15/98 | 18/225 | 1/9 | 1/11 | 2/19 | 91/195 | 208/1022 | 355/2565 | |||
| 87 | 建水县 | 0/12 | 0/14 | 0/15 | 0/23 | 0/33 | 0/46 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 30/144 | 56/603 | 69/1094 | |||
| 88 | 石屏县 | 0/11 | 0/13 | 0/14 | 0/24 | 0/38 | 0/53 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 31/146 | 53/606 | 67/1103 | |||
| 89 | 红河县 | 0/20 | 0/26 | 0/44 | 0/21 | 0/30 | 0/42 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/7 | 28/141 | 47/582 | 58/1047 | |||
| 90 | 元阳县 | 1/31 | 1/64 | 1/100 | 5/38 | 8/92 | 11/210 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 34/154 | 60/669 | 76/1241 | |||
| 91 | 绿春县 | 1/39 | 1/86 | 1/170 | 7/38 | 8/92 | 8/189 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 48/164 | 87/754 | 119/1482 | |||
| 92 | 河口县 | 0/43 | 0/79 | 0/131 | 11/44 | 14/91 | 21/252 | 1/5 | 1/5 | 1/9 | 67/183 | 135/937 | 182/1939 | |||
| 93 | 景洪市 | 0/61 | 0/128 | 0/239 | 7/48 | 10/95 | 12/228 | 1/8 | 1/9 | 2/16 | 82/197 | 195/1212 | 286/2931 | |||
| 94 | 勐腊县 | 2/59 | 2/135 | 2/286 | 8/44 | 9/90 | 11/205 | 0/7 | 0/8 | 0/13 | 86/199 | 194/1225 | 300/2952 | |||
| 95 | 勐海县 | 0/58 | 0/116 | 0/224 | 5/39 | 6/75 | 7/155 | 1/8 | 1/9 | 2/14 | 80/193 | 167/1131 | 233/2603 | |||
| 96 | 楚雄市 | 1/16 | 1/31 | 1/39 | 0/26 | 0/38 | 0/59 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 0/8 | 30/143 | 40/544 | 47/945 | |||
| 97 | 禄丰县 | 1/12 | 1/19 | 1/22 | 0/29 | 0/50 | 0/83 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 0/9 | 23/137 | 28/494 | 30/836 | |||
| 98 | 武定县 | 1/20 | 1/30 | 1/39 | 0/30 | 0/52 | 0/93 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 0/9 | 19/142 | 23/505 | 25/854 | |||
| 99 | 元谋县 | 1/13 | 1/21 | 1/24 | 5/24 | 8/30 | 11/48 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 0/8 | 34/139 | 60/520 | 76/880 | |||
| 100 | 永仁县 | 1/14 | 1/21 | 1/24 | 2/26 | 2/47 | 2/84 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/9 | 23/136 | 25/473 | 26/784 | |||
| 101 | 大姚县 | 3/20 | 3/32 | 3/39 | 4/32 | 4/60 | 4/125 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 0/8 | 38/153 | 57/583 | 73/1041 | |||
| 102 | 姚安县 | 1/13 | 1/20 | 1/23 | 0/21 | 0/26 | 0/38 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 0/8 | 17/132 | 18/453 | 19/753 | |||
| 103 | 牟定县 | 1/13 | 1/20 | 1/23 | 0/21 | 0/26 | 0/38 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 0/8 | 16/129 | 17/440 | 18/723 | |||
| 104 | 南华县 | 1/14 | 1/21 | 1/24 | 0/22 | 0/29 | 0/42 | 0/4 | 0/8 | 0/8 | 19/130 | 20/445 | 23/734 | |||
| 105 | 双柏县 | 1/14 | 1/21 | 1/24 | 5/38 | 8/79 | 9/150 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 0/10 | 44/150 | 52/561 | 61/983 | |||
| 106 | 大理市 | 3/41 | 3/119 | 3/211 | 8/33 | 9/72 | 10/177 | 1/6 | 1/11 | 1/16 | 67/177 | 158/860 | 313/2308 | |||
| 107 | 漾濞县 | 0/30 | 0/47 | 0/64 | 8/41 | 11/93 | 13/220 | 0/5 | 0/7 | 0/8 | 51/158 | 84/682 | 124/1378 | |||
| 108 | 祥云县 | 0/11 | 0/14 | 0/15 | 0/21 | 0/29 | 0/41 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 15/134 | 24/460 | 28/746 | |||
| 109 | 宾川县 | 0/27 | 0/66 | 0/95 | 3/28 | 3/56 | 3/107 | 0/5 | 0/7 | 0/8 | 50/157 | 80/633 | 117/1202 | |||
| 110 | 洱源县 | 0/14 | 0/17 | 0/20 | 4/27 | 5/41 | 5/93 | 0/5 | 0/8 | 0/9 | 49/164 | 110/716 | 170/1560 | |||
| 111 | 鹤庆县 | 0/21 | 0/28 | 0/35 | 2/29 | 2/50 | 2/122 | 0/8 | 0/11 | 0/17 | 53/161 | 122/757 | 210/1767 | |||
| 112 | 剑川县 | 0/17 | 0/21 | 0/25 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/46 | 0/5 | 0/8 | 0/9 | 34/154 | 45/554 | 60/1050 | |||
| 113 | 云龙县 | 0/13 | 0/17 | 0/19 | 1/22 | 1/32 | 1/56 | 0/7 | 0/9 | 0/13 | 21/142 | 31/473 | 36/791 | |||
| 114 | 永平县 | 0/19 | 0/27 | 0/38 | 1/23 | 1/33 | 1/47 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 21/142 | 29/492 | 33/799 | |||
| 115 | 巍山县 | 0/12 | 0/15 | 0/16 | 0/21 | 0/30 | 0/42 | 0/4 | 0/4 | 0/5 | 20/143 | 36/475 | 40/828 | |||
| 116 | 南涧县 | 0/14 | 0/17 | 0/19 | 0/22 | 0/30 | 0/43 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 16/135 | 23/461 | 25/736 | |||
| 117 | 弥渡县 | 0/15 | 0/15 | 0/15 | 0/24 | 0/33 | 0/47 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 14/133 | 22/455 | 26/737 | |||
| 118 | 潞西市 | 0/11 | 0/14 | 0/15 | 0/24 | 0/34 | 0/47 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 38/133 | 57/455 | 68/737 | |||
| 119 | 瑞丽市 | 1/29 | 1/54 | 1/78 | 1/30 | 1/50 | 1/76 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 2/6 | 36/160 | 55/625 | 69/1048 | |||
| 120 | 陇川县 | 0/12 | 0/15 | 0/16 | 0/24 | 0/32 | 0/42 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 28/138 | 37/513 | 41/834 | |||
| 121 | 盈江县 | 0/18 | 0/28 | 0/41 | 3/42 | 4/82 | 4/178 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/6 | 42/158 | 61/642 | 81/1125 | |||
| 122 | 梁河县 | 0/14 | 0/17 | 0/22 | 0/24 | 0/32 | 0/41 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/4 | 22/137 | 31/514 | 33/826 | |||
| 123 | 泸水县 | 2/38 | 2/64 | 2/87 | 9/41 | 13/100 | 18/241 | 1/5 | 1/6 | 2/8 | 53/156 | 86/673 | 126/1344 | |||
| 124 | 兰坪县 | 1/18 | 1/21 | 1/24 | 0/27 | 0/42 | 0/72 | 2/5 | 2/8 | 2/9 | 33/137 | 44/536 | 54/944 | |||
| 125 | 福贡县 | 3/50 | 3/121 | 3/258 | 6/39 | 9/84 | 11/209 | 1/5 | 1/9 | 2/13 | 54/156 | 111/690 | 180/1593 | |||
| 126 | 贡山县 | 10/78 | 12/253 | 12/724 | 12/46 | 28/124 | 49/412 | 2/7 | 2/14 | 3/23 | 82/177 | 189/873 | 419/2821 | |||
| 127 | 香格里拉县 | 4/51 | 4/155 | 4/316 | 3/29 | 4/54 | 5/166 | 2/7 | 2/14 | 3/31 | 70/169 | 188/893 | 453/3361 | |||
| 128 | 维西县 | 5/59 | 5/152 | 5/328 | 3/28 | 6/57 | 11/175 | 2/8 | 2/17 | 3/31 | 65/164 | 149/821 | 310/2480 | |||
| 129 | 德钦县 | 4/64 | 4/155 | 5/312 | 8/27 | 11/56 | 12/179 | 1/7 | 1/16 | 1/33 | 67/159 | 151/826 | 356/2988 | |||
| 1 | Chen LZ (陈灵芝) (1993) Biodiversity in China: Current Situation and Conservation Strategy (中国的生物多样性: 现状及其保护对策). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 2 | Li G (李果), Wu XP (吴晓莆), Luo ZL (罗遵兰), Li JS (李俊生) (2011) Establishing an indicator system for biodiversity assessment in China.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 19, 497-504. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 3 | Li XW (李锡文) (1985) Floristic study of Yunnan Province.Acta Botanica Yunnanica(云南植物研究), 7, 361-382. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 4 | Li XW (李锡文) (1994) A floristic study on the seed plants from the region of Yunnan Plateau.Acta Botanica Yunnanica(云南植物研究), 17, 1-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 5 | Li XW (李锡文) (1995) A floristic study on the seed plants from tropical Yunnan.Acta Botanica Yunnanica(云南植物研究), 17, 115-128. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 6 | Ma KP (马克平), Lou ZP (娄治平), Su RH (苏荣辉) (2010) Review and outlook of biodiversity research in Chinese Academy of Sciences.Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences(中国科学院院刊), 25, 634-644. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 7 | Tan WF (谭伟福) (2005) Study of Guangxi biodiversity and its protection.Guizhou Science(贵州科学), 23(2), 50-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 8 | Thorn H, Brooks TM, Fonseca GABD, Hoffmann M, Lamoreux JF, Machilis G, Mittermeier CG, Mittermeier RA, Pilgrim JD (2009) Warfare in biodiversity hotspots.Conservation Biology, 23, 578-587. |
| 9 | Wan BT (万本太), Xu HG (徐海根), Ding H (丁晖), Liu ZL (刘志磊), Wang J (王捷) (2007) Methodology of comprehensive biodiversity assessment.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 15, 97-106. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 10 | Wu CY, Wu SG (1996) A proposal for new floristic kingdom (realm). In: Floristic Characteristics and Diversity of East Asian Plants (eds Zhang AL, Wu SG), pp. 3-42. China. Higher Education Press, Beijing. Springer-Verlag, Hongkong. |
| 11 | Wu ZY (吴征镒), Sun H (孙航), Zhou ZK (周浙昆), Li DZ (李德铢), Peng H (彭华) (2011) Floristics of Seed Plants from China(中国种子植物区系地理). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 12 | Zhu H (朱华) (2008) Distribution patterns of genera of Yunnan seed plants with references to their bio-geographical significances.Advances in Earth Science(地球科学进展), 23, 830-839. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| [2] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [3] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [4] | 连佳丽, 陈婧, 杨雪琴, 赵莹, 罗叙, 韩翠, 赵雅欣, 李建平. 荒漠草原植物多样性和微生物多样性对降水变化的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24044-. |
| [5] | 王鹏, 隋佳容, 丁欣瑶, 王伟中, 曹雪倩, 赵海鹏, 王彦平. 郑州城市公园鸟类群落嵌套分布格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23359-. |
| [6] | 万凤鸣, 万华伟, 张志如, 高吉喜, 孙晨曦, 王永财. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的应用潜力[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23381-. |
| [7] | 林迪, 陈双林, 杜榷, 宋文龙, 饶固, 闫淑珍. 大别山黏菌的物种多样性调查[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23242-. |
| [8] | 孟敬慈, 王国栋, 曹光兰, 胡楠林, 赵美玲, 赵延彤, 薛振山, 刘波, 朴文华, 姜明. 中国芦苇沼泽植物物种丰富度分布格局及其驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23194-. |
| [9] | 张乃鹏, 梁洪儒, 张焱, 孙超, 陈勇, 王路路, 夏江宝, 高芳磊. 土壤类型和地下水埋深对黄河三角洲典型盐沼植物群落空间分异的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23370-. |
| [10] | 蒋陈焜, 郁文彬, 饶广远, 黎怀成, Julien B. Bachelier, Hartmut H. Hilger, Theodor C. H. Cole. 植物系统发生海报——以演化视角介绍植物多样性的科教资料项目[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24210-. |
| [11] | 王丽媛, 胡慧建, 姜杰, 胡一鸣. 南岭哺乳类和鸟类物种丰富度空间分布格局及其影响因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23026-. |
| [12] | 宋柱秋, 叶文, 董仕勇, 金梓超, 钟星杰, 王震, 张步云, 徐晔春, 陈文俐, 李世晋, 姚纲, 徐洲锋, 廖帅, 童毅华, 曾佑派, 曾云保, 陈又生. 广东省高等植物多样性编目和分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23177-. |
| [13] | 陈又生, 宋柱秋, 卫然, 罗艳, 陈文俐, 杨福生, 高连明, 徐源, 张卓欣, 付鹏程, 向春雷, 王焕冲, 郝加琛, 孟世勇, 吴磊, 李波, 于胜祥, 张树仁, 何理, 郭信强, 王文广, 童毅华, 高乞, 费文群, 曾佑派, 白琳, 金梓超, 钟星杰, 张步云, 杜思怡. 西藏维管植物多样性编目和分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23188-. |
| [14] | 韩赟, 迟晓峰, 余静雅, 丁旭洁, 陈世龙, 张发起. 青海野生维管植物名录[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23280-. |
| [15] | 刘志发, 王新财, 龚粤宁, 陈道剑, 张强. 基于红外相机监测的广东南岭国家级自然保护区鸟兽多样性及其垂直分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 22689-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn