



生物多样性 ›› 2009, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (6): 635-643. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09143 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2009.09143
所属专题: 群落中的物种多样性:格局与机制; 物种形成与系统进化
收稿日期:2009-06-03
接受日期:2009-11-12
出版日期:2009-11-20
发布日期:2009-11-20
通讯作者:
唐志尧
作者简介:*E-mail: zytang@urban.pku.edu.cn基金资助:
Zhiyao Tang*( ), Zhiheng Wang, Jingyun Fang
), Zhiheng Wang, Jingyun Fang
Received:2009-06-03
Accepted:2009-11-12
Online:2009-11-20
Published:2009-11-20
Contact:
Zhiyao Tang
摘要:
生物多样性的大尺度分布格局是现代环境与地史过程共同作用的结果。本文从影响机制、参数选择及与现代气候假说的关系等方面回顾了地史成因假说的最新进展, 并得出以下认识: (1) 地史过程对生物多样性的分布格局有显著影响, 但地史过程与现代环境之间强烈的共线性使得两者的影响常叠加在一起; (2) 与广域物种的多样性相比, 地史过程更有利于解释狭域物种(或特有物种)的多样性; (3) 地史过程的参数选择是地史假说所面临的挑战之一, 目前所用的指标与现代环境具有显著的共线性, 难以直观地体现地史过程对生物多样性的影响, 对不同区域内物种系统发育过程的对比或者物种形成速率及灭绝速率分布格局的分析可能有助于评价地史成因假说的影响。
唐志尧, 王志恒, 方精云 (2009) 生物多样性分布格局的地史成因假说. 生物多样性, 17, 635-643. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09143.
Zhiyao Tang, Zhiheng Wang, Jingyun Fang (2009) Historical hypothesis in explaining spatial patterns of species richness. Biodiversity Science, 17, 635-643. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09143.
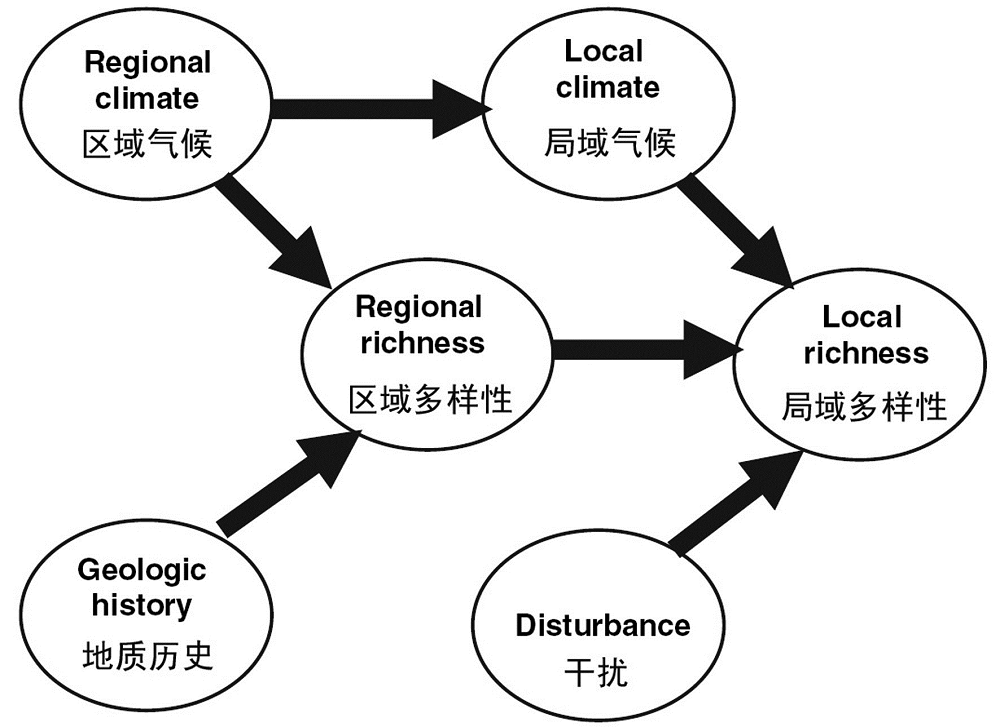
图1 影响不同尺度生物多样性格局的主要因素(引自Harrison & Cornell, 2008)
Fig. 1 Factors influencing biodiversity patterns at different scales (after Harrison & Cornell, 2008)
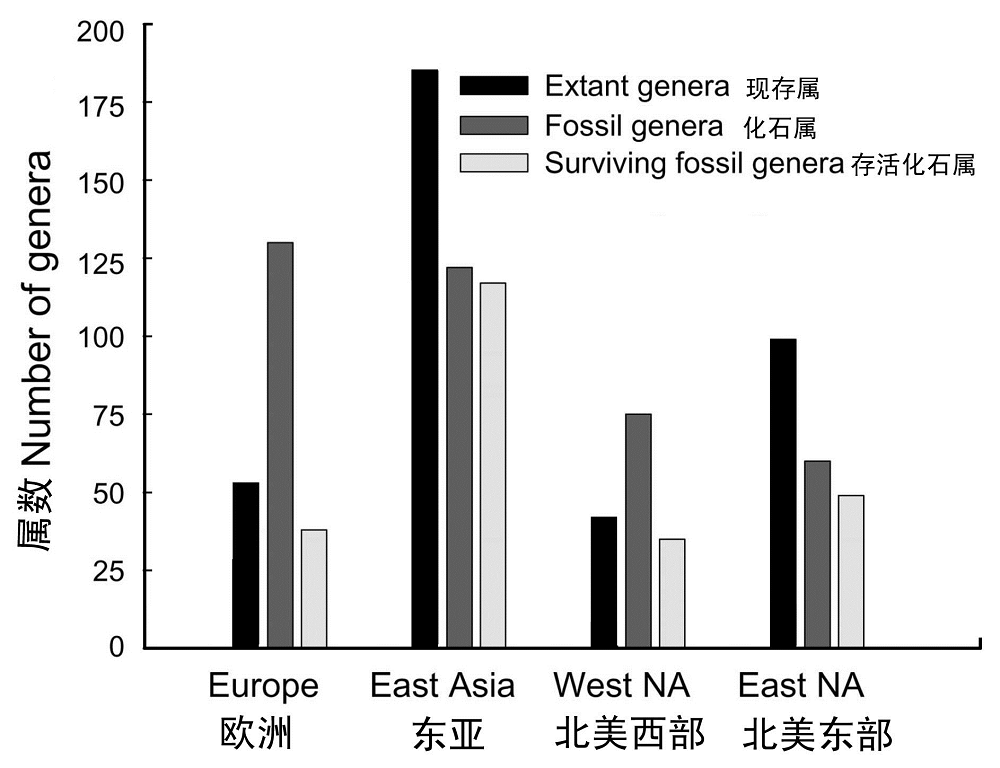
图2 北半球不同区域现存树木及第三纪树木化石的(属)数量比较(引自Ricklefs, 2005)
Fig. 2 The comparison of current and fossil tree genera in different regions of the Northern Hemisphere (revised from Ricklefs, 2005)
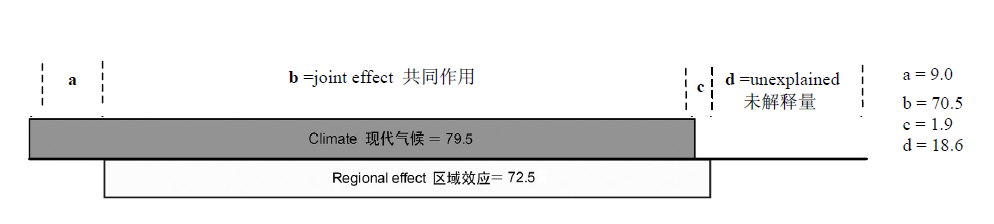
图3 生物地理区和现代气候对中国木本植物多样性分布格局的影响, 其中a, b, c, d 分别表示气候的独立解释量, 气候与区域效应的共同作用, 区域效应的独立解释量, 以及未解释量 (引自王志恒, 2008)
Fig. 3 The relative effects of biogeographic regions and contemporary climate on the patterns of woody plant richness in China. a, b, c represent the variance explained by the pure effect of climate, joint effect of climate and regional effect, pure effect of regional effect; d represents the unexplained variance (after Wang, 2008).
| [1] | Adams JM, Woodward FI (1989) Patterns in tree species richness as a test of the glacial extinction hypothesis. Nature, 339, 699-701. |
| [2] |
Algar AC, Kerr JT, Currie DJ (2009) Evolutionary constraints on regional faunas, whom, but not how many. Ecology Letters, 12, 57-65.
URL PMID |
| [3] |
Allen AP, Brown JH, Gillooly JF (2002) Global biodiversity, biochemical kinetics, and the energetic equivalence rule. Science, 297, 1545-1548.
DOI URL PMID |
| [4] | Alroy J, Aberhan M, Bottjer DJ, Foote M, Fursich FT, Harries PJ, Hendy AJW, Holland SM, Ivany LC, Kiessling W, Kosnik MA, Marshall CR, McGowan AJ, Miller AI, Olszewski TD, Patzkowsky ME, Peters SE, Villier L, Wagner PJ, Bonuso N, Borkow PS, Brenneis B, Clapham ME, Fall LM, Ferguson CA, Hanson VL, Krug AZ, Layou KM, Leckey EH, Nurnberg S, Powers CM, Sessa JA, Simpson C, Tomasovych A, Visaggi CC (2008) Phanerozoic trends in the global diversity of marine invertebrates. Science, 321, 97-100. |
| [5] | Araujo MB, Nogues-Bravo D, Diniz-Filho JAF, Haywood AM, Valdes PJ, Rahbek C (2008) Quaternary climate changes explain diversity among reptiles and amphibians. Ecography, 31, 8-15. |
| [6] | Arita HT, Rodriguez P (2004) Local-regional relationships and the geographical distribution of species. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 13, 15-21. |
| [7] | Brown J (1995) Macroecology. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [8] | Brown JH, Lomolino MV (1998) Biogeography, 2nd edn. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Massachusetts. |
| [9] | Brown JH, Gillooly JF, Allen AP, Savage VM, West GB (2004) Toward a metabolic theory of ecology. Ecology, 85, 1771-1789. |
| [10] | Chown SL, Gaston KJ (2000) Areas, cradles and museums, the latitudinal gradient in species richness. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 15, 311-315. |
| [11] |
Clarke A, Gaston KJ (2006) Climate, energy and diversity. Proceedings of the Royal Society B, Biological Sciences, 273, 2257-2266.
URL PMID |
| [12] | Crame JA (2001) Taxonomic diversity gradients through geological time. Diversity and Distributions, 7, 175-189. |
| [13] | Currie DJ, Francis AP (2004) Regional versus climatic effect on taxon richness in angiosperms: reply to Qian and Ricklefs. The American Naturalist, 163, 780-785. |
| [14] | Currie DJ, Paquin V (1987) Large scale biogeographical patterns of species richness of trees. Nature, 329, 326-328. |
| [15] | Currie DJ (1991) Energy and large-scale patterns of animal- and plant-species richness. The American Naturalist, 137, 27-49. |
| [16] | Currie DJ, Mittelbach GG, Cornell HV, Field R, Guegan JF, Hawkins BA, Kaufman DM, Kerr JT, Oberdorff T, O’Brien E, Turner JRG (2004) Predictions and tests of climate based hypotheses of broad-scale variation in taxonomic richness. Ecology Letters, 7, 1121-1134. |
| [17] | Ellison AM, Farnsworth EJ, Merkt RE (1999) Origins of mangrove ecosystems and the mangrove biodiversity anomaly. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 8, 95-115. |
| [18] | Fang J, Lechowicz MJ (2006) Climatic limits for the present distribution of beech ( Fagus L.) species in the world. Journal of Biogeography, 33, 1804-1819. |
| [19] | Field R, O’Brien EM, Whittaker RJ (2005) Global models for predicting woody plant richness from climate, development and evaluation. Ecology, 86, 2263-2277. |
| [20] | Fischer AG (1981) Climatic oscillations in the biosphere. In: Biotic Crises in Ecological and Evolutionary Time (ed. Nitecki MH), pp. 103-131. Academic Press, New York. |
| [21] | Francis AP, Currie DJ (1998) Global patterns of tree species richness in moist forests: another look. Oikos, 81, 598-602. |
| [22] | Francis AP, Currie DJ (2003) A globally consistent richness-climate relationship for angiosperms. The American Naturalist, 161, 523-536. |
| [23] |
Gaston KJ (2000) Global patterns in biodiversity. Nature, 405, 220-227.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] | Guo Q (1999) Ecological comparisons between Eastern Asia and North America: historical and geographical perspectives. Journal of Biogeography, 26, 199-206. |
| [25] |
Harrison S, Cornell H (2008) Toward a better understanding of the regional causes of local community richness. Ecology Letters, 11, 969-979.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] | Hawkins AB, Porter EE (2003) Relative influences of current and historical factors on mammal and bird diversity patterns in deglaciated North America. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 12, 475-481. |
| [27] | Hawkins BA, Diniz-Filho JAF, Jaramillo CA, Soeller SA (2006) Post-Eocene climate change, niche conservatism, and the latitudinal diversity gradient of New World birds. Journal of Biogeography, 33, 770-780. |
| [28] | Hawkins BA, Diniz-Filho JAF, Jaramillo CA, Soeller SA (2007) Climate, niche conservatism, and the global bird diversity gradient. The American Naturalist, 170, S16-S27. |
| [29] | Hortal J, Rodriguez J, Nieto-Diaz M, Lobo JM (2008) Regional and environmental effects on the species richness of mammal assemblages. Journal of Biogeography, 35, 1202-1214. |
| [30] | Huntley B (1993) Species richness in the north temperate zone forests. Journal of Biogeography, 20, 163-180. |
| [31] | Huston MA (1999) Local processes and regional patterns, appropriate scales for understanding variation in the diversity of plants and animals. Oikos, 86, 393-401. |
| [32] | Jablonski D (1993) The tropics as a source of evolutionary novelty through geological time. Nature, 364, 142-144. |
| [33] |
Jablonski D, Roy K, Valentine JW (2006) Out of the tropics: evolutionary dynamics of the latitudinal diversity gradient. Science, 314, 102-106.
URL PMID |
| [34] | Jetz W, Rahbek C, Colwell RK (2004) The coincidence of rarity and richness and the potential signature of history in centres of endemism. Ecology Letters, 7, 1180-1191. |
| [35] | Latham RE, Ricklefs RE (1993) Global patterns of tree species richness in moist forests, energy-diversity theory does not account for variation in species richness. Oikos, 67, 325-333. |
| [36] | Leighton LR (2005) The latitudinal diversity gradient through deep time, testing the “Age of the Tropics” hypothesis using Carboniferous productidine brachiopods. Evolutionary Ecology, 19, 563-581. |
| [37] | McMaster RT (2005) Factors influencing vascular plant diversity on 22 islands off the coast of eastern North America. Journal of Biogeography, 32, 475-492. |
| [38] |
Mittelbach GG, Schemske DW, Cornell HV, Allen AP, Brown JM, Bush MB, Harrison SP, Hurlbert AH, Knowlton N, Lessios HA, McCain CM, McCune AR, McDade LA, McPeek MA, Near TJ, Price TO, Ricklefs RE, Roy K, Sax DF, Schluter D, Sobel JM, Turelli M (2007) Evolution and the latitudinal diversity gradient, speciation, extinction and biogeography. Ecology Letters, 10, 315-331.
URL PMID |
| [39] | Montoya D, Rodriguez MA, Zavala MA, Hawkins BA (2007) Contemporary richness of holarctic trees and the historical pattern of glacial retreat. Ecography, 30, 173-182. |
| [40] | O’Brien EM (1998) Water-energy dynamics, climate, and prediction of woody plant species richness: an interim general model. Journal of Biogeography, 25, 379-398. |
| [41] | O’Brien EM, Field R, Whittaker RJ (2000) Climatic gradients in woody plant (tree and shrub) diversity: water-energy dynamics, residual variation, and topography. Oikos, 89, 588-600. |
| [42] |
Ohlemuller R, Anderson BJ, Araujo MB, Butchart SM, Kudrna O, Ridgely RS, Thomas CD (2008) The coincidence of climatic and species rarity: high risk to small-range species from climate change. Biology Letters, 4, 568-572.
URL PMID |
| [43] |
Pawar SS (2005) Geographical variation in the rate of evolution: effect of available energy or fluctuating environment? Evolution, 59, 234-237.
URL PMID |
| [44] | Pianka ER (1966) Latitudinal gradients in species diversity: a review of concepts. The American Naturalist, 100, 33-46. |
| [45] | Qian H (2002) A comparison of the taxonomic richness of temperate plants in East Asia and North America. American Journal of Botany, 89, 1818-1825. |
| [46] |
Qian H, Ricklefs RE (2004) Taxon richness and climate in angiosperms, is there a globally consistent relationship that precludes region effects? The American Naturalist, 163, 773-779.
DOI URL PMID |
| [47] |
Qian H, White PS, Song JS (2007) Effects of regional vs. ecological factors on plant species richness: an intercontinental analysis. Ecology, 88, 1440-1453.
DOI URL PMID |
| [48] |
Qian H, Ricklefs RE (2000) Large-scale processes and the Asian bias in species diversity of temperate plants. Nature, 407, 180-182.
URL PMID |
| [49] |
Ricklefs RE (1987) Community diversity, relative roles of local and regional processes. Science, 235, 167-171.
URL PMID |
| [50] | Ricklefs RE (2004) A comprehensive framework for global patterns in biodiversity. Ecology Letters, 7, 1-15. |
| [51] | Ricklefs RE (2005) Historical and ecological dimensions of global patterns in plant diversity. Biologiske Skrifte, 55, 583-603. |
| [52] | Ricklefs RE (2006) Global variation in the diversification rate of passerine birds. Ecology, 87, 2468-2478. |
| [53] | Ricklefs RE, Latham RE, Qian H (1999) Global patterns of tree species richness in moist forests, distinguishing ecological influences and historical contingency. Oikos, 86, 369-373. |
| [54] | Rohde K (1992) Latitudinal gradients in species diversity, the search for the primary causes. Oikos, 65, 514-527. |
| [55] | Rosenzweig ML (1995) Species Diversity in Space and Time. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [56] | Svenning JC, Skov F (2005) The relative roles of environment and history as controls of tree species composition and richness in Europe. Journal of Biogeography, 32, 1019-1033. |
| [57] | Svenning JC, Skov F (2007a) Ice age legacies in the geographic distribution of tree species richness in Europe. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 16, 234-245. |
| [58] |
Svenning JC, Skov F (2007b) Could the tree diversity pattern in Europe be generated by postglacial dispersal limitation? Ecology Letters, 10, 453-460.
URL PMID |
| [59] | Svenning JC, Normand S, Skov F (2008) Postglacial dispersal limitation of widespread forest plant species in nemoral Europe. Ecography, 31, 316-326. |
| [60] | Taplin JRD, Lovett JC (2003) Can we predict centres of plant species richness and rarity from environmental variables in sub-Saharan Africa? Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 142, 187-197. |
| [61] | Thomas GH, Orme CDL, Davies RG, Olson VA, Bennett PM, Gaston KJ, Owens IPF, Blackburn TM (2008) Regional variation in the historical components of global avian species richness. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 17, 340-351. |
| [62] | Wang XP (王襄平), Fang JY (方精云), Tang ZY (唐志尧) (2009) The mid-domain effect hypothesis: models, evidence and limitations. Biodiversity Science, 17, 568-578. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [63] | Wang ZH (王志恒) (2008) Species Diversity of Woody Plants in China: Patterns, Determinants and Scale Effects (中国木本植物物种多样性的地理格局、影响因子及尺度效应). PhD dissertation, Peking University, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [64] | Wang ZH (王志恒), Tang ZY (唐志尧), Fang JY (方精云) (2009) The species-energy hypothesis as a mechanism for species richness patterns. Biodiversity Science, 17, 613-624. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [65] |
Warren MS, Hill JK, Thomas JA, Asher J, Fox R, Huntley B, Royk DB, Telferk MG, Jeffcoate S, Hardingk P, Jeffcoate G, Willis SG, Greatorex-Daviesk JN, Mossk D, Thomas CD (2001) Rapid responses of British butterflies to opposing forces of climate and habitat change. Nature, 414, 65-69.
DOI URL PMID |
| [66] |
Weir JT, Schluter D (2007) The latitudinal gradient in recent speciation and extinction rates of birds and mammals. Science, 315, 1574-1576.
URL PMID |
| [67] | Whittaker RJ, Field R (2000) Tree species richness modelling, an approach of global applicability? Oikos, 89, 399-402. |
| [68] |
Wiens JJ (2004) Speciation and ecology revisited, phylogenetic niche conservatism and the origin of species. Evolution, 58, 193-197.
DOI URL PMID |
| [69] |
Wiens JJ (2007) Global patterns of diversification and species richness in amphibians. The American Naturalist, 170, S86-S106.
URL PMID |
| [70] | Willis KJ, Kleczkowski A, New M, Whittaker RJ (2007) Testing the impact of climate variability on European plant diversity, 320 000 years of water-energy dynamics and its long-term influence on plant taxonomic richness. Ecology Letters, 10, 673-679. |
| [71] | Wolfe JA (1975) Some aspects of plant geography of the northern hemisphere during the late Cretaceous and Tertiary. Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden, 62, 264-279. |
| [72] |
Wright SD, Gray RD, Gardner RC (2003) Energy and the rate of evolution, inferences from plant rDNA substitution rates in the western Pacific. Evolution, 57, 2893-2898.
URL PMID |
| [73] | Wright DH (1983) Species-energy theory: an extension of species-area theory. Oikos, 41, 496-506. |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [3] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [4] | 周昊, 王茗毅, 张楚格, 肖治术, 欧阳芳. 昆虫旅馆在独栖蜂多样性保护中的现状与挑战[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24472-. |
| [5] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [6] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [7] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [8] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [9] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [10] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [11] | 徐欢, 辛凤飞, 施宏亮, 袁琳, 薄顺奇, 赵欣怡, 邓帅涛, 潘婷婷, 余婧, 孙赛赛, 薛程. 生态修复技术集成应用对长江口北支生境与鸟类多样性提升效果评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24478-. |
| [12] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [13] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [14] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [15] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn