



生物多样性 ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (7): 24581. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024581 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024581
田书荣1,*( )(
)( ), 魏营2(
), 魏营2( ), 肖芬1(
), 肖芬1( ), 周芸芸1(
), 周芸芸1( ), 解宜兴2, 王丞2(
), 解宜兴2, 王丞2( ), 宋芬1, 梁志强3(
), 宋芬1, 梁志强3( ), 桂小杰4,*(
), 桂小杰4,*( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-23
接受日期:2025-05-14
出版日期:2025-07-20
发布日期:2025-08-27
通讯作者:
*Email: 139685878@qq.com;wildlifecn@163.com
基金资助:
Shurong Tian1,*( )(
)( ), Ying Wei2(
), Ying Wei2( ), Fen Xiao1(
), Fen Xiao1( ), Yunyun Zhou1(
), Yunyun Zhou1( ), Yixing Xie2, Cheng Wang2(
), Yixing Xie2, Cheng Wang2( ), Fen Song1, Zhiqiang Liang3(
), Fen Song1, Zhiqiang Liang3( ), Xiaojie Gui4,*(
), Xiaojie Gui4,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-12-23
Accepted:2025-05-14
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-08-27
Contact:
*Email: 139685878@qq.com;wildlifecn@163.com
Supported by:摘要: 种群动态分析是制定濒危物种保护策略的重要依据。中国大鲵(Andrias davidianus)为我国特有两栖动物, 其野外种群状况不明。为探讨种群增长模型在种群动态分析及物种保护成效量化评价中的可行性, 本文以湖南张家界大鲵国家级自然保护区的中国大鲵为研究对象, 基于2006-2021年的野外调查数据和2000-2024年的增殖放流统计数据, 应用种群增长模型模拟分析了该保护区中国大鲵的种群动态、环境容纳量及增殖放流效果。结果表明: (1)该种群年均增长率为0.1722 ± 0.0324, 环境容纳量K值为51,190条, 目前种群处于指数增长阶段; (2)中国大鲵种群在增殖放流和无增殖放流两种情形下, 其种群增长曲线呈现极显著差异。在无增殖放流情形下, 种群指数和Logistic增长模型中的瞬时增长率分别下降了16.27%和32.11%。(3)增殖放流对中国大鲵野生种群复壮效果明显, 按照目前增殖放流量测算, 40年后种群数量将达到环境容纳量的峰值。基于种群增长模型分析种群动态具有可行性, 其研究成果对制定中长期濒危物种保护策略具有较好的应用前景; 对张家界大鲵保护区中国大鲵种群动态分析研究结果显示, 增殖放流(种群补充)效果明显; 中国大鲵种群增长率相对较低, 实施增殖放流和栖息地修复等保护措施十分必要。鉴于目前的种群增长率、种群增长趋势及环境容纳量, 建议持续实施增殖放流措施, 并按水系和遗传支系筛选增殖放流个体, 以本地亲本繁育后代为增殖放流个体来源, 防止野生种群基因混杂并确保种群稳定增长, 重点加强出苗点的保护和恢复。本结果可为中国大鲵或其他濒危物种种群动态分析、保护成效评估和保护策略制定提供参考。
田书荣, 魏营, 肖芬, 周芸芸, 解宜兴, 王丞, 宋芬, 梁志强, 桂小杰 (2025) 湖南张家界大鲵国家级自然保护区中国大鲵种群动态及保护策略. 生物多样性, 33, 24581. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024581.
Shurong Tian, Ying Wei, Fen Xiao, Yunyun Zhou, Yixing Xie, Cheng Wang, Fen Song, Zhiqiang Liang, Xiaojie Gui (2025) Population dynamics and conservation strategies of Andrias davidianus in Hunan Zhangjiajie Giant Salamander National Nature Reserve, China. Biodiversity Science, 33, 24581. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024581.
| 年份 Year | 种群数量 Population size | 种群增长率 Population growth rate (%) | 样线长度密度(尾/km) Density of transect length (ind./km) | 样线面积密度(尾/100 m2) Density of transect area (ind./100 m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | 2,000 | 1.53 | 0.14 | |
| 2013 | 7,360 | 20.45 | 5.62 | 0.51 |
| 2021 | 20,963 | 13.97 | 16.00 | 1.47 |
表1 湖南张家界大鲵国家级自然保护区中国大鲵种群动态
Table 1 Population dynamics of Andrias davidianus in the Hunan Zhangjiajie Giant Salamander National Nature Reserve, China
| 年份 Year | 种群数量 Population size | 种群增长率 Population growth rate (%) | 样线长度密度(尾/km) Density of transect length (ind./km) | 样线面积密度(尾/100 m2) Density of transect area (ind./100 m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | 2,000 | 1.53 | 0.14 | |
| 2013 | 7,360 | 20.45 | 5.62 | 0.51 |
| 2021 | 20,963 | 13.97 | 16.00 | 1.47 |
| 年份 Year | 种群数量 Population size | 补充个体数量 Individuals of supplementation | 无补充情形种群数量 Population size under non-supplementation scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | 2,000 | 992 | 1,008 |
| 2013 | 7,360 | 5,952 | 1,408 |
| 2021 | 20,963 | 13,889 | 7,075 |
表2 无补充情形种群动态模拟分析参数
Table 2 Parameters for population dynamics simulation analysis under non-supplementation scenario
| 年份 Year | 种群数量 Population size | 补充个体数量 Individuals of supplementation | 无补充情形种群数量 Population size under non-supplementation scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | 2,000 | 992 | 1,008 |
| 2013 | 7,360 | 5,952 | 1,408 |
| 2021 | 20,963 | 13,889 | 7,075 |
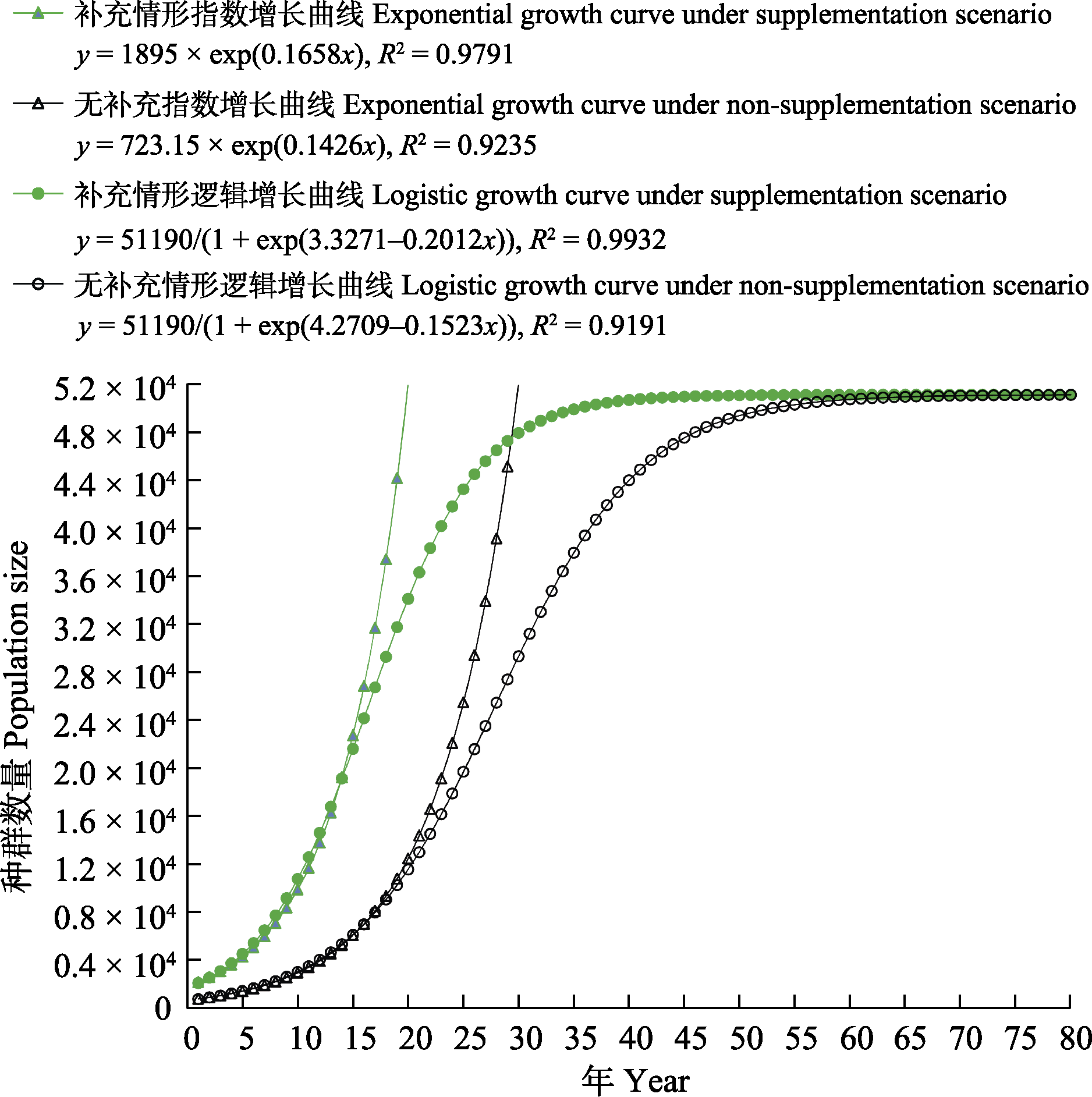
图1 在补充和无补充情形下中国大鲵种群指数和Logistic增长曲线
Fig. 1 The population exponential growth curve and logistic growth curve of the Chinese giant salamander under supplementation and non-supplementation scenarios
| 参数 Parameters | 补充 Supp. | 无补充 NSupp. | 增加 Increase (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 指数增长模型r值 r value of EGM | 0.1658 | 0.1426 | 16.27 |
| Logistic增长模型r值 r value of LGM | 0.2012 | 0.1523 | 32.11 |
| 种群增长到K峰值时间(年) The time of population reaches the peak of K (Year) | 40 | 60 | ‒50 |
表3 在补充和无补充情形下中国大鲵种群增长模型主要参数值比较
Table 3 Comparison and analysis of key parameters for population growth models of the Chinese giant salamander under supplementation (Supp.) and non-supplementation (NSupp.) scenarios
| 参数 Parameters | 补充 Supp. | 无补充 NSupp. | 增加 Increase (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 指数增长模型r值 r value of EGM | 0.1658 | 0.1426 | 16.27 |
| Logistic增长模型r值 r value of LGM | 0.2012 | 0.1523 | 32.11 |
| 种群增长到K峰值时间(年) The time of population reaches the peak of K (Year) | 40 | 60 | ‒50 |
| [1] | Bartlett MS, Hiorns RW (1973) The Mathematical Theory of the Dynamics of Biological Populations. Academic Press, London. |
| [2] | Begon M, Townsend CR, Harper R (2021) Ecology: From Individuals to Ecosystems, 5th edn. Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford. |
| [3] | Borzée A, Angulo A, Meredith H, Taguchi Y, Groffen J, Kohler DB, Abernethy JPD, Othman SN, Messenger K, Heo K, Wan L, Um TE, Zhang X, Shin Y, Bae Y, Wang Z, Qiu Z, Pearce R (2024) Protecting Japanese giant salamanders (Andrias japonicus) in the Nawa River Basin, Japan:Policy recommendations addressing water pollution and waterway disruption. Frontiers in Amphibian and Reptile Science, 2, 1348251. |
| [4] | Chen WG, Li X, Liu C, Wang L, Yu XP (2013) Status of a reintroduced population of the crested ibis (Nipponia nippon) in Ningshan County, Shaanxi Province. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 34, 23-24, 49. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈文贵, 李夏, 刘超, 王莉, 于晓平 (2013) 陕西省宁陕朱鹮再引入种群之现状. 野生动物, 34, 23-24, 49.] | |
| [5] | Gao JW (2022) Study of population dynamics based on time series analysis. Journal of Taiyuan University (Natural Science Edition), 40(1), 48-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [高继文 (2022) 基于时间序列分析法的种群动态变化研究. 太原学院学报(自然科学版), 40(1), 48-52.] | |
| [6] | Gu SY, Chen K, Jin XW, Li WP, Chen XF, Xiong J, Tang MZ, Jiang CQ, Xiong J, Li T, Zhang Q, Cui YD, Zeng HH, He SP, Wang YY, Miao W (2024) Development, applications, and standardization of environmental DNA monitoring technology for aquatic organisms. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 48, 1443-1458. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [谷思雨, 陈凯, 金小伟, 李文攀, 陈晓飞, 熊晶, 汤敏喆, 姜传奇, 熊杰, 李涛, 张琪, 崔永德, 曾宏辉, 何舜平, 王业耀, 缪炜 (2024) 水生生物环境DNA监测技术的发展、应用与标准化. 水生生物学报, 48, 1443-1458.] | |
| [7] | Hastings A (1997) Population Biology: Concepts and Models. Springer, New York. |
| [8] | He YJ, Li Z, Cui GF, Wei WC, Feng ZW (2004) Advances in conservation methods of endangered species. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24, 338-346. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [何友均, 李忠, 崔国发, 魏文超, 冯宗炜 (2004) 濒危物种保护方法研究进展. 生态学报, 24, 338-346.] | |
| [9] | Hidaka S, Jo TS, Yamamoto S, Katsuhara KR, Tomita S, Miya M, Ikegami M, Ushimaru A, Minamoto T (2024) Sensitive and efficient surveillance of Japanese giant salamander (Andrias japonicus) distribution in western Japan using multi-copy nuclear DNA marker. Limnology, 25, 189-198. |
| [10] | Huang JB, Zhang GH (1990) Comparison of theory and case fitting between Logistic and Cui-Lawson population increment models. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 1, 301-305. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄晋彪, 张根海 (1990) Logistic、崔-Lawson种群增长模型理论及实例拟合比较. 应用生态学报, 1, 301-305.] | |
| [11] | IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) (2012) IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. http://www.iucnredlist.org. (accessed 2024-10-15). |
| [12] | Jaeger RG (2018) Population dynamics of the Eastern Red-backed Salamander (Plethodon cinereus). Journal of Herpetology, 52, 123-134. |
| [13] | Jiang WS, Lan XY, Wang JX, Xiang HM, Tian H, Luo QH (2022) Recent progress in the germplasm resources conservation and utilization of the Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus). Journal of Fisheries of China, 46, 683-705. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [蒋万胜, 兰香英, 王金秀, 向红梅, 田贺, 罗庆华 (2022) 中国大鲵种质资源保护与利用研究进展. 水产学报, 46, 683-705.] | |
| [14] | Kot M (2001) Elements of Mathematical Ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [15] | Li CX, Jiang LN, Shao Y, Zhang DJ (2013) Biometrics. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李春喜, 姜丽娜, 邵云, 张黛静 (2013) 生物统计学, 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [16] | Li WL, Luo L, Li H, Wang S, Li ZF, Zhai XL, Xue Y (2018) Advance on the artificial breeding technologies of Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus). Chinese Fishery Quality and Standards, 8(5), 18-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李伟龙, 罗莉, 李虹, 王双, 李战福, 翟旭亮, 薛洋 (2018) 中国大鲵人工养殖技术研究进展. 中国渔业质量与标准, 8(5), 18-24.] | |
| [17] | Li YM (2003) Population viability analysis in conservation biology: Precision and uses. Chinese Biodiversity, 11, 340-350. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[李义明 (2003) 种群生存力分析: 准确性和保护应用. 生物多样性, 11, 340-350.]
DOI |
|
| [18] | Liang ZQ, Zhang SH, Wang CR, Wei QW, Wu YA (2013) Present situation of natural resources and protection recommendations of Andrias davidianus. Freshwater Fisheries, 43(7), 13-17. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [梁志强, 张书环, 王崇瑞, 危起伟, 伍远安 (2013) 大鲵资源现状与保护建议. 淡水渔业, 43(7), 13-17.] | |
| [19] | Liu P, Zhao CL, Xiong S, Wang J, Zhao T, Li C, Xie F (2021) Population monitoring and effect evaluation of the stock enhancement of Chinese giant salamander in the Gutian Mountain National Nature Reserve. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 27, 823-830. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘萍, 赵春霖, 熊姗, 王杰, 赵天, 李成, 谢锋 (2021) 中国大鲵古田山放流种群监测及成效评估. 应用与环境生物学报, 27, 823-830.] | |
| [20] | Lötters S (2019) Population decline of the European fire salamander (Salamandra salamandra). Biodiversity and Conservation, 28, 1011-1023. |
| [21] | Luo QH, Cao W, Wei MY, Yang J, Zhu SH, Fu L (2022) Functional zoning study for Zhangjiajie Chinese Giant Salamander National Nature Reserve based on “3S” technology. Ecological Science, 41(4), 102-110. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [罗庆华, 曹威, 魏梦雅, 杨杰, 朱深海, 付磊 (2022) 基于“3S”技术的张家界大鲵国家级自然保护区功能分区研究. 生态科学, 41(4), 102-110.] | |
| [22] | Luo QH, Liu Y, Zhang LY (2009a) Effectiveness of releasing artificially-bred Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus) into the wild in Zhangjiajie, Hunan. Biodiversity Science, 17, 310-317. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [罗庆华, 刘英, 张立云 (2009a) 张家界大鲵人工放流效果及其影响因素分析. 生物多样性, 17, 310-317.] | |
| [23] | Luo QH, Liu Y, Zhang LY, Chen GJ, Kang LC (2009b) Investigation on resources of Chinese giant salamander in Zhangjiajie City. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 28, 422-426. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [罗庆华, 刘英, 张立云, 陈功建, 康练常 (2009b) 湖南张家界市大鲵资源调查. 四川动物, 28, 422-426.] | |
| [24] | Luo QH, Tong F, Tao SX, Cao W, Fu L, Zhu SH (2019) Effects of tourism disturbance on the habitat and water quality for Andrias davidianus in Zhangjiajie, Hunan, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 30, 2101-2108. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[罗庆华, 童芳, 陶水秀, 曹威, 付磊, 朱深海 (2019) 旅游干扰对张家界大鲵生境及水质的影响. 应用生态学报, 30, 2101-2108.]
DOI |
|
| [25] | Ma SC (1964) The structure of dynamics of space, number, and time of insect population. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 13, 38-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马世骏 (1964) 昆虫种群的空间、数量、时间结构及其动态. 昆虫学报, 13, 38-55.] | |
| [26] | Ma ZF (2003) Analysis of Basic Characteristics of Population Spatio-temporal Dynamics. PhD dissertation, Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马祖飞 (2003) 种群时空动态基本特征分析. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院动物研究所, 北京.] | |
| [27] | May RM (1976) Theoretical Ecology: Principles and Applications. Saunders, Philadelphia. |
| [28] | Minar J, Verhulst P (1993) The discoverer of the logistic curve. Human Biology, 5, 673-689. |
| [29] | Murray JD (2002) Mathematical Biology: I. An Introduction, 3rd edn. Springer-Verlag, New York. |
| [30] | Okada S, Utsunomiya T, Okada T, Felix Z, Ito F (2008) Characteristics of Japanese giant salamander (Andrias japonicus) populations in two small tributary streams in Hiroshima Prefecture, western Honshu, Japan. Herpetological Conservation and Biology, 3, 192-202. |
| [31] | Pei PZ, Wang L, Shao YP, Shi CH, Yang YW, Bao XK (2018) Reintroduced Prezewalski’s horses’s breeding success and population viability analysis in Anxi National Nature Reserve. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 38, 128-138. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [裴鹏祖, 王亮, 邵亚平, 石存海, 杨永伟, 包新康 (2018) 安西极旱荒漠国家级自然保护区重引入普氏野马繁殖成效与种群生存力分析. 兽类学报, 38, 128-138.] | |
| [32] | Petranka JW (2020) Conservation and recovery of the eastern red-backed salamander. Conservation Biology, 34, 456-467. |
| [33] | Shu GC, Liu P L, Zhao T, Li C, Hou YM, Zhao CL, Wang J, Shu XX, Chang J, Jiang JP, Xie F (2021) Disordered translocation is hastening local extinction of the Chinese giant salamander. Asian Herpetological Research, 12, 271-279. |
| [34] | Steinfartz S (2021) Habitat restoration and population recovery of the European fire salamander. Ecological Applications, 31, 567-578. |
| [35] | Sun RY (1985) Scientific Management and Mathematical Models of Population. Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai. (in Chinese) |
| [孙儒泳 (1985) 种群的科学管理与数学模型. 上海科学技术出版社, 上海.] | |
| [36] | Sun RY, Wang DH, Niu CJ, Liu DZ, Zhang L (2019) Principles of Animal Ecology, 4rd edn. Beijing Normal University Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [孙儒泳, 王德华, 牛翠娟, 刘定震, 张立 (2019) 动物生态学原理(第4版). 北京师范大学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [37] | Tian Y, Wu JG, Kou XJ, Li ZW, Wang TM, Mou P, Ge JP (2009) Spatiotemporal pattern and major causes of the Amur tiger population dynamics. Biodiversity Science, 17, 11-225. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[田瑜, 邬建国, 寇晓军, 李钟汶, 王天明, 牟溥, 葛剑平 (2009) 东北虎种群的时空动态及其原因分析. 生物多样性, 17, 211-225.]
DOI |
|
| [38] | Turchin P (2003) Complex Population Dynamics:A Theoretical Empirical Synthesis. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [39] | Unger SD, Sutton TM, Williams RN (2013) Projected population persistence of eastern hellbenders (Cryptobranchus alleganiensis alleganiensis) using a stage-structured life-history model and population viability analysis. Journal for Nature Conservation, 21, 423-432. |
| [40] | Wang C, Liu Y, Xie YX, Zhou SH, Chen JF (2023) Spatial and temporal variation of habitat quality in Zhangjiajie Giant Salamander National Nature Reserve and Zhangjiajie City. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 39, 1114-1122. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王丞, 刘懿, 解宜兴, 周韶辉, 陈家法 (2023) 湖南张家界大鲵国家级自然保护区及张家界市生境质量时空变化研究. 生态与农村环境学报, 39, 1114-1122.] | |
| [41] | Wang HQ, Tong YW, Zhang YS, Yu XP (2024) Sustainability and conservation strategies of reintroduced crested ibis population in Tongchuan, Shaanxi based on population viability analysis. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 45(1), 75-83. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王华强, 仝艺玮, 张雅帅, 于晓平 (2024) 基于种群生存力分析的陕西铜川朱鹮再引入种群的可持续性及保护对策. 野生动物学报, 45(1), 75-83.] | |
| [42] | Wang J (2015) Current status of Japanese giant salamander and the enlightenment on the conservation of Chinese giant salamander. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 21, 683-688. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王杰 (2015) 日本大鲵的现状及对中国大鲵保护的启示. 应用与环境生物学报, 21, 683-688.] | |
| [43] | Wang S, Zhao EM (1998) Red Data Book of Endangered Animals of China:Amphibia and Reptilia. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [汪松, 赵尔宓 (1998) 中国濒危动物红皮书: 两栖类和爬行类. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [44] | Wang XM, Zhang KJ, Wang ZH, Ding YZ, Wu W, Huang S (2004) The decline of the Chinese giant salamander Andrias davidianus and implications for its conservation. Oryx, 38, 197-202. |
| [45] | Wheeler BA, Prosen E, Mathis A, Wilkinson RF (2003) Population declines of a long-lived salamander: A 20 ± year study of hellbenders, Cryptobranchus alleganiensis. Biological Conservation, 109, 151-156. |
| [46] | Wu JG (1992) Mathematical modelling and nature conservation. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 3, 286-288. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [邬建国 (1992) 数学模型与自然保护科学. 应用生态学报, 3, 286-288.] | |
| [47] | Yan F, Lü JC, Zhang BL, Yuan ZY, Zhao HP, Huang S, Wei G, Mi X, Zou DH, Xu W, Chen S, Wang J, Xie F, Wu MY, Xiao HB, Liang ZQ, Jin JQ, Wu SF, Xu CS, Tapley B, Turvey ST, Papenfuss TJ, Cunningham AA, Murphy RW, Zhang YP, Che J (2018) The Chinese giant salamander exemplifies the hidden extinction of cryptic species. Current Biology, 28, R590-R592. |
| [48] | Yang DD, Ma JZ, He Z, Li PF, Wen HJ, Jiang ZG (2007) Population dynamics of the Père David’s deer (Elaphurus davidianus) in Shishou Milu National Nature Reserve, Hubei Province, China. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 53, 947-952. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨道德, 马建章, 何振, 李鹏飞, 温华军, 蒋志刚 (2007) 湖北石首麋鹿国家级自然保护区麋鹿种群动态. 动物学报, 53, 947-952.] | |
| [49] | Yang ZS, Gu XD, Nie YG, Huang F, Huang Y, Dai Q, Hua YB, Yang Y, Zhou X, Zhang HM, Yang XY, Wei FW (2018) Reintroduction of the giant panda into the wild: A good start suggests a bright future. Biological Conservation, 217, 181-186. |
| [50] | Ye CY, Fei L, Hu SQ (1993) Rare and Economically Important Amphibians of China. Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [叶昌媛, 费梁, 胡淑琴 (1993) 中国珍稀及经济两栖动物. 四川科学技术出版社, 成都.] | |
| [51] | Ye XL, Guo KJ, Li XR, Wu Q, Zhang MF, Li M, Zhao XM (2023) Climate change results in imbalance population growth and change in suitable habitat for red deer in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: A case study in the Leiwuqi National Nature Reserve. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 43, 149-156. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[叶秀林, 郭克疾, 李欣蕊, 吴庆, 张梦斐, 李明, 赵序茅 (2023) 气候变化导致青藏高原马鹿种群适应性分布退缩: 以类乌齐马鹿国家级自然保护区为例. 兽类学报, 43, 149-156.]
DOI |
|
| [52] | Yi MR, Lu P, Peng Y, Tang Y, Xu JH, Yin HP, Zhang LY, Weng XD, Di MX, Lei J, Lu CQ, Cao RJ, Dai NH, Zhan DY, Tong M, Lou ZM, Ding YG, Chai J, Che J (2024) Population status and habitat of critically endangered Jiangxi giant salamander (Andrias jiangxiensis). Biodiversity Science, 32, 24145. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [易木荣, 卢萍, 彭勇, 汤勇, 许久恒, 尹浩萍, 张路杨, 翁晓东, 底明晓, 雷隽, 卢宸祺, 曹如君, 戴年华, 占德洋, 童媚, 楼智明, 丁永刚, 柴静, 车静 (2024) 北潦河金家水支流江西大鲵野外种群现状及栖息地评估. 生物多样性, 32, 24145.] | |
| [53] | Yuan JL, Wu GF, Yang YJ, Liu JD, Lian QP (2013) Monitoring and evaluation on the effectiveness of releasing artificial-bred giant salamander (Andrias davidianus) into different wild habitat. Freshwater Fisheries, 43(7), 8-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [原居林, 吴根峰, 杨元杰, 刘金殿, 练青平 (2013) 不同生境下大鲵放流效果的监测与评价. 淡水渔业, 43(7), 8-12.] | |
| [54] | Zhang KJ, Wang XM, Wu W, Wang ZH, Huang S (2002) Advances in conservation biology of Chinese giant salamander. Biodiversity Science, 10, 291-297. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[章克家, 王小明, 吴巍, 王正寰, 黄松 (2002) 大鲵保护生物学及其研究进展. 生物多样性, 10, 291-297.]
DOI |
|
| [55] | Zhou YH, Xu LP (2012) Study on the model governing the growth of Milu population in Dafeng Nature Reserve region and the affection of density of the population to the growth of the population. Journal of Biomathematics, 27, 673-676. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周宇虹, 许丽萍 (2012) 大丰自然保护区麋鹿种群增长模型以及种群密度对种群增长影响的研究. 生物数学学报, 27, 673-676.] | |
| [56] | Zhu W, Zhao T, Zhao CL, Li C, Xie F, Liu JY, Jiang JP (2023) How will warming affect the growth and body size of the largest extant amphibian? More than the temperature-size rule. Science of the Total Environment, 859, 160105. |
| [57] | Zhu Y, Lu ZY, Li D, Wang Q, Su HJ (2019) Population dynamics of semi-free-ranging rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta) in Qianlingshan Park, Guizhou, China. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 39, 630-638. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱源, 卢志远, 李达, 王琦, 粟海军 (2019) 贵州黔灵山公园半野生猕猴的种群动态. 兽类学报, 39, 630-638.] |
| [1] | 周冯祥, 鲁夕霞, 雍李明, 曾千慧, 杨亮亮, 李平, 张语克, 王先艳. 鲸类动物声学监测研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(7): 24556-. |
| [2] | 易木荣, 卢萍, 彭勇, 汤勇, 许久恒, 尹浩萍, 张路杨, 翁晓东, 底明晓, 雷隽, 卢宸祺, 曹如君, 戴年华, 占德洋, 童媚, 楼智明, 丁永刚, 柴静, 车静. 北潦河金家水支流江西大鲵野外种群现状及栖息地评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24145-. |
| [3] | 王春晓, 张正旺, 夏少霞, 段后浪, 王稳, 贾亦飞, 张立勋, 冯刚, 杨亚桥, 李桐, 丁长青, 王春平, 原宝东, 雷进宇, 刘宇, 石建斌, 兰科其, 石青青, 肖晴, 于秀波. 黄河流域水鸟多样性季节和区域特征及保护策略[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 23490-. |
| [4] | 李仕裕, 张奕奇, 邹璞, 宁祖林, 廖景平. 广东省植物园植物多样性迁地保护现状及发展建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22647-. |
| [5] | 李钊丞, 张燕雪丹. 基于物种濒危状况评价与种群增长的一种新评估方法在水生野生动物保护司法中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22319-. |
| [6] | 初漠嫣, 梁书洁, 李沛芸, 贾丁, 阿卜杜赛麦提·买尔迪亚力, 李雪阳, 姜楠, 赵翔, 李发祥, 肖凌云, 吕植. 三江源国家级自然保护区内云塔村雪豹种群动态[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 22157-. |
| [7] | 姬云瑞, 韦雪蕾, 张国锋, 向明贵, 王永超, 龚仁琥, 胡杨, 李迪强, 刘芳. 湖北五峰后河国家级自然保护区鸟类多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21475-. |
| [8] | 祖奎玲, 王志恒. 山地物种海拔分布对气候变化响应的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21451-. |
| [9] | 刘艳艳, 刘畅, 魏晓新. 我国及周边地区松属白松亚组系统学研究进展和保护现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21344-. |
| [10] | 杨国平, 吴涛, 耿云芬, 李小双, 郝佳波, 袁春明. 生境片断化对濒危植物景东翅子树种群结构与动态的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(4): 449-455. |
| [11] | 杨永. 中国裸子植物红色名录评估(2021版)[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1599-1606. |
| [12] | 王文婷, 杨婷婷, 金磊, 蒋家民. 未来气候变化下两种红景天植物的脆弱性[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1620-1628. |
| [13] | 杨永, 檀超, 杨智. 从《国家重点保护野生植物名录》看我国裸子植物保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1591-1598. |
| [14] | 刘学琴, 贺达汉, 王新谱. 宁夏六盘山国家级自然保护区眼蝶群落多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(8): 973-982. |
| [15] | 王群, 郭志祥, 李进斌, 王凯博, 吴文伟, 浦恩堂, 马方舟, 何成兴. 云南哀牢山、无量山国家级自然保护区蝴蝶种群动态及多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(8): 921-930. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()