



生物多样性 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (7): 24040. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024040 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024040
孙怡欣( ), 侯春雨, 周磊, 魏雪(
), 侯春雨, 周磊, 魏雪( ), 马金豪(
), 马金豪( ), 薛娟, 李小涵(
), 薛娟, 李小涵( ), 吴鹏飞*(
), 吴鹏飞*( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-29
接受日期:2024-05-20
出版日期:2024-07-20
发布日期:2024-05-30
通讯作者:
*E-mail: wupf@swun.edu.cn
基金资助:
Yixin Sun( ), Chunyu Hou, Lei Zhou, Xue Wei(
), Chunyu Hou, Lei Zhou, Xue Wei( ), Jinhao Ma(
), Jinhao Ma( ), Juan Xue, Xiaohan Li(
), Juan Xue, Xiaohan Li( ), Pengfei Wu*(
), Pengfei Wu*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-01-29
Accepted:2024-05-20
Online:2024-07-20
Published:2024-05-30
Contact:
*E-mail: wupf@swun.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
查明一年生及多年生豆科牧草对土壤线虫群落的影响, 可为青藏高原地区科学种植豆科牧草提供技术支撑。作者于2020-2022年在川西北红原县盆栽种植一年生光叶紫花苕(Vicia villosa, VV)和多年生紫花苜蓿(Medicago sativa, MS), 以天然草地的植物作对照(control, CK)。每年9月下旬对土壤线虫组成、密度、多样性和营养类群, 植物的高度、盖度、生物量及土壤理化性质进行调查。结果表明: (1) 3种处理间的线虫群落组成结构存在差异, 并随年际变化而增大; (2)光叶紫花苕的土壤线虫群落密度显著高于紫花苜蓿和对照, 紫花苜蓿的线虫类群数和Shannon-Wiener指数显著高于光叶紫花苕和对照; 随着年际变化, 光叶紫花苕的线虫类群数及Shannon-Wiener指数、紫花苜蓿的线虫密度及Shannon-Wiener指数均显著下降; (3)光叶紫花苕的食真菌和植物寄生线虫密度显著高于紫花苜蓿和对照, 捕食杂食线虫相对密度显著低于紫花苜蓿和对照; 紫花苜蓿的植物寄生线虫相对密度显著低于光叶紫花苕和对照; 随年际变化, 光叶紫花苕的食细菌和植物寄生线虫相对密度分别显著下降和上升, 紫花苜蓿和对照的食细菌线虫和食真菌线虫密度及食细菌线虫相对密度显著下降, 捕食杂食线虫相对密度显著上升; (4)光叶紫花苕线虫群落的基础指数、结构指数和通道指数显著高于紫花苜蓿; (5)影响土壤线虫群落的主要环境因子主要为土壤pH、有效钾和植物群落高度、盖度和地上生物量。研究结果表明, 一年生和多年生豆科牧草分别有利于维持较高的线虫群落密度和多样性, 二者间作可能有利于提高线虫群落密度、多样性及生态功能。
孙怡欣, 侯春雨, 周磊, 魏雪, 马金豪, 薛娟, 李小涵, 吴鹏飞 (2024) 青藏高原盆栽一年生和多年生豆科牧草对土壤线虫群落的影响. 生物多样性, 32, 24040. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024040.
Yixin Sun, Chunyu Hou, Lei Zhou, Xue Wei, Jinhao Ma, Juan Xue, Xiaohan Li, Pengfei Wu (2024) Effects of annual and perennial potted legume forages on soil nematode communities in the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Biodiversity Science, 32, 24040. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024040.
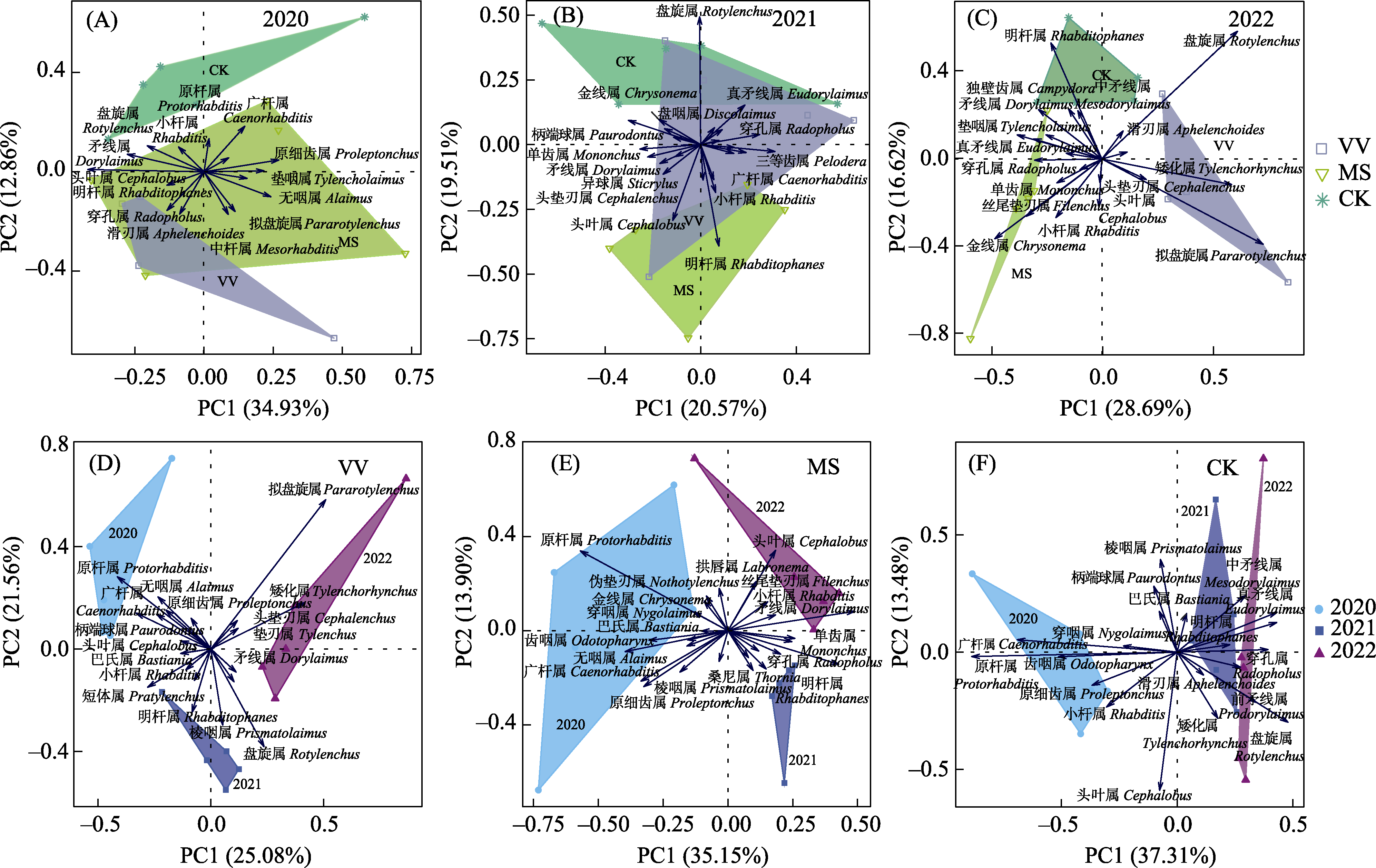
图1 不同年份(A, B, C)和不同处理(D, E, F)土壤线虫群落组成主成分分析。VV: 光叶紫花苕; MS: 紫花苜蓿; CK: 对照。
Fig. 1 Principal component analysis of soil nematode community composition in different cultivating years (A, B, C) and different treatments (D, E, F). VV, Vicia villosa; MS, Medicago sativa; CK, Control.
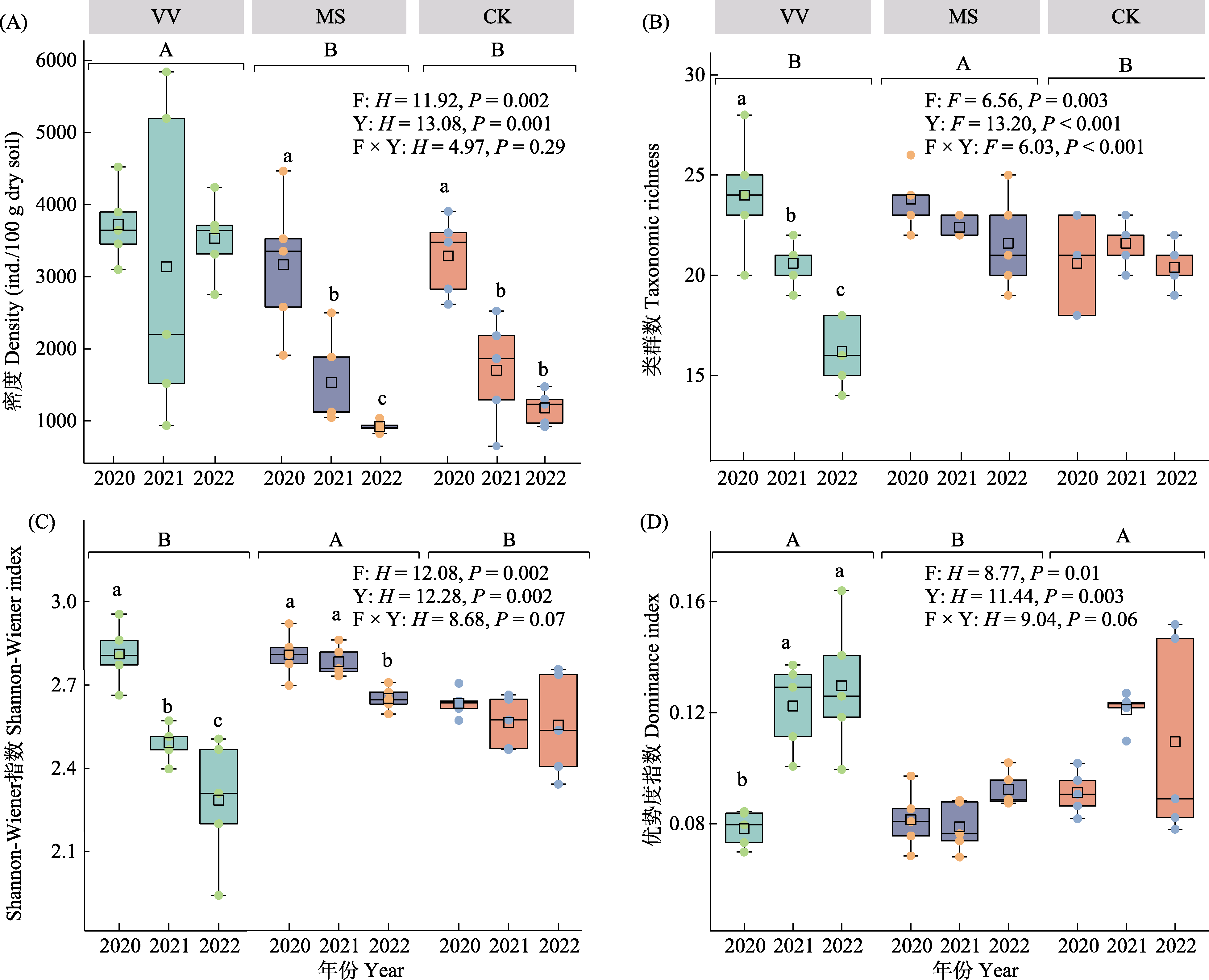
图2 不同年份和不同处理间土壤线虫群落密度及多样性。VV: 光叶紫花苕; MS: 紫花苜蓿; CK: 对照。F表示牧草间效应, Y表示年间效应, F × Y表示牧草与年间的交互效应。F为参数检验, H为非参数检验。不同大写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P < 0.05), 不同小写字母表示同种处理不同年份间的差异显著(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 2 Density and diversity of soil nematode community in different cultivating years and different treatments. VV, Vicia villosa; MS, Medicago sativa; CK, Control. F represents the effects of forages, Y represents the effects of cultivating years, and F × Y represents the interactional effects of forages and cultivating years. F represents the parameter test, H represents the nonparametric test. Different capital letters represent the significant difference between treatments (P < 0.05), and different lowercase letters represent the significant difference between different cultivating years (P < 0.05) of the same treatment.
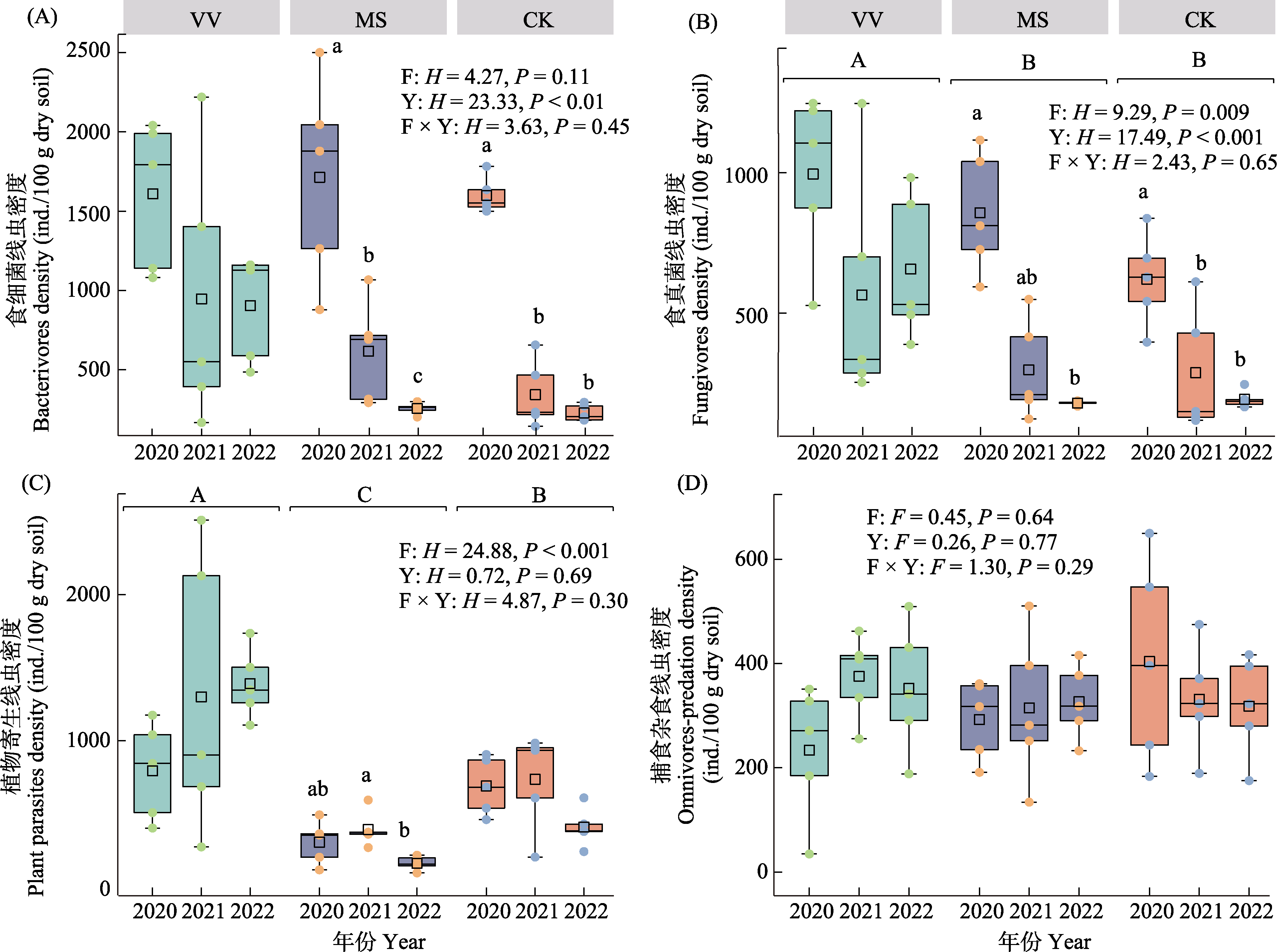
图3 不同年份和不同处理间土壤线虫群落不同营养类群的密度。VV: 光叶紫花苕; MS: 紫花苜蓿; CK: 对照。F表示牧草间效应, Y表示年间效应, F × Y表示牧草与年间的交互效应。F为参数检验, H为非参数检验。不同大写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P < 0.05), 不同小写字母表示同种处理不同年份间的差异显著(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 3 Density of different trophic groups of soil nematode communities in different cultivating years and different treatments. VV, Vicia villosa; MS, Medicago sativa; CK, Control. F represents the effects of forages, Y represents the effects of cultivating years, and F × Y represents the interactional effects of forages and cultivating years. F represents the parameter test, H represents the nonparametric test; Different capital letters represent the significant difference between treatments (P < 0.05), and different lowercase letters represent the significant difference between the different cultivating years (P < 0.05) of the same treatment.
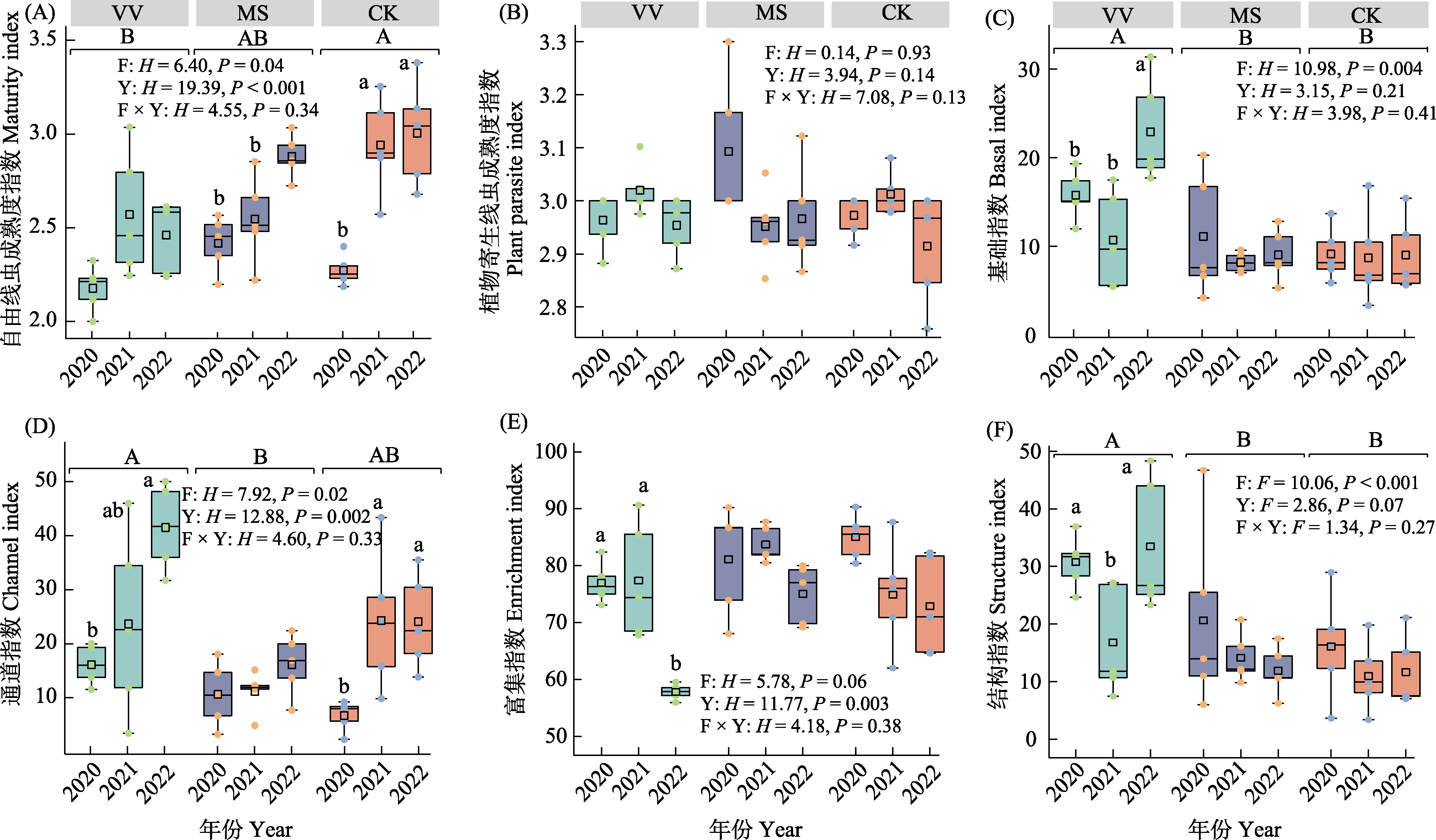
图4 土壤线虫群落生态指数。VV: 光叶紫花苕; MS: 紫花苜蓿; CK: 对照。F表示牧草间效应, Y表示年间效应, F × Y表示牧草与年间的交互效应。F为参数检验, H为非参数检验。不同大写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P < 0.05), 不同小写字母表示同种处理不同年份间的差异显著(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 4 Ecological indices of soil nematode communities. VV, Vicia villosa; MS, Medicago sativa; CK, Control. F represents the effects of forages, Y represents the effects of cultivating years, and F × Y represents the interactional effects of forages and cultivating years. F represents the parameter test, H represents the nonparametric test. Different capital letters represent the significant difference between treatments (P < 0.05), and different lowercase letters represent the significant difference between different cultivating years (P < 0.05) of the same treatment.
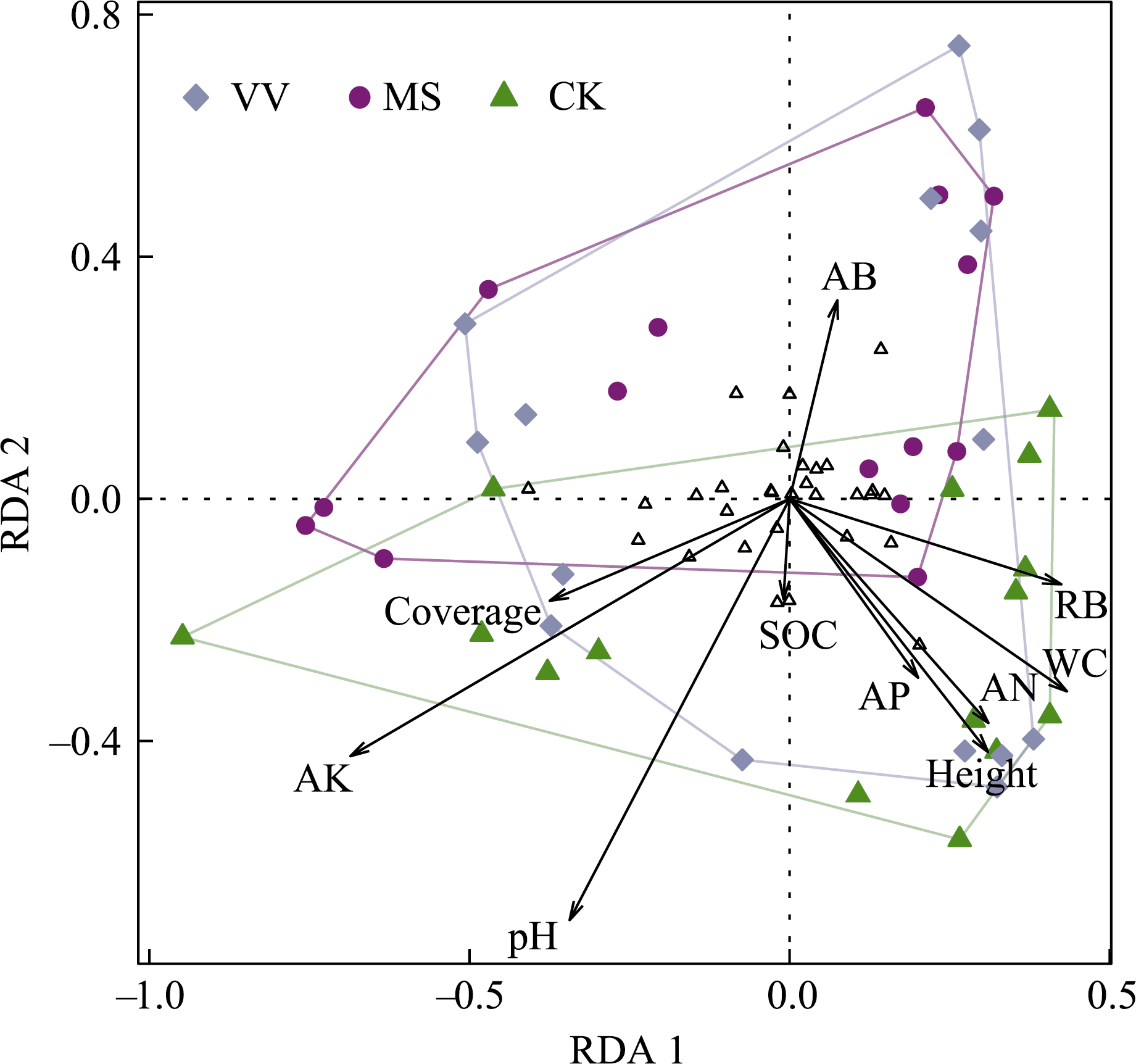
图5 土壤线虫群落与环境因子的冗余分析。VV: 光叶紫花苕; MS: 紫花苜蓿; CK: 对照。AB: 地上生物量; Coverage: 植物群落盖度; RB: 根系生物量; Height: 植物群落高度; SOC: 土壤有机碳; AP: 有效磷; AN: 有效氮; AK: 有效钾; WC: 土壤含水量。
Fig. 5 Redundancy analysis on the relationships between soil nematode community and environmental factors. VV, Vicia villosa; MS, Medicago sativa; CK, Control. AB, Aboveground biomass; Coverage, Plant community coverage; RB, Root biomass; Height, Plant community height; SOC, Soil organic carbon; AP, Available P; AN, Available N; AK, Available K; WC, Soil water content.
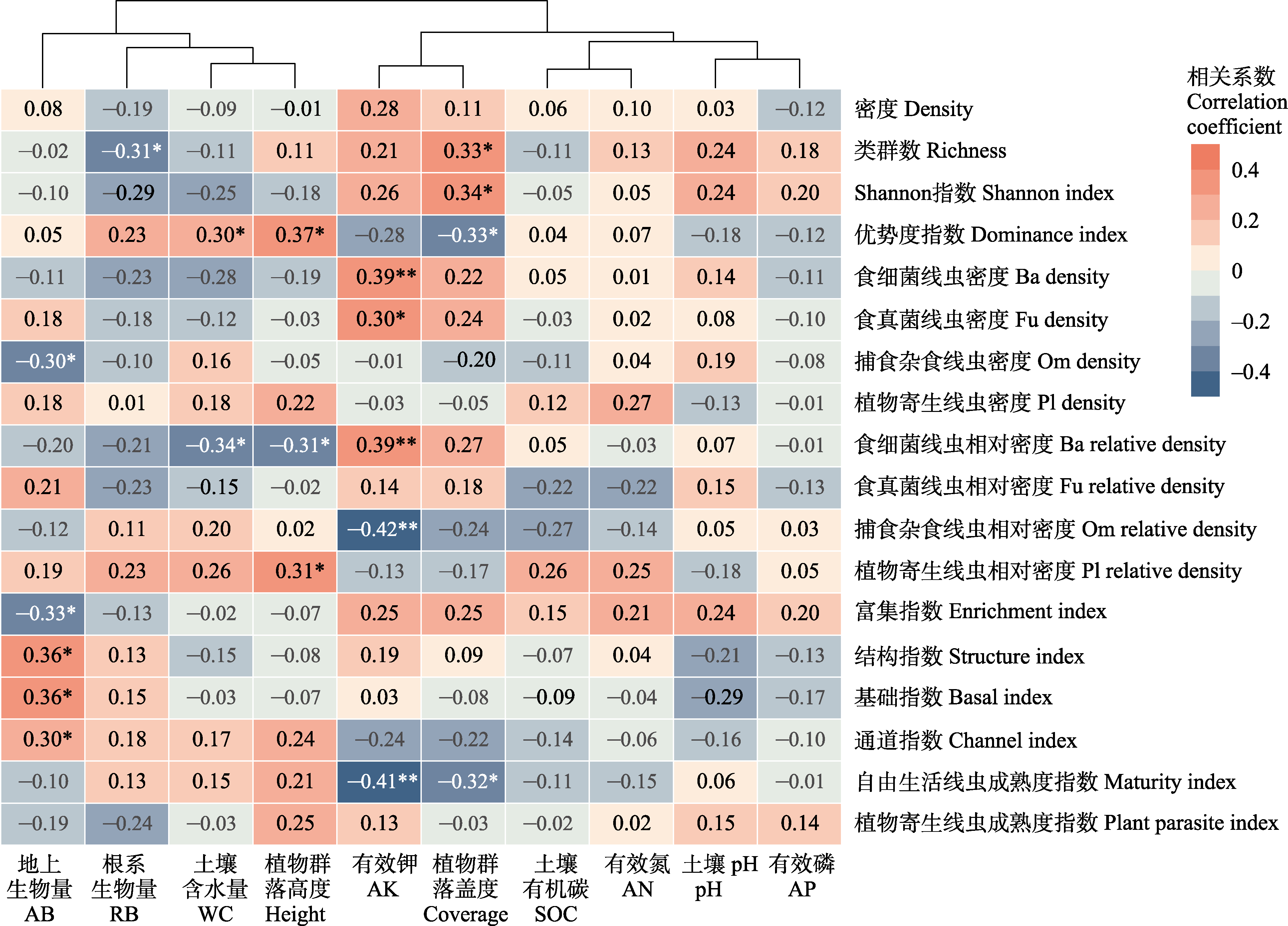
图6 土壤线虫群落各指数与环境因子相关分析热图。Ba: 食细菌线虫; Fu: 食真菌线虫; Om: 捕食杂食线虫; Pl: 植物寄生线虫。* P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01。
Fig. 6 Heat map of correlation analysis between indices of soil nematode community and environmental factors. AB, Aboveground biomass; RB, Root biomass; WC, Soil water content; Height, Plant community height; AK, Available K; Coverage, Plant community coverage; SOC, Soil organic carbon; AN, Available N; AP, Available P; Ba, Bacterivores; Fu, Fungivores; Om, Omnivores-predation; Pl, Plant parasites. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.
| [1] | Bardgett RD, van der Putten WH (2014) Belowground biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Nature, 515, 505-511. |
| [2] | Bardgett RD, Wardle DA (2011) Aboveground-Belowground Linkages: Biotic Interactions, Ecosystem Processes, and Global Change. Oxford University Press, Oxford. |
| [3] | Bell NL, Watson RN (2001) Population dynamics of Paratylenchus nanus in soil under pasture: 1. Aggregation and abiotic factors. Nematology, 3, 187-197. |
| [4] |
Bengtsson J, Viketoft M, Petchey O, Huss DK, Berg MP (2009) Long-term effects of plant diversity and composition on soil nematode communities in model grasslands. Ecology, 90, 90-99.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Blanchart E, Villenave C, Viallatoux A, Barthès B, Girardin C, Azontonde A, Feller C (2006) Long-term effect of a legume cover crop (Mucuna pruriens var. utilis) on the communities of soil macrofauna and nematofauna, under maize cultivation, in southern Benin. European Journal of Soil Biology, 42, S136-S144. |
| [6] |
Bongers T (1990) The maturity index: An ecological measure of environmental disturbance based on nematode species composition. Oecologia, 83, 14-19.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | Christensen S, Griffiths BS, Ekelund F, Rønn R (1992) Huge increase in bacterivores on freshly killed barley roots. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 86, 303-309. |
| [8] | Dai JH, Wu PF, Tang SS, Wang CT, Wang YY, Ren X, Wei X (2023) Effects of altered precipitation on soil nematode communities in an alpine meadow. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43, 9371-9383. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [代江慧, 吴鹏飞, 唐思思, 王长庭, 王玉英, 任晓, 魏雪 (2023) 降水变化对高寒草甸土壤线虫群落的影响. 生态学报, 43, 9371-9383.] | |
| [9] | De Deyn GB, Raaijmakers CE, Van Ruijven J, Berendse F, van der Putten WH (2004) Plant species identity and diversity effects on different trophic levels of nematodes in the soil food web. Oikos, 106, 576-586. |
| [10] | De KJ, Xu CT (2009) Wild legume grass—Medicago archiducis-Nicolai Sirj planting and domesticating in alpine region. Seed, 28(7), 73-75. (in Chinese) |
| [德科加, 徐成体 (2009) 高寒地区天然豆科牧草——青藏扁蓿豆的引种驯化. 种子, 28(7), 73-75.] | |
| [11] | De La Peña E, Echeverria SR, van der Putten WH, Freitas H, Moens M (2006) Mechanism of control of root-feeding nematodes by mycorrhizal fungi in the dune grass Ammophila arenaria. New Phytologist, 169, 829-840. |
| [12] | Dong SK, Pu XP, Hu ZZ (2013) Productive and Ecological Paradigm of Alpine Cultivated Grasslands in the Region of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [董世魁, 蒲小鹏, 胡自治 (2013) 青藏高原高寒人工草地生产-生态范式研究. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [13] | Ferris H, Bongers T (1999) Nematode community structure as a bioindicator in environmental monitoring. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 14, 224-228. |
| [14] | Ferris H, Bongers T, de Goede RGM (2001) A framework for soil food web diagnostics: Extension of the nematode faunal analysis concept. Applied Soil Ecology, 18, 13-29. |
| [15] | Freckman DW, Caswell EP (1985) The ecology of nematodes in agroecosystems. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 23, 275-296. |
| [16] | Freckman DW, Ettema CH (1993) Assessing nematode communities in agroecosystems of varying human intervention. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 45, 239-261. |
| [17] | Geng DZ, Huang JH, Huo N, Wang N, Yang PP, Zhao SW (2020) Characteristics of soil microbial and nematode communities under artificial Medicago sativa grasslands with different cultivation years in semi-arid region of Loess Plateau, Northwest China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31, 1365-1377. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[耿德洲, 黄菁华, 霍娜, 王楠, 杨盼盼, 赵世伟 (2020) 黄土高原半干旱区不同种植年限紫花苜蓿人工草地土壤微生物和线虫群落特征. 应用生态学报, 31, 1365-1377.]
DOI |
|
| [18] | Giannakis N (1990) Interactions Between Mycophagous Nematodes, Mycorrhizal and Other Soil Fungi. PhD dissertation, University of Leeds, Leeds, UK. |
| [19] | Griffiths BS, Ekelund F, Rønn R, Christensen S (1993) Protozoa and nematodes on decomposing barley roots. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 25, 1293-1295. |
| [20] | Hua JF, Jiang Q, Bai JF, Ding F, Lin XG, Yin YL (2014) Interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and fungivorous nematodes on the growth and arsenic uptake of tobacco in arsenic-contaminated soils. Applied Soil Ecology, 84, 176-184. |
| [21] |
Inserra RN, Griffin GD, Sisson DV (1983) Effects of temperature and root leachates on embryogenic development and hatching of Meloidogyne chitwoodi and M. hapla. Journal of Nematology, 15, 123-127.
PMID |
| [22] | Jiang YJ, Sun B, Li HX, Li MQ, Chen LJ, Zhou S (2015) Aggregate-related changes in network patterns of nematodes and ammonia oxidizers in an acidic soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 88, 101-109. |
| [23] |
Kooyers NJ (2015) The evolution of drought escape and avoidance in natural herbaceous populations. Plant Science, 234, 155-162.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | Kou XC, Su TQ, Ma NN, Li Q, Wang P, Wu ZF, Liang WJ, Cheng WX (2018) Soil micro-food web interactions and rhizosphere priming effect. Plant and Soil, 432, 129-142. |
| [25] | Lagerlöf J, Insunza V, Lundegårdh B, Rämert B (2011) Interaction between a fungal plant disease, fungivorous nematodes and compost suppressiveness. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section B: Soil & Plant Science, 61, 372-377. |
| [26] |
Li Q, Liang WJ, Jiang Y (2007) Present situation and prospect of soil nematode diversity in farmland ecosystems. Biodiversity Science, 15, 134-141. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[李琪, 梁文举, 姜勇 (2007) 农田土壤线虫多样性研究现状及展望. 生物多样性, 15, 134-141.]
DOI |
|
| [27] | Liu WH, Zhou QP, Jia ZF, Liang GL (2010) Effects of potassium fertilization on fodder yield and root system of Avena sativa cv. Qingyin No. 1. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 16, 419-424. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘文辉, 周青平, 贾志锋, 梁国玲 (2010) 施钾对青引1号燕麦草产量及根系的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 16, 419-424.] | |
| [28] | Liu XY, Long RJ, Shang ZH (2012) Interactive mechanism of service function of alpine rangeland ecosystems in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32, 7688-7697. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘兴元, 龙瑞军, 尚占环 (2012) 青藏高原高寒草地生态系统服务功能的互作机制. 生态学报, 32, 7688-7697.] | |
| [29] | Liu YF, Liu P, Wang WY, Mao XF, Dong SK, Yang C, Gao JC (2020) The research progress of soil nematodes as ecological indicator organisms. Ecological Science, 39, 207-214. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘艳方, 刘攀, 王文颖, 毛旭峰, 董世魁, 杨冲, 高俊程 (2020) 土壤线虫作为生态指示生物的研究进展. 生态科学, 39, 207-214.] | |
| [30] |
Lynch MJ, Mulvaney MJ, Hodges SC, Thompson TL, Thomason WE (2016) Decomposition, nitrogen and carbon mineralization from food and cover crop residues in the central plateau of Haiti. SpringerPlus, 5, 973.
DOI PMID |
| [31] | Ma JH, Luan JW, Wang H, Ye XD, Wang Y, Ming AG, Liu SR (2023) Differential impacts of tree root and litter on soil nematode communities in three artificial stands in subtropical south China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43, 7367-7380. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马金豪, 栾军伟, 王晖, 叶晓丹, 王一, 明安刚, 刘世荣 (2023) 乔木根系和凋落物对南亚热带3种人工林中土壤线虫群落的差异化影响. 生态学报, 43, 7367-7380.] | |
| [32] | Mariotte P, Mehrabi Z, Bezemer TM, de Deyn GB, Kulmatiski A, Drigo B, Veen GF, van der Heijden MGA, Kardol P (2018) Plant-soil feedback: Bridging natural and agricultural sciences. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 33, 129-142. |
| [33] | Nanjing Agricultural College (1980) Soil Agro-chemistry Analysis. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [南京农学院 (1980) 土壤农化分析. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [34] | Ning ZY, Li YL, Zhao XY, Han D, Zhan J (2022) Comparison of leaf and fine root traits between annuals and perennials, implicating the mechanism of species changes in desertified grasslands. Frontiers in Plant Science, 12, 778547. |
| [35] | Qu SL, Wu YF, Liu ZK, Wang GL, Chen YJ, Rong YP (2022) Research progress for effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth and development of alfalfa. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 30, 2529-2534. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[瞿宋林, 吴一凡, 刘忠宽, 王国良, 陈妍静, 戎郁萍 (2022) 丛枝菌根真菌对紫花苜蓿生长发育特性的影响. 草地学报, 30, 2529-2534.]
DOI |
|
| [36] | Sprunger CD, Culman SW, Peralta AL, DuPont ST, Lennon JT, Snapp SS (2019) Perennial grain crop roots and nitrogen management shape soil food webs and soil carbon dynamics. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 137, 107573. |
| [37] | Taylor K, Samaddar S, Schmidt R, Lundy M, Scow K (2023) Soil carbon storage and compositional responses of soil microbial communities under perennial grain IWG vs. annual wheat. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 184, 10911. |
| [38] | Viketoft M, Palmborg C, Sohlenius B, Huss DK, Bengtsson J (2005) Plant species effects on soil nematode communities in experimental grasslands. Applied Soil Ecology, 30, 90-103. |
| [39] | Wang FC, Wei XH, Ma SJ (2021) The study on forage yield and stocking rate of alpine meadow based on normalized difference vegetation index data. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 43(7), 78-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王福成, 魏学红, 马素洁 (2021) 基于NDVI数据的高寒草甸产量及载畜状况研究——以2019年青海玉树州为例. 中国草地学报, 43(7), 78-85.] | |
| [40] |
Wang YT, Niu KC (2020) Effect of soil environment on functional diversity of soil nematodes in Tibetan alpine meadows. Biodiversity Science, 28, 707-717. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[王宇彤, 牛克昌 (2020) 青藏高原高寒草甸土壤环境对线虫功能多样性的影响. 生物多样性, 28, 707-717.]
DOI |
|
| [41] | Wardle DA (2002) Communities and Ecosystems:Linking the Aboveground and Belowground Components. Princeton University Press, New Jersey. |
| [42] |
Wardle DA, Bardgett RD, Klironomos J, Setälä H, van der Putten WH, Wall DH (2004) Ecological linkages between aboveground and belowground biota. Science, 304, 1629-1633.
DOI PMID |
| [43] | Wardle DA, Yeates GW, Williamson W, Bonner KI (2003) The response of a three trophic level soil food web to the identity and diversity of plant species and functional groups. Oikos, 102, 45-56. |
| [44] | Wei X, Li Y, Wu PF (2022) Effects of artificial grasslands with different forage species on soil nematode communities on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42, 1071-1087. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [魏雪, 李雨, 吴鹏飞 (2022) 青藏高原不同牧草人工草地对土壤线虫群落的影响. 生态学报, 42, 1071-1087.] | |
| [45] | Xiao Y, Ji SAW, Zhao WX, Tian LH (2022) Soil nutrients, enzyme activities and microbial biomass characteristics of different artificial grasslands in the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 44(9), 90-99. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [肖颖, 吉使阿微, 赵文学, 田莉华 (2022) 青藏高原东缘不同人工草地土壤养分、酶活性及微生物生物量特征. 中国草地学报, 44(9), 90-99.] | |
| [46] | Xue HY, Hu F, Luo DQ (2013) Effects of alpine meadow plant communities on soil nematode functional structure in Northern Tibet, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 1482-1494. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [薛会英, 胡锋, 罗大庆 (2013) 藏北高寒草甸植物群落对土壤线虫群落功能结构的影响. 生态学报, 33, 1482-1494.] | |
| [47] | Yang QC, Kang JM, Zhang TJ, Liu FQ, Long RC, Sun Y (2016) Distribution, breeding and utilization of alfalfa germplasm resources. Chinese Science Bulletin, 61, 261-270. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨青川, 康俊梅, 张铁军, 刘凤歧, 龙瑞才, 孙彦 (2016) 苜蓿种质资源的分布、育种与利用. 科学通报, 61, 261-270.] | |
| [48] | Yang R, Wu PF, Wei X (2020) Effects of the transformation from natural alpine grassland to artificial oat grassland on the soil nematode communities. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40, 4903-4920. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨锐, 吴鹏飞, 魏雪 (2020) 天然高寒草地转变为燕麦人工草地对土壤线虫群落的影响. 生态学报, 40, 4903-4920.] | |
| [49] |
Yang Y, Zhang N, Jiang LL, Chen KL (2021) Effects of simulated precipitation on soil edaphic physicochemical factors and microbial community characteristics in Bird Island of Qinghai Lake on the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 29, 1043-1052. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[杨阳, 章妮, 蒋莉莉, 陈克龙 (2021) 青海湖高寒草地土壤理化性质及微生物群落特征对模拟降水的响应. 草地学报, 29, 1043-1052.]
DOI |
|
| [50] | Yeates GW, Bongers T (1999) Nematode diversity in agroecosystems. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 74, 113-135. |
| [51] |
Yeates GW, Bongers T, De Goede RG, Freckman DW, Georgieva SS (1993) Feeding habits in soil nematode families and genera—An outline for soil ecologists. Journal of Nematology, 25, 315-331.
PMID |
| [52] | Yin WY (2000) Pictorial Keys to Soil Animals of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [尹文英 (2000) 中国土壤动物检索图鉴. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [53] |
Yin XQ, Song B, Dong WH, Xin WD (2010) A review on the eco-geography of soil fauna in China. Acta Geographica Sinica, 65, 91-102. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [殷秀琴, 宋博, 董炜华, 辛未冬 (2010) 我国土壤动物生态地理研究进展. 地理学报, 65, 91-102.] | |
| [54] | Yu H, Liu Y, Deng Y, Lu GX, Yan HL, Wang YC (2023) Effects of the transformation from natural alpine grassland to mixed artificial grassland on the characteristics of soil microbial community. Environmental Science, 44, 2928-2935. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [于皓, 刘悦, 邓晔, 芦光新, 颜珲璘, 王英成 (2023) 天然高寒草地转变为混播人工草地对土壤微生物群落特征的影响. 环境科学, 44, 2928-2935.] | |
| [55] | Zhang CZ, Xue JR, Li N, Xue WF, Chen XY, Hu F, Liu MQ (2022) Afterlife effect of cover crops on soil nematode food web: Implications from the plant ecological strategy. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 58, 937-947. |
| [56] | Zhang XK, Liang WJ, Li Q (2013) Forest Soil Nematodes in Changbai Mountain: Morphology and Distribution. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张晓珂, 梁文举, 李琪 (2013) 长白山森林土壤线虫: 形态分类与分布格局. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [57] | Zhao CC, Li Y, Zhang CL, Miao Y, Liu MZ, Zhuang WL, Shao YH, Zhang WX, Fu SL (2021) Considerable impacts of litter inputs on soil nematode community composition in a young Acacia crassicapa plantation. Soil Ecology Letters, 3, 145-155. |
| [58] | Zhao J, Wang FM, Li J, Zou B, Wang XL, Li ZA, Fu SL (2014) Effects of experimental nitrogen and/or phosphorus additions on soil nematode communities in a secondary tropical forest. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 75, 1-10. |
| [59] |
Zhou TQ, Kong WD, Chen H (2023) Research progress of grassland soil microorganisms in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 42, 983-990. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [周天祺, 孔维栋, 陈昊 (2023) 青藏高原草地土壤微生物研究进展. 生态学杂志, 42, 983-990.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [3] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [4] | 周昊, 王茗毅, 张楚格, 肖治术, 欧阳芳. 昆虫旅馆在独栖蜂多样性保护中的现状与挑战[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24472-. |
| [5] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [6] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [7] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [8] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [9] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [10] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [11] | 徐欢, 辛凤飞, 施宏亮, 袁琳, 薄顺奇, 赵欣怡, 邓帅涛, 潘婷婷, 余婧, 孙赛赛, 薛程. 生态修复技术集成应用对长江口北支生境与鸟类多样性提升效果评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24478-. |
| [12] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [13] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [14] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [15] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()