



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (7): 23092. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023092 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023092
杨胜娴1,2,3, 杨清1,2,3, 李晓东1,2,3, 巢欣1,2,3, 刘惠秋1,2,3, 魏蓝若雪1,2,3, 巴桑1,2,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-03-30
接受日期:2023-06-14
出版日期:2023-07-20
发布日期:2023-07-31
通讯作者:
*E-mail: 作者简介:*E-mail: basang2003@utibet.edu.cn基金资助:
Shengxian Yang1,2,3, Qing Yang1,2,3, Xiaodong Li1,2,3, Xin Chao1,2,3, Huiqiu Liu1,2,3, Lanruoxue Wei1,2,3, Sang Ba1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2023-03-30
Accepted:2023-06-14
Online:2023-07-20
Published:2023-07-31
Contact:
*E-mail: 摘要:
浮游植物在河流生态系统的生物地球化学循环中起着重要作用, 然而, 雅鲁藏布江作为我国典型的高寒河流, 关于调控其浮游植物群落结构的机制尚不清楚。为探究雅鲁藏布江中上游浮游植物群落分布格局及其构建机制, 我们于2019年8月(夏季)、11月(秋季)和2020年5月(春季)对该水域进行了浮游植物样品采集、鉴定及水体理化因子测定。通过固定染色法鉴定浮游植物物种、统计物种丰度。结果表明: 雅鲁藏布江中上游共鉴定浮游植物452种, 隶属8门11纲24目44科121属。浮游植物群落的构建由环境异质性、扩散限制和物种互作关系共同影响。研究区域浮游植物群落在时空上存在显著的地理距离衰减趋势和环境距离衰减趋势; 物种互作关系以协作关系为主; 地理因素中的海拔(ALT)与水环境因子中的酸碱度(pH)、总溶解性固体(TDS)、盐度(Salt)、溶解氧(DO)、浊度(TUR)和水流速度(V)是驱动雅鲁藏布江中上游浮游植物群落构建的重要影响因子, 可通过驱动浮游植物自身的代谢速率及其生态适应性影响群落的地理分布和时空分布格局, 间接介导浮游植物群落的构建过程。距离衰减和中性模型结果表明: 确定性(环境选择)主导了雅鲁藏布江中上游的浮游植物群落构建。
杨胜娴, 杨清, 李晓东, 巢欣, 刘惠秋, 魏蓝若雪, 巴桑 (2023) 确定性过程主导高原典型河流浮游植物地理分布格局和群落构建. 生物多样性, 31, 23092. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023092.
Shengxian Yang, Qing Yang, Xiaodong Li, Xin Chao, Huiqiu Liu, Lanruoxue Wei, Sang Ba (2023) Deterministic processes dominate the geographic distribution pattern and community assembly of phytoplankton in typical plateau rivers. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23092. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023092.
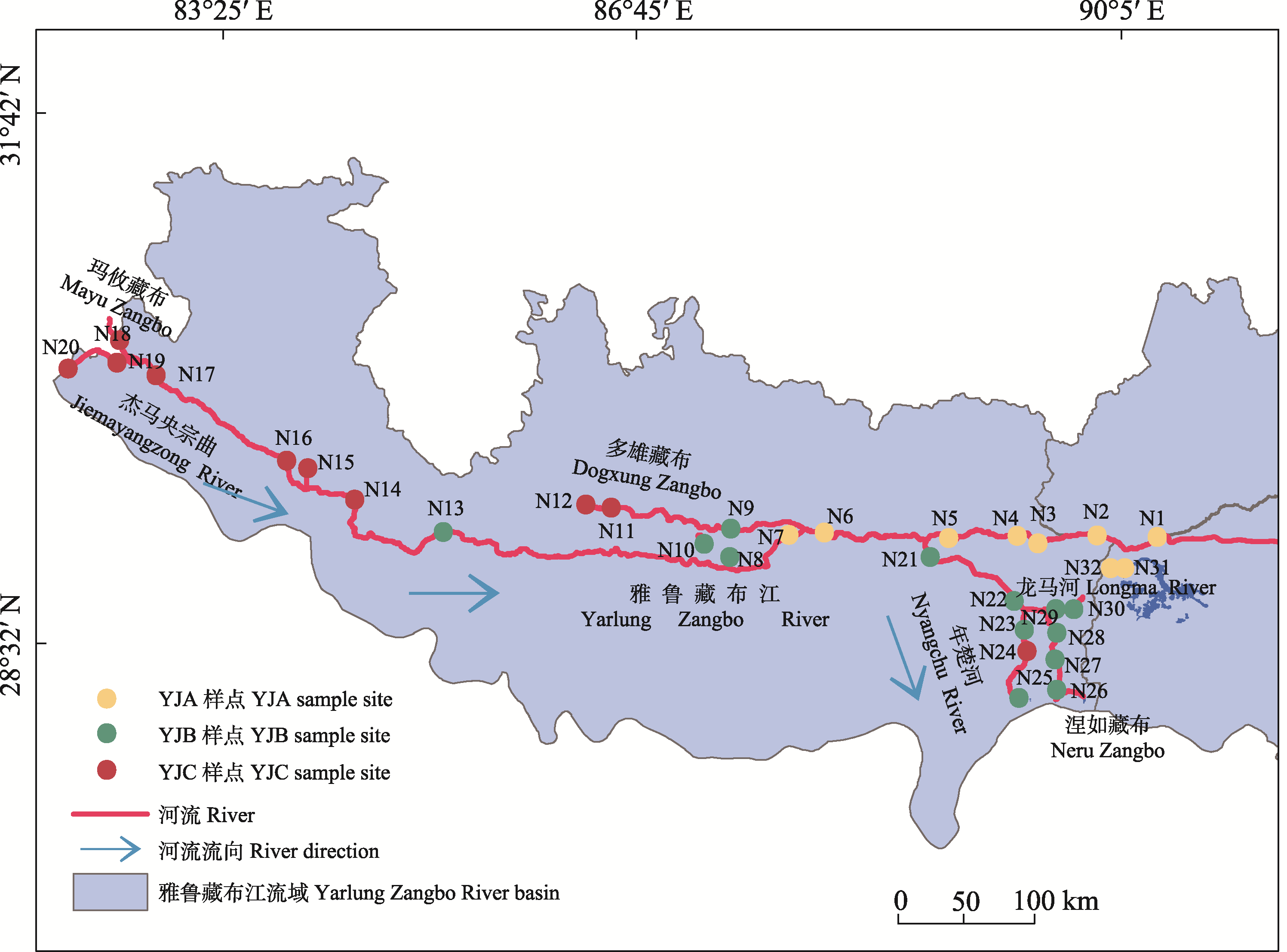
图1 雅鲁藏布江中上游样点分布示意图。N1-N32为样点名称。YJA、YJB、YJC指3个海拔梯度, 其海拔分别为3,497-3,945 m、4,008-4,508 m和4,546-4,846 m。
Fig. 1 Distribution of sample sites in the middle and upper reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River. The sample names are called N1-N32. YJA, YJB, YJC are three altitude gradients with 3,497-3,945 m, 4,008-4,508 m and 4,546-4,846 m, respectively.
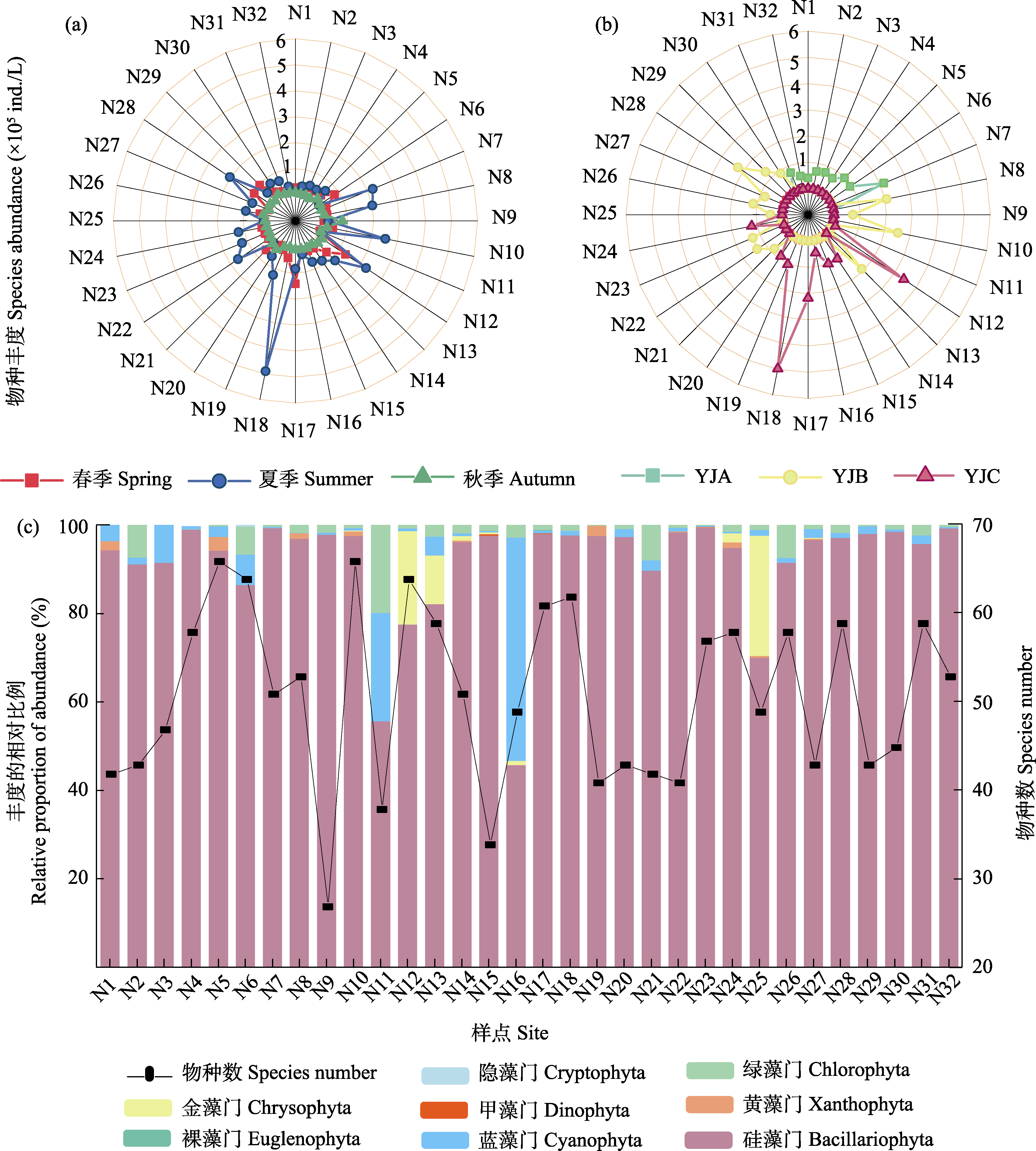
图2 雅鲁藏布江中上游浮游植物群落结构特征。(a)各季节浮游植物群落丰度变化; (b)各海拔浮游植物群落丰度变化; (c) 3个季节不同浮游植物类群的相对丰度和物种数的空间分布。YJA、YJB、YJC见图1。
Fig. 2 Phytoplankton community structure in the upper and middle reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River. (a) Variation of phytoplankton abundance in different seasons; (b) Variation of phytoplankton abundance at different elevations; (c) Spatial distribution of the relative proportion of abundance and species number of different groups of phytoplankton communities in three seasons. YJA, YJB, YJC see Fig. 1.
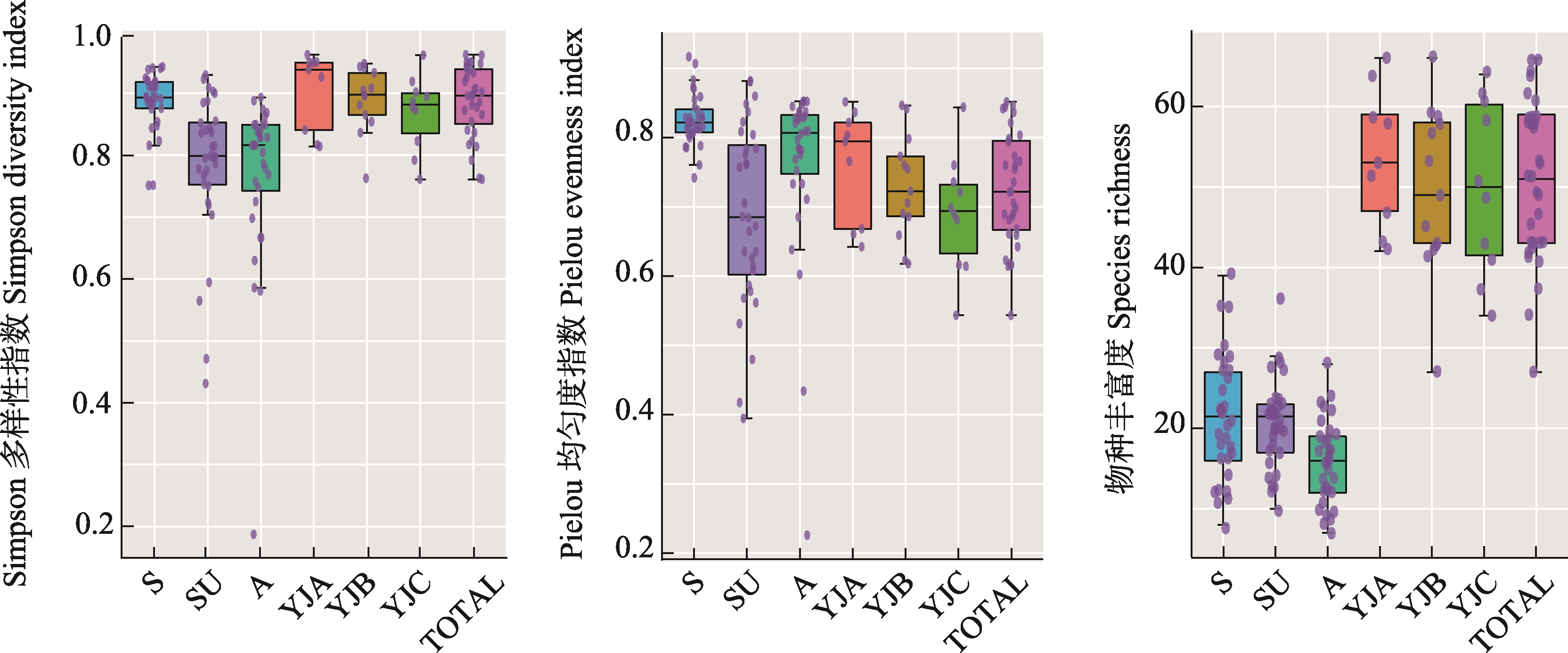
图3 雅鲁藏布江中上游浮游植物群落的α多样性。S: 春季; SU: 夏季; A: 秋季; TOTAL: 总流域。YJA、YJB、YJC见图1。
Fig. 3 Phytoplankton community α-diversity in the upper and middle reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River. S, Spring; SU, Summer; A, Autumn; TOTAL, The total watershed. YJA, YJB, YJC see Fig. 1.
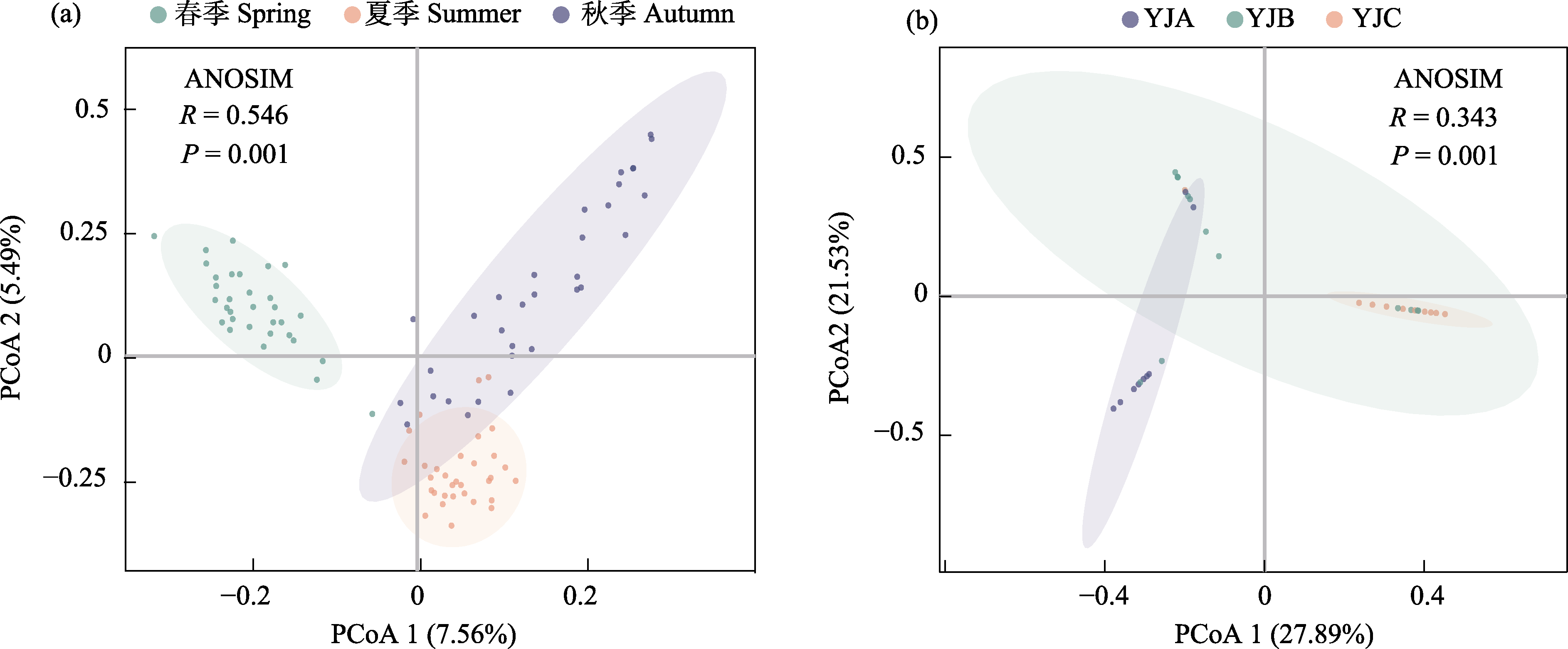
图4 基于雅鲁藏布江中上游浮游植物群落Bray-Curtis相似性的主坐标分析(PCoA)。(a)不同季节浮游植物群落的主坐标分析(PCoA); (b)不同海拔浮游植物群落主坐标分析(PCoA)。YJA、YJB、YJC见图1。
Fig. 4 Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) of phytoplankton community based on Bray-Curtis similarity in the upper and middle reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River. (a) PCoA of the phytoplankton community in different seasons; (b) PCoA of the phytoplankton community at different altitudes. YJA, YJB, YJC see Fig. 1.
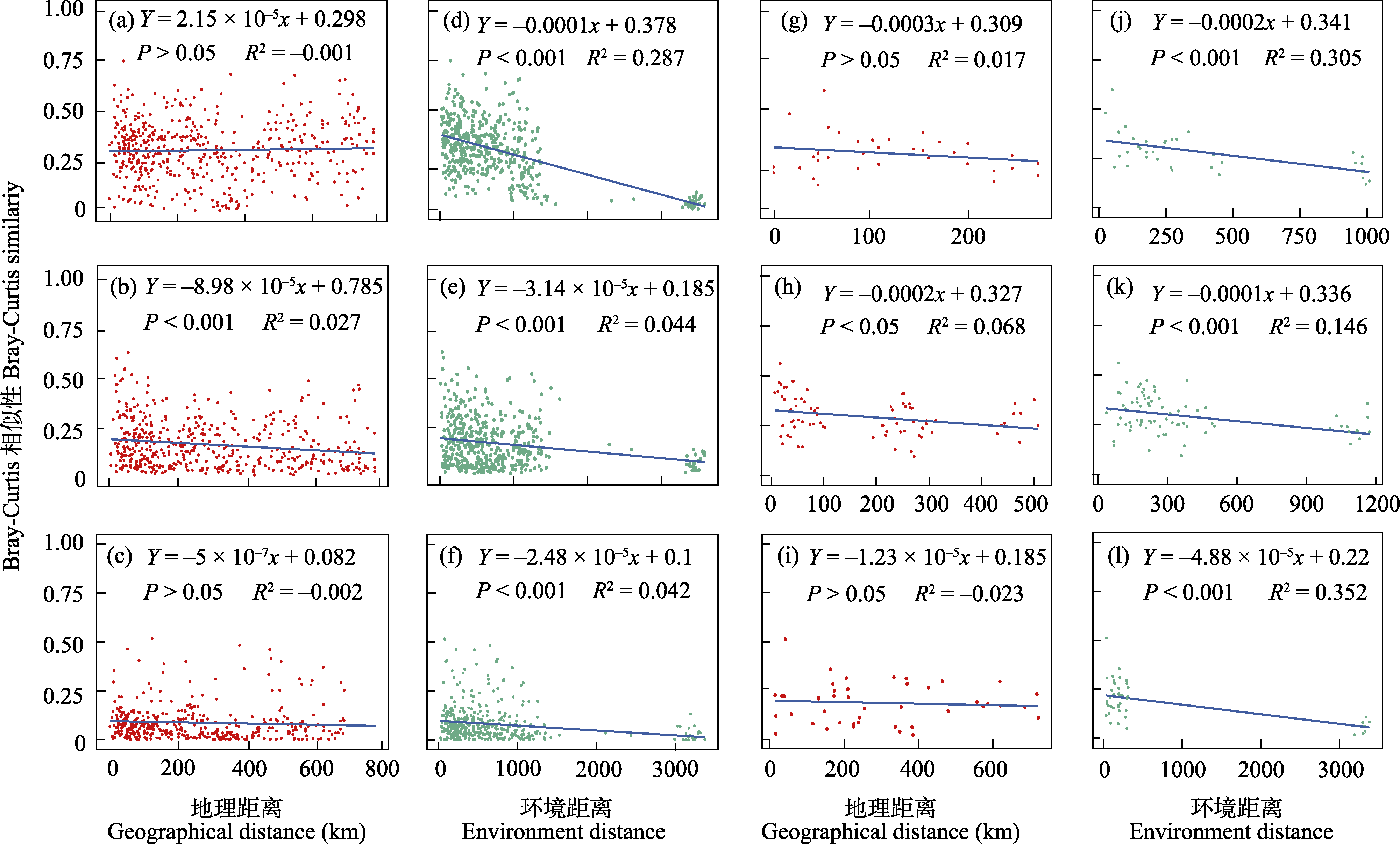
图5 雅鲁藏布江中上游浮游植物群落距离衰减分析。a-c、g-i分别为春季、夏季、秋季、YJA、YJB和YJC浮游植物群落地理距离衰减; d-f、j-l分别为春季、夏季、秋季、YJA、YJB和YJC浮游植物群落环境距离衰减。YJA、YJB、YJC见图1。
Fig. 5 Distance decay analysis of phytoplankton community in the upper and middle reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River. a-c, g-i, The geographic distance attenuation of phytoplankton in spring, summer, autumn, YJA, YJB, and YJC, respectively; d-f, j-l, The environmental distance decay change of phytoplankton community in spring, summer, autumn, YJA, YJB, and YJC, respectively. YJA, YJB, YJC see Fig. 1.
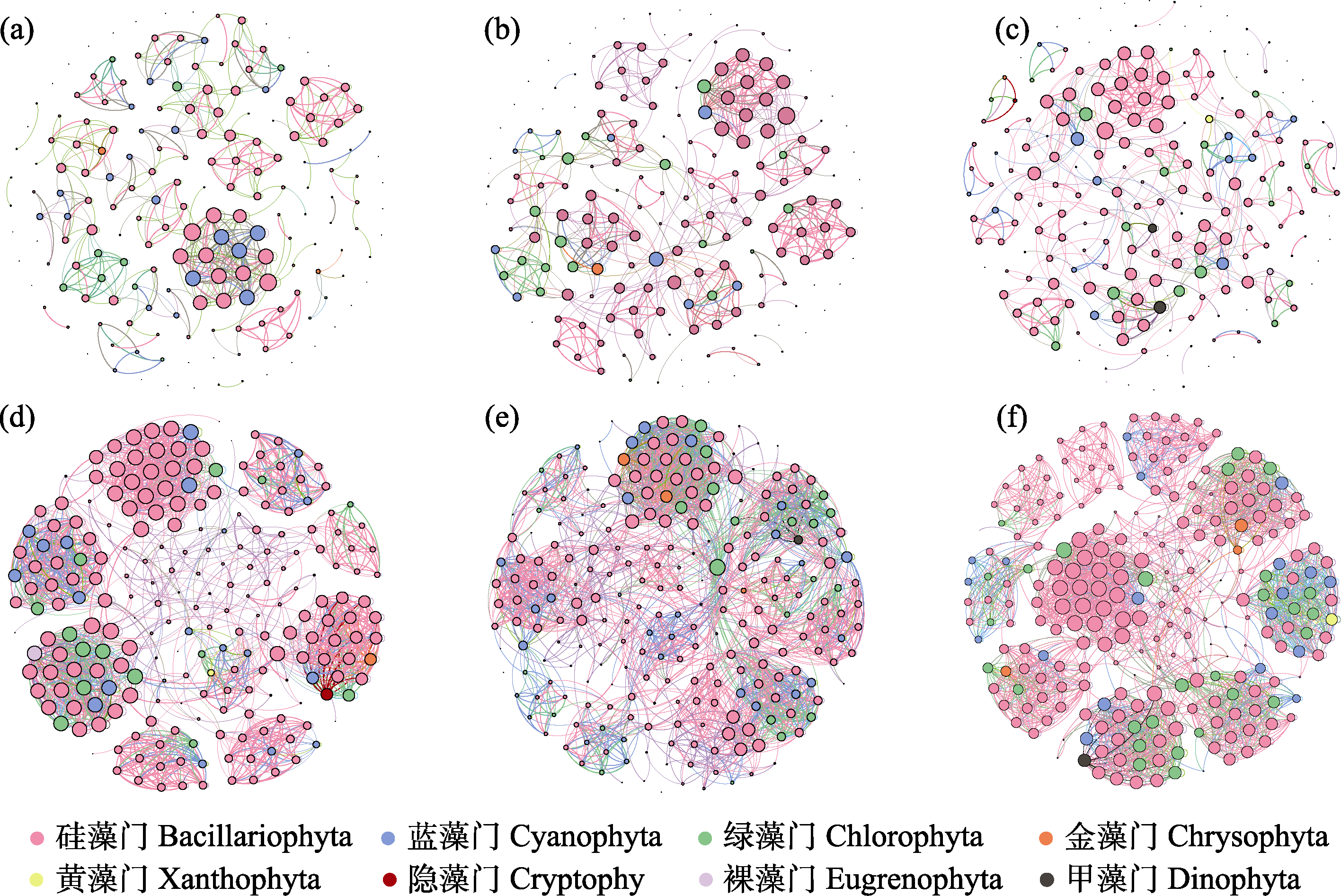
图6 雅鲁藏布江中上游浮游植物群落共现网络。a-c分别为春季、夏季、秋季浮游植物群落; d-f分别为YJA、YJB、YJC浮游植物群落。YJA、YJB、YJC见图1。
Fig. 6 Phytoplankton community co-occurrence network in the upper and middle reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River. a-c, Spring, summer, and autumn phytoplankton communities, respectively; d-f, YJA, YJB, YJC phytoplankton communities, respectively. YJA, YJB, YJC see Fig. 1.
| 网络拓扑指标 Network topological indicators | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | YJA | YJB | YJC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 节点数 Number of nodes | 188 | 181 | 204 | 224 | 246 | 246 |
| 边数 Edges | 642 | 686 | 687 | 2,050 | 2,365 | 2,558 |
| 连接部件 Connected component | 45 | 40 | 43 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| 网络直径 Network diameter | 15 | 18 | 12 | 9 | 8 | 11 |
| 平均度 Average degree | 6.830 | 7.580 | 6.735 | 18.304 | 19.228 | 20.797 |
| 模块化系数 Modularity coefficient | 0.820 | 0.829 | 0.806 | 0.850 | 0.765 | 0.853 |
| 图密度 Density of figure | 0.037 | 0.042 | 0.033 | 0.082 | 0.078 | 0.085 |
| 平均聚类系数 Mean clustering coefficient | 0.854 | 0.847 | 0.792 | 0.841 | 0.750 | 0.841 |
| 平均路径长度 Mean path length | 6.147 | 6.981 | 5.332 | 3.953 | 3.302 | 3.851 |
| 正相关比例 Positive correlation (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99.375 | 99.493 | 97.757 |
| 负相关比例 Negative correlation (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.625 | 0.507 | 2.243 |
表1 浮游植物群落共现网络的拓扑结构特征。YJA、YJB、YJC见图1。
Table 1 The topological characteristics of co-occurrence networks of phytoplankton communities. YJA, YJB, YJC see Fig. 1.
| 网络拓扑指标 Network topological indicators | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | YJA | YJB | YJC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 节点数 Number of nodes | 188 | 181 | 204 | 224 | 246 | 246 |
| 边数 Edges | 642 | 686 | 687 | 2,050 | 2,365 | 2,558 |
| 连接部件 Connected component | 45 | 40 | 43 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| 网络直径 Network diameter | 15 | 18 | 12 | 9 | 8 | 11 |
| 平均度 Average degree | 6.830 | 7.580 | 6.735 | 18.304 | 19.228 | 20.797 |
| 模块化系数 Modularity coefficient | 0.820 | 0.829 | 0.806 | 0.850 | 0.765 | 0.853 |
| 图密度 Density of figure | 0.037 | 0.042 | 0.033 | 0.082 | 0.078 | 0.085 |
| 平均聚类系数 Mean clustering coefficient | 0.854 | 0.847 | 0.792 | 0.841 | 0.750 | 0.841 |
| 平均路径长度 Mean path length | 6.147 | 6.981 | 5.332 | 3.953 | 3.302 | 3.851 |
| 正相关比例 Positive correlation (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99.375 | 99.493 | 97.757 |
| 负相关比例 Negative correlation (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.625 | 0.507 | 2.243 |
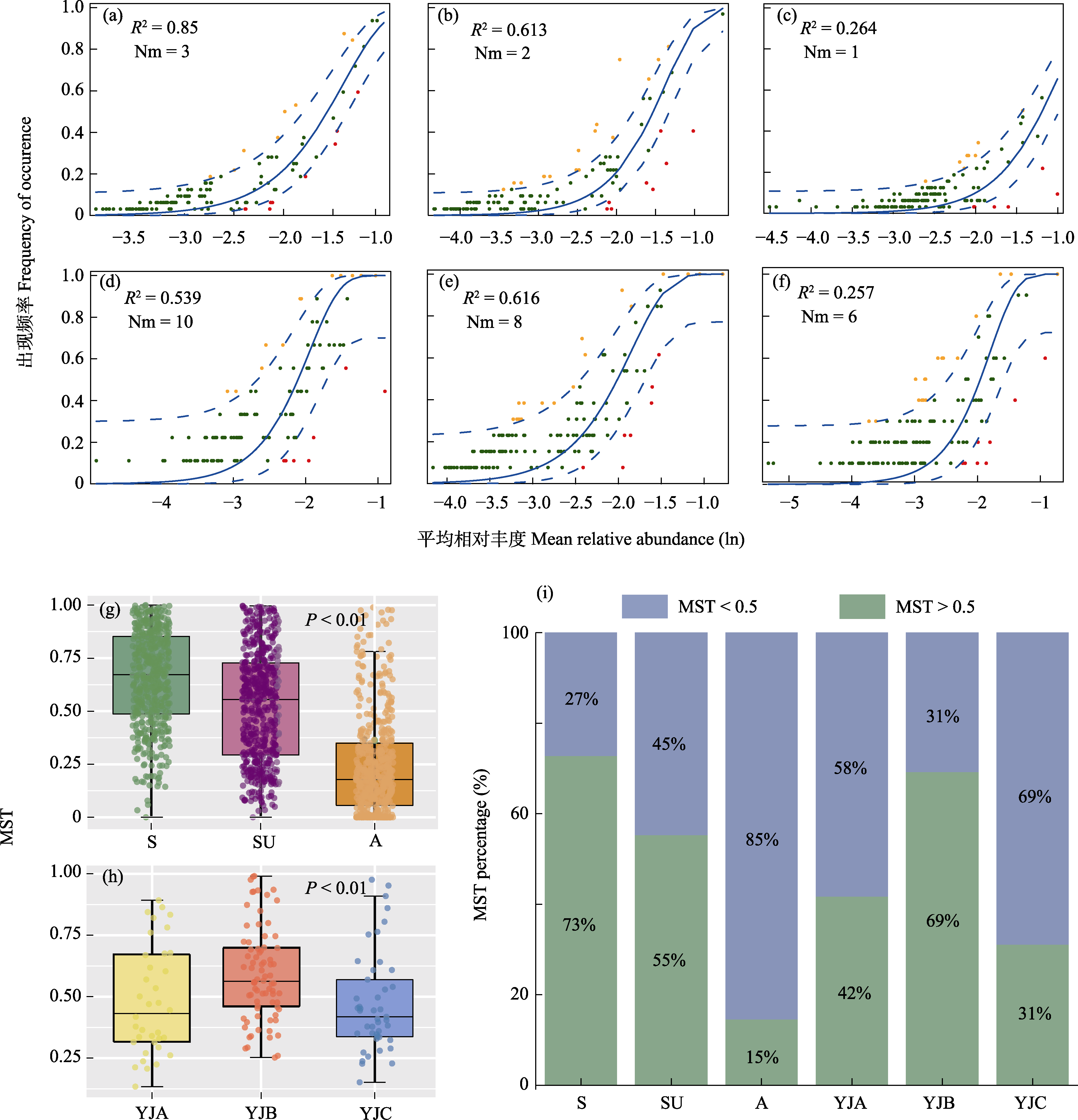
图7 雅鲁藏布江中上游浮游植物群落中性模型(a-f)和校正随机率(MST) (g-i)。频率高于模型预测值的物种显示为黄色; 频率较低的物种显示为红色; 预测范围内的物种显示为绿色; 蓝色虚线表示模型预测的95%置信区间。R2为中性群落模型的整体拟合优度, Nm是元群落规模(N)与迁移率(m)的乘积, 量化了对群落之间扩散的估计。a-c分别为春季、夏季、秋季浮游植物群落; d-f分别为YJA、YJB、YJC浮游植物群落; (g) 3个季节浮游植物群落MST; (h) 3个海拔梯度浮游植物群落MST; (i)校正随机率在不同季节和海拔梯度上的变化。S: 春季; SU: 夏季; A: 秋季。YJA、YJB、YJC见图1。
Fig. 7 Neutral model of phytoplankton community (a-f) and modified stochasticity ratio (MST) (g-j). Species whose frequency is higher than predicted by the model are shown in yellow; Less frequent species are shown in red; Species within the predicted range are shown in green; The blue dashed line represents the 95% confidence interval for the model's prediction. R2 is the overall goodness of fit of the neutral community model, and Nm is the product of meta-community size (N) and mobility (m), quantifying the estimate of diffusion between community assembly. a-c, Spring, summer, and autumn phytoplankton communities, respectively; d-f, YJA, YJB, YJC phytoplankton communities, respectively; (g) Three seasonal phytoplankton communities MST; (h) Three altitudinal gradient phytoplankton communities MST; (i) Modified stochasticity ratio in different seasons and altitude gradients. S, Spring; SU, Summer; A, Autumn. YJA, YJB, YJC see Fig. 1.
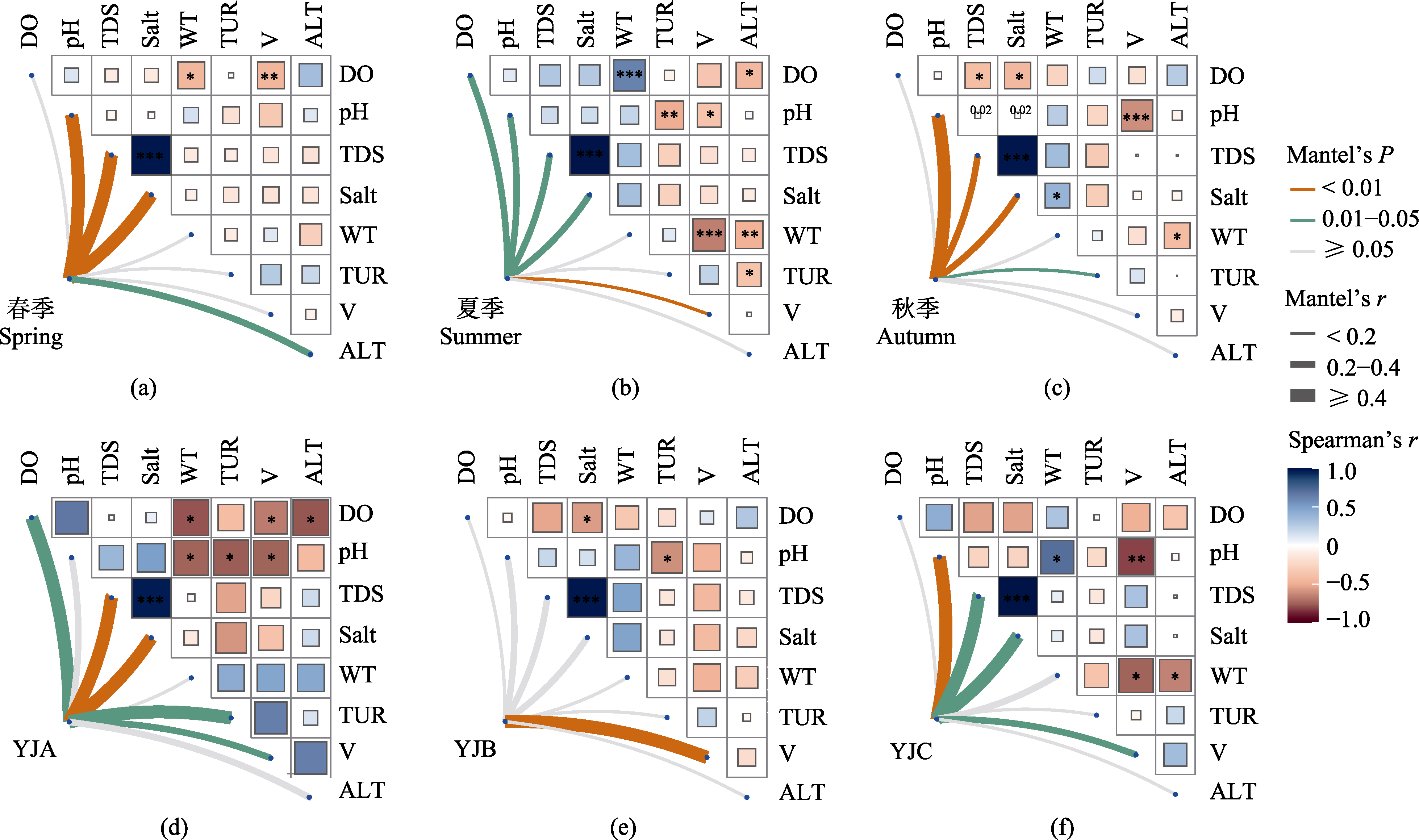
图8 雅鲁藏布江中上游浮游植物群落与环境因子相关性分析。TDS: 总溶解固体; WT: 水温; DO: 溶解氧; TUR: 浊度; V: 水流速度; ALT: 海拔; Salt: 盐度。YJA、YJB、YJC见图1。
Fig. 8 Correlation analysis between phytoplankton communities and environmental factors. TDS, Total dissolved solid, WT, Water temperature; DO, Dissolved oxygen; TUR: Turbidity; WS, Waterflow speed; ALT, Altitude; Salt, Salinity. YJA, YJB, YJC see Fig. 1.
| [1] | Bai HF, Wang YR, Song JX, Huang P, Xu WJ, Yin XW, Liu G, Li HJ (2021) Spatio-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of phytoplankton community structure in the Shaanxi Section of Weihe River, China. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 41, 3290-3301. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [白海锋, 王怡睿, 宋进喜, 黄鹏, 徐文瑾, 殷旭旺, 刘钢, 李红娟 (2021) 渭河陕西段浮游植物群落结构时空变化与影响因子分析. 环境科学学报, 41, 3290-3301.] | |
| [2] | Bu YQ, Zhu LY, Chen X, Dong HH, Sun Y, Wang C (2019) Community structure of zooplankton and its relationship with environmental factors in the Bohai and the North Huanghai Sea in summer and winter. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 49(2), 59-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [卜亚谦, 朱丽岩, 陈香, 董辉辉, 孙跃, 王超 (2019) 夏冬季渤海、北黄海浮游动物群落结构及其与环境因子的关系. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 49(2), 59-66.] | |
| [3] | Chen HS, Liu SP, Yang WQ, Liang GQ (2022) Structure and diversity of bacterial community in rhizosphere soil of four dominant species along the bank of the lower reaches of Yarlung Zangbo River. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42, 1527-1537. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈海生, 刘守平, 杨万勤, 梁国钱 (2022) 雅鲁藏布江下游沿岸湿地建群种植物根际土壤细菌群落结构和多样性特征. 生态学报, 42, 1527-1537.] | |
| [4] |
Chen K, Meng ZH, Li XM, Zhu TB, Hu FF, Liu L, Zhu YJ, Fan CL, Yang DG (2022) Phytoplankton community structure and its driving mechanism of construction process in autumn in Zhelin Reservoir, Lake Poyang Basin. Journal of Lake Sciences, 34, 433-444. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [陈康, 孟子豪, 李学梅, 朱挺兵, 胡飞飞, 刘璐, 朱永久, 范春林, 杨德国 (2022) 鄱阳湖流域柘林水库秋季浮游植物群落结构及其构建过程驱动机制. 湖泊科学, 34, 433-444.] | |
| [5] |
Chen ZJ, Tian W, Li YJ, Sun LN, Chen Y, Zhang H, Li YY, Han H (2021) Responses of rhizosphere bacterial communities, their functions and their network interactions to Cd stress under phytostabilization by Miscanthus spp. Environmental Pollution, 287, 117663.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Chi RW (1990) Atlas of Bacillariophy in Tibet. Tibet People's Publishing House, Lhasa. (in Chinese) |
| [迟若文 (1990) 西藏硅藻图集. 西藏人民出版社, 拉萨.] | |
| [7] |
Deng Y, Jiang YH, Yang YF, He ZL, Luo F, Zhou JZ (2012) Molecular ecological network analyses. BMC Bioinformatics, 13, 113.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Gao BB, Zheng CF, Xu JT, Zheng QS, Liu ZP, Zhai RT, Jiang HP (2012) Physiological responses of Enteromorpha linza and Enteromorpha prolifera to seawater salinity stress. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 23, 1913-1920. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [高兵兵, 郑春芳, 徐军田, 郑青松, 刘兆普, 翟瑞婷, 蒋和平 (2012) 缘管浒苔和浒苔对海水盐度胁迫的生理响应. 应用生态学报, 23, 1913-1920.] | |
| [9] | Guo X, Lin XQ, Zheng XY, Liu Q, Huang C, Pang MW, Chen XX, Huang LF (2022) Distribution patterns and assembly mechanisms of dominant and rare species of microbial flagellate communities in the subtropic-tropic marine areas in China. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 41, 356-374. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭馨, 林晓晴, 郑欣怡, 刘强, 黄成, 逄萌雯, 陈星星, 黄凌风 (2022) 中国亚热带-热带3个海区微型鞭毛虫群落优势种和稀有种的分布特征和建群机制. 应用海洋学学报, 41, 356-374.] | |
| [10] | Han X, Pan BZ, Zhao GN, Li DB, Sun H, Zhu PH, Lu Y (2021) Local and geographical factors jointly drive elevational patterns of phytoplankton in the source region of the Yangtze River, China. River Research and Applications, 37, 1145-1155. |
| [11] |
Hanson CA, Fuhrman JA, Horner-Devine MC, Martiny JBH (2012) Beyond biogeographic patterns: Processes shaping the microbial landscape. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 10, 497-506.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | He FZ, Dong XY, Sun MQ, Cai QH (2015) Altitudinal pattern of stream periphyton biomass in tributaries of the Lancang-Mekong River: An indicator of anthropogenic impact? Quaternary International, 380/381, 282-287. |
| [13] | He JZ, Wang JT (2015) Mechanisms of community organization and spatiotemporal patterns of soil microbial communities. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 6575-6583. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [贺纪正, 王军涛 (2015) 土壤微生物群落构建理论与时空演变特征. 生态学报, 35, 6575-6583.] | |
| [14] | Hou CW, Sun XY, Liu YL, Zhang C, Zhang WJ, Zhao JM, Dong ZJ (2020) Spatial niche of dominant zooplankton species in Yantai offshore waters. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40, 5822-5833. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [侯朝伟, 孙西艳, 刘永亮, 张晨, 张文静, 赵建民, 董志军 (2020) 烟台近海浮游动物优势种空间生态位研究. 生态学报, 40, 5822-5833.] | |
| [15] | Hu HJ, Wei YX (2016) Chinese Freshwater Algae-system Classification and Ecology. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [胡鸿钧, 魏印心 (2016) 中国淡水藻类系统分类及生态. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [16] | Hubbell SP (2001) The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [17] |
Hunt DE, Ward CS (2015) A network-based approach to disturbance transmission through microbial interactions. Frontiers in Microbiology, 6, 1182.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Jiang XM, Xie ZC, Chen YF (2013) Longitudinal patterns of macroinvertebrate communities in relation to environmental factors in a Tibetan-Plateau River system. Quaternary International, 304, 107-114.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Lei J, Liu CQ, Zhang M, Yang JS, Wu F, Ren MD, Wu QL, Shi XL (2021) The daily effect is more important than the diurnal effect when shaping photosynthetic picoeukaryotes (PPEs) communities in Lake Taihu at a small temporal scale. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 97, fiab090. |
| [20] |
Li C, Xu WL, Li QK, Wang JS (2021) Community structure and diversity distribution pattern of sandy plants in the middle and upper reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River. Journal of Resources and Ecology, 12, 11-21.
DOI |
| [21] | Li HD, Shen WS, Cai BF, Ji D, Zhang XY (2013) The coupling relationship between variations of NDVI and change of aeolian sandy land in the Yarlung Zangbo River basin of Tibet, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 7729-7738. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李海东, 沈渭寿, 蔡博峰, 纪迪, 张晓勇 (2013) 雅鲁藏布江流域NDVI变化与风沙化土地演变的耦合关系. 生态学报, 33, 7729-7738.] | |
| [22] |
Li XD, Yang Q, Liu HQ, Chao X, Yang SX, Ba S (2023) Response of river ecosystem health status to water environmental factors in the middle reaches of Yarlung Zangbo River. Environmental Science, doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202211063. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[李晓东, 杨清, 刘惠秋, 巢欣, 杨胜娴, 巴桑 (2023) 雅鲁藏布江中游河流生态系统健康状态对水环境因子的响应. 环境科学, doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202211063.]
DOI |
|
| [23] |
Li ZF, Jiang XM, Wang J, Meng XL, Zhang JQ, Xie ZC (2022) Species diversity and driving factors of benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in the middle and lower reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21431. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[李正飞, 蒋小明, 王军, 孟星亮, 张君倩, 谢志才 (2022) 雅鲁藏布江中下游底栖动物物种多样性及其影响因素. 生物多样性, 30, 21431.]
DOI |
|
| [24] | Liu SS, Wang F, Yang L (2022) The diversity of autumn birds in the upper and middle reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River. Wetland Science and Management, 18(4), 31-35, 40. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘善思, 王芳, 杨乐 (2022) 雅鲁藏布江中上游流域秋季鸟类多样性. 湿地科学与管理, 18(4), 31-35, 40.] | |
| [25] | Liu XT, He WC, Peng H, Xiao SB, Liu J (2023) Rare earth elements in the upper reaches of Yarlung Zangbo River. China Environmental Science, 43, 3068-3076. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘心庭, 贺文枨, 彭辉, 肖尚斌, 刘佳 (2023) 雅鲁藏布江上游干支流河水稀土元素地球化学特征研究. 中国环境科学, 43, 3068-3076.] | |
| [26] |
Luo ZM, Liu JX, Zhao PY, Jia T, Li C, Chai BF (2019) Biogeographic patterns and assembly mechanisms of bacterial communities differ between habitat generalists and specialists across elevational gradients. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10, 169.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | Ma BS, Yang XF, Xie CX, Huo B, Ding HP (2015) Resource status and seasonal variation of plankton in the Xaitongmoin Reach of the Yarlung Zangbo River. Journal of Hydroecology, 36(6), 19-28, (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马宝珊, 杨学峰, 谢从新, 霍斌, 丁慧萍 (2015) 雅鲁藏布江谢通门江段浮游生物资源现状及其季节动态. 水生态学杂志, 36(6), 19-28.] | |
| [28] |
Nekola JC, White PS (1999) The distance decay of similarity in biogeography and ecology. Journal of Biogeography, 26, 867-878.
DOI URL |
| [29] | Ning DL, Deng Y, Tiedje JM, Zhou JZ (2019) A general framework for quantitatively assessing ecological stochasticity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 116, 16892-16898. |
| [30] |
Novakovskaya IV, Patova EN, Dubrovskiy YA, Novakovskiy AB, Kulyugina EE (2022) Distribution of algae and cyanobacteria of biological soil crusts along the elevation gradient in mountain plant communities at the Northern Urals (Russian European Northeast). Journal of Mountain Science, 19, 637-646.
DOI |
| [31] |
Pan CM, Liu Y, An RZ, Huang X, Ba S (2021) Phytoplankton in the Mitika Wetland, Tibet, China. 1. Spatio-temporal niche of dominant species. Journal of Lake Sciences, 33, 1805-1819. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [潘成梅, 刘洋, 安瑞志, 黄香, 巴桑 (2021) 西藏麦地卡湿地的浮游植物. 1. 优势种的时空生态位. 湖泊科学, 33, 1805-1819.] | |
| [32] | Pei GF, Cao JX, Liu GX (2012) Variations of phytoplankton biodiversity in different streams of Niyang River. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 21, 24-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [裴国凤, 曹金象, 刘国祥 (2012) 尼洋河不同河段浮游植物群落多样性差异研究. 长江流域资源与环境, 21, 24-29.] | |
| [33] |
Sloan WT, Lunn M, Woodcock S, Head IM, Nee S, Curtis TP (2006) Quantifying the roles of immigration and chance in shaping prokaryote community structure. Environmental Microbiology, 8, 732-740.
PMID |
| [34] |
Sun D, Wang CS (2017) Latitudinal distribution of zooplankton communities in the Western Pacific along 160° E during summer 2014. Journal of Marine Systems, 169, 52-60.
DOI URL |
| [35] | The Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Comperhensive Scientific Expedition of Chinese Academy of Sciences (1992) Tibet Algae. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [中国科学院青藏高原综合科学考察队 (1992) 西藏藻类. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [36] |
Walker CE, Pan YD (2006) Using diatom assemblages to assess urban stream conditions. Hydrobiologia, 561, 179-189
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Wang JW, Liu QX, Zhao XF, Borthwick AGL, Liu YX, Chen Q, Ni JR (2019) Molecular biogeography of planktonic and benthic diatoms in the Yangtze River. Microbiome, 7, 153.
DOI PMID |
| [38] | Wang JY, Huo Z, Guo CX, Zhu GW, Gong ZJ, Fan YW, Wang JJ (2022) Vertical distribution characteristics and influencing factors of phytoplankton community structure in Qiandao Lake. Environmental Science, 43, 3575-3586. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王吉毅, 霍翟, 国超旋, 朱广伟, 龚志军, 范亚文, 王建军 (2022) 千岛湖浮游植物群落结构的垂向分布特征及其影响因素. 环境科学, 43, 3575-3586.] | |
| [39] |
Wang K, Yan HZ, Peng X, Hu HJ, Zhang HJ, Hou DD, Chen W, Qian P, Liu JF, Cai JB, Chai XL, Zhang DM (2020) Community assembly of bacteria and archaea in coastal waters governed by contrasting mechanisms: A seasonal perspective. Molecular Ecology, 29, 3762-3776.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Wang X, Qin GH, Li HX (2016) Analysis on characteristics and variation trend of annual runoff of mainstream of Yarlung Tsangpo River. Yangtze River, 47(1), 23-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王欣, 覃光华, 李红霞(2016) 雅鲁藏布江干流年径流变化趋势及特性分析. 人民长江, 47(1), 23-26.] | |
| [41] | Wei M, Zhu AM, Wang R, Hu JX (2022) Spring phytoplankton community structure and niche analysis of dominant species in Chishui River. Journal of Hydroecology, 43(5), 49-58 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [魏秘, 朱爱民, 王瑞, 胡菊香 (2022) 赤水河春季浮游植物群落结构变化及其优势种生态位分析. 水生态学杂志, 43(5), 49-58.] | |
| [42] | Wu BB, Wang P, Ding MJ, Huang GX, Zhang H, Yan CX, Nie MH (2022) Effects of anthropogenic intensity on bacterioplankton community structure in Jinjiang River. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 42, 459-473. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴波波, 王鹏, 丁明军, 黄高翔, 张华, 晏彩霞, 聂明华 (2022) 人类活动强度对锦江浮游细菌群落结构的影响. 环境科学学报, 42, 459-473.] | |
| [43] |
Yang Q, Zhang P, An RZ, Qiao NQ, Da Z, Ba S (2022) Spatial and temporal distribution patterns and driving mechanisms of ciliate communities in the midstream and downstream reaches of the Lhasa River. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[杨清, 张鹏, 安瑞志, 乔楠茜, 达珍, 巴桑 (2022) 拉萨河中下游纤毛虫群落时空分布模式及其驱动机制. 生物多样性, 30, 22012.]
DOI |
|
| [44] | Ye R, Liu L, Wang Q, Qi P, Chen DQ, Yu HB, Yang Q, Lu S, Jin YD, Ye XS, Fei YJ (2017) Biogeography of spring phytoplankton community in the coastal waters of northern Zhejiang. China Environmental Science, 37, 1492-1504. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [叶然, 刘莲, 王琼, 齐平, 陈丹琴, 俞海波, 杨晴, 鲁水, 金余娣, 叶仙森, 费岳军 (2017) 春季浙北海域浮游植物群落的空间分布. 中国环境科学, 37, 1492-1504.] | |
| [45] | Zhang CX, He YX, Guo XM, Meng HQ, Wu L, Huang J, Li WG, Zhao TQ (2022) Community structure variations and driving factors of eukaryotes phytoplankton in Danjiangkou Reservoir in summer and winter. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University (Natural Science), 41(6), 110-122. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张春霞, 贺玉晓, 郭晓明, 孟红旗, 武俐, 黄进, 李卫国, 赵同谦 (2022) 丹江口水库夏冬季真核浮游植物群落结构变化及其驱动因素. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 41(6), 110-122.] | |
| [46] |
Zhang T, Xu S, Yan RM, Wang RY, Gao YX, Kong M, Yi QT, Zhang YM (2022) Similar geographic patterns but distinct assembly processes of abundant and rare bacterioplankton communities in river networks of the Taihu Basin. Water Research, 211, 118057.
DOI URL |
| [47] | Zhang ZS, Huang XF (1991) Research Methods of Freshwater Plankton. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [章宗涉, 黄祥飞 (1991) 淡水浮游生物研究方法. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [48] | Zhong JL, Li YH, Zheng MS, Zang R, Xu NJ (2019) Effects of different hypersalinity models on the photo-physiological performances and related gene expression in Ulva prolifera. Journal of Marine Sciences, 37(2), 72-80. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[钟佳丽, 李亚鹤, 郑明山, 臧茹, 徐年军 (2019) 不同模式高盐胁迫对浒苔光合生理及相关基因表达的影响. 海洋学研究, 37(2), 72-80.]
DOI |
|
| [49] | Zhou JZ, Ning DL (2017) Stochastic community assembly: Does it matter in microbial ecologyv Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 81, e00002-17. |
| [50] | Zhu HZ, Chen JY (2000) Bacillariophyta of the Xizang Plateau. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [朱蕙忠, 陈嘉佑 (2000) 中国西藏硅藻. 科学出版社, 北京.] |
| [1] | 曲锐, 左振君, 王有鑫, 张良键, 吴志刚, 乔秀娟, 王忠. 基于元素组的生物地球化学生态位及其在不同生态系统中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23378-. |
| [2] | 郑梦瑶, 李媛, 王雪蓉, 张越, 贾彤. 芦芽山不同植被类型土壤原生动物群落构建机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23419-. |
| [3] | 徐凯伦, 陈小荣, 张敏华, 于婉婉, 吴素美, 朱志成, 陈定云, 兰荣光, 董舒, 刘宇. 演替和地形共同影响浙江百山祖森林群落的性系统多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24338-. |
| [4] | 杜芳, 荣晓莹, 徐鹏, 尹本丰, 张元明. 降水对古尔班通古特沙漠细菌群落多样性和构建过程的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22492-. |
| [5] | 孟宏虎, 宋以刚. 东南亚生物地理格局: 回溯与思考[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23261-. |
| [6] | 董建宇, 孙昕, 詹启鹏, 张宇洋, 张秀梅. 莱州湾东岸潮下带大型底栖动物群落beta多样性格局及其驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(3): 21388-. |
| [7] | 王寅, 王健铭, 曲梦君, 李景文. 干旱内陆河流域植物群落构建过程及其关键驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21419-. |
| [8] | 雍青措姆, 习新强, 牛克昌. 高寒草甸植物物种丧失对草原毛虫的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22069-. |
| [9] | 米湘成, 王绪高, 沈国春, 刘徐兵, 宋晓阳, 乔秀娟, 冯刚, 杨洁, 毛子昆, 徐学红, 马克平. 中国森林生物多样性监测网络: 二十年群落构建机制探索的回顾与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22504-. |
| [10] | 高程, 郭良栋. 微生物物种多样性、群落构建与功能性状研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22429-. |
| [11] | 王少鹏, 罗明宇, 冯彦皓, 储诚进, 张大勇. 生物多样性理论最新进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22410-. |
| [12] | 康佳鹏, 韩路, 冯春晖, 王海珍. 塔里木荒漠河岸林不同生境群落物种多度分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(7): 875-886. |
| [13] | 董雷, 王静, 刘永刚, 赵志平, 米湘成, 郭柯. 太行山北段地区荆条灌丛和三裂绣线菊灌丛群落谱系结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(1): 21-31. |
| [14] | 桂旭君, 练琚愉, 张入匀, 李艳朋, 沈浩, 倪云龙, 叶万辉. 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林群落垂直结构及其物种多样性特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(6): 619-629. |
| [15] | 翁昌露,张田田,巫东豪,陈声文,金毅,任海保,于明坚,罗媛媛. 古田山10种主要森林群落类型的α和β多样性格局及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(1): 33-41. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn