



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 21388. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021388 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021388
董建宇1, 孙昕1, 詹启鹏1, 张宇洋1, 张秀梅2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-09-24
接受日期:2021-10-28
出版日期:2022-03-20
发布日期:2022-01-10
通讯作者:
张秀梅
作者简介:*E-mail: xmzhang1227@163.com基金资助:
Jianyu Dong1, Xin Sun1, Qipeng Zhan1, Yuyang Zhang1, Xiumei Zhang2,*( )
)
Received:2021-09-24
Accepted:2021-10-28
Online:2022-03-20
Published:2022-01-10
Contact:
Xiumei Zhang
摘要:
群落β多样性格局的形成与维持机制一直是群落生态学研究的热点与核心。然而, 与陆生生态系统相比, 海洋生态系统尤其是海洋底栖生态系统中生物群落β多样性的研究明显滞后。本研究从分类(即物种组成)和功能(即性状组成)两个方面出发, 应用Mantel分析和基于矩阵的多元回归(multiple regression on distance matrices, MRM)分析, 探究了莱州湾东岸潮下带大型底栖动物群落β多样性及其周转(turnover)和嵌套(nestedness)组分与环境因子和空间距离的关系, 揭示了环境过滤和扩散限制两种生态学过程对其群落构建机制的影响。结果显示: (1)莱州湾东岸潮下带大型底栖动物群落的分类与功能性状β多样性均维持在较高水平且均以周转组分占主导, 表明研究区域大型底栖动物群落在物种和功能性状组成上差异较大, 而这种差异大部分来自物种或功能性状在空间或群落间的更替; (2)空间地理距离对大型底栖动物群落分类与功能性状β多样性及其组分无显著影响(Mantel检验, P > 0.05), 表明扩散限制对莱州湾东岸潮下带大型底栖动物群落的影响有限; (3) MRM分析表明, 沉积物总有机质(total organic matter, TOM)和粉砂含量显著影响大型底栖动物群落分类β多样性, 而TOM则显著影响功能性状β多样性。上述结果表明, 环境过滤是驱动莱州湾东岸潮下带大型底栖动物群落构建机制的首要因素。本研究阐明了莱州湾东岸潮下带大型底栖动物群落构建机制, 同时也为理解我国其他海域大型底栖动物群落的形成与维持机制提供了参考。
董建宇, 孙昕, 詹启鹏, 张宇洋, 张秀梅 (2022) 莱州湾东岸潮下带大型底栖动物群落beta多样性格局及其驱动因素. 生物多样性, 30, 21388. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021388.
Jianyu Dong, Xin Sun, Qipeng Zhan, Yuyang Zhang, Xiumei Zhang (2022) Patterns and drivers of beta diversity of subtidal macrobenthos community on the eastern coast of Laizhou Bay. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21388. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021388.
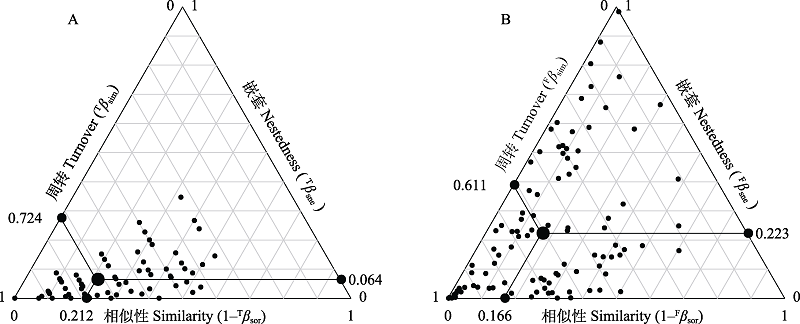
图2 分类β多样性和功能性状β多样性及其周转和嵌套组分。A: 分类β多样性; B: 功能β多样性。图中每个点代表1个样方对的数据。黑色大点表示3个组分的均值。
Fig. 2 Taxonomic and functional trait beta diversity and its components (turnover and nestedness). A, Taxonomic beta diversity; B, Functional beta diversity. The points represent the data of the pairwise sites. The larger black points represent the mean values of turnover, nestedness, and similarity (1 - βsor).
| 系数 Coefficient | 截距 Intercept | R2 | P | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水深 Depth (m) | 总有机质 Total organic matter (%) | 粉砂 Silt (%) | ||||
| 分类β多样性 Taxonomic beta diversity (Tβsor) | - | 0.0727** | 0.0735** | 0.7883*** | 0.4559 | 0.0001 |
| 周转组分 Turnover (Tβsim) | - | - | 0.1004** | 0.7243** | 0.2355 | 0.0070 |
| 嵌套组分 Nestedness (Tβsne) | - | - | -0.0216* | 0.0640* | 0.0859 | 0.0353 |
| 功能性状β多样性 Functional trait beta diversity (Fβsor) | -0.0400 | 0.0643* | - | 0.8340* | 0.1847 | 0.0487 |
| 周转组分 Turnover (Fβsim) | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 嵌套组分 Nestedness (Fβsne) | - | - | - | - | - | - |
表1 分类β多样性与功能性状β多样性及其组分与环境因子的多元回归分析(MRM)结果
Table 1 The results of taxonomic and functional trait beta diversity and its components with environmental factors based on multiple regression on distance matrices (MRM)
| 系数 Coefficient | 截距 Intercept | R2 | P | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水深 Depth (m) | 总有机质 Total organic matter (%) | 粉砂 Silt (%) | ||||
| 分类β多样性 Taxonomic beta diversity (Tβsor) | - | 0.0727** | 0.0735** | 0.7883*** | 0.4559 | 0.0001 |
| 周转组分 Turnover (Tβsim) | - | - | 0.1004** | 0.7243** | 0.2355 | 0.0070 |
| 嵌套组分 Nestedness (Tβsne) | - | - | -0.0216* | 0.0640* | 0.0859 | 0.0353 |
| 功能性状β多样性 Functional trait beta diversity (Fβsor) | -0.0400 | 0.0643* | - | 0.8340* | 0.1847 | 0.0487 |
| 周转组分 Turnover (Fβsim) | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 嵌套组分 Nestedness (Fβsne) | - | - | - | - | - | - |
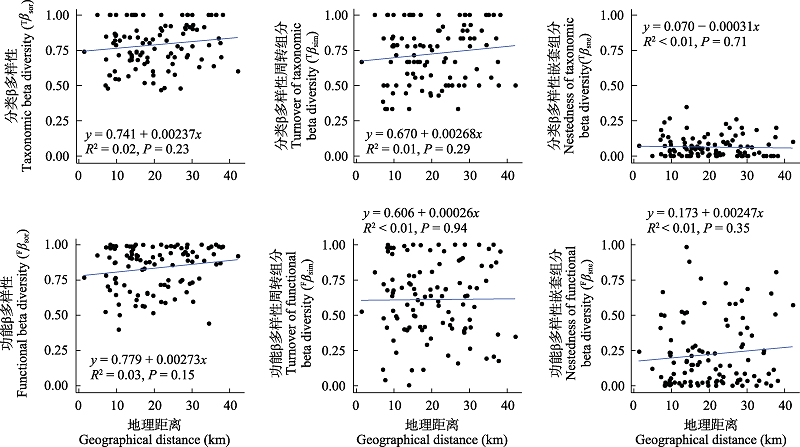
图3 大型底栖动物群落分类与功能性状β多样性及其组分(周转和嵌套)和群落间地理距离的关系
Fig. 3 The relationship of taxonomic and functional trait beta diversity and its components (turnover and nestedness) of macrobenthic communities with difference in geographic distance
| [1] |
Anderson MJ, Crist TO, Chase JM, Vellend M, Inouye BD, Freestone AL, Sanders NJ, Cornell HV, Comita LS, Davies KF, Harrison SP, Kraft NJB, Stegen JC, Swenson NG (2011) Navigating the multiple meanings of β diversity: A roadmap for the practicing ecologist. Ecology Letters, 14, 19-28.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Barros F, Blanchet H, Hammerstrom K, Sauriau PG, Oliver J (2014) A framework for investigating general patterns of benthic β-diversity along estuaries. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 149, 223-231.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Bartoń K (2020) MuMIn: Multi-Model Inference. R package version 1.43.17. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=MuMIn . (accessed on 2021-05-14) |
| [4] |
Baselga A (2010) Partitioning the turnover and nestedness components of beta diversity. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 19, 134-143.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Baselga A (2012) The relationship between species replacement, dissimilarity derived from nestedness, and nestedness. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 1223-1232.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Baselga A, Orme D, Villeger S, Bortoli JD, Leprieur F, Logez M (2021) betapart: Partitioning Beta Diversity into Turnover and Nestedness Components. R package version 1.5.4. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=betapart . (accessed on 2021-05-16) |
| [7] |
Beauchard O, Veríssimo H, Queirós AM, Herman PMJ (2017) The use of multiple biological traits in marine community ecology and its potential in ecological indicator development. Ecological Indicators, 76, 81-96.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Bender MG, Leprieur F, Mouillot D, Kulbicki M, Parravicini V, Pie MR, Barneche DR, Oliveira-Santos LGR, Floeter SR (2017) Isolation drives taxonomic and functional nestedness in tropical reef fish faunas. Ecography, 40, 425-435.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Bevilacqua S, Plicanti A, Sandulli R, Terlizzi A (2012) Measuring more of β-diversity: Quantifying patterns of variation in assemblage heterogeneity. An insight from marine benthic assemblages. Ecological Indicators, 18, 140-148.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Bevilacqua S, Terlizzi A (2020) Nestedness and turnover unveil inverse spatial patterns of compositional and functional β-diversity at varying depth in marine benthos. Diversity and Distributions, 26, 743-757.
DOI URL |
| [11] | Bivand R, Lewin-Koh N (2020) maptools: Tools for Handling Spatial Objects. R package version 1.0-1. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=maptools . (accessed on 2021-05-15) |
| [12] |
Boyé A, Thiébaut É, Grall J, Legendre P, Broudin C, Houbin C le Garrec V, Maguer M, Droual G, Gauthier O (2019) Trait-based approach to monitoring marine benthic data along 500 km of coastline. Diversity and Distributions, 25, 1879-1896.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Chen GG, Wang WQ, Liu Y, Zhang YM, Ma W, Xin K, Wang M (2019) Uncovering the relative influences of space and environment in shaping the biogeographic patterns of mangrove mollusk diversity. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 77, 30-39.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Chen SB, Ouyang ZY, Xu WH, Xiao Y (2010) A review of beta diversity studies. Biodiversity Science, 18, 323-335. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 陈圣宾, 欧阳志云, 徐卫华, 肖燚 (2010) Beta多样性研究进展. 生物多样性, 18, 323-335.]
DOI |
|
| [15] |
Chevenet F, Dolédec S, Chessel D (1994) A fuzzy coding approach for the analysis of long-term ecological data. Freshwater Biology, 31, 295-309.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Dong JY, Sun X, Zhang YY, Zhan QP, Zhang XM (2021a) Assessing benthic habitat ecological quality using four benthic indices in the coastal waters of Sanshandao, Laizhou Bay, China. Ecological Indicators, 129, 107980.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Dong JY, Zhao LL, Sun X, Hu CY, Wang YH, Li WT, Zhang PD, Zhang XM (2021b) Response of macrobenthic communities to heavy metal pollution in Laoshan Bay, China: A trait-based method. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 167, 112292.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Dray S, Dufour AB (2007) The ade 4 package: Implementing the duality diagram for ecologists. Journal of Statistical Software, 22, 1-20. |
| [19] | Dunnington D (2021) ggspatial: Spatial Data Framework for ggplot2. R package version 1.1.5. https://CRAN.R-project. org/package=ggspatial . (accessed on 2021-05-21) |
| [20] | Goslee SC, Urban DL (2007) The ecodist package for dissimilarity-based analysis of ecological data. Journal of Statistical Software, 22, 1-19. |
| [21] |
Gray JS (2000) The measurement of marine species diversity, with an application to the benthic fauna of the Norwegian continental shelf. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 250, 23-49.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Greve M, Gremmen NJM, Gaston KJ, Chown SL (2005) Nestedness of Southern Ocean island biotas: Ecological perspectives on a biogeographical conundrum. Journal of Biogeography, 32, 155-168.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Harrell FE, Dupont C (2021) Hmisc: Harrell Miscellaneous. R package version 4.5-0. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=Hmisc . (accessed on 2021-05-23) |
| [24] |
Harrison S, Ross SJ, Lawton JH (1992) Beta diversity on geographic gradients in Britain. Journal of Animal Ecology, 61, 151-158.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Hu CY, Dong JY, Gao LJ, Yang XL, Wang Z, Zhang XM (2019) Macrobenthos functional trait responses to heavy metal pollution gradients in a temperate lagoon. Environmental Pollution, 253, 1107-1116.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Laliberté E, Legendre P (2010) A distance-based framework for measuring functional diversity from multiple traits. Ecology, 91, 299-305.
PMID |
| [27] |
Lam-Gordillo O, Baring R, Dittmann S (2020) Ecosystem functioning and functional approaches on marine macrobenthic fauna: A research synthesis towards a global consensus. Ecological Indicators, 115, 106379.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Legendre P (2014) Interpreting the replacement and richness difference components of beta diversity. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 23, 1324-1334.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Lennon JJ, Koleff P, Greenwood JJD, Gaston KJ (2001) The geographical structure of British bird distributions: Diversity, spatial turnover and scale. Journal of Animal Ecology, 70, 966-979.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Li XZ (2011) An overview of studies on marine macrobenthic biodiversity from Chinese waters: Principally from the Yellow Sea. Biodiversity Science, 19, 676-684. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 李新正 (2011) 我国海洋大型底栖生物多样性研究及展望: 以黄海为例. 生物多样性, 19, 676-684.]
DOI |
|
| [31] | Li YF, Du FY, Wang LG, Wang XH, Ning JJ (2018) Effects of the sediment type on ecological functions of macrobenthos in the intertidal zones of Sanya Bay. Journal of Fisheries of China, 42, 1559-1571. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李亚芳, 杜飞雁, 王亮根, 王雪辉, 宁加佳 (2018) 底质类型对三亚湾潮间带大型底栖动物生态功能的影响. 水产学报, 42, 1559-1571.] | |
| [32] |
Lichstein JW (2007) Multiple regression on distance matrices: A multivariate spatial analysis tool. Plant Ecology, 188, 117-131.
DOI URL |
| [33] | Liu RY (2008) Checklist of Marine Biota of China Seas. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 刘瑞玉 (2008) 中国海洋生物名录. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [34] | MarLIN (2006) BIOTIC-Biological Traits Information Catalogue. https://www.marlin.ac.uk/biotic . (accessed on 2021-04-12) |
| [35] |
Mumby PJ (2001) Beta and habitat diversity in marine systems: A new approach to measurement, scaling and interpretation. Oecologia, 128, 274-280.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Niu KC, Liu YN, Shen ZH, He FL, Fang JY (2009) Community assembly: The relative importance of neutral theory and niche theory. Biodiversity Science, 17, 579-593. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 牛克昌, 刘怿宁, 沈泽昊, 何芳良, 方精云 (2009) 群落构建的中性理论和生态位理论. 生物多样性, 17, 579-593.]
DOI |
|
| [37] | Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Friendly M, Kindt R, Legendre P, McGlinn D, Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Szoecs E, Wagner H (2019) vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package version 2.5-6. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan . (accessed on 2021-05-28) |
| [38] | Paradis E, Schliep K (2018) ape 5.0: An environment for modern phylogenetics and evolutionary analyses in R. Bioinformatics, 35, 526-528. |
| [39] |
Pitacco V, Mistri M, Aleffi IF, Lardicci C, Prato S, Tagliapietra D, Munari C (2019) Spatial patterns of macrobenthic alpha and beta diversity at different scales in Italian transitional waters (central Mediterranean). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 222, 126-138.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Podani J, Ricotta C, Schmera D (2013) A general framework for analyzing beta diversity, nestedness and related community-level phenomena based on abundance data. Ecological Complexity, 15, 52-61.
DOI URL |
| [41] | Polytraits Team (2020) Polytraits: A Database on Biological Traits of Polychaetes. http://polytraits.lifewatchgreece.eu . (accessed on 2021-04-12) |
| [42] | R Core Team (2019) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R version 3.6.2 Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. . (accessed on 2020-01-10) |
| [43] |
Saracho Bottero MA, Jaubet ML, Llanos EN, Becherucci ME, Elías R, Garaffo GV (2020) Spatial-temporal variations of a SW Atlantic macrobenthic community affected by a chronic anthropogenic disturbance. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 156, 111189.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Si XF, Baselga A, Leprieur F, Song X, Ding P (2016) Selective extinction drives taxonomic and functional alpha and beta diversities in island bird assemblages. Journal of Animal Ecology, 85, 409-418.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Si XF, Zhao YH, Chen CW, Ren P, Zeng D, Wu LB, Ding P (2017) Beta-diversity partitioning: Methods, applications and perspectives. Biodiversity Science, 25, 464-480. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 斯幸峰, 赵郁豪, 陈传武, 任鹏, 曾頔, 吴玲兵, 丁平 (2017) Beta多样性分解: 方法、应用与展望. 生物多样性, 25, 464-480.]
DOI |
|
| [46] |
Socolar JB, Gilroy JJ, Kunin WE, Edwards DP (2016) How should beta-diversity inform biodiversity conservation? Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 31, 67-80.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Soininen J, Heino J, Wang JJ (2018) A meta-analysis of nestedness and turnover components of beta diversity across organisms and ecosystems. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 27, 96-109.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Su GH, Xu J, Akasaka M, Molinos JG, Matsuzaki SIS (2015) Human impacts on functional and taxonomic homogenization of plateau fish assemblages in Yunnan, China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 4, 470-478.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Villéger S, Mason NWH, Mouillot D (2008) New multidimensional functional diversity indices for a multifaceted framework in functional ecology. Ecology, 89, 2290-2301.
DOI URL |
| [50] | Wang W (2019) The Impacts of Environmental Change on the Biogeographic Patterns of Rocky Shore Macrobenthos along China’s Coast. PhD dissertation, Xiamen University, Xiamen. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王伟 (2019) 环境变化对我国岩相潮间带大型底栖生物地理格局的影响. 博士学位论文, 厦门大学, 厦门.] | |
| [51] |
Wang XB, Lü XT, Yao J, Wang ZW, Deng Y, Cheng WX, Zhou JZ, Han XG (2017) Habitat-specific patterns and drivers of bacterial β-diversity in China’s drylands. The ISME Journal, 11, 1345-1358.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Wang YP, Bao YX, Yu MJ, Xu GF, Ding P (2010) Nestedness for different reasons: The distributions of birds, lizards and small mammals on Islands of an inundated lake. Diversity and Distributions, 16, 862-873.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Whittaker RH (1960) Vegetation of the Siskiyou Mountains, Oregon and California. Ecological Monographs, 30, 279- 338.
DOI URL |
| [54] | Wickham H (2016) Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. Springer, New York, |
| [55] | Williams PH (1996) Mapping variations in the strength and breadth of biogeographic transition zones using species turnover. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 263, 579-588. |
| [56] | Witman JD, Etter RJ, Smith F (2004) The relationship between regional and local species diversity in marine benthic communities: A global perspective. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 101, 15664-15669. |
| [57] | Yang DJ, Sun RP (1988) The Polychaetes in Coastal Waters of China. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 杨德渐, 孙瑞平 (1988) 中国近海环节多毛动物. 农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [58] | Yang DJ, Wang YL (1996) Marine Invertebrates in Northern China. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 杨德渐, 王永良 (1996) 中国北部海洋无脊椎动物. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [59] |
Yao ZL, Wen HD, Deng Y, Cao M, Lin LX (2020) Driving forces underlying the beta diversity of tree species in subtropical mid-mountain moist evergreen broad-leaved forests in Ailao Mountains. Biodiversity Science, 28, 445-454. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 姚志良, 温韩东, 邓云, 曹敏, 林露湘 (2020) 哀牢山亚热带中山湿性常绿阔叶林树种beta多样性格局形成的驱动力. 生物多样性, 28, 445-454.]
DOI |
|
| [60] | Yu GC (2020) scatterpie: Scatter Pie Plot. R package version 0.1.5. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=scatterpie . (accessed on 2021-05-16) |
| [61] |
Zhang CL, Chen Y, Xu BD, Xue Y, Ren YP (2019) How to predict biodiversity in space? An evaluation of modelling approaches in marine ecosystems. Diversity and Distributions, 25, 1697-1708.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
Zhang D, Wan FY, Chu L, Yan YZ (2018) Longitudinal patterns in α and β diversity of the taxonomic and functional organizations of stream fish assemblages in the Qingyi River. Biodiversity Science, 26, 1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 张东, 宛凤英, 储玲, 严云志 (2018) 青弋江鱼类分类群和功能群的α和β多样性纵向梯度格局. 生物多样性, 26, 1-13.]
DOI |
|
| [63] |
Zhao YQ, Zeng JN, Gao AG, Chen QZ, Liao YB, Shou L (2009) Community pattern and diversity of macrozoobenthos in an intertidal flat, Jiaojiang Estuary. Biodiversity Science, 17, 303-309. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 赵永强, 曾江宁, 高爱根, 陈全震, 廖一波, 寿鹿 (2009) 椒江口滩涂大型底栖动物群落格局与多样性. 生物多样性, 17, 303-309.]
DOI |
| [1] | 宋远昊, 龚吕, 李贲, 胡阳, 李秀珍. 辽河口不同退塘还湿方式对大型底栖动物的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24316-. |
| [2] | 郑梦瑶, 李媛, 王雪蓉, 张越, 贾彤. 芦芽山不同植被类型土壤原生动物群落构建机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23419-. |
| [3] | 曲锐, 左振君, 王有鑫, 张良键, 吴志刚, 乔秀娟, 王忠. 基于元素组的生物地球化学生态位及其在不同生态系统中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23378-. |
| [4] | 倪艳梅, 陈莉, 董志远, 孙德斌, 李宝泉, 王绪敏, 陈琳琳. 黄河三角洲湿地生态修复区大型底栖动物群落结构与生态健康评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23303-. |
| [5] | 施国杉, 刘峰, 曹光宏, 陈典, 夏尚文, 邓云, 王彬, 杨效东, 林露湘. 西双版纳热带季节雨林木本植物的beta多样性: 空间、环境与林分结构的作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24285-. |
| [6] | 徐凯伦, 陈小荣, 张敏华, 于婉婉, 吴素美, 朱志成, 陈定云, 兰荣光, 董舒, 刘宇. 演替和地形共同影响浙江百山祖森林群落的性系统多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24338-. |
| [7] | 冯尔辉, 梁伟诺, 胡亮, 张旭. 海南东寨港国家级自然保护区潮间带蟹类(十足目: 短尾下目)物种多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23030-. |
| [8] | 梁伟诺, 张旭, 胡亮. 广东东海岛与硇洲岛潮间带蟹类(十足目: 短尾下目)物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23086-. |
| [9] | 杨胜娴, 杨清, 李晓东, 巢欣, 刘惠秋, 魏蓝若雪, 巴桑. 确定性过程主导高原典型河流浮游植物地理分布格局和群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23092-. |
| [10] | 杜芳, 荣晓莹, 徐鹏, 尹本丰, 张元明. 降水对古尔班通古特沙漠细菌群落多样性和构建过程的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22492-. |
| [11] | 王健铭, 雷训, 冯益明, 吴波, 卢琦, 何念鹏, 李景文. 中国温带荒漠植物群落生态特异性格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(10): 23144-. |
| [12] | 王健铭, 曲梦君, 王寅, 冯益明, 吴波, 卢琦, 何念鹏, 李景文. 青藏高原北部戈壁植物群落物种、功能与系统发育β多样性分布格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 21503-. |
| [13] | 王寅, 王健铭, 曲梦君, 李景文. 干旱内陆河流域植物群落构建过程及其关键驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21419-. |
| [14] | 雍青措姆, 习新强, 牛克昌. 高寒草甸植物物种丧失对草原毛虫的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22069-. |
| [15] | 曲梦君, 努尔依拉·阿巴拜克, 邹旭阁, 赵航, 朱威霖, 王健铭, 李景文. 地理距离和环境因子对阿拉善戈壁植物群落β多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22029-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn