



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 22429. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022429 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022429
收稿日期:2022-07-26
接受日期:2022-10-03
出版日期:2022-10-20
发布日期:2022-11-01
通讯作者:
郭良栋
作者简介:* E-mail: guold@im.ac.cn基金资助:
Cheng Gao1,2, Liang-Dong Guo1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-07-26
Accepted:2022-10-03
Online:2022-10-20
Published:2022-11-01
Contact:
Liang-Dong Guo
摘要:
微生物主要包括细菌、真菌、古菌、病毒等类群, 是地球上出现时间最早、分布最广泛、个体数量最多, 以及物种和基因多样性十分丰富的生物类群。为了适应各种生境, 微生物衍生出腐生、寄生、共生等多样的生存策略, 在生物地球化学循环、生态系统演替与稳定性、环境修复以及人类健康等方面发挥着重要作用。传统的微生物监测方法限制了我们对微生物多样性的认知; 但是, 近年来高通量测序技术和生物信息学的发展极大推动了微生物多样性的研究进展。本文概述了近年来在微生物多样性分布格局与维持、群落构建以及功能属性多样性的最新进展; 总结分析了细菌、古菌、真菌的多样性纬度分布格局及其驱动因子, 选择、扩散、成种、漂变等过程对细菌、古菌、真菌的群落构建的贡献, 以及细菌和真菌的形态、生理生化、生长繁殖、扩散、基因组等功能性状的多样性; 提出了未来微生物多样性研究的重要领域: 环境宏真菌组研究, 微生物多样性与生态系统多功能性的关系研究, 以及微生物互作网络的生态功能研究。
高程, 郭良栋 (2022) 微生物物种多样性、群落构建与功能性状研究进展. 生物多样性, 30, 22429. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022429.
Cheng Gao, Liang-Dong Guo (2022) Progress on microbial species diversity, community assembly and functional traits. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22429. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022429.
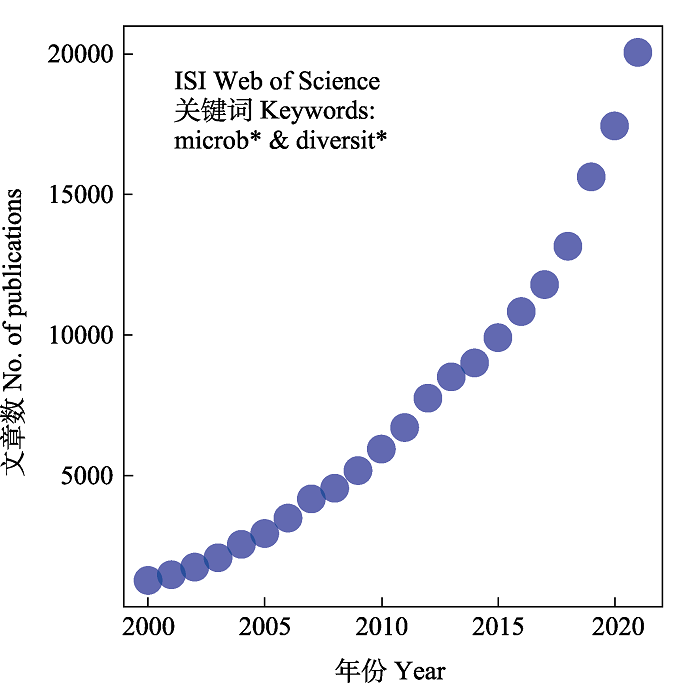
图1 微生物多样性研究发表文章数量逐年增加。在ISI Web of Science数据库中以microb*和diversit*为关键词进行检索, 检索期限为2000-2020, 检索时间为2022年9月15日。每个点代表每年发表的文章数。
Fig. 1 Numbers of published papers of microbial diversity in recent years. We performed search in ISI Web of Science using keywords microb* and diversit*, ranged from 2000 to 2020, at the date of September 15, 2022.
| [1] |
Adams RI, Miletto M, Taylor JW, Bruns TD (2013) Dispersal in microbes: Fungi in indoor air are dominated by outdoor air and show dispersal limitation at short distances. The ISME Journal, 7, 1262-1273.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Adriaenssens EM, Kramer R, van Goethem MW, Makhalanyane TP, Hogg I, Cowan DA (2017) Environmental drivers of viral community composition in Antarctic soils identified by viromics. Microbiome, 5, 83.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Agerer R (2001) Exploration types of ectomycorrhizae. Mycorrhiza, 11, 107-114.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Aguilar-Trigueros CA, Powell JR, Anderson IC, Antonovics J, Rillig MC (2014) Ecological understanding of root-infecting fungi using trait-based approaches. Trends in Plant Science, 19, 432-438.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
Arnold AE, Lutzoni F (2007) Diversity and host range of foliar fungal endophytes: Are tropical leaves biodiversity hotspots? Ecology, 88, 541-549.
PMID |
| [6] | Averill C, Bhatnagar JM, Dietze MC, Pearse WD, Kivlin SN (2019) Global imprint of mycorrhizal fungi on whole-plant nutrient economics. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 116, 23163-23168. |
| [7] |
Babalola BJ, Li J, Willing CE, Zheng Y, Wang YL, Gan HY, Li XC, Wang C, Adams CA, Gao C, Guo LD (2022) Nitrogen fertilisation disrupts the temporal dynamics of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal hyphae but not spore density and community composition in a wheat field. New Phytologist, 234, 2057-2072.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Bagchi R, Gallery RE, Gripenberg S, Gurr SJ, Narayan L, Addis CE, Freckleton RP, Lewis OT (2014) Pathogens and insect herbivores drive rainforest plant diversity and composition. Nature, 506, 85-88.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Bahram M, Hildebrand F, Forslund SK, Anderson JL, Soudzilovskaia NA, Bodegom PM, Bengtsson-Palme J, Anslan S, Coelho LP, Harend H, Huerta-Cepas J, Medema MH, Maltz MR, Mundra S, Olsson PA, Pent M, Põlme S, Sunagawa S, Ryberg M, Tedersoo L, Bork P (2018) Structure and function of the global topsoil microbiome. Nature, 560, 233-237.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Bahram M, Netherway T (2021) Fungi as mediators linking organisms and ecosystems. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 46, fuab058.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Baker BJ, de Anda V, Seitz KW, Dombrowski N, Santoro AE, Lloyd KG (2020) Diversity, ecology and evolution of archaea. Nature Microbiology, 5, 887-900.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Bakker MR, Augusto L, Achat DL (2006) Fine root distribution of trees and understory in mature stands of maritime pine (Pinus pinaster) on dry and humid sites. Plant and Soil, 286, 37-51.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Baldrian P, Větrovský T, Lepinay C, Kohout P (2022) High-throughput sequencing view on the magnitude of global fungal diversity. Fungal Diversity, 114, 539-547.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Banerjee S, Schlaeppi K, van der Heijden MGA (2018) Keystone taxa as drivers of microbiome structure and functioning. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 16, 567-576.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Banerjee S, Schlaeppi K, van der Heijden MGA (2019) Reply to ‘Can We Predict Microbial Keystones?’. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 17, 194.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Bennett JA, Maherali H, Reinhart KO, Lekberg Y, Hart MM, Klironomos J (2017) Plant-soil feedbacks and mycorrhizal type influence temperate forest population dynamics. Science, 355, 181-184.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Berg G, Cernava T (2022) The plant microbiota signature of the Anthropocene as a challenge for microbiome research. Microbiome, 10, 54.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Bertness MD, Callaway R (1994) Positive interactions in communities. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 9, 191-193.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | Bogar LM, Peay KG (2017) Processes maintaining the coexistence of ectomycorrhizal fungi at a fine spatial scale. In: Biogeography of Mycorrhizal Symbiosis (ed. Tedersoo L), pp. 79-105. Springer International Publishing, Cham, Switzerland. |
| [20] |
Booth MG (2004) Mycorrhizal networks mediate overstorey- understorey competition in a temperate forest. Ecology Letters, 7, 538-546.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Brundrett M, Tedersoo L (2019) Misdiagnosis of mycorrhizas and inappropriate recycling of data can lead to false conclusions. New Phytologist, 221, 18-24.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Brundrett MC, Tedersoo L (2018) Evolutionary history of mycorrhizal symbioses and global host plant diversity. New Phytologist, 220, 1108-1115.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Bryant JA, Lamanna C, Morlon H, Kerkhoff AJ, Enquist BJ, Green JL (2008) Microbes on mountainsides: Contrasting elevational patterns of bacterial and plant diversity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 105, 11505-11511. |
| [24] |
Bueno CG, Aldrich-Wolfe L, Chaudhary VB, Gerz M, Helgason T, Hoeksema JD, Klironomos J, Lekberg Y, Leon D, Maherali H, Öpik M, Zobel M, Moora M (2019) Misdiagnosis and uncritical use of plant mycorrhizal data are not the only elephants in the room. New Phytologist, 224, 1415-1418.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Callaway RM, Brooker RW, Choler P, Kikvidze Z, Lortie CJ, Michalet R, Paolini L, Pugnaire FI, Newingham B, Aschehoug ET, Armas C, Kikodze D, Cook BJ (2002) Positive interactions among alpine plants increase with stress. Nature, 417, 844-848.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Camarillo-Guerrero LF, Almeida A, Rangel-Pineros G, Finn RD, Lawley TD (2021) Massive expansion of human gut bacteriophage diversity. Cell, 184, 1098-1109.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Chagnon PL, Bradley RL, Maherali H, Klironomos JN (2013) A trait-based framework to understand life history of mycorrhizal fungi. Trends in Plant Science, 18, 484-491.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Chase JM (2007) Drought mediates the importance of stochastic community assembly. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 104, 17430-17434. |
| [29] |
Chase JM (2010) Stochastic community asssembly causes higher biodiversity in more productive environments. Science, 328, 1388-1391.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Chase JM, Biro EG, Ryberg WA, Smith KG (2009) Predators temper the relative importance of stochastic processes in the assembly of prey metacommunities. Ecology Letters, 12, 1210-1218.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
Chaudhary VB, Nolimal S, Sosa-Hernández MA, Egan C, Kastens J (2020) Trait-based aerial dispersal of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytologist, 228, 238-252.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Chen L, Swenson NG, Ji NN, Mi XC, Ren HB, Guo LD, Ma KP (2019) Differential soil fungus accumulation and density dependence of trees in a subtropical forest. Science, 366, 124-128.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | Chen WL, Eissenstat DM, Koide RT (2018) Root diameter predicts the extramatrical hyphal exploration distance of the ectomycorrhizal fungal community. Ecosphere, 9, e02202. |
| [34] |
Coyte KZ, Schluter J, Foster KR (2015) The ecology of the microbiome: Networks, competition, and stability. Science, 350, 663-666.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Craig ME, Turner BL, Liang C, Clay K, Johnson DJ, Phillips RP (2018) Tree mycorrhizal type predicts within-site variability in the storage and distribution of soil organic matter. Global Change Biology, 24, 3317-3330.
DOI PMID |
| [36] |
Danovaro R, Molari M, Corinaldesi C, Dell’Anno A (2016) Macroecological drivers of archaea and bacteria in benthic deep-sea ecosystems. Science Advances, 2, e1500961.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Davison J, Moora M, Öpik M, Adholeya A, Ainsaar L, Bâ A, Burla S, Diedhiou AG, Hiiesalu I, Jairus T, Johnson NC, Kane A, Koorem K, Kochar M, Ndiaye C, Pärtel M, Reier Ü, Saks Ü, Singh R, Vasar M, Zobel M (2015) Global assessment of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus diversity reveals very low endemism. Science, 349, 970-973.
DOI PMID |
| [38] |
de Vries FT, Griffiths RI, Bailey M, Craig H, Girlanda M, Gweon HS, Hallin S, Kaisermann A, Keith AM, Kretzschmar M, Lemanceau P, Lumini E, Mason KE, Oliver A, Ostle N, Prosser JI, Thion C, Thomson B, Bardgett RD (2018) Soil bacterial networks are less stable under drought than fungal networks. Nature Communications, 9, 3033.
DOI PMID |
| [39] |
Delgado-Baquerizo M, Maestre FT, Reich PB, Trivedi P, Osanai Y, Liu YR, Hamonts K, Jeffries TC, Singh BK (2016) Carbon content and climate variability drive global soil bacterial diversity patterns. Ecological Monographs, 86, 373-390.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Delgado-Baquerizo M, Reith F, Dennis PG, Hamonts K, Powell JR, Young A, Singh BK, Bissett A (2018) Ecological drivers of soil microbial diversity and soil biological networks in the Southern Hemisphere. Ecology, 99, 583-596.
DOI PMID |
| [41] |
Deveautour C, Chieppa J, Nielsen UN, Boer MM, Mitchell C, Horn S, Power SA, Guillen A, Bennett AE, Powell JR (2020) Biogeography of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore traits along an aridity gradient, and responses to experimental rainfall manipulation. Fungal Ecology, 46, 100899.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Dion MB, Oechslin F, Moineau S (2020) Phage diversity, genomics and phylogeny. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 18, 125-138.
DOI PMID |
| [43] |
Fierer N (2017) Embracing the unknown: Disentangling the complexities of the soil microbiome. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 15, 579-590.
DOI PMID |
| [44] | Fierer N, Jackson RB (2006) The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 103, 626-631. |
| [45] |
Fitzpatrick CR, Salas-González I, Conway JM, Finkel OM, Gilbert S, Russ D, Teixeira PJPL, Dangl JL (2020) The plant microbiome: From ecology to reductionism and beyond. Annual Review of Microbiology, 74, 81-100.
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
Fodelianakis S, Washburne AD, Bourquin M, Pramateftaki P, Kohler TJ, Styllas M, Tolosano M, de Staercke V, Schön M, Busi SB, Brandani J, Wilmes P, Peter H, Battin TJ (2022) Microdiversity characterizes prevalent phylogenetic clades in the glacier-fed stream microbiome. The ISME Journal, 16, 666-675.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Fransson P (2012) Elevated CO2 impacts ectomycorrhiza- mediated forest soil carbon flow: Fungal biomass production, respiration and exudation. Fungal Ecology, 5, 85-98.
DOI URL |
| [48] | Frenken T, Brussaard CPD, Velthuis M, Aben R, Kazanjian G, Hilt S, Kosten S, Peeters ETHM, de Senerpont Domis LN, Stephan S, van Donk E, van de Waal DB (2020) Warming advances virus population dynamics in a temperate freshwater plankton community. Limnology and Oceanography Letters, 5, 295-304. |
| [49] |
Gao C, Courty PE, Varoquaux N, Cole B, Montoya L, Xu L, Purdom E, Vogel J, Hutmacher RB, Dahlberg JA, Coleman- Derr D, Lemaux PG, Taylor JW (2022) Successional adaptive strategies revealed by correlating arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal abundance with host plant gene expression. Molecular Ecology, doi: 10.1111/mec.16343.
DOI |
| [50] |
Gao C, Guo LD (2013) Distribution pattern and maintenance of ectomycorrhizal fungus diversity. Biodiversity Science, 21, 488-498. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[高程, 郭良栋 (2013) 外生菌根真菌多样性的分布格局与维持机制研究进展. 生物多样性, 21, 488-498.]
DOI |
|
| [51] |
Gao C, Kim YC, Zheng Y, Yang W, Chen L, Ji NN, Wan SQ, Guo LD (2016) Increased precipitation, rather than warming, exerts a strong influence on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community in a semiarid steppe ecosystem. Botany, 94, 459-469.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Gao C, Montoya L, Xu L, Madera M, Hollingsworth J, Purdom E, Singan V, Vogel J, Hutmacher RB, Dahlberg JA, Coleman-Derr D, Lemaux PG, Taylor JW (2020) Fungal community assembly in drought-stressed Sorghum shows stochasticity, selection, and universal ecological dynamics. Nature Communications, 11, 34.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Gao C, Shi NN, Chen L, Ji NN, Wu BW, Wang YL, Xu Y, Zheng Y, Mi XC, Ma KP, Guo LD (2017) Relationships between soil fungal and woody plant assemblages differ between ridge and valley habitats in a subtropical mountain forest. New Phytologist, 213, 1874-1885.
DOI PMID |
| [54] |
Gao C, Shi NN, Liu YX, Peay KG, Zheng Y, Ding Q, Mi XC, Ma KP, Wubet T, Buscot F, Guo LD (2013) Host plant genus-level diversity is the best predictor of ectomycorrhizal fungal diversity in a Chinese subtropical forest. Molecular Ecology, 22, 3403-3414.
PMID |
| [55] |
Gao C, Zhang Y, Shi NN, Zheng Y, Chen L, Wubet T, Bruelheide H, Both S, Buscot F, Ding Q, Erfmeier A, Kühn P, Nadrowski K, Scholten T, Guo LD (2015) Community assembly of ectomycorrhizal fungi along a subtropical secondary forest succession. New Phytologist, 205, 771-785.
DOI PMID |
| [56] |
Genre A, Lanfranco L, Perotto S, Bonfante P (2020) Unique and common traits in mycorrhizal symbioses. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 18, 649-660.
DOI URL |
| [57] | Gilbert B, Levine JM (2017) Ecological drift and the distribution of species diversity. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 284, 20170507. |
| [58] |
Gregory AC, Zayed AA, Conceição-Neto N, Temperton B, Bolduc B, Alberti A, Ardyna M, Arkhipova K, Carmichael M, Cruaud C, Dimier C, Domínguez-Huerta G, Ferland J, Kandels S, Liu Y, Marec C, Pesant S, Picheral M, Pisarev S, Poulain J, Tremblay JÉ, Vik D, Tara Oceans Coordinators, Babin M, Bowler C, Culley AI, de Vargas C, Dutilh BE, Iudicone D, Karp-Boss L, Roux S, Sunagawa S, Wincker P, Sullivan MB (2019) Marine DNA viral macro- and microdiversity from pole to pole. Cell, 177, 1109-1123.
DOI PMID |
| [59] |
Grime JP (1974) Vegetation classification by reference to strategies. Nature, 250, 26-31.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
Guittar J, Shade A, Litchman E (2019) Trait-based community assembly and succession of the infant gut microbiome. Nature Communications, 10, 512.
DOI PMID |
| [61] | Hammarlund SP, Harcombe WR (2019) Refining the stress gradient hypothesis in a microbial community. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 116, 15760-15762. |
| [62] |
Han YF, Feng JG, Han MG, Zhu B (2020) Responses of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to nitrogen addition: A meta-analysis. Global Change Biology, 26, 7229-7241.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
Hawksworth DL (1991) The fungal dimension of biodiversity: Magnitude, significance, and conservation. Mycological Research, 95, 641-655.
DOI URL |
| [64] | Hawksworth DL, Lücking R (2017) Fungal diversity revisited: 2.2 to 3.8 million species. Microbiology Spectrum, 5(4), FUNK-0052-2016. |
| [65] |
He XH, Critchley C, Bledsoe C (2003) Nitrogen transfer within and between plants through common mycorrhizal networks (CMNs). Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 22, 531-567.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
Hillebrand H (2004) On the generality of the latitudinal diversity gradient. The American Naturalist, 163, 192-211.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
Hoek TA, Axelrod K, Biancalani T, Yurtsev EA, Liu JH, Gore J (2016) Resource availability modulates the cooperative and competitive nature of a microbial cross-feeding mutualism. PLoS Biology, 14, e1002540.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
Huang ZJ, Zeng SZ, Xiong JB, Hou DW, Zhou RJ, Xing CG, Wei DD, Deng XS, Yu LF, Wang H, Deng ZX, Weng SP, Kriengkrai S, Ning DL, Zhou JZ, He JG (2020) Microecological Koch’s postulates reveal that intestinal microbiota dysbiosis contributes to shrimp white feces syndrome. Microbiome, 8, 32.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
Ji NN, Gao C, Sandel B, Zheng Y, Chen L, Wu BW, Li XC, Wang YL, Lü PP, Sun X, Guo LD (2019) Late Quaternary climate change explains soil fungal community composition rather than fungal richness in forest ecosystems. Ecology and Evolution, 9, 6678-6692.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Jiao S, Chen WM, Wei GH (2021) Linking phylogenetic niche conservatism to soil archaeal biogeography, community assembly and species coexistence. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 30, 1488-1501.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
Jiao S, Xu YQ, Zhang J, Lu YH (2019) Environmental filtering drives distinct continental atlases of soil archaea between dryland and wetland agricultural ecosystems. Microbiome, 7, 15.
DOI PMID |
| [72] |
Jiao S, Yang YF, Xu YQ, Zhang J, Lu YH (2020) Balance between community assembly processes mediates species coexistence in agricultural soil microbiomes across Eastern China. The ISME Journal, 14, 202-216.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
Jumpponen A, Jones KL (2009) Massively parallel 454 sequencing indicates hyperdiverse fungal communities in temperate Quercus macrocarpa phyllosphere. New Phytologist, 184, 438-448.
DOI PMID |
| [74] |
Kearns PJ, Shade A (2018) Trait-based patterns of microbial dynamics in dormancy potential and heterotrophic strategy: Case studies of resource-based and post-press succession. The ISME Journal, 12, 2575-2581.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
Kim M, Jung JY, Laffly D, Kwon HY, Lee YK (2016) Shifts in bacterial community structure during succession in a glacier foreland of the High Arctic. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 93, fiw213.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
Koide RT, Sharda JN, Herr JR, Malcolm GM (2008) Ectomycorrhizal fungi and the biotrophy-saprotrophy continuum. New Phytologist, 178, 230-233.
DOI PMID |
| [77] |
Kranabetter JM, Durall DM, MacKenzie WH (2009) Diversity and species distribution of ectomycorrhizal fungi along productivity gradients of a southern boreal forest. Mycorrhiza, 19, 99-111.
DOI PMID |
| [78] |
Krause S, le Roux X, Niklaus PA, van Bodegom PM, Lennon JT, Bertilsson S, Grossart HP, Philippot L, Bodelier PLE(2014) Trait-based approaches for understanding microbial biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Frontiers in Microbiology, 5, 251.
DOI PMID |
| [79] | Laforest-Lapointe I, Messier C, Kembel SW (2017) Tree leaf bacterial community structure and diversity differ along a gradient of urban intensity. mSystems, 2, e00087-17. |
| [80] | Leff JW, Jones SE, Prober SM, Barberán A, Borer ET, Firn JL, Harpole WS, Hobbie SE, Hofmockel KS, Knops JMH, McCulley RL la Pierre K, Risch AC, Seabloom EW, Schütz M, Steenbock C, Stevens CJ, Fierer N (2015) Consistent responses of soil microbial communities to elevated nutrient inputs in grasslands across the globe. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 112, 10967-10972. |
| [81] |
Lekberg Y, Arnillas CA, Borer ET, Bullington LS, Fierer N, Kennedy PG, Leff JW, Luis AD, Seabloom EW, Henning JA (2021) Nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization consistently favor pathogenic over mutualistic fungi in grassland soils. Nature Communications, 12, 3484.
DOI PMID |
| [82] |
Li D, Ni HW, Jiao S, Lu YH, Zhou JZ, Sun B, Liang YT (2021) Coexistence patterns of soil methanogens are closely tied to methane generation and community assembly in rice paddies. Microbiome, 9, 20.
DOI PMID |
| [83] |
Liu L, Barberán A, Gao C, Zhang ZC, Wang M, Wurzburger N, Wang X, Zhang R, Li JX, Zhang J (2022) Impact of urbanization on soil microbial diversity and composition in the megacity of Shanghai. Land Degradation and Development, 33, 282-293.
DOI URL |
| [84] | Liu WX, Jiang L, Yang S, Wang Z, Tian R, Peng ZY, Chen YL, Zhang XX, Kuang JL, Ling N, Wang SP, Liu LL (2020) Critical transition of soil bacterial diversity and composition triggered by nitrogen enrichment. Ecology, 101, e03053. |
| [85] |
Liu XB, Liang MX, Etienne RS, Wang YF, Staehelin C, Yu SX (2012) Experimental evidence for a phylogenetic Janzen- Connell effect in a subtropical forest. Ecology Letters, 15, 111-118.
DOI URL |
| [86] | Liu XJ, Ma KP (2015) Plant functional traits—Concepts, applications and future directions. Scientia Sinica (Vitae), 45, 325-339. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘晓娟, 马克平 (2015) 植物功能性状研究进展. 中国科学: 生命科学, 45, 325-339.] | |
| [87] | Locey KJ, Lennon JT (2016) Scaling laws predict global microbial diversity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 113, 5970-5975. |
| [88] |
Louca S, Mazel F, Doebeli M, Parfrey LW (2019) A census-based estimate of Earth’s bacterial and archaeal diversity. PLoS Biology, 17, e3000106.
DOI URL |
| [89] | Maestre FT, Delgado-Baquerizo M, Jeffries TC, Eldridge DJ, Ochoa V, Gozalo B, Quero JL, García-Gómez M, Gallardo A, Ulrich W, Bowker MA, Arredondo T, Barraza-Zepeda C, Bran D, Florentino A, Gaitán J, Gutiérrez JR, Huber- Sannwald E, Jankju M, Mau RL, Miriti M, Naseri K, Ospina A, Stavi I, Wang DL, Woods NN, Yuan X, Zaady E, Singh BK (2015) Increasing aridity reduces soil microbial diversity and abundance in global drylands. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 112, 15684-15689. |
| [90] | Neilson JW, Califf K, Cardona C, Copeland A, van Treuren W, Josephson KL, Knight R, Gilbert JA, Quade J, Caporaso JG, Maier RM (2017) Significant impacts of increasing aridity on the arid soil microbiome. mSystems, 2, e00195-e00116. |
| [91] | Nelson MB, Martiny AC, Martiny JBH (2016) Global biogeography of microbial nitrogen-cycling traits in soil. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 113, 8033-8040. |
| [92] |
Nemergut DR, Knelman JE, Ferrenberg S, Bilinski T, Melbourne B, Jiang L, Violle C, Darcy JL, Prest T, Schmidt SK, Townsend AR (2016) Decreases in average bacterial community rRNA operon copy number during succession. The ISME Journal, 10, 1147-1156.
DOI URL |
| [93] |
Nemergut DR, Schmidt SK, Fukami T, O’Neill SP, Bilinski TM, Stanish LF, Knelman JE, Darcy JL, Lynch RC, Wickey P, Ferrenberg S (2013) Patterns and processes of microbial community assembly. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 77, 342-356.
DOI PMID |
| [94] |
Nguyen NH, Song ZW, Bates ST, Branco S, Tedersoo L, Menke J, Schilling JS, Kennedy PG (2016) FUNGuild: An open annotation tool for parsing fungal community datasets by ecological guild. Fungal Ecology, 20, 241-248.
DOI URL |
| [95] |
Ortiz-Álvarez R, Fierer N, de losíos A de los Ríos A, Casamayor EO, Barberán A (2018) Consistent changes in the taxonomic structure and functional attributes of bacterial communities during primary succession. The ISME Journal, 12, 1658-1667.
DOI URL |
| [96] |
Paz C, Öpik M, Bulascoschi L, Bueno CG, Galetti M (2021) Dispersal of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: Evidence and insights for ecological studies. Microbial Ecology, 81, 283-292.
DOI URL |
| [97] |
Peay KG, Kennedy PG, Talbot JM (2016) Dimensions of biodiversity in the earth mycobiome. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 14, 434-447.
DOI PMID |
| [98] |
Peay KG, Schubert MG, Nguyen NH, Bruns TD (2012) Measuring ectomycorrhizal fungal dispersal: Macroecological patterns driven by microscopic propagules. Molecular Ecology, 21, 4122-4136.
DOI PMID |
| [99] |
Petro C, Starnawski P, Schramm A, Kjeldsen KU (2017) Microbial community assembly in marine sediments. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 79, 177-195.
DOI URL |
| [100] | Piccardi P, Vessman B, Mitri S (2019) Toxicity drives facilitation between 4 bacterial species. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 116, 15979-15984. |
| [101] | Põlme S, Abarenkov K, Henrik Nilsson R, Lindahl BD, Clemmensen KE, Kauserud H, Nguyen N, Kjøller R, Bates ST, Baldrian P, Frøslev TG, Adojaan K, Vizzini A, Suija A, Pfister D, Baral HO, Järv H, Madrid H, Nordén J, Liu JK, Pawlowska J, Põldmaa K, Pärtel K, Runnel K, Hansen KR, Larsson KH, Hyde KD, Sandoval-Denis M, Smith ME, Toome-Heller M, Wijayawardene NN, Menolli N, Reynolds NK, Drenkhan R, Maharachchikumbura SSN, Gibertoni TB, Læssøe T, Davis W, Tokarev Y, Corrales A, Soares AM, Agan A, Machado AR, Argüelles-Moyao A, Detheridge A, Meiras-Ottoni A, Verbeken A, Dutta AK, Cui BK, Pradeep CK, Marín C, Stanton D, Gohar D, Wanasinghe DN, Otsing E, Aslani F, Griffith GW, Lumbsch TH, Grossart HP, Masigol H, Timling I, Hiiesalu I, Oja J, Kupagme JY, Geml J, Alvarez-Manjarrez J, Ilves K, Loit K, Adamson K, Nara K, Küngas K, Rojas-Jimenez K, Bitenieks K, Irinyi L, Nagy LG, Soonvald L, Zhou LW, Wagner L, Aime MC, Öpik M, Mujica MI, Metsoja M, Ryberg M, Vasar M, Murata M, Nelsen MP, Cleary M, Samarakoon MC, Doilom M, Bahram M, Hagh-Doust N, Dulya O, Johnston P, Kohout P, Chen Q, Tian Q, Nandi R, Amiri R, Perera RH, Santos Chikowski R, Mendes-Alvarenga RL, Garibay-Orijel R, Gielen R, Phookamsak R, Jayawardena RS, Rahimlou S, Karunarathna SC, Tibpromma S, Brown SP, Sepp SK, Mundra S, Luo ZH, Bose T, Vahter T, Netherway T, Yang T, May T, Varga T, Li W, Coimbra VRM, Oliveira VRT, Lima VX, Mikryukov VS, Lu YZ, Matsuda Y, Miyamoto Y, Kõljalg U, Tedersoo L (2020) FungalTraits: A user-friendly traits database of fungi and fungus-like stramenopiles. Fungal Diversity, 105, 1-16. |
| [102] |
Prest TL, Kimball AK, Kueneman JG, McKenzie VJ (2018) Host-associated bacterial community succession during amphibian development. Molecular Ecology, 27, 1992-2006.
DOI PMID |
| [103] |
Rohwer F (2003) Global phage diversity. Cell, 113, 141.
PMID |
| [104] |
Röttjers L, Faust K (2019) Can we predict keystones? Nature Reviews Microbiology, 17, 193.
DOI PMID |
| [105] |
Seabloom EW, Borer ET, Gross K, Kendig AE, Lacroix C, Mitchell CE, Mordecai EA, Power AG (2015) The community ecology of pathogens: Coinfection, coexistence and community composition. Ecology Letters, 18, 401-415.
DOI PMID |
| [106] |
Sheik CS, Beasley WH, Elshahed MS, Zhou XH, Luo YQ, Krumholz LR (2011) Effect of warming and drought on grassland microbial communities. The ISME Journal, 5, 1692-1700.
DOI URL |
| [107] |
Shen CC, Liang WJ, Shi Y, Lin XG, Zhang HY, Wu X, Xie G, Chain P, Grogan P, Chu HY (2014) Contrasting elevational diversity patterns between eukaryotic soil microbes and plants. Ecology, 95, 3190-3202.
DOI URL |
| [108] | Smith SE, Read DJ (2008) Mycorrhizal Symbiosis, 3rd edn. Academic Press, New York. |
| [109] | Soudzilovskaia NA, Vaessen S, Barcelo M, He JH, Rahimlou S, Abarenkov K, Brundrett MC, Gomes SIF, Merckx V, Tedersoo L (2020) FungalRoot: Global online database of plant mycorrhizal associations. New Phytologist, 227, 955-966. |
| [110] |
Stegen JC, Lin XJ, Fredrickson JK, Konopka AE (2015) Estimating and mapping ecological processes influencing microbial community assembly. Frontiers in Microbiology, 6, 370.
DOI PMID |
| [111] | Taylor JW, Branco S, Gao C, Hann-Soden C, Montoya L, Sylvain I, Gladieux P (2017) Sources of fungal genetic variation and associating it with phenotypic diversity. n: The Fungal Kingdom (eds Heitman J, Crous PW, Gow NAR, Howlett BJ, James TY, Stukenbrock EH). ASM Press, Washington. |
| [112] |
Tedersoo L, Bahram M, Põlme S, Kõljalg U, Yorou NS, Wijesundera R, Ruiz LV, Vasco-Palacios AM, Thu PQ, Suija A, Smith ME, Sharp C, Saluveer E, Saitta A, Rosas M, Riit T, Ratkowsky D, Pritsch K, Põldmaa K, Piepenbring M, Phosri C, Peterson M, Parts K, Pärtel K, Otsing E, Nouhra E, Njouonkou AL, Nilsson RH, Morgado LN, Mayor J, May TW, Majuakim L, Lodge DJ, Lee SS, Larsson KH, Kohout P, Hosaka K, Hiiesalu I, Henkel TW, Harend H, Guo LD, Greslebin A, Grelet G, Geml J, Gates G, Dunstan W, Dunk C, Drenkhan R, Dearnaley J, de Kesel A, Dang T, Chen X, Buegger F, Brearley FQ, Bonito G, Anslan S, Abell S, Abarenkov K (2014) Global diversity and geography of soil fungi. Science, 346, 1256688.
DOI URL |
| [113] |
Tedersoo L, Nara K (2010) General latitudinal gradient of biodiversity is reversed in ectomycorrhizal fungi. New Phytologist, 185, 351-354.
DOI PMID |
| [114] |
Thurber RV (2009) Current insights into phage biodiversity and biogeography. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 12, 582-587.
DOI PMID |
| [115] |
Tian J, He NP, Hale L, Niu SL, Yu GR, Liu Y, Blagodatskaya E, Kuzyakov Y, Gao Q, Zhou JZ (2018) Soil organic matter availability and climate drive latitudinal patterns in bacterial diversity from tropical to cold temperate forests. Functional Ecology, 32, 61-70.
DOI URL |
| [116] |
Treseder KK, Lennon JT (2015) Fungal traits that drive ecosystem dynamics on land. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 79, 243-262.
DOI PMID |
| [117] |
Tripathi BM, Stegen JC, Kim M, Dong K, Adams JM, Lee YK (2018) Soil pH mediates the balance between stochastic and deterministic assembly of bacteria. The ISME Journal, 12, 1072-1083.
DOI URL |
| [118] |
Vályi K, Mardhiah U, Rillig MC, Hempel S (2016) Community assembly and coexistence in communities of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. The ISME Journal, 10, 2341-2351.
DOI URL |
| [119] |
van der Linde S, Suz LM, Orme CDL, Cox F, Andreae H, Asi E, Atkinson B, Benham S, Carroll C, Cools N, de Vos B, Dietrich HP, Eichhorn J, Gehrmann J, Grebenc T, Gweon HS, Hansen K, Jacob F, Kristöfel F, Lech P, Manninger M, Martin J, Meesenburg H, Merilä P, Nicolas M, Pavlenda P, Rautio P, Schaub M, Schröck HW, Seidling W, Šrámek V, Thimonier A, Thomsen IM, Titeux H, Vanguelova E, Verstraeten A, Vesterdal L, Waldner P, Wijk S, Zhang YX, Žlindra D, Bidartondo MI (2018) Environment and host as large-scale controls of ectomycorrhizal fungi. Nature, 558, 243-248.
DOI URL |
| [120] |
van’t Padje A, Oyarte Galvez L, Klein M, Hink MA, Postma M, Shimizu T, Kiers ET (2021) Temporal tracking of quantum-dot apatite across in vitro mycorrhizal networks shows how host demand can influence fungal nutrient transfer strategies. The ISME Journal, 15, 435-449.
DOI URL |
| [121] |
Velez P, Espinosa-Asuar L, Figueroa M, Gasca-Pineda J, Aguirre-von-Wobeser E, Eguiarte LE, Hernandez-Monroy A, Souza V (2018) Nutrient dependent cross-kingdom interactions: Fungi and bacteria from an oligotrophic desert oasis. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9, 1755.
DOI PMID |
| [122] |
Vellend M (2010) Conceptual synthesis in community ecology. The Quarterly Review of Biology, 85, 183-206.
DOI URL |
| [123] | Vellend M (2016) The Theory of Ecological Communities. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [124] |
Vellend M, Srivastava DS, Anderson KM, Brown CD, Jankowski JE, Kleynhans EJ, Kraft NJB, Letaw AD, Macdonald AAM, Maclean JE, Myers-Smith IH, Norris AR, Xue XX (2014) Assessing the relative importance of neutral stochasticity in ecological communities. Oikos, 123, 1420-1430.
DOI URL |
| [125] |
Větrovský T, Kohout P, Kopecký M, Machac A, Man M, Bahnmann BD, Brabcová V, Choi J, Meszárošová L, Human ZR, Lepinay C, Lladó S, López-Mondéjar R, Martinović T, Mašínová T, Morais D, Navrátilová D, Odriozola I, Štursová M, Švec K, Tláskal V, Urbanová M, Wan J, Žifčáková L, Howe A, Ladau J, Peay KG, Storch D, Wild J, Baldrian P (2019) A meta-analysis of global fungal distribution reveals climate-driven patterns. Nature Communications, 10, 5142.
DOI PMID |
| [126] |
Wang BL, Liu N, Yang ML, Wang LJ, Liang X, Liu CQ (2021) Co-occurrence of planktonic bacteria and archaea affects their biogeographic patterns in China’s coastal wetlands. Environmental Microbiome, 16, 19.
DOI URL |
| [127] |
Wang JT, Zhang YB, Xiao Q, Zhang LM (2022) Archaea is more important than bacteria in driving soil stoichiometry in phosphorus deficient habitats. Science of the Total Environment, 827, 154417.
DOI URL |
| [128] |
Wang S, Wang XB, Han XG, Deng Y (2018) Higher precipitation strengthens the microbial interactions in semi- arid grassland soils. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 27, 570-580.
DOI URL |
| [129] | Waters CN, Zalasiewicz J, Summerhayes C, Barnosky AD, Poirier C, Gałuszka A, Cearreta A, Edgeworth M, Ellis EC, Ellis M, Jeandel C, Leinfelder R, McNeill JR, Richter DD, Steffen W, Syvitski J, Vidas D, Wagreich M, Williams M, An ZS, Grinevald J, Odada E, Oreskes N, Wolfe AP (2016) The Anthropocene is functionally and stratigraphically distinct from the Holocene. Science, 351, aad2622. |
| [130] |
Westoby M, Gillings MR, Madin JS, Nielsen DA, Paulsen IT, Tetu SG (2021) Trait dimensions in bacteria and archaea compared to vascular plants. Ecology Letters, 24, 1487-1504.
DOI URL |
| [131] |
Wipf D, Krajinski F, van Tuinen D, Recorbet G, Courty PE (2019) Trading on the arbuscular mycorrhiza market: From arbuscules to common mycorrhizal networks. New Phytologist, 223, 1127-1142.
DOI PMID |
| [132] |
Wu LW, Zhang Y, Guo X, Ning DL, Zhou XS, Feng JJ, Yuan MM, Liu S, Guo JJ, Gao ZP, Ma J, Kuang JL, Jian SY, Han S, Yang ZF, Ouyang Y, Fu Y, Xiao NJ, Liu XD, Wu LY, Zhou AF, Yang YF, Tiedje JM, Zhou JZ (2022) Reduction of microbial diversity in grassland soil is driven by long-term climate warming. Nature Microbiology, 7, 1054-1062.
DOI URL |
| [133] |
Xu L, Dong ZB, Chiniquy D, Pierroz G, Deng SW, Gao C, Diamond S, Simmons T, Wipf HML, Caddell D, Varoquaux N, Madera MA, Hutmacher R, Deutschbauer A, Dahlberg JA, Guerinot ML, Purdom E, Banfield JF, Taylor JW, Lemaux PG, Coleman-Derr D (2021) Genome-resolved metagenomics reveals role of iron metabolism in drought-induced rhizosphere microbiome dynamics. Nature Communications, 12, 3209.
DOI PMID |
| [134] | Xu L, Naylor D, Dong ZB, Simmons T, Pierroz G, Hixson KK, Kim YM, Zink EM, Engbrecht KM, Wang Y, Gao C, DeGraaf S, Madera MA, Sievert JA, Hollingsworth J, Birdseye D, Scheller HV, Hutmacher R, Dahlberg J, Jansson C, Taylor JW, Lemaux PG, Coleman-Derr D (2018) Drought delays development of the Sorghum root microbiome and enriches for monoderm bacteria. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 115, E4284-E4293. |
| [135] |
Yang T, Tedersoo L, Soltis PS, Soltis DE, Gilbert JA, Sun M, Shi Y, Wang HF, Li YT, Zhang J, Chen ZD, Lin HY, Zhao YP, Fu CX, Chu HY (2019) Phylogenetic imprint of woody plants on the soil mycobiome in natural mountain forests of Eastern China. The ISME Journal, 13, 686-697.
DOI URL |
| [136] |
Yang YF (2021) Emerging patterns of microbial functional traits. Trends in Microbiology, 29, 874-882.
DOI URL |
| [137] |
Zanne AE, Abarenkov K, Afkhami ME, Aguilar-Trigueros CA, Bates S, Bhatnagar JM, Busby PE, Christian N, Cornwell WK, Crowther TW, Flores-Moreno H, Floudas D, Gazis R, Hibbett D, Kennedy P, Lindner DL, Maynard DS, Milo AM, Nilsson RH, Powell J, Schildhauer M, Schilling J, Treseder KK (2020) Fungal functional ecology: Bringing a trait-based approach to plant-associated fungi. Biological Reviews, 95, 409-433
DOI |
| [138] |
Zhang Q, Li Y, Xing JJ, Brookes PC, Xu JM (2019) Soil available phosphorus content drives the spatial distribution of archaeal communities along elevation in acidic terrace paddy soils. Science of the Total Environment, 658, 723-731.
DOI |
| [139] |
Zhang XM, Johnston ER, Liu W, Li LH, Han XG (2016) Environmental changes affect the assembly of soil bacterial community primarily by mediating stochastic processes. Global Change Biology, 22, 198-207.
DOI PMID |
| [140] |
Zhang ZF, Pan J, Pan YP, Li M (2021) Biogeography, assembly patterns, driving factors, and interactions of archaeal community in mangrove sediments. mSystems, 6, e0138120.
DOI URL |
| [141] |
Zheng Y, Chen L, Ji NN, Wang YL, Gao C, Jin SS, Hu HW, Huang ZQ, He JZ, Guo LD, Powell JR (2021) Assembly processes lead to divergent soil fungal communities within and among 12 forest ecosystems along a latitudinal gradient. New Phytologist, 231, 1183-1194.
DOI PMID |
| [142] |
Zhou JZ, Deng Y, Shen LN, Wen CQ, Yan QY, Ning DL, Qin YJ, Xue K, Wu LY, He ZL, Voordeckers JW, Nostrand JDV, Buzzard V, Michaletz ST, Enquist BJ, Weiser MD, Kaspari M, Waide R, Yang YF, Brown JH (2016) Temperature mediates continental-scale diversity of microbes in forest soils. Nature Communications, 7, 12083.
DOI PMID |
| [143] | Zhou JZ, Deng Y, Zhang P, Xue K, Liang YT, van Nostrand JD, Yang YF, He ZL, Wu LY, Stahl DA, Hazen TC, Tiedje JM, Arkin AP (2014) Stochasticity, succession, and environmental perturbations in a fluidic ecosystem. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 111, E836-E845. |
| [144] | Zhou JZ, Ning DL (2017) Stochastic community assembly: Does it matter in microbial ecology? Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 81, e00002-00017. |
| [145] |
Zhou ZH, Wang CK, Luo YQ (2020) Meta-analysis of the impacts of global change factors on soil microbial diversity and functionality. Nature Communications, 11, 3072.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 罗敏, 杨永川, 靳程, 周礼华, 龙宇潇. 城市森林兽类组成特征及人类活动的影响——以重庆中心城区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24402-. |
| [3] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [4] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [5] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [6] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [7] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [8] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [9] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [10] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [11] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [12] | 靳川, 张子嘉, 底凯, 张卫荣, 乔栋, 程思源, 胡中民. 海南热带雨林植物光合荧光气体交换和叶功能性状数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24139-. |
| [13] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [14] | 白雪, 李正飞, 刘洋, 张君倩, 张多鹏, 罗鑫, 杨佳莉, 杜丽娜, 蒋玄空, 武瑞文, 谢志才. 西江流域大型底栖无脊椎动物物种多样性及维持机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [15] | 许佳, 崔小娟, 张翼飞, 吴昌, 孙远东. 南岭地区鱼类多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()