



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 21448. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021448 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021448
所属专题: 昆虫多样性与生态功能
韩艺茹1,2, 薛琪琪1,2, 宋厚娟1, 祁靖宇1,2, 高瑞贺1,2, 崔绍朋1,2, 门丽娜1,2,*( ), 张志伟1,2,*(
), 张志伟1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-11-09
接受日期:2022-01-29
出版日期:2022-03-20
发布日期:2022-03-02
通讯作者:
门丽娜,张志伟
作者简介:linamen81@163.com基金资助:
Yiru Han1,2, Qiqi Xue1,2, Houjuan Song1, Jingyu Qi1,2, Ruihe Gao1,2, Shaopeng Cui1,2, Lina Men1,2,*( ), Zhiwei Zhang1,2,*(
), Zhiwei Zhang1,2,*( )
)
Received:2021-11-09
Accepted:2022-01-29
Online:2022-03-20
Published:2022-03-02
Contact:
Lina Men,Zhiwei Zhang
摘要:
为了解燕山地区访花昆虫的群落结构及与其生境类型、干扰程度、海拔之间的关系, 本文采用样线法和灯诱法于2019年、2020年每年的7-8月对该地区湿地、森林、灌丛、草地、农田5种生境, 不同海拔梯度(0-1,200 m)的访花昆虫进行了采集。共采集访花昆虫1,306头, 隶属7目44科153种, 其中鳞翅目昆虫物种数最多, 半翅目昆虫个体数最多。灌丛生境的访花昆虫多样性最高。在中低海拔200-400 m段, Shannon-Wiener多样性指数、Margalef丰富度指数和Simpson优势度指数均最高。双变量回归结果表明, Shannon-Wiener多样性指数和Margalef丰富度指数分别与最暖季降水量和年降水量显著正相关(P < 0.05)。冗余分析(redundancy analysis)结果表明, 环境因子显著影响访花昆虫多样性, 但不同测度之间存在一定差异。温度和湿度均与Pielou均匀度指数呈正相关, 与Shannon-Wiener多样性指数、Margalef丰富度指数和Simpson优势度指数呈负相关; 弱干扰和中干扰程度对访花昆虫多样性影响最小, 科学管理农牧活动是保护访花昆虫多样性的关键。
韩艺茹, 薛琪琪, 宋厚娟, 祁靖宇, 高瑞贺, 崔绍朋, 门丽娜, 张志伟 (2022) 燕山地区访花昆虫多样性及其影响因子. 生物多样性, 30, 21448. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021448.
Yiru Han, Qiqi Xue, Houjuan Song, Jingyu Qi, Ruihe Gao, Shaopeng Cui, Lina Men, Zhiwei Zhang (2022) Diversity and influencing factors of flower-visiting insects in the Yanshan area. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21448. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021448.
| 类群 Order | 科数 No. of families | 种数 No. of species | 个体数 No. of individuals |
|---|---|---|---|
| 螳螂目 Mantodea | 1 (2.27%) | 2 (1.32%) | 20 (1.53%) |
| 直翅目 Orthoptera | 3 (6.82%) | 4 (2.62%) | 51 (3.91%) |
| 半翅目 Hemiptera | 8 (18.18%) | 35 (22.88%) | 634 (48.55%) |
| 鞘翅目 Coleoptera | 8 (18.18%) | 33 (21.57%) | 341 (26.11%) |
| 双翅目 Diptera | 6 (13.65%) | 17 (11.11%) | 60 (4.59%) |
| 鳞翅目 Lepidoptera | 9 (20.45%) | 40 (26.14%) | 98 (7.5%) |
| 膜翅目 Hymenoptera | 9 (20.45%) | 22 (14.37%) | 102 (7.81%) |
| 合计 Total | 44 | 153 | 1,306 |
表1 燕山地区访花昆虫群落结构
Table 1 Composition and structure of flower-visiting insect communities in the Yanshan area
| 类群 Order | 科数 No. of families | 种数 No. of species | 个体数 No. of individuals |
|---|---|---|---|
| 螳螂目 Mantodea | 1 (2.27%) | 2 (1.32%) | 20 (1.53%) |
| 直翅目 Orthoptera | 3 (6.82%) | 4 (2.62%) | 51 (3.91%) |
| 半翅目 Hemiptera | 8 (18.18%) | 35 (22.88%) | 634 (48.55%) |
| 鞘翅目 Coleoptera | 8 (18.18%) | 33 (21.57%) | 341 (26.11%) |
| 双翅目 Diptera | 6 (13.65%) | 17 (11.11%) | 60 (4.59%) |
| 鳞翅目 Lepidoptera | 9 (20.45%) | 40 (26.14%) | 98 (7.5%) |
| 膜翅目 Hymenoptera | 9 (20.45%) | 22 (14.37%) | 102 (7.81%) |
| 合计 Total | 44 | 153 | 1,306 |
| 类群 Order | 湿地 Wetland | 草地 Grassland | 农田 Farmland | 灌丛 Shrub | 森林 Forest | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 科数 F | 种数 S | 个体数 Ind. | 科数 F | 种数 S | 个体数 Ind. | 科数 F | 种数 S | 个体数 Ind. | 科数 F | 种数 S | 个体数 Ind. | 科数 F | 种数 S | 个体数 Ind. | |
| 螳螂目 Mantodea | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 6 |
| 直翅目 Orthoptera | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 4 | 29 | 2 | 2 | 7 |
| 半翅目 Hemiptera | 4 | 4 | 22 | 5 | 15 | 293 | 5 | 7 | 54 | 7 | 24 | 145 | 6 | 23 | 120 |
| 鞘翅目 Coleoptera | 3 | 3 | 15 | 6 | 15 | 139 | 3 | 5 | 15 | 6 | 21 | 106 | 7 | 17 | 66 |
| 双翅目 Diptera | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 13 | 4 | 8 | 17 | 6 | 10 | 21 |
| 鳞翅目 Lepidoptera | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 6 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 11 | 13 | 9 | 30 | 73 |
| 膜翅目 Hymenoptera | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 6 | 10 | 3 | 3 | 12 | 6 | 12 | 49 | 5 | 8 | 30 |
| 合计 Total | 10 | 10 | 41 | 26 | 47 | 473 | 15 | 19 | 105 | 32 | 81 | 364 | 37 | 92 | 323 |
表2 燕山地区不同生境下访花昆虫群落结构
Table 2 Composition and structure of flower-visiting insects communities under different habitats in the Yanshan area
| 类群 Order | 湿地 Wetland | 草地 Grassland | 农田 Farmland | 灌丛 Shrub | 森林 Forest | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 科数 F | 种数 S | 个体数 Ind. | 科数 F | 种数 S | 个体数 Ind. | 科数 F | 种数 S | 个体数 Ind. | 科数 F | 种数 S | 个体数 Ind. | 科数 F | 种数 S | 个体数 Ind. | |
| 螳螂目 Mantodea | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 6 |
| 直翅目 Orthoptera | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 4 | 29 | 2 | 2 | 7 |
| 半翅目 Hemiptera | 4 | 4 | 22 | 5 | 15 | 293 | 5 | 7 | 54 | 7 | 24 | 145 | 6 | 23 | 120 |
| 鞘翅目 Coleoptera | 3 | 3 | 15 | 6 | 15 | 139 | 3 | 5 | 15 | 6 | 21 | 106 | 7 | 17 | 66 |
| 双翅目 Diptera | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 13 | 4 | 8 | 17 | 6 | 10 | 21 |
| 鳞翅目 Lepidoptera | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 6 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 11 | 13 | 9 | 30 | 73 |
| 膜翅目 Hymenoptera | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 6 | 10 | 3 | 3 | 12 | 6 | 12 | 49 | 5 | 8 | 30 |
| 合计 Total | 10 | 10 | 41 | 26 | 47 | 473 | 15 | 19 | 105 | 32 | 81 | 364 | 37 | 92 | 323 |
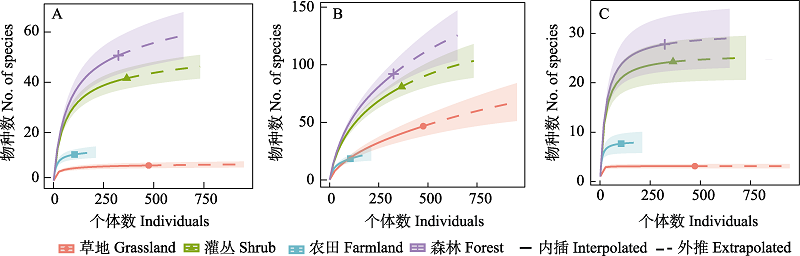
图1 燕山地区不同生境访花昆虫多样性。(A) Shannon-Wiener 多样性; (B) 物种丰富度; (C) Simpson 多样性。
Fig. 1 Diversity of flower-visiting insects under different habitats in the Yanshan area. (A) Shannon-Wiener diversity; (B) Species richnes; (C) Simpson diversity.
| 类群 Orders | 0-200 m | 200-400 m | 400-600 m | 600-800 m | 800-1000 m | 1000-1200 m | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 科数 F | 种数 S | 个体数 Ind. | 科数 F | 种数 S | 个体数 Ind. | 科数 F | 种数 S | 个体数 Ind. | 科数 F | 种数 S | 个体数 Ind. | 科数 F | 种数 S | 个体数 Ind. | 科数 F | 种数 S | 个体数 Ind. | |
| 螳螂目 Mantodea | 1 | 1 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 直翅目 Orthoptera | 2 | 2 | 17 | 2 | 2 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| 半翅目 Hemiptera | 5 | 13 | 296 | 6 | 14 | 44 | 8 | 24 | 166 | 7 | 20 | 57 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 11 | 64 |
| 鞘翅目 Coleoptera | 6 | 16 | 155 | 5 | 15 | 44 | 7 | 20 | 95 | 3 | 8 | 24 | 2 | 4 | 12 | 2 | 3 | 11 |
| 双翅目 Diptera | 2 | 3 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 11 | 6 | 9 | 26 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 9 |
| 鳞翅目 Lepidoptera | 5 | 6 | 12 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 8 | 19 | 39 | 7 | 19 | 35 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 膜翅目 Hymenoptera | 4 | 6 | 21 | 7 | 8 | 11 | 6 | 11 | 34 | 4 | 6 | 15 | 3 | 3 | 14 | 3 | 3 | 7 |
| 合计 Total | 25 | 47 | 519 | 31 | 53 | 136 | 38 | 86 | 379 | 25 | 57 | 143 | 9 | 12 | 35 | 15 | 22 | 94 |
表3 燕山地区不同海拔访花昆虫群落结构
Table 3 Composition and structure of flower-visiting insects community under different altitudes in the Yanshan area
| 类群 Orders | 0-200 m | 200-400 m | 400-600 m | 600-800 m | 800-1000 m | 1000-1200 m | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 科数 F | 种数 S | 个体数 Ind. | 科数 F | 种数 S | 个体数 Ind. | 科数 F | 种数 S | 个体数 Ind. | 科数 F | 种数 S | 个体数 Ind. | 科数 F | 种数 S | 个体数 Ind. | 科数 F | 种数 S | 个体数 Ind. | |
| 螳螂目 Mantodea | 1 | 1 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 直翅目 Orthoptera | 2 | 2 | 17 | 2 | 2 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| 半翅目 Hemiptera | 5 | 13 | 296 | 6 | 14 | 44 | 8 | 24 | 166 | 7 | 20 | 57 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 11 | 64 |
| 鞘翅目 Coleoptera | 6 | 16 | 155 | 5 | 15 | 44 | 7 | 20 | 95 | 3 | 8 | 24 | 2 | 4 | 12 | 2 | 3 | 11 |
| 双翅目 Diptera | 2 | 3 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 11 | 6 | 9 | 26 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 9 |
| 鳞翅目 Lepidoptera | 5 | 6 | 12 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 8 | 19 | 39 | 7 | 19 | 35 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 膜翅目 Hymenoptera | 4 | 6 | 21 | 7 | 8 | 11 | 6 | 11 | 34 | 4 | 6 | 15 | 3 | 3 | 14 | 3 | 3 | 7 |
| 合计 Total | 25 | 47 | 519 | 31 | 53 | 136 | 38 | 86 | 379 | 25 | 57 | 143 | 9 | 12 | 35 | 15 | 22 | 94 |
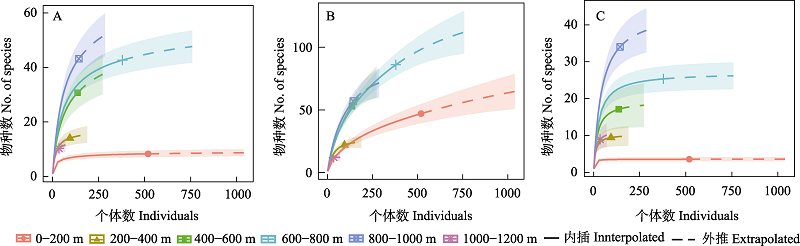
图4 燕山地区不同海拔访花昆虫多样性。(A) Shannon-Wiener 多样性; (B) 物种丰富度; (C) Simpson 多样性。
Fig. 4 Diversity of flower-visiting insects under different altitudes in Yanshan area. (A) Shannon-Wiener diversity; (B) Species richnes; (C) Simpson diversity.
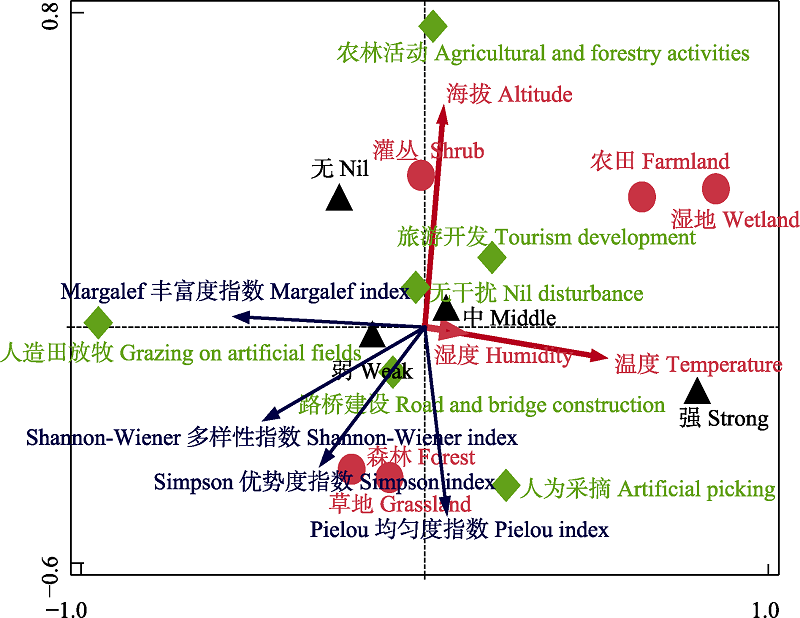
图7 燕山地区访花昆虫群落多样性与环境因子的RDA排序。 生境类型; 干扰程度; 干扰类型。
Fig. 7 RDA sequence diagram of community diversity of flower-visiting insects and five environmental factors in the Yanshan area. Habitat type; Disturbance degree; Disturbance type.
| [1] | Chou I (2000) Monographia Rhopalocerorum Sinensium. Henan Scientific andTechnological Publishing House, Zhengzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [ 周尧 (2000) 中国蝶类志. 河南科学技术出版社, 郑州.] | |
| [2] | Du XJ, Ji GQ, Zhang F, Wu XQ, Zhao LX, Qin DF (2021) Diversity of flower-visiting insects from various habitats in Shanxi Province. Journal of Jilin Forestry Science and Technology, 50(1), 25-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杜秀娟, 吉国强, 张芳, 武新琴, 赵立曦, 秦东凤 (2021) 山西省几种生境访显花昆虫多样性分析. 吉林林业科技, 50(1), 25-30.] | |
| [3] | Du XJ, Ren BZ, Wu YG, Song LW (2009) Differences of flower-visiting hoverfly (Diptera: Syrphidae) communities in habitats with various degrees of disturbance and altitude in Changbai Mountain, N. E. China. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 52, 551-560. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杜秀娟, 任炳忠, 吴艳光, 宋丽文 (2009) 长白山北坡不同海拔及干扰程度下访花食蚜蝇群落的差异. 昆虫学报, 52, 551-560.] | |
| [4] | Feng LC, Meng QF, Gao WT (2015) Diversity and behavior of flower visitors insects of Malus komarovii in the southwest slope of Changbai Mountain. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 42(3), 147-152. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 冯立超, 孟庆繁, 高文韬 (2015) 长白山西南坡山楂海棠访花昆虫多样性及其行为研究. 广东农业科学, 42(3), 147-152.] | |
| [5] | Feng YQ (2017) Cold Hardiess and Adaptive Mechanism of the Anoplophora glabripennis Larva. PhD dissertation, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 冯宇倩 (2017) 光肩星天牛幼虫的耐寒性及其适应机制. 博士学位论文, 北京林业大学, 北京.] | |
| [6] | Hebert P, Cywinska A, Ball SL, Dewaard JR (2003) Biological identification through DNA barcodes. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological ences, 270, 313-321. |
| [7] |
Hsieh TC, Ma KH, Chao A (2016) iNEXT: An R package for rarefaction and extrapolation of species diversity (Hill numbers). Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 7, 1451-1456.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Jaccard P (1912) The distribution of the flora in the alpine zone. New Phytologist, 11, 37-50.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Kehinde T, Samways MJ (2014) Effects of vineyard management on biotic homogenization of insect-flower interaction networks in the Cape Floristic Region biodiversity hotspot. Journal of Insect Conservation, 18, 469-477.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Li HR (2004) Review on study of biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 23(3), 109-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李慧蓉 (2004) 生物多样性和生态系统功能研究综述. 生态学杂志, 23(3), 109-114.] | |
| [11] | Li ML (2005) Resource Entomology. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李孟楼 (2005) 资源昆虫学. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [12] | Li SH (2002) On fauna of butterflies in Chongqing and their geographic division. Journal of Southwest Agricultural University, 24, 542-545. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李树恒 (2002) 重庆蝶类区系与地理区划的探讨. 西南农业大学学报, 24, 542-545.] | |
| [13] | Li XY, Yang YC, He ZS, Yang GJ (2020) Diversity of butterflies community and its environmental factors in Helan Mountain Nature Reserve, Ningxia. Journal of Environmental Entomology, 42, 660-673. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李欣芸, 杨益春, 贺泽帅, 杨贵军 (2020) 宁夏贺兰山自然保护区蝴蝶群落多样性及其环境影响因子. 环境昆虫学报, 42, 660-673.] | |
| [14] | Liu LD, Li W, Zhu N, Shen JH, Zhao HX (2002) The relations among the nectar secretive rhythms, nectar compositions and diversities of floral visitors for both Eleutherococcus senticosus and E. sessiliflorus. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 22, 847-853. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘林德, 李玮, 祝宁, 申家恒, 赵惠勋 (2002) 刺五加、短梗五加的花蜜分泌节律、花蜜成分及访花者多样性的比较研究. 生态学报, 22, 847-853.] | |
| [15] | Liu S, Lü ZY, Gao HH, Zhai YF, Liu Q, Yang PY, Li P, Zheng L, Li Q, Yu Y (2018) Research advances on flight capacity of insect. Journal of Environmental Entomology, 40, 995-1002. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘莎, 吕召云, 高欢欢, 翟一凡, 刘倩, 杨普云, 李萍, 郑礼, 李强, 于毅 (2018) 昆虫飞行能力研究进展. 环境昆虫学报, 40, 995-1002.] | |
| [16] | Ma KP, Huang JH, Yu SL, Chen LZ (1995) Plant community diversity in Dongling Mountain, Beijing, China. II. Species richness, evenness and species diversities. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 15, 268-277. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马克平, 黄建辉, 于顺利, 陈灵芝 (1995) 北京东灵山地区植物群落多样性的研究. Ⅱ. 丰富度、均匀度和物种多样性指数. 生态学报, 15, 268-277.] | |
| [17] | Nedvěd O (1998) Modelling the relationship between cold injury and accumulated degree days in terrestrial arthropods. Cryo-Letters, 19, 267-274.] |
| [18] | North China Agricultural University (1997) Moths of North China (I). North China Agricultural University Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 华北农业大学 (1997) 华北灯下蛾类图志 (上). 华北农业大学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [19] | Qin JD, Wang CZ (2001) The relation of interaction between insects and plants to evolution. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 44, 360-365. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 钦俊德, 王琛柱 (2001) 论昆虫与植物的相互作用和进化的关系. 昆虫学报, 44, 360-365.] | |
| [20] | Qian YQ, Ma KP (1994) Principles and Methods of Biodiversity Research. China Science & Technology Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 钱迎倩, 马克平 (1994) 生物多样性研究的原理与方法. 中国科学技术出版社, 北京.] | |
| [21] | Ren BZ, Shang LN, Gao Y, Wang XS, Lu Y, Dong Q (2012) Relationship between floral scent of the major nectar source plants and their flower visitors in Changbai Mountain region. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 34(1), 24-30, 36. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 任炳忠, 尚利娜, 高毅, 王雪松, 鲁莹, 董琴 (2012) 长白山地区优势蜜源植物花的气味与访花昆虫种类的关系. 吉林农业大学学报, 34(1), 24-30, 36.] | |
| [22] | Ren BZ, Wu YG, Du XJ, Guan ZY, Li N, Yuan HB (2006) Research on pollinators in north slope of Changbai Mountain Ⅲ): Diversity of pollinators. Journal of Northeast Normal University, 38(3), 96-100. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 任炳忠, 吴艳光, 杜秀娟, 官昭瑛, 李娜, 袁海滨 (2006) 长白山北坡访花昆虫研究(Ⅲ): 访花昆虫多样性. 东北师大学报(自然科学版), 38(3), 96-100.] | |
| [23] | Shang LN (2010) Coadaptation of Flowers and Their Visitors in Changbai Mountain Region. PhD dissertation, Northeast Normal University, Changchun. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 尚利娜 (2010) 长白山地区访花昆虫与蜜源植物的协同适应. 博士学位论文, 东北师范大学, 长春.] | |
| [24] | Shang LN, Wang P, Lu Y, Gao Y, Zhang X, Yu C, Ren BZ (2012) Diversity and spatio-temporal dynamics of flower visitors in the northern slope of Changbai Mountain. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 34, 395-408. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 尚利娜, 王璞, 鲁莹, 高毅, 张雪, 于晨, 任炳忠 (2012) 长白山北坡访花昆虫的多样性及时空动态. 吉林农业大学学报, 34, 395-408.] | |
| [25] | Song HT, Li BP, Meng L (2013) Flower-visiting insect diversity of the alien plant Erigeron annuus (Asteraceae) in Nanjing, southeastern China and an analysis of factors influencing their foraging preference. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 56, 293-298. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 宋海天, 李保平, 孟玲 (2013) 南京地区外来植物一年蓬上访花昆虫的多样性及其访花选择性的影响因素分析. 昆虫学报, 56, 293-298.] | |
| [26] |
Sousa PF, Eduardo PC, De B, Lucia I, Cristina GT (2021) Edible fruit plant species in the Amazon forest rely mostly on bees and beetles as pollinators. Journal of Economic Entomology, 114, 710-722.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Uhl P, Brühl CA (2019) The impact of pesticides on flower-visiting insects: A review with regard to European risk assessment. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 38, 2355-2370.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Wang MN, Lu XL, Cui Y, Wang MR, Ding SY (2018) Effects of woodland types with different levels of human disturbance on pollinators: A case study in Gongyi, Henan, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 464-474. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王美娜, 卢训令, 崔洋, 王梦茹, 丁圣彦 (2018) 不同人为干扰下林地类型对传粉昆虫的影响--以河南省巩义市为例. 生态学报, 38, 464-474.] | |
| [29] |
Wardhaugh KG (1980) The effects of temperature and moisture on the inception of diapause in eggs of the Australian plague locust, Chortoicetes terminifera Walker (Orthoptera: Acrididae). Austral Ecology, 5, 187-191.]
DOI URL |
| [30] | Wei XP, Lin P, Wang H, Li Y, Li HJ, He XJ (2020) Pollinator diversity of Camellia oleifera forest and foraging behavior of dominant species under different habitat of Guizhou. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 33, 2145-2152. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 韦小平, 林平, 王海, 李应, 黎华君, 贺兴江 (2020) 贵州不同生境油茶林传粉昆虫的多样性及其优势种的访花行为. 西南农业学报, 33, 2145-2152.] | |
| [31] | Yang YC, Yang GJ, Wang J (2017) Effects of topographic factors on the distribution pattern of carabid species diversity in the Helan Mountains, northwestern China. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 60, 1060-1073. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨益春, 杨贵军, 王杰 (2017) 地形对贺兰山步甲群落物种多样性分布格局的影响. 昆虫学报, 60, 1060-1073.] | |
| [32] | Yu GY (2019) Photographic Atlas of Beijing Flower-visiting Insects. Publishing House of Electronics Industry, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 虞国跃 (2019) 北京访花昆虫图谱. 电子工业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [33] | Zhang J, Jiang XF, Chen LL, Li QJ (2017) Altitudinal variations of the reproductive strategies of Primula florindae. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 37, 1404-1413. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张杰, 蒋显锋, 陈玲玲, 李庆军 (2017) 巨伞钟报春繁殖策略随海拔梯度的变异. 西北植物学报, 37, 1404-1413.] | |
| [34] | Zhang ML, Wang RJ (2011) The status and trend of insect diversity conservation. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 48, 739-745. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张茂林, 王戎疆 (2011) 昆虫多样性的保护现状与趋势. 应用昆虫学报, 48, 739-745.] | |
| [35] | Zhang XF, Shao YQ (2014) Species and diversity analysis of flower-visiting insects of Asian sacred Lotus in Jiangxi, Hunan and Hubei provinces. Agricultural Science & Technology, 15, 269-274. |
| [36] | Zheng XX, Xiao NW, Zhao MH, Wen D, He SJ, Li XM, Yang FL, Wu G (2020) Investigation and evaluation of insect diversity in Xingshan County, Three Gorges Reservoir Area, Hubei Province, Central China. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 63, 1497-1507. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郑晓旭, 肖能文, 赵慕华, 文栋, 何帅洁, 李雪梅, 杨凤连, 吴刚 (2020) 湖北三峡库区兴山县昆虫多样性调查与评估. 昆虫学报, 63, 1497-1507.] | |
| [37] | Zhou LY, Ding SY, Lu XL, Liu YM (2020) Effects of anthropogenic disturbance on species diversity and niche of dominant group in pollinators community. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40, 2111-2121. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 周立垚, 丁圣彦, 卢训令, 刘娅萌 (2020) 人为干扰对传粉昆虫群落物种多样性及其优势类群生态位的影响. 生态学报, 40, 2111-2121.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [3] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [4] | 周昊, 王茗毅, 张楚格, 肖治术, 欧阳芳. 昆虫旅馆在独栖蜂多样性保护中的现状与挑战[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24472-. |
| [5] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [6] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [7] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [8] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [9] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [10] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [11] | 徐欢, 辛凤飞, 施宏亮, 袁琳, 薄顺奇, 赵欣怡, 邓帅涛, 潘婷婷, 余婧, 孙赛赛, 薛程. 生态修复技术集成应用对长江口北支生境与鸟类多样性提升效果评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24478-. |
| [12] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [13] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [14] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [15] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()