



生物多样性 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (1): 32-42. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020067 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020067
余宏昌1( ), 毕宝帅1(
), 毕宝帅1( ), 唐文乔1,2,*(
), 唐文乔1,2,*( )(
)( ), 张亚1,2(
), 张亚1,2( ), 郭弘艺1,2(
), 郭弘艺1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2020-03-02
接受日期:2020-05-23
出版日期:2021-01-20
发布日期:2020-09-12
通讯作者:
唐文乔
基金资助:
Hongchang Yu1( ), Baoshuai Bi1(
), Baoshuai Bi1( ), Wenqiao Tang1,2,*(
), Wenqiao Tang1,2,*( )(
)( ), Ya Zhang1,2(
), Ya Zhang1,2( ), Hongyi Guo1,2(
), Hongyi Guo1,2( )
)
Received:2020-03-02
Accepted:2020-05-23
Online:2021-01-20
Published:2020-09-12
Contact:
Wenqiao Tang
摘要:
为了评估近20年来上海苏州河环境综合整治过程中鱼类多样性的变化状况, 本文于2019年6月(夏季)和9月(秋季)对苏州河13个断面的鱼类样本进行了采集, 对鱼类多样性和群落结构作了分析。结果显示, 2次采集共获得鱼类样本10,102号, 隶属于8目15科37属45种。夏季和秋季, 上游8个断面的鱼类均为36种, 下游5个断面则为12种和15种。从上游到下游, Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(H')、Margalef种类丰富度指数(D)和Simpson优势度指数(C)总体呈逐渐降低的趋势。相对重要性指数(IRI)显示, 夏秋两季上游断面共同的优势种为似鳊(Pseudobrama simoni), 下游为鲫(Carassius auratus)和泥鳅(Misgurnus anguillicaudatus)。丰度生物量曲线表明, 全河段鱼类群落结构总体上并不稳定, 特别是夏季的下游河段。Cluster聚类和非参数多维标度排序分析可明显将鱼类群落分为上游群组(I)与下游群组(II), 似鳊、泥鳅、鲫、光泽黄颡鱼(Pelteobagrus nitidus)和兴凯鱊(Acheilognathus chankaensis)等是造成群组间差异性的主要分歧种。与2001年的43种、2006年的28种相比, 本次调查的物种数出现了明显回升, 特别是下游河段。这种上游鱼类向下游迁移的趋势, 预示着下游中心城区与上游郊区河段的水质差别正在缩小, 水生态系统恢复迹象明显。本文认为, 上下游之间鱼类群落结构差异的缩小以及翘嘴鲌(Culter alburnus)、红鳍原鲌(Cultrichthys erythropterus)、棒花鱼(Abbottina rivularis)、子陵吻虾虎鱼(Rhinogobius giurinus)等在下游河段的出现, 可作为苏州河综合整治效果的重要生态标志。
余宏昌, 毕宝帅, 唐文乔, 张亚, 郭弘艺 (2021) 上海苏州河治理中鱼类多样性及群落结构变化. 生物多样性, 29, 32-42. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020067.
Hongchang Yu, Baoshuai Bi, Wenqiao Tang, Ya Zhang, Hongyi Guo (2021) Changes in fish diversity and assemblage during comprehensive restoration of the Suzhou River in Shanghai. Biodiversity Science, 29, 32-42. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020067.
| 代号 Codes | 断面名称 Section names | 中心经纬度 Coordinates |
|---|---|---|
| 上游 Upstream | ||
| S1 | 赵屯 Zhaotun | 121°04′ E, 31°16′ N |
| S2 | 白鹤 Baihe | 121°08′ E, 31°16′ N |
| S3 | 油墩港 Youdungang | 121°09′ E, 31°14′ N |
| S4 | 蕰藻浜 Wenzaobang | 121°12′E, 31°18′ N |
| S5 | 黄渡 Huangdu | 121°12′ E, 31°15′ N |
| S6 | 新通波塘 Xintongbotang | 121°12′ E, 31°14′ N |
| S7 | 封浜河口 Fengbanghekou | 121°18′ E, 31°13′ N |
| S8 | 北新泾 Beixinjing | 121°22′ E, 31°13′ N |
| 下游 Downstream | ||
| S9 | 中山西路桥 Zhongshanxilu Bridge | 121°23′ E, 31°13′ N |
| S10 | 武宁路桥 Wuninglu Bridge | 121°25′ E, 31°14′ N |
| S11 | 昌化路桥 Changhualu Bridge | 121°26′ E, 31°15′ N |
| S12 | 成都路桥 Chengdulu Bridge | 121°27′ E, 31°14′ N |
| S13 | 外白渡桥 Waibaidu Bridge | 121°29′ E, 31°14′ N |
表1 上海苏州河各采样断面位置信息表
Table 1 The coordinates of sections of the Suzhou River in Shanghai
| 代号 Codes | 断面名称 Section names | 中心经纬度 Coordinates |
|---|---|---|
| 上游 Upstream | ||
| S1 | 赵屯 Zhaotun | 121°04′ E, 31°16′ N |
| S2 | 白鹤 Baihe | 121°08′ E, 31°16′ N |
| S3 | 油墩港 Youdungang | 121°09′ E, 31°14′ N |
| S4 | 蕰藻浜 Wenzaobang | 121°12′E, 31°18′ N |
| S5 | 黄渡 Huangdu | 121°12′ E, 31°15′ N |
| S6 | 新通波塘 Xintongbotang | 121°12′ E, 31°14′ N |
| S7 | 封浜河口 Fengbanghekou | 121°18′ E, 31°13′ N |
| S8 | 北新泾 Beixinjing | 121°22′ E, 31°13′ N |
| 下游 Downstream | ||
| S9 | 中山西路桥 Zhongshanxilu Bridge | 121°23′ E, 31°13′ N |
| S10 | 武宁路桥 Wuninglu Bridge | 121°25′ E, 31°14′ N |
| S11 | 昌化路桥 Changhualu Bridge | 121°26′ E, 31°15′ N |
| S12 | 成都路桥 Chengdulu Bridge | 121°27′ E, 31°14′ N |
| S13 | 外白渡桥 Waibaidu Bridge | 121°29′ E, 31°14′ N |
| 种类 Species | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上游 Upstream | 下游 Downstream | 上游 Upstream | 下游 Downstream | |
| 刀鲚 Coilia nasus | 1,045.89 | 154.59 | ||
| 翘嘴鲌 Culter alburnus | 130.01 | |||
| 达氏鲌 Culter dabryi | 920.05 | 827.64 | ||
| 红鳍原鲌 Cultrichthys erythropterus | 454.52 | 109.75 | ||
| 贝氏䱗 Hemiculter bleekeri | 1,116.50 | 139.41 | ||
| 䱗 Hemiculter leucisculus | 2,898.83 | 183.99 | ||
| 似鳊 Pseudobrama simoni | 10,159.54 | 309.94 | 11,302.52 | 756.94 |
| 麦穗鱼 Pseudorasbora parva | 391.31 | 244.64 | ||
| 兴凯鱊 Acheilognathus chankaensis | 1,024.73 | 976.12 | ||
| 大鳍鱊 Acheilognathus macropterus | 215.51 | |||
| 高体鳑鲏 Rhodeus ocellatus | 274.22 | |||
| 鲫 Carassius auratus | 549.44 | 6,752.95 | 1,798.81 | 7,029.52 |
| 鲤 Cyprinus carpio | 1,666.27 | |||
| 泥鳅 Misgurnus anguillicaudatus | 167.30 | 5,946.77 | 264.08 | 5,202.53 |
| 光泽黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus nitidus | 179.78 | 932.39 | ||
| 子陵吻虾虎鱼 Rhinogobius giurinus | 182.71 | |||
| 乌鳢 Channa argus | 1,334.40 | 765.65 | ||
表2 上海苏州河鱼类优势种(IRI ≥ 1,000)和常见种(100 ≤ IRI < 1,000)的相对重要性指数
Table 2 Index of relative importance (IRI) of the dominant (IRI ≥ 1,000) and common (100 ≤ IRI < 1,000) fish species of the Suzhou River in Shanghai
| 种类 Species | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上游 Upstream | 下游 Downstream | 上游 Upstream | 下游 Downstream | |
| 刀鲚 Coilia nasus | 1,045.89 | 154.59 | ||
| 翘嘴鲌 Culter alburnus | 130.01 | |||
| 达氏鲌 Culter dabryi | 920.05 | 827.64 | ||
| 红鳍原鲌 Cultrichthys erythropterus | 454.52 | 109.75 | ||
| 贝氏䱗 Hemiculter bleekeri | 1,116.50 | 139.41 | ||
| 䱗 Hemiculter leucisculus | 2,898.83 | 183.99 | ||
| 似鳊 Pseudobrama simoni | 10,159.54 | 309.94 | 11,302.52 | 756.94 |
| 麦穗鱼 Pseudorasbora parva | 391.31 | 244.64 | ||
| 兴凯鱊 Acheilognathus chankaensis | 1,024.73 | 976.12 | ||
| 大鳍鱊 Acheilognathus macropterus | 215.51 | |||
| 高体鳑鲏 Rhodeus ocellatus | 274.22 | |||
| 鲫 Carassius auratus | 549.44 | 6,752.95 | 1,798.81 | 7,029.52 |
| 鲤 Cyprinus carpio | 1,666.27 | |||
| 泥鳅 Misgurnus anguillicaudatus | 167.30 | 5,946.77 | 264.08 | 5,202.53 |
| 光泽黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus nitidus | 179.78 | 932.39 | ||
| 子陵吻虾虎鱼 Rhinogobius giurinus | 182.71 | |||
| 乌鳢 Channa argus | 1,334.40 | 765.65 | ||
| 种类 Species | 平均相似性贡献率 Average similarity contribution (%) | 平均相异性贡献率 Average dissimilarity contribution (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 群组I Group I | 群组II Group II | 群组I-群组II Group I-Group II | |
| 似鳊 Pseudobrama simoni | 66.34 | 4.43 | 26.37 |
| 䱗 Hemiculter leucisculus | 8.61 | 4.65 | |
| 兴凯鱊 Acheilognathus chankaensis | 7.18 | 5.63 | |
| 达氏鲌 Culter dabryi | 3.05 | 2.62 | |
| 鲫 Carassius auratus | 2.58 | 34.68 | 15.62 |
| 泥鳅 Misgurnus anguillicaudatus | 47.65 | 21.45 | |
| 光泽黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus nitidus | 4.36 | 6.19 | |
| 麦穗鱼 Pseudorasbora parva | 2.67 | ||
| 乌鳢 Channa argus | 2.43 | ||
| 贝氏䱗 Hemiculter bleekeri | 2.25 | ||
| 鲤 Cyprinus carpio | 2.16 | ||
| 不足1% Less than 1% | 4.23 | ||
| 总计 Total | 91.99 | 91.12 | 92.04 |
| 平均值 Average values | 59.73 | 43.90 | 82.93 |
表3 上海苏州河鱼类群组内相似性(或群组间相异性)贡献率之和占90%以上的特征种(或分歧种)
Table 3 Fish characteristic species (or divergent species) with more than 90% of the total contribution rate of similarity within group (or dissimilarity between groups) of the Suzhou River in Shanghai
| 种类 Species | 平均相似性贡献率 Average similarity contribution (%) | 平均相异性贡献率 Average dissimilarity contribution (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 群组I Group I | 群组II Group II | 群组I-群组II Group I-Group II | |
| 似鳊 Pseudobrama simoni | 66.34 | 4.43 | 26.37 |
| 䱗 Hemiculter leucisculus | 8.61 | 4.65 | |
| 兴凯鱊 Acheilognathus chankaensis | 7.18 | 5.63 | |
| 达氏鲌 Culter dabryi | 3.05 | 2.62 | |
| 鲫 Carassius auratus | 2.58 | 34.68 | 15.62 |
| 泥鳅 Misgurnus anguillicaudatus | 47.65 | 21.45 | |
| 光泽黄颡鱼 Pelteobagrus nitidus | 4.36 | 6.19 | |
| 麦穗鱼 Pseudorasbora parva | 2.67 | ||
| 乌鳢 Channa argus | 2.43 | ||
| 贝氏䱗 Hemiculter bleekeri | 2.25 | ||
| 鲤 Cyprinus carpio | 2.16 | ||
| 不足1% Less than 1% | 4.23 | ||
| 总计 Total | 91.99 | 91.12 | 92.04 |
| 平均值 Average values | 59.73 | 43.90 | 82.93 |
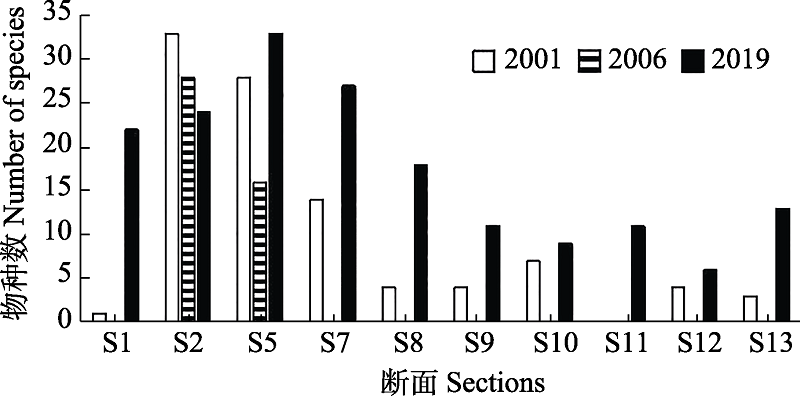
图7 上海苏州河各断面鱼类种类的历年变化。2001年数据引自夏建宏等(2009); 2006年数据引自陈小华等(2008)。断面代号见表1。
Fig. 7 Changes of fish species in different sections of Suzhou River in Shanghai over the years. Data for 2011 from Xia et al, 2009; Data for 2006 from Chen et al, 2008. Section codes see Table 1.
| [1] | Beugly J, Pyron M (2010) Temporal and spatial variation in the long-term functional organization of fish assemblages in a large river. Hydrobiologia, 654, 215-226. |
| [2] | Chen XH, Li XP, Cheng X (2008) Spatial-temporal distribution of fish assemblages in the upstreams of Huangpu River and Suzhou Creek. Biodiversity Science, 16, 191-196. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈小华, 李小平, 程曦 (2008) 黄浦江和苏州河上游鱼类多样性组成的时空特征. 生物多样性, 16, 191-196.] | |
| [3] | Chen YL, Shan XJ, Jin XS, Arne J, Yang T, Dai FQ (2018) Changes in fish diversity and community structure in the central and southern Yellow Sea from 2003 to 2015. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 36, 805-817. |
| [4] | Chen YS, Wu GH, Huang JT (1997) Analysis on current status of Suzhou Creek pollution. Shanghai Environmental Science, 16(1), 11-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈一申, 吴国豪, 黄解田 (1997) 苏州河水环境污染现状分析. 上海环境科学, 16(1), 11-14.] | |
| [5] | Cheng JS, Yu LF (2004) The change of structure and diversity of demersal fish communities in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea in winter. Journal of Fisheries of China, 28, 29-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 程济生, 俞连福 (2004) 黄、东海冬季底层鱼类群落结构及多样性变化. 水产学报, 28, 29-34.] | |
| [6] | Cheng QT, Zheng BS (1987) Systematic Synopsis of Chinese Fishes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 成庆泰, 郑葆珊 (1987) 中国鱼类系统检索. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [7] | Cheng X, Li XP, Chen XH (2009) An assessment of long-term changes in water quality and benthos community of Suzhou Creek (1996-2006). Acta Ecologica Sinica, 29, 3278-3287. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 程曦, 李小平, 陈小华 (2009) 苏州河水质和底栖动物群落1996-2006年的时空变化. 生态学报, 29, 3278-3287.] | |
| [8] | Chiu MC, Kuo MH (2012) Application of r/k selection to macroinvertebrate responses to extreme floods. Ecological Entomology, 37, 145-154. |
| [9] | Clarke KR, Warwick RM (2001) Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation, 2nd edn. PRIMER-E Ltd., Plymouth, |
| [10] | Dai SY, Yu J, Ding B, Yin WQ (2013) Application and developmental tendency of biomonitoring in water environmental monitoring. Pollution Control Technology, 26(5), 62-65, 71. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 戴舒雅, 余俭, 丁波, 殷伟庆 (2013) 生物监测在水环境监测中的应用及发展趋势. 污染防治技术, 26(5), 62-65, 71.] | |
| [11] | Ding Y, Sun ZZ, Zhang YP, Lin HS, Hong B, Qi JY, Zhao R, Zhang D (2013) Analysis and assessment of long-term changes in water quality of Suzhou River (2007-2012). Fisheries Science and Technology Information, 40, 199-203. (in Chinese) |
| [ 丁义, 孙振中, 张玉平, 林惠山, 洪波, 戚隽渊, 赵冉, 张丹 (2013) 2007-2012年苏州河水质变化分析与评价. 水产科技情报, 40, 199-203.] | |
| [12] | East China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Shanghai Fisheries Research Institute(1990) Fishes of Shanghai. Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai. (in Chinese) |
| [ 中国水产科学研究院东海水产研究所, 上海市水产研究所(1990) 上海鱼类志. 上海科学技术出版社, 上海.] | |
| [13] | Ji YX, Liu SQ (2020) Review and prospect of Suzhou Creek water environment treatment in 20 years. Water Resources Protection, 36(1), 25-30, 51. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 季永兴, 刘水芹 (2020) 苏州河水环境治理20年回顾与展望. 水资源保护, 36(1), 25-30, 51.] | |
| [14] | Li SF (2008) Status of fish community in East China Sea using the method of abundance-biomass comparison (ABC) curve. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 15, 136-143. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李圣法 (2008) 以数量生物量比较曲线评价东海鱼类群落的状况. 中国水产科学, 15, 136-143.] | |
| [15] | Liao ZH, Gu YJ (2003) The relationship between periphytic biology communities and water quality in Suzhou River. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), (3), 109-112. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 廖祖荷, 顾泳洁 (2003) 苏州河着生生物群落结构的变化与水质的关系. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), (3), 109-112.] | |
| [16] | Lin LS, Zhao GG, Li Y, Gao TX, Zhang J (2012) Diversity of nekton in Dongshan Bay and adjacent areas. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 36, 1119-1127. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 林龙山, 赵贵根, 李渊, 高天翔, 张静 (2012) 东山湾及其邻近海域游泳动物多样性的分析. 水生生物学报, 36, 1119-1127.] | |
| [17] | Liu DY, Lin WP, Zhao M (2009) Community structural characteristics of phytoplankton in Suzhou Creek. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 18, 914-918. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘冬燕, 林文鹏, 赵敏 (2009) 苏州河浮游植物群落结构特征. 长江流域资源与环境, 18, 914-918.] | |
| [18] | Liu HZ, Yang JX, Liu SW, Gao X, Chen YS, Zhang CG, Zhao K, Li XH, Liu W (2016) Theory and methods on fish diversity monitoring with an introduction to the inland water fish diversity observation in China. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1227-1233. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘焕章, 杨君兴, 刘淑伟, 高欣, 陈宇顺, 张春光, 赵凯, 李新辉, 刘伟 (2016) 鱼类多样性监测的理论方法及中国内陆水体鱼类多样性监测. 生物多样性, 24, 1227-1233.] | |
| [19] |
Lozupone C, Knight R (2005) UniFrac: A new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71, 8228-8235.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] | Nelson JS, Grande TC, Wilson MVH (2016) Fishes of the World, 5th edn. Wiley, New York, |
| [21] | Ni Y, Wu HL (2006) Fishes of the Jiangsu Province. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 倪勇, 伍汉霖 (2006) 江苏鱼类志. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [22] | Prista N, Vasconcelos RP, Costa MJ (2003) The demersal fish assemblage of the coastal area adjacent to the Tagus: Relationships with environmental conditions. Acta Oceanologica, 26, 525-536. |
| [23] | Sá-Oliveira JC, Isaac VJ, Ferrari SF (2015) Fish community structure as an indicator of the long-term effects of the damming of an Amazonian river. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 98, 273-286. |
| [24] | Sun SS, Tang WQ, Guo HY, Li HH, Liu D, Zhou TS, Chen HZ, Shen LH, Gu SX (2013) Composition and changes in abundance and biomass of fish assemblages along the Jingjiang section of the Yangtze River over the last decade. Biodiversity Science, 21, 688-698. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙莎莎, 唐文乔, 郭弘艺, 李辉华, 刘东, 周天舒, 陈浩洲, 沈林宏, 顾树信 (2013) 靖江沿岸秋季鱼类群聚的组成特点及其丰度生物量变化. 生物多样性, 21, 688-698.] | |
| [25] | Tang WQ, Zhu TJ, Chen JK, Han HF, Sun Y (2003) Resources and conservation of fishes of Jiuduansha wetland in Changjiang River estuary. Journal of Shanghai Fisheries University, 12(3), 193-200. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 唐文乔, 诸廷俊, 陈家宽, 韩洪发, 孙瑛 (2003) 长江口九段沙湿地的鱼类资源及其保护价值. 上海水产大学学报, 12(3), 193-200.] | |
| [26] | Wang Z, Song C, Yan WL, Zhu LF (2019) Biodiversity and spatial pattern of fish in the Pingchuan segment of the upper reaches of Hanjiang River. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 28, 1675-1681. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王卓, 宋策, 闫文龙, 朱来福 (2019) 汉江上游平川段鱼类群落多样性及空间格局分析. 长江流域资源与环境, 28, 1675-1681.] | |
| [27] | Wang ZH, Wang K, Zhao J, Zhang SY (2011) Fish community structure and its seasonal change in subtidal sandy beach habitat off southern Gouqi Island. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 22, 1332-1342. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 汪振华, 王凯, 赵静, 章守宇 (2011) 枸杞岛潮下带沙地生境鱼类群落结构和季节变化. 应用生态学报, 22, 1332-1342.] | |
| [28] | Warwick RM (1986) A new method for detecting pollution effects on marine macrobenthic community. Marine Biology, 92, 557-562. |
| [29] | Xia JH, Lu JF, Zhou BC, Tan HZ (2009) A preliminary study on fish communities in Suzhou Creek, Shanghai. Journal of Lake Sciences, 21, 538-546. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 夏建宏, 陆剑锋, 周保春, 谈慧珍 (2009) 上海苏州河鱼类群落的初步研究. 湖泊科学, 21, 538-546.] | |
| [30] | Yan Y, He S, Chu L (2010) Spatial and temporal variation of fish assemblages in a subtropical small stream of the Huangshan Mountain. Current Zoology, 6, 30-37. |
| [31] | Zhang GQ, Zhang MX, Han ZH, Hu XX (2009) The research on the Suzhou River water quality for the latest 20 years. Environmental Monitoring in China, 25(2), 39-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张广强, 张明旭, 韩中豪, 胡雄星 (2009) 苏州河近20年水质状况研究. 中国环境监测, 25(2), 39-44.] | |
| [32] | Zhang SW, Kong XF, Jiang YQ, Lü J, Wu N, Zhang J, Ma R, Zou Y (2015) Review of application and research of biological monitoring technologies in aquatic environment. Environmental Protection Science, 191, 107-111. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张述伟, 孔祥峰, 姜源庆, 吕婧, 吴宁, 张婧, 马然, 邹妍 (2015) 生物监测技术在水环境中的应用及研究. 环境保护科学, 191, 107-111.] | |
| [33] | Zhao MH, Gong YW (2018) Review and achievement of Suzhou Creek environment treatment in 20 years. China Flood and Drought Management, 28(12), 38-41. (in Chinese) |
| [ 赵敏华, 龚屹巍 (2018) 上海苏州河治理20年回顾及成效. 中国防汛抗旱, 28(12), 38-41.] | |
| [34] | Zheng YT, Han P, Ni JR, Xiong MH (2019) Studies on structure of fish community and species diversity in Wuhan section of the Yangtze River. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 27(1), 29-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郑亦婷, 韩鹏, 倪晋仁, 熊美华 (2019) 长江武汉江段鱼类群落结构及其多样性研究. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 27(1), 29-40.] |
| [1] | 张明燡, 王晓梅, 郑言鑫, 吴楠, 李东浩, 樊恩源, 李娜, 单秀娟, 于涛, 赵春暖, 李波, 徐帅, 吴玉萍, 任利群. 黄河口典型牡蛎礁分布区资源状况和栖息地功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [2] | 仝淼, 王欢, 张文双, 王超, 宋建潇. 重金属污染土壤中细菌抗生素抗性基因分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [3] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [4] | 魏诗雨, 宋天骄, 罗佳宜, 张燕, 赵子萱, 茹靖雯, 易华, 林雁冰. 秦岭火地塘针叶林土壤细菌群落的海拔分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [5] | 时永强, 栾青杉, 单秀娟, 韦超, 赵永松, 孙策策, 金显仕. 长岛南部海域浮游动物多样性周年变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [6] | 倪艳梅, 陈莉, 董志远, 孙德斌, 李宝泉, 王绪敏, 陈琳琳. 黄河三角洲湿地生态修复区大型底栖动物群落结构与生态健康评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23303-. |
| [7] | 魏嘉欣, 姜治国, 杨林森, 熊欢欢, 金胶胶, 罗方林, 李杰华, 吴浩, 徐耀粘, 乔秀娟, 魏新增, 姚辉, 余辉亮, 杨敬元, 江明喜. 湖北神农架中亚热带山地落叶阔叶林25 ha动态监测样地群落物种组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23338-. |
| [8] | 刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇. 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [9] | 吴芳芳, 刘娜, 何春梅, 原作强, 郝占庆, 尹秋龙. 秦岭山地木本植物群落结构及多样性的海拔梯度格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24239-. |
| [10] | 单航, 雷祖培, 郑方东, 韦博良, 仲磊, 于明坚. 2013-2023年浙江乌岩岭次生常绿阔叶林群落动态变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24372-. |
| [11] | 冯嘉谊, 练琚愉, 冯瑜莙, 张东旭, 曹洪麟, 叶万辉. 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林群落垂直分层对群落结构及功能的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24306-. |
| [12] | 王兴煜, 孟京辉, 任思远, 祝燕. 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林群落生物多样性与地上生物量的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24230-. |
| [13] | 杜晴晴, 任思远, Nicole Tsz Shun Yuan, 祝燕. 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林幼树及成树生产力的影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24284-. |
| [14] | 黄骏涵, 余梵冬, 王裕祥, 黄哲, 张铭斯, 房苗, 舒璐, 徐猛, 韦慧, 汪学杰, 顾党恩, 罗思. 花地河中下游外来鱼类入侵现状及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24249-. |
| [15] | 杨舒涵, 王贺, 陈磊, 廖蓥飞, 严光, 伍一宁, 邹红菲. 松嫩平原异质生境对土壤线虫群落特征的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23295-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()