



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 21517. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021517 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021517
孙哲明1,2, 刘亚恒3, 彭秋桐1, 徐芷妍1, 杨予静1, 欧文慧4, 李中强1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-12-13
接受日期:2022-02-21
出版日期:2022-06-20
发布日期:2022-04-20
通讯作者:
李中强
作者简介:* E-mail: lizhq@hubu.edu.cn基金资助:
Zheming Sun1,2, Yaheng Liu3, Qiutong Peng1, Zhiyan Xu1, Yujing Yang1, Wenhui Ou4, Zhongqiang Li1,*( )
)
Received:2021-12-13
Accepted:2022-02-21
Online:2022-06-20
Published:2022-04-20
Contact:
Zhongqiang Li
摘要:
极小种群野生植物是亟需保护、最为濒危的植物, 研究极小种群野生植物物种重要值和竞争格局对保护与恢复具有重要实践意义。本文通过野外群落调查, 研究了湖北省分布的7种极小种群野生植物大别山五针松(Pinus fenzeliana var. dabeshanensis)、水杉(Metasequoia glyptostroboides)、峨眉含笑(Michelia wilsonii)、小勾儿茶(Berchemiella wilsonii)、长果秤锤树(Sinojackia dolichocarpa)、黄梅秤锤树(S. huangmeiensis)和庙台槭(Acer miaotaiense)的重要值及改进后的Hegyi竞争指数。结果表明: 从重要值来看, 水杉、长果秤锤树在各自所属的群落中具有较高的重要值及较低的变异系数, 为群落中的优势种; 庙台槭和黄梅秤锤树重要值较高, 为群落中的亚优势种; 大别山五针松、峨眉含笑、小勾儿茶重要值较低, 为群落伴生种。从改进后的Hegyi竞争指数来看, 湖北省7种极小种群野生植物受到的竞争压力的来源和强度存在较大差异, 大别山五针松、峨眉含笑、小勾儿茶、黄梅秤锤树主要受到种间竞争, 而水杉、长果秤锤树、庙台槭主要受到种内竞争, 因此在制定保护措施前要充分考虑物种间的竞争情况, 才能采取更有针对性的保护措施。
孙哲明, 刘亚恒, 彭秋桐, 徐芷妍, 杨予静, 欧文慧, 李中强 (2022) 湖北省极小种群野生植物在原生群落中的竞争地位及保护建议. 生物多样性, 30, 21517. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021517.
Zheming Sun, Yaheng Liu, Qiutong Peng, Zhiyan Xu, Yujing Yang, Wenhui Ou, Zhongqiang Li (2022) Competition status and conservation suggestions for Wild Plant with Extremely Small Populations in primary communities in Hubei Province. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21517. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021517.
| 物种 Species | 分布区域 Distribution area | 保护等级 Protection level* | IUCN评级 IUCN grade | RLCHP评级 RLCHP grade** | 现存数量 Survival number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大别山五针松 Pinus fenzeliana var. dabeshanensis | 英山县 Yingshan County | I | VU | - | 4 |
| 水杉 Metasequoia glyptostroboides | 利川市 Lichuan City | I | EN | CR | 5,630 |
| 峨眉含笑 Michelia wilsonii | 利川市 Lichuan City | II | DD | VU | 8 |
| 小勾儿茶 Berchemiella wilsonii | 保康县、长阳县等 Baokang County, Changyang County, etc. | II | - | - | 113 |
| 黄梅秤锤树 Sinojackia huangmeiensis | 黄梅县 Huangmei County | II | VU | VU | 462 |
| 长果秤锤树 Sinojackia dolichocarpa | 秭归县 Zigui County | II | VU | EN | 13 |
| 庙台槭 Acer miaotaiense | 神农架林区 Shennongjia Forestry District | II | VU | VU | 13 |
表1 湖北省分布的7种极小种群野生植物的分布及数量信息
Table 1 Distribution and quantity information of seven Wild Plant with Extremely Small Populations (WPESP) in Hubei Province
| 物种 Species | 分布区域 Distribution area | 保护等级 Protection level* | IUCN评级 IUCN grade | RLCHP评级 RLCHP grade** | 现存数量 Survival number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大别山五针松 Pinus fenzeliana var. dabeshanensis | 英山县 Yingshan County | I | VU | - | 4 |
| 水杉 Metasequoia glyptostroboides | 利川市 Lichuan City | I | EN | CR | 5,630 |
| 峨眉含笑 Michelia wilsonii | 利川市 Lichuan City | II | DD | VU | 8 |
| 小勾儿茶 Berchemiella wilsonii | 保康县、长阳县等 Baokang County, Changyang County, etc. | II | - | - | 113 |
| 黄梅秤锤树 Sinojackia huangmeiensis | 黄梅县 Huangmei County | II | VU | VU | 462 |
| 长果秤锤树 Sinojackia dolichocarpa | 秭归县 Zigui County | II | VU | EN | 13 |
| 庙台槭 Acer miaotaiense | 神农架林区 Shennongjia Forestry District | II | VU | VU | 13 |
| 物种 Species | 样方数 No. of samples | 最大值 Max. value (%) | 最小值 Min. value (%) | 标准差 Standard deviation | 平均值 Mean (%) | 变异系数 Variation coefficient (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大别山五针松 Pinus fenzeliana var. dabeshanensis | 4 | 21.10 | 8.45 | 5.10 | 15.56 | 32.77 |
| 水杉 Metasequoia glyptostroboides | 10 | 81.26 | 21.54 | 19.36 | 51.82 | 37.37 |
| 峨眉含笑 Michelia wilsonii | 5 | 17.45 | 9.58 | 2.65 | 14.09 | 18.79 |
| 小勾儿茶 Berchemiella wilsonii | 2 | 10.55 | 7.61 | 1.47 | 9.08 | 16.19 |
| 黄梅秤锤树 Sinojackia huangmeiensis | 10 | 72.96 | 10.98 | 18.42 | 33.16 | 55.54 |
| 长果秤锤树 Sinojackia dolichocarpa | 7 | 91.88 | 46.69 | 13.64 | 66.77 | 20.43 |
| 庙台槭 Acer miaotaiense | 4 | 70.99 | 8.51 | 24.82 | 36.03 | 68.89 |
表2 湖北省7个极小种群野生植物在群落中的重要值
Table 2 Importance values of seven Wild Plant with Extremely Small Populations (WPESP) in their communities in Hubei Province
| 物种 Species | 样方数 No. of samples | 最大值 Max. value (%) | 最小值 Min. value (%) | 标准差 Standard deviation | 平均值 Mean (%) | 变异系数 Variation coefficient (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大别山五针松 Pinus fenzeliana var. dabeshanensis | 4 | 21.10 | 8.45 | 5.10 | 15.56 | 32.77 |
| 水杉 Metasequoia glyptostroboides | 10 | 81.26 | 21.54 | 19.36 | 51.82 | 37.37 |
| 峨眉含笑 Michelia wilsonii | 5 | 17.45 | 9.58 | 2.65 | 14.09 | 18.79 |
| 小勾儿茶 Berchemiella wilsonii | 2 | 10.55 | 7.61 | 1.47 | 9.08 | 16.19 |
| 黄梅秤锤树 Sinojackia huangmeiensis | 10 | 72.96 | 10.98 | 18.42 | 33.16 | 55.54 |
| 长果秤锤树 Sinojackia dolichocarpa | 7 | 91.88 | 46.69 | 13.64 | 66.77 | 20.43 |
| 庙台槭 Acer miaotaiense | 4 | 70.99 | 8.51 | 24.82 | 36.03 | 68.89 |
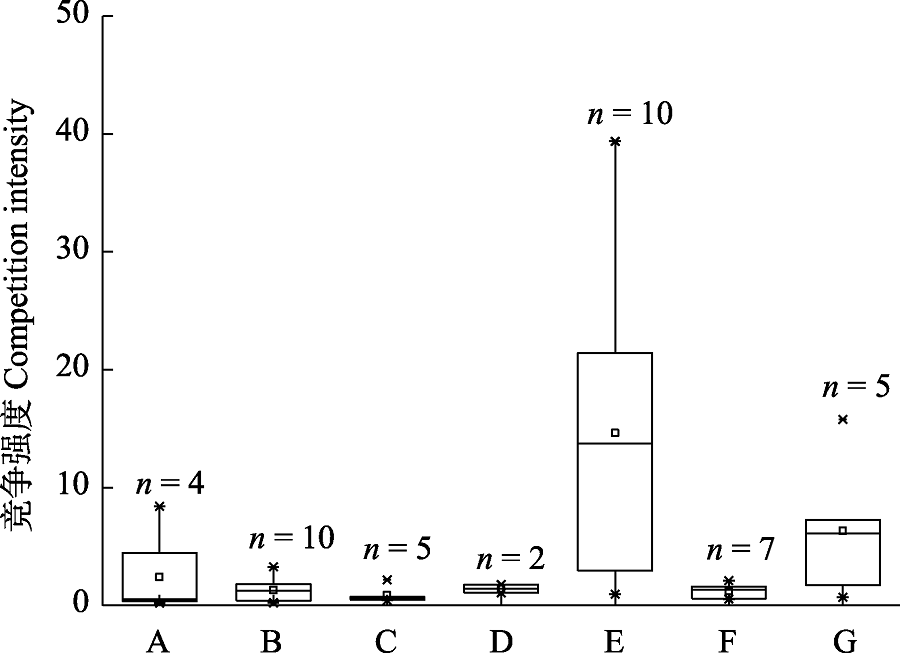
图1 湖北省7个极小种群野生植物在群落中受到的竞争强度。A: 大别山五针松; B: 水杉; C: 峨眉含笑; D: 小勾儿茶; E: 黄梅秤锤树; F: 长果秤锤树; G: 庙台槭。
Fig. 1 The competition intensity of seven Wild Plant with Extremely Small Populations (WPESP) in their communities in Hubei Province. A, Pinus fenzeliana var. dabeshanensis; B, Metasequoia glyptostroboides; C, Michelia wilsonii; D, Berchemiella wilsonii; E, Sinojackia huangmeiensis; F, S. dolichocarpa; G, Acer miaotaiense.
| 对象木 Objective tree | 竞争木 Competitive tree | 样方出现 频率 Occurrence frequency (%) | 株数 Individual number | 竞争强度 Competition intensity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值 Max. | 最小值 Min. | 竞争指数 Competition intensity | 平均值 Mean | 占总竞争指数百分比 % of total competition intensity | 排名 Rank | ||||
| 大别山五针松 Pinus var. dabeshanensis | 黄山松 Pinus taiwanensis | 100.0 | 21 | 8.18 | 0.16 | 9.13 | 0.43 | 94.8 | 1 |
| 山梅花 Philadelphus incanus | 25.0 | 2 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 2.0 | 2 | |
| 紫茎 Stewartia sinensis | 50.0 | 2 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 1.9 | 3 | |
| 金缕梅 Hamamelis mollis | 25.0 | 1 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.9 | 4 | |
| 茅栗 Castanea seguinii | 50.0 | 2 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.3 | 5 | |
| 其他伴生种 Other trees | - | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.1 | - | |
| 水杉 Metasequoia glyptostroboides | 水杉 M. glyptostroboides | 90.0 | 33 | 3.27 | 0.20 | 10.58 | 0.32 | 80.9 | 1 |
| 柳杉 Cryptomeria japonica var. sinensis | 40.0 | 17 | 0.91 | 0.02 | 1.95 | 0.11 | 14.9 | 2 | |
| 毛竹 Phyllostachys edulis | 10.0 | 9 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.03 | 2.0 | 3 | |
| 棕榈 Trachycarpus fortunei | 20.0 | 3 | 0.25 | 0.01 | 0.26 | 0.09 | 2.0 | 4 | |
| 银杏 Ginkgo biloba | 10.0 | 1 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.2 | - | |
| 峨眉含笑 Michelia wilsonii | 鸡爪槭 Acer palmatum | 20.0 | 2 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.47 | 21.2 | 1 |
| 北枳椇 Hovenia dulcis | 20.0 | 3 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.15 | 10.4 | 2 | |
| 青冈 Cyclobalanopsis glauca | 40.0 | 2 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 0.43 | 0.22 | 9.8 | 3 | |
| 长蕊杜鹃 Rhododendron stamineum | 80.0 | 9 | 0.17 | 0.02 | 0.35 | 0.04 | 8.0 | 4 | |
| 鹅耳枥 Carpinus turczaninowii | 20.0 | 2 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.17 | 7.6 | 5 | |
| 其他伴生种 Other trees | - | 30 | - | - | 1.89 | - | 43.1 | - | |
| 小勾儿茶 Berchemiella wilsonii | 鹅耳枥 Carpinus turczaninowii | 100.0 | 5 | 0.52 | 0.33 | 0.85 | 0.17 | 30.1 | 1 |
| 湖北紫荆 Cercis glabra | 100.0 | 6 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.34 | 0.06 | 12.1 | 2 | |
| 朴树 Celtis sinensis | 50.0 | 3 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.11 | 11.7 | 3 | |
| 榔榆 Ulmus parvifolia | 50.0 | 1 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 8.0 | 4 | |
| 化香树 Platycarya strobilacea | 50.0 | 1 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 7.7 | 5 | |
| 其他伴生种 Other trees | - | 16 | - | - | 0.86 | - | 30.5 | - | |
| 黄梅秤锤树 Sinojackia huangmeiensis | 麻栎 Quercus acutissima | 50.0 | 15 | 33.76 | 4.14 | 75.72 | 5.05 | 51.8 | 1 |
| 枸骨 Ilex cornuta | 80.0 | 19 | 5.70 | 0.05 | 16.75 | 0.88 | 11.5 | 2 | |
| 枫香树 Liquidambar formosana | 10.0 | 2 | 11.89 | 4.80 | 16.70 | 8.35 | 11.4 | 3 | |
| 樟 Cinnamomum camphora | 30.0 | 6 | 7.26 | 0.54 | 8.65 | 1.44 | 5.9 | 4 | |
| 黄梅秤锤树 S. huangmeiensis | 100.0 | 43 | 1.65 | 0.04 | 8.13 | 0.19 | 5.6 | 5 | |
| 其他伴生种 Other trees | - | 28 | - | - | 20.34 | - | 13.9 | - | |
| 长果秤锤树 Sinojackia dolichocarpa | 长果秤锤树 S. dolichocarpa | 100.0 | 13 | 1.48 | 0.17 | 5.68 | 0.25 | 66.0 | 1 |
| 青冈 Cyclobalanopsis glauca | 42.9 | 3 | 0.44 | 0.24 | 1.08 | 0.36 | 12.5 | 2 | |
| 侧柏 Platycladus orientalis | 14.3 | 1 | 0.61 | 0.61 | 0.61 | 0.61 | 7.1 | 3 | |
| 杨梅叶蚊母树 Distylium myricoides | 42.9 | 9 | 0.26 | 0.15 | 0.60 | 0.07 | 7.0 | 4 | |
| 朴树 Celtis sinensis | 57.1 | 4 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.45 | 0.11 | 5.3 | 5 | |
| 其他伴生种 Other trees | - | 3 | - | - | 0.18 | - | 2.1 | - | |
| 庙台槭 Acer miaotaiense | 庙台槭 A. miaotaiense | 75.0 | 13 | 6.55 | 0.47 | 9.81 | 0.75 | 66.2 | 1 |
| 苦树 Picrasma quassioides | 25.0 | 8 | 1.94 | 1.94 | 1.94 | 0.24 | 13.1 | 2 | |
| 枫杨 Pterocarya stenoptera | 25.0 | 2 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.40 | 5.4 | 3 | |
| 房县槭 A. sterculiaceum subsp. franchetii | 25.0 | 4 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.13 | 3.6 | 4 | |
| 盐肤木 Rhus chinensis | 25.0 | 3 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.11 | 2.2 | 5 | |
| 其他伴生种 Other trees | - | 12 | - | - | 2.39 | - | 9.6 | - | |
表3 湖北省7种极小种群野生植物主要竞争木种类组成和竞争强度
Table 3 Species composition of competitive tree and the competition intensity of seven Wild Plant with Extremely Small Populations (WPESP) in Hubei Province
| 对象木 Objective tree | 竞争木 Competitive tree | 样方出现 频率 Occurrence frequency (%) | 株数 Individual number | 竞争强度 Competition intensity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值 Max. | 最小值 Min. | 竞争指数 Competition intensity | 平均值 Mean | 占总竞争指数百分比 % of total competition intensity | 排名 Rank | ||||
| 大别山五针松 Pinus var. dabeshanensis | 黄山松 Pinus taiwanensis | 100.0 | 21 | 8.18 | 0.16 | 9.13 | 0.43 | 94.8 | 1 |
| 山梅花 Philadelphus incanus | 25.0 | 2 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 2.0 | 2 | |
| 紫茎 Stewartia sinensis | 50.0 | 2 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 1.9 | 3 | |
| 金缕梅 Hamamelis mollis | 25.0 | 1 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.9 | 4 | |
| 茅栗 Castanea seguinii | 50.0 | 2 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.3 | 5 | |
| 其他伴生种 Other trees | - | 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.1 | - | |
| 水杉 Metasequoia glyptostroboides | 水杉 M. glyptostroboides | 90.0 | 33 | 3.27 | 0.20 | 10.58 | 0.32 | 80.9 | 1 |
| 柳杉 Cryptomeria japonica var. sinensis | 40.0 | 17 | 0.91 | 0.02 | 1.95 | 0.11 | 14.9 | 2 | |
| 毛竹 Phyllostachys edulis | 10.0 | 9 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.03 | 2.0 | 3 | |
| 棕榈 Trachycarpus fortunei | 20.0 | 3 | 0.25 | 0.01 | 0.26 | 0.09 | 2.0 | 4 | |
| 银杏 Ginkgo biloba | 10.0 | 1 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.2 | - | |
| 峨眉含笑 Michelia wilsonii | 鸡爪槭 Acer palmatum | 20.0 | 2 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.47 | 21.2 | 1 |
| 北枳椇 Hovenia dulcis | 20.0 | 3 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.15 | 10.4 | 2 | |
| 青冈 Cyclobalanopsis glauca | 40.0 | 2 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 0.43 | 0.22 | 9.8 | 3 | |
| 长蕊杜鹃 Rhododendron stamineum | 80.0 | 9 | 0.17 | 0.02 | 0.35 | 0.04 | 8.0 | 4 | |
| 鹅耳枥 Carpinus turczaninowii | 20.0 | 2 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.17 | 7.6 | 5 | |
| 其他伴生种 Other trees | - | 30 | - | - | 1.89 | - | 43.1 | - | |
| 小勾儿茶 Berchemiella wilsonii | 鹅耳枥 Carpinus turczaninowii | 100.0 | 5 | 0.52 | 0.33 | 0.85 | 0.17 | 30.1 | 1 |
| 湖北紫荆 Cercis glabra | 100.0 | 6 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.34 | 0.06 | 12.1 | 2 | |
| 朴树 Celtis sinensis | 50.0 | 3 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.11 | 11.7 | 3 | |
| 榔榆 Ulmus parvifolia | 50.0 | 1 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 8.0 | 4 | |
| 化香树 Platycarya strobilacea | 50.0 | 1 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 7.7 | 5 | |
| 其他伴生种 Other trees | - | 16 | - | - | 0.86 | - | 30.5 | - | |
| 黄梅秤锤树 Sinojackia huangmeiensis | 麻栎 Quercus acutissima | 50.0 | 15 | 33.76 | 4.14 | 75.72 | 5.05 | 51.8 | 1 |
| 枸骨 Ilex cornuta | 80.0 | 19 | 5.70 | 0.05 | 16.75 | 0.88 | 11.5 | 2 | |
| 枫香树 Liquidambar formosana | 10.0 | 2 | 11.89 | 4.80 | 16.70 | 8.35 | 11.4 | 3 | |
| 樟 Cinnamomum camphora | 30.0 | 6 | 7.26 | 0.54 | 8.65 | 1.44 | 5.9 | 4 | |
| 黄梅秤锤树 S. huangmeiensis | 100.0 | 43 | 1.65 | 0.04 | 8.13 | 0.19 | 5.6 | 5 | |
| 其他伴生种 Other trees | - | 28 | - | - | 20.34 | - | 13.9 | - | |
| 长果秤锤树 Sinojackia dolichocarpa | 长果秤锤树 S. dolichocarpa | 100.0 | 13 | 1.48 | 0.17 | 5.68 | 0.25 | 66.0 | 1 |
| 青冈 Cyclobalanopsis glauca | 42.9 | 3 | 0.44 | 0.24 | 1.08 | 0.36 | 12.5 | 2 | |
| 侧柏 Platycladus orientalis | 14.3 | 1 | 0.61 | 0.61 | 0.61 | 0.61 | 7.1 | 3 | |
| 杨梅叶蚊母树 Distylium myricoides | 42.9 | 9 | 0.26 | 0.15 | 0.60 | 0.07 | 7.0 | 4 | |
| 朴树 Celtis sinensis | 57.1 | 4 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.45 | 0.11 | 5.3 | 5 | |
| 其他伴生种 Other trees | - | 3 | - | - | 0.18 | - | 2.1 | - | |
| 庙台槭 Acer miaotaiense | 庙台槭 A. miaotaiense | 75.0 | 13 | 6.55 | 0.47 | 9.81 | 0.75 | 66.2 | 1 |
| 苦树 Picrasma quassioides | 25.0 | 8 | 1.94 | 1.94 | 1.94 | 0.24 | 13.1 | 2 | |
| 枫杨 Pterocarya stenoptera | 25.0 | 2 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.40 | 5.4 | 3 | |
| 房县槭 A. sterculiaceum subsp. franchetii | 25.0 | 4 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.13 | 3.6 | 4 | |
| 盐肤木 Rhus chinensis | 25.0 | 3 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.11 | 2.2 | 5 | |
| 其他伴生种 Other trees | - | 12 | - | - | 2.39 | - | 9.6 | - | |
| [1] | Dang HS, Zhang YJ, Jiang MX, Huang HD, Jin X (2005) A preliminary study on dormancy and germination physiology of endangered species Berchemiella wilsonii (Schneid.) Nakai var. pubipetiolata H. Qian seeds. Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research, 23, 327-331. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [党海山, 张燕君, 江明喜, 黄汉东, 金霞 (2005) 濒危植物毛柄小勾儿茶种子休眠与萌发生理的初步研究. 武汉植物学研究, 23, 327-331.] | |
| [2] | Du XF, Tang MP, Pan JY, Shen QY, Yang F (2020) Study on competition index of different typical forest types on Lin’an region. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40, 4064-4072. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杜秀芳, 汤孟平, 潘建勇, 沈钱勇, 杨帆 (2020) 临安区不同森林类型竞争指数比较研究. 生态学报, 40, 4064-4072.] | |
| [3] | Hegyi F (1974) A simulation model for managing Jack-pine stands. In: Growth Models for Tree and Stand Simulation (ed. Fries J). Royal College of Forestry, Stockholm. |
| [4] | Hu LL, Jiang MX, Huang HD, Dang HS, Xiang QB, Huang H (2003) Studies on traits of concomitant community of endangered plant Berchemiella wilsonii. Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research, 21, 327-331. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [胡理乐, 江明喜, 黄汉东, 党海山, 向启波, 黄辉 (2003) 濒危植物小勾儿茶伴生群落特征研究. 武汉植物学研究, 21, 327-331.] | |
| [5] |
Huang X, Zhu J, Yao L, Ai XR, Wang J, Wu ML, Zhu Q, Chen SL (2020) Structure and spatial distribution pattern of a native Metasequoia glyptostroboides population in Hubei. Biodiversity Science, 28, 463-473 (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[黄小, 朱江, 姚兰, 艾训儒, 王进, 吴漫玲, 朱强, 陈绍林 (2020) 水杉原生种群结构及空间分布格局. 生物多样性, 28, 463-473.]
DOI |
|
| [6] | Jiang MX (2019) Rare and Endangered Plants in Hubei. Hubei Science and Technology Press, Wuhan. (in Chinese) |
| [江明喜 (2019) 湖北珍稀濒危植物. 湖北科学技术出版社, 武汉.] | |
| [7] | Jiang YH, Shen WH, Tan ZQ, Xiang WH, Peng YH, Pan GB (2016) The population structure and dynamics analysis and protection strategy of Vatica guangxiensis extremely small population. Ecological Science, 35(6), 67-72. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [蒋迎红, 申文辉, 谭长强, 项文化, 彭玉华, 潘光波 (2016) 极小种群广西青梅种群结构、动态分析及保护策略. 生态科学, 35(6), 67-72.] | |
| [8] | Li X, Hou L, Li SX, Li YY (2018) Population quantitative characteristics and dynamic analysis of the endangered plant Acer miaotaiense. Plant Science Journal, 36, 524-533. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李翔, 侯璐, 李双喜, 李颖岳 (2018) 濒危树种庙台槭种群数量特征及动态分析. 植物科学学报, 36, 524-533.] | |
| [9] | Long SS, Zeng SQ, Xiao HS, Liu FL, Hu M (2018) Analysis on the competitive status of Cyclobalanopsis glauca secondary forest based on the improved Hegyi model. Forest Resources Management, (1), 50-56. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [龙时胜, 曾思齐, 肖化顺, 刘发林, 胡满 (2018) 基于Hegyi改进模型的青冈栎次生林竞争分析. 林业资源管理, (1), 50-56.] | |
| [10] | Qin AL, Ma FQ, Xu GX, Shi ZM, Chen QY (2020) Population structure and dynamic characteristics of a rare and endangered tree species Michelia wilsonii Finet et Gagn. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40, 4445-4454. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [秦爱丽, 马凡强, 许格希, 史作民, 陈其勇 (2020) 珍稀濒危树种峨眉含笑种群结构与动态特征. 生态学报, 40, 4445-4454.] | |
| [11] |
Qin HN, Yang Y, Dong SY, He Q, Jia Y, Zhao LN, Yu SX, Liu HY, Liu B, Yan YH, Xiang JY, Xia NH, Peng H, Li ZY, Zhang ZX, He XJ, Yin LK, Lin YL, Liu QR, Hou YT, Liu Y, Liu QX, Cao W, Li JQ, Chen SL, Jin XH, Gao TG, Chen WL, Ma HY, Geng YY, Jin XF, Chang CY, Jiang H, Cai L, Zang CX, Wu JY, Ye JF, Lai YJ, Liu B, Lin QW, Xue NX (2017) Threatened species list of China’s higher plants. Biodiversity Science, 25, 696-744. (in Chinese and in English)
DOI URL |
|
[覃海宁, 杨永, 董仕勇, 何强, 贾渝, 赵莉娜, 于胜祥, 刘慧圆, 刘博, 严岳鸿, 向建英, 夏念和, 彭华, 李振宇, 张志翔, 何兴金, 尹林克, 林余霖, 刘全儒, 侯元同, 刘演, 刘启新, 曹伟, 李建强, 陈世龙, 金效华, 高天刚, 陈文俐, 马海英, 耿玉英, 金孝锋, 常朝阳, 蒋宏, 蔡蕾, 臧春鑫, 武建勇, 叶建飞, 赖阳均, 刘冰, 林秦文, 薛纳新 (2017) 中国高等植物受威胁物种名录. 生物多样性, 25, 696-744.]
DOI |
|
| [12] |
Ren H, Zhang QM, Lu HF, Liu HX, Guo QF, Wang J, Jian SG, Bao HO (2012) Wild plant species with extremely small populations require conservation and reintroduction in China. Ambio, 41, 913-917.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Song YC (2017) Vegetation Ecology, 2nd edn. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [宋永昌 (2017) 植被生态学(第二版). 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [14] |
Sun WB, Ma YP, Blackmore S (2019) How a new conservation action concept has accelerated plant conservation in China. Trends in Plant Science, 24, 4-6.
DOI URL |
| [15] | Tang MP, Chen YG, Shi YJ, Zhou GM, Zhao MS (2007) Intraspecific and interspecific competition analysis of community dominant plant populations based on Voronoi diagram. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 27, 4707-4716. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [汤孟平, 陈永刚, 施拥军, 周国模, 赵明水 (2007) 基于Voronoi图的群落优势树种种内种间竞争. 生态学报, 27, 4707-4716.] | |
| [16] |
Volis S (2016) How to conserve threatened Chinese plant species with extremely small populations? Plant Diversity, 38, 45-52.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Wade EM, Nadarajan J, Yang XY, Ballesteros D, Sun WB, Pritchard HW (2016) Plant species with extremely small populations (PSESP) in China: A seed and spore biology perspective. Plant Diversity, 38, 209-220.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Wang H (2010) Genetic Diversity of Germplasm Resources on Walnut in Tibet Region. PhD dissertation. Chinese Academy of Forestry, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王滑 (2010) 西藏核桃种质资源遗传多样性研究. 博士学位论文, 中国林业科学研究院, 北京.] | |
| [19] |
Wang ST, Wu H, Liu MT, Zhang JX, Liu JM, Meng HJ, Xu YZ, Qiao XJ, Wei XZ, Lu ZJ, Jiang MX (2018) Community structure and dynamics of a remnant forest dominated by a plant species with extremely small population (Sinojackia huangmeiensis) in Central China. Biodiversity Science, 26, 749-759. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[王世彤, 吴浩, 刘梦婷, 张佳鑫, 刘检明, 孟红杰, 徐耀粘, 乔秀娟, 魏新增, 卢志军, 江明喜 (2018) 极小种群野生植物黄梅秤锤树群落结构与动态. 生物多样性, 26, 749-759.]
DOI |
|
| [20] |
Wei XY, Ye YS, Lin XP, Cui YW, Zeng FY, Wang FG (2020) Population status and conservation of an extremely small population species Euryodendron excelsum. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 44, 1236-1246. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [魏雪莹, 叶育石, 林喜珀, 崔煜文, 曾飞燕, 王发国 (2020) 极小种群植物猪血木的种群现状及保护对策. 植物生态学报, 44, 1236-1246.] | |
| [21] | Wu JQ, Wang YX, Yang Y, Yang Y (2014) Design and development of competition index calculation system based on GIS technology. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 29(4), 175-181. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴建强, 王懿祥, 杨峪, 杨一 (2014) 基于GIS技术的林木竞争指数计算系统的设计与开发. 西北林学院学报, 29(4), 175-181.] | |
| [22] |
Wu ML, Yao L, Ai XR, Zhu J, Zhu Q, Wang J, Huang X, Hong JF (2020) The reproductive characteristics of core germplasm in a native Metasequoia glyptostroboides population. Biodiversity Science, 28, 303-313. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[吴漫玲, 姚兰, 艾训儒, 朱江, 朱强, 王进, 黄小, 洪建峰 (2020) 水杉原生种群核心种质资源的繁殖特性. 生物多样性, 28, 303-313.]
DOI |
|
| [23] | Xiang XY, Wu GL, Duan RY, Yan YM, Zhang XP (2015) Intraspecific and interspecific competition of Pinus dabeshanesis. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 389-395. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [项小燕, 吴甘霖, 段仁燕, 闫玉梅, 张小平 (2015) 大别山五针松种内和种间竞争强度. 生态学报, 35, 389-395.] | |
| [24] | Xiao SL, Fu MY, Yang K, Chen XH (2019) Population structure and quantitative dynamics of an extremely small population, Michelia wilsonii. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 39, 1279-1288. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [肖书礼, 付梦媛, 杨科, 陈小红 (2019) 极小种群野生植物峨眉含笑的种群结构与数量动态. 西北植物学报, 39, 1279-1288.] | |
| [25] | Xie CP, Fang Y, Fang YM (2011) Analysis of the vertical structure and importance value of Quercus phillyraeoides community in different districts. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 38, 176-184. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [谢春平, 方彦, 方炎明 (2011) 乌冈栎群落垂直结构与重要值分析. 安徽农业大学学报, 38, 176-184.] | |
| [26] | Xie FL, Zhou Q, Shi H, Jiang MX, Zhang QF, Dang HS (2019) Studies on habit characteristics of endangered Berchemiella wilsonii (Schneid.) Nakai var. pubipetiolata H. Qian. Hubei Forestry Science and Technology, 48(4), 19-23, 84. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [谢峰淋, 周全, 史航, 江明喜, 张全发, 党海山 (2019) 濒危植物毛柄小勾儿茶生境特征研究. 湖北林业科技, 48(4), 19-23, 84.] | |
| [27] | Xu FH, Kang M, Huang HW, Jiang MX (2006) Genetic diversity in fragmented populations of Berchemiella wilsonii var. pubipetiolata, an endangered plant endemic to Eastern China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 30, 157-164. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[许凤华, 康明, 黄宏文, 江明喜 (2006) 濒危植物毛柄小勾儿茶片断化居群的遗传多样性. 植物生态学报, 30, 157-164.]
DOI |
|
| [28] | Xu H, Liu YH (2018) Relationship between diameter class structure and intraspecific and interspecific competitions of precious and endangering plant Acer catalpifolium. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 38, 1160-1170. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [许恒, 刘艳红 (2018) 珍稀濒危植物梓叶槭种群径级结构与种内种间竞争关系. 西北植物学报, 38, 1160-1170.] | |
| [29] | Xu JW, Shi FX, Zhang CH, Wan SZ, Wu PP, Liu SS, Mao R (2020) Difference in intra- and inter-specific competition of two endangered plant species (Toona ciliate var. pubescens and Taxus chinensis var. mairei) in the middle subtropical zone of China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31, 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐佳文, 石福习, 张朝晖, 万松泽, 吴盼盼, 刘姗姗, 毛瑢 (2020) 中亚热带濒危植物毛红椿和南方红豆杉种内与种间竞争差异. 应用生态学报, 31, 1-8.] | |
| [30] |
Zang RG (2020) Research progress in wild plant with extremely small populations in China. Biodiversity Science, 28, 263-268. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
[臧润国 (2020) 中国极小种群野生植物保护研究进展. 生物多样性, 28, 263-268.]
DOI |
|
| [31] |
Zhang ZJ, Guo YP, He JS, Tang ZY (2018) Conservation status of wild plant species with extremely small populations in China. Biodiversity Science, 26, 572-577. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张则瑾, 郭焱培, 贺金生, 唐志尧 (2018) 中国极小种群野生植物的保护现状评估. 生物多样性, 26, 572-577.]
DOI |
|
| [32] | Zheng SQ, Yang WQ, Fang ZF, Zheng N, Liu JF, Lin KQ, Xiao LF, Li L (2021) Population status and protection evaluation of Syzygium album, a species with extremely small population. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32, 103-112. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郑世群, 杨皖乔, 方镇福, 郑柠, 刘金福, 林凯琴, 肖丽芳, 李霖 (2021) 极小种群植物白果蒲桃种群现状与保护评价. 应用生态学报, 32, 103-112.] | |
| [33] | Zheng Y, Zhao WZ, Zhang GF (2017) Spatial analysis of competition in Haloxylon ammodendron community based on the V_Hegyi index in an oasis-desert ecotone. Journal of Desert Research, 27, 1127-1134. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郑颖, 赵文智, 张格非 (2017) 基于V_Hegyi竞争指数的绿洲边缘人工固沙植被梭梭(Haloxylon ammodendron)的种群竞争. 中国沙漠, 27, 1127-1134.] |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 周昊, 王茗毅, 张楚格, 肖治术, 欧阳芳. 昆虫旅馆在独栖蜂多样性保护中的现状与挑战[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24472-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [6] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [7] | 易木荣, 卢萍, 彭勇, 汤勇, 许久恒, 尹浩萍, 张路杨, 翁晓东, 底明晓, 雷隽, 卢宸祺, 曹如君, 戴年华, 占德洋, 童媚, 楼智明, 丁永刚, 柴静, 车静. 北潦河金家水支流江西大鲵野外种群现状及栖息地评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24145-. |
| [8] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [9] | 李沫潼, 何拓, 李薇, 廖菁, 曾岩. 从CITES的术语看野生动植物国际贸易监管规则[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24545-. |
| [10] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [11] | 张明燡, 王晓梅, 郑言鑫, 吴楠, 李东浩, 樊恩源, 李娜, 单秀娟, 于涛, 赵春暖, 李波, 徐帅, 吴玉萍, 任利群. 黄河口典型牡蛎礁分布区资源状况和栖息地功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [14] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| [15] | 周志华, 金效华, 罗颖, 李迪强, 岳建兵, 刘芳, 何拓, 李希, 董晖, 罗鹏. 中国林草部门落实《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》的机制、成效分析及建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24487-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()