



生物多样性 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (1): 51-63. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018182 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2018182
所属专题: 钱江源国家公园生物多样性保护与管理; 土壤生物与土壤健康
孙孝平1,李双1,余建平3,方彦君4,张银龙1,*( ),曹铭昌2,*(
),曹铭昌2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2018-07-02
接受日期:2018-12-24
出版日期:2019-01-20
发布日期:2019-03-15
通讯作者:
张银龙,曹铭昌
基金资助:
Sun Xiaoping1,Li Shuang1,Yu Jianping3,Fang Yanjun4,Zhang Yinlong1,*( ),Cao Mingchang2,*(
),Cao Mingchang2,*( )
)
Received:2018-07-02
Accepted:2018-12-24
Online:2019-01-20
Published:2019-03-15
Contact:
Zhang Yinlong,Cao Mingchang
摘要:
土地利用变化是生物多样性与生态系统服务变化的主要原因之一。评估土地利用变化对生物多样与生态系统服务影响对于政府决策具有重要作用。钱江源国家公园体制试点区是钱塘江的源头, 也是国家的重点生态功能区。本研究以钱江源国家公园体制试点区为研究区, 首先设计自然发展情景、规划情景、生态保护情景和开发利用情景等4种2025年不同土地利用变化情景, 随后采用InVEST模型和CLUE-S模型分析不同情景下钱江源国家公园水资源供给、涵养水源、固碳释氧、土壤保持、环境净化和生境质量等生态系统服务及其价值变化。结果表明: (1)核心保护区和生态保育区的生态系统服务价值占钱江源国家公园总价值的88.30%。(2)生态保护情景下钱江源国家公园生态系统服务价值最高, 有129.17亿元; 规划情景下生态系统服务价值次之, 有126.92亿元。(3)规划情景下钱江源国家公园水资源供给服务优于生态保护情景, 其他生态系统服务则次于生态保护情景。考虑到钱江源国家公园为下游提供重要的水资源这一功能, 将规划情景作为试点区2025年最优的土地利用变化情景。
孙孝平,李双,余建平,方彦君,张银龙,曹铭昌 (2019) 基于土地利用变化情景的生态系统服务价值评估: 以钱江源国家公园体制试点区为例. 生物多样性, 27, 51-63. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018182.
Sun Xiaoping,Li Shuang,Yu Jianping,Fang Yanjun,Zhang Yinlong,Cao Mingchang (2019) Evaluation of ecosystem service value based on land use scenarios: A case study of Qianjiangyuan National Park pilot. Biodiversity Science, 27, 51-63. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018182.
| 土地利用类型 Land use type (ha) | 2015 | 自然发展情景 Business as usual | 规划情景 Strategic planning | 生态保护情景 Ecological protection | 开发利用情景 Development |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阔叶林 Broad-leaved forest | 17,166.9 | 17,369.7 | 17,962.9 | 19,074.8 | 17,123.6 |
| 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 4,670.1 | 4,655.0 | 4,634.3 | 4,383.9 | 4,652.9 |
| 针阔混交林 Mixed broadleaf-conifer forest | 1,412.2 | 1,409.2 | 1,286.7 | 1,248.8 | 1,404.1 |
| 灌木林 Shrubbery | 957.3 | 953.3 | 665.8 | 124.4 | 937.6 |
| 园地 Garden | 24.2 | 23.6 | 11.1 | 13.3 | 18.9 |
| 草丛 Grassland | 159.9 | 158.4 | 154.8 | 39.7 | 151.1 |
| 水田 Paddy field | 388.4 | 234.9 | 142.0 | 13.1 | 306.2 |
| 旱地 Dry land | 98.6 | 96.9 | 13.8 | 3.8 | 79.9 |
| 水域 Water area | 148.0 | 120.4 | 148.5 | 148.0 | 148.0 |
| 建设用地 Built-up land | 57.3 | 59.3 | 65.3 | 36.4 | 263.5 |
| 裸地 Unused land | 4.1 | 6.3 | 1.8 | 0.8 | 1.2 |
| 合计 Total | 25,087 | 25,087 | 25,087 | 25,087 | 25,087 |
表1 2015-2025年钱江源国家公园土地利用类型面积
Table 1 Land use/land cover of the Qianjiangyuan National Park pilot between 2015 and 2025
| 土地利用类型 Land use type (ha) | 2015 | 自然发展情景 Business as usual | 规划情景 Strategic planning | 生态保护情景 Ecological protection | 开发利用情景 Development |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阔叶林 Broad-leaved forest | 17,166.9 | 17,369.7 | 17,962.9 | 19,074.8 | 17,123.6 |
| 针叶林 Coniferous forest | 4,670.1 | 4,655.0 | 4,634.3 | 4,383.9 | 4,652.9 |
| 针阔混交林 Mixed broadleaf-conifer forest | 1,412.2 | 1,409.2 | 1,286.7 | 1,248.8 | 1,404.1 |
| 灌木林 Shrubbery | 957.3 | 953.3 | 665.8 | 124.4 | 937.6 |
| 园地 Garden | 24.2 | 23.6 | 11.1 | 13.3 | 18.9 |
| 草丛 Grassland | 159.9 | 158.4 | 154.8 | 39.7 | 151.1 |
| 水田 Paddy field | 388.4 | 234.9 | 142.0 | 13.1 | 306.2 |
| 旱地 Dry land | 98.6 | 96.9 | 13.8 | 3.8 | 79.9 |
| 水域 Water area | 148.0 | 120.4 | 148.5 | 148.0 | 148.0 |
| 建设用地 Built-up land | 57.3 | 59.3 | 65.3 | 36.4 | 263.5 |
| 裸地 Unused land | 4.1 | 6.3 | 1.8 | 0.8 | 1.2 |
| 合计 Total | 25,087 | 25,087 | 25,087 | 25,087 | 25,087 |
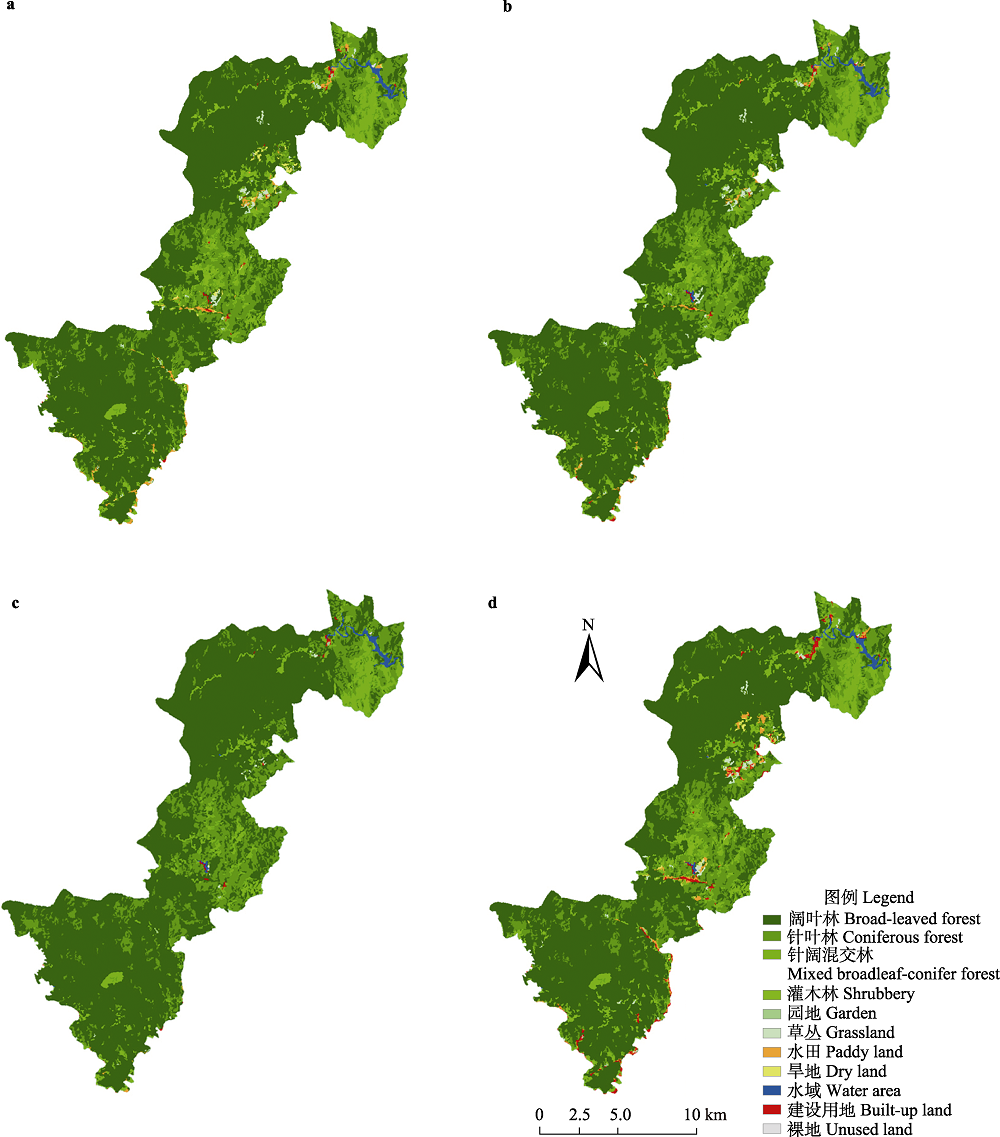
图2 钱江源国家公园体制试点区2025年土地利用类型图。(a)自然发展情景; (b)规划情景; (c)生态保护情景; (d)开发利用情景。
Fig. 2 Land use types of the Qianjiangyuan National Park pilot in 2025. (a) Business as usual; (b)Strategic planning; (c) Ecological protection; (d) Development.
| 核心保护区 Core protection area | 生态保育区 Ecological conservation area | 游憩展示区 Recreation area | 传统利用区 Traditional utilization area | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 供给服务 Provisioning services | ||||
| 水资源供给 Water yield (×104 m3) | 6,721.613 | 19,460.106 | 682.811 | 4,457.063 |
| 调节服务 Regulating services | ||||
| 涵养水源 Water conservation (×104 m3) | 639.814 | 840.122 | 59.338 | 136.947 |
| 土壤保持 Soil conservation (×104 t) | 546.608 | 721.516 | 29.546 | 96.026 |
| 固碳量 Carbon sequestration (×104 t) | 183.773 | 258.128 | 13.635 | 34.921 |
| 释氧量 Oxygen release (×104 t) | 135.294 | 190.033 | 10.038 | 25.708 |
| 环境净化 Environment purification | ||||
| SO2吸收 SO2 absorption (t) | 996.312 | 1,504.517 | 104.472 | 225.932 |
| 滞尘清理 Clean detaining dust (×104 t) | 11.553 | 22.016 | 0.738 | 1.874 |
| N输出量 Nitrogen output (t) | 11.198 | 31.121 | 12.083 | 59.054 |
| P输出量 Phosphorus output (t) | 0.466 | 1.411 | 0.418 | 2.262 |
| 栖息地服务 Supporting services | ||||
| 生境质量得分 Habitat quality | 0.936 | 0.888 | 0.855 | 0.815 |
| 最优生境质量面积 Area of the optimal habitat quality (km2) | 70.633 | 89.032 | 3.845 | 8.933 |
表2 2015年各功能分区生态系统服务的物质量
Table 2 The quality of ecosystem services of different functional areas in 2015
| 核心保护区 Core protection area | 生态保育区 Ecological conservation area | 游憩展示区 Recreation area | 传统利用区 Traditional utilization area | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 供给服务 Provisioning services | ||||
| 水资源供给 Water yield (×104 m3) | 6,721.613 | 19,460.106 | 682.811 | 4,457.063 |
| 调节服务 Regulating services | ||||
| 涵养水源 Water conservation (×104 m3) | 639.814 | 840.122 | 59.338 | 136.947 |
| 土壤保持 Soil conservation (×104 t) | 546.608 | 721.516 | 29.546 | 96.026 |
| 固碳量 Carbon sequestration (×104 t) | 183.773 | 258.128 | 13.635 | 34.921 |
| 释氧量 Oxygen release (×104 t) | 135.294 | 190.033 | 10.038 | 25.708 |
| 环境净化 Environment purification | ||||
| SO2吸收 SO2 absorption (t) | 996.312 | 1,504.517 | 104.472 | 225.932 |
| 滞尘清理 Clean detaining dust (×104 t) | 11.553 | 22.016 | 0.738 | 1.874 |
| N输出量 Nitrogen output (t) | 11.198 | 31.121 | 12.083 | 59.054 |
| P输出量 Phosphorus output (t) | 0.466 | 1.411 | 0.418 | 2.262 |
| 栖息地服务 Supporting services | ||||
| 生境质量得分 Habitat quality | 0.936 | 0.888 | 0.855 | 0.815 |
| 最优生境质量面积 Area of the optimal habitat quality (km2) | 70.633 | 89.032 | 3.845 | 8.933 |
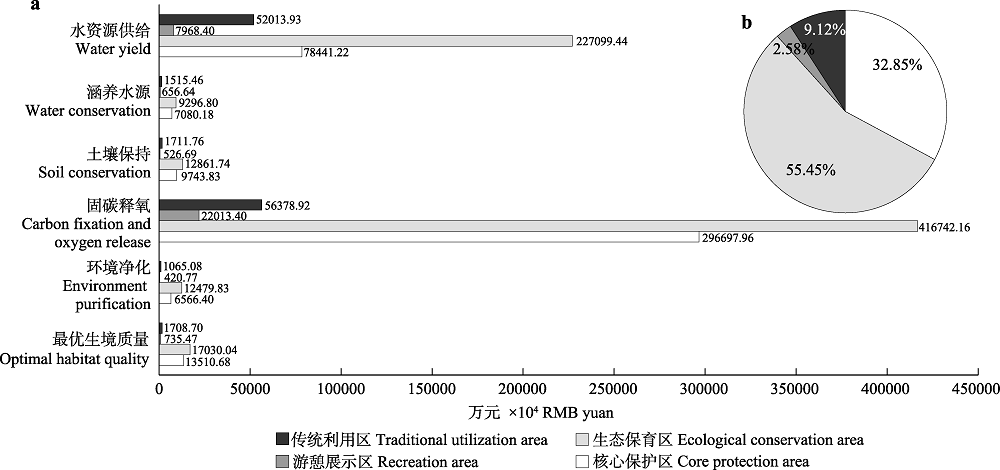
图3 2015年各功能分区生态系统服务价值及其比例。(a)生态系统服务价值; (b)生态系统服务价值比例。
Fig. 3 The value and percentage of ecosystem services of different functional areas in 2015. (a) The value of ecosystem services of different functional areas; (b) The percentage of ecosystem services of different functional areas
| 2015 | 自然发展情景 Business as usual | 规划情景 Strategic planning | 生态保护情景 Ecological protection | 开发利用情景 Development | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 供给服务 Provisioning services | |||||
| 水资源供给 Water yield (×104 m3) | 31,321.593 | 31,306.852 | 31,199.755 | 30,900.282 | 31,355.505 |
| 调节服务 Regulating services | |||||
| 涵养水源 Water conservation (×104 m3) | 1,676.222 | 1,682.344 | 1,687.435 | 1,665.958 | 1,674.278 |
| 土壤保持 Soil conservation (×104 t) | 1,393.696 | 1,394.248 | 1,394.778 | 1,395.213 | 1,394.026 |
| 固碳释氧 Carbon fixation and oxygen release | |||||
| 固碳量 Carbon sequestration (×104 t) | 490.457 | 492.860 | 499.544 | 514.359 | 488.556 |
| 释氧量 Oxygen release (×104 t) | 361.073 | 362.841 | 367.762 | 378.669 | 359.673 |
| 环境净化 Environment purification | |||||
| SO2吸收 SO2 absorption (t) | 2,831.233 | 2,853.432 | 2,902.315 | 3,005.724 | 2,822.379 |
| 滞尘清理 Clean detaining dust (×104 t) | 36.181 | 36.328 | 36.548 | 36.689 | 36.059 |
| N输出量 Nitrogen output (t) | 113.456 | 90.301 | 59.424 | 42.602 | 94.647 |
| P输出量 Phosphorus output (t) | 4.557 | 3.507 | 2.206 | 1.463 | 3.700 |
| 栖息地服务 Supporting services | |||||
| 生境质量得分 Habitat quality | 0.938 | 0.941 | 0.954 | 0.968 | 0.934 |
| 最优生境质量面积 Area of the optimal habitat quality (km2) | 172.443 | 174.480 | 179.253 | 190.691 | 170.635 |
表3 不同土地利用情景下生态系统服务的物质量
Table 3 The quality of ecosystem services under various land use scenarios
| 2015 | 自然发展情景 Business as usual | 规划情景 Strategic planning | 生态保护情景 Ecological protection | 开发利用情景 Development | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 供给服务 Provisioning services | |||||
| 水资源供给 Water yield (×104 m3) | 31,321.593 | 31,306.852 | 31,199.755 | 30,900.282 | 31,355.505 |
| 调节服务 Regulating services | |||||
| 涵养水源 Water conservation (×104 m3) | 1,676.222 | 1,682.344 | 1,687.435 | 1,665.958 | 1,674.278 |
| 土壤保持 Soil conservation (×104 t) | 1,393.696 | 1,394.248 | 1,394.778 | 1,395.213 | 1,394.026 |
| 固碳释氧 Carbon fixation and oxygen release | |||||
| 固碳量 Carbon sequestration (×104 t) | 490.457 | 492.860 | 499.544 | 514.359 | 488.556 |
| 释氧量 Oxygen release (×104 t) | 361.073 | 362.841 | 367.762 | 378.669 | 359.673 |
| 环境净化 Environment purification | |||||
| SO2吸收 SO2 absorption (t) | 2,831.233 | 2,853.432 | 2,902.315 | 3,005.724 | 2,822.379 |
| 滞尘清理 Clean detaining dust (×104 t) | 36.181 | 36.328 | 36.548 | 36.689 | 36.059 |
| N输出量 Nitrogen output (t) | 113.456 | 90.301 | 59.424 | 42.602 | 94.647 |
| P输出量 Phosphorus output (t) | 4.557 | 3.507 | 2.206 | 1.463 | 3.700 |
| 栖息地服务 Supporting services | |||||
| 生境质量得分 Habitat quality | 0.938 | 0.941 | 0.954 | 0.968 | 0.934 |
| 最优生境质量面积 Area of the optimal habitat quality (km2) | 172.443 | 174.480 | 179.253 | 190.691 | 170.635 |
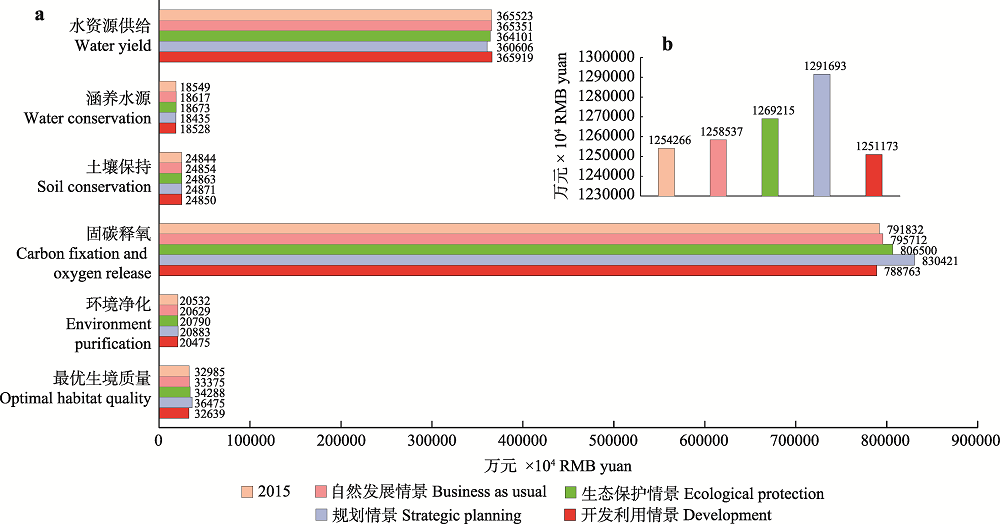
图4 不同土地利用情景下的生态系统服务价值。(a)各生态系统服务价值(万元); (b)生态系统服务总价值(万元)。
Fig. 4 The value of ecosystem services under different land use scenarios. (a) The value of multiple ecosystem services under different land use scenarios (×104 RMB yuan); (b) The total value of ecosystem services under different land use scenarios (×104 RMB yuan)
| [1] | Bai Y, Ouyang ZY, Zheng H, Xu WH, Jiang B, Fang Y ( 2011) Evaluation of the forest ecosystem services in Haihe River Basin, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31, 2029-2039. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 白杨, 欧阳志云, 郑华, 徐卫华, 江波, 方瑜 ( 2011) 海河流域森林生态系统服务功能评估. 生态学报, 31, 2029-2039.] | |
| [2] |
Bai Y, Zheng H, Zhuang CW, Ouyang ZY, Xu WH ( 2013) Ecosystem services valuation and its regulation in Baiyangdian basin: Based on InVEST model. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 711-717. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 白杨, 郑华, 庄长伟, 欧阳志云, 徐卫华 ( 2013) 白洋淀流域生态系统服务评估及其调控. 生态学报, 33, 711-717.]
DOI URL |
|
| [3] | Bao R, Liu F, Zhang JP, Duan YL, Zhao S, Yan XY, Liu Y ( 2018) Multi-objective linear programming-based trade-off and optimization of the ecosystem services in Jiajiyu small watershed in the Loess Plateau, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 812-828. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 包蕊, 刘峰, 张建平, 段颖琳, 赵帅, 严晓亚, 刘英 ( 2018) 基于多目标线性规划的甲积峪小流域生态系统服务权衡优化. 生态学报, 38, 812-828.] | |
| [4] |
Butler JRA, Wong GY, Metcalfe DJ ( 2013) An analysis of trade-offs between multiple ecosystem services and stakeholders linked to land use and water quality management in the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 180, 176-191.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Cao W, Li R, Chi X, Chen N, Chen J, Zhang H, Zhang F ( 2017) Island urbanization and its ecological consequences: A case study in the Zhoushan Island, East China. Ecological Indicators, 76, 1-14.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Delphin SF, Escobedo J, Elrahman AA, Cropper WP ( 2016) Urbanization as a land use change driver of forest ecosystem services. Land Use Policy, 54, 188-199.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Fu B, Xu P, Wang YK, Peng Y, Ren J ( 2013) Spatial pattern of water retention in Dujiangyan County. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 789-797. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 傅斌, 徐佩, 王玉宽, 彭怡, 任静 ( 2013) 都江堰市水源涵养功能空间格局. 生态学报, 33, 789-797.]
DOI URL |
|
| [8] |
Fu BJ, Zhang LW ( 2014) Land-use change and ecosystem services: Concepts, methods and progress. Progress in Geograpy, 33, 441-446. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 傅伯杰, 张立伟 ( 2014) 土地利用变化与生态环境服务: 概念、方法与进展. 地理科学进展, 33, 441-446.]
DOI URL |
|
| [9] | Fu MD, Li JS, Zhang RA, Gao XQ, Xiao NW ( 2016) Valuation of the ecosystem services in southern mountain of Zhejiang Province. Ecological Economy, 32, 189-193. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 付梦娣, 李俊生, 章荣安, 高晓奇, 肖能文 ( 2016) 浙江省南部山区生态系统服务价值评估. 生态经济, 32, 189-193.] | |
| [10] |
Gao J, Li F, Gao H, Zhou C, Zhang X ( 2017) The impact of land-use change on water-related ecosystem services: A study of the Guishui River Basin, Beijing, China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 163, 148-155.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Goldstein J, Caldarone G, Duarte TK, Ennaanay D, Hannahs N, Mendoza G, Polasky S, Wolny S, Daily GC ( 2015) Integrating ecosystem-service tradeoffs into land-use decisions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 109, 7565-7570.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] |
Gong X, Cao MC, Sun XP, Le ZF, Li S, Xu HG ( 2017) Valuation of ecosystem services in Wuyishan City. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 33, 1094-1101. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 龚溪, 曹铭昌, 孙孝平, 乐志芳, 李双, 徐海根 ( 2017) 武夷山市生态系统服务价值评估. 生态与农村环境学报, 33, 1094-1101.]
DOI URL |
|
| [13] |
He S, Su Y, Wang L, Gallagher L, Cheng H ( 2018) Taking an ecosystem services approach for a new national park system in China. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 137, 136-144.
DOI URL |
| [14] | Huang HC, Yun YX, Miao ZT, Hao C, Li HY ( 2013) Multi-scenario and prediction of ecosystem services as affected by urban expansion: A case study in coastal area of Tianjin, North China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 24, 697-704. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 黄焕春, 运迎霞, 苗展堂, 郝翠, 李洪远 ( 2013) 城市扩张影响下生态系统服务的多情景模拟和预测——以天津市滨海地区为例. 应用生态学报, 24, 697-704.] | |
| [15] | Huang J, Zhang XM, Zhang JC ( 2010) Comprehensive evaluation on soil and water conservation function of main forest types of ecological protection forest in Kaihua County. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 17, 88-90. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 黄进, 张晓勉, 张金池 ( 2010) 开化生态公益林主要森林类型水土保持功能综合评价. 水土保持研究, 17, 88-90.] | |
| [16] | Jiang B, Ouyang ZY, Miao H, Zheng H, Bai Y, Zhuang CW, Fang Y ( 2011) Ecosystem services valuation of the Haihe River Basin wetlands. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31, 2236-2244. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 江波, 欧阳志云, 苗鸿, 郑华, 白杨, 庄长伟, 方瑜 ( 2011) 海河流域湿地生态系统服务功能价值评价. 生态学报, 31, 2236-2244.] | |
| [17] |
Jiang W, Chen Z, Lei X, He B, Jia K, Zhang Y ( 2016) Simulation of urban agglomeration ecosystem spatial distributions under different scenarios: A case study of the Changsha- Zhuzhou-Xiangtan urban agglomeration. Ecological Engineering, 88, 112-121.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Lacher IL, Ahmadisharaf E, Fergus C, Akre T, McShea WJ, Benham BL, Kline KS ( 2018) Scale-dependent impacts of urban and agricultural land use on nutrients, sediment, and runoff. Science of Total Environment, 652, 611-622.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Li C, Zheng H, Li S, Chen X, Li J, Zeng W, Liang Y, Polasky S, Feldman MW, Ruckelshaus M, Ouyang ZY, Daily GC ( 2015) Impacts of conservation and human development policy across stakeholders and scales. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 112, 7396-7401.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] |
Li LY, Xing H, Wu YJ, Gong XF, Li L ( 2012) Assessment of forest ecosystem services value based on MA—Taking Suichang County in Zhejiang Province as the case. Issues of Forestry Economics, 32, 317-322. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 李兰英, 邢红, 吴英俊, 龚笑飞, 李浪 ( 2012) 基于MA的森林生态系统服务价值评价——以浙江省遂昌县为例. 林业经济问题, 32, 317-322.]
DOI URL |
|
| [21] |
Li YF, Luo YC, Liu G, Ouyang ZY, Zheng H ( 2013) Effects of land use change on ecosystem services: A case study in Miyun Reservoir watershed. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 726-736. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 李屹峰, 罗跃初, 刘纲, 欧阳志云, 郑华 ( 2013) 土地利用变化对生态系统服务功能的影响——以密云水库流域为例. 生态学报, 33, 726-736.]
DOI URL |
|
| [22] | MA (Millennium Ecosystem Assessment) (2005) Ecosystems and Human Well-being: Synthesis. Island Press/World Resources Institute, Washington, DC. |
| [23] |
Mukul SA, Sohel MSI, Herbohn J, Inostroza L, K?nig H ( 2017) Integrating ecosystem services supply potential from future land-use scenarios in protected area management: A Bangladesh case study. Ecosystem Services, 26, 355-364.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Nelson E, Mendoza G, Regetz J ( 2009) Modeling multiple ecosystem services, biodiversity conservation, commodity production, and tradeoffs at landscape scales. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 7, 4-11.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Polasky S, Nelson E, Pennington D ( 2011) The impact of land- use change on ecosystem services, biodiversity and returns to landowners: A case study in the State of Minnesota. Environmental & Resource Economics, 48, 219-242.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Qian YF, Yi LT, Dou PM, Zhu GL, Ying BG, Yu SQ ( 2012) Biomass and carbon fixation with oxygen release benefits in an ecological service forest of Jinyun County, China. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 29, 257-264. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 钱逸凡, 伊力塔, 钭培民, 朱国亮, 应宝根, 余树全 ( 2012) 浙江缙云公益林生物量及固碳释氧效益. 浙江农业大学学报, 29, 257-264.]
DOI URL |
|
| [27] | Ramachandra TV, Bharath S, Gupta N ( 2018) Modelling landscape dynamics with LST in protected areas of Western Ghats, Karnataka. Journal of Environment Management, 206, 1253-1262. |
| [28] |
Shao XY, Zhang ZF, Liu Z, Jing CW, Qi JG, Jiang JG, Cai XM, Liu QK ( 2018) Effects of land use change and planning regulation on ecosystem service values of islands: A case study of Putuo District, Zhoushan Archipelago. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 37, 514-522. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 邵小云, 张则飞, 刘中, 荆长伟, 齐家国, 蒋锦刚, 蔡秀敏, 刘乾坤 ( 2018) 土地利用变化及规划结构对海岛生态系统服务价值的影响——以舟山市普陀区为例. 生态学杂志, 37, 514-522.]
DOI URL |
|
| [29] |
Sun X, Lu Z, Li F, Crittenden JC ( 2018) Analyzing spatio-temporal changes and trade-offs to support the supply of multiple ecosystem services in Beijing, China. Ecological Indicators, 94, 117-129.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Swetnam RD, Fisher B, Mbilinyi BP ( 2011) Mapping socio- economic scenarios of land cover change: A GIS method to enable ecosystem service modelling. Journal of Environmental Management, 92, 563-574.
DOI URL PMID |
| [31] | Tallis H, Ricketts T, Guerry A ( 2011) InVEST 2.4.4 User’s Guide. The Natural Capital Project, Stanford. |
| [32] |
Trisurat Y, Eawpanich P, Kalliola R ( 2016) Integrating land use and climate change scenarios and models into assessment of forested watershed services in Southern Thailand. Environment Research, 147, 611-620.
DOI URL PMID |
| [33] |
Wang J, Peng J, Zhao M, Liu Y, Chen Y ( 2017) Significant trade-off for the impact of Grain-for-Green Programme on ecosystem services in North-western Yunnan, China. Science of Total Environment, 574, 57-64.
DOI URL PMID |
| [34] |
Xiao Q, Xiao Y, Ouyang ZY, Xu WH, Xiang S, Li YZ ( 2014) Value assessment of the function of the forest ecosystem services in Chongqing. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34, 216-223. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 肖强, 肖洋, 欧阳志云, 徐卫华, 向轼, 李勇志 ( 2014) 重庆市森林生态系统服务功能价值评估. 生态学报, 34, 216-223.]
DOI URL |
|
| [35] | Zhang J, Yuan WG, Ge Y, Jiang B, Zhu JR, Shen AH, Chang J ( 2010) Carbon storage and its sequestration potential by ecological service forest in Zhejiang. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30, 3839-3848. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张骏, 袁位高, 葛滢, 江波, 朱锦茹, 沈爱华, 常杰 ( 2010) 浙江省生态公益林碳储量和固碳现状及潜力. 生态学报, 30, 3839-3848.] | |
| [36] | Zhang Y ( 2015) Forest Ecological Benefit Evaluation and Construction of Balance Sheet. China Economic Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张颖 ( 2015) 生态效益评估与资产负债表编制. 中国经济出版社, 北京.] | |
| [37] |
Zheng H, Li Y, Robinson BE, Liu G, Ma D, Wang F, Lu F, Ouyang Z, Daily GC ( 2016) Using ecosystem service trade-offs to inform water conservation policies and management practices. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 14, 527-532.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Zheng H, Li YF, Ouyang ZY, Luo YC ( 2013) Progress and perspectives of ecosystem services management. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 702-710. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 郑华, 李屹峰, 欧阳志云, 罗跃初 ( 2013) 生态系统服务功能管理研究进展. 生态学报, 33, 702-710.]
DOI URL |
|
| [39] |
Zhu KW, Li YC, Zhou MT ( 2015) Land use scenario simulation of the main city of Chongqing based on the CLUE-S model. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 24, 789-797. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 朱康文, 李月臣, 周梦甜 ( 2015) 基于CLUE-S模型的重庆市主城区土地利用情景模拟. 长江流域资源与环境, 24, 789-797.]
DOI URL |
|
| [40] | Zhu YB, Shi YJ ( 2018) Value evaluation and pricing of water resources in major cities in China. Resources Science, 40, 1040-1050. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱永彬, 史雅娟 ( 2018) 中国主要城市水资源价值评价与定价研究. 资源科学, 40, 1040-1050.] |
| [1] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [2] | 耿宜佳, 田瑜, 李俊生, 李子圆, 潘玉雪. 《生物多样性公约》框架下外来入侵物种管控的全球进展、挑战和展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24275-. |
| [3] | 杨俊毅, 关潇, 李俊生, 刘晶晶, 郝颢晶, 王槐睿. 乌江流域生物多样性与生态系统服务的空间格局及相互关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23061-. |
| [4] | 廖美哲, 张宗文, 白可喻. 中国农业生态系统多样性保护研究现状与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23017-. |
| [5] | 吴杨, 田瑜, 戴逢斌, 李子圆. “自然对人类的贡献”的实现、发展趋势和启示[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21549-. |
| [6] | 胡官正, 曾维华, 马冰然. 保护地区域经济建设与生态保护协同发展路线图: 以三江源地区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21225-. |
| [7] | 徐靖, 王金洲, 李俊生. 商业界参与生物多样性主流化的进展、路径与建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22078-. |
| [8] | 傅声雷, 刘满强, 张卫信, 邵元虎. 土壤动物多样性的地理分布及其生态功能研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22435-. |
| [9] | 戴逢斌, 吴杨, 潘玉雪, 张博雅, 田瑜. IPBES工作效率和科学职能的有效性分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 688-692. |
| [10] | 曹明, 李俊生, 王伟, 夏聚一, 冯春婷, 付刚, 黄文婕, 刘方正. 基于InVEST与倾向评分匹配模型评估秦岭国家级自然保护区水源涵养服务保护成效[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 617-628. |
| [11] | 王伟, 李俊生. 中国生物多样性就地保护成效与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(2): 133-149. |
| [12] | 郑晓明, 杨庆文. 中国农业生物多样性保护进展概述[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(2): 167-176. |
| [13] | 吴杨, 潘玉雪, 张博雅, 戴逢斌, 田瑜. IPBES框架下的生物多样性和生态系统服务区域评估及政策经验[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(7): 913-919. |
| [14] | 刘向, 陈立范, 周淑荣. 生物多样性与传染性疾病的关系: 进展、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(11): 1376-1390. |
| [15] | 潘玉雪, 张博雅, 吴杨, 戴逢斌, 田瑜. IPBES工作进展及我国对策建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(10): 1286-1291. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()