



生物多样性 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (5): 617-628. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020271 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020271
曹明1,2, 李俊生1,2, 王伟1,2,*( ), 夏聚一1,2,3, 冯春婷1,2, 付刚1,2, 黄文婕1,2, 刘方正1,2
), 夏聚一1,2,3, 冯春婷1,2, 付刚1,2, 黄文婕1,2, 刘方正1,2
收稿日期:2020-07-07
接受日期:2020-11-04
出版日期:2021-05-20
发布日期:2020-12-31
通讯作者:
王伟
作者简介:* E-mail: wang.wei@craes.org.cn基金资助:
Ming Cao1,2, Junsheng Li1,2, Wei Wang1,2,*( ), Juyi Xia1,2,3, Chunting Feng1,2, Gang Fu1,2, Wenjie Huang1,2, Fangzheng Liu1,2
), Juyi Xia1,2,3, Chunting Feng1,2, Gang Fu1,2, Wenjie Huang1,2, Fangzheng Liu1,2
Received:2020-07-07
Accepted:2020-11-04
Online:2021-05-20
Published:2020-12-31
Contact:
Wei Wang
摘要:
自然保护区在保障水源涵养等生态系统服务方面发挥了重要作用, 对区域水资源的可持续利用具有重要意义。然而, 自然保护区水源涵养服务保护成效的主要影响因素仍然不清, 不利于自然保护区的有效管理和区域可持续发展目标的实现。本文拟探讨: (1)秦岭区域水源涵养服务的总体情况; (2)自然保护区对水源涵养服务的保护成效; (3)自然保护区水源涵养服务保护成效的主要影响因素是什么。本文采用InVEST模型计算秦岭区域19个国家级自然保护区2010-2015年的水源涵养量, 基于倾向评分配比法研究了自然保护区水源涵养服务保护成效, 并通过随机森林回归判断自然保护区水源涵养服务保护成效的主要影响因素。研究结果表明, 虽然在2010-2015年秦岭区域水源涵养服务整体降低, 但与自然保护区外的配对样本相比, 大多数自然保护区(63.16%)水源涵养服务保护成效显著(N = 12, P < 0.05); 少数保护区(26.32%)在减缓水源涵养服务降低的作用不如自然保护区外(N = 5, P < 0.05); 也有个别自然保护区(10.52%)对水源涵养服务保护成效不明显(N = 2, P > 0.05)。从主要影响因素来看, 自然保护区水源涵养服务保护成效主要受降水量变化和自然保护区资金投入的影响。结果显示: (1) 2010-2015年间秦岭区域水源涵养量减少较为明显, 但总体来看自然保护区在减缓水源涵养服务降低方面取得了积极成效。(2)降水量变化对水源涵养服务保护成效起到主导作用; (3)管理因素也对保护区水源涵养服务保护成效有一定影响, 在管理因素中资金投入的大小对水源涵养服务保护效果影响最大。因此, 建议进一步增加资金投入, 以提升自然保护区水源涵养服务的保护成效。
曹明, 李俊生, 王伟, 夏聚一, 冯春婷, 付刚, 黄文婕, 刘方正 (2021) 基于InVEST与倾向评分匹配模型评估秦岭国家级自然保护区水源涵养服务保护成效. 生物多样性, 29, 617-628. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020271.
Ming Cao, Junsheng Li, Wei Wang, Juyi Xia, Chunting Feng, Gang Fu, Wenjie Huang, Fangzheng Liu (2021) Assessing the effectiveness of water retention ecosystem service in Qinling National Nature Reserve based on InVEST and propensity score matching model. Biodiversity Science, 29, 617-628. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020271.
| 数据类型 Data type | 来源与获取方法 Data sources |
|---|---|
| 土地利用数据(2010, 2015年) Land use data (2010, 2015) | 2010-2015年全国生态状况变化遥感调查与评估项目 2010-2015 Remote Sensing Investigation and Assessment Project of Ecological Status Change in China |
| 数字高程模型数据 Digital elevation model (DEM) data | 地理空间数据云GDEMV2数据(30 m分辨率) GDEMV2 data from Geospatial data cloud with 30 m resolution |
| 子流域数据 Sub-watersheds data | 根据数字高程模型数据进行水文提取 Hydrological information extraction based on DEM data |
| 降雨数据 Precipitation data | 数据来源于资源环境数据云平台(分辨率1 km) Precipitation data with 1 km resolution obtained from the website of |
| 蒸散数据 Evapotranspiration | 数据来源于谷歌地球引擎平台, MOD16A2产品(500 m分辨率) Data were extracted from the MOD16A2 products (500 m resolution), which were obtained from the Google Earth Engine. |
| 土壤数据 Soil data | 数据来源于第二次土壤普查, 国家青藏高原数据科学中心( Data were obtained from the second soil census of National Tibetan Plateau Data Center ( |
| 植物有效含水量 Plant available water capacity (PAWC) | 根据土壤普查数据采用土壤质地数据进行计算得到 The data were calculated from the soil texture data based on the soil census. |
| 根系深度 Root depth | 第二次土壤普查土壤剖层, 结合研究区文献校正得到( Adjusted from the soil profile in the second soil census combined with related literature in the study area ( |
| Zhang系数 Zhang coefficient | 根据自然径流反复计算, 结合研究区文献( According to the repeated calculation of natural runoff, combined with repeated verification of the literature in the study area①②, the estimated value was 4.35. |
| 流速系数 Velocity coefficient | 查阅相关文献( |
| 地形指数 Terrain index | 根据数字高程模型数据计算 Calculated from DEM |
| 土壤饱和导水率 Soil saturated hydraulic conductivity | 根据Vereecken模型计算( |
| 自然保护区边界 Nature reserves’ boundaries | 生态环境部 Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China |
| 自然保护区相关管理数据 Management data of nature reserves | 现场调查, 查阅资料 On-site investigation and archives searching |
| 路网数据 Roads data | Open Street Map ( |
表1 数据获取来源与参数计算
Table 1 Data sources and parameters
| 数据类型 Data type | 来源与获取方法 Data sources |
|---|---|
| 土地利用数据(2010, 2015年) Land use data (2010, 2015) | 2010-2015年全国生态状况变化遥感调查与评估项目 2010-2015 Remote Sensing Investigation and Assessment Project of Ecological Status Change in China |
| 数字高程模型数据 Digital elevation model (DEM) data | 地理空间数据云GDEMV2数据(30 m分辨率) GDEMV2 data from Geospatial data cloud with 30 m resolution |
| 子流域数据 Sub-watersheds data | 根据数字高程模型数据进行水文提取 Hydrological information extraction based on DEM data |
| 降雨数据 Precipitation data | 数据来源于资源环境数据云平台(分辨率1 km) Precipitation data with 1 km resolution obtained from the website of |
| 蒸散数据 Evapotranspiration | 数据来源于谷歌地球引擎平台, MOD16A2产品(500 m分辨率) Data were extracted from the MOD16A2 products (500 m resolution), which were obtained from the Google Earth Engine. |
| 土壤数据 Soil data | 数据来源于第二次土壤普查, 国家青藏高原数据科学中心( Data were obtained from the second soil census of National Tibetan Plateau Data Center ( |
| 植物有效含水量 Plant available water capacity (PAWC) | 根据土壤普查数据采用土壤质地数据进行计算得到 The data were calculated from the soil texture data based on the soil census. |
| 根系深度 Root depth | 第二次土壤普查土壤剖层, 结合研究区文献校正得到( Adjusted from the soil profile in the second soil census combined with related literature in the study area ( |
| Zhang系数 Zhang coefficient | 根据自然径流反复计算, 结合研究区文献( According to the repeated calculation of natural runoff, combined with repeated verification of the literature in the study area①②, the estimated value was 4.35. |
| 流速系数 Velocity coefficient | 查阅相关文献( |
| 地形指数 Terrain index | 根据数字高程模型数据计算 Calculated from DEM |
| 土壤饱和导水率 Soil saturated hydraulic conductivity | 根据Vereecken模型计算( |
| 自然保护区边界 Nature reserves’ boundaries | 生态环境部 Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China |
| 自然保护区相关管理数据 Management data of nature reserves | 现场调查, 查阅资料 On-site investigation and archives searching |
| 路网数据 Roads data | Open Street Map ( |
| 自然保护区 Nature reserve | 对比结果Comparison results (E) | N | P | 自然保护区 Nature reserve | 对比结果 Comparison results (E) | N | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 周至 Zhouzhi | + | 358 | 0.000** | 太白山 Taibaishan | + | 185 | 0.006** |
| 汉中朱鹮 Hanzhong crested Ibis | + | 349 | 0.000** | 天华山 Tianhuashan | + | 170 | 0.000** |
| 观音山 Guanyinshan | + | 97 | 0.000** | 小陇山 Xiaolongshan | ? | 199 | 0.000** |
| 佛坪 Foping | + | 223 | 0.000** | 紫柏山 Zibaishan | ? | 110 | 0.009** |
| 黄柏塬 Huangbaiyuan | + | 108 | 0.000** | 宝天曼 Baotianman | ? | 53 | 0.000** |
| 老县城 Laoxiancheng | + | 67 | 0.020* | 伏牛山 Funiushan | ? | 471 | 0.000** |
| 长青 Changqing | + | 178 | 0.000** | 南阳恐龙蛋化石群 Nanyang Dinosaur Egg Fossil | ? | 650 | 0.000** |
| 牛背梁 Niubeiliang | + | 81 | 0.000** | 摩天岭 Motianling | 不显著 Nonsignificant | 49 | 0.689 |
| 平河梁 Pingheliang | + | 140 | 0.000** | 小秦岭 Xiaoqinling | 不显著 Nonsignificant | 132 | 0.213 |
| 桑园 Sangyuan | + | 82 | 0.000** | 总体 Overall | + | 3,721 | 0.018** |
表2 秦岭19处自然保护区2010-2015年水源涵养量变化率内外配对Wilcoxon符号秩检验
Table 2 Paired Wilcoxon sign rank tests for the change rate of water retention of 19 national nature reserves in Qinling region between 2010 and 2015
| 自然保护区 Nature reserve | 对比结果Comparison results (E) | N | P | 自然保护区 Nature reserve | 对比结果 Comparison results (E) | N | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 周至 Zhouzhi | + | 358 | 0.000** | 太白山 Taibaishan | + | 185 | 0.006** |
| 汉中朱鹮 Hanzhong crested Ibis | + | 349 | 0.000** | 天华山 Tianhuashan | + | 170 | 0.000** |
| 观音山 Guanyinshan | + | 97 | 0.000** | 小陇山 Xiaolongshan | ? | 199 | 0.000** |
| 佛坪 Foping | + | 223 | 0.000** | 紫柏山 Zibaishan | ? | 110 | 0.009** |
| 黄柏塬 Huangbaiyuan | + | 108 | 0.000** | 宝天曼 Baotianman | ? | 53 | 0.000** |
| 老县城 Laoxiancheng | + | 67 | 0.020* | 伏牛山 Funiushan | ? | 471 | 0.000** |
| 长青 Changqing | + | 178 | 0.000** | 南阳恐龙蛋化石群 Nanyang Dinosaur Egg Fossil | ? | 650 | 0.000** |
| 牛背梁 Niubeiliang | + | 81 | 0.000** | 摩天岭 Motianling | 不显著 Nonsignificant | 49 | 0.689 |
| 平河梁 Pingheliang | + | 140 | 0.000** | 小秦岭 Xiaoqinling | 不显著 Nonsignificant | 132 | 0.213 |
| 桑园 Sangyuan | + | 82 | 0.000** | 总体 Overall | + | 3,721 | 0.018** |
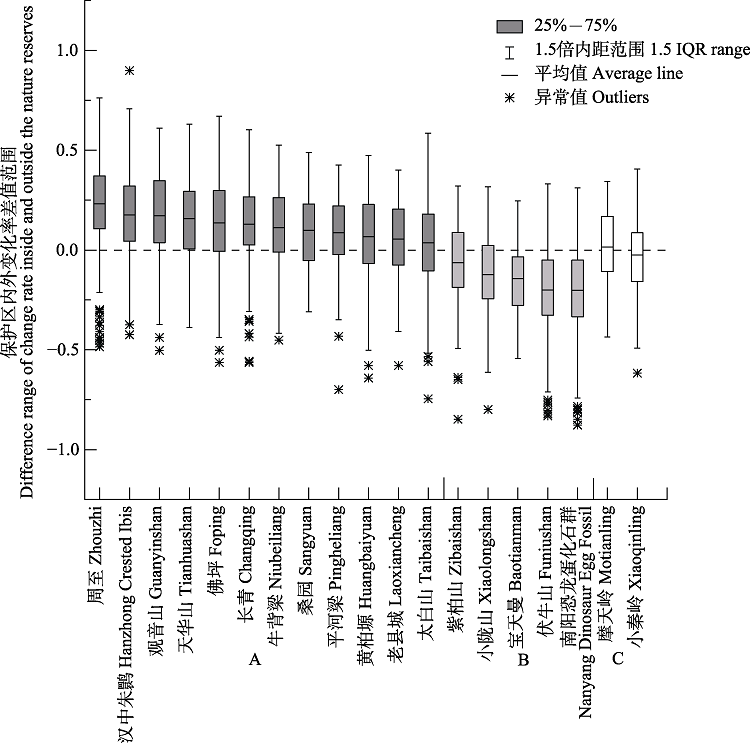
图4 秦岭国家级自然保护区内外水源涵养量变化率差值分布图。A组表示自然保护区内水源涵养量减少程度低于自然保护区外; B组表示自然保护区内水源涵养量减少程度高于保护区外; C组表示自然保护区内外水源涵养变化无显著差异。
Fig. 4 Difference of changes in water retention inside and outside nature reserves in Qinling Mountains. Group A shows that the changes of water retention inside the nature reserves are better than that outside nature reserves; Group B shows that the changes of water retention inside the nature reserves are worse than that outside nature reserves; Group C shows that there is no significant difference in the changes of water retention inside and outside the nature reserves.
| 影响因素 Influencing factor | Spearman相关系数 Spearman correlation coefficient | P |
|---|---|---|
| 降水变化率 Precipitation change rate | 0.926 | 0.000** |
| 平均高程 Average elevation | 0.235 | 0.363 |
| 形状指数 Landscape shape index | ?0.260 | 0.314 |
| 资金投入 Funding investment | 0.542 | 0.025* |
| 路网密度 Road density | 0.047 | 0.859 |
| 单位面积工作人员数量 Number of staff per km2 | ?0.056 | 0.83 |
| 单位面积巡护人员数量 Number of patrolling personnel per km2 | ?0.105 | 0.687 |
| 保护区建立时长 Period from the establishment of nature reserves | ?0.205 | 0.430 |
表3 秦岭19处自然保护区水源涵养保护成效与影响因素的Spearman相关性分析
Table 3 Spearman correlation coefficients between the influencing factors and the conservation effectiveness of water retention in 19 nature reserves in Qinling Mountains
| 影响因素 Influencing factor | Spearman相关系数 Spearman correlation coefficient | P |
|---|---|---|
| 降水变化率 Precipitation change rate | 0.926 | 0.000** |
| 平均高程 Average elevation | 0.235 | 0.363 |
| 形状指数 Landscape shape index | ?0.260 | 0.314 |
| 资金投入 Funding investment | 0.542 | 0.025* |
| 路网密度 Road density | 0.047 | 0.859 |
| 单位面积工作人员数量 Number of staff per km2 | ?0.056 | 0.83 |
| 单位面积巡护人员数量 Number of patrolling personnel per km2 | ?0.105 | 0.687 |
| 保护区建立时长 Period from the establishment of nature reserves | ?0.205 | 0.430 |
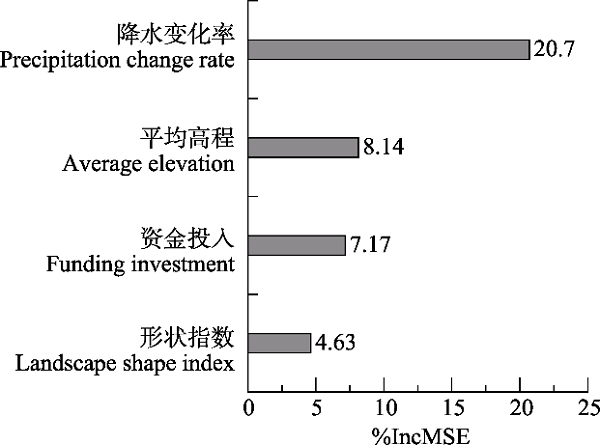
图5 秦岭区域国家级自然保护区水源涵养服务保护成效的主要影响因子。%IncMSE越大表示影响效果越大。
Fig. 5 The main factors influencing the conservation effectiveness of national nature reserves in ensuring water retention in Qinling Mountains. The greater the %IncMSE is, the more important the factor is.
| [1] |
Amin A, Choumert-Nkolo J, Combes JL, Combes Motel P, Kéré EN, Ongono-Olinga JG, Schwartz S (2019) Neighborhood effects in the Brazilian Amazônia: Protected areas and deforestation. Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, 93, 272-288.
DOI |
| [2] |
Austin PC, Mamdani MM (2006) A comparison of propensity score methods: A case study estimating the effectiveness of post-AMI statin use. Statistics in Medicine, 25, 2084-2106.
PMID |
| [3] | Bao YB, Li T, Liu H, Ma T, Wang HX, Liu K, Shen X, Liu XH (2016) Spatial and temporal changes of water conservation of Loess Plateau in northern Shaanxi Province by InVEST model. Geographical Research, 35, 664-676. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 包玉斌, 李婷, 柳辉, 马涛, 王怀香, 刘康, 沈茜, 刘心浩 (2016) 基于InVEST模型的陕北黄土高原水源涵养功能时空变化. 地理研究, 35, 664-676.] | |
| [4] | Bridgewater P, Babin D (2017) UNESCO-MAB Biosphere Reserves already deal with ecosystem services and sustainable development. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 114, E4318. |
| [5] | Briggs J (2016) Global biodiversity loss: Exaggerated versus realistic estimates. Environmental Skeptics and Critics, 5(2), 20-27. |
| [6] |
Burgess ND, Butynski TM, Cordeiro NJ, Doggart NH, Fjeldså J, Howell KM, Kilahama FB, Loader SP, Lovett JC, Mbilinyi B, Menegon M, Moyer DC, Nashanda E, Perkin A, Rovero F, Stanley WT, Stuart SN (2007) The biological importance of the Eastern Arc Mountains of Tanzania and Kenya. Biological Conservation, 134, 209-231.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Chen HG, Pan XF, Huang YY, He BC, Chen F, Pan A (2017) Propensity score matching method and its implementation in Stata software. Chinese Journal of Health Statistics, 34, 987-990. (in Chinese) |
| [ 陈亨贵, 潘雄飞, 黄媛媛, 何保昌, 陈法, 潘安 (2017) 倾向评分配比法及其在Stata软件实现. 中国卫生统计, 34, 987-990.] | |
| [8] | Chen KH, Zhang XY (2006) Research on system of comprehensive evaluation of Zhouzhi National-level Nature Reserve. Resource Development & Market, 22(2), 118-120. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈凯华, 张孝远 (2006) 周至国家级自然保护区综合评价体系研究. 资源开发与市场, 22(2), 118-120.] | |
| [9] | Chen SS, Liu K, Bao YB, Chen H (2016) Spatial pattern and influencing factors of water conservation service function in Shangluo City. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 36, 1546-1554. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈姗姗, 刘康, 包玉斌, 陈海 (2016) 商洛市水源涵养服务功能空间格局与影响因素. 地理科学, 36, 1546-1554.] | |
| [10] |
Chiu M, Rezai MR, Maclagan LC, Austin PC, Shah BR, Redelmeier DA, Tu JV (2016) Moving to a highly walkable neighborhood and incidence of hypertension: A propensity-score matched cohort study. Environmental Health Perspectives, 124, 754-760.
DOI URL |
| [11] | Dudley N (2008) Guidelines for Applying Protected Area Management Categories. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland. |
| [12] | Fan YN, Liu K, Chen SS, Yuan JG (2017) Spatial pattern analysis on water conservative functionality of land ecosystem in northern slope of Qinling Mountains. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 37(2), 50-56. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 范亚宁, 刘康, 陈姗姗, 袁家根 (2017) 秦岭北麓陆地生态系统水源涵养功能的空间格局. 水土保持通报, 37(2), 50-56.] | |
| [13] | Finlayson M, Cruz R, Davidson N, Alder J, Cork S, Groot RS, Lévêque C, Milton GR, Peterson G, Pritchard D (2005) Millennium Ecosystem Assessment: Ecosystems and Human Well-being: Wetlands and Water Synthesis. Island Press, Washington, DC. |
| [14] | Gong J, Yan LL, Xu CX, Guo QH (2020) A comparative review of research highlights on ecosystem services of China and USA in the past 30 years. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40, 3537-3547. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 巩杰, 燕玲玲, 徐彩仙, 郭青海 (2020) 近30年来中美生态系统服务研究热点对比分析. 生态学报, 40, 3537-3547.] | |
| [15] |
Grömping U (2009) Variable importance assessment in regression: Linear regression versus random forest. The American Statistician, 63, 308-319.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Hansen AJ, Rotella JJ (2002) Biophysical factors, land use, and species viability in and around nature reserves. Conservation Biology, 16, 1112-1122.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Huang CH, Yang J, Zhang WJ (2013) Development of ecosystem services evaluation models: Research progress. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 32, 3360-3367. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 黄从红, 杨军, 张文娟 (2013) 生态系统服务功能评估模型研究进展. 生态学杂志, 32, 3360-3367.] | |
| [18] | Ian G, Richard G, Sharif J, Maaike M, Ian M, Gill B, Pierre C, Nina M, John W, Naamal S, Tesfay W, Matt F, Neil B, Nigel V (2012) Eastern Afromontane Biodiversity Hotspot. Birdlife International, Nairobi, Kenya. |
| [19] | Ingram JC, Redford KH, Watson JEM (2012) Applying ecosystem services approaches for biodiversity conservation: Benefits and challenges. Sapiens, 5, 1-10. |
| [20] | Jin L (2008) Evaluation of Ecosystem Services of Xilingol Grassland Nature Reserve. PhD dissertation, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 金良 (2008) 锡林郭勒草原自然保护区生态系统服务功能价值评估研究. 博士学位论文, 内蒙古农业大学, 呼和浩特.] | |
| [21] | Jin X (2015) Valuation of Ecosystem Services of Hongxing Wetland National Nature Reserve in Heilongjiang Province. PhD dissertation, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 金辛 (2015) 黑龙江红星湿地国家级自然保护区生态系统服务功能价值评估. 博士学位论文, 东北林业大学, 哈尔滨.] | |
| [22] | Joppa LN, Pfaff A (2011) Global protected area impacts. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 278, 1633-1638. |
| [23] |
Kandziora M, Burkhard B, Müller F (2013) Interactions of ecosystem properties, ecosystem integrity and ecosystem service indicators—A theoretical matrix exercise. Ecological Indicators, 28, 54-78.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Lehrer D, Becker N, Bar P (2019) The drivers behind nature conservation cost. Land Use Policy, 89, 104222.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Li B, Zhang JT (2010) Patch shape indices and scale fractal analysis of steppe landscape in the Loess Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 18(2), 141-147. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李斌, 张金屯 (2010) 黄土高原草原景观斑块形状的指数和分形分析. 草地学报, 18(2), 141-147.] | |
| [26] | Li JS, Jin YC, Wang W, Zhao ZP, Wu XP (2016) Conservation of Terrestrial Biodiversity in China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李俊生, 靳勇超, 王伟, 赵志平, 吴晓莆 (2016) 中国陆域生物多样性保护优先区域. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [27] |
Li SC, Zhang H, Zhou XW, Yu HB, Li WJ (2020) Enhancing protected areas for biodiversity and ecosystem services in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecosystem Services, 43, 101090.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Liao KH, Xu SH, Wu JC, Shi XQ (2012) Uncertainty analysis for spatial prediction of soil saturated hydraulic conductivity. Advances in Water Science, 23, 200-205. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 廖凯华, 徐绍辉, 吴吉春, 施小清 (2012) 土壤饱和导水率空间预测的不确定性分析. 水科学进展, 23, 200-205.] | |
| [29] | Liu JH, Zhang H, Zhao AQ (2007) Preliminary research on sustainable development of Taibai Mountain National Nature Reserve. Forest Resources Management, (2), 15-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 柳江华, 张海, 赵爱青 (2007) 太白山国家级自然保护区可持续发展初步研究. 林业资源管理, (2), 15-19.] | |
| [30] | Liu JL, Ma XY, Zhang ZH, Zhao WS (2013) Multi-scale prediction model and transformation relation of soil saturated hydraulic conductivity. Advances in Water Science, 24, 568-573. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘继龙, 马孝义, 张振华, 赵伟森 (2013) 土壤饱和导水率的多尺度预测模型与转换关系. 水科学进展, 24, 568-573.] | |
| [31] | Liu ZQ (1983) The distribution of soil zones in Shaanxi. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 11, 131-137. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘兆谦 (1983) 陕西土壤地带性分布规律. 陕西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 11, 131-137.] | |
| [32] | Machado M, Young CEF, Clauzet M (2020) Environmental funds to support protected areas: Lessons from Brazilian experiences. Parks, 26, 47-62. |
| [33] | Miao JQ, Sun S, Wang ZQ, Huang GQ (2017) Evaluating the ecosystem services of Gaotianyan Nature Reserve in Lianhua County, Jiangxi Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 6422-6430. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 缪建群, 孙松, 王志强, 黄国勤 (2017) 江西高天岩自然保护区生态系统服务功能价值评估. 生态学报, 37, 6422-6430.] | |
| [34] | Ning YZ, Zhang FP, Feng Q, Wei YF, Ding JB, Zhang Y (2020) Temporal and spatial variation of water conservation function in Qinling Mountain and its influencing factors. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39, 3080-3091. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 宁亚洲, 张福平, 冯起, 魏永芬, 丁家宝, 张元 (2020) 秦岭水源涵养功能时空变化及其影响因素. 生态学杂志, 39, 3080-3091.] | |
| [35] | Pearson LJ, Dare M (2019) Framing up the “stretching” of co-management. Society & Natural Resources, 32, 363-381. |
| [36] |
Rosenbaum PR (1989) Optimal matching for observational studies. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 84, 1024-1032.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Schirpke U, de Marino D, Marucci A, Palmieri M, Scolozzi R (2017) Operationalising ecosystem services for effective management of protected areas: Experiences and challenges. Ecosystem Services, 28, 105-114.
DOI URL |
| [38] | Shangguan W, Dai YJ (2013) A China Dataset of Soil Properties for Land Surface Modeling. National Tibetan Plateau Data Center, Lhasa. (in Chinese) |
| [ 上官微, 戴永久 (2013) 面向陆面模拟的中国土壤数据集. 国家青藏高原科学数据中心, 拉萨.] | |
| [39] | Sharp R, Tallis HT, Ricketts T, Guerry AD, Wood SA, Chapin-Kramer R, Nelson E, Ennaanay D, Wolny S, Olwero N, Vigerstol K, Pennington D, Mendoza G, Aukema J, Foster J, Forrest J, Cameron D, Arkema K, Lonsdorf E, Kennedy C, Verutes G, Kim CK, Guannel G, Papenfus M, Toft J, Marsik M, Bernhardt J, Griffin R, Gowinski K, Chaumont N, Perelman A, Lacayo M, Mandle L, Hamel P, Vogl AL, Rogers L, Bierbower W (2015) InVEST 3.2.0 User’s Guide. The Natural Capital Project, Stanford University, University of Minnesota, The Nature Conservancy, and World Wildlife Fund, Palo Alto, California. |
| [40] |
Su CH, Fu BJ (2013) Evolution of ecosystem services in the Chinese Loess Plateau under climatic and land use changes. Global and Planetary Change, 101, 119-128.
DOI URL |
| [41] | Tang Y, Zhu WP, Zhang H, Song Y (2015) A review on principle and application of the InVEST model. Ecological Science, 34, 204-208. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 唐尧, 祝炜平, 张慧, 宋瑜 (2015) InVEST模型原理及其应用研究进展. 生态科学, 34, 204-208.] | |
| [42] |
Vereecken H, Diels J, van Orshoven J, Feyen J, Bouma J (1992) Functional evaluation of pedotransfer functions for the estimation of soil hydraulic properties. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 56, 1371-1378.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Wang W, Pechacek P, Zhang MX, Xiao NW, Zhu JG, Li JS (2013) Effectiveness of nature reserve system for conserving Tropical Forests: A statistical evaluation of Hainan Island, China. PLoS ONE, 8, e57561.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Wang Y, Xu P, Fu B, Wang W, Wang HW (2018) Water conservation function assessment models of forest ecosystem: A review. Ecological Economy, 34, 158-164, 169. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 王尧, 徐佩, 傅斌, 王威, 王海雯 (2018) 森林生态系统水源涵养功能评估模型研究进展. 生态经济, 34, 158-164, 169.] | |
| [45] | Wu N, Chen N, Wang ZG (2019) Evaluating conservation effectiveness of ecological protected areas in Anhui Province based on ecosystem services value. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 46, 75-82. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴楠, 陈凝, 王在高 (2019) 基于生态系统服务价值的安徽省生态保护地保护成效评估. 安徽农业大学学报, 46, 75-82.] | |
| [46] |
Xiao Y, Ouyang ZY (2019) Spatial-temporal patterns and driving forces of water retention service in China. Chinese Geographical Science, 29, 100-111.
DOI URL |
| [47] | Xu WH, Xiao Y, Zhang JJ, Yang W, Zhang L, Hull V, Wang Z, Zheng H, Liu JG, Polasky S, Jiang L, Xiao Y, Shi XW, Rao EM, Lu F, Wang XK, Daily GC, Ouyang ZY (2017) Strengthening protected areas for biodiversity and ecosystem services in China. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 114, 1601-1606. |
| [48] | Yang XH, Guo RF (2002) Study on the relationship between precipitation and forest ecosystem. Forestry Science & Technology, 27(6), 11-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨新华, 郭荣发 (2002) 论森林生态系统与降水的关系. 林业科技, 27(6), 11-15.] | |
| [49] | You SC, Di SC, Yuan Y (2009) Study on soil field capacity estimation in the Loess Plateau Region. Journal of Natural Resources, 24, 545-552. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 游松财, 邸苏闯, 袁晔 (2009) 黄土高原地区土壤田间持水量的计算. 自然资源学报, 24, 545-552.] | |
| [50] | Yu BW, Rao EM, Chao XL, Shi JK, Zhang CP, Xu WH, Xiao Y, Ouyang ZY (2016) Evaluating the effectiveness of nature reserves in soil conservation on Hainan Island. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 3694-3702. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 于博威, 饶恩明, 晁雪林, 史建康, 张翠萍, 徐卫华, 肖燚, 欧阳志云 (2016) 海南岛自然保护区对土壤保持服务功能的保护效果. 生态学报, 36, 3694-3702.] | |
| [51] | Yu FZ, Zhang ZQ, Chen LQ, Shen ZP, You HM (2014) Study on water conservation function of different forestlands in Lushan Nature Reserve, Jiangxi Province. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 21, 255-259. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 于法展, 张忠启, 陈龙乾, 沈正平, 尤海梅 (2014) 江西庐山自然保护区不同林地水源涵养功能研究. 水土保持研究, 21, 255-259.] | |
| [52] | Zhang L, Li CJ, Xia JL, Wang YJ, Wang L, Jiang ZW (2012) Study on propensity score interval matching in non-randomization controlled trials. Chinese Journal of Health Statistics, 29(1), 53-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张亮, 李婵娟, 夏结来, 王永吉, 王陵, 蒋志伟 (2012) 倾向得分区间匹配法用于非随机对照试验的探索与研究. 中国卫生统计, 29(1), 53-57.] | |
| [53] |
Zhao HW, Wu RD, Long YC, Hu JM, Yang FL, Jin T, Wang JJ, Hu PJ, Wu W, Diao YX, Guo Y (2019) Individual-level performance of nature reserves in forest protection and the effects of management level and establishment age. Biological Conservation, 233, 23-30.
DOI URL |
| [54] | Zhuo J, He HJ, Wang J (2015) Assessment of water conservation capacity in Qinling Mountains area. Journal of Shaanxi Meteorology, (3), 12-16. (in Chinese) |
| [ 卓静, 何慧娟, 王娟 (2015) 秦岭地区水源涵养能力评估. 陕西气象, (3), 12-16.] |
| [1] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [2] | 耿宜佳, 田瑜, 李俊生, 李子圆, 潘玉雪. 《生物多样性公约》框架下外来入侵物种管控的全球进展、挑战和展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24275-. |
| [3] | 杨俊毅, 关潇, 李俊生, 刘晶晶, 郝颢晶, 王槐睿. 乌江流域生物多样性与生态系统服务的空间格局及相互关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23061-. |
| [4] | 董庆栋, 陈超男, 李艳红, 赵体侠, 孙梓欣, 张哲, 朱连奇. 基于NPP和人类扰动指数评估河南伏牛山地区国家级自然保护区群保护成效与溢出/泄漏效应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22503-. |
| [5] | 吴杨, 田瑜, 戴逢斌, 李子圆. “自然对人类的贡献”的实现、发展趋势和启示[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21549-. |
| [6] | 胡官正, 曾维华, 马冰然. 保护地区域经济建设与生态保护协同发展路线图: 以三江源地区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21225-. |
| [7] | 徐靖, 王金洲, 李俊生. 商业界参与生物多样性主流化的进展、路径与建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22078-. |
| [8] | 傅声雷, 刘满强, 张卫信, 邵元虎. 土壤动物多样性的地理分布及其生态功能研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22435-. |
| [9] | 王博驰, 裴雯, 杨巨才, 色拥军, 李雪竹, 娜尔力玛, 杨海蓉. 甘肃盐池湾黑颈鹤筑巢栖息地偏好及人为干扰的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(1): 21241-. |
| [10] | 戴逢斌, 吴杨, 潘玉雪, 张博雅, 田瑜. IPBES工作效率和科学职能的有效性分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 688-692. |
| [11] | 王伟, 李俊生. 中国生物多样性就地保护成效与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(2): 133-149. |
| [12] | 郑晓明, 杨庆文. 中国农业生物多样性保护进展概述[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(2): 167-176. |
| [13] | 吴杨, 潘玉雪, 张博雅, 戴逢斌, 田瑜. IPBES框架下的生物多样性和生态系统服务区域评估及政策经验[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(7): 913-919. |
| [14] | 刘向, 陈立范, 周淑荣. 生物多样性与传染性疾病的关系: 进展、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(11): 1376-1390. |
| [15] | 潘玉雪, 张博雅, 吴杨, 戴逢斌, 田瑜. IPBES工作进展及我国对策建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(10): 1286-1291. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn