



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 22435. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022435 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022435
所属专题: 土壤生物与土壤健康
收稿日期:2022-07-30
接受日期:2022-10-11
出版日期:2022-10-20
发布日期:2022-10-22
通讯作者:
傅声雷
作者简介:* E-mail: fsl@vip.henu.edu.cn基金资助:
Shenglei Fu1,*( ), Manqiang Liu2, Weixin Zhang1, Yuanhu Shao1
), Manqiang Liu2, Weixin Zhang1, Yuanhu Shao1
Received:2022-07-30
Accepted:2022-10-11
Online:2022-10-20
Published:2022-10-22
Contact:
Shenglei Fu
摘要:
土壤动物多样性地理分布及其生态功能研究已成为地学和生态学等领域共同关注的科学前沿。本文在介绍相关研究最新进展的基础上, 讨论已有研究的局限性或不确定性, 展望未来研究的重点方向。近10年来, 代表性土壤动物类群的全球分布研究取得突破性进展; 国内土壤动物研究的尺度和采样区域也有明显拓展, 尤其在蚯蚓和线虫相关研究上取得了系列成果。结果表明, 土壤动物多样性随纬度的变化模式主要有两种, 即在低纬度的热带最高或在中纬度的温带最高; 而土壤动物多度与多样性可能同步变化、无明显关系、截然不同甚至相反; 降水、植物生产力和土壤有机质是土壤动物分布格局的关键驱动力, 但它们的影响力因土壤动物类群不同而异。土壤动物具有改善土壤物理结构、促进养分循环和有机碳稳定、提高作物健康水平等多重功能; 土壤动物的多功能性评估方兴未艾, 但仍面临诸多挑战。简单分析土壤动物随经纬度等的变化规律存在较大局限性, 考虑在基于地质-生态历史及“经纬度-海拔-离海岸距离”等构建的多维时空框架内, 探究土壤动物分布特征及其驱动力。土壤动物分布格局对其潜在的生态功能有关键影响, 但是目前对土壤动物分布格局的预测和模拟仍主要依靠经验模型; 代谢生态学等理论在土壤动物群落研究中的应用值得关注。探究分类多样性的冗余机制, 突出功能多样性, 可以将生物多样性与生态功能更好地联系起来; 同时, 需要在特定条件和时空下, 从整个土壤食物网及其与植物的联系中理解土壤动物多样性与多功能性的联系。建议未来关注两个研究方向: (1)量化人类活动和气候变化给土壤动物多样性和生态功能带来的巨大不确定性; (2)完善土壤动物群落特征预测的理论框架和开展土壤动物群落的精准调控, 综合评价其多功能性, 进而将土壤动物与人类福祉更紧密地联系起来。
傅声雷, 刘满强, 张卫信, 邵元虎 (2022) 土壤动物多样性的地理分布及其生态功能研究进展. 生物多样性, 30, 22435. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022435.
Shenglei Fu, Manqiang Liu, Weixin Zhang, Yuanhu Shao (2022) A review of recent advances in the study of geographical distribution and ecological functions of soil fauna diversity. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22435. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022435.
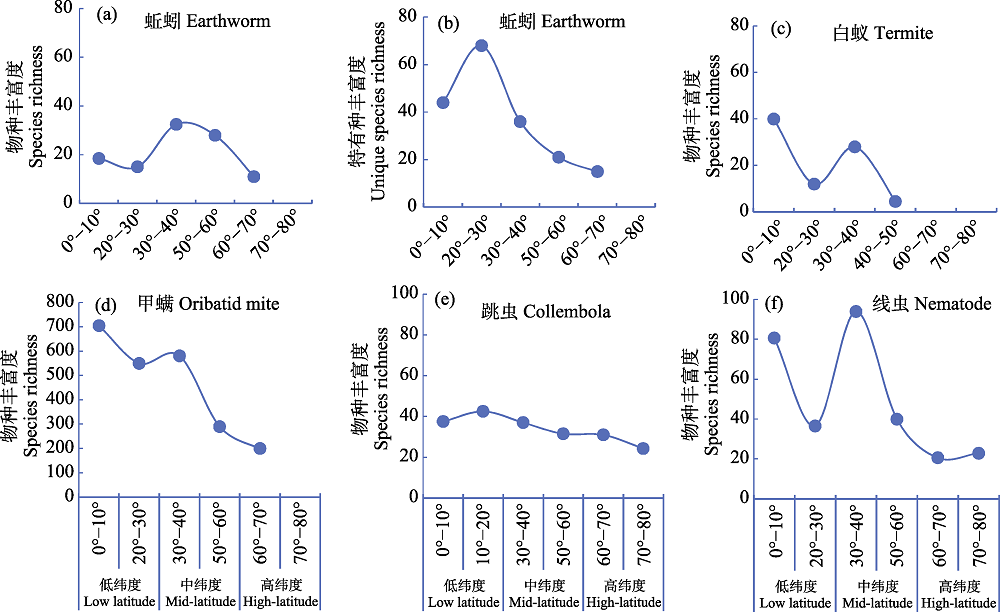
图1 代表性土壤动物物种丰富度在北半球随纬度的分布规律。a-f为北半球相应纬度区间内给定土壤动物类群的物种丰富度的均值。因为跳虫在20°-30° N区间未找到有效数据, 故以10°-20° N区间的数据替代; 而白蚁在大于50° N后几无分布, 故这里展示了40°-50° N区间而不是50°-60° N的数据; 数据来源: 蚯蚓(Phillips et al, 2019)、白蚁(Deca?ns, 2010)、甲螨(Maraun et al, 2007; Deca?ns, 2010)、跳虫(Potapov et al, 2022a)和线虫(Boag & Yeates, 1998)。
Fig. 1 The distribution of species richness of representative soil fauna along latitudes in northern hemisphere. Species richness in panels a-f refers to the mean value of species richness within a specific latitude range for a given group of soil fauna; data for collembola within 10°-20° N was shown, instead of that within 20°-30° N since the data was not available; data for termite within 40°-50° N, instead of that within 50°-60° N, was shown since almost no termite was reported in further northern regions with higher latitude. Data sources: earthworm (Phillips et al, 2019), termite (Deca?ns, 2010), oribatid mite (Maraun et al, 2007; Deca?ns, 2010), collembola (Potapov et al, 2022a) and nematode (Boag & Yeates, 1998).
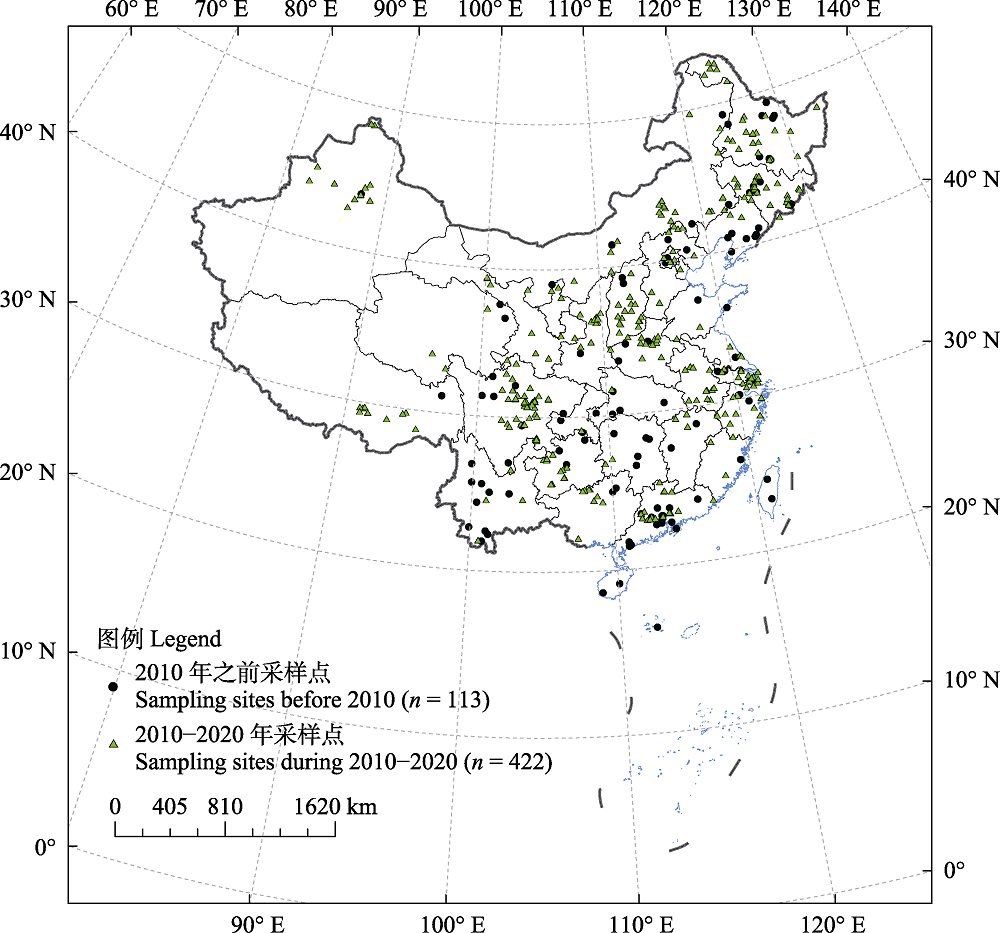
图2 我国土壤动物群落野外采样点的发展变化。“2010-2020年采样点”指的是2010-2020年间新增土壤动物采样点, 数据来自对CNKI文献的整理; “2010年之前采样点”指以尹文英先生为代表的老一辈土壤动物学者的采样地, 采样时间在1980-2008年间, 数据主要来自尹文英、陈鹏、张夫道、廖崇惠和殷秀琴等领衔撰写的专著(尹文英, 1992, 2000; 赵小鲁和谢炳庚, 1996; 殷秀琴, 2001; 张夫道, 2006; 廖崇惠和李健雄, 2009)。
Fig. 2 The changes in sampling sites of soil fauna community in China. The legend of “sampling sites during 2010-2020” refers to the new sampling sites during 2010-2020 based on literature analysis from CNKI; while the “sampling sites before 2010” refers to the sampling sites during 1980-2008 in studies represented by Yin et al, and the main data sources are from monographs edited by Yin, 1992, 2000; Zhao & Xie, 1996; Yin, 2001; Zhang, 2006; Liao & Li, 2009.
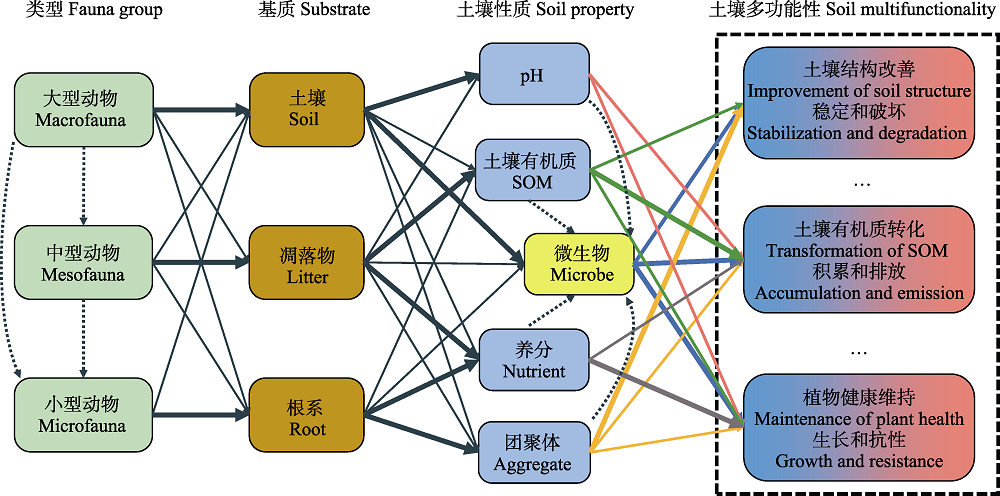
图3 土壤动物影响土壤多功能性的路径图。不同类型的土壤动物会对土壤、凋落物以及植物根系产生不同的影响, 其中, 大型土壤动物(如蚯蚓等)、中型土壤动物(弹尾虫等)和小型土壤动物(线虫等)可能分别对土壤、凋落物和根系的影响最大。这些变化会进一步对土壤性质造成直接影响, 同时还会通过影响土壤非生物性质(如pH、土壤有机质、养分和团聚体)从而对土壤微生物性质(如生物量、多样性和活性)造成间接影响。最后, 会对多种土壤生态功能, 如土壤结构、有机碳库和植物健康等, 产生正向或负向的影响。箭头的粗细与影响的强弱成比例; 实线表示直接影响, 虚线表示间接影响。
Fig. 3 Conceptual diagram of pathways for the effects of soil fauna on soil multifunctionality. Soil fauna have different effects on soils, litters and plant roots, among which, macrofauna (e.g. earthworm), mesofauna (e.g. springtail) and microfauna (e.g. nematode) potentially show the strong impact on soils, litters and plant roots, respectively. These changes can directly affect soil properties, as well as indirectly affect soil microbial properties such as microbial biomass, diversity and activity via modifying soil abiotic properties, e.g., pH, soil organic matter (SOM), nutrient and aggregate. Finally, these changes could also positively or negatively affect soil multifunctionality, such as the improvement of soil structure, the transformation of soil organic matter and the maintaining of plant health. The arrow width is proportional to the strength of the relationship. Solid and dashed arrows indicate direct and indirect effects, respectively.
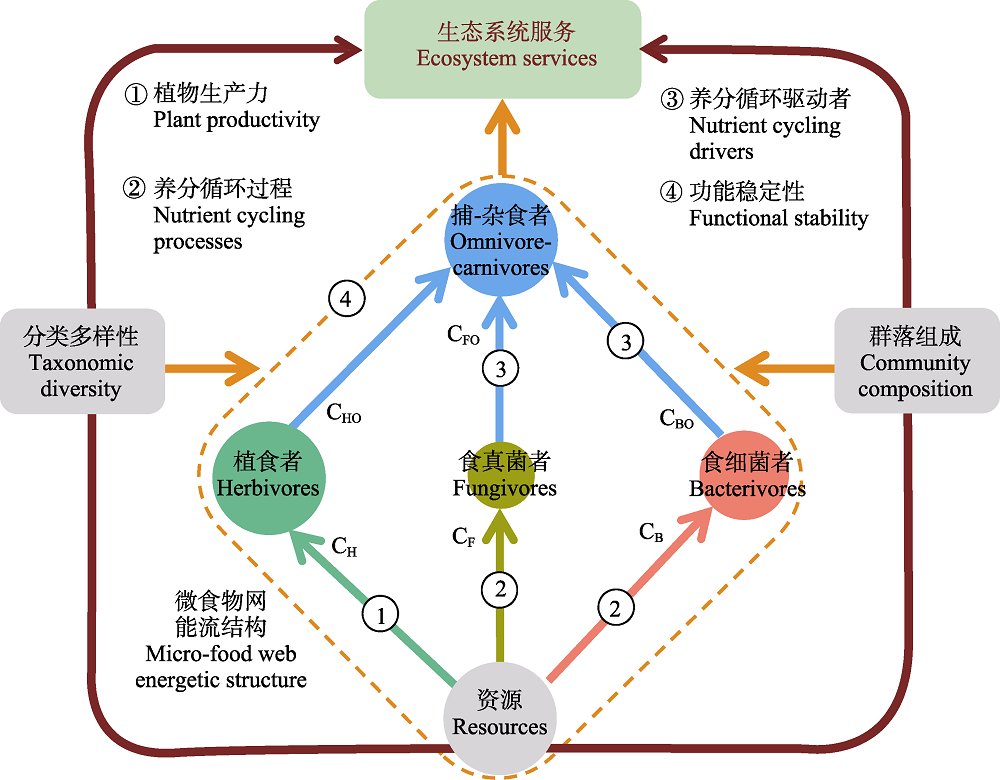
图4 土壤微食物网能流结构与生态系统多功能性的关系。C表示消费者代谢的能流通量, 例如, CH, CF, CB分别代表植食者、食真菌者和食细菌者获取的能流通量, CHO, CFO, CBO分别是捕食杂食者从植食者, 食真菌者和食细菌者获取的能流通量。其中, 经过植食者的能流通量跟植物生产力密切相关, 经过食微者(食真菌者和食细菌者)的能流通量与养分循环过程密切相关, 而捕食杂食者从食微者获取的能流通量代表捕食者自上而下的调控作用, 能够表征对养分循环驱动者的调控作用。土壤微食物网能流结构的均匀度代表不同能流通道之间的平衡, 能够表征土壤食物网的功能稳定性。资源主要通过调控土壤微食物网的组成和多样性来促进其对资源的利用, 优化整个土壤微食物网能流结构, 从而提高生态系统多功能性。
Fig. 4 A schematic diagram showing energetic structure of soil micro-food webs and their relation to ecosystem multifunctionality. The C refers to the flux of energy through a given taxa of consumption, i.e., CH, CF, CB indicates flux of energy through herbivores, fungivores and bacterivores, respectively. The flux of energy through microbivores (CF and CB) has been shown to be related to litter decomposition and nutrient cycling, while the flux of energy through herbivores is typically related to plant productivity, and the flux of energy through predators is related to top-down controls on ecosystem drivers. The flow uniformity of energy in the soil micro-food web indicates the energy distribution of different channels, which determines the functional stability of food webs. Resources exert strong effects on the energetic structure of food webs by shifting the diversity and composition of soil micro-food webs. These shifts in soil biodiversity and composition could optimize the energetic structure of soil micro-food webs to support ecosystem services.
| [1] | Abe T, Bignell DE, Higashi M (2000) Termites: Evolution, Sociality, Symbioses, Ecology. Springer, Dordrecht, |
| [2] |
Bahram M, Hildebrand F, Forslund SK, Anderson JL, Soudzilovskaia NA, Bodegom PM, Bengtsson-Palme J, Anslan S, Coelho LP, Harend H, Huerta-Cepas J, Medema MH, Maltz MR, Mundra S, Olsson PA, Pent M, Põlme S, Sunagawa S, Ryberg M, Tedersoo L, Bork P (2018) Structure and function of the global topsoil microbiome. Nature, 560, 233-237.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Barrios E (2007) Soil biota, ecosystem services and land productivity. Ecological Economics, 64, 269-285.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Bertrand M, Barot S, Blouin M, Whalen J, de Oliveira T, Roger-Estrade J (2015) Earthworm services for cropping systems. A review. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 35, 553-567.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Bi YM, Sun ZJ (2018) Mechanisms of earthworms to alleviate continuous cropping obstacles through regulating soil microecology. Biodiversity Science, 26, 1103-1115. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[毕艳孟, 孙振钧 (2018) 蚯蚓调控土壤微生态缓解连作障碍的作用机制. 生物多样性, 26, 1103-1115.]
DOI |
|
| [6] |
Blanchart E, Ratsiatosika O, Raveloson H, Razafimbelo T, Razafindrakoto M, Sester M, Becquer T, Bernard L, Trap J (2020) Nitrogen supply reduces the earthworm-silicon control on rice blast disease in a Ferralsol. Applied Soil Ecology, 145, 103341.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Blouin M, Hodson ME, Delgado EA, Baker G, Brussaard L, Butt KR, Dai J, Dendooven L, Peres G, Tondoh JE, Cluzeau D, Brun JJ (2013) A review of earthworm impact on soil function and ecosystem services. European Journal of Soil Science, 64, 161-182.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Boag B, Yeates G (1998) Soil nematode biodiversity in terrestrial ecosystems. Biodiversity & Conservation, 7, 617-630. |
| [9] |
Bradford MA, Eggers T, Newington JE, Tordoff GM (2007) Soil faunal assemblage composition modifies root in-growth to plant litter patches. Pedobiologia, 50, 505-513.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Briones MJI (2014) Soil fauna and soil functions: A jigsaw puzzle. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2, 1-22. |
| [11] |
Cameron EK, Martins IS, Lavelle P, Mathieu J, Tedersoo L, Bahram M, Gottschall F, Guerra CA, Hines J, Patoine G, Siebert J, Winter M, Cesarz S, Ferlian O, Kreft H, Lovejoy TE, Montanarella L, Orgiazzi A, Pereira HM, Phillips HRP, Settele J, Wall DH, Eisenhauer N (2019) Global mismatches in aboveground and belowground biodiversity. Conservation Biology, 33, 1187-1192.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Cameron EK, Martins IS, Lavelle P, Mathieu J, Tedersoo L, Gottschall F, Guerra CA, Hines J, Patoine G, Siebert J, Winter M, Cesarz S, Delgado-Baquerizo M, Ferlian O, Fierer N, Kreft H, Lovejoy TE, Montanarella L, Orgiazzi A, Pereira HM, Phillips HRP, Settele J, Wall DH, Eisenhauer N (2018) Global gaps in soil biodiversity data. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2, 1042-1043. |
| [13] |
Chen DM, Cheng JH, Chu PF, Hu SJ, Xie YC, Tuvshintogtokh I, Bai YF (2015) Regional-scale patterns of soil microbes and nematodes across grasslands on the Mongolian plateau: Relationships with climate, soil, and plants. Ecography, 38, 622-631.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Chen DM, Cheng JH, Chu PF, Mi J, Hu SJ, Xie YC, Tuvshintogtokh I, Bai YF (2016) Effect of diversity on biomass across grasslands on the Mongolian plateau: Contrasting effects between plants and soil nematodes. Journal of Biogeography, 43, 955-966.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Chen J, Ferris H (1999) The effects of nematode grazing on nitrogen mineralization during fungal decomposition of organic matter. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 31, 1265-1279.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Chen JX, Ma ZC, Yan HJ, Zhang F (2007) Roles of springtails in soil ecosystem. Biodiversity Science, 15, 154-161. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[陈建秀, 麻智春, 严海娟, 张峰 (2007) 跳虫在土壤生态系统中的作用. 生物多样性, 15, 154-161.]
DOI |
|
| [17] | Chen Y (1956) Earthworm in China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [陈义 (1956) 中国蚯蚓. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [18] | Curtis TP, Sloan WT, Scannell JW (2002) Estimating prokaryotic diversity and its limits. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 99, 10494-10499. |
| [19] |
Decaëns T (2010) Macroecological patterns in soil communities. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 19, 287-302.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Delgado-Baquerizo M, Oliverio AM, Brewer TE, Benavent- González A, Eldridge DJ, Bardgett RD, Maestre FT, Singh BK, Fierer N (2018) A global atlas of the dominant bacteria found in soil. Science, 359, 320-325.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | Edwards CA (2004) Earthworm Ecology, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida. |
| [22] | Eggleton P (2000) Global patterns of termite diversity. In: Termites: Evolution, Sociality, Symbioses, Ecology (eds Abe T, Bignell DE, Higashi M), pp. 25-51. Springer, Dordrecht. |
| [23] | Eisenbeis G (2006) Biology of soil invertebrates. In: Intestinal Microorganisms of Termites and Other Invertebrates (eds König H, Varma A), pp.3-53. Springer, Berlin. |
| [24] |
Eisenhauer N, Bonn A, Guerra CA (2019) Recognizing the quiet extinction of invertebrates. Nature Communications, 10, 50.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Eisenhauer N, Hörsch V, Moeser J, Scheu S (2010) Synergistic effects of microbial and animal decomposers on plant and herbivore performance. Basic and Applied Ecology, 11, 23-34.
DOI URL |
| [26] | FAO (2015) Healthy soils are the basis for healthy food production. https://www.fao.org/3/i4405e/I4405E.pdf. (acce-ssed on 2022-11-11) |
| [27] |
Ferlian O, Eisenhauer N, Aguirrebengoa M, Camara M, Ramirez-Rojas I, Santos F, Tanalgo K, Thakur MP (2018) Invasive earthworms erode soil biodiversity: A meta-analysis. Journal of Animal Ecology, 87, 162-172.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
Fierer N, Grandy AS, Six J, Paul EA (2009) Searching for unifying principles in soil ecology. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 41, 2249-2256.
DOI URL |
| [29] | Fierer N, Jackson RB (2006) The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 103, 626-631. |
| [30] |
Filser J, Faber JH, Tiunov AV, Brussaard L, Frouz J, De Deyn G, Uvarov AV, Berg MP, Lavelle P, Loreau M, Wall DH, Querner P, Eijsackers H, Jiménez JJ (2016) Soil fauna: Key to new carbon models. Soil, 2, 565-582.
DOI URL |
| [31] | Folgarait PJ (1998) Ant biodiversity and its relationship to ecosystem functioning: A review. Biodiversity & Conservation, 7, 1221-1244. |
| [32] |
Forey E, Coulibaly SFM, Chauvat M (2015) Flowering phenology of a herbaceous species (Poa annua) is regulated by soil Collembola. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 90, 30-33.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Frelich LE, Blossey B, Cameron EK, Dávalos A, Eisenhauer N, Fahey T, Ferlian O, Groffman PM, Larson E, Loss SR, Maerz JC, Nuzzo V, Yoo K, Reich PB (2019) Side-swiped: Ecological cascades emanating from earthworm invasion. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 17, 502-510.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
Fu SL (2007) A review and perspective on soil biodiversity research. Biodiversity Science, 15, 109-115. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[傅声雷 (2007) 土壤生物多样性的研究概况与发展趋势. 生物多样性, 15, 109-115.]
DOI |
|
| [35] |
Fu SL (2018) Strengthening the research on soil fauna diversity and their ecological functions using novel technology and field experimental facility. Biodiversity Science, 26, 1031-1033. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[傅声雷 (2018) 利用新方法和野外实验平台加强土壤动物多样性及其生态功能的研究. 生物多样性, 26, 1031-1033.]
DOI |
|
| [36] | Fu SL, Zhang WX, Shao YH, Shi LL, Liu ZF (2019) Soil Ecology:Soil Food Web and Its Ecological Function. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [傅声雷, 张卫信, 邵元虎, 时雷雷, 刘占锋 (2019) 土壤生态学: 土壤食物网及其生态功能. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [37] |
Fu SL, Zou XM, Coleman D (2009) Highlights and perspectives of soil biology and ecology research in China. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 41, 868-876.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Fujii S, Berg MP, Cornelissen JHC (2020) Living litter: Dynamic trait spectra predict fauna composition. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 35, 886-896.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Gao ZL, Karlsson I, Geisen S, Kowalchuk G, Jousset A (2019) Protists: Puppet masters of the rhizosphere microbiome. Trends in Plant Science, 24, 165-176.
DOI PMID |
| [40] |
Gaüzère P, O’Connor L, Botella C, Poggiato G, Münkemüller T, Pollock LJ, Brose U, Maiorano L, Harfoot M, Thuiller W (2022) The diversity of biotic interactions complements functional and phylogenetic facets of biodiversity. Current Biology, 32, 2093-2100.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Gebremikael MT, Steel H, Buchan D, Bert W, De Neve S (2016) Nematodes enhance plant growth and nutrient uptake under C and N-rich conditions. Scientific Reports, 6, 32862.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
Gong X, Chen XY, Geisen S, Zhang JR, Zhu HM, Hu F, Liu MQ (2021) Agricultural habitats are dominated by rapidly evolving nematodes revealed through phylogenetic comparative methods. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 155, 108183.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Grabmaier A, Heigl F, Eisenhauer N, van der Heijden MGA, Zaller JG (2014) Stable isotope labelling of earthworms can help deciphering belowground-aboveground interactions involving earthworms, mycorrhizal fungi, plants and aphids. Pedobiologia, 57, 197-203.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Grandy AS, Wieder WR, Wickings K, Kyker-Snowman E (2016) Beyond microbes: Are fauna the next frontier in soil biogeochemical models? Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 102, 40-44.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Griffiths BS (1994) Microbial-feeding nematodes and protozoa in soil: Their effects on microbial activity and nitrogen mineralization in decomposition hotspots and the rhizosphere. Plant and Soil, 164, 25-33.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Guerra CA, Heintz-Buschart A, Sikorski J, Chatzinotas A, Guerrero-Ramírez N, Cesarz S, Beaumelle L, Rillig MC, Maestre FT, Delgado-Baquerizo M, Buscot F, Overmann J, Patoine G, Phillips HRP, Winter M, Wubet T, Küsel K, Bardgett RD, Cameron EK, Cowan D, Grebenc T, Marín C, Orgiazzi A, Singh BK, Wall DH, Eisenhauer N (2020) Blind spots in global soil biodiversity and ecosystem function research. Nature Communications, 11, 3870.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
Ingham RE, Detling JK (1984) Plant-herbivore interactions in a North American mixed-grass prairie: III. Soil nematode populations and root biomass on Cynomys ludovicianus colonies and adjacent uncolonized areas. Oecologia, 63, 307-313.
DOI PMID |
| [48] |
Ingham RE, Trofymow JA, Ingham ER, Coleman DC (1985) Interactions of bacteria, fungi, and their nematode grazers: Effects on nutrient cycling and plant growth. Ecological Monographs, 55, 119-140.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Janzen HH, van Groenigen KJ, Powlson DS, Schwinghamer T, van Groenigen JW (2022) Photosynthetic limits on carbon sequestration in croplands. Geoderma, 416, 115810.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Jiang YB, Wang J, Muhammad S, Zhou AQ, Hao R, Wu YP (2018) How do earthworms affect decomposition of residues with different quality apart from fragmentation and incorporation? Geoderma, 326, 68-75.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Kemp PF, Aller JY (2004) Bacterial diversity in aquatic and other environments: What 16S rDNA libraries can tell us. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 47, 161-177.
DOI PMID |
| [52] |
Khan Z, Kim YH (2007) A review on the role of predatory soil nematodes in the biological control of plant parasitic nematodes. Applied Soil Ecology, 35, 370-379.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Li WL, Wang C, Sun ZJ (2011) Vermipharmaceuticals and active proteins isolated from earthworms. Pedobiologia, 54, S49-S56.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Li XP, Zhu HM, Geisen S, Bellard C, Hu F, Li HX, Chen XY, Liu MQ (2020) Agriculture erases climate constraints on soil nematode communities across large spatial scales. Global Change Biology, 26, 919-930.
DOI PMID |
| [55] |
Li YS, Sun ZJ, Hu F, Butt KR, Whalen JK (2021) Earthworms in soil ecology and organic waste management. Pedosphere, 31, 373-374.
DOI URL |
| [56] | Liao CH, Li JX (2009) Forest Soil Animal Community Ecology in South China Tropical and Subtropical Zones. Guangdong Science & Technology Press, Guangzhou. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [廖崇惠, 李健雄 (2009) 华南热带和南亚热带地区森林土壤动物群落生态. 广东科技出版社, 广州.] | |
| [57] |
Liu F, Li Q, Shen CC, Chu HY, Liang WJ (2014) Distribution of gymnamoebae communities along an elevational gradient in Changbai Mountains. Biodiversity Science, 22, 608-617. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[刘芳, 李琪, 申聪聪, 褚海燕, 梁文举 (2014) 长白山不同海拔梯度裸肉足虫群落分布特征. 生物多样性, 22, 608-617.]
DOI |
|
| [58] |
Liu L, Alpert P, Dong BC, Li JM, Yu FH (2017) Combined effects of soil heterogeneity, herbivory and detritivory on growth of the clonal plant Hydrocotyle vulgaris. Plant and Soil, 421, 429-437.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
Liu MQ, Hu ZK, Yao JN, Chen XY, Griffiths B, Hu F (2022) After-life legacy effects of enchytraeids increase the functional capability of arable soil following stress. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 58, 721-732.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
Liu SJ, Chen J, Gan WJ, Fu SL, Schaefer D, Gan JM, Yang XD (2016) Cascading effects of spiders on a forest-floor food web in the face of environmental change. Basic and Applied Ecology, 17, 527-534.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
Liu T, Chen XY, Gong X, Lubbers IM, Jiang YY, Feng W, Li XP, Whalen JK, Bonkowski M, Griffiths BS, Hu F, Liu MQ (2019) Earthworms coordinate soil biota to improve multiple ecosystem functions. Current Biology, 29, 3420-3429.
DOI PMID |
| [62] |
Lubbers IM, van Groenigen KJ, Fonte SJ, Six J, Brussaard L, van Groenigen JW (2013) Greenhouse-gas emissions from soils increased by earthworms. Nature Climate Change, 3, 187-194.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
Luo TX, Hu F, Li HX (2013) Influence of residues and earthworms application on N2O emissions of winter wheat. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 7545-7552. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [罗天相, 胡锋, 李辉信 (2013) 施加秸秆和蚯蚓活动对麦田N2O排放的影响. 生态学报, 33, 7545-7552.] | |
| [64] | Ma RZ, Hou GJ, Huang RC, Hou XY, Chen HK, Zhu KG (1957) The overview and academy activities of the Sixth Congress of the International Society of Soil Science. Chinese Science Bulletin, 8, 59-61. (in Chinese) |
| [马溶之, 侯光炯, 黄瑞采, 侯学煜, 陈华葵, 朱克贵 (1957) 国际土壤学会第六届会议概况及学术活动. 科学通报, 8, 59-61.] | |
| [65] |
Mao XF, Hu F, Griffiths B, Chen XY, Liu MQ, Li HX (2007) Do bacterial-feeding nematodes stimulate root proliferation through hormonal effects? Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 39, 1816-1819.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
Maraun M, Schatz H, Scheu S (2007) Awesome or ordinary? Global diversity patterns of oribatid mites. Ecography, 30, 209-216.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
Matus-Acuña V, Caballero-Flores G, Reyes-Hernandez BJ, Martínez-Romero E (2018) Bacterial preys and commensals condition the effects of bacteriovorus nematodes on Zea mays and Arabidopsis thaliana. Applied Soil Ecology, 132, 99-106.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
Na LP, Abail Z, Whalen JK, Liang B, Hu CX, Hu RG, Wu YP (2022) Earthworms increase nitrogen uptake by lettuce and change short-term soil nitrogen dynamics. Applied Soil Ecology, 176, 104488.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
Naeem S, Hahn DR, Schuurman G (2000) Producer- decomposer co-dependency influences biodiversity effects. Nature, 403, 762-764.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Neher DA (2010) Ecology of plant and free-living nematodes in natural and agricultural soil. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 48, 371-394.
DOI PMID |
| [71] |
Neher DA, Barbercheck ME (2019) Soil microarthropods and soil health: Intersection of decomposition and pest suppression in agroecosystems. Insects, 10, 414.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
Nielsen UN, Ayres E, Wall DH, Li G, Bardgett RD, Wu TH, Garey JR (2014) Global-scale patterns of assemblage structure of soil nematodes in relation to climate and ecosystem properties. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 23, 968-978.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
Nyffeler M, Birkhofer K (2017) An estimated 400-800 million tons of prey are annually killed by the global spider community. The Science of Nature, 104, 30.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
Oliverio AM, Geisen S, Delgado-Baquerizo M, Maestre FT, Turner BL, Fierer N (2020) The global-scale distributions of soil protists and their contributions to belowground systems. Science Advances, 6, eaax8787.
DOI URL |
| [75] | Orgiazzi A, Bardgett RD, Barrios E, Behan-Pelletier V, Briones MJI, Chotte J-L, De Deyn GB, Eggleton P, Fierer N, Fraser T, Hedlund K, Jeffery S, Johnson NC, Jones A, Kandeler E, Kaneko N, Lavelle P, Lemanceau P, Miko L, Montanarella L, Moreira FMS, Ramirez KS, Scheu S, Singh BK, Six J, van der Putten WH, Wall DH (2016) Global Soil Biodiversity Atlas. European Commission, Publications Office of the European Union, Luxembourg. |
| [76] | Oxbrough A, Ziesche T (2013) Spiders in forest ecosystems, In: Integrative Approaches as An Opportunity for the Conservation of Forest Biodiversity (eds Kraus D, Krumm F), pp. 186-193. European Forest Institute, Joensuu. |
| [77] |
Phillips HRP, Guerra CA, Bartz MLC, Briones MJI, Brown G, Crowther TW, Ferlian O, Gongalsky KB, van den Hoogen J, Krebs J, Orgiazzi A, Routh D, Schwarz B, Bach EM, Bennett J, Brose U, Decaëns T, König-Ries B, Loreau M, Mathieu J, Mulder C, van der Putten WH, Ramirez KS, Rillig MC, Russell D, Rutgers M, Thakur MP, de Vries FT, Wall DH, Wardle DA, Arai M, Ayuke FO, Baker GH, Beauséjour R, Bedano JC, Birkhofer K, Blanchart E, Blossey B, Bolger T, Bradley RL, Callaham MA, Capowiez Y, Caulfield ME, Choi A, Crotty FV, Dávalos A, Cosin DJD, Dominguez A, Duhour AE, van Eekeren N, Emmerling C, Falco LB, Fernández R, Fonte SJ, Fragoso C, Franco ALC, Fugère M, Fusilero AT, Gholami S, Gundale MJ, López MG, Hackenberger DK, Hernández LM, Hishi T, Holdsworth AR, Holmstrup M, Hopfensperger KN, Lwanga EH, Huhta V, Hurisso TT, Iannone BV III, Iordache M, Joschko M, Kaneko N, Kanianska R, Keith AM, Kelly CA, Kernecker ML, Klaminder J, Koné AW, Kooch Y, Kukkonen ST, Lalthanzara H, Lammel DR, Lebedev IM, Li YQ, Lidon JBJ, Lincoln NK, Loss SR, Marichal R, Matula R, Moos JH, Moreno G, Morón-Ríos A, Muys B, Neirynck J, Norgrove L, Novo M, Nuutinen V, Nuzzo V, Rahman PM, Pansu J, Paudel S, Pérès G, Pérez-Camacho L, Piñeiro R, Ponge JF, Rashid MI, Rebollo S, Rodeiro-Iglesias J, Rodríguez MÁ, Roth AM, Rousseau GX, Rozen A, Sayad E, van Schaik L, Scharenbroch BC, Schirrmann M, Schmidt O, Schröder B, Seeber J, Shashkov MP, Singh J, Smith SM, Steinwandter M, Talavera JA, Trigo D, Tsukamoto J, Vanek SJ, Virto I, Wackett AA, Warren MW, Wehr NH, Whalen JK, Wironen MB, Wolters V, Zenkova IV, Zhang WX, Cameron EK, Eisenhauer N (2019) Global distribution of earthworm diversity. Science, 366, 480-485.
DOI PMID |
| [78] | Potapov AM, Bellini BC, Chown SL, Deharveng L, Janssens F, Kováč Ľ, Kuznetsova NA, Ponge JF, Potapov M, Querner P, Russell DJ, Sun X, Zhang F, Berg MP (2020) Towards a global synthesis of Collembola knowledge—Challenges and potential solutions. Soil Organisms, 92, 161-188. |
| [79] |
Potapov AM, Guerra CA, van den Hoogen J, Babenko A, Bellini BC, Berg MP, Chown SL, Deharveng L, Kovac L, Kuznetsova NA, Ponge JF, Potapov MB, Russell DJ, Alexandre D, Alatalo JM, Arbea JI, Bandyopadhyay I, Bernava V, Bokhorst S, Bolger T, Castaño-Meneses G, Chauvat M, Chen TW, Chomel M, Classen AT, Cortet J, Čuchta P, de la Pedrosa AM, Ferreira SSD, Fiera C, Filser J, Franken O, Fujii S, Koudji EG, Gao MX, Gendreau- Berthiaume B, Gomez-Pamies DF, Greve M, Tanya-Handa I, Heiniger C, Holmstrup M, Homet P, Ivask M, Janion-Scheepers C, Jochum M, Joimel S, Jorge BCS, Jucevica E, Klauberg-Filho O, Baretta D, Krab EJ, Kuu A, de Lima ECA, Lin DM, Liu A, Lu JZ, Luciañez MJ, Marx MT, McCary MM, Minor MA, Nakamori T, Negri I, Ochoa-Hueso R, Palacios-Vargas JG, Pollierer MM, Querner P, Raschmanová N, Rashid MI, Raymond-Léonard LJ, Rousseau L, Saifutdinov RA, Salmon S, Sayer EJ, Scheunemann N, Scholz C, Seeber J, Shveenkova YB, Stebaeva SK, Sterzynska M, Sun X, Susanti WI, Taskaeva AA, Thakur MP, Tsiafouli MA, Turnbull MS, Twala MN, Uvarov AV, Venier LA, Widenfalk LA, Winck BR, Winkler D, Wu DH, Xie ZJ, Yin R, Zeppelini D, Crowther TW, Eisenhauer N, Scheu S (2022a) Globally invariant metabolism but density-diversity mismatch in springtails. bioRxiv, doi: 10.1101/2022.01.07.475345.
DOI |
| [80] | Potapov AM, Sun X, Barnes AD, Briones MJI, Brown GG, Cameron EK, Chang CH, Cortet J, Eisenhauer N, Franco AL, Fujii S, Geisen S, Guerra C, Gongalsky K, Haimi J, Handa IT, Janion-Sheepers C, Karaban K, Lindo Z, Mathieu J, Moreno ML, Murvanidze M, Nielsen U, Scheu S, Schmidt O, Schneider C, Seeber J, Tsiafouli M, Tuma J, Tiunov A, Zaytsev AS, Ashwood F, Callaham M, Wall D (2022b) Global monitoring of soil animal communities using a common methodology. Soil Organisms, 94, 55-68. |
| [81] |
Procter DLC (1984) Towards a biogeography of free-living soil nematodes. I. Changing species richness, diversity and densities with changing latitude. Journal of Biogeography, 11, 103-117.
DOI URL |
| [82] |
Sackett TE, Classen AT, Sanders NJ (2010) Linking soil food web structure to above- and belowground ecosystem processes: A meta-analysis. Oikos, 119, 1984-1992.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
Schlesinger WH (2022) Biogeochemical constraints on climate change mitigation through regenerative farming. Biogeochemistry, 161, 9-17.
DOI URL |
| [84] |
Schmitz OJ (2008) Effects of predator hunting mode on grassland ecosystem function. Science, 319, 952-954.
DOI PMID |
| [85] |
Schmitz OJ, Raymond PA, Estes JA, Kurz WA, Holtgrieve GW, Ritchie ME, Schindler DE, Spivak AC, Wilson RW, Bradford MA, Christensen V, Deegan L, Smetacek V, Vanni MJ, Wilmers CC (2014) Animating the carbon cycle. Ecosystems, 17, 344-359.
DOI URL |
| [86] |
Schuldt A, Assmann T, Brezzi M, Buscot F, Eichenberg D, Gutknecht J, Härdtle W, He JS, Klein AM, Kühn P, Liu XJ, Ma KP, Niklaus PA, Pietsch KA, Purahong W, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Schmid B, Scholten T, Staab M, Tang ZY, Trogisch S, von Oheimb G, Wirth C, Wubet T, Zhu CD, Bruelheide H (2018) Biodiversity across trophic levels drives multifunctionality in highly diverse forests. Nature Communications, 9, 2989.
DOI PMID |
| [87] | Shao YH, Wang ZY, Liu T, Kardol P, Ma CE, Hu YH, Cui Y, Zhao CC, Zhang WX, Guo DL, Fu SL (2022) Drivers of nematode diversity in forest soils across climatic zones. bioRxiv, https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.18.484848. |
| [88] |
Shao YH, Zhang WX, Eisenhauer N, Liu T, Xiong YM, Liang CF, Fu SL (2017) Nitrogen deposition cancels out exotic earthworm effects on plant-feeding nematode communities. Journal of Animal Ecology, 86, 708-717.
DOI PMID |
| [89] | Shao YH, Zhang WX, Liu SJ, Wang XL, Fu SL (2015) Diversity and function of soil fauna. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 6614-6625. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [邵元虎, 张卫信, 刘胜杰, 王晓丽, 傅声雷 (2015) 土壤动物多样性及其生态功能. 生态学报, 35, 6614-6625.] | |
| [90] |
Shen HY, Shiratori Y, Ohta S, Masuda Y, Isobe K, Senoo K (2021) Mitigating N2O emissions from agricultural soils with fungivorous mites. The ISME Journal, 15, 2427-2439.
DOI URL |
| [91] | Sohlenius B, Boström S, Sandor A (1988) Carbon and nitrogen budgets of nematodes in arable soil. Biology & Fertility of Soils, 6, 1-8. |
| [92] | Soliveres S, van Der Plas F, Manning P, Prati D, Gossner MM, Renner SC, Alt F, Arndt H, Baumgartner V, Binkenstein J, Birkhofer K, Blaser S, Blüthgen N, Boch S, Böhm S, Börschig C, Buscot F, Diekötter T, Heinze J, Hölzel N, Jung K, Klaus VH, Kleinebecker T, Klemmer S, Krauss J, Lange M, Morris EK, Müller J, Oelmann Y, Overmann J, Pašalić E, Rillig MC, Schaefer HM, Schloter M, Schmitt B, Schöning I, Schrumpf M, Sikorski J, Socher SA, Solly EF, Sonnemann I, Sorkau E, Steckel J, Steffan-Dewenter I, Stempfhuber B, Tschapka M, Türke M, Venter PC, Weiner CN, Weisser WW, Werner M, Westphal C, Wilcke W, Wolters V, Wubet T, Wurst S, Fischer M, Allan E (2016) Biodiversity at multiple trophic levels is needed for ecosystem multifunctionality. Nature, 536, 456-459. |
| [93] |
Soong JL, Nielsen UN (2016) The role of microarthropods in emerging models of soil organic matter. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 102, 37-39.
DOI URL |
| [94] |
Tedersoo L, Bahram M, Põlme S, Kõljalg U, Yorou NS, Wijesundera R, Ruiz LV, Vasco-Palacios AM, Thu PQ, Suija A, Smith ME, Sharp C, Saluveer E, Saitta A, Rosas M, Riit T, Ratkowsky D, Pritsch K, Põldmaa K, Piepenbring M, Phosri C, Peterson M, Parts K, Pärtel K, Otsing E, Nouhra E, Njouonkou AL, Nilsson RH, Morgado LN, Mayor J, May TW, Majuakim L, Lodge DJ, Lee SS, Larsson KH, Kohout P, Hosaka K, Hiiesalu I, Henkel TW, Harend H, Guo LD, Greslebin A, Grelet G, Geml J, Gates G, Dunstan W, Dunk C, Drenkhan R, Dearnaley J, de Kesel A, Dang T, Chen X, Buegger F, Brearley FQ, Bonito G, Anslan S, Abell S, Abarenkov K (2014) Global diversity and geography of soil fungi. Science, 346, 1256688.
DOI URL |
| [95] |
van den Hoogen J, Geisen S, Routh D, Ferris H, Traunspurger W, Wardle DA, de Goede RGM, Adams BJ, Ahmad W, Andriuzzi WS, Bardgett RD, Bonkowski M, Campos- Herrera R, Cares JE, Caruso T, Caixeta LDB, Chen XY, Costa SR, Creamer R, Castro JMDC, Dam M, Djigal D, Escuer M, Griffiths BS, Gutiérrez C, Hohberg K, Kalinkina D, Kardol P, Kergunteuil A, Korthals G, Krashevska V, Kudrin AA, Li Q, Liang WJ, Magilton M, Marais M, Martín JAR, Matveeva E, Mayad EH, Mulder C, Mullin P, Neilson R, Nguyen TAD, Nielsen UN, Okada H, Rius JEP, Pan KW, Peneva V, Pellissier L, da Silva JCP, Pitteloud C, Powers TO, Powers K, Quist CW, Rasmann S, Moreno SS, Scheu S, Setälä H, Sushchuk A, Tiunov AV, Trap J, van der Putten W, Vestergård M, Villenave C, Waeyenberge L, Wall DH, Wilschut R, Wright DG, Yang JI, Crowther TW (2019) Soil nematode abundance and functional group composition at a global scale. Nature, 572, 194-198.
DOI URL |
| [96] | van Groenigen JW, Lubbers IM, Vos HMJ, Brown GG, de Deyn GB, van Groenigen KJ (2014) Earthworms increase plant production: A meta-analysis. Scientific Reports, 4, 6365. |
| [97] |
Walker BH (1992) Biodiversity and ecological redundancy. Conservation Biology, 6, 18-23.
DOI URL |
| [98] | Wall DH, Bardgett RD, Behan-Pelletier V, Herrick JE, Jones TH, Ritz K, Six J, Strong DR, van der Putten WH (2012) Soil Ecology and Ecosystem Services. Oxford University Press, Oxford. |
| [99] |
Wall DH, Nielsen UN, Six J (2015) Soil biodiversity and human health. Nature, 528, 69-76.
DOI URL |
| [100] |
Wan BB, Hu ZK, Liu T, Yang Q, Li DM, Zhang CZ, Chen XY, Hu F, Kardol P, Griffiths BS, Liu MQ (2022a) Organic amendments increase the flow uniformity of energy across nematode food webs. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 170, 108695.
DOI URL |
| [101] |
Wan BB, Liu T, Gong X, Zhang Y, Li CJ, Chen XY, Hu F, Griffiths BS, Liu MQ (2022b) Energy flux across multitrophic levels drives ecosystem multifunctionality: Evidence from nematode food webs. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 169, 108656.
DOI URL |
| [102] |
Wang MR, Fu SL, Xu HX, Wang MN, Shi LL (2018) Ecological functions of millipedes in the terrestrial ecosystem. Biodiversity Science, 26, 1051-1059. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[王梦茹, 傅声雷, 徐海翔, 王美娜, 时雷雷 (2018) 陆地生态系统中马陆的生态功能. 生物多样性, 26, 1051-1059.]
DOI |
|
| [103] | Wang PY (1958) Soil zoology. Chinese Bulletin of Entomology, 4, 49. (in Chinese) |
| [王平远 (1958) 土壤动物学. 昆虫知识, 4, 49.] | |
| [104] | Wang RH, Liu QY, Wang XY, Zhao ZY, Dou YJ (2022) Responses of soil mite community diversity to altitude gradients in Luya Mountain, China. Journal of Shanxi University, 45, 1138-1150. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王让虎, 刘倩煜, 王啸宇, 赵子义, 窦永静 (2022) 芦芽山土壤螨类群落多样性对海拔梯度的响应. 山西大学学报(自然科学版), 45, 1138-1150.] | |
| [105] |
Weidner S, Latz E, Agaras B, Valverde C, Jousset A (2017) Protozoa stimulate the plant beneficial activity of rhizospheric pseudomonads. Plant and Soil, 410, 509-515.
DOI URL |
| [106] |
Wellnitz T, Poff NL (2001) Functional redundancy in heterogeneous environments: Implications for conservation. Ecology Letters, 4, 177-179.
DOI URL |
| [107] |
Wolters V (2000) Invertebrate control of soil organic matter stability. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 31, 1-19.
DOI URL |
| [108] |
Wu D, Liu MQ, Song XC, Jiao JG, Li HX, Hu F (2015) Earthworm ecosystem service and dis-service in an N-enriched agroecosystem: Increase of plant production leads to no effects on yield-scaled N2O emissions. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 82, 1-8.
DOI URL |
| [109] |
Wu JH, Chen HL, Zhang YZ (2016) Latitudinal variation in nematode diversity and ecological roles along the Chinese coast. Ecology and Evolution, 6, 8018-8027.
DOI PMID |
| [110] |
Wu JH, Song CY, Chen JK (2007) Effect of microbivorous nematodes on plant growth and soil nutrient cycling: A review. Biodiversity Science, 15, 124-133. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[吴纪华, 宋慈玉, 陈家宽 (2007) 食微线虫对植物生长及土壤养分循环的影响. 生物多样性, 15, 124-133.]
DOI |
|
| [111] |
Wurst S (2010) Effects of earthworms on above- and belowground herbivores. Applied Soil Ecology, 45, 123-130.
DOI URL |
| [112] | Wurst S, de Deyn GB, Orwin K (2012) Soil biodiversity and functions, In: Soil Ecology and Ecosystem Services (eds Wall DH, Bardgett RD, Behan-Pelletler V, Herrick JE, Jones TH, Ritz K, Six J, Strong DR, van der Putten WH), pp. 28-44. Oxford University Press, Oxford. |
| [113] |
Xiao HF, Wang WT, Xia SW, Li ZP, Gan JM, Yang XD (2021) Distributional patterns of soil nematodes in relation to environmental variables in forest ecosystems. Soil Ecology Letters, 3, 115-124.
DOI |
| [114] |
Xiao ZG, Wang X, Koricheva J, Kergunteuil A, Le Bayon RC, Liu MQ, Hu F, Rasmann S (2018) Earthworms affect plant growth and resistance against herbivores: A meta-analysis. Functional Ecology, 32, 150-160.
DOI URL |
| [115] | Xie ZJ, Chang L, Scheu S, Wu DH, Sun X (2022) Taxonomic and functional diversity of Collembola in litter and soil along an altitudinal gradient at Changbai Mountain, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42, 3471-3481. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [谢致敬, 常亮, Scheu S, 吴东辉, 孙新 (2022) 长白山森林生态系统凋落物层和土壤层跳虫物种多样性和功能多样性对海拔梯度的响应. 生态学报, 42, 3471-3481.] | |
| [116] |
Xiong D, Wei CZ, Wubs ERJ, Veen GF, Liang WJ, Wang XB, Li Q, van der Putten WH, Han XG (2020) Nonlinear responses of soil nematode community composition to increasing aridity. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 29, 117-126.
DOI |
| [117] |
Xu HJ, Bai J, Li WY, Murrell JC, Zhang YL, Wang JJ, Luo CL, Li YT (2021) Mechanisms of the enhanced DDT removal from soils by earthworms: Identification of DDT degraders in drilosphere and non-drilosphere matrices. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 404, 124006.
DOI URL |
| [118] |
Xu L, Xu WS, Jiang Y, Hu F, Li HX (2015) Effects of interactions of auxin-producing bacteria and bacterial- feeding nematodes on regulation of peanut growths. PLoS ONE, 10, e0124361.
DOI URL |
| [119] | Xu SB, Li YH, Zhu LQ, Li L (2020) A review on the vertical distribution patterns of soil animal communities in mountains. Journal of Henan University (Natural Science), 50(1), 19-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐帅博, 李艳红, 朱连奇, 李理 (2020) 山地土壤动物群落垂直分布格局研究进展. 河南大学学报(自然科学版), 50(1), 19-28.] | |
| [120] |
Xu W, Ma ZY, Jing X, He JS (2016) Biodiversity and ecosystem multifunctionality: Advances and perspectives. Biodiversity Science, 24, 55-71. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[徐炜, 马志远, 井新, 贺金生 (2016) 生物多样性与生态系统多功能性: 进展与展望. 生物多样性, 24, 55-71.]
DOI |
|
| [121] | Yin WY (2001) A brief review and prospect on soil zoology. Bulletin of Biology, 36(8), 1-3. (in Chinese) |
| [尹文英 (2001) 土壤动物学研究的回顾与展望. 生物学通报, 36(8), 1-3.] | |
| [122] | Yin WY (1992) Soil Animals in Subtropical China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [尹文英 (1992) 中国亚热带土壤动物. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [123] | Yin WY (2000) Soil Animals of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [尹文英 (2000) 中国土壤动物. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [124] | Yin XQ (2001) Study on Forest Soil Animals in Northeast China. Northeast Normal University Press, Changchun. (in Chinese) |
| [殷秀琴 (2001) 东北森林土壤动物研究. 东北师范大学出版社, 长春.] | |
| [125] |
Yin XQ, Song B, Dong WH, Xin WD (2010) A review on the eco-geography of soil fauna in China. Acta Geographica Sinica, 65, 91-102. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [殷秀琴, 宋博, 董炜华, 辛未冬 (2010) 我国土壤动物生态地理研究进展. 地理学报, 65, 91-102.] | |
| [126] | Zhang FD (2006) Chinese Soil Biological Evolution and Safety Evaluation. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张夫道 (2006) 中国土壤生物演变及安全评价. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [127] | Zhang RZ (1964) Earthworms in the meadow-cinnamon soils in Beijing. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 8(1), 31-33. (in Chinese) |
| [张荣祖 (1964) 北京草甸褐土中的蚯蚓. 土壤通报, 8(1), 31-33.] | |
| [128] | Zhang RZ, Liu XL, Zhong HM, Wu Q, Wu PF (2016) Distribution pattern of soil nematode communities along the vertical climate zones on the eastern slope of Gongga Mountain. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 22, 959-971. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张荣芝, 刘兴良, 钟红梅, 武崎, 吴鹏飞 (2016) 土壤线虫群落在贡嘎山东坡不同垂直气候带间的分布格局. 应用与环境生物学报, 22, 959-971.] | |
| [129] | Zhang RZ, Yang MX, Chen P, Zhang TW (1980) A preliminary survey on soil animals in the forest ecosystems on northern slope of Changbaishan Mountain. Research of Forest Ecosystem, 1, 133-152. (in Chinese) |
| [张荣祖, 杨明宪, 陈鹏, 张庭伟 (1980) 长白山北坡森林生态系统土壤动物初步调查. 森林生态系统研究, 1, 133-152.] | |
| [130] |
Zhang WX, Chen DM, Zhao CC (2007) Functions of earthworm in ecosystem. Biodiversity Science, 15, 142-153. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张卫信, 陈迪马, 赵灿灿 (2007) 蚯蚓在生态系统中的作用. 生物多样性, 15, 142-153.]
DOI |
|
| [131] |
Zhang WX, Hendrix PF, Dame LE, Burke RA, Wu JP, Neher DA, Li JX, Shao YH, Fu SL (2013) Earthworms facilitate carbon sequestration through unequal amplification of carbon stabilization compared with mineralization. Nature Communications, 4, 2576.
DOI PMID |
| [132] | Zhang XK, Liang WJ, Li Q (2013) Forest Soil Nematodes in Changbai Mountain: Morphology and Distribution. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张晓珂, 梁文举, 李琪 (2013) 长白山森林土壤线虫: 形态分类与分布格局. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [133] |
Zhang Y, Xiao ZG, Jiang LH, Qian L, Chen XY, Chen FJ, Hu F, Liu MQ (2018) Nitrogen levels modify earthworm- mediated tomato growth and resistance to pests. Biodiversity Science, 26, 1296-1307. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张宇, 肖正高, 蒋林惠, 钱蕾, 陈小云, 陈法军, 胡锋, 刘满强 (2018) 施氮水平影响蚯蚓介导的番茄生长及抗虫性. 生物多样性, 26, 1296-1307.]
DOI |
|
| [134] |
Zhang YZ, Li B, Wu JH, Pennings SC (2020) Contrasting latitudinal clines of nematode diversity in Spartina alterniflora salt marshes between native and introduced ranges. Diversity and Distributions, 26, 623-631.
DOI URL |
| [135] | Zhao SH, Pang XF (1958) Introduction to the status of soil entomology in the Academy of Sciences of the USSR. Chinese Bulletin of Entomology, 4(3), 107-111. (in Chinese) |
| [赵善欢, 庞雄飞 (1958) 介绍苏联科学院关于土壤昆虫学的研究情况. 昆虫知识, 4(3), 107-111.] | |
| [136] | Zhao XL, Xie BG (1996) Studies on Ecological Zoogeography. Chengdu Map Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [赵小鲁, 谢炳庚 (1996) 动物生态地理研究. 成都地图出版社, 成都.] | |
| [137] |
Zhu BJ, Xue JR, Xia R, Jin MM, Wu Y, Tian SY, Chen XY, Liu MQ, Hu F (2019) Effect of soil nematode functional guilds on plant growth and aboveground herbivores. Biodiversity Science, 27, 409-418. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[朱柏菁, 薛敬荣, 夏蓉, 靳苗苗, 吴攸, 田善义, 陈小云, 刘满强, 胡锋 (2019) 不同土壤线虫功能团对水稻生长及地上部植食者的影响. 生物多样性, 27, 409-418.]
DOI |
| [1] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [2] | 罗敏, 杨永川, 靳程, 周礼华, 龙宇潇. 城市森林兽类组成特征及人类活动的影响——以重庆中心城区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24402-. |
| [3] | 刘淑琪, 崔东, 江智诚, 刘江慧, 闫江超. 短期氮、水添加和刈割减弱了苦豆子型退化草地土壤生物多样性与生态系统多功能性的联系[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24305-. |
| [4] | 陈楠, 张全国. 实验进化研究途径[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24171-. |
| [5] | 董云伟, 鲍梦幻, 程娇, 陈义永, 杜建国, 高养春, 胡利莎, 李心诚, 刘春龙, 秦耿, 孙进, 王信, 杨光, 张崇良, 张雄, 张宇洋, 张志新, 战爱斌, 贺强, 孙军, 陈彬, 沙忠利, 林强. 中国海洋生物地理学研究进展和热点: 物种分布模型及其应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23453-. |
| [6] | 钟超, 廖亚琴, 刘伟杰, 隋昊志, 陈清华. 广东沿海海草床的现状、面临的威胁与保护建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23201-. |
| [7] | 耿宜佳, 田瑜, 李俊生, 李子圆, 潘玉雪. 《生物多样性公约》框架下外来入侵物种管控的全球进展、挑战和展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24275-. |
| [8] | 韩丽霞, 王永健, 刘宣. 外来物种入侵与本土物种分布区扩张的异同[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23396-. |
| [9] | 牛永杰, 马全会, 朱玉, 刘海荣, 吕佳乐, 邹元春, 姜明. 氮沉降对草地昆虫多样性影响的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23130-. |
| [10] | 杨俊毅, 关潇, 李俊生, 刘晶晶, 郝颢晶, 王槐睿. 乌江流域生物多样性与生态系统服务的空间格局及相互关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23061-. |
| [11] | 董庆栋, 陈超男, 李艳红, 赵体侠, 孙梓欣, 张哲, 朱连奇. 基于NPP和人类扰动指数评估河南伏牛山地区国家级自然保护区群保护成效与溢出/泄漏效应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22503-. |
| [12] | 肖媛媛, 冯薇, 乔艳桂, 张宇清, 秦树高. 固沙灌木林地土壤微生物群落特征对土壤多功能性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22585-. |
| [13] | 江艺欣, 时莹莹, 高朔, 王苏盆. 人为噪音、夜间人造光和路杀对两栖动物的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22427-. |
| [14] | 宋亮, 吴毅, 胡海霞, 刘文耀, 中村彰宏, 陈亚军, 马克平. 基于塔吊的林冠科学研究进展及展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23363-. |
| [15] | 程文达, 邢爽, 刘阳. 华莱士在动物体色演化研究中的贡献和当代启示[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23434-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn