



生物多样性 ›› 2015, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (2): 183-191. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014126 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2014126
• 研究报告: 热带亚热带森林大样地群落结构与格局 • 上一篇 下一篇
郭屹立, 王斌, 向悟生, 丁涛, 陆树华, 黄俞淞, 黄甫昭, 李冬兴, 李先琨*( )
)
收稿日期:2014-06-16
接受日期:2014-10-20
出版日期:2015-03-20
发布日期:2015-04-09
通讯作者:
李先琨
基金资助:
Yili Guo, Bin Wang, Wusheng Xiang, Tao Ding, Shuhua Lu, Yusong Huang, Fuzhao Huang, Dongxing Li, Xiankun Li*( )
)
Received:2014-06-16
Accepted:2014-10-20
Online:2015-03-20
Published:2015-04-09
Contact:
Li Xiankun
摘要:
种群的空间分布格局是由多种机制的交互作用而形成, 是探究生物多样性维持机制的基础。北热带喀斯特季节性雨林是我国北热带石灰岩山地具有地带性特征的植被, 其生境的典型特征在于土层浅薄、岩石裸露率高、贮水能力低和周期性水淹, 以及富钙强碱性环境等。本研究基于广西弄岗北热带喀斯特季节性雨林15 ha动态监测样地的第一次调查资料, 采用双关联g(r)函数点格局方法, 分析了雨林中出现个体数≥15株的160个种的种群空间分布格局以及不同类群间种群分布的差异。研究表明: 160种木本植物中有146种在0-10 m的尺度上呈聚集分布, 且随着空间尺度的增大, 聚集度呈下降趋势; 物种的种群聚集度与其物种多度、平均胸径和最大胸径成负相关; 常绿物种的种群聚集度与落叶物种间差异不显著; 不同生活型间的种群聚集度差异显著, 总体表现为亚乔木层物种高于乔木层, 灌木层物种显著高于亚乔木层; 剔除生境异质性后大部分物种表现为随机分布, 仅少部分物种的种群表现为聚集分布。这表明物种的功能属性如物种多度、生活型等可较好地预测物种的分布格局。此外, 物种种群的分布格局还受生境异质性的影响, 且不同物种受生境异质性影响的程度不同。
郭屹立, 王斌, 向悟生, 丁涛, 陆树华, 黄俞淞, 黄甫昭, 李冬兴, 李先琨 (2015) 广西弄岗北热带喀斯特季节性雨林监测样地种群空间点格局分析. 生物多样性, 23, 183-191. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014126.
Yili Guo, Bin Wang, Wusheng Xiang, Tao Ding, Shuhua Lu, Yusong Huang, Fuzhao Huang, Dongxing Li, Xiankun Li (2015) Spatial distribution of tree species in a tropical karst seasonal rainforest in Nonggang, Guangxi, southern China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 183-191. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014126.
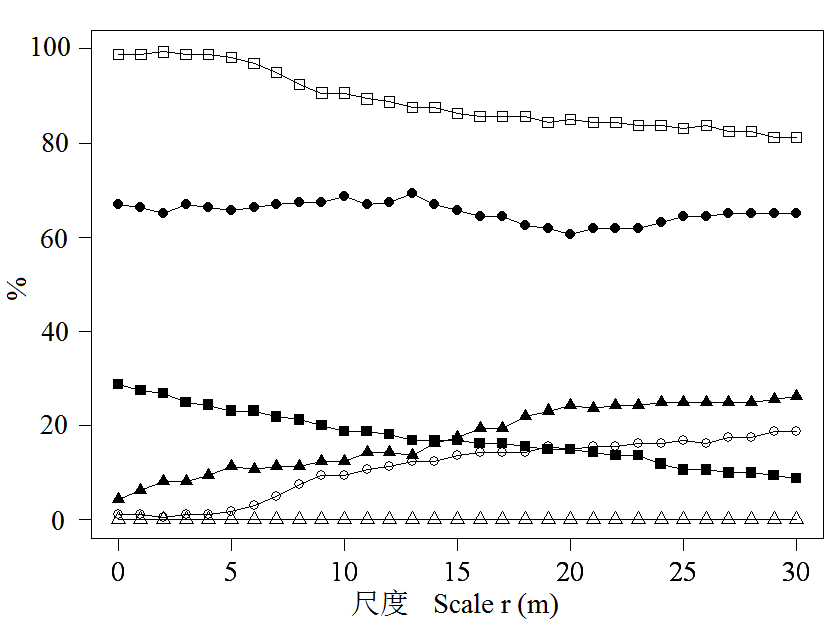
图2 弄岗样地物种种群在不同尺度下表现聚集、规则和随机格局的比例。空心符号为基于完全随机零模型, 实心符号为基于泊松异质性零模型。其中, 正方形表示聚集分布、三角形表示规则分布、圆形表示随机分布。
Fig. 2 Proportion of species showing significantly aggregation, regularity and random over scales under the complete spatial randomness (CSR, open signs) and heterogeneous Poisson process (HPP, solid signs) in the Nonggang Forest Dynamics Plot. Aggregation (squares), regularity (triangles) and random (circles).
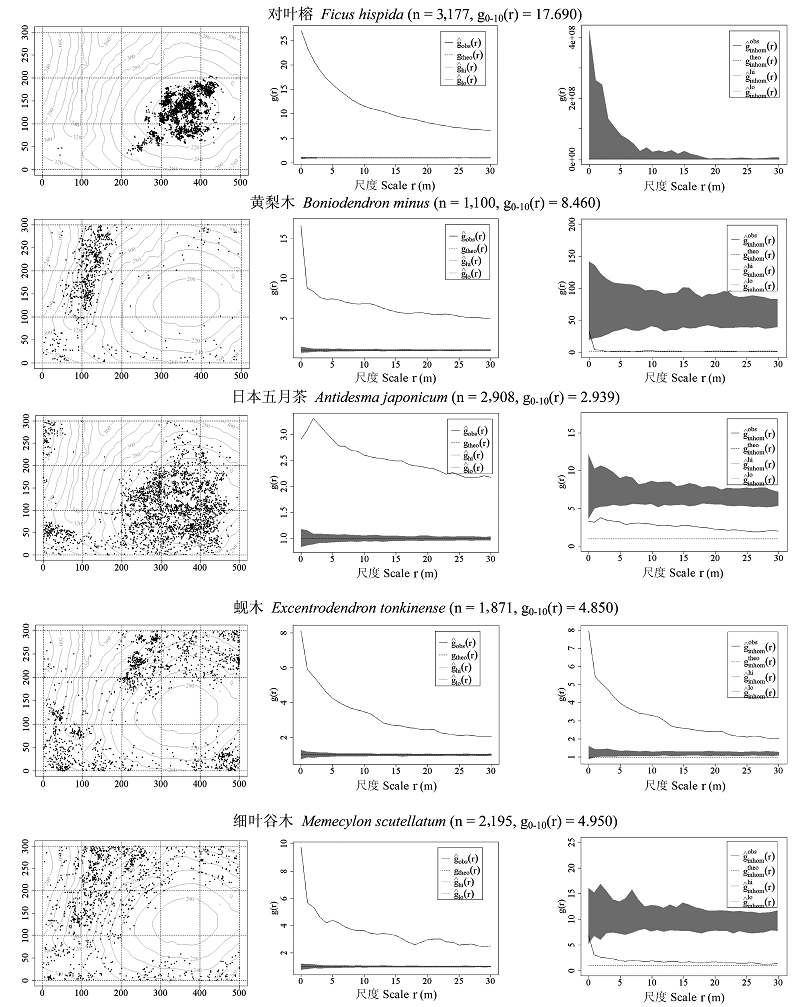
图3 弄岗样地物种分布散点图(左列)、基于完全随机(中间列)和泊松异质性(右列)零模型的物种分布格局图, 以5个常见物种为例。左图中左下方为样地的西南角。
Fig. 3 Five examples of species distribution in the Nonggang Forest Dynamics Plot. Middle and right panels showing the relationship between g(r) and scales for the five species, while left panels showing their corresponding distribution patterns. The lines with points are for g(r); the other lines are the simulation envelopes generated from 999 Monte Carlo simulations under the null hypothesis of Complete Spatial Randomness (CSR) and Heterogeneous Poisson process (HPP).
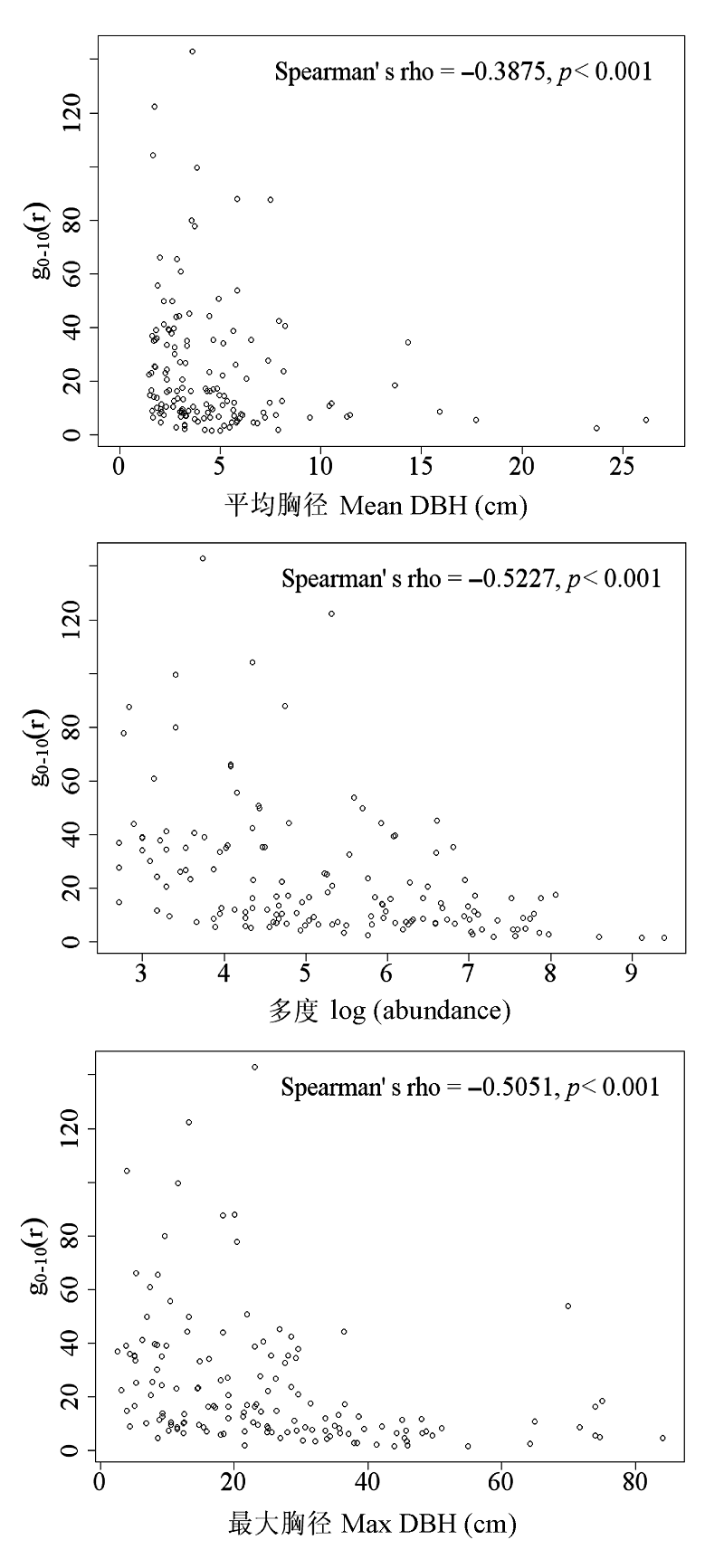
图4 弄岗样地物种属性(平均胸径、最大胸径和多度)与聚集度关联性分析
Fig. 4 Relationship between aggregation index (g0-10(r)) and mean DBH, maximumal DBH and abundance of species with abundance ≥ 15 in the Nonggang Forest Dynamics Plot.
| 1 | Antonovics J, Levin DA (1980) The ecological and genetic consequences of density-dependent regulation in plants.Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 11, 411-452. |
| 2 | Baddeley A, Turner R (2005) Spatstat: an R package for Analyzing Spatial Point Patterns.Journal of Statistical Software, 12, 1-42. |
| 3 | Barot S, Gignoux J, Menaut JC (1999) Demography of a Savanna palm tree: predictions from comprehensive spatial pattern analyses. Ecology, 80, 1987-2005. |
| 4 | Comita LS, Aguilar S, Pérez R, Lao S, Hubble SP (2007) Patterns of woody plant species abundance and diversity in the seedling layer of a tropical forest.Journal of Vegetation Science, 18, 163-174. |
| 5 | Condit R, Ashton PS, Baker P, Bunyavejchewin S, Gunatilleke S, Gunatilleke N, Hubbell SP, Foster SP, Itoh RB, LaFrankie A, Lee JV, Losos E, Manokaran N, Sukumar R, Yamakura T (2000) Spatial patterns in the distribution of tropical tree species.Science, 288, 1414-1418. |
| 6 | Davis MA, Curran C, Tietmeyer A, Miller A (2005) Dynamic tree aggregation patterns in a species-poor temperate woodland disturbed by fire.Journal of Vegetation Science, 16, 167-174. |
| 7 | Diggle PJ (2003) Statistical Analysis of Spatial Point Patterns. Arnold Press, London. |
| 8 | Dixon PM (2002) Ripley’s K function. Encyclopedia of Environmetrics, 3, 1796-1803. |
| 9 | Engelbrecht BM, Comita LS, Condit R, Kursar TA, Tyree MT, Turner BL, Hubbell SP (2007) Drought sensitivity shapes species distribution patterns in tropical forests.Nature, 447, 80-82. |
| 10 | Greig-Smith P (1983) Quantitative Plant Ecology, 3rd edn. Butterworths, London. |
| 11 | Guo K (郭柯), Liu CC (刘长成), Dong M (董鸣) (2011) Ecological adaptation of plants and control of rocky-desertifica- tion on karst region of Southwest China. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version) (植物生态学报), 35, 991-999. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 12 | Guo YL, Lu JM, Franklin SB, Wang QG, Xu YZ, Zhang KH, Bao DC, Qiao XJ, Huang HD, Lu ZJ, Jiang MX (2013) Spatial distribution of tree species in a species-rich subtropical mountain forest in central China.Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 43, 826-835. |
| 13 | Hardya OJ, Sonke B (2004) Spatial pattern analysis of tree species distribution in a tropical rain forest of cameroon: assessing the role of limited dispersal and niche differentiation.Forest Ecology and Management, 179, 191-202. |
| 14 | Harms KE, Wright JS, Calderón O, Hernández A, Herre EA (2000) Pervasive density-dependent recruitment enhances seedling diversity in a tropical forest.Nature, 404, 493-495. |
| 15 | He FL, Legendre P, LaFrankie JV (1997) Distribution patterns of tree species in a Malaysian tropical rain forest.Journal of Vegetation Science, 8, 105-114. |
| 16 | Huang FZ (黄甫昭), Wang B (王斌), Ding T (丁涛), Xiang WS (向悟生), Li XK (李先琨), Zhou AP (周爱萍) (2014) Numerical classification of associations in a northern tropical karst seasonal rain forest and the relationships of these associations with environmental factors.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 22, 157-166. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 17 | Hubbell SP, Foster RB (1983) Diversity of canopy trees in a neotropical forest and implications for the conservation of tropical trees. In: Tropical Rainforest Ecology and Management (eds Sutton SJ, Whitmore TC, Chadwick AC), pp. 314-329. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford, UK. |
| 18 | Hubbell SP (1979) Tree dispersion, abundance, and diversity in a tropical dry forest.Science, 203, 1299-1309. |
| 19 | John R, Dalling JW, Harms KE, Yavitt JB, Stallard RF, Mirabello M, Hubbell SP, Valencia R, Navarrete H, Vallejo M, Foster RB (2007) Soil nutrients influence spatial distributions of tropical tree species. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 104, 864-869. |
| 20 | Kershaw KA (1963) Pattern in vegetation and its causality.Ecology, 44, 377-388. |
| 21 | Law R, Illian J, Burslem DFRP, Gratzer G, Gunatilleke CVS, Gunatilleke IAUN (2009) Ecological information from spatial patterns of plants: insights from point process theory.Journal of Ecology, 97, 616-628. |
| 22 | Lepš J (1990) Can underlying mechanisms be deduced from observed patterns? In: Spatial Processes in Plant Communities (eds Krahulec F, Agnew ADQ, Agnew S, Willems JH), pp.1-11. SPB, The Hague, The Netherlands. |
| 23 | Levin SA (1992) The problem of pattern and scale in ecology.Ecology, 73, 1943-1967. |
| 24 | Li L, Huang ZL, Ye WH, Cao HL, Wei SG, Wang ZG, Lian JY, Sun YF, Ma KP, He FL (2009) Spatial distributions of tree species in a subtropical forest of China.Oikos, 118, 495-502. |
| 25 | Li XK (李先琨), He CX (何成新), Tang JS (唐建生), Jiang ZC (蒋忠诚), Huang YQ (黄玉清) (2008) Evolution and ecological processes of karst ecosystem of Guangxi.Guangxi Sciences(广西科学), 15, 80-86, 91. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 26 | Mangan SA, Schnitzer SA, Herre EA, Mack KML, Valencia MC, Sanchez EI, Bever JD (2010) Negative plant-soil feedback predicts tree-species relative abundance in a tropical forest.Nature, 466, 752-755. |
| 27 | McDonald RI, Peet RK, Urban DL (2003) Spatial pattern of Quercus regeneration limitation and Acer rubrum invasion in a piedmont forest. Journal of Vegetation Science, 14, 441-450. |
| 28 | McIntire EJB, Fajardo A (2009) Beyond description: the active and effective way to infer processes from spatial patterns. Ecology, 90, 45-56. |
| 29 | Murrell D, Purves D, Law R (2002) Intraspecific aggregation and species coexistence.Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 17, 210-211. |
| 30 | Perry GLW, Enright NJ, Miller BP, Lamont BB (2008) Spatial patterns in species-rich sclerophyll shrublands of southwestern Australia.Journal of Vegetation Science, 19, 705-716. |
| 31 | Perry GLW, Miller BP, Enright NJ (2006) A comparison of methods for the statistical analysis of spatial point patterns in plant ecology.Plant Ecology, 187, 59-82. |
| 32 | Plotkin JB, Potts MD, Leslie N, Manokaran N, Lafrankie J, Ashton PS (2000) Species-area curves, spatial aggregation, and habitat specialization in tropical forests.Journal of Theoretical Biology, 207, 81-99. |
| 33 | Seidler TG, Plotkin JB (2006) Seed dispersal and spatial pattern in tropical trees.PLoS Biology, 4, 2132-2137. |
| 34 | Tilman D, Kareiva P (1997) Spatial Ecology: The Role of Space in Population Dynamics and Interspecific Interactions. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| 35 | Tuda M (2007) Understanding mechanism of spatial ecological phenomena: a preface to the special feature on “spatial statistics”.Ecological Research, 22, 183-184. |
| 36 | Wang B (王斌), Huang YS (黄俞淞), Li XK (李先琨), Xiang WS (向悟生), Ding T (丁涛), Huang FZ (黄甫昭), Lu SH (陆树华), Han WH (韩文衡), Wen SJ (文淑均), He LJ (何兰军) (2014) Species composition and spatial distribution of a 15 ha northern tropical karst seasonal rain forest dynamics study plot in Nonggang, Guangxi, southern China.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 22, 141-156. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 37 | Wang XG, Ye J, Li BH, Zhang J, Lin F, Hao ZQ (2010) Spatial distributions of species in an old-growth temperate forest, northeastern China.Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 40, 1011-1019. |
| 38 | Watt AS (1947) Pattern and process in the plant community.Journal of Ecology, 35, 1-22. |
| 39 | Wiegand T, Moloney KA (2004) Ring, circles, and null-models for point pattern analysis in ecology.Oikos, 104, 209-229. |
| 40 | Wiegand T, Gunatilleke S, Gunatilleke N (2007a) Species associations in heterogeneous Sri Lankan Dipterocarp forest.The American Naturalist, 170, 77-95. |
| 41 | Wiegand T, Gunatilleke S, Gunatilleke N, Okuda T (2007b) Analyzing the spatial structure of a Sri Lankan tree species with multiple scales of clustering.Ecology, 88, 3088-3102. |
| 42 | Wiegand T, Jeltsch F, Hanski I, Grimm V (2003) Using pattern-oriented modeling for revealing hidden information: a key for reconciling ecological theory and application.Oikos, 100, 209-222. |
| 43 | Wright SJ, Muller-Landau HC, Condit R, Hubbell SP (2003) Gap-dependent recruitment, realized vital rates, and size distributions of tropical trees.Ecology, 84, 3174-3185. |
| [1] | 李世东. 中国和美国国家公园时空发展及驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 23040-. |
| [2] | 陈宏, 冼晓青, 陈宜雪, 林娜, 王苗苗, 李志鹏, 赵健. 海岛型城市红火蚁发生程度空间格局及驱动因子——以福建海坛岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22501-. |
| [3] | 李佳奇, 郭屹立, 李冬兴, 王斌, 向悟生, 黄甫昭, 陆芳, 文淑均, 李健星, 陆树华, 李先琨. 桂西南北热带喀斯特季节性雨林土壤钾、钙、镁空间分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22352-. |
| [4] | 张伟, 翟东东, 熊飞, 刘红艳, 陈元元, 王莹, 廖传松, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 邓华堂, 陈大庆. 三峡库区鱼类群落结构和功能多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22136-. |
| [5] | 田希, 刘文聪, 饶杰生, 王晓凤, 杨涛, 陈稀, 张秋雨, 刘其明, 徐衍潇, 张旭, 沈泽昊. 云南鸡足山半湿润常绿阔叶林的林隙干扰格局与成因[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23219-. |
| [6] | 付飞, 魏慧玉, 常育腾, 王备新, 陈凯. 澜沧江中游水生昆虫生活史和生态学性状多样性的海拔格局: 气候和土地利用的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21332-. |
| [7] | 孙佳欢, 刘冬, 朱家祺, 张书宁, 高梅香. 小麦-玉米轮作农田土壤螨多样性空间分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22292-. |
| [8] | 宋垚彬, 徐力, 段俊鹏, 张卫军, 申屠晓露, 李天翔, 臧润国, 董鸣. 西藏极小种群野生植物密叶红豆杉种群的性比及雌雄空间格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(3): 269-276. |
| [9] | 葛振鹏, 刘权兴. 整体大于部分之和: 生态自组织斑图及其涌现属性[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(11): 1431-1443. |
| [10] | 梁健超, 丁志锋, 张春兰, 胡慧建, 朵海瑞, 唐虹. 青海三江源国家级自然保护区麦秀分区鸟类多样性空间格局及热点区域研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(3): 294-303. |
| [11] | 许玥, 李鹏, 刘晔, 张婉君, 秦思雨, 沈泽昊. 怒江河谷入侵植物与乡土植物丰富度的分布格局与影响因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(4): 389-398. |
| [12] | 郭屹立, 王斌, 向悟生, 丁涛, 陆树华, 黄甫昭, 文淑均, 李冬兴, 何运林, 李先琨. 喀斯特季节性雨林木本植物胸高断面积分布格局及其对地形因子的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(1): 30-39. |
| [13] | 陈圣宾, 欧阳志云, 方瑜, 李振基. 中国种子植物特有属的地理分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(4): 414-423. |
| [14] | 袁志良, 王婷, 朱学灵, 沙迎迎, 叶永忠. 宝天曼落叶阔叶林样地栓皮栎种群空间格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(2): 224-231. |
| [15] | 刘海丰, 李亮, 桑卫国. 东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶次生林动态监测样地:物种组成与群落结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(2): 232-242. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn