



Biodiv Sci ›› 2013, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (3): 343-351. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.09039 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2013.09039
Special Issue: 昆虫多样性与生态功能
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhixing Lu1,2, Youqing Chen1,2,*( ), Wei Zhang3, Siming Wang1,2, Qiao Li3
), Wei Zhang3, Siming Wang1,2, Qiao Li3
Received:2013-02-05
Accepted:2013-04-22
Online:2013-05-20
Published:2013-06-05
Contact:
Chen Youqing
Zhixing Lu,Youqing Chen,Wei Zhang,Siming Wang,Qiao Li. Effects of facultative mutualism between ants and lac insects on the diversity of ant communities[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2013, 21(3): 343-351.
| 样地 Sites | 常见种 Common species | 转换后多度百分率(%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12月 Dec. | 1月 Jan. | 2月 Feb. | 3月 Mar. | 4月 Apr. | 5月 May | ||
| I | 飘细长蚁 Tetraponera allaborans | <10 | <10 | <10 | 14.74 | <10 | 21.71 |
| 粗纹举腹蚁 Crematogaster macaoensis | 68.57 | 73.40 | 64.49 | 56.84 | 56.72 | 45.39 | |
| 黑头酸臭蚁 Tapinoma melanocephalum | <10 | - | - | - | 10.45 | - | |
| 黑可可臭蚁 Dolichoderus thoracicus | <10 | <10 | <10 | 13.68 | <10 | <10 | |
| II | 飘细长蚁 Tetraponera allaborans | <10 | <10 | 21.51 | 21.95 | 14.53 | 29.91 |
| 粗纹举腹蚁 Crematogaster macaoensis | 26.25 | 25.32 | 29.03 | 18.29 | 33.33 | 11.97 | |
| 立毛举腹蚁 C. ferrarii | 42.50 | 46.84 | 24.73 | 25.61 | 36.75 | 41.88 | |
| 罗氏棒切叶蚁 Rhoptromyrmex wroughtonii | 12.50 | - | <10 | - | - | - | |
| 黑可可臭蚁 Dolichoderus thoracicus | <10 | 16.46 | 12.90 | 15.85 | <10 | <10 | |
| 光胫多刺蚁 Polyrhachis tibialis | - | - | <10 | 10.98 | - | - | |
| III | 飘细长蚁 Tetraponera allaborans | <10 | 10.53 | 16.39 | 28.57 | 16.67 | 34.38 |
| 粗纹举腹蚁 Crematogaster macaoensis | 36.84 | 31.58 | 22.95 | 21.43 | 26.32 | 13.54 | |
| 立毛举腹蚁 C. ferrarii | 28.95 | 31.58 | 44.26 | 21.43 | 27.19 | 30.21 | |
| 罗氏棒切叶蚁 Rhoptromyrmex wroughtonii | 20.18 | 11.84 | - | - | <10 | - | |
| 皮氏大头蚁 Pheidole pieli | - | - | - | - | 14.91 | - | |
| IV | 飘细长蚁 Tetraponera allaborans | 11.54 | 28.21 | 27.59 | 25.00 | 10.71 | 23.46 |
| 粗纹举腹蚁 Crematogaster macaoensis | <10 | - | - | 11.36 | 14.29 | <10 | |
| 立毛举腹蚁 C. ferrarii | 42.31 | 35.90 | 41.38 | 45.45 | 38.10 | 55.56 | |
| 皮氏大头蚁 Pheidole pieli | - | - | - | - | 10.71 | - | |
| 黑头酸臭蚁 Tapinoma melanocephalum | 19.23 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 黑可可臭蚁 Dolichoderus thoracicus | <10 | 35.90 | 20.69 | 13.64 | <10 | - | |
| 光胫多刺蚁 Polyrhachis tibialis | 11.54 | - | 10.34 | <10 | - | - | |
Table 1 Common ant species in different months in lac plantation
| 样地 Sites | 常见种 Common species | 转换后多度百分率(%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12月 Dec. | 1月 Jan. | 2月 Feb. | 3月 Mar. | 4月 Apr. | 5月 May | ||
| I | 飘细长蚁 Tetraponera allaborans | <10 | <10 | <10 | 14.74 | <10 | 21.71 |
| 粗纹举腹蚁 Crematogaster macaoensis | 68.57 | 73.40 | 64.49 | 56.84 | 56.72 | 45.39 | |
| 黑头酸臭蚁 Tapinoma melanocephalum | <10 | - | - | - | 10.45 | - | |
| 黑可可臭蚁 Dolichoderus thoracicus | <10 | <10 | <10 | 13.68 | <10 | <10 | |
| II | 飘细长蚁 Tetraponera allaborans | <10 | <10 | 21.51 | 21.95 | 14.53 | 29.91 |
| 粗纹举腹蚁 Crematogaster macaoensis | 26.25 | 25.32 | 29.03 | 18.29 | 33.33 | 11.97 | |
| 立毛举腹蚁 C. ferrarii | 42.50 | 46.84 | 24.73 | 25.61 | 36.75 | 41.88 | |
| 罗氏棒切叶蚁 Rhoptromyrmex wroughtonii | 12.50 | - | <10 | - | - | - | |
| 黑可可臭蚁 Dolichoderus thoracicus | <10 | 16.46 | 12.90 | 15.85 | <10 | <10 | |
| 光胫多刺蚁 Polyrhachis tibialis | - | - | <10 | 10.98 | - | - | |
| III | 飘细长蚁 Tetraponera allaborans | <10 | 10.53 | 16.39 | 28.57 | 16.67 | 34.38 |
| 粗纹举腹蚁 Crematogaster macaoensis | 36.84 | 31.58 | 22.95 | 21.43 | 26.32 | 13.54 | |
| 立毛举腹蚁 C. ferrarii | 28.95 | 31.58 | 44.26 | 21.43 | 27.19 | 30.21 | |
| 罗氏棒切叶蚁 Rhoptromyrmex wroughtonii | 20.18 | 11.84 | - | - | <10 | - | |
| 皮氏大头蚁 Pheidole pieli | - | - | - | - | 14.91 | - | |
| IV | 飘细长蚁 Tetraponera allaborans | 11.54 | 28.21 | 27.59 | 25.00 | 10.71 | 23.46 |
| 粗纹举腹蚁 Crematogaster macaoensis | <10 | - | - | 11.36 | 14.29 | <10 | |
| 立毛举腹蚁 C. ferrarii | 42.31 | 35.90 | 41.38 | 45.45 | 38.10 | 55.56 | |
| 皮氏大头蚁 Pheidole pieli | - | - | - | - | 10.71 | - | |
| 黑头酸臭蚁 Tapinoma melanocephalum | 19.23 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 黑可可臭蚁 Dolichoderus thoracicus | <10 | 35.90 | 20.69 | 13.64 | <10 | - | |
| 光胫多刺蚁 Polyrhachis tibialis | 11.54 | - | 10.34 | <10 | - | - | |
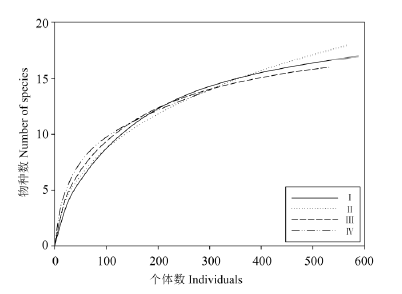
Fig. 1 Species accumulation curve of ants based on number of individuals after scales. I, II, III, IV represent plots that lac insect infestation rates were 60%, 30%, 10% and 0, respectively.
| 因子 Factor | F | P | 偏Eta平方 Partial Eta squared | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 多度 Abundance | 样地 Sites | 26.19 | 0.001 | 0.540 |
| 月份 Months | 23.43 | 0.001 | 0.259 | |
| 物种丰富度 Species richness (S) | 样地 Sites | 5.53 | 0.002 | 0.198 |
| 月份 Months | 11.60 | 0.001 | 0.148 | |
| ACE估计值 | 样地 Sites | 4.62 | 0.005 | 0.171 |
| 月份 Months | 10.81 | 0.002 | 0.139 |
Table 2 Results of ANCOVA models testing of ant community diversity index among different sites and months
| 因子 Factor | F | P | 偏Eta平方 Partial Eta squared | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 多度 Abundance | 样地 Sites | 26.19 | 0.001 | 0.540 |
| 月份 Months | 23.43 | 0.001 | 0.259 | |
| 物种丰富度 Species richness (S) | 样地 Sites | 5.53 | 0.002 | 0.198 |
| 月份 Months | 11.60 | 0.001 | 0.148 | |
| ACE估计值 | 样地 Sites | 4.62 | 0.005 | 0.171 |
| 月份 Months | 10.81 | 0.002 | 0.139 |
| 样地 Sites | 多度 Abundance | 物种丰富度 Species richness (S) | ACE |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | 6.13 ± 0.19a | 1.65 ± 0.16a | 1.68 ± 0.09a |
| II | 5.56 ± 0.20b | 1.63 ± 0.11a | 1.66 ± 0.07a |
| III | 5.38 ± 0.18b | 1.70 ± 0.14a | 1.75 ± 0.06a |
| IV | 3.98 ± 0.24c | 1.38 ± 0.09b | 1.41 ± 0.07b |
Table 3 Comparison of diversity of ants in different sites (Mean ± SE)
| 样地 Sites | 多度 Abundance | 物种丰富度 Species richness (S) | ACE |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | 6.13 ± 0.19a | 1.65 ± 0.16a | 1.68 ± 0.09a |
| II | 5.56 ± 0.20b | 1.63 ± 0.11a | 1.66 ± 0.07a |
| III | 5.38 ± 0.18b | 1.70 ± 0.14a | 1.75 ± 0.06a |
| IV | 3.98 ± 0.24c | 1.38 ± 0.09b | 1.41 ± 0.07b |
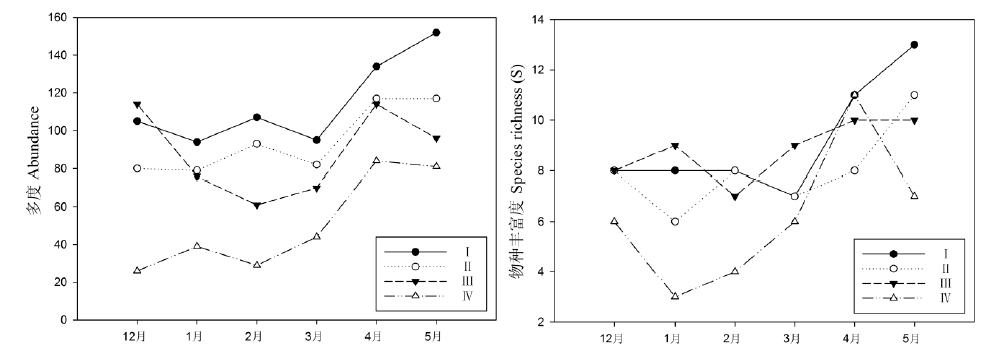
Fig. 2 Abundance and species richness of ants in different months in lac plantations. I, II, III, IV represent plots that lac insect infestation rates were 60%, 30%, 10% and 0, respectively.
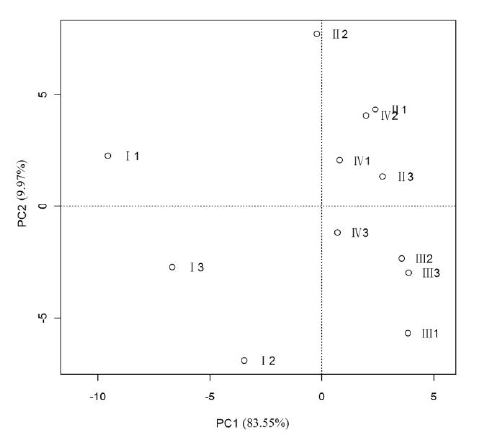
Fig. 3 Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) for ant community. I, II, III, IV represent plots that lac insect infestation rates were 60%, 30%, 10% and 0, respectively. The number represent different groups.
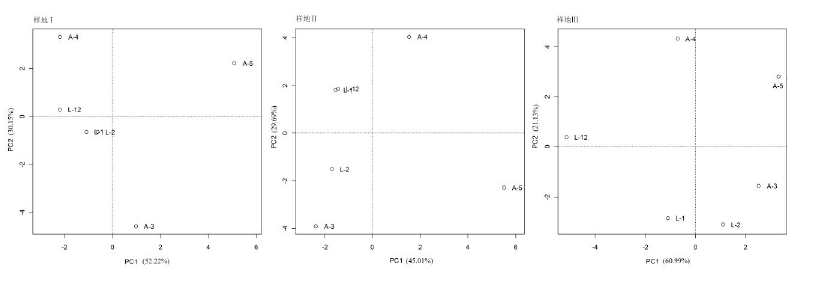
Fig. 4 Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) for ant community in different months. “L” represent the larval stage, “A” represent the adult stage, the number represent different months.
| 1 | Andersen AN (1991) Responses of ground-foraging ant communities to three experimental fire regimes in a savanna forest of tropical Australia. Biotropica, 23, 575-585. |
| 2 | Andersen AN (1995) A classification of Australian ant communities, based on functional groups which parallel plant life-forms in relation to stress and disturbance. Journal of Biogeography, 22, 15-29. |
| 3 | Bestelmeyer BT,Agosti D,Alonso LE,Brandão CRF,Brown WL,Delabie JHC,Silvestre R(2000) Field techniques for the study of ground-dwelling ants: an overview, description and evaluation. In: Ants: Standard Methods for Measuring and Monitoring Biodiversity (eds Agosti D, Majer JD, Alonso LE, Schultz TR), pp. 1-8 |
| . Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington DC. | |
| 4 | Bestelmeyer BT, Wiens JA (1996) The effects of land use on the structure of ground-foraging ant communities in the Argentine Chaco. Ecological Applications, 6, 1225-1240. |
| 5 | Blüthgen N, Stork NE, Fiedler K (2004) Bottom-up control and co-occurrence in complex communities: honeydew and nectar determine a rainforest ant mosaic. Oikos, 106, 344-358. |
| 6 | Buckley RC (1987a) Ant-plant-Homopteran interactions. Advances in Ecological Research, 16, 53-85. |
| 7 | Buckley RC (1987b) Interactions involving plants, Homoptera, and ants. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 18, 111-135. |
| 8 | Buckley RC, Gullan P (1991) More aggressive ant species (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) provide better protection for soft scales and mealybugs (Homoptera: Coccidae, Pseudococcidae). Biotropica, 23, 282-286. |
| 9 | Chen QS (陈青山), Zhong QH (钟倩红), Lin PX (林佩贤), Wang W (王维), Yu SY (俞守义) (2009) Experiment object randomized grouping used Excel. Chinese Journal of Health Statistics(中国卫生统计), 26, 298-299. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 10 | Chen XM(陈晓鸣),Chen YQ(陈又清),Zhang H(张弘),Shi L(石雷) (2008) Lac Insect Cultivation and Lac Processing (紫胶虫培育与紫胶加工). China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 11 | Chen YL (陈彦林), Chen YQ (陈又清), Li Q (李巧), Zhang Y (章彦), Zhou XY (周兴银) (2008) Preliminary study on the spider community in Kerria spp. ecosystem. Journal of Fujian College of Foresry(福建林学院学报), 28, 179-183. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 12 | Chen YL (陈彦林), Chen YQ (陈又清), Li Q (李巧), Shu ZJ (舒哲俊), Yang Q (杨栖) (2009) Bug diversity in habitats with Kerria yunnannensis cultivation. Chinese Journal of Ecology(生态学杂志), 28, 1351-1355. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 13 | Chen YQ (陈又清), Yao WJ (姚万军) (2007) Lac resources and their utilization in the world. World Forestry Research(世界林业研究), 20, 61-65. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 14 | Chen YQ (陈又清), Li Q (李巧), Wang SM (王思铭) (2009) Diversity of ground-dwelling beetles in lac-plantation- farmland ecosystem: a case study in Luchun, Yunnan, South-western China. Acta Entomologica Sinica(昆虫学报), 52, 1319-1327. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 15 | Chen YQ, Li Q, Chen YL, Wang SM, Yang YC (2010) Lac-production, arthropod biodiversity and abundance, and pesticide use in Yunnan Province, China. Tropical Ecology, 51, 255-263. |
| 16 | Chen YQ, Wang SM, Lu ZX (2011a) Foraging strategies may mediate the coexistence of ant species attending Kerria yunnanensis on their host plant. Bulletin of Insectology, 64, 181-188. |
| 17 | Chen YQ, Li Q, Chen YL, Lu ZX, Zhou XY (2011b) Ant diversity and bio-indicators in land management of lac insect agroecosystem in Southwestern China. Biodiversity and Conservation, 20, 3017-3038. |
| 18 | Colwell RK (2004) Estimates: statistical estimation of species richness and shared species from samples. |
| 19 | Del-Claro K, Oliveira PS (1996) Honeydew flicking by treehoppers provides cues to potential tending ants. Animal Behaviour, 51, 1071-1075. |
| 20 | Del-Claro K, Oliveira PS (1999) Ant-Homoptera interactions in a neotropical savanna: the honeydew-producing treehopper, Guayaquila xiphias (Membracidae), and its associated ant fauna on Didymopanax vinosum (Araliaceae). Biotropica, 31, 135-144. |
| 21 | Hill JG, Summerville KS, Brown RL (2008) Habitat associations of ant species (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in a heterogeneous Mississippi landscape. Environmental Entomology, 37, 453-463. |
| 22 | Hill MG, Blackmore PJM (1980) Interactions between ants and the coccid Icerya seychellarum on Aldabra Atoll. Oecologia, 45, 360-365. |
| 23 | Hoffmann BD, Kay A (2009) Pisonia grandis monocultures limit the spread of an invasive ant: a case of carbohydrate quality? Biological Invasions, 11, 1403-1410. |
| 24 | Hölldobler B,Wilson EO(1990) The Ants. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA |
| 25 | Holway DA, Lach L, Suarez AV, Tsutsui ND, Case TJ (2002) The causes and consequences of ant invasions. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 33, 181-233. |
| 26 | Itioka T, Inoue T (1996) The consequences of ant-attendance to the biological control of the red wax scale insect Ceroplastes rubens by Anicetus beneficus. Journal of Applied Ecology, 33, 609-618. |
| 27 | Jackson D (1984a) Competition in the tropics: ants on trees. Antenna, 8, 19-22. |
| 28 | Jackson D (1984b) Ant distribution patterns in a Cameroonian cocoa plantation: investigation of the ant mosaic hypothesis. Oecologia, 62, 318-324. |
| 29 | Kennedy TA (1998) Patterns of an invasion by Argentine ants (Linepithema humile) in a riparian corridor and its effects on ant diversity. The American Midland Naturalist, 140, 343-350. |
| 30 | Klimes P, Idigel C, Rimandai M, Fayle TM, Janda M, Weiblen GD, Novotny V (2012) Why are there more arboreal ant species in primary than in secondary tropical forests?Journal of Animal Ecology, 81, 1103-1112. |
| 31 | Li Q (李巧), Chen YQ (陈又清), Guo X (郭萧), Duan Y (段艳), Chen YL (陈彦林), Xu ZH (徐正会) (2007) Diversity of ants on the ground in different habitats in Yuanmou arid-hot valley, Yunnan. Journal of Fujian College of Forestry(福建林学院学报), 27, 272-277. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 32 | Li Q (李巧), Chen YQ (陈又清), Chen YL (陈彦林) (2009a) Diversity of Heteropteran communities in lac plantation-farmland ecosystem. Journal of Yunnan University(云南大学学报), 31, 208-216. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 33 | Li Q (李巧), Chen YQ (陈又清), Chen YL (陈彦林), Yan WW (严伟伟), Wang SM (王思铭) (2009b) Diversity of beetle assemblages in lac-plantation-farmland ecosystem. Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 29, 3872-3881. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 34 | Li Q (李巧), Chen YQ (陈又清), Chen YL (陈彦林), Chen Z (陈祯) (2009c) Diversity of grasshopper community in lac plantation-farmland ecosystem. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology(应用生态学报), 20, 729-735. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 35 | Li Q (李巧), Chen YQ (陈又清), Wang SM (王思铭), Zheng Y (郑勇), Zhu YH (朱云辉), Wang SY (王绍云) (2009d) Diversity of ants in subtropical evergreen broadleaved forest in Pu’er City, Yunnan. Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 17, 233-239. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 36 | Li Q (李巧), Chen YQ (陈又清), Xu ZH (徐正会) (2009e) Research methods on ant community. Chinese Journal of Ecology(生态学杂志), 28, 1862-1870. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 37 | Li Q (李巧), Tu J (涂璟), Zhang XS (张学仕), Zhang YY (张榆英), Liu CJ (刘春菊), Lu ZX (卢志兴), Xiong ZP (熊忠平) (2011) Diversity of ground-dwelling ants in Pinus yunnanensis forest in Songhuaba Water Protection Area, Kunming. Journal of Yunnan University(云南大学学报), 33, 210-217. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 38 | Li ZH(李志辉),Luo P(罗平) (2010) |
| 39 | Lu ZX (卢志兴), Chen YQ (陈又清), Li Q (李巧), Wang SM (王思铭), Liu CJ (刘春菊), Zhang W (张威) (2012a) Effects of lac insect honeydew on the diversity of ground-dwelling ants in lac plantation. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology(应用生态学报), 23, 1117-1122. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 40 | Lu ZX (卢志兴), Chen YQ (陈又清), Li Q (李巧), Wang SM (王思铭), Liu CJ (刘春菊), Zhang W (张威) (2012b) Effect of population of Kerria yunnanensis on diversity of ground-dwelling ant. Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 32, 6195-6202. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 41 | Moya-Raygoza G, Nault LR (2000) Obligatory mutualism between Dalbulus quinquenotatus (Homoptera: Ciccadellidae) and attendant ants. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 93, 929-940. |
| 42 | Oksanen J,Kindt R,Legendre P,O’Hara B,Simpson GL,Solymos P,Stevens MHH,Wagner H (2012) vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package version 2.0-5. |
| 43 | Philpott SM, Armbrecht I (2006) Biodiversity in tropical agroforests and the ecological role of ants and ant diversity in predatory function. Ecological Entomology, 31, 369-377. |
| 44 | Pontin AJ (1958) Preliminary note on the eating of aphids by ants of the genus Lasius. Entomologist’s Monthly Magazine, 94, 9-11. |
| 45 | R Development Core Team (2008) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. . |
| 46 | Ríos-Casanova L, Valiente-Banuet A, Rico-Gray V (2006) Ant diversity and its relationship with vegetation and soil factors in an alluvial fan of the Tehuacán Valley, Mexico. Acta Oecologica, 29, 316-323. |
| 47 | Rosario SA, Farrow RA, Gullan PJ (1993) Effects of ant attendance on reproduction and survival of Eurmeloides punctata (Signoret) and Eurymela distincta Signoret (Hemiptera: Eurymelidae) on eucalypts. Australian Journal of Entomology, 32, 177-186. |
| 48 | Roth DS, Perfecto I, Rathcke B (1994) The effects of management systems on ground-foraging ant diversity in Costa Rica. Ecological Applications, 4, 423-436. |
| 49 | Saint-Pierre C, Bingrong O (1994) Lac host-trees and the balance of agroecosystems in South Yunnan, China. Economic Botany, 48, 21-28. |
| 50 | Samson DA, Rickart EA, Gonzales PC (2006) Ant diversity and abundance along an elevational gradient in the Philippines. Biotropica, 29, 349-363. |
| 51 | Schonberg LA, Longino JT, Nadkarni NM, Yanoviak SP, Gering JC (2004) Arboreal ant species richness in primary forest, secondary forest, and pasture habitats of a tropical montane landscape. Biotropica, 36, 402-409. |
| 52 | Schulz A, Wagner T (2002) Influence of forest type and tree species on canopy ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Budongo Forest, Uganda. Oecologia, 133, 224-232. |
| 53 | SPSS, P (2010) Statistics 18. SPSS Inc. , Chicago. |
| 54 | Stadler B, Dixon AFG (2005) Ecology and evolution of aphid-ant interactions. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 36, 345-372. |
| 55 | Styrsky JD, Eubanks MD (2007) Ecological consequences of interactions between ants and honeydew-producing insects. Proceedings of the Royal Society B:Biological Sciences, 274, 151-164. |
| 56 | Suarez AV, Bolger DT, Case TJ (1998) Effects of fragmentation and invasion on native ant communities in coastal southern California. Ecology, 79, 2041-2056. |
| 57 | Vasconcelos HL (1999) Effects of forest disturbance on the structure of ground-foraging ant communities in central Amazonia. Biodiversity and Conservation, 8, 407-418. |
| 58 | Wang SM (王思铭), Chen YQ (陈又清), Li Q (李巧), Lu ZX (卢志兴), Liu CJ (刘春菊), Guo ZX (郭祖学) (2010) The influence of ant-visiting Kerria yunnanensis on populations of Holcocera pulverea in lac plantation. Chinese Bulletin of Entomology(昆虫知识), 47, 730-735. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 59 | Wu BQ (吴碧球), Lu YY (陆永跃), Liang GW (梁广文), Zeng L (曾玲) (2010) Influence of the red imported fire ant, Solenopsis invicta Buren (Hymenoptera: Formiciddae) on the diversity of ant communities in a newly infested longan orchard and grass areas nearby. Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 30, 2075-2083. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 60 | Wu BQ (吴碧球), Lu YY (陆永跃), Zeng L (曾玲), Liang GW (梁广文) (2008) Influences of Solenopsis invicta Buren invasion on the native ant communities in different habitats in Guangdong. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology(应用生态学报), 19, 151-156. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 61 | Xu ZH (徐正会), Zeng G (曾光), Liu TY (柳太勇), He YF (何云峰) (1999) A study on communities of Formicidae ants in different subtypes of vegetation in Xishuangbanna District of China. Zoological Research(动物学研究), 20, 39-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 62 | Yang XD (杨效东), She YP (佘宇平), Zhang ZY (张智英), Cao M (曹敏), Deng XB (邓小宝) (2001) Studies on structure and diversity of ant groups in the fragmentary tropical rainforests of “Holy Hills” of Dai nationality in Xishuangbanna, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 21, 1321-1328. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 63 | Yang ZW (杨忠文), Xu ZH (徐正会), Guo X (郭萧), Shi SL (史胜利), Chen LG (陈龙官) (2009) Ant species diversity in the Mt. Cangshan and adjacent area in Dali, Yunnan Province. Journal of Southwest Forestry University(西南林学院学报), 29, 47-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 64 | Yanoviak SP, Kaspari M (2000) Community structure and the habitat templet: ants in the tropical forest canopy and litter. Oikos, 89, 259-266. |
| 65 | Zhang CL (张成林), Xu ZH (徐正会), Yang BL (杨比伦), Chu JJ (褚姣娇), Yu NN (于娜娜), Liu X (刘霞) (2011) Species composition and diversity of ant communities in Mount Sejila in Southeastern Tibet. Journal of Northeast Forestry University(东北林业大学学报), 39, 79-82. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 66 | Zhang S, Zhang YX, Ma KM (2012) The ecological effects of the ant-hemipteran mutualism: a meta-analysis. Basic and Applied Ecology, 13, 116-124. |
| 67 | Zhang ZY (张智英), Li YH (李玉辉), Chai DM (柴冬梅), Zhang L (张亮) (2005) Ant biodiversity in different habitats in Shilin Park, Yunnan Province. Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 13, 357-362. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 68 | Zhu CQ (朱朝芹), Chi K (池康), Ye XQ (叶雪琴), Zhou H (周虹), Liu CM (刘缠民) (2010) Community structure and species diversity of ants in Xuzhou, Jiangsu Province. Journal of Jiangsu Forestry Science and Technology(江苏林业科技), 37, 7-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | Jing Gan Xiangxu Liu Xueming Lu Xing Yue. China's Large Cities in Global Biodiversity Hotspots: Conservation Policies and Optimization Directions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | Zixuan Zeng Rui Yang Yue Huang Luyao Chen. Characteristics of bird diversity and environmental relationships in Tsinghua University campus [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | Mingyue Zang, Li Liu, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feilong Hu, Xiaoqiang Lu, Jiaqi Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. China’s urban biodiversity conservation under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | Xiaoyu Zhu, Chenhao Wang, Zhongjun Wang, Yujun Zhang. Research progress and prospect of urban green space biodiversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | Lin Yuan, Siqi Wang, Jingxuan Hou. “Leaving space for wildness” in metropolitan region: Trends and prospects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | Min Hu, Binbin Li, Coraline Goron. Green is not enough: A management framework for urban biodiversity-friendly parks [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | Xin Wang, Femgyu Bao. Analysis of the ecological restoration effect of South Dianchi National Wetland Park based on the enhancement of bird diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | Yue Ming, Peiyao Hao, Lingqian Tan, Xi Zheng. A study on urban biodiversity conservation and enhancement in china based on the concept of green and high-quality development of cities [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | Gan Xie, Jing Xuan, Qidi Fu, Ze Wei, Kai Xue, Hairui Luo, Jixi Gao, Min Li. Establishing an intelligent identification model for unmanned aerial vehicle surveys of grassland plant diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | Xiaolin Chu, Quanguo Zhang. A review of experimental evidence for the evolutionary speed hypothesis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | Zhiyu Liu, Xin Ji, Guohui Sui, Ding Yang, Xuankun Li. Invertebrate diversity in buffalo grass and weedy lawns at Beijing Capital International Airport [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24456-. |
| [12] | Mingyi Zhang, Xiaomei Wang, Yanxin Zheng, Nan Wu, Donghao Li, Enyuan Fan, Na Li, Xiujuan Shan, Tao Yu, Chunnuan Zhao, Bo Li, Shuai Xu, Yuping Wu, Liqun Ren. Resource status and habitat function of typical oyster reef areas in the Yellow River Estuary [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [13] | Xiaoqiang Lu, Shanshan Dong, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feng Qiu, Mingyue Zang, Yaqiong Wan, Luanxin Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. Current status, challenges, and prospects of frontier technologies in biodiversity conservation applications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [14] | Qiaoyi Nong, Jun Cao, Wenda Cheng, Yanqiong Peng. Comparative study of monitoring methods for Apoidea resources and diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [15] | Tong Miao, Wang Huan, Zhang Wenshuang, Wang Chao, Song Jianxiao. Distribution characteristics of antibiotic resistance genes in soil bacterial communities exposed to heavy metal pollution [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()