



Biodiv Sci ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5): 24524. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024524 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024524
Special Issue: 昆蒙框架目标12下的中国城市生物多样性研究专辑
• Conservation and Governance • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yue Ming( ), Peiyao Hao*(
), Peiyao Hao*( )(
)( ), Lingqian Tan(
), Lingqian Tan( ), Xi Zheng(
), Xi Zheng( )
)
Received:2024-12-01
Accepted:2025-03-27
Online:2025-05-20
Published:2025-06-23
Contact:
Peiyao Hao
Supported by:Yue Ming, Peiyao Hao, Lingqian Tan, Xi Zheng. Urban biodiversity conservation and enhancement in China based on the concept of green and high-quality development of cities[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24524.
| 行动目标 Target | 对城市生物多样性做出的要求 Requirements for urban biodiversity | 城市生物多样性层次 Urban biodiversity hierarchy | 实施路径 Urban biodiversity implementation pathway |
|---|---|---|---|
| 目标1 Target 1 | 空间规划和管理、遏制生物多样性丧失 Spatial planning and management, combating biodiversity loss | 生态系统多样性 Ecosystem diversity | 保护规划、监测评估 Conservation planning, monitoring and evaluation |
| 目标2 Target 2 | 生态系统恢复 Ecosystem restoration | 生态系统多样性 Ecosystem diversity | 调查评价、保护规划 Survey and evaluation, conservation planning |
| 目标4 Target 4 | 维持和恢复物种丰度与遗传多样性 Maintaining and restoring species abundance and genetic diversity | 物种多样性 Species diversity | 调查评价、监测评估 Survey and evaluation, monitoring and evaluation |
| 目标6 Target 6 | 外来入侵物种引入减半 Halving the introduction of invasive alien species | 物种多样性 Species diversity | 防控管理 Prevention and control management |
| 目标9 Target 9 | 野生物种管理和可持续利用 Wild species management and sustainable use | 物种多样性 Species diversity | 防控管理、社会参与 Prevention and control management, public participation |
| 目标10 Target 10 | 农、林业等可持续管理 Sustainable management of agriculture, forestry, etc. | 生态系统多样性 Ecosystem diversity | 防控管理、社会参与 Prevention and control management, public participation |
| 目标11 Target 11 | 恢复、维持和增进自然对人类的贡献 Restore, maintain and enhance nature’s contribution to humanity | 生态系统多样性 Ecosystem diversity | 保护规划、社会参与 Conservation planning, public participation |
| 目标12 Target 12 | 将生物多样性的保护和可持续利用纳入主流; 确保城市规划中的多层次生物多样性; 加强生物多样性与人类健康福祉联系 Mainstreaming conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity; ensuring multi-level biodiversity in urban planning; strengthening links between biodiversity and human health and well-being | 生态系统多样性 Ecosystem diversity 景观多样性 Landscape diversity 物种多样性 Species diversity | 保护规划、防控管理、社会参与 Conservation planning, prevention and control management, public participation |
| 目标13 Target 13 | 公平利用遗传资源及惠益 Equitable utilization of genetic resources and benefits | 遗传多样性 Genetic diversity | 防控管理 Prevention and control management |
| 目标14 Target 14 | 纳入政策、法规、规划和发展进程 Integration into policies, regulations, planning and development processes | 保护规划 Conservation planning |
Table 1 Urban biodiversity conservation in the targets of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework
| 行动目标 Target | 对城市生物多样性做出的要求 Requirements for urban biodiversity | 城市生物多样性层次 Urban biodiversity hierarchy | 实施路径 Urban biodiversity implementation pathway |
|---|---|---|---|
| 目标1 Target 1 | 空间规划和管理、遏制生物多样性丧失 Spatial planning and management, combating biodiversity loss | 生态系统多样性 Ecosystem diversity | 保护规划、监测评估 Conservation planning, monitoring and evaluation |
| 目标2 Target 2 | 生态系统恢复 Ecosystem restoration | 生态系统多样性 Ecosystem diversity | 调查评价、保护规划 Survey and evaluation, conservation planning |
| 目标4 Target 4 | 维持和恢复物种丰度与遗传多样性 Maintaining and restoring species abundance and genetic diversity | 物种多样性 Species diversity | 调查评价、监测评估 Survey and evaluation, monitoring and evaluation |
| 目标6 Target 6 | 外来入侵物种引入减半 Halving the introduction of invasive alien species | 物种多样性 Species diversity | 防控管理 Prevention and control management |
| 目标9 Target 9 | 野生物种管理和可持续利用 Wild species management and sustainable use | 物种多样性 Species diversity | 防控管理、社会参与 Prevention and control management, public participation |
| 目标10 Target 10 | 农、林业等可持续管理 Sustainable management of agriculture, forestry, etc. | 生态系统多样性 Ecosystem diversity | 防控管理、社会参与 Prevention and control management, public participation |
| 目标11 Target 11 | 恢复、维持和增进自然对人类的贡献 Restore, maintain and enhance nature’s contribution to humanity | 生态系统多样性 Ecosystem diversity | 保护规划、社会参与 Conservation planning, public participation |
| 目标12 Target 12 | 将生物多样性的保护和可持续利用纳入主流; 确保城市规划中的多层次生物多样性; 加强生物多样性与人类健康福祉联系 Mainstreaming conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity; ensuring multi-level biodiversity in urban planning; strengthening links between biodiversity and human health and well-being | 生态系统多样性 Ecosystem diversity 景观多样性 Landscape diversity 物种多样性 Species diversity | 保护规划、防控管理、社会参与 Conservation planning, prevention and control management, public participation |
| 目标13 Target 13 | 公平利用遗传资源及惠益 Equitable utilization of genetic resources and benefits | 遗传多样性 Genetic diversity | 防控管理 Prevention and control management |
| 目标14 Target 14 | 纳入政策、法规、规划和发展进程 Integration into policies, regulations, planning and development processes | 保护规划 Conservation planning |
| 城市发展模式 Urban development model | 政策文本数量(份) Number of policy texts | 直接提及“生物多样性”文本 Direct reference to “biodiversity” text | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 文本数量(份) Number of texts | 文本占比 Percentage of texts (%) | ||
| 园林城市 Landscape Garden City | 160 | 56 | 35.00 |
| 生态园林城市 Ecological Garden City | 123 | 65 | 52.85 |
| 森林城市 Forest City | 144 | 63 | 43.75 |
| 公园城市 Park City | 23 | 11 | 47.83 |
| 花园城市 Garden City | 3 | 3 | 100 |
Table 2 Statistics on policy texts on green and high-quality development models in different cities
| 城市发展模式 Urban development model | 政策文本数量(份) Number of policy texts | 直接提及“生物多样性”文本 Direct reference to “biodiversity” text | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 文本数量(份) Number of texts | 文本占比 Percentage of texts (%) | ||
| 园林城市 Landscape Garden City | 160 | 56 | 35.00 |
| 生态园林城市 Ecological Garden City | 123 | 65 | 52.85 |
| 森林城市 Forest City | 144 | 63 | 43.75 |
| 公园城市 Park City | 23 | 11 | 47.83 |
| 花园城市 Garden City | 3 | 3 | 100 |
| 城市发展模式 Urban development model | 生物多样性指标数量 Number of biodiversity indicators | 生物多样性指标总数 Total number of biodiversity indicators | 生物多样性底线指标数量 Number of biodiversity bottom-line indicators | 生物多样性底线指标占生物多样性指标数量比例 Biodiversity bottom-line indicators as a proportion of the number of biodiversity indicators (%) | 评价标准 Evaluation criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 园林城市 Landscape Garden City | 10 | 18 | 4 | 25 | 《国家园林城市评选标准》建城〔2022〕2号 Selection Criteria for National Garden Cities, Jiancheng [2022] No. 2 |
| 生态园林城市 Ecological Garden City | 10 | 18 | 4 | 25 | 《国家园林城市评选标准》建城〔2022〕2号 Selection Criteria for National Garden Cities, Jiancheng [2022] No. 2 |
| 森林城市 Forest City | 9 | 23 | 8 | 88.89 | 《国家森林城市评价指标》Evaluation Indicators for National Forest Cities (GB/T 37342-2024) |
| 公园城市 Park City | 18 | 76 | 15 | 83.33 | 《公园城市评价标准》Evaluation Standards for Park Cities (T/CHSLA50008-2021) |
| 花园城市 Garden City | 9 | 29 | 2 | 22.22 | 《北京花园城市专项规划(2023年-2035年)》Beijing Garden City Special Plan (2023-2035) |
Table 3 Statistics on biodiversity conservation indicators in different urban green and high-quality development models
| 城市发展模式 Urban development model | 生物多样性指标数量 Number of biodiversity indicators | 生物多样性指标总数 Total number of biodiversity indicators | 生物多样性底线指标数量 Number of biodiversity bottom-line indicators | 生物多样性底线指标占生物多样性指标数量比例 Biodiversity bottom-line indicators as a proportion of the number of biodiversity indicators (%) | 评价标准 Evaluation criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 园林城市 Landscape Garden City | 10 | 18 | 4 | 25 | 《国家园林城市评选标准》建城〔2022〕2号 Selection Criteria for National Garden Cities, Jiancheng [2022] No. 2 |
| 生态园林城市 Ecological Garden City | 10 | 18 | 4 | 25 | 《国家园林城市评选标准》建城〔2022〕2号 Selection Criteria for National Garden Cities, Jiancheng [2022] No. 2 |
| 森林城市 Forest City | 9 | 23 | 8 | 88.89 | 《国家森林城市评价指标》Evaluation Indicators for National Forest Cities (GB/T 37342-2024) |
| 公园城市 Park City | 18 | 76 | 15 | 83.33 | 《公园城市评价标准》Evaluation Standards for Park Cities (T/CHSLA50008-2021) |
| 花园城市 Garden City | 9 | 29 | 2 | 22.22 | 《北京花园城市专项规划(2023年-2035年)》Beijing Garden City Special Plan (2023-2035) |
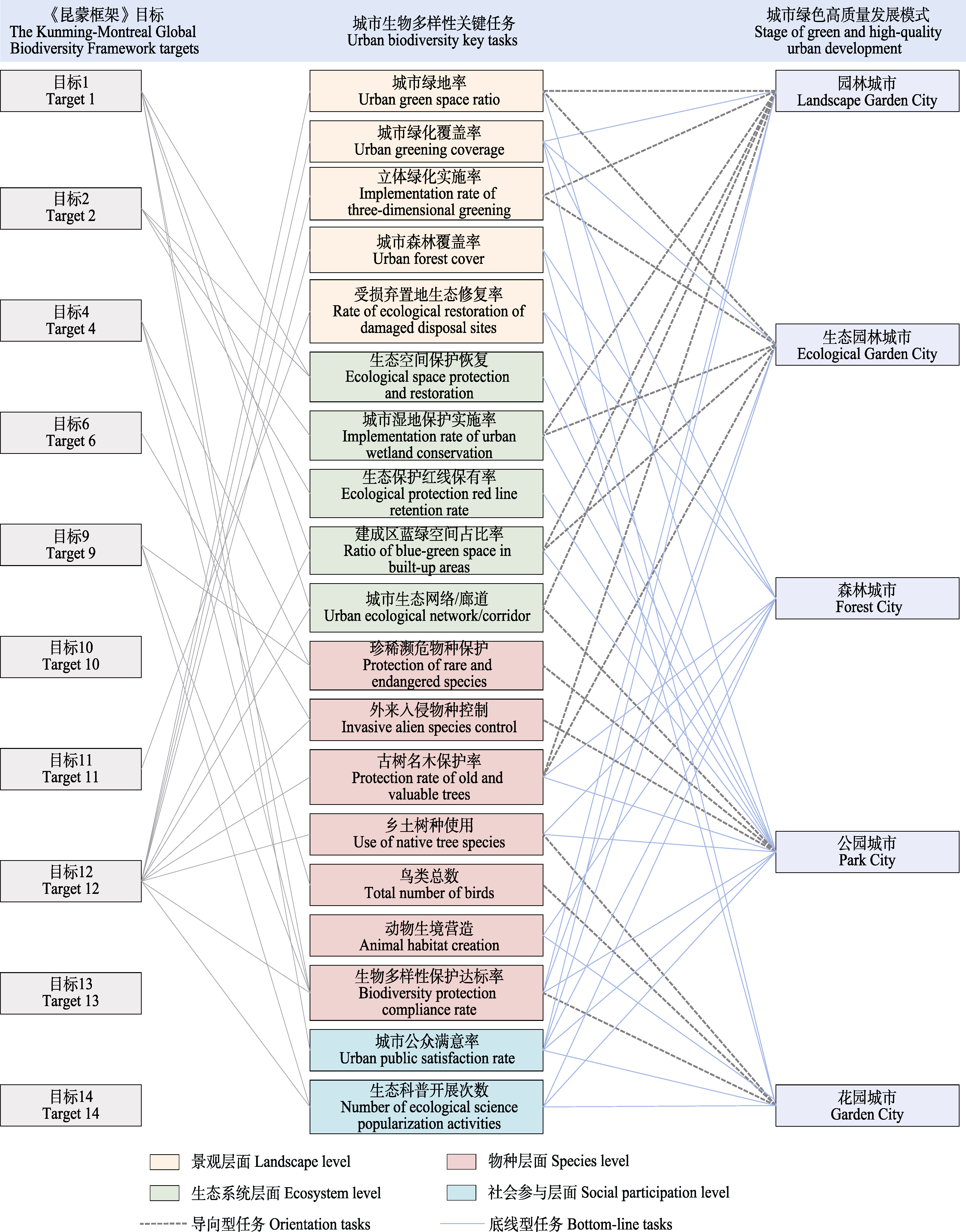
Fig. 6 Correspondence between green and high-quality urban development and the key tasks of urban biodiversity conservation and enhancement. The gray line in the figure corresponds to the targets and key tasks, the gray dashed line corresponds to the orientation tasks, and the blue line corresponds to the bottom-line tasks.
| [1] | Aguilera MA, González MG (2023) Urban infrastructure expansion and artificial light pollution degrade coastal ecosystems, increasing natural-to-urban structural connectivity. Landscape and Urban Planning, 229, 104609. |
| [2] | Alberti M, Marzluff J, Shulenberger E, Bradlry G, Ryan C, Zumbrunnen C (2003) Integrating humans into ecosystems: Opportunities and challenges for urban ecology. BioScience, 53, 1169-1179. |
| [3] | Benz SA, Davis SJ, Burney JA (2021) Drivers and projections of global surface temperature anomalies at the local scale. Environmental Research Letters, 16, 064093. |
| [4] | Cai WT, Wang Y, Chen Y, Jiang N, Wang XC (2021) Thinking on the Evaluation Standard for Park City. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 37(8), 29-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [蔡文婷, 王钰, 陈艳, 姜娜, 王香春 (2021) 团体标准《公园城市评价标准》的编制思考. 中国园林, 37(8), 29-33.] | |
| [5] | Chen XD (2024) Theoretical origins and practical progress of biophilic urban planning and design. Planners, 40(7), 56-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈晓东 (2024) 亲生物城市规划与设计的理论源起和实践进展. 规划师, 40(7), 56-64.] | |
| [6] | Cheng H (2015) Establishment of national forest city based on the construction of ecological civilization in China. Journal of Beijing Forestry University (Social Sciences), 14(2), 17-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [程红 (2015) 试论基于生态文明建设的国家森林城市创建. 北京林业大学学报(社会科学版), 14(2), 17-20.] | |
| [7] | Cheng S, Cheng YN (2018) Form garden city to park city design—The dialectic relationship between urban ecology and morphology. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 34(12), 41-45. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [成实, 成玉宁 (2018) 从园林城市到公园城市设计——城市生态与形态辨证. 中国园林, 34(12), 41-45.] | |
| [8] | Cui JL, Zou J (2021) Exploring the relationship between urban ecological garden construction and biodiversity conservation. Contemporary Horticulture, 44(24), 155-156. (in Chinese) |
| [崔竣岭, 邹瑾 (2021) 探究城市生态园林建设与生物多样性保护的关系. 现代园艺, 44(24), 155-156.] | |
| [9] |
Deng J, Li Y, Hou YL (2023) Urban biodiversity conservation: Experience from the comparative perspective of China and Europe. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23070. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[邓晶, 李艺, 侯一蕾 (2023) 城市生物多样性保护: 基于中欧对比视角下的经验借鉴. 生物多样性, 31, 23070.]
DOI |
|
| [10] | Dong XD, Gong JR, Zhang WY, Zhang SQ, Hu YX, Yang GS, Yan CY, Li YH (2024) Importance of including Key Biodiversity Areas in China’s conservation area-based network. Biological Conservation, 296, 110676. |
| [11] | Duan J, Hua SE, Lan WL (2023) Reflections on the value orientation of the Park City Index. City Planning Review, 47(S1), 5-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [段进, 华澍而, 兰文龙 (2023) 《公园城市指数》的价值取向思考. 城市规划, 47(S1), 5-11.] | |
| [12] | Fairbairn AJ, Meyer ST, Mühlbauer M, Jung K, Apfelbeck B, Berthon K, Frank A, Guthmann L, Jokisch J, Kerler K, Müller N, Obster C, Unterbichler M, Webersberger J, Matejka J, Depner P, Weisser WW (2024) Urban biodiversity is affected by human-designed features of public squares. Nature Cities, 1, 706-715. |
| [13] |
Fang RX, Wang XQ, Bai C, Yan WH, Yang QS, Li WY, Gao L (2021) Knowledge mapping of the research on the convention on biological diversity: Based on bibliometrics analysis of CiteSpace. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1718-1726. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[方睿霞, 王修齐, 白春, 岩温罕, 杨青松, 李文义, 高路 (2021) 《生物多样性公约》研究知识图谱: 基于CiteSpace的文献计量分析. 生物多样性, 29, 1718-1726.]
DOI |
|
| [14] | Fu F, Li H, Zhao CJ (2020) From Shan-Shui City to Park City—The way of city development in China. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 36(4), 12-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [傅凡, 李红, 赵彩君 (2020) 从山水城市到公园城市——中国城市发展之路. 中国园林, 36(4), 12-15.] | |
| [15] | Gan J, Wu ZQ (2018) Urban biodiversity planning review and strategy. Planners, 34(1), 87-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [干靓, 吴志强 (2018) 城市生物多样性规划研究进展评述与对策. 规划师, 34(1), 87-91.] | |
| [16] | Goddard MA, Dougill AJ, Benton TG (2010) Scaling up from gardens: Biodiversity conservation in urban environments. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 25, 90-98. |
| [17] | Guo X, Chen N, Ji LM, Tan XD, Tao HQ (2023) Evaluation of the ecological status of park city in Chengdu from 2015 to 2020. Sichuan Environment, 42(3), 221-226. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭欣, 陈楠, 吉栗漫, 谭显东, 陶红群 (2023) 成都市2015-2020年公园城市生态现状评估. 四川环境, 42(3), 221-226.] | |
| [18] | Huang YL, Fu WC, Chen ZR, Ren W, Dong JW (2024) Research progress in the biodiversity of urban green space based on citizen science. Journal of Chinese Urban Forestry, 22(4), 84-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄雅凌, 傅伟聪, 陈梓茹, 任维, 董建文 (2024) 基于公众科学的城市绿地生物多样性研究进展. 中国城市林业, 22(4), 84-91.] | |
| [19] |
Li GD, Fang CL, Li YJ, Wang ZB, Sun SA, He SW, Qi W, Bao C, Ma HT, Fan YP, Feng YX, Liu XP (2022) Global impacts of future urban expansion on terrestrial vertebrate diversity. Nature Communications, 13, 1628.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | Li XX, Ou XY, Sun XY, Li HR, Li YX, Zheng X (2024) Urban biodiversity conservation: A framework for ecological network construction and priority areas identification considering habit differences within species. Journal of Environmental Management, 365, 121512. |
| [21] | Liu HY, Zhang HY, Feng J, Li YY, Zhang YB, Hao HG, Zhang Z (2024) Progress and countermeasure of biodiversity mainstreaming. Research of Environmental Sciences, 37, 2110-2117. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘海燕, 张惠远, 冯骥, 李圆圆, 张英博, 郝海广, 张哲 (2024) 生物多样性主流化进展与对策. 环境科学研究, 37, 2110-2117.] | |
| [22] | Luo MF, Yang M, Ma KP (2023) Core targets of Kunming-Montreal Global Framework and recommendations for conservation action in China. Guihaia, 43, 1350-1355. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [罗茂芳, 杨明, 马克平 (2023) 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》核心目标与我国的保护行动建议. 广西植物, 43, 1350-1355.] | |
| [23] |
Ma KP (2023) Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework: An important global agenda for biodiversity conservation. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23133. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[马克平 (2023) 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》是重要的全球生物多样性保护议程. 生物多样性, 31, 23133.]
DOI |
|
| [24] | Mao QZ, Ma KM, Wu JG, Tang RL, Zhang YX, Luo SH, Bao L, Cai XH (2013) An overview of advances in distributional pattern of urban biodiversity. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 1051-1064. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [毛齐正, 马克明, 邬建国, 唐荣莉, 张育新, 罗上华, 宝乐, 蔡小虎 (2013) 城市生物多样性分布格局研究进展. 生态学报, 33, 1051-1064.] | |
| [25] | Meng LS, Kang N, Gong C, Li SH (2022) Systematic review on the effect of levels of biodiversity on psychological health and wellbeing. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 38(11), 82-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孟令爽, 康宁, 宫宸, 李树华 (2022) 生物多样性水平对心理健康与福祉的影响系统性综述. 中国园林, 38(11), 82-87.] | |
| [26] | Ministry of Ecology and Environment (2021) Opinions on Further Strengthening Biodiversity Protection. (in Chinese) |
| [生态环境部 (2021) 关于进一步加强生物多样性保护的意见.] https://www.mee.gov.cn/zcwj/zyygwj/202110/t20211019_957149.shtml. (accessed on 2024-10-22) ] | |
| [27] | Mo F, Xu Y, Fu YR, Che SQ (2022) The evolution of urban biodiversity conservation strategies in London from the perspective of blue and green space management (2002-2021). Landscape Architecture, 29(4), 101-106. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [莫非, 徐悦, 付彦荣, 车生泉 (2022) 蓝绿空间管理视角下伦敦城市生物多样性保护策略演变(2002-2021年). 风景园林, 29(4), 101-106.] | |
| [28] | Müller N, Ignatieva M, Nilon CH, Werner P, Zipperer WC (eds 2013) Patterns and trends in urban biodiversity and landscape design. In: Urbanization, Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services: Challenges and Opportunities (eds Elmqvist T, Fragkias M, Goodness J, Güneralp B, Marcotullio PJ, McDonald RI, Parnell S, Schewenius M, Sendstad M, Seto KC, Wilkinson C). Springer, Dordrecht. |
| [29] | National Parks (2021) The Singapore Index is the Most Comprehensive Index on Cities’ Biodiversity. https://www.nparks.gov.sg/. (accessed on 2021-09-23) |
| [30] |
Pereira HM, Martins IS, Rosa IMD, Kim H, Leadley P, Popp A, van Vuuren DP, Hurtt G, Quoss L, Arneth A, Baisero D, Bakkenes M, Chaplin-Kramer R, Chini L, Di Marco M, Ferrier S, Fujimori S, Guerra CA, Harfoot M, Harwood TD, Hasegawa T, Haverd V, Havlík P, Hellweg S, Hilbers JP, Hill SLL, Hirata A, Hoskins AJ, Humpenöder F, Janse JH, Jetz W, Johnson JA, Krause A, Leclère D, Matsui T, Meijer JR, Merow C, Obersteiner M, Ohashi H, De Palma A, Poulter B, Purvis A, Quesada B, Rondinini C, Schipper AM, Settele J, Sharp R, Stehfest E, Strassburg BBN, Takahashi K, Talluto L, Thuiller W, Titeux N, Visconti P, Ware C, Wolf F, Alkemade R (2024) Global trends and scenarios for terrestrial biodiversity and ecosystem services from 1900 to 2050. Science, 384, 458-465.
DOI PMID |
| [31] | Qi LW, Chen WJ, Li CY, Song XT, Ge LQ (2024) Quantitative evaluation of China’s biogenetic resources conservation policies based on the policy modeling consistency index model. Sustainability, 16, 5158. |
| [32] | Qi SP, Wang ZQ, Chen X (2004) Exploratory study on biodiversity in urban landscape architecture (LA). World Forestry Research, 17(1), 31-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [祁素萍, 王兆骞, 陈欣 (2004) 城市园林的生物多样性保护. 世界林业研究, 17(1), 31-36.] | |
| [33] |
Qi W, Liu SH, Jin HR (2016) Applicability of the new standard of city-size classification in China. Progress in Geography, 35(1), 47-56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [戚伟, 刘盛和, 金浩然 (2016) 中国城市规模划分新标准的适用性研究. 地理科学进展, 35(1), 47-56.] | |
| [34] | Qian XS (1992) Qian Xuesen’s letter on fine arts. Art Magazine, (11), 4. (in Chinese) |
| [钱学森 (1992) 钱学森关于美术的一封信. 美术, (11), 4.] | |
| [35] |
Rodenbiker J (2020) Urban ecological enclosures: Conservation planning, peri-urban displacement, and local state formations in China. International Journal of Urban and Regional Research, 44, 691-710.
DOI |
| [36] | Rui Y, Tang BP, Wang X, Ma T, Liu XQ (2018) The spatio-temporal evolutionary characteristics and the impact mechanism of national garden cities in China. Geographical Research, 37(1), 20-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[芮旸, 唐蓓佩, 王兴, 马滕, 刘晓琼 (2018) 国家园林城市时空演变特征及其影响机理. 地理研究, 37(1), 20-36.]
DOI |
|
| [37] | Sadeghian MM, Vardanyan Z (2013) The benefits of urban parks, a review of urban research. Journal of Novel Applied Sciences, 2, 231-237. |
| [38] | Sha O, Fang Z, Xiong YP (2022) Biodiversity protection strategies in territorial space planning system: Bird protection. Planners, 38(S1), 31-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [沙鸥, 方舟, 熊耀平 (2022) 国土空间规划体系下生物多样性保护策略——以鸟类保护为例. 规划师, 38(S1), 31-36.] | |
| [39] | UNEP (United Nations Environment Programme) (2020) UNEP Annual Report 2020. https://digitallibrary.un.org/record/4047745. (accessed on 2024-10-22) |
| [40] | UNEP (United Nations Environment Programme) (2022) Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework. https://www.cbd.int/doc/c/e6d3/cd1d/daf663719a03902a9b116c34/cop-15-l-25-en.pdf. (accessed on 2022-12-18) |
| [41] | Wang H (2018) Discussion on the planning and construction of park cities. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 34(10), 16-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王浩 (2018) “自然山水园中城, 人工山水城中园”——公园城市规划建设讨论. 中国园林, 34(10), 16-21.] | |
| [42] | Wang HY, Wang HQ, Chen XY, Han BL, Shu CJ, Zhang T, Ding SY (2023) Review on evaluation and enhancement of urban biodiversity. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43, 2995-3006. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王海洋, 王浩琪, 陈禧悦, 韩宝龙, 束承继, 张童, 丁仕宇 (2023) 国内外城市生物多样性评价与提升研究综述. 生态学报, 43, 2995-3006.] | |
| [43] | Wang XC, Wang RQ, Cai WT (2020) Discussion on the construction of park cities. Urban Development Studies, 27(9), 19-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王香春, 王瑞琦, 蔡文婷 (2020) 公园城市建设探讨. 城市发展研究, 27(9), 19-24.] | |
| [44] | Wang XR (2021) Biodiversity is what a city should have. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 37(5), 2-3. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王向荣 (2021) 生物多样是城市本应具有的状态. 中国园林, 37(5), 2-3.] | |
| [45] | Wang Y, Xu SX, Tan RH, Chen Y, Cai WT, Wang XC (2022) Discussion on strategies and paths adapted to green and high quality development of China urban landscape architecture. Landscape Architecture Academic Journal, 39(6), 111-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王钰, 许士翔, 谭人华, 陈艳, 蔡文婷, 王香春 (2022) 适应绿色高质量发展的中国城市园林绿化策略研究. 园林, 39(6), 111-117.] | |
| [46] | Wang YC (2014) The framework of biodiversity for landscape architecture. Landscape Architecture, (1), 36-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王云才 (2014) 基于风景园林学科的生物多样性框架. 风景园林, (1), 36-41.] | |
| [47] |
Wen Z, Zheng H, Ouyang ZY (2020) Research progress on the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem services. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31, 340-348. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[文志, 郑华, 欧阳志云 (2020) 生物多样性与生态系统服务关系研究进展. 应用生态学报, 31, 340-348.]
DOI |
|
| [48] | World Wildlife Fund (2020) 2020 Annual Report. https://www.worldwildlife.org/pages/2020-annual-report. (accessed on 2022-12-18) |
| [49] | Wu RW (1999) Urban biodiversity strategies. Urban Planning Review, (1), 18-20, 46-80. (in Chinese) |
| [吴人韦 (1999) 城市生物多样性策略. 城市规划汇刊, (1), 18-20, 46-80.] | |
| [50] | Xiao NW (2021) The global biodiversity conservation situation and China’s role. Contemporary World, (11), 10-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [肖能文 (2021) 全球生物多样性保护形势与中国作用. 当代世界, (11), 10-15.] | |
| [51] | Xiao NW, Zhao ZP, Li G, Gao XQ, Ji SN, Xu J, Liu DM, Li JS (2022) Biodiversity survey and assessment methods in biodiversity conservation priority areas in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42, 2523-2531. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [肖能文, 赵志平, 李果, 高晓奇, 吉晟男, 徐靖, 刘冬梅, 李俊生 (2022) 中国生物多样性保护优先区域生物多样性调查和评估方法. 生态学报, 42, 2523-2531.] | |
| [52] |
Xu J, Wang JZ (2023) Analysis of the main elements and implications of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[徐靖, 王金洲 (2023) 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》主要内容及其影响. 生物多样性, 31, 23020.]
DOI |
|
| [53] |
Xue DY (2015) On establishing the national synergy strategy for the implementation of international agreements related to biodiversity conservation. Biodiversity Science, 23, 673-680. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[薛达元 (2015) 建立生物多样性保护相关国际公约的国家履约协同战略. 生物多样性, 23, 673-680.]
DOI |
|
| [54] |
Yan DK (2024) Common elements, deficiencies, and optimization suggestions of biodiversity conservation policies in China. Biodiversity Science, 32, 23293. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [鄢德奎 (2024) 中国生物多样性保护政策的共同要素、不足和优化建议. 生物多样性, 32, 23293.] | |
| [55] |
Yang R, Peng QY, Cao Y, Zhong N, Hou SY, Zhao ZC, Huang C (2019) Transformative changes and paths toward biodiversity conservation in China. Biodiversity Science, 27, 1032-1040. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[杨锐, 彭钦一, 曹越, 钟乐, 侯姝彧, 赵智聪, 黄澄 (2019) 中国生物多样性保护的变革性转变及路径. 生物多样性, 27, 1032-1040.]
DOI |
|
| [56] | Yang WY, Qiu YX (2022) The experience of biophilic city planning and construction in Singapore. Science & Technology Review, 40(22), 33-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[杨文越, 邱宇欣 (2022) 新加坡“亲生物城市”规划建设经验. 科技导报, 40(22), 33-42.]
DOI |
|
| [57] | Yang Z, Mao P, He YX, Ju PJ, Huang SL, Feng Y, Chen H, Wu N (2022) Hot topics and research trends in park city based on a bibliometrics analysis. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 28, 1084-1093. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨早, 毛萍, 何奕忻, 鞠佩君, 黄硕磊, 冯毅, 陈槐, 吴宁 (2022) 基于VOSviewer的公园城市计量特征、热点与趋势. 应用与环境生物学报, 28, 1084-1093.] | |
| [58] | Yu CM, Hao SM (2017) A study on the sustainable land use pattern based on the integration of urban design and landscape architecture. Landscape Architecture, (4), 14-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [于长明, 郝石盟 (2017) 基于城市设计与风景园林相融合的可持续土地利用模式研究. 风景园林, (4), 14-20.] | |
| [59] |
Yu SX, Deng LC, Wu Q, Wang Z (2021) The review mechanism of the convention on biological diversity: Status, challenges and prospects. Biodiversity Science, 29, 238-246. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[于书霞, 邓梁春, 吴琼, 王真 (2021) 《生物多样性公约》审查机制的现状、挑战和展望. 生物多样性, 29, 238-246.]
DOI |
|
| [60] | Zhang HW, Xia HS, Wei M (2009) Guiding the construction of Green City with the theory of green infrastructure. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 25(9), 28-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张红卫, 夏海山, 魏民 (2009) 运用绿色基础设施理论, 指导“绿色城市”建设. 中国园林, 25(9), 28-30.] | |
| [61] | Zhang YL, Guan HL, Li X (2017) Response of urban green space system planning from Garden City to Ecological Garden City. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 33(2), 71-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张云路, 关海莉, 李雄 (2017) 从园林城市到生态园林城市的城市绿地系统规划响应. 中国园林, 33(2), 71-77.] | |
| [62] | Zhang ZY, Cenci J, Zhang JZ (2024) Policies for equity in access to urban green space: A spatial perspective of the Chinese national forest city policy. Forests, 15, 608. |
| [63] | Zhao Y, Wang YF (2021) Comparative study on implementing Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) between Japan & Korea and useful reference to China. Environmental Protection, 49(21), 64-67. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵阳, 王宇飞 (2021) 日本与韩国履行《生物多样性公约》比较研究及对我国的借鉴. 环境保护, 49(21), 64-67.] | |
| [64] | Zheng X (2022) Urban biodiversity. Landscape Architecture, 29(1), 8-9. (in Chinese) |
| [郑曦 (2022) 城市生物多样性. 风景园林, 29(1), 8-9.] | |
| [65] | Zhong L, Yang R, Fu YR (2022) Research on the progress of urban biodiversity governance in China based on policy text analysis. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 38(9), 51-56. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [钟乐, 杨锐, 付彦荣 (2022) 基于政策文本分析的中国城市生物多样性治理进展研究. 中国园林, 38(9), 51-56.] |
| [1] | Wenyan Chen, Xiuqin Ci, Junling Chen, Zhifang Liu, Lang Li, Jie Li. Multidimensional diversity patterns and their environmental drivers of Lauraceae plants in Yunnan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(6): 24558-. |
| [2] | Yun'ao Li, Wenfu Zhang, Guigang Zhao, Chunyan Yang, Xiangqing Chen, Shengdong Yuan, Min Cao, Wang Cai, Jie Yang. Application of airborne eDNA for terrestrial animal diversity monitoring: A case study of 20-ha forest dynamics plot in Xishuangbanna, Yunnan, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(6): 24318-. |
| [3] | Lulu Zhang, Zhaojie Ren, Ningning Yu, Fengxi Zhao, Zuntian Zhao. List of bryophytes in Gansu Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(6): 24451-. |
| [4] | Jing Gan, Xiangxu Liu, Xueming Lu, Xing Yue. China’s large cities in global biodiversity hotspots: Conservation policies and optimization directions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [5] | Tz-Hsuan Tseng, Rui Yang, Yue Huang, Luyao Chen. Characteristics of bird diversity and environmental relationships in Tsinghua University campus [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [6] | Mingyue Zang, Li Liu, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feilong Hu, Xiaoqiang Lu, Jiaqi Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. China’s urban biodiversity conservation under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [7] | Xiaoyu Zhu, Chenhao Wang, Zhongjun Wang, Yujun Zhang. Research progress and prospect of urban green space biodiversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [8] | Lin Yuan, Siqi Wang, Jingxuan Hou. Leaving space for wildness in metropolitan region: Trends and prospects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [9] | Min Hu, Binbin V. Li, Coraline Goron. Green is not enough: A management framework for urban biodiversity-friendly parks [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [10] | Xin Wang, Fengyu Bao. Ecological restoration effect of South Dianchi National Wetland Park based on the enhancement of bird diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [11] | Jun Yang, Xudong Yang, Xinyi Liu, Jing Zhou. Perspectives of urban biodiversity studies in China serving Target 12 of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 25104-. |
| [12] | Mengchan Yang, Qinian Fang, Canzhong Rong, Sifan Hu, Jingjing Zhao, Zhijian Liang, Tien Ming Lee. Review of the application and outlook of citizen science as an approach for monitoring urban biodiversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24464-. |
| [13] | Yue Qi, Junsheng Li, Yanan Hou. Human effect factors on urban plant diversity and management strategies [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24484-. |
| [14] | Xie Gan, Xuan Jing, Fu Qidi, Wei Ze, Xue Kai, Luo Hairui, Gao Jixi, Li Min. Establishing an intelligent identification model for unmanned aerial vehicle surveys of grassland plant diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [15] | Chu Xiaolin, Zhang Quanguo. A review of experimental evidence for the evolutionary speed hypothesis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn