



生物多样性 ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (3): 312-324. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016350 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2016350
收稿日期:2016-12-11
接受日期:2017-02-07
出版日期:2017-03-20
发布日期:2017-04-07
通讯作者:
崔国发
基金资助:
Ziliang Guo1,2, Shaohua Xing1, Guofa Cui1,*( )
)
Received:2016-12-11
Accepted:2017-02-07
Online:2017-03-20
Published:2017-04-07
Contact:
Cui Guofa
摘要:
如何客观地确定自然保护区的保护优先性, 为自然保护区的晋级和确定管理类型提供科学依据, 已成为当前亟待解决的问题。本研究通过对已有评价指标和方法的对比、专家咨询、评价指标量化处理, 提出了量化评价自然保护区物种多样性保护价值的方法。此评价方法包括了自然保护区野生植物、野生动物、珍稀濒危野生植物和珍稀濒危野生动物多样性保护价值指数等量化模型。同时我们应用此方法对华北暖温带区域的39个自然保护区和东北温带区域的67个自然保护区的物种多样性保护价值进行了评价。结果表明, 位于华北暖温带区域的河北南大港湿地和辽河源及北京雾灵山, 以及位于东北温带区域的黑龙江镜泊湖、大佳河和翠北湿地等省级自然保护区的物种多样性保护价值较高, 可推荐优先晋级国家级自然保护区。该物种多样性保护价值评价方法能够较好地反映自然保护区之间物种及各类群多样性保护价值的差异, 确定自然保护区保护优先序列。此外自然保护区物种多样性保护价值在不同自然保护地理区和不同类型自然保护区之间存在显著差别。
郭子良, 邢韶华, 崔国发 (2017) 自然保护区物种多样性保护价值评价方法. 生物多样性, 25, 312-324. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016350.
Ziliang Guo, Shaohua Xing, Guofa Cui (2017) A method for assessing species diversity conservation value of nature reserves. Biodiversity Science, 25, 312-324. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016350.
| 评价指标 Evaluation index | 分级赋值 Assignment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
| 濒危性 Endangerment | 极危Critically Endangered | 濒危Endangered | 易危Vulnerable | 近危和无危Near Threatened and Least Concern |
| 特有性 Endemism | 植物地区特有 Endemic to plant province | 植物亚区特有 Endemic to plant subarea | 中国特有 Endemic to China | 非中国特有 Not endemic to China |
| 保护等级 Conservation level | 国家一级保护或特殊保护 First-category national protected or special protected | 国家二级保护 Second-category national protected | 地方重点保护 Provincial key protected | 其他 Others |
表1 野生植物的保护重要性评价指标分级赋值标准
Table 1 Assignment for evaluation index of conservation importance of wild plants
| 评价指标 Evaluation index | 分级赋值 Assignment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
| 濒危性 Endangerment | 极危Critically Endangered | 濒危Endangered | 易危Vulnerable | 近危和无危Near Threatened and Least Concern |
| 特有性 Endemism | 植物地区特有 Endemic to plant province | 植物亚区特有 Endemic to plant subarea | 中国特有 Endemic to China | 非中国特有 Not endemic to China |
| 保护等级 Conservation level | 国家一级保护或特殊保护 First-category national protected or special protected | 国家二级保护 Second-category national protected | 地方重点保护 Provincial key protected | 其他 Others |
| 评价指标 Evaluation index | 分级赋值 Assignment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
| 濒危性 Endangerment | 极危Critically Endangered | 濒危Endangered | 易危Vulnerable | 近危和无危Near Threatened and Least Concern |
| 特有性* Endemism | 动物地理地区特有 Endemic to animal province | 中国特有 Endemic to China | 中国主要分布 Distributed mainly in China | 中国次要或边缘分布 Distributed secondary or marginal in China |
| 保护等级 Conservation level | 国家一级保护或特殊保护 First-category national protected or special protected | 国家二级保护 Second-category national protected | 地方重点保护 Provincial key protected | 其他 Others |
表2 野生动物的保护重要性评价指标分级赋值标准
Table 2 Assignment for evaluation index of conservation importance of wild animals
| 评价指标 Evaluation index | 分级赋值 Assignment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
| 濒危性 Endangerment | 极危Critically Endangered | 濒危Endangered | 易危Vulnerable | 近危和无危Near Threatened and Least Concern |
| 特有性* Endemism | 动物地理地区特有 Endemic to animal province | 中国特有 Endemic to China | 中国主要分布 Distributed mainly in China | 中国次要或边缘分布 Distributed secondary or marginal in China |
| 保护等级 Conservation level | 国家一级保护或特殊保护 First-category national protected or special protected | 国家二级保护 Second-category national protected | 地方重点保护 Provincial key protected | 其他 Others |
| 自然保护地理区 Natural conservation geographical area | 自然保护区 Nature reserve (NR) | 省份 Province | NP | VP | NPT | VPT | NA | VA | NAT | VAT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 森林 Forest | ||||||||||||
| 辽西冀北山地落叶阔叶林区 The North Hebei Province and West Liaoning Province Mountains Deciduous Broadleaf Forest Area | 努鲁儿虎山 Nuluerhu Mountain NR* | 辽宁Liaoning | 866 | 33.91 | 5 | 5.66 | 323 | 43.55 | 37 | 23.58 | ||
| 大黑山 Dahei Mountain NR* | 辽宁Liaoning | 792 | 33.48 | 4 | 4.90 | 352 | 47.91 | 50 | 29.87 | |||
| 白狼山 Bailang Mountain NR* | 辽宁Liaoning | 799 | 33.02 | 5 | 5.66 | 198 | 31.76 | 19 | 13.71 | |||
| 虹螺山 Hongluo Mountain NR* | 辽宁Liaoning | 783 | 32.83 | 8 | 7.21 | 197 | 31.89 | 18 | 14.00 | |||
| 海棠山 Haitang Mountain NR* | 辽宁Liaoning | 729 | 31.64 | 7 | 7.21 | 226 | 37.20 | 36 | 24.25 | |||
| 七老图山落叶阔叶林与草原区 Qilaotu Mountains Deciduous Broadleaf Forest and Steppe Area | 辽河源 Liaohe River Source NR | 河北Hebei | 831 | 34.64 | 5 | 6.00 | 241 | 39.18 | 37 | 24.49 | ||
| 北大山 Beida Mountain NR | 河北Hebei | 715 | 32.30 | 5 | 6.00 | 213 | 36.78 | 33 | 23.75 | |||
| 燕山落叶阔叶林区 Yanshan Mountains Deciduous Broadleaf Forest Area | 松山 Songshan Mountain NR* | 北京Beijing | 740 | 34.07 | 7 | 10.39 | 167 | 29.10 | 19 | 15.10 | ||
| 雾灵山 Wuling Mountain NR | 北京Beijing | 680 | 33.33 | 7 | 10.20 | 165 | 30.02 | 21 | 16.97 | |||
| 青龙都山 Dushan Mountain NR, Qinglong | 河北Hebei | 691 | 32.3 | 6 | 6.63 | 203 | 33.27 | 28 | 20.49 | |||
| 青龙河 Qinglong River NR* | 辽宁Liaoning | 730 | 32.08 | 4 | 5.29 | 193 | 34.73 | 27 | 20.88 | |||
| 喇叭沟门 Labagoumen NR | 北京Beijing | 622 | 29.97 | 4 | 5.29 | 152 | 30.35 | 24 | 19.08 | |||
| 六里坪猕猴 Liuliping Rhesus Monkeys NR | 河北Hebei | 604 | 29.78 | 4 | 5.29 | 206 | 36.46 | 28 | 22.09 | |||
| 宽城都山 Dushan Mountain NR, Kuancheng | 河北Hebei | 545 | 28.37 | 5 | 6.00 | 205 | 36.73 | 28 | 22.63 | |||
| 宽城千鹤山 Qianhe Mountain NR, Kuancheng | 河北Hebei | 572 | 28.32 | 4 | 5.29 | 221 | 41.80 | 33 | 28.28 | |||
| 八仙山 Baxian Mountain NR* | 天津Tianjin | 510 | 26.85 | 2 | 4.00 | 189 | 30.38 | 23 | 16.00 | |||
| 晋北中山落叶阔叶林与草原区 The North Shanxi Province Mountains Deciduous Broadleaf Forest and Steppe Area | 驼梁 Tuoliang NR* | 河北Hebei | 843 | 36.77 | 6 | 6.63 | 283 | 48.15 | 44 | 33.41 | ||
| 灵空山 Lingkong Mountain NR* | 山西Shanxi | 811 | 34.60 | 6 | 7.75 | 215 | 39.01 | 33 | 25.61 | |||
| 芦芽山 Luya Mountain NR* | 山西Shanxi | 651 | 30.97 | 3 | 4.90 | 299 | 44.38 | 40 | 28.21 | |||
| 银河山 Yinhe Mountain NR | 河北Hebei | 613 | 30.40 | 2 | 4.00 | 175 | 32.37 | 23 | 19.18 | |||
| 漫山 Manshan Mountain NR | 河北Hebei | 480 | 27.18 | 5 | 8.00 | 168 | 31.72 | 22 | 19.18 | |||
| 太行山东麓栽培植被与落叶阔叶林区 The East Taihang Mountains Cultivate Vegetation and Deciduous Broadleaf Forest Area | 小五台山 Xiaowutai Mountain NR* | 河北Hebei | 1,305 | 46.70 | 9 | 14.56 | 150 | 33.78 | 23 | 25.30 | ||
| 青崖寨 Qingyazhai NR* | 河北Hebei | 847 | 42.68 | 5 | 23.24 | 187 | 32.45 | 27 | 19.70 | |||
| 百花山 Baihua Mountain NR* | 北京Beijing | 821 | 37.84 | 11 | 14.97 | 172 | 31.80 | 14 | 19.80 | |||
| 摩天岭 Motianling NR | 河北Hebei | 775 | 34.31 | 6 | 6.63 | 177 | 33.78 | 23 | 22.09 | |||
| 金华山-横岭子褐马鸡 Jinhua Mountain-Henglingzi Brown Eared-Pheasant NR | 河北Hebei | 672 | 31.95 | 6 | 6.63 | 150 | 32.95 | 22 | 24.00 | |||
| 三峰山 Sanfeng Mountain NR | 河北Hebei | 676 | 31.84 | 4 | 5.29 | 161 | 29.36 | 19 | 16.73 | |||
| 云蒙山 Yunmeng Mountain NR | 北京Beijing | 514 | 27.29 | 2 | 4.00 | 123 | 26.80 | 13 | 16.49 | |||
| 大茂山 Damao Mountain NR | 河北Hebei | 413 | 24.49 | 2 | 3.46 | 118 | 23.09 | 14 | 11.31 | |||
| 太行山南段山地落叶阔叶林与湿地区 The South Taihang Mountains Deciduous Broadleaf Forest and Wetland Area | 蟒河猕猴 Manghe River Rhesus Monkeys NR* | 山西Shanxi | 773 | 35.10 | 6 | 8.49 | 280 | 41.70 | 33 | 25.14 | ||
| 草原草甸 Steppe and Meadow | ||||||||||||
| 燕山落叶阔叶林区 Yanshan Mountains Deciduous Broadleaf Forest Area | 白草洼 Baicaowa NR | 河北Hebei | 783 | 35.01 | 6 | 10.00 | 207 | 32.74 | 29 | 18.97 | ||
| 滦河源草地 Luanhe River Source Steppe NR | 河北Hebei | 682 | 31.35 | 6 | 8.25 | 101 | 24.06 | 16 | 14.97 | |||
| 红松洼 Hongsongwa NR* | 河北Hebei | 517 | 27.89 | 3 | 8.94 | 267 | 43.31 | 42 | 28.57 | |||
| 御道口 Yudaokou NR | 河北Hebei | 495 | 27.33 | 3 | 6.93 | 196 | 39.32 | 36 | 28.35 | |||
| 湿地 Wetland | ||||||||||||
| 海河平原栽培植被与湿地区 Haihe Plain Cultivate Vegetation and Wetland Area | 曹妃甸湿地和鸟类 Caofeidian Wetland and Bird NR | 河北Hebei | 217 | 16.09 | 0 | 0 | 297 | 52.89 | 55 | 39.24 | ||
| 衡水湖 Hengshui Lake NR* | 河北Hebei | 285 | 18.63 | 1 | 2 | 339 | 52.86 | 58 | 36.93 | |||
| 南大港湿地 Nandagang Wetland NR | 河北Hebei | 216 | 16.03 | 1 | 2 | 276 | 52.57 | 53 | 40.25 | |||
| 古海岸与湿地 Palecoast and Wetland NR* | 天津Tianjin | 194 | 15.3 | 1 | 2 | 271 | 50.57 | 45 | 36.82 | |||
| 白洋淀 Baiyangdian NR | 河北Hebei | 324 | 19.95 | 0 | 0 | 220 | 42.93 | 33 | 29.73 | |||
表3 华北暖温带区域部分自然保护区物种多样性保护价值指数(* 截止到2015年确定的国家级自然保护区)
Table 3 The species diversity conservation value index of some nature reserves in North China Warm Temperate Region (* National nature reserve by 2015)
| 自然保护地理区 Natural conservation geographical area | 自然保护区 Nature reserve (NR) | 省份 Province | NP | VP | NPT | VPT | NA | VA | NAT | VAT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 森林 Forest | ||||||||||||
| 辽西冀北山地落叶阔叶林区 The North Hebei Province and West Liaoning Province Mountains Deciduous Broadleaf Forest Area | 努鲁儿虎山 Nuluerhu Mountain NR* | 辽宁Liaoning | 866 | 33.91 | 5 | 5.66 | 323 | 43.55 | 37 | 23.58 | ||
| 大黑山 Dahei Mountain NR* | 辽宁Liaoning | 792 | 33.48 | 4 | 4.90 | 352 | 47.91 | 50 | 29.87 | |||
| 白狼山 Bailang Mountain NR* | 辽宁Liaoning | 799 | 33.02 | 5 | 5.66 | 198 | 31.76 | 19 | 13.71 | |||
| 虹螺山 Hongluo Mountain NR* | 辽宁Liaoning | 783 | 32.83 | 8 | 7.21 | 197 | 31.89 | 18 | 14.00 | |||
| 海棠山 Haitang Mountain NR* | 辽宁Liaoning | 729 | 31.64 | 7 | 7.21 | 226 | 37.20 | 36 | 24.25 | |||
| 七老图山落叶阔叶林与草原区 Qilaotu Mountains Deciduous Broadleaf Forest and Steppe Area | 辽河源 Liaohe River Source NR | 河北Hebei | 831 | 34.64 | 5 | 6.00 | 241 | 39.18 | 37 | 24.49 | ||
| 北大山 Beida Mountain NR | 河北Hebei | 715 | 32.30 | 5 | 6.00 | 213 | 36.78 | 33 | 23.75 | |||
| 燕山落叶阔叶林区 Yanshan Mountains Deciduous Broadleaf Forest Area | 松山 Songshan Mountain NR* | 北京Beijing | 740 | 34.07 | 7 | 10.39 | 167 | 29.10 | 19 | 15.10 | ||
| 雾灵山 Wuling Mountain NR | 北京Beijing | 680 | 33.33 | 7 | 10.20 | 165 | 30.02 | 21 | 16.97 | |||
| 青龙都山 Dushan Mountain NR, Qinglong | 河北Hebei | 691 | 32.3 | 6 | 6.63 | 203 | 33.27 | 28 | 20.49 | |||
| 青龙河 Qinglong River NR* | 辽宁Liaoning | 730 | 32.08 | 4 | 5.29 | 193 | 34.73 | 27 | 20.88 | |||
| 喇叭沟门 Labagoumen NR | 北京Beijing | 622 | 29.97 | 4 | 5.29 | 152 | 30.35 | 24 | 19.08 | |||
| 六里坪猕猴 Liuliping Rhesus Monkeys NR | 河北Hebei | 604 | 29.78 | 4 | 5.29 | 206 | 36.46 | 28 | 22.09 | |||
| 宽城都山 Dushan Mountain NR, Kuancheng | 河北Hebei | 545 | 28.37 | 5 | 6.00 | 205 | 36.73 | 28 | 22.63 | |||
| 宽城千鹤山 Qianhe Mountain NR, Kuancheng | 河北Hebei | 572 | 28.32 | 4 | 5.29 | 221 | 41.80 | 33 | 28.28 | |||
| 八仙山 Baxian Mountain NR* | 天津Tianjin | 510 | 26.85 | 2 | 4.00 | 189 | 30.38 | 23 | 16.00 | |||
| 晋北中山落叶阔叶林与草原区 The North Shanxi Province Mountains Deciduous Broadleaf Forest and Steppe Area | 驼梁 Tuoliang NR* | 河北Hebei | 843 | 36.77 | 6 | 6.63 | 283 | 48.15 | 44 | 33.41 | ||
| 灵空山 Lingkong Mountain NR* | 山西Shanxi | 811 | 34.60 | 6 | 7.75 | 215 | 39.01 | 33 | 25.61 | |||
| 芦芽山 Luya Mountain NR* | 山西Shanxi | 651 | 30.97 | 3 | 4.90 | 299 | 44.38 | 40 | 28.21 | |||
| 银河山 Yinhe Mountain NR | 河北Hebei | 613 | 30.40 | 2 | 4.00 | 175 | 32.37 | 23 | 19.18 | |||
| 漫山 Manshan Mountain NR | 河北Hebei | 480 | 27.18 | 5 | 8.00 | 168 | 31.72 | 22 | 19.18 | |||
| 太行山东麓栽培植被与落叶阔叶林区 The East Taihang Mountains Cultivate Vegetation and Deciduous Broadleaf Forest Area | 小五台山 Xiaowutai Mountain NR* | 河北Hebei | 1,305 | 46.70 | 9 | 14.56 | 150 | 33.78 | 23 | 25.30 | ||
| 青崖寨 Qingyazhai NR* | 河北Hebei | 847 | 42.68 | 5 | 23.24 | 187 | 32.45 | 27 | 19.70 | |||
| 百花山 Baihua Mountain NR* | 北京Beijing | 821 | 37.84 | 11 | 14.97 | 172 | 31.80 | 14 | 19.80 | |||
| 摩天岭 Motianling NR | 河北Hebei | 775 | 34.31 | 6 | 6.63 | 177 | 33.78 | 23 | 22.09 | |||
| 金华山-横岭子褐马鸡 Jinhua Mountain-Henglingzi Brown Eared-Pheasant NR | 河北Hebei | 672 | 31.95 | 6 | 6.63 | 150 | 32.95 | 22 | 24.00 | |||
| 三峰山 Sanfeng Mountain NR | 河北Hebei | 676 | 31.84 | 4 | 5.29 | 161 | 29.36 | 19 | 16.73 | |||
| 云蒙山 Yunmeng Mountain NR | 北京Beijing | 514 | 27.29 | 2 | 4.00 | 123 | 26.80 | 13 | 16.49 | |||
| 大茂山 Damao Mountain NR | 河北Hebei | 413 | 24.49 | 2 | 3.46 | 118 | 23.09 | 14 | 11.31 | |||
| 太行山南段山地落叶阔叶林与湿地区 The South Taihang Mountains Deciduous Broadleaf Forest and Wetland Area | 蟒河猕猴 Manghe River Rhesus Monkeys NR* | 山西Shanxi | 773 | 35.10 | 6 | 8.49 | 280 | 41.70 | 33 | 25.14 | ||
| 草原草甸 Steppe and Meadow | ||||||||||||
| 燕山落叶阔叶林区 Yanshan Mountains Deciduous Broadleaf Forest Area | 白草洼 Baicaowa NR | 河北Hebei | 783 | 35.01 | 6 | 10.00 | 207 | 32.74 | 29 | 18.97 | ||
| 滦河源草地 Luanhe River Source Steppe NR | 河北Hebei | 682 | 31.35 | 6 | 8.25 | 101 | 24.06 | 16 | 14.97 | |||
| 红松洼 Hongsongwa NR* | 河北Hebei | 517 | 27.89 | 3 | 8.94 | 267 | 43.31 | 42 | 28.57 | |||
| 御道口 Yudaokou NR | 河北Hebei | 495 | 27.33 | 3 | 6.93 | 196 | 39.32 | 36 | 28.35 | |||
| 湿地 Wetland | ||||||||||||
| 海河平原栽培植被与湿地区 Haihe Plain Cultivate Vegetation and Wetland Area | 曹妃甸湿地和鸟类 Caofeidian Wetland and Bird NR | 河北Hebei | 217 | 16.09 | 0 | 0 | 297 | 52.89 | 55 | 39.24 | ||
| 衡水湖 Hengshui Lake NR* | 河北Hebei | 285 | 18.63 | 1 | 2 | 339 | 52.86 | 58 | 36.93 | |||
| 南大港湿地 Nandagang Wetland NR | 河北Hebei | 216 | 16.03 | 1 | 2 | 276 | 52.57 | 53 | 40.25 | |||
| 古海岸与湿地 Palecoast and Wetland NR* | 天津Tianjin | 194 | 15.3 | 1 | 2 | 271 | 50.57 | 45 | 36.82 | |||
| 白洋淀 Baiyangdian NR | 河北Hebei | 324 | 19.95 | 0 | 0 | 220 | 42.93 | 33 | 29.73 | |||
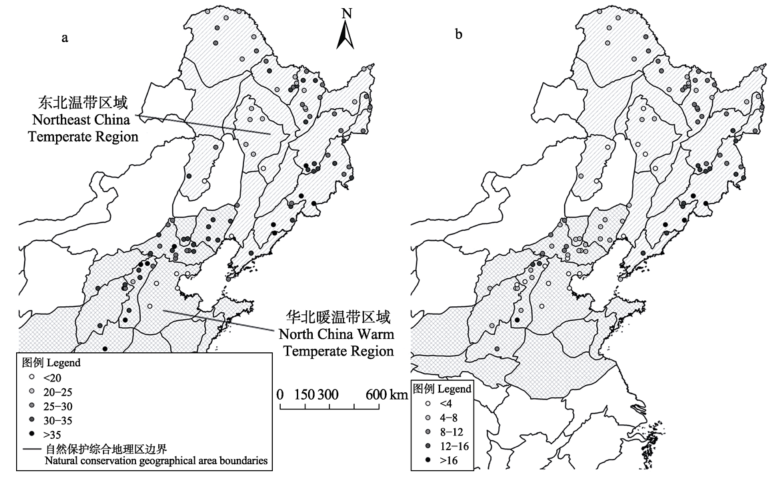
图1 东北温带区域和华北暖温带区域部分自然保护区野生植物多样性保护价值指数(a)和珍稀濒危野生植物多样性保护价值指数(b)分布图
Fig. 1 The pattern for the wild plant conservation value index (a) and rare and endangered wild plant conservation value index (b) of some nature reserves in Northeast China Temperate Region and North China Warm Temperate Region
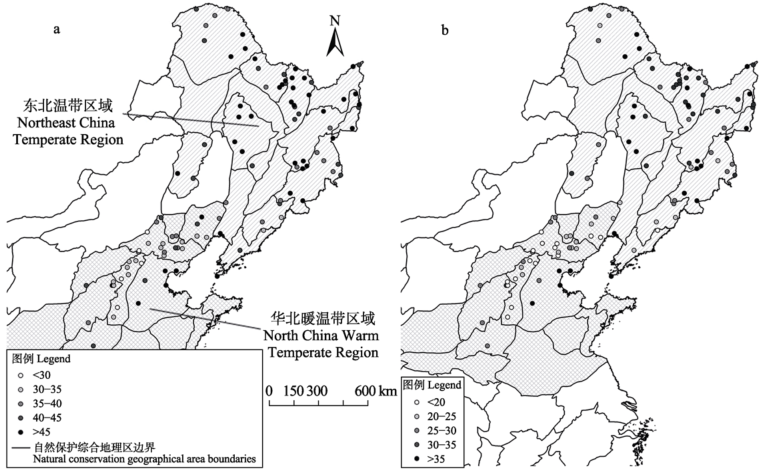
图2 东北温带区域和华北暖温带区域部分自然保护区野生动物多样性保护价值指数(a)和珍稀濒危野生动物多样性保护价值指数(b)分布图
Fig. 2 The pattern for the wild animal conservation value index (a) and rare and endangered wild animal conservation value index (b) of some nature reserves in Northeast China Temperate Region and North China Warm Temperate Region
| 自然保护地理区 Natural conservation geographical area | 自然保护区 Nature reserve (NR) | 省份 Province | NP | VP | NPT | VPT | NA | VA | NAT | VAT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 森林 Forest | ||||||||||||
| 大兴安岭北段落叶针叶林区 The North Daxing’an Mountains Deciduous Coniferous Forest Area | 岭峰 Lingfeng NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 612 | 28.20 | 7 | 7.48 | 250 | 38.92 | 41 | 24.41 | ||
| 中央站黑嘴松鸡 Zhongyangzhan Black-billed Capercaillie NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 588 | 27.69 | 11 | 8.72 | 324 | 49.26 | 61 | 35.33 | |||
| 汗马 Khan Ma NR* | 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | 526 | 26.34 | 6 | 6.63 | 265 | 42.98 | 49 | 29.87 | |||
| 盘中 Panzhong NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 414 | 23.11 | 5 | 6.32 | 238 | 39.34 | 43 | 26.38 | |||
| 北极村 Beijicun NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 414 | 22.87 | 4 | 5.29 | 226 | 41.63 | 51 | 31.56 | |||
| 大兴安岭南段森林草原区 The South Daxing’an Mountains Forest and Steppe Area | 乌兰坝 Wulanba NR* | 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | 824 | 32.57 | 5 | 6.32 | 296 | 47.30 | 50 | 32.80 | ||
| 青山 Qingshan Mountain NR* | 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | 528 | 25.57 | 2 | 3.46 | 221 | 41.30 | 41 | 29.93 | |||
| 小兴安岭北部针阔混交林区 The North Xiaoxing’an Mountains Coniferous and Broadleaf Mixed Forest Area | 胜山 Shengshan Mountain NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 726 | 30.63 | 12 | 9.17 | 282 | 44.65 | 51 | 31.56 | ||
| 友好 Youhao NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 634 | 28.91 | 11 | 8.94 | 285 | 46.68 | 45 | 33.47 | |||
| 小兴安岭南部针阔混交林区 The South Xiaoxing’an Mountains Coniferous and Broadleaf Mixed Forest Area | 平顶山 Pingding Mountain NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 724 | 31.26 | 12 | 9.17 | 253 | 40.36 | 39 | 27.13 | ||
| 太平沟 Taipinggou NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 654 | 29.17 | 10 | 8.72 | 249 | 41.22 | 43 | 28.07 | |||
| 茅兰沟 Maolangou NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 626 | 28.69 | 11 | 8.94 | 268 | 47.02 | 48 | 35.94 | |||
| 朗乡 Langxiang NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 502 | 25.87 | 10 | 8.72 | 261 | 44.33 | 44 | 32.06 | |||
| 乌马河紫貂 Wuma River Sable NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 482 | 25.50 | 10 | 8.49 | 281 | 45.65 | 51 | 32.68 | |||
| 丰林 Fenglin NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 501 | 25.00 | 6 | 6.32 | 283 | 46.94 | 48 | 35.04 | |||
| 凉水 Liangshui NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 447 | 24.56 | 9 | 8.49 | 306 | 50.16 | 58 | 37.31 | |||
| 碧水中华秋沙鸭 Bishui Chinese Merganser NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 439 | 24.31 | 9 | 8.49 | 266 | 44.63 | 40 | 31.69 | |||
| 辽河平原栽培植被与草原草甸区 Liaohe Plain Cultivate Vegetation and Steppe Area | 章古台 Zhanggutai NR* | 辽宁 Liaoning | 492 | 25.57 | 5 | 6.00 | 237 | 37.78 | 30 | 20.59 | ||
| 张广才岭-完达山针阔混交林区 Zhangguangcai Mountains-Wanda Mountains Coniferous and Broadleaf Mixed Forest Area | 大峡谷 Daxiagu NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 861 | 35.26 | 15 | 14.00 | 284 | 45.71 | 43 | 32.43 | ||
| 黄泥河 Huangni River NR* | 吉林 Jilin | 711 | 32.17 | 12 | 12.17 | 208 | 37.09 | 32 | 24.98 | |||
| 小北湖 Xiaobei Lake NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 592 | 30.92 | 7 | 10.77 | 327 | 51.43 | 57 | 37.68 | |||
| 七星砬子东北虎 Qixinglazi Siberian Tiger NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 679 | 29.75 | 11 | 8.94 | 306 | 47.69 | 53 | 34.53 | |||
| 曙光 Shuguang NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 543 | 29.09 | 13 | 13.42 | 237 | 38.73 | 34 | 25.14 | |||
| 长白山阔叶红松林区 Changbai Mountains Broadleaf Korean Pine Forest Area | 长白山 Changbai Mountain NR * | 吉林 Jilin | 1,312 | 45.19 | 26 | 19.49 | 309 | 48.86 | 52 | 35.10 | ||
| 松花江三湖 Songhua River Three Lake NR* | 吉林 Jilin | 1,236 | 42.81 | 20 | 18.55 | 331 | 57.11 | 62 | 44.54 | |||
| 穆棱东北红豆杉 Muling Japanese Yew NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 805 | 33.12 | 13 | 10.95 | 203 | 36.19 | 33 | 24.17 | |||
| 珲春东北虎 Hunchun Siberian Tiger NR* | 吉林 Jilin | 663 | 32.28 | 12 | 15.10 | 279 | 44.81 | 44 | 31.11 | |||
| 凤凰山 Fenghuang Mountain NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 607 | 30.46 | 13 | 13.27 | 310 | 50.18 | 53 | 36.99 | |||
| 汪清 Wangqing NR* | 吉林 Jilin | 538 | 29.98 | 14 | 14.56 | 233 | 39.55 | 35 | 25.85 | |||
| 牡丹峰 Mudanfeng NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 627 | 29.85 | 10 | 11.31 | 241 | 39.89 | 38 | 28.00 | |||
| 老爷岭东北虎 Laoyeling Siberian Tiger NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 550 | 27.75 | 12 | 10.77 | 238 | 40.34 | 38 | 28.07 | |||
| 龙岗山针阔混交林区 Longgang Mountains Coniferous and Broadleaf Mixed Forest Area | 老秃顶子 Laotudingzi NR* | 辽宁 Liaoning | 972 | 38.65 | 17 | 16.37 | 221 | 37.12 | 33 | 24.49 | ||
| 哈泥 Hani NR* | 吉林 Jilin | 689 | 32.11 | 13 | 13.42 | 257 | 40.72 | 38 | 26.23 | |||
| 通化石湖 Tonghua Shihu NR | 吉林 Jilin | 593 | 31.80 | 15 | 17.55 | 219 | 34.99 | 35 | 20.98 | |||
| 辽东半岛落叶阔叶林与湿地区 Liaodong Peninsula Deciduous Broadleaf Forest and Wetland Area | 白石砬子 Baishilazi NR* | 辽宁 Liaoning | 971 | 37.54 | 14 | 13.42 | 171 | 30.59 | 23 | 17.66 | ||
| 仙人洞 Xianrendong NR* | 辽宁 Liaoning | 729 | 33.05 | 9 | 12.49 | 331 | 42.63 | 41 | 22.00 | |||
| 草原草甸 Steppe and Meadow | ||||||||||||
| 大兴安岭南段森林草原区 The South Daxing’an Mountains Forest and Steppe Area | 阿鲁科尔沁 Ar Horqin NR* | 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | 261 | 17.66 | 1 | 2.00 | 184 | 40.55 | 37 | 29.73 | ||
| 湿地 Wetland | ||||||||||||
| 大兴安岭北段落叶针叶林区 The North Daxing’an Mountains Deciduous Coniferous Forest Area | 绰纳河 Chuona River NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 443 | 24.74 | 10 | 8.49 | 301 | 49.98 | 57 | 38.37 | ||
| 多布库尔 Duobukuer NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 406 | 22.69 | 6 | 6.93 | 297 | 49.40 | 54 | 37.63 | |||
| 双河 Shuanghe NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 394 | 22.38 | 5 | 6.00 | 221 | 39.24 | 45 | 27.78 | |||
| 小兴安岭北部针阔混交林区 The North Xiaoxing’an Mountains Coniferous and Broadleaf Mixed Forest Area | 库尔滨河 Kuerbin River NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 424 | 23.92 | 7 | 7.48 | 271 | 46.90 | 50 | 34.64 | ||
| 大沾河湿地 Dazhan River Wetland NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 713 | 30.35 | 11 | 8.94 | 265 | 46.50 | 51 | 34.87 | |||
| 公别拉河 Gongbiela River NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 631 | 28.64 | 9 | 8.25 | 253 | 46.11 | 46 | 34.53 | |||
| 红星湿地 Hongxing Wetland NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 342 | 21.35 | 5 | 6.32 | 259 | 44.87 | 45 | 33.17 | |||
| 翠北湿地 Cuibei Wetland NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 850 | 32.95 | 13 | 9.59 | 217 | 41.95 | 41 | 31.05 | |||
| 山口 Shankou NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 421 | 22.96 | 5 | 6.00 | 207 | 39.27 | 37 | 28.07 | |||
| 小兴安岭南部针阔混交林区 The South Xiaoxing’an Mountains Coniferous and Broadleaf Mixed Area | 乌伊岭 Wuyiling NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 707 | 30.32 | 12 | 8.94 | 311 | 48.11 | 54 | 34.93 | ||
| 细鳞河 Xilin River NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 511 | 26.12 | 7 | 7.48 | 285 | 46.31 | 51 | 33.41 | |||
| 新青白头鹤 Xinqing Hooded Crane NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 730 | 30.40 | 10 | 8.49 | 291 | 46.18 | 51 | 32.86 | |||
| 松嫩平原外围蒙古栎、草原草甸区 The Periphery of Songnen Plain Quercus mongolica and Steppe Area | 波罗湖 Boluo Lake NR* | 吉林 Jilin | 187 | 14.73 | 1 | 2.00 | 169 | 40.51 | 29 | 30.46 | ||
| 松嫩平原栽培植被与草原草甸区 Songnen Plain Cultivate Vegetation and Steppe Area | 莫莫格 Momoge NR* | 吉林 Jilin | 332 | 20.07 | 2 | 3.46 | 334 | 52.88 | 53 | 38.11 | ||
| 扎龙 Zhalong NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 436 | 23.07 | 4 | 4.90 | 314 | 52.32 | 50 | 38.83 | |||
| 乌裕尔河 Wuyuer River NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 431 | 22.56 | 1 | 2.00 | 314 | 52.28 | 50 | 38.83 | |||
| 查干湖 Chagan Lake NR* | 吉林 Jilin | 402 | 22.20 | 2 | 3.46 | 273 | 51.32 | 46 | 39.09 | |||
| 明水 Mingshui NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 452 | 23.19 | 3 | 4.47 | 271 | 45.61 | 37 | 31.43 | |||
| 辽河平原栽培植被与草原草甸区 Liaohe Plain Cultivate Vegetation and Steppe Area | 辽河口 Liaohe River Estuary NR* | 辽宁 Liaoning | 124 | 12.45 | 1 | 2.00 | 302 | 52.37 | 47 | 38.26 | ||
| 穆棱-三江平原湿地、草甸区 Muling-Sanjiang Plain Wetland and Meadow Area | 兴凯湖 Xingkai Lake NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 670 | 29.50 | 10 | 8.25 | 283 | 50.05 | 57 | 38.11 | ||
| 黑瞎子岛 Bolshoy Ussuriysky Island NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 453 | 24.06 | 8 | 7.21 | 274 | 48.15 | 48 | 35.38 | |||
| 东方红湿地 Dongfanghong Wetland NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 683 | 30.00 | 11 | 8.72 | 274 | 46.11 | 47 | 33.29 | |||
| 三环泡 Sanhuanpao NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 402 | 22.34 | 5 | 5.29 | 258 | 45.78 | 36 | 31.75 | |||
| 三江 Sanjiang NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 470 | 24.52 | 6 | 6.32 | 215 | 44.34 | 44 | 34.70 | |||
| 珍宝岛 Zhenbao Island NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 385 | 22.65 | 7 | 7.21 | 228 | 42.10 | 37 | 30.79 | |||
| 张广才岭-完达山针阔混交林区 Zhangguangcai Mountain-Wanda Mountains Coniferous and Broadleaf Mixed Forest Area | 大佳河 Dajia River NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 486 | 25.08 | 6 | 6.63 | 322 | 55.49 | 63 | 43.77 | ||
| 雁鸣湖 Yanming Lake NR* | 吉林 Jilin | 819 | 34.83 | 14 | 14.70 | 324 | 50.40 | 53 | 35.72 | |||
| 镜泊湖 Jingpo Lake NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 754 | 32.77 | 14 | 13.56 | 289 | 49.96 | 52 | 38.47 | |||
| 长白山阔叶红松林区 Changbai Mountains Broadleaf Korean Pine Forest Area | 龙湾 Longwan NR* | 吉林 Jilin | 412 | 25.55 | 9 | 12.17 | 235 | 39.65 | 36 | 26.31 | ||
| 辽东半岛落叶阔叶林与湿地区 Liaodong Peninsula Deciduous Broadleaf Forest and Wetland Area | 蛇岛老铁山 Snake Island-Laotie Mountain NR* | 辽宁 Liaoning | 560 | 28.34 | 4 | 7.75 | 331 | 51.27 | 59 | 36.33 | ||
表4 东北温带区域部分自然保护区物种多样性保护价值指数(* 截止到2015年确定的国家级自然保护区)
Table 4 The species diversity conservation value index of some nature reserves in Northeast China Temperate Region (* National nature reserve by 2015)
| 自然保护地理区 Natural conservation geographical area | 自然保护区 Nature reserve (NR) | 省份 Province | NP | VP | NPT | VPT | NA | VA | NAT | VAT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 森林 Forest | ||||||||||||
| 大兴安岭北段落叶针叶林区 The North Daxing’an Mountains Deciduous Coniferous Forest Area | 岭峰 Lingfeng NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 612 | 28.20 | 7 | 7.48 | 250 | 38.92 | 41 | 24.41 | ||
| 中央站黑嘴松鸡 Zhongyangzhan Black-billed Capercaillie NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 588 | 27.69 | 11 | 8.72 | 324 | 49.26 | 61 | 35.33 | |||
| 汗马 Khan Ma NR* | 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | 526 | 26.34 | 6 | 6.63 | 265 | 42.98 | 49 | 29.87 | |||
| 盘中 Panzhong NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 414 | 23.11 | 5 | 6.32 | 238 | 39.34 | 43 | 26.38 | |||
| 北极村 Beijicun NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 414 | 22.87 | 4 | 5.29 | 226 | 41.63 | 51 | 31.56 | |||
| 大兴安岭南段森林草原区 The South Daxing’an Mountains Forest and Steppe Area | 乌兰坝 Wulanba NR* | 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | 824 | 32.57 | 5 | 6.32 | 296 | 47.30 | 50 | 32.80 | ||
| 青山 Qingshan Mountain NR* | 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | 528 | 25.57 | 2 | 3.46 | 221 | 41.30 | 41 | 29.93 | |||
| 小兴安岭北部针阔混交林区 The North Xiaoxing’an Mountains Coniferous and Broadleaf Mixed Forest Area | 胜山 Shengshan Mountain NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 726 | 30.63 | 12 | 9.17 | 282 | 44.65 | 51 | 31.56 | ||
| 友好 Youhao NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 634 | 28.91 | 11 | 8.94 | 285 | 46.68 | 45 | 33.47 | |||
| 小兴安岭南部针阔混交林区 The South Xiaoxing’an Mountains Coniferous and Broadleaf Mixed Forest Area | 平顶山 Pingding Mountain NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 724 | 31.26 | 12 | 9.17 | 253 | 40.36 | 39 | 27.13 | ||
| 太平沟 Taipinggou NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 654 | 29.17 | 10 | 8.72 | 249 | 41.22 | 43 | 28.07 | |||
| 茅兰沟 Maolangou NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 626 | 28.69 | 11 | 8.94 | 268 | 47.02 | 48 | 35.94 | |||
| 朗乡 Langxiang NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 502 | 25.87 | 10 | 8.72 | 261 | 44.33 | 44 | 32.06 | |||
| 乌马河紫貂 Wuma River Sable NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 482 | 25.50 | 10 | 8.49 | 281 | 45.65 | 51 | 32.68 | |||
| 丰林 Fenglin NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 501 | 25.00 | 6 | 6.32 | 283 | 46.94 | 48 | 35.04 | |||
| 凉水 Liangshui NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 447 | 24.56 | 9 | 8.49 | 306 | 50.16 | 58 | 37.31 | |||
| 碧水中华秋沙鸭 Bishui Chinese Merganser NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 439 | 24.31 | 9 | 8.49 | 266 | 44.63 | 40 | 31.69 | |||
| 辽河平原栽培植被与草原草甸区 Liaohe Plain Cultivate Vegetation and Steppe Area | 章古台 Zhanggutai NR* | 辽宁 Liaoning | 492 | 25.57 | 5 | 6.00 | 237 | 37.78 | 30 | 20.59 | ||
| 张广才岭-完达山针阔混交林区 Zhangguangcai Mountains-Wanda Mountains Coniferous and Broadleaf Mixed Forest Area | 大峡谷 Daxiagu NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 861 | 35.26 | 15 | 14.00 | 284 | 45.71 | 43 | 32.43 | ||
| 黄泥河 Huangni River NR* | 吉林 Jilin | 711 | 32.17 | 12 | 12.17 | 208 | 37.09 | 32 | 24.98 | |||
| 小北湖 Xiaobei Lake NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 592 | 30.92 | 7 | 10.77 | 327 | 51.43 | 57 | 37.68 | |||
| 七星砬子东北虎 Qixinglazi Siberian Tiger NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 679 | 29.75 | 11 | 8.94 | 306 | 47.69 | 53 | 34.53 | |||
| 曙光 Shuguang NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 543 | 29.09 | 13 | 13.42 | 237 | 38.73 | 34 | 25.14 | |||
| 长白山阔叶红松林区 Changbai Mountains Broadleaf Korean Pine Forest Area | 长白山 Changbai Mountain NR * | 吉林 Jilin | 1,312 | 45.19 | 26 | 19.49 | 309 | 48.86 | 52 | 35.10 | ||
| 松花江三湖 Songhua River Three Lake NR* | 吉林 Jilin | 1,236 | 42.81 | 20 | 18.55 | 331 | 57.11 | 62 | 44.54 | |||
| 穆棱东北红豆杉 Muling Japanese Yew NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 805 | 33.12 | 13 | 10.95 | 203 | 36.19 | 33 | 24.17 | |||
| 珲春东北虎 Hunchun Siberian Tiger NR* | 吉林 Jilin | 663 | 32.28 | 12 | 15.10 | 279 | 44.81 | 44 | 31.11 | |||
| 凤凰山 Fenghuang Mountain NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 607 | 30.46 | 13 | 13.27 | 310 | 50.18 | 53 | 36.99 | |||
| 汪清 Wangqing NR* | 吉林 Jilin | 538 | 29.98 | 14 | 14.56 | 233 | 39.55 | 35 | 25.85 | |||
| 牡丹峰 Mudanfeng NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 627 | 29.85 | 10 | 11.31 | 241 | 39.89 | 38 | 28.00 | |||
| 老爷岭东北虎 Laoyeling Siberian Tiger NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 550 | 27.75 | 12 | 10.77 | 238 | 40.34 | 38 | 28.07 | |||
| 龙岗山针阔混交林区 Longgang Mountains Coniferous and Broadleaf Mixed Forest Area | 老秃顶子 Laotudingzi NR* | 辽宁 Liaoning | 972 | 38.65 | 17 | 16.37 | 221 | 37.12 | 33 | 24.49 | ||
| 哈泥 Hani NR* | 吉林 Jilin | 689 | 32.11 | 13 | 13.42 | 257 | 40.72 | 38 | 26.23 | |||
| 通化石湖 Tonghua Shihu NR | 吉林 Jilin | 593 | 31.80 | 15 | 17.55 | 219 | 34.99 | 35 | 20.98 | |||
| 辽东半岛落叶阔叶林与湿地区 Liaodong Peninsula Deciduous Broadleaf Forest and Wetland Area | 白石砬子 Baishilazi NR* | 辽宁 Liaoning | 971 | 37.54 | 14 | 13.42 | 171 | 30.59 | 23 | 17.66 | ||
| 仙人洞 Xianrendong NR* | 辽宁 Liaoning | 729 | 33.05 | 9 | 12.49 | 331 | 42.63 | 41 | 22.00 | |||
| 草原草甸 Steppe and Meadow | ||||||||||||
| 大兴安岭南段森林草原区 The South Daxing’an Mountains Forest and Steppe Area | 阿鲁科尔沁 Ar Horqin NR* | 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | 261 | 17.66 | 1 | 2.00 | 184 | 40.55 | 37 | 29.73 | ||
| 湿地 Wetland | ||||||||||||
| 大兴安岭北段落叶针叶林区 The North Daxing’an Mountains Deciduous Coniferous Forest Area | 绰纳河 Chuona River NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 443 | 24.74 | 10 | 8.49 | 301 | 49.98 | 57 | 38.37 | ||
| 多布库尔 Duobukuer NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 406 | 22.69 | 6 | 6.93 | 297 | 49.40 | 54 | 37.63 | |||
| 双河 Shuanghe NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 394 | 22.38 | 5 | 6.00 | 221 | 39.24 | 45 | 27.78 | |||
| 小兴安岭北部针阔混交林区 The North Xiaoxing’an Mountains Coniferous and Broadleaf Mixed Forest Area | 库尔滨河 Kuerbin River NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 424 | 23.92 | 7 | 7.48 | 271 | 46.90 | 50 | 34.64 | ||
| 大沾河湿地 Dazhan River Wetland NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 713 | 30.35 | 11 | 8.94 | 265 | 46.50 | 51 | 34.87 | |||
| 公别拉河 Gongbiela River NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 631 | 28.64 | 9 | 8.25 | 253 | 46.11 | 46 | 34.53 | |||
| 红星湿地 Hongxing Wetland NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 342 | 21.35 | 5 | 6.32 | 259 | 44.87 | 45 | 33.17 | |||
| 翠北湿地 Cuibei Wetland NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 850 | 32.95 | 13 | 9.59 | 217 | 41.95 | 41 | 31.05 | |||
| 山口 Shankou NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 421 | 22.96 | 5 | 6.00 | 207 | 39.27 | 37 | 28.07 | |||
| 小兴安岭南部针阔混交林区 The South Xiaoxing’an Mountains Coniferous and Broadleaf Mixed Area | 乌伊岭 Wuyiling NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 707 | 30.32 | 12 | 8.94 | 311 | 48.11 | 54 | 34.93 | ||
| 细鳞河 Xilin River NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 511 | 26.12 | 7 | 7.48 | 285 | 46.31 | 51 | 33.41 | |||
| 新青白头鹤 Xinqing Hooded Crane NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 730 | 30.40 | 10 | 8.49 | 291 | 46.18 | 51 | 32.86 | |||
| 松嫩平原外围蒙古栎、草原草甸区 The Periphery of Songnen Plain Quercus mongolica and Steppe Area | 波罗湖 Boluo Lake NR* | 吉林 Jilin | 187 | 14.73 | 1 | 2.00 | 169 | 40.51 | 29 | 30.46 | ||
| 松嫩平原栽培植被与草原草甸区 Songnen Plain Cultivate Vegetation and Steppe Area | 莫莫格 Momoge NR* | 吉林 Jilin | 332 | 20.07 | 2 | 3.46 | 334 | 52.88 | 53 | 38.11 | ||
| 扎龙 Zhalong NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 436 | 23.07 | 4 | 4.90 | 314 | 52.32 | 50 | 38.83 | |||
| 乌裕尔河 Wuyuer River NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 431 | 22.56 | 1 | 2.00 | 314 | 52.28 | 50 | 38.83 | |||
| 查干湖 Chagan Lake NR* | 吉林 Jilin | 402 | 22.20 | 2 | 3.46 | 273 | 51.32 | 46 | 39.09 | |||
| 明水 Mingshui NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 452 | 23.19 | 3 | 4.47 | 271 | 45.61 | 37 | 31.43 | |||
| 辽河平原栽培植被与草原草甸区 Liaohe Plain Cultivate Vegetation and Steppe Area | 辽河口 Liaohe River Estuary NR* | 辽宁 Liaoning | 124 | 12.45 | 1 | 2.00 | 302 | 52.37 | 47 | 38.26 | ||
| 穆棱-三江平原湿地、草甸区 Muling-Sanjiang Plain Wetland and Meadow Area | 兴凯湖 Xingkai Lake NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 670 | 29.50 | 10 | 8.25 | 283 | 50.05 | 57 | 38.11 | ||
| 黑瞎子岛 Bolshoy Ussuriysky Island NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 453 | 24.06 | 8 | 7.21 | 274 | 48.15 | 48 | 35.38 | |||
| 东方红湿地 Dongfanghong Wetland NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 683 | 30.00 | 11 | 8.72 | 274 | 46.11 | 47 | 33.29 | |||
| 三环泡 Sanhuanpao NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 402 | 22.34 | 5 | 5.29 | 258 | 45.78 | 36 | 31.75 | |||
| 三江 Sanjiang NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 470 | 24.52 | 6 | 6.32 | 215 | 44.34 | 44 | 34.70 | |||
| 珍宝岛 Zhenbao Island NR* | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 385 | 22.65 | 7 | 7.21 | 228 | 42.10 | 37 | 30.79 | |||
| 张广才岭-完达山针阔混交林区 Zhangguangcai Mountain-Wanda Mountains Coniferous and Broadleaf Mixed Forest Area | 大佳河 Dajia River NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 486 | 25.08 | 6 | 6.63 | 322 | 55.49 | 63 | 43.77 | ||
| 雁鸣湖 Yanming Lake NR* | 吉林 Jilin | 819 | 34.83 | 14 | 14.70 | 324 | 50.40 | 53 | 35.72 | |||
| 镜泊湖 Jingpo Lake NR | 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 754 | 32.77 | 14 | 13.56 | 289 | 49.96 | 52 | 38.47 | |||
| 长白山阔叶红松林区 Changbai Mountains Broadleaf Korean Pine Forest Area | 龙湾 Longwan NR* | 吉林 Jilin | 412 | 25.55 | 9 | 12.17 | 235 | 39.65 | 36 | 26.31 | ||
| 辽东半岛落叶阔叶林与湿地区 Liaodong Peninsula Deciduous Broadleaf Forest and Wetland Area | 蛇岛老铁山 Snake Island-Laotie Mountain NR* | 辽宁 Liaoning | 560 | 28.34 | 4 | 7.75 | 331 | 51.27 | 59 | 36.33 | ||
| 1 | Abell R, Thieme ML, Revenga C, Bryer M, Kottelat M, Bogutskaya N, Coad B, Mandrak N, Balderas SC, Bussing W, Stiassny MLJ, Skelton P, Allen GR, Unmack P, Naseka A, Ng R, Sindorf N, Robertson J, Armijo E, Higgins JV, Heibel TJ, Wikramanayake E, Olson D, López HL, Reis RE, Lundberg JG, Pérez MHS, Petry P (2008) Freshwater ecoregions of the world: a new map of biogeographic units for freshwater biodiversity conservation. BioScience, 58, 403-414. |
| 2 | Brooks TM, Mittermeier RA, da Fonseca GA, Gerlach J, Hoffmann M, Lamoreux JF, Mittermeier CG, Pilgrim JD, Rodrigues ASL (2006) Global biodiversity conservation priorities. Science, 313, 58-61. |
| 3 | Butchart SHM, Walpole M, Collen B, Strien AV, Scharlemann JPW, Almond REA, Baillie JEM, Bomhard B, Brown C, Bruno J, Carpenter KE, Carr GM, Chanson J, Chenery AM, Csirke J, Davidson NC, Dentener F, Foster M, Galli A, Galloway JN, Genovesi P, Gregory RD, Hockings M, Kapos V, Lamarque JF, Leverington F, Loh J, McGeoch MA, McRae L, Minasyan A, Morcillo MH, Oldfield TEE, Pauly D, Quader S, Revenga C, Sauer JR, Skolnik B, Spear D, Stanwell-Smith D, Stuart SN, Symes A, Tierney M, Tyrrell TD, Vié JC, Watson R (2010) Global biodiversity: indicators of recent declines. Science, 328, 1164-1168. |
| 4 | Ceballos G, Rodríguez P, Medellín RA (2008) Assessing conservation priorities in megadiverse Mexico: mammalian diversity, endemicity, and endangerment. Ecological Applications, 8, 8-17. |
| 5 | Clarke KR, Warwick RM (1998) A taxonomic distinctness index and its statistical properties. Journal of Applied Ecology, 35, 523-531. |
| 6 | Cui GF, Sun R (2014) Technique of Conservation Priority Assessment of Wetland Nature Reserves. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing.(in Chinese) |
| [崔国发, 孙锐 (2014) 湿地自然保护区保护优先性评价技术. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| 7 | Duelli P, Obrist MK (2003) Biodiversity indicators: the choice of values and measures. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 98, 87-98. |
| 8 | Freitag S, Jaarsveld ASV, Biggs HC (1997) Ranking priority biodiversity areas: an iterative conservation value-based approach. Biological Conservation, 82, 263-272. |
| 9 | Gibbs D, While A, Jonas AEG (2007) Governing nature conservation: the European Union Habitats Directive and conflict around estuary management. Environment and Planning A, 39, 339-358. |
| 10 | Guo ZL, Cui GF (2014) The comprehensive geographical regionalization of China supporting natural conservation. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34, 1284-1294.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭子良, 崔国发 (2014) 中国自然保护综合地理区划. 生态学报 34, 1284-1294.] | |
| 11 | Humphries CJ, And PHW, Wright RIV (1995) Measuring biodiversity value for conservation. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 26, 93-111. |
| 12 | Jenkins CN, Joppa L (2009) Expansion of the global terrestrial protected area system. Biological Conservation, 142, 2166-2174. |
| 13 | Jiang ZG, Jiang JP, Wang YZ, Zhang E, Zhang YY, Li LL, Xie F, Cai B, Cao L, Zheng GM, Dong L, Zhang ZW, Ding P, Luo ZH, Ding CQ, Ma ZJ, Tang SH, Cao WX, Li CW, Hu HJ, Ma Y, Wu Y, Wang YX, Zhou KY, Liu SY, Chen YY, Li JT, Feng ZJ, Wang Y, Wang B, Li C, Song XL, Cai L, Zang CX, Zeng Y, Meng ZB, Fang HX, Ping XG (2016) Red list of China’s vertebrates. Biodiversity Science, 24, 500-551.(in Chinese and in English) |
| [蒋志刚, 江建平, 王跃招, 张鹗, 张雁云, 李立立, 谢锋, 蔡波, 曹亮, 郑光美, 董路, 张正旺, 丁平, 罗振华, 丁长青, 马志军, 汤宋华, 曹文宣, 李春旺, 胡慧建, 马勇, 吴毅, 王应祥, 周开亚, 刘少英, 陈跃英, 李家堂, 冯祚建, 王燕, 王斌, 李成, 宋雪琳, 蔡蕾, 臧春鑫, 曾岩, 孟智斌, 方红霞, 平晓鸽 (2016) 中国脊椎动物红色名录. 生物多样性 24, 500-551.] | |
| 14 | Li WH, Zhao XY (1984) Nature Reserves of China. The Commercial Press, Beijing.(in Chinese) |
| [李文华, 赵献英 (1984) 中国的自然保护区. 商务印书馆, 北京.] | |
| 15 | Li XY (2011) Conservation Value Evaluation and Reasonable Distribution of National Nature Reserve for Forest. PhD dissertation, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李霄宇 (2011) 国家级森林类型自然保护区保护价值评价及合理布局研究. 博士学位论文, 北京林业大学, 北京.] | |
| 16 | Luan XF, Xie YM, Du DC, Xu HF (2002) The ecological and management evaluation of Chongming Dongtan Birds Nature Reserve. Journal of Shanghai Normal University (Nature Sciences), 31(3), 73-79.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [栾晓峰, 谢一民, 杜德昌, 徐宏发 (2002) 上海崇明东滩鸟类自然保护区生态环境及有效管理评价. 上海师范大学学报(自然科学版) 31(3), 73-79.] | |
| 17 | Ma JZ, Rong K, Cheng K (2012) Research and practice on biodiversity in situ conservation in China: progress and prospect. Biodiversity Science, 20, 551-558.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马建章, 戎可, 程鲲 (2012) 中国生物多样性就地保护的研究与实践. 生物多样性 20, 551-558.] | |
| 18 | Ma KP (1993) On the concept of biodiversity. Chinese Biodiversity, 1, 20-22.(in Chinese) |
| [马克平 (1993) 试论生物多样性的概念. 生物多样性 1, 20-22.] | |
| 19 | Margules CR, Pressey RL (2000) Systematic conservation planning. Nature, 405, 243-253. |
| 20 | Margules CR, Pressey RL, Williams PH (2002) Representing biodiversity: data and procedures for identifying priority areas for conservation. Journal of Biosciences, 27, 309-326. |
| 21 | Mcgillivray D (2012) Compensating biodiversity loss: The EU Commission’s approach to compensation under article 6 of the habitats directive. Journal of Environmental Law, 24, 417-450. |
| 22 | McIntosh RP (1967) An index of diversity and the relation of certain concepts to diversity. Ecology, 48, 392-404. |
| 23 | Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences (2013) Chinese Biodiversity Red List: Higher Plant Volume. (in Chinese) |
| [中华人民共和国环境保护部和中国科学院 (2013) 中国生物多样性红色名录——高等植物卷.]. (accessed on 2015-12-10 | |
| 24 | Naeem S, Thompson LJ, Lawler SP, Lawton JH, Woodfin RM (1994) Declining biodiversity can alter the performance of ecosystem. Nature, 368, 734-737. |
| 25 | Nelson E, Mendoza G, Regetz J, Polasky S, Tallis H, Cameron DR, Chan KMA, Daily GC, Goldstein J, Kareiva PM, Lonsdorf E, Naidoo R, Ricketts TH, Shaw MR (2009) Modeling multiple ecosystem services, biodiversity conservation, commodity production, and tradeoffs at landscape scales. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 7, 4-11. |
| 26 | Prendergast JR, Quinn RM, Lawton JH, Eversham BC, Gibbons DW (1993) Rare species, the coincidence of diversity hotspots and conservation strategies. Nature, 365, 335-337. |
| 27 | Primack RB, Ma KP, Jiang ZG (2014) Conservation Biology. Science Press, Beijing.(in Chinese) |
| [Primack RB, 马克平, 蒋志刚 (2014) 保护生物学. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 28 | Qi JZ, Zhang JC (2004) Ecological evaluation for Hunchun Nature Reserve. Journal of Beihua University (Natural Science), 5, 453-457.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [戚继忠, 张吉春 (2004) 珲春自然保护区生态评价. 北华大学学报(自然科学版) 5, 453-457.] | |
| 29 | Rands MR, Adams WM, Bennun L, Butchart SH, Clements A, Coomes D, Entwistle A, Hodge I, Kapos V, Scharlemann JP, Sutherland WJ, Vira B (2010) Biodiversity conservation: challenges beyond 2010. Science, 329, 1298-1303. |
| 30 | Song XJ, Zhao TR (1997) Study on ecological evaluation of Songshan Nature Reserve. Environmental Science, 18(4), 76-78.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宋秀杰, 赵彤润 (1997) 松山自然保护区的生态评价. 环境科学 18(4), 76-78.] | |
| 31 | Sun R, Cui GF, Lei T, Zheng YM (2013) An evaluation index system classifying the conservation value of wetland nature reserves based on AHP. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 1952-1963.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙锐, 崔国发, 雷霆, 郑姚闽 (2013) 湿地自然保护区保护价值评价方法. 生态学报 33, 1952-1963.] | |
| 32 | Tilman D, Wedin D, Knops J (1996) Productivity and sustainability influenced by biodiversity in grassland ecosystems. Nature, 379, 718-720. |
| 33 | Timonen J, Gustafsson L, Kotiaho JS, Mönkkönen M (2011) Hotspots in cold climate: conservation value of woodland key habitats in boreal forests. Biological Conservation, 144, 2061-2067. |
| 34 | Veríssimo A, Júnior CS, Stone S, Uhl C (1998) Zoning of timber extraction in the Brazilian Amazon. Conservation Biology, 12, 128-136. |
| 35 | Wang B, Song QF (2012) Value assessing methods of species diversity conservation in forest ecosystem. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 34, 155-160.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王兵, 宋庆丰 (2012) 森林生态系统物种多样性保育价值评估方法. 北京林业大学学报 34, 155-160.] | |
| 36 | Wei YJ, Guo ZL, Cui GF (2014) Assessment methods on biodiversity conservation value in nature reserves: research progress. World Forestry Research, 27(5), 37-42.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [魏永久, 郭子良, 崔国发 (2014) 国内外保护区生物多样性保护价值评价方法研究进展. 世界林业研究 27(5), 37-42.] | |
| 37 | Whittaker RH (1972) Evolution and measurement of species diversity. Taxon, 21, 213-251. |
| 38 | Zhang HQ, Zhang WH (2009) Conservation Biology. Science Press, Beijing. |
| (in Chinese) [张恒庆, 张文辉 (2009) 保护生物学. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 39 | Zhang Z, Zhu L, Zhang JW, Wang X, Zhang T, Zhu T (2000) Study on ecological quality evaluation method for wetland in China. China Environmental Science, 20(Suppl.), 55-58.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张峥, 朱琳, 张建文, 王欣, 张涛, 朱彤 (2000) 我国湿地生态质量评价方法的研究. 中国环境科学 20(增刊), 55-58.] | |
| 40 | Zheng YW, Xue DY, Zhang GS (1994) Study on ecological evaluation criteria and standards for nature reserves in China. Rural Eco-Environment, 10(3), 22-25.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郑允文, 薛达元, 张更生 (1994) 我国自然保护区生态评价指标和评价标准. 农村生态环境 10(3), 22-25.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [3] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [4] | 周昊, 王茗毅, 张楚格, 肖治术, 欧阳芳. 昆虫旅馆在独栖蜂多样性保护中的现状与挑战[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24472-. |
| [5] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [6] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [7] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [8] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [9] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [10] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [11] | 徐欢, 辛凤飞, 施宏亮, 袁琳, 薄顺奇, 赵欣怡, 邓帅涛, 潘婷婷, 余婧, 孙赛赛, 薛程. 生态修复技术集成应用对长江口北支生境与鸟类多样性提升效果评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24478-. |
| [12] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [13] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [14] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [15] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()