



Biodiv Sci ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (12): 1298-1308. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019157 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019157
• Original Papers: Animal Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Shuoran Liu1,2,3,Daode Yang1,*( ),Xianfu Li2,3,4,Lu Tan4,Jun Sun5,Xiaoyang He5,Wenshu Yang5,Guopeng Ren2,3,Davide Fornacca2,3,Qinghua Cai4,Wen Xiao2,3,*(
),Xianfu Li2,3,4,Lu Tan4,Jun Sun5,Xiaoyang He5,Wenshu Yang5,Guopeng Ren2,3,Davide Fornacca2,3,Qinghua Cai4,Wen Xiao2,3,*( )
)
Received:2019-05-08
Accepted:2019-09-26
Online:2019-12-20
Published:2020-02-22
Contact:
Yang Daode,Xiao Wen
Shuoran Liu, Daode Yang, Xianfu Li, Lu Tan, Jun Sun, Xiaoyang He, Wenshu Yang, Guopeng Ren, Davide Fornacca, Qinghua Cai, Wen Xiao. Diversity in benthic and environmental characteristics on alpine micro-waterbodies and stream ecosystems in northwest Yunnan[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(12): 1298-1308.
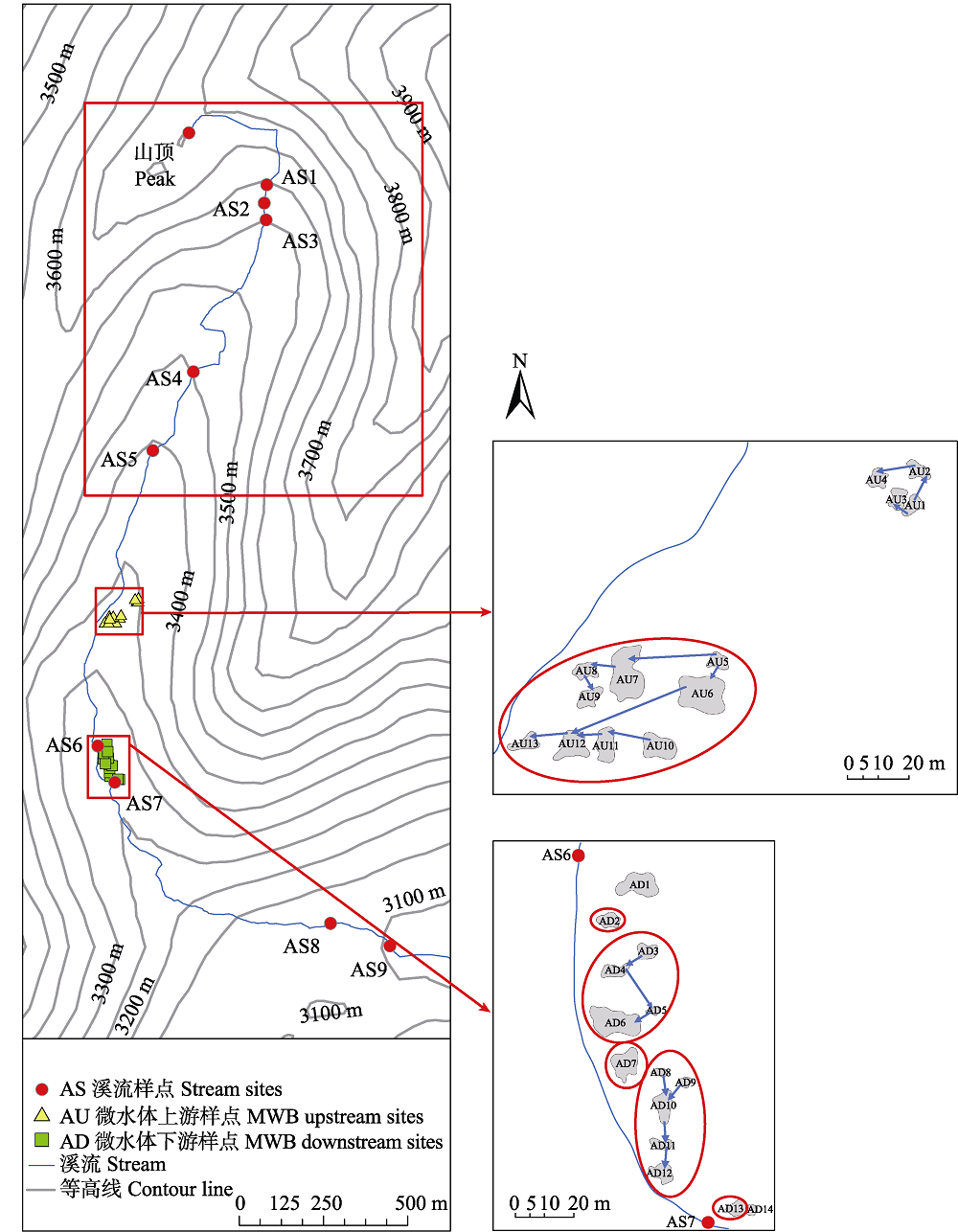
Fig. 1 Research area and sampling sites. The micro-waterbodies (MWB) which are circled indicate that the water flow from the micro-waterbody cascades is running into the stream finally.
| 环境因子 Environmental variables | 微水体 Micro-waterbody | 溪流 Stream | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 Min. | 最大值 Max. | 平均值 ± 标准差 Mean ± SD | 最小值 Min. | 最大值 Max. | 平均值 ± 标准差 Mean ± SD | |
| 海拔 Alt (m) ns2 | 3,266.00 | 3,332.00 | 3,299.70 ± 27.34 | 3,087.00 | 3,586.00 | 3,364.90 ± 188.82 |
| 电导率 Cond (μs/cm) **2 | 2.94 | 10.45 | 5.12 ± 1.33 | 10.82 | 34.50 | 17.54 ± 8.84 |
| 溶解氧含量 DO (mg/L) **1 | 3.13 | 7.51 | 5.68 ± 0.92 | 6.22 | 7.18 | 6.72 ± 0.27 |
| pH值 pH **1 | 5.48 | 6.20 | 5.84 ± 0.24 | 5.80 | 6.55 | 6.23 ± 0.26 |
| 面积 Area (m2) none | 3.00 | 160.00 | 26.15 ± 33.65 | / | / | / |
| 水深 Depth (cm) *1 | 8.00 | 43.00 | 27.70 ± 10.09 | 6.00 | 26.00 | 18.33 ± 6.48 |
| 底泥深度 BSD (cm) none | 9.50 | 58.00 | 26.09 ± 13.02 | / | / | / |
| 浊度 Turb (NTU) ns1 | 0.00 | 3.70 | 1.42 ± 1.08 | 0.00 | 2.40 | 0.98 ± 1.06 |
| 总氮 TN (mg/L) ns1 | 0.096 | 0.729 | 0.300 ± 0.170 | 0.115 | 0.445 | 0.280 ± 0.110 |
| 总磷 TP (mg/L) ns1 | 0.024 | 0.104 | 0.046 ± 0.016 | 0.036 | 0.068 | 0.050 ± 0.010 |
| 化学需氧量 COD (mg/L) *1 | 0.160 | 4.730 | 2.150 ± 1.290 | 0.160 | 5.056 | 3.320 ± 1.420 |
| 总有机碳含量 TOC (mg/L) ns1 | 0.924 | 7.590 | 4.270 ± 1.640 | 3.043 | 6.963 | 4.800 ± 1.070 |
| 溪流宽度 Width (m) none | / | / | / | 0.50 | 5.30 | 2.53 ±1.78 |
| 溪流流速 FV (m/s) none | / | / | / | 0.16 | 0.93 | 0.58 ± 0.31 |
Table 1 List of the descriptive statistics and difference in environmental variables between stream and micro-waterbody
| 环境因子 Environmental variables | 微水体 Micro-waterbody | 溪流 Stream | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 Min. | 最大值 Max. | 平均值 ± 标准差 Mean ± SD | 最小值 Min. | 最大值 Max. | 平均值 ± 标准差 Mean ± SD | |
| 海拔 Alt (m) ns2 | 3,266.00 | 3,332.00 | 3,299.70 ± 27.34 | 3,087.00 | 3,586.00 | 3,364.90 ± 188.82 |
| 电导率 Cond (μs/cm) **2 | 2.94 | 10.45 | 5.12 ± 1.33 | 10.82 | 34.50 | 17.54 ± 8.84 |
| 溶解氧含量 DO (mg/L) **1 | 3.13 | 7.51 | 5.68 ± 0.92 | 6.22 | 7.18 | 6.72 ± 0.27 |
| pH值 pH **1 | 5.48 | 6.20 | 5.84 ± 0.24 | 5.80 | 6.55 | 6.23 ± 0.26 |
| 面积 Area (m2) none | 3.00 | 160.00 | 26.15 ± 33.65 | / | / | / |
| 水深 Depth (cm) *1 | 8.00 | 43.00 | 27.70 ± 10.09 | 6.00 | 26.00 | 18.33 ± 6.48 |
| 底泥深度 BSD (cm) none | 9.50 | 58.00 | 26.09 ± 13.02 | / | / | / |
| 浊度 Turb (NTU) ns1 | 0.00 | 3.70 | 1.42 ± 1.08 | 0.00 | 2.40 | 0.98 ± 1.06 |
| 总氮 TN (mg/L) ns1 | 0.096 | 0.729 | 0.300 ± 0.170 | 0.115 | 0.445 | 0.280 ± 0.110 |
| 总磷 TP (mg/L) ns1 | 0.024 | 0.104 | 0.046 ± 0.016 | 0.036 | 0.068 | 0.050 ± 0.010 |
| 化学需氧量 COD (mg/L) *1 | 0.160 | 4.730 | 2.150 ± 1.290 | 0.160 | 5.056 | 3.320 ± 1.420 |
| 总有机碳含量 TOC (mg/L) ns1 | 0.924 | 7.590 | 4.270 ± 1.640 | 3.043 | 6.963 | 4.800 ± 1.070 |
| 溪流宽度 Width (m) none | / | / | / | 0.50 | 5.30 | 2.53 ±1.78 |
| 溪流流速 FV (m/s) none | / | / | / | 0.16 | 0.93 | 0.58 ± 0.31 |
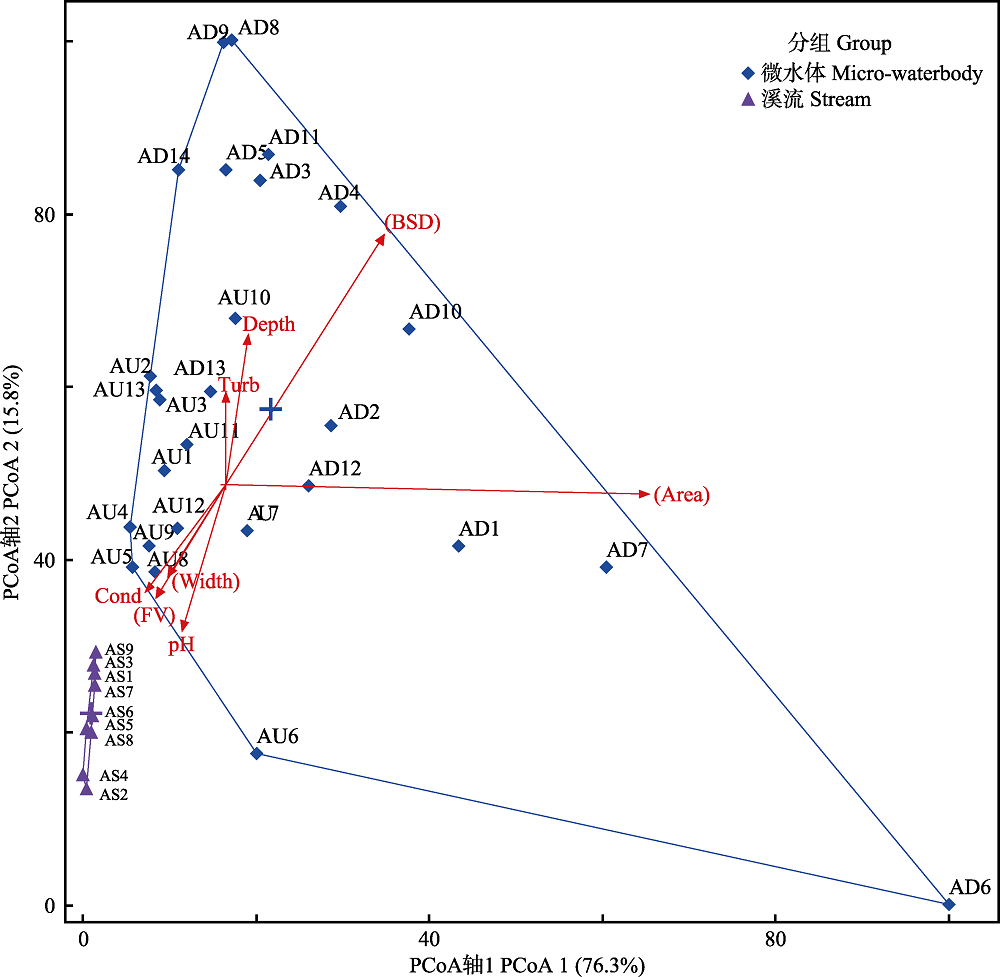
Fig. 2 Biplot of PCoA calculated based on environmental factors. AS indicates stream sites, AU and AD indicate micro-waterbody sites. Depth, Water depth; Area, Waterbody surface area; Width, Stream width; FV, Flow velocity; Cond, Conductivity; Turb, Turbidity.
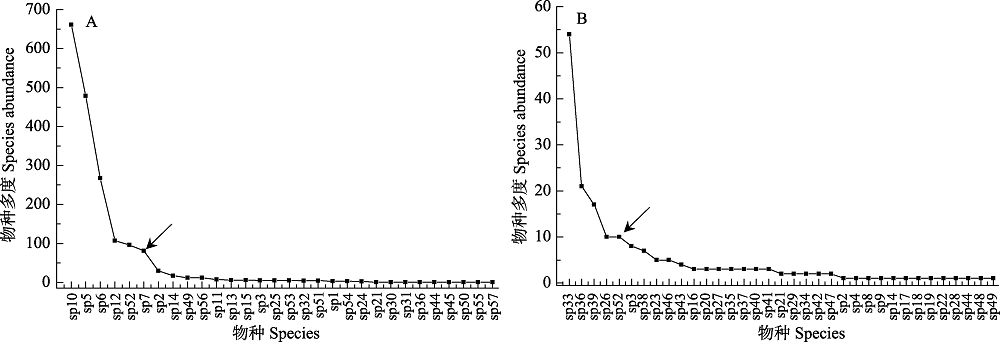
Fig. 3 Species abundance ranking curves for alpine micro-waterbody (A) and stream (B). Arrows indicate the inflection point of the curve between the dominant taxa and rare taxa. X axis refers to the species order in Appendix 1.
| 微水体 Micro-waterbody | 溪流 Stream | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 Min. | 最大值 Max. | 平均值 ± 标准差 Mean ± SD | 最小 值 Min. | 最大 值 Max. | 平均值 ± 标准差 Mean ± SD | |
| S ns1 | 3.00 | 10.00 | 6.26 ± 2.07 | 3.00 | 12.00 | 8.67 ± 3.43 |
| H' *1 | 0.882 | 1.649 | 1.240 ± 0.250 | 1.011 | 2.265 | 1.720 ± 0.460 |
| FDis **1 | 0.000 | 0.469 | 0.220 ± 0.130 | 0.544 | 0.968 | 0.820 ± 0.130 |
Table 2 List of the species richness, species diversity and functional diversity between stream and micro-waterbody
| 微水体 Micro-waterbody | 溪流 Stream | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 Min. | 最大值 Max. | 平均值 ± 标准差 Mean ± SD | 最小 值 Min. | 最大 值 Max. | 平均值 ± 标准差 Mean ± SD | |
| S ns1 | 3.00 | 10.00 | 6.26 ± 2.07 | 3.00 | 12.00 | 8.67 ± 3.43 |
| H' *1 | 0.882 | 1.649 | 1.240 ± 0.250 | 1.011 | 2.265 | 1.720 ± 0.460 |
| FDis **1 | 0.000 | 0.469 | 0.220 ± 0.130 | 0.544 | 0.968 | 0.820 ± 0.130 |
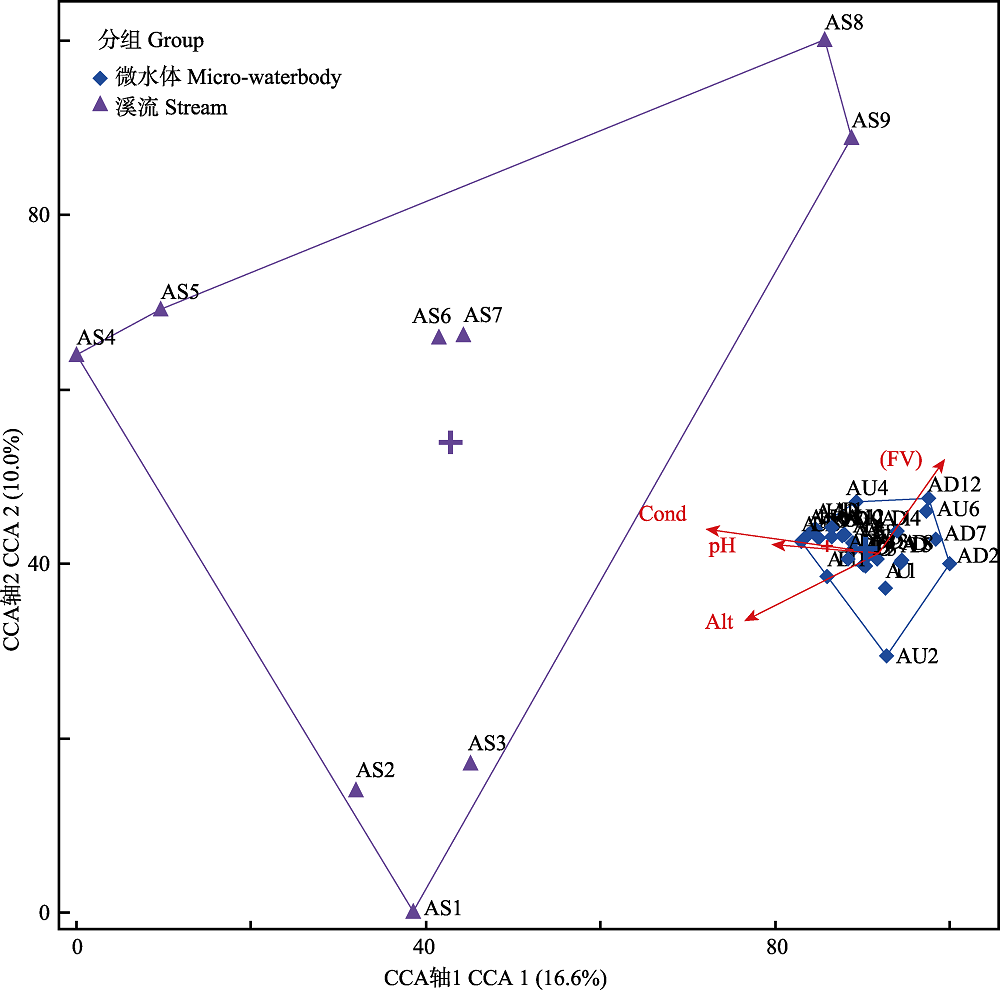
Fig. 6 Biplot of CCA which calculated based on the benthic community data and environmental factors. hydrogen ion concentration (pH), flow velocity (FV) and conductivity (Cond). AS indicates stream sites, AU and AD indicate micro-waterbody sites. Alt, Altitude; FV, Flow velocity; Cond, Conductivity.
| [1] | Altermatt F ( 2013) Diversity in riverine metacommunities: A network perspective. Aquatic Ecology, 47, 365-377. |
| [2] | Bazzanti M, Bella VD, Seminara M ( 2003) Factors affecting macroinvertebrate communities in astatic ponds in central Italy. Journal of Freshwater Ecology, 18, 537-548. |
| [3] | Belletti B, Rinaldi M, Buijse AD, Gurnell AM, Mosselman E ( 2015) A review of assessment methods for river hydromorphology. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73, 2079-2100. |
| [4] | Belmar O, Velasco J, Gutierrezcanovas C, Melladodiaz A, Millan A, Wood PJ ( 2013) The influence of natural flow regimes on macroinvertebrate assemblages in a semiarid Mediterranean basin. Ecohydrology, 6, 363-379. |
| [5] | Biggs J, Williams P, Whitfield M, Nicolet P, Weatherby AJ ( 2005) 15 years of pond assessment in Britain: Results and lessons learned from the work of pond conservation. Aquatic Conservation-Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 15, 693-714. |
| [6] | Bogan MT, Boersma KS, Lytle DA ( 2013) Flow intermittency alters longitudinal patterns of invertebrate diversity and assemblage composition in an arid-land stream network. Freshwater Biology, 58, 1016-1028. |
| [7] | Bonada N, Rieradevall M, Prat N ( 2007) Macroinvertebrate community structure and biological traits related to flow permanence in a Mediterranean river network. Hydrobiologia, 589, 91-106. |
| [8] | Borcard D, Legendre P ( 2002) All-scale spatial analysis of ecological data by means of principal coordinates of neighbour matrices. Ecological Modelling, 153, 51-68. |
| [9] | Carrara F, Altermatt F, Rodrigueziturbe I, Rinaldo A ( 2012) Dendritic connectivity controls biodiversity patterns in experimental metacommunities. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 109, 5761-5766. |
| [10] | Carrara F, Rinaldo A, Giometto A, Altermatt F ( 2014) Complex interaction of dendritic connectivity and hierarchical patch size on biodiversity in river-like landscapes. The American Naturalist, 183, 13-25. |
| [11] | Chakona A, Phiri C, Magadza CH, Brendonck L ( 2008) The influence of habitat structure and flow permanence on macroinvertebrate assemblages in temporary rivers in northwestern Zimbabwe. Hydrobiologia, 607, 199-209. |
| [12] | Dudgeon D, Arthington AH, Gessner MO, Kawabata ZI, Knowler D, Leveque C, Naiman RJ, Prieur-Richard AH, Soto D, Stiassny MLJ, Sullivan CA ( 2006) Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biological Reviews, 81, 163-182. |
| [13] | Henriques-Oliveira AL, Nessimian JL ( 2010) Aquatic macroinvertebrate diversity and composition in streams along an altitudinal gradient in southeastern Brazil. Biota Neotropica, 10, 115-128. |
| [14] | Hoffman M, Koenig K, Bunting G, Costanza J, Kristen JM ( 2016) Biodiversity Hotspots (version 2016.1). . (accessed on 2019-03-18) |
| [15] | Laliberte E, Legendre PA ( 2010) Distance-based framework for measuring functional diversity from multiple traits. Ecology, 91, 299-305. |
| [16] | Leibold MA, Holyoak M, Mouquet N, Amarasekare P, Chase JM, Hoopes MF, Holt RD, Shurin JB, Tilman D, Loreau M, Gonzalez A ( 2004) The metacommunity concept: A framework for multi-scale community ecology. Ecology Letters, 7, 601-613. |
| [17] | Liu SR, He XY, Yang WS, Ren GP, Li YP, Zhou J, Cai QH, Xiao W ( 2017) Spatial distribution and significance of high mountain micro-waterbodies in northwestern Yunnan, China. Journal of Hydroecology, 38, 18-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘硕然, 和晓阳, 杨文书, 任国鹏, 李延鹏, 周俊, 蔡庆华, 肖文 ( 2017) 滇西北高山微水体空间分布格局及研究意义初探. 水生态学杂志, 38, 18-23.] | |
| [18] | Liu SR, Li YP, Yan JG, Xiao W ( 2018) A Waterbody, Organisms and Sediment Sampling Equipment Used for Different Kinds of Water Environments. Chinese Patent. ZL201510837357.X. 2018-10-19. (in Chinese) |
| [ 刘硕然, 李延鹏, 闫家国, 肖文 ( 2018) 一种适用于不同水体环境的水体、生物、沉积物采集器. 中国专利: ZL201510837357. X. 2018-10-19.] | |
| [19] | Liu SR, Lu T, Yang DD, Ren GP, He XY, Yang WS, Cai QH, Xiao W ( 2018) Spatiotemporal environmental heterogeneity of alpine micro-waterbodies. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 27, 8088-8095. |
| [20] | McCune B, Mefford MJ ( 2016) PC-ORD Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data, Version 7.04. MjM Software, Gleneden Beach, Oregon. |
| [21] | Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China ( 2017) HJ 828-2017. Water Quality Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand: Dichromate Method . China Environmental Press, Beijing. (in Chinese with) |
| [ 中华人民共和国生态环境部 ( 2017) HJ 828-2017 水质化学需氧量的测定: 重铬酸盐法. 中国环境出版社, 北京.] | |
| [22] | Miserendino ML ( 2001) Macroinvertebrate assemblages in Andean Patagonian rivers and streams: Environmental relationships. Hydrobiologia, 444, 147-158. |
| [23] | Myers N ( 1988) Threatened biotas: Hot spots in tropical forests. The Environmentalist, 8, 187-208. |
| [24] | Myers N, Mittermeier RA, Mittermeier CG, Fonseca GA, Kent J ( 2000) Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature, 403, 853-858. |
| [25] | National Environmental Protection Administration ( 1990a) GB 11893-1989. Water Quality Determination of Total Phosphorus: Ammonium Molybdate Spectrophotometric Method. China Standard Press, Beijing. (in Chinese with) |
| [ 国家环境保护总局 ( 1990) GB 11893-1989 水质总磷的测定: 钼酸铵分光光度法. 中国标准出版社, 北京.] | |
| [26] | National Environmental Protection Administration ( 1990b) GB 11894-1989. Water Quality Determination of Total Nitrogen: Alkaline Potassium Persulfate Digestion UV Spectrophotometric Method. China Standard Press, Beijing. (in Chinese with) |
| [ 国家环境保护总局 ( 1990) GB 11894-1989 水质总氮的测定: 碱性过硫酸钾消解紫外分光光度法. 中国标准出版社, 北京.] | |
| [27] | Poff NL, Olden JD, Vieira NK, Finn DS, Simmons MP, Kondratieff BC ( 2006) Functional trait niches of North American lotic insects: Traits-based ecological applications in light of phylogenetic relationships. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 25, 730-755. |
| [28] | Real M, Rieradevall M, Prat N ( 2000) Chironomus species (Diptera: Chironomidae) in the profundal benthos of Spanish reservoirs and lakes: Factors affecting distribution patterns. Freshwater Biology, 43, 1-18. |
| [29] | Sala OE, Chapin FS, Armesto JJ, Berlow EL, Bloomfield J, Dirzo R, Huber-Sanwald E, Huenneke LF, Jackson RB, Kinzig AP, Leemans R, Lodge DM, Mooney HA, Oesterheld M, Poff NL, Sykes MT, Walker BH, Walker M, Wall DH ( 2000) Global biodiversity scenarios for the year 2100. Science, 287, 1770-1774. |
| [30] | Scheffer M, Van Geest GJ, Zimmer KD, Jeppesen E, Sondergaard M, Butler MG, Hanson MA, Declerck S, De Meester L ( 2006) Small habitat size and isolation can promote species richness: Second-order effects on biodiversity in shallow lakes and ponds. Oikos, 112, 227-231. |
| [31] | Stokstad E ( 2014) EPA science report signals start of wetlands battle. Science, 343, 15. |
| [32] | Taft B, Koncelik JP ( 2006) Methods for Assessing Habitat in Flowing Waters: Using the Qualitative Habitat Evaluation Index (QHEI). Division of Surface Water, Ohio EPA. . (accessed on 2019-05-07) |
| [1] | Mingyi Zhang, Xiaomei Wang, Yanxin Zheng, Nan Wu, Donghao Li, Enyuan Fan, Na Li, Xiujuan Shan, Tao Yu, Chunnuan Zhao, Bo Li, Shuai Xu, Yuping Wu, Liqun Ren. Resource status and habitat function of typical oyster reef areas in the Yellow River Estuary [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [2] | Tong Miao, Wang Huan, Zhang Wenshuang, Wang Chao, Song Jianxiao. Distribution characteristics of antibiotic resistance genes in soil bacterial communities exposed to heavy metal pollution [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [3] | Li Yanpeng, Chen Jie, Lu Chunyang, Xu Han. Community characteristics of a 64-ha secondary forest dynamics plot in a tropical montane rainforest in Jianfengling, Hainan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [4] | Zihong Chen, Yifei Zhang, Kai Chen, Jianying Chen, Ling Xu. Species diversity of entomopathogenic fungi and the influencing factors in the Southern Gaoligong Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [5] | Shiyu Wei, Tianjiao Song, Jiayi Luo, Yan Zhang, Zixuan Zhao, Jingwen Ru, Hua Yi, Yanbing Lin. Altitudinal distribution patterns of soil bacterial communities in the Huoditang coniferous forests of the Qinling Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [6] | Yongqiang Shi, Qingshan Luan, Xiujuan Shan, Chao Wei, Yongsong Zhao, Cece Sun, Xianshi Jin. Annual changes in zooplankton biodiversity in the southern waters of Changdao [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [7] | Yanmei Ni, Li Chen, Zhiyuan Dong, Debin Sun, Baoquan Li, Xumin Wang, Linlin Chen. Community structure of macrobenthos and ecological health evaluation in the restoration area of the Yellow River Delta wetland [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23303-. |
| [8] | Yaoqi Chen, Jingjing Guo, Guojun Cai, Yili Ge, Yu Liao, Zheng Dong, Hui Fu. Evolution characteristics of submerged macrophyte community diversity in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River in the past seventy years (1954-2021) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23319-. |
| [9] | Jiaxin Wei, Zhiguo Jiang, Linsen Yang, Huanhuan Xiong, Jiaojiao Jin, Fanglin Luo, Jiehua Li, Hao Wu, Yaozhan Xu, Xiujuan Qiao, Xinzeng Wei, Hui Yao, Huiliang Yu, Jingyuan Yang, Mingxi Jiang. Community composition and structure in a 25 ha mid-subtropical mountain deciduous broad-leaved forest dynamics plot in Shennongjia, Hubei, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23338-. |
| [10] | Xiaolin Liu, Yougui Wu, Minhua Zhang, Xiaorong Chen, Zhicheng Zhu, Dingyun Chen, Shu Dong, Buhang Li, Bingyang Ding, Yu Liu. Community composition and structure of a 25-ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical forest in Baishanzu, Zhejiang Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [11] | Fangfang Wu, Na Liu, Chunmei He, Zuoqiang Yuan, Zhanqing Hao, Qiulong Yin. Elevational gradient pattern of woody plant community structure and diversity in the Qinling Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24239-. |
| [12] | Hang Shan, Zupei Lei, Fangdong Zheng, Boliang Wei, Lei Zhong, Mingjian Yu. Dynamic changes in the community of a secondary evergreen broad-leaved forest in Wuyanling, Zhejiang Province from 2013 to 2023 [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24372-. |
| [13] | Jiayi Feng, Juyu Lian, Yujun Feng, Dongxu Zhang, Honglin Cao, Wanhui Ye. Effects of vertical stratification on community structure and functions in a subtropical, evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Dinghushan National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24306-. |
| [14] | Xingyu Wang, Jinghui Meng, Siyuan Ren, Yan Zhu. Relationship between biodiversity and aboveground biomass in the warm temperate deciduous broad-leaved forest of Donglingshan, Beijing [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24230-. |
| [15] | Qingqing Du, Siyuan Ren, Nicole Tsz Shun Yuan, Yan Zhu. Factors affecting the productivity of sapling and adult trees in the warm temperate deciduous broad-leaved forest of Donglingshan, Beijing [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24284-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()