



Biodiv Sci ›› 2018, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (2): 111-129. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017021 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2017021
Special Issue: 生物多样性与生态系统功能; 青藏高原生物多样性与生态安全
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhonghua Zhang1,6, Huakun Zhou1,2,*( ), Xinquan Zhao1,2,*(
), Xinquan Zhao1,2,*( ), Buqing Yao1, Zhen Ma1, Quanmin Dong3, Zhenhua Zhang1, Wenying Wang4, Yuanwu Yang5
), Buqing Yao1, Zhen Ma1, Quanmin Dong3, Zhenhua Zhang1, Wenying Wang4, Yuanwu Yang5
Received:2017-01-23
Accepted:2017-07-15
Online:2018-02-20
Published:2018-05-05
Contact:
Zhou Huakun,Zhao Xinquan
About author:# Co-first authors
Zhonghua Zhang, Huakun Zhou, Xinquan Zhao, Buqing Yao, Zhen Ma, Quanmin Dong, Zhenhua Zhang, Wenying Wang, Yuanwu Yang. Relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in alpine meadows of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(2): 111-129.
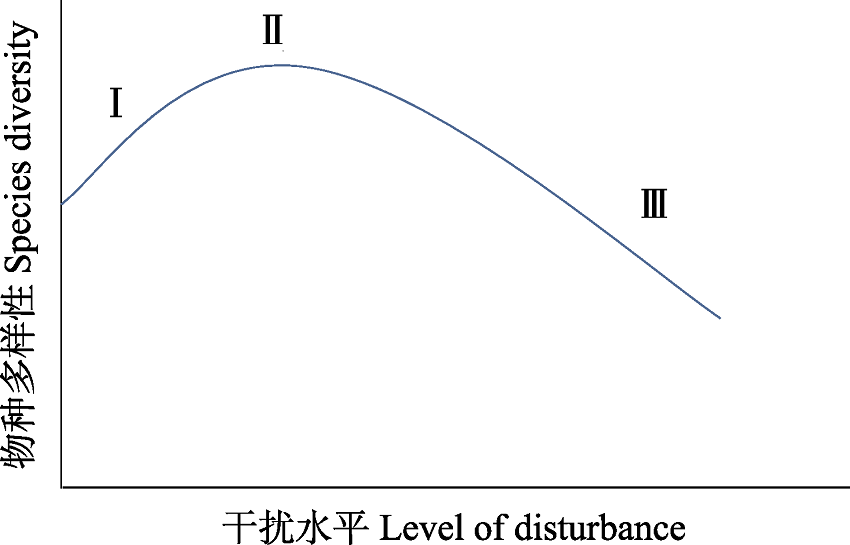
Fig. 1 Relationship between species diversity and level of disturbance. I, At low level of disturbance, species diversity is at a lower level due to competitive exclusion; II, At moderate level of disturbance, species diversity can be greatest due to the coexistence of species in the early and late stages of succession; III, At high level of disturbance, species richness decreases due to increased disturbance.
| 实验期限 Experimental period (year) | 高度 Height | 盖度 Coverage | 生物多样性 Biodiversity | 地下生物量 Underground biomass | 地上生物量 Above ground biomass | 总生物量 Total biomass | 参考文献 Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高寒草原 Alpine grassland | 3 | - | 驼峰曲线 Hump | - | Chen et al, 2015 | |||
| 高寒草甸 Alpine meadow | 6 | * | - * | Zhao et al, 2009 | ||||
| 小嵩草草甸 Kobresia pygmae meadow | 2 | * | * | 驼峰曲线 Hump | - | - | Dong et al, 2012 | |
| 金露梅灌丛 Potentilla fruticosa shrubs | 18 | - | - | 驼峰曲线 Hump | * | Zhou et al, 2004 | ||
| 高寒草甸 Alpine meadow | 自然放牧 Natural grazing | 驼峰曲线 Hump | Jiang et al, 2003 | |||||
| 金露梅灌丛 Potentilla fruticosa shrubs | 1 | 正相关 Positive | - | Liu et al, 1999 | ||||
| 高寒草甸 Alpine meadow | 自然放牧 Natural grazing | - | - | 驼峰曲线 Hump | - | Ren et al, 2009 |
Table 1 Effect of grazing on the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in alpine grassland
| 实验期限 Experimental period (year) | 高度 Height | 盖度 Coverage | 生物多样性 Biodiversity | 地下生物量 Underground biomass | 地上生物量 Above ground biomass | 总生物量 Total biomass | 参考文献 Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高寒草原 Alpine grassland | 3 | - | 驼峰曲线 Hump | - | Chen et al, 2015 | |||
| 高寒草甸 Alpine meadow | 6 | * | - * | Zhao et al, 2009 | ||||
| 小嵩草草甸 Kobresia pygmae meadow | 2 | * | * | 驼峰曲线 Hump | - | - | Dong et al, 2012 | |
| 金露梅灌丛 Potentilla fruticosa shrubs | 18 | - | - | 驼峰曲线 Hump | * | Zhou et al, 2004 | ||
| 高寒草甸 Alpine meadow | 自然放牧 Natural grazing | 驼峰曲线 Hump | Jiang et al, 2003 | |||||
| 金露梅灌丛 Potentilla fruticosa shrubs | 1 | 正相关 Positive | - | Liu et al, 1999 | ||||
| 高寒草甸 Alpine meadow | 自然放牧 Natural grazing | - | - | 驼峰曲线 Hump | - | Ren et al, 2009 |
| 草地类型 Grassland types | 生物量和群落生产力 Biomass and community productivity | 文献 References |
|---|---|---|
| 川西北亚高山草地 Subalpine grassland in Northwest Sichuan Province | 糙野青茅、牛尾草、发草生物量增加 The biomass of Deyeuxia scabrescens, Festuca elatior and Deschampsia caespitosa increase | Shi et al, 2008; Xu et al, 2009 |
| 高寒草甸 Alpine meadow | 禾本科牧草生物量下降 Biomass of gramineous forage decreased | Li et al, 2011 |
| 青藏铁路沿线高寒草甸 Alpine meadow along the Qinghai-Tibet Railway | 增温使生物量更多分配到地上部分, 而冻土融化致使深层土壤水分对生物量产生影响。根系生物量略有增加, 但在生长季不同月份其增加的程度不同, 致使年际间的增幅出现差异。 Warming makes more biomass allocation to aboveground parts, and the melting of frozen soil leads to the effect of soil moisture on biomass. The root biomass increased slightly, but the degree of increase was different in different months of growing season, resulting in a difference in interannual growth. | Xu et al, 2016a |
| 青海海北矮嵩草草甸 Kobresia humilis meadow in Haibei, Qinghai | 禾草生物量增加, 杂草生物量下降; 提高地上生产力40%以上。 Grasses biomass increased, weeds biomass decreased, and aboveground productivity increased by over 40%. | Zhou et al, 2000; Li et al, 2004; Wang et al, 2012 |
| 新疆天山高寒草原 Alpine grassland in Tianshan Mountain, Xinjiang Province | 生物量先增加后减少 Biomass increased first and then decreased | Li et al, 2007b |
Table 2 Response of biomass and community productivity to climate warming in alpine grassland
| 草地类型 Grassland types | 生物量和群落生产力 Biomass and community productivity | 文献 References |
|---|---|---|
| 川西北亚高山草地 Subalpine grassland in Northwest Sichuan Province | 糙野青茅、牛尾草、发草生物量增加 The biomass of Deyeuxia scabrescens, Festuca elatior and Deschampsia caespitosa increase | Shi et al, 2008; Xu et al, 2009 |
| 高寒草甸 Alpine meadow | 禾本科牧草生物量下降 Biomass of gramineous forage decreased | Li et al, 2011 |
| 青藏铁路沿线高寒草甸 Alpine meadow along the Qinghai-Tibet Railway | 增温使生物量更多分配到地上部分, 而冻土融化致使深层土壤水分对生物量产生影响。根系生物量略有增加, 但在生长季不同月份其增加的程度不同, 致使年际间的增幅出现差异。 Warming makes more biomass allocation to aboveground parts, and the melting of frozen soil leads to the effect of soil moisture on biomass. The root biomass increased slightly, but the degree of increase was different in different months of growing season, resulting in a difference in interannual growth. | Xu et al, 2016a |
| 青海海北矮嵩草草甸 Kobresia humilis meadow in Haibei, Qinghai | 禾草生物量增加, 杂草生物量下降; 提高地上生产力40%以上。 Grasses biomass increased, weeds biomass decreased, and aboveground productivity increased by over 40%. | Zhou et al, 2000; Li et al, 2004; Wang et al, 2012 |
| 新疆天山高寒草原 Alpine grassland in Tianshan Mountain, Xinjiang Province | 生物量先增加后减少 Biomass increased first and then decreased | Li et al, 2007b |
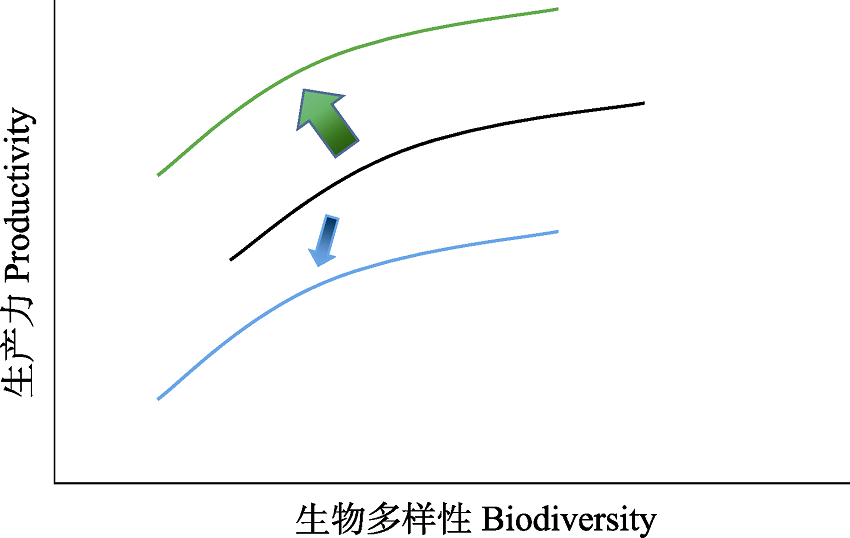
Fig. 2 Changes in the curve of relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem function (BEF) before and after warming. To facilitate understanding, it is assumed BEF curve as log- linear curve (some experimental results supports the model). Arrow size indicates size of the possibility.
| [130] | Zhao LQ, Wang G (2009) Relationship between species diversity and productivity of alpine meadow in Gannan Prefecture. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 45(6), 82-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵陆强, 王刚 (2009) 甘南高寒草甸物种多样性与生产力的关系. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 45(6), 82-86.] | |
| [131] | Zhao XQ, Cao GM, Li YN (2009) Alpine Meadow Ecosystem and Global Change. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [赵新全, 曹广民, 李英年 (2009) 高寒草甸生态系统与全球变化. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [132] | Zhao XQ, Chen SL, Cao GM, Shi SB, Xu SX, Wang QL (2003) Study on interacting mechanisms of alpine meadow ecosystem with global change in Tibetan Plateau. Science Technology and Industrial, 3(8), 51-59. (in Chinese) |
| [赵新全, 陈世龙, 曹广民, 师生波, 徐世晓, 王启兰 (2003) 青藏高原高寒草甸生态系统与全球气候变化的相互作用机理研究. 科技与产业, 3(8), 51-59.] | |
| [133] | Zhao XQ, Ma YS, Zhou HK (2011) Restoration and Sustainable Management of Degraded Ecosystem in the Three-River Headwaters Region. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [赵新全, 马玉寿, 周华坤 (2011) 三江源区退化生态系统恢复及可持续管理化. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [134] | Zhao XQ, Zhou HK (2005) Eco-environment degradation, vegetation restoration and sustainable development in the Headwaters of Three Rivers on Tibetan Plateau. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 20, 471-476. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵新全, 周华坤 (2005) 三江源生态环境退化、恢复治理及其可持续发展. 中国科学院院刊, 20, 471-476.] | |
| [135] | Zhao YY, Zhou HK, Yao BQ, Wang WY, Dong SK, Zhao XQ (2015) The influence of long-term simulating warming to the plant community and soil nutrient of alpine meadow. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 23, 665-671. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | Anwar M, Yang YH, Guo ZD, Fang JY, Pan BR, Hu YK (2006) Relationship between the species richness and the productivity of alpine steppes in Bayanbulak, Xin¬jiang. Arid Zone Research, 23, 289-294. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [安尼瓦尔·买买提, 杨元合, 郭兆迪, 方精云, 潘伯荣, 胡玉昆 (2006) 新疆巴音布鲁克高山草地物种丰富度与生产力的关系. 干旱区研究, 23, 289-294.] | |
| [135] | [赵艳艳, 周华坤, 姚步青, 王文颖, 董世魁, 赵新全 (2015) 长期增温对高寒草甸植物群落和土壤养分的影响. 草地学报, 23, 665-671.] |
| [136] | Zheng HP, Chen ZX, Niu JY, Gao YH (2009) Effects of inter¬seeding on plant diversity and productivity in Maqu alpine desertified meadow. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 18, 28-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郑华平, 陈子萱, 牛俊义, 高玉红 (2009) 补播禾草对玛曲高寒沙化草地植物多样性和生产力的影响. 草业学报, 18, 28-33.] | |
| [137] | Zhou GS, Wang YH, Zhang XS (1999) Chinaʼs vegetation/ecosystem response to global change: Research progress and prospects. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 13, 158-165. |
| [138] | Zhou HK, Yao BQ, Yu L, Zhao XQ (2016) Degraded Succession and Ecological Restoration of Alpine Grassland in the Three-River Headwaters Region. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [2] | Bai YF, Wu JG, Clark CM, Naeem S, Pan QM, Huang JH, Zhang LX, Han XG (2010) Tradeoffs and thresholds in the effects of nitrogen addition on biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: Evidence from Inner Mongolia grasslands. Global Change Biology, 16, 358-372. |
| [3] | Balvanera P, Pfisterer AB, Buchmann N, He JS, Nakashizuka T, Raffaelli D, Schmid B (2006) Quantifying the evidence for biodiversity effects on ecosystem functioning and ser¬vices. Ecology Letters, 9, 1146-1156. |
| [4] | Bellard C, Bertelsmeier C, Leadley P, Thuiller W, Courchamp F (2012) Impacts of climate change on the future of biodiversity. Ecology Letters, 15, 365-377. |
| [5] | Bengtsson J (1998) Which species? What kind of diversity? Which ecosystem function? Some problems in studies of relations between biodiversity and ecosystem function. Applied Soil Ecology, 10, 191-199. |
| [138] | [周华坤, 姚步青, 于龙, 赵新全 (2016) 三江源区高寒草地退化演替与生态恢复. 科学出版社, 北京.] |
| [139] | Zhou HK, Zhao XQ, Tang YH, Zhou L (2005) Alpine grassland degradation and its control in the source regions of Yangtze and Yellow rivers. China Grassland Science, 51, 191-203. |
| [140] | Zhou HK, Zhao XQ, Tang YH, Zhou L, Liu W, Yu L (2004) Effect of long-term grazing on alpine shrub vegetation in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Grassland of China, 26, 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周华坤, 赵新全, 唐艳鸿, 周立, 刘伟, 于龙 (2004) 长期放牧对青藏高原高寒灌丛植被的影响. 中国草地, 26, 1-11.] | |
| [141] | Zhou HK, Zhao XQ, Wen J, Chen Z, Yao BQ, Yang YW, Xu WX, Duan JC (2012) The characteristics of soil and vegetation of degenerated alpine steppe in the Yellow River Source Region. Acta Prataculture Sinica, 21, 1-11. (in Chi¬nese with English abstract) |
| [6] | Bu WS, Zang RG, Ding Y (2014) Functional diversity increases with species diversity along successional gradient in a secondary tropical lowland rainforest. Tropical Ecology, 55, 393-401. |
| [7] | Cardinale BJ, Wright JP, Cadotte MW, Carroll IT, Hector A, Srivastava DS, Loreau M, Weis JJ (2007) Impacts of plant diversity on biomass production increase through time because of species complementarity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 104, 18123-18128. |
| [8] | Chapin FS III, Zavaleta ES, Eviner VT, Naylor RL, Vitousek PM, Reynolds HL, Hooper DU, Lavorel S, Sala OE, Hobbie SE, Mack MC, Díaz S (2000) Consequences of changing biodiversity. Nature, 405, 234-242. |
| [141] | [周华坤, 赵新全, 温军, 陈哲, 姚步青, 杨元武, 徐维新, 段吉闯 (2012) 黄河源区高寒草原的植被退化与土壤退化特征. 草业学报, 21, 1-11.] |
| [142] | Zhou HK, Zhao XQ, Zhou L, Liu W, Li YN, Tang YH (2005) A study on correlations between vegetation degradation and soil degradation in the “Alpine Meadow” of the Qing¬¬hai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Prataculture Sinica, 14(3), 31-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Chen H, Zhu QA, Peng CH, Wu N, Wang YF, Fang XQ, Gao YH, Zhu D, Yang G, Tian JQ, Kang XM, Piao SL, Yang HO, Xiang WH, Luo ZB, Jiang H, Song XZ, Zhang Y, Yu GR, Zhao XQ, Gong P, Yao TD, Wu JH (2013) The impacts of climate change and human activities on biog¬eochemical cycles on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Global Change Biology, 19, 2940-2955. |
| [10] | Chen LZ, Chen WL (1995) Study on degraded ecosystem in China. Science and Technology of China Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [142] | [周华坤, 赵新全, 周立, 刘伟, 李英年, 唐艳鸿 (2005) 青藏高原高寒草甸的植被退化与土壤退化特征研究. 草业学报, 14(3), 31-40.] |
| [143] | Zhou HK, Zhou L, Zhao XQ, Liu W, Li YN, Gu S, Zhou XM (2006) Stability of alpine meadow ecosystem on the Qinghai- Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Science Bulletin, 51, 320-327. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [10] | [陈灵芝, 陈伟烈 (1995) 中国退化生态系统研究. 中国科学技术出版社, 北京.] |
| [11] | Chen Z, Liang XP, Hou FJ, Tian MM, Zhang HR, Yu Y, Guan YZ, Wang CZ, Yan XB (2015) Genetic diversity of Elymus nutans under different grazing intensities. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 24, 159-165. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [143] | [周华坤, 周立, 赵新全, 刘伟, 李英年, 古松, 周兴民 (2006) 青藏高原高寒草甸生态系统稳定性研究. 科学通报, 51, 63-69.] |
| [144] | Zhou HK, Zhou L, Zhao XQ, Liu W, Yan ZL, Shi Y (2003) Degradation process and integrated treatment of “black soil beach” grassland in the source regions of Yangtze and Yellow rivers. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 22, 51-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] | [陈钊, 梁新平, 侯扶江, 田苗苗, 张红瑞, 余莹, 管永卓, 王成章, 严学兵 (2015) 不同放牧强度下垂穗披碱草遗传多样性分析. 草业学报, 24, 159-165.] |
| [12] | Chu D, Pubuciren, Dejiyangzong, Ji QM, Tang H (2013) Sea¬sonal variation of typical grassland biomass in Tibet. Grass¬land Science, 30, 1071-1081. (in Chinese with English ab¬stract) |
| [144] | [周华坤, 周立, 赵新全, 刘伟, 严作良, 师燕 (2003) 江河源区“黑土滩”型退化草场的形成过程与综合治理. 生态学杂志, 22, 51-55.] |
| [145] | Zhou HK, Zhou L, Zhao XQ, Yan ZL, Liu W, Shi Y (2002) Influence of grazing disturbance on alpine grassland. Grass¬land of China, 24, 53-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] | [除多, 普布次仁, 德吉央宗, 姬秋梅, 唐洪 (2013) 西藏典型草地地生物量季节变化特征. 草业科学, 30, 1071-1081.] |
| [13] | de Deyn GB, van der Putten WH (2005) Linking aboveground and belowground diversity. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 20, 625-633. |
| [14] | Díaz S, Lavorel S, Ntyres S, Falczuk V, Casanoves F, Milchunas DG, Skarpe C, Rusch G, Sternberg M, Noy-Meir I, Landsberg J, Zhang W, Clark H, Campbell BD (2007) Plant trait responses to grazing—A global synthesis. Global Change Biology, 13, 313-341. |
| [145] | [周华坤, 周立, 赵新全, 严作良, 刘伟, 师燕 (2002) 放牧干扰对高寒草场的影响. 中国草地, 24, 53-61.] |
| [146] | Zhou HK, Zhou XM, Zhao XQ (2000) A preliminary study of the influence of simulated greenhouse effect on a Kobresia humilis meadow. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 24, 547-553. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [15] | Dong QM, Zhao XQ, Ma YS, Shi JJ, Wang YL, Li SX, Yang SH, Wang LY, Sheng L (2012) Influence of grazing on biomass, growth ratio and compensatory effect of different plant groups in Kobresia parva meadow. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32, 2640-2650. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [董全民, 赵新全, 马玉寿, 施建军, 王彦龙, 李世雄, 杨时海, 王柳英, 盛丽 (2012) 放牧对小嵩草草甸生物量及不同植物类群生长率和补偿效应的影响. 生态学报, 32, 2640-2650.] | |
| [146] | [周华坤, 周兴民, 赵新全 (2000) 模拟增温效应对矮嵩草草甸影响的初步研究. 植物生态学报, 24, 547-553.] |
| [147] | Zhou XM, Wang QJ, Zhao XQ (2001) Chinese Kobresia Mea¬dow. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [周兴民, 王启基, 赵新全 (2001) 中国嵩草草甸. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [16] | Dong SK, Tang L, Zhang XF, Liu SL, Liu QR, Su XK, Zhang Y, Wu XY, Zhao ZZ, Li Y, Sha W (2016) Relationship between plant species diversity and functional diversity in alpine grasslands. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 1472-1483. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [董世魁, 汤琳, 张相锋, 刘世梁, 刘全儒, 苏旭坤, 张勇, 武晓宇, 赵珍珍, 李钰, 沙威 (2016) 高寒草地植物物种多样性与功能多样性的关系. 生态学报, 37, 1472-1483.] | |
| [148] | Zhu ZH, Li XL, Liu W, Qiao YM, Xu ZW (2002) Studies on responses of Kobresia humilis to simulated grazing. Pra¬tacultural Science, 19, 42-44. (in Chinese with English ab¬stract) |
| [朱志红, 李希来, 刘伟, 乔有明, 徐志伟 (2002) 矮嵩草对模拟放牧反应的研究. 草业科学, 19, 42-44.] | |
| [17] | Dormann CF, Woodin SJ (2002) Climate change in the Arctic: Using plant functional types in a meta-analysis of field experiments. Functional Ecology, 16, 4-17. |
| [18] | Du GZ, Qin GL, Li ZZ, Liu ZH, Dong GS (2003) Relationship between species richness and productivity in an alpine meadow plant community. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 27, 125-132. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [149] | Zou JR, Zhao XQ (2015) Effects of livestock exclosure and grazing on carbon sequestration in grassland ecosystem. Pratacultural Science, 32, 1748-1756. (in Chinese with Eng¬lish abstract) |
| [邹婧汝, 赵新全 (2015) 围栏禁牧与放牧对草地生态系统固碳能力的影响. 草业科学, 32, 1748-1756.] | |
| [18] | [杜国祯, 覃光莲, 李自珍, 刘正恒, 董高生 (2003) 高寒草甸植物群落中物种丰富度与生产力的关系研究. 植物生态学报, 27, 125-132.] |
| [19] | Du YT, Zhang DJ (2007) The effect of fencing measures for improving degraded grassland in alpine region. Pratacultural Science, 24, 22-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [都耀庭, 张东杰 (2007) 禁牧封育措施改良高寒地区退化草地的效果. 草业科学, 24, 22-24.] | |
| [20] | Duan KQ, Yao TD, Wang NL, Tian LD, Xu BQ (2008) The difference in precipitation variability between the north and south Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 30, 726-732. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [段克勤, 姚檀栋, 王宁练, 田立德, 徐柏青 (2008) 青藏高原南北降水变化差异研究. 冰川冻土, 30, 726-732.] | |
| [21] | Duan MJ, Gao QZ, Guo YQ, Wan YF, Li YE, Ganzhu Zhabu, Danjiu Luobu, Wei LT, Xirao Zhuoma (2011) Species diver¬sity distribution pattern of alpine grassland com¬munities along an altitudinal gradient in the northern Tibet. Pratacul¬tural Science, 28, 1845-1850. (in Chinese with English ab¬stract) |
| [段敏杰, 高清竹, 郭亚奇, 万运帆, 李玉娥, 干珠扎布, 旦久罗布, 韦兰亭, 西饶卓玛 (2011) 藏北高寒草地植物群落物种多样性沿海拔梯度的分布格局. 草业科学, 28, 1845-1850.] | |
| [22] | Firincioğlu HK, Seefeldt SS, Sahin B (2007) The effect of long-term gr¬azing exclosures on range plants in the central Anatolian Re¬g¬ion of Turkey. Environmental Management, 39, 326-337. |
| [23] | Fu W, Zhao JQ, Du GZ (2013) Study on sustainable deve¬lopment of grazing ecosystem in alpine grassland of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Grassland and Turf, 33(1), 84-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [付伟, 赵俊权, 杜国祯 (2013) 青藏高原高寒草地放牧生态系统可持续发展研究. 草原与草坪, 33(1), 84-88.] | |
| [24] | Ganzhuzhabu, Duan MJ, Guo YQ, Zhang WN, Liang Y, Gao QZ, Danjiuluobu, Baimayuzhen, Xiraozhuoma (2015) Effects of irrigation on alpine grassland Northern Tibet. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 7485-7493. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [干珠扎布, 段敏杰, 郭亚奇, 张伟娜, 梁艳, 高清竹, 旦久罗布, 白玛玉珍, 西绕卓玛 (2015) 喷灌对藏北高寒草地生产力和物种多样性的影响. 生态学报, 35, 7485-7493. ] | |
| [25] | Gillen RL, Eckroat JA, Mccollum FT (2000) Vegetation response to stocking rate in southern mixed-grass prairie. Journal of Range Management, 53, 471-478. |
| [26] | Giller PS, Hillebrand H, Berninger UG, Gessner MO, Hawkins S, Inchausti P, Inglis C, Leslie H, Malmqvist B, Monaghan MT, Morin PJ, OʼMullan G (2004) Biodiversity effects on ecosystem functioning: Emerging issues and their exper¬¬imental test in aquatic environments. Oikos, 104, 423-436. |
| [27] | Greenwood KL, Hutchinson KJ (1998) Root characteristics of temperate pasture in New South Wales after grazing at three stocking rates for 30 years. Grass and Forage Science, 53, 120-128. |
| [28] | He JS, Fang JY, Ma KP, Huang JH (2003) Biodiversity and ecosystem productivity: Why is there a discrepancy in the relationship between experimental and natural ecosystems? Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 27, 835-843. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [贺金生, 方精云, 马克平, 黄建辉 (2003) 生物多样性与生态系统生产力: 为什么野外观测和受控实验结果不一致? 植物生态学报, 27, 835-843.] | |
| [29] | Hector A, Bagchi R (2007) Biodiversity and ecosystem mu¬ltifunctionality. Nature, 448, 188-190. |
| [30] | Hector A, Schmid B, Beierkuhnlein C, Caldeira M, Diemer M, Dimitrakopoulos P, Finn J, Freitas H, Giller P, Good J, Harris R, Högberg P, Huss-Danell K, Joshi J, Jumpponen A, Körner C, Leadley PW, Loreau M, Minns A, Mulder CPH, OʼDonovan G, Otway SJ, Pereira JS, Prinz A, Read DJ, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Schulze ED, Siamantziouras ASD, Spehn EM, Terry AC, Troumbis AY, Woodward FI, Yachi S, Lawton JH (1999) Plant diversity and productivity experi¬ments in Euro¬pean grasslands. Science, 286, 1123-1127. |
| [31] | Hillebrand H, Bennett DM, Cadotte MW (2008) Consequences of dominance: A review of evenness effects on local and regional ecosystem processes. Ecology, 89, 1510-1520. |
| [32] | Hooper DU, Adair EC, Cardinale BJ, Byrnes JE, Hungate BA, Matulich KL, Gonzalez A, Duffy JE, Gamfeldt L, O’Connor MI (2012) A global synthesis reveals biodiversity loss as a major driver of ecosystem change. Nature, 486, 105-108. |
| [33] | Hooper DU, Chapin FS III, Ewel J, Hector A, Inchausti P, La¬v¬¬orel S, Lawton J, Lodge D, Loreau M, Naeem S (2005) Ef¬fects of biodiversity on ecosystem functioning: A consens¬us of current knowledge. Ecological Monographs, 75, 3-35. |
| [34] | Hu G, Jin Y, Liu J, Yu M (2014) Functional diversity versus species diversity: Relationships with habitat heterogeneity at multiple scales in a subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest. Ecological Research, 29, 897-903. |
| [35] | Huntly NJ (1991) Herbivores and the dynamics of communities and ecosystems. Annual Review of Ecology and Syste¬matics, 22, 477-503. |
| [36] | Jia HT (2007) Analysis on ecological effect of enclosure in degraded grassland of Xinjiang. PhD dissertation, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Urumqi. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [贾宏涛 (2007) 新疆退化草地围封的生态效应分析. 博士学位论文, 新疆农业大学, 乌鲁木齐.] | |
| [37] | Jiang XL, Zhang WG, Yang ZY, Wang G (2003) The influence of disturbance on community structure and plant diversity of alpine meadow. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 23, 1479-1485. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [江小蕾, 张卫国, 杨振宇, 王刚 (2003) 不同干扰类型对高寒草甸群落结构和植物多样性的影响. 西北植物学报, 23, 1479-1485.] | |
| [38] | Jing X, Sanders NJ, Shi Y, Chu HY, Classen AT, Zhao K, Chen LT, Shi Y, Jiang YX, He JS (2015) The links between ecosystem multifunctionality and above- and below-ground biodiversity are mediated by climate. Nature Communica¬¬tions, 6, 8159. |
| [39] | Karl TR, Trenberth KE (2003) Modern global climate change. Science, 302, 1719-1723. |
| [40] | Klein JA, Harte J, Zhao XQ (2004) Experimental warming causes large and rapid species loss, dampened by simulated grazing, on the Tibetan Plateau. Ecology Letters, 7, 1170-1179. |
| [41] | Li CB, Peng YF, Zhao DZ, Ning Y, Zhou GY (2016) Effects of precipitation change and nitrogen addition on community structure and plant diversity in an alpine steppe on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Research of Soil and Water Con¬¬servation, 23, 185-191. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李长斌, 彭云峰, 赵殿智, 宁祎, 周国英 (2016) 降水变化和氮素添加对青藏高原高寒草原群落结构和物种多样性的影响. 水土保持研究, 23, 185-191.] | |
| [42] | Li KH, Hu YK, Adeli M, Yu JM, Gao GG (2007a) Species diversity and above-ground biomass of alpine grassland on the southern slope of Tianshan Mountain. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 21, 155-159. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李凯辉, 胡玉昆, 阿德力·麦地, 于建梅, 高国刚 (2007a) 天山南坡高寒草地物种多样性及地上生物量研究. 干旱区资源与环境, 21, 155-159.] | |
| [43] | Li KH, Hu YK, Wang X, Fan YG, Wu-Maier W (2007b) Relationship between aboveground biomass and environ¬mental factors along an altitude gradient of alpine grassland. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 18, 2019-2024. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李凯辉, 胡玉昆, 王鑫, 范永刚, 吾买尔·吾守 (2007b) 不同海拔梯度高寒草地地上生物量与环境因子关系. 应用生态学报, 18, 2019-2024.] | |
| [44] | Li L, Liu W (2011) Relationship between plant functional groups, species richness and community’s productivity in degraded grassland. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 19, 917-921. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李里, 刘伟 (2011) 退化草地植物功能群和物种丰富度与群落生产力关系的研究. 草地学报, 19, 917-921.] | |
| [45] | Li N, Wang GX, Yang Y, Gao YH, Liu LA, Liu GS (2011) Short-term effects of temperature enhancement on commu¬nity structure and biomass of alpine meadow in the Qing¬hai-¬Tibet Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31, 895-905. (in Chi¬nese with English abstract) |
| [李娜, 王根绪, 杨燕, 高永恒, 柳林安, 刘光生 (2011) 短期增温对青藏高原高寒草甸植物群落结构和生物量的影响. 生态学报, 31, 895-905. ] | |
| [46] | Li WL, Zhang YY, Li ZZ, Du GZ, Huang L (2007) The rela¬tionships between niche fitness and the productivity, diversity in alpine meadow and its responses to grazing. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 43(2), 53-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李文龙, 张彦宇, 李自珍, 杜国祯, 黄磊 (2007) 高寒草地植物生态位适宜度与生产力和多样性的关系及其对放牧的响应. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 43(2), 53-57.] | |
| [47] | Li XG, Zhu ZH, Zhou XS, Yuan FR, Fan RJ, Xu ML (2011) Effects of clipping, fertilizing and watering on the relation¬ship between species diversity, functional diversity and primary productivity in alpine meadow of China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 35, 1136-1147. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李晓刚, 朱志红, 周晓松, 袁芙蓉, 樊瑞俭, 许曼丽 (2011) 刈割、施肥和浇水对高寒草甸物种多样性、功能多样性与初级生产力关系的影响. 植物生态学报, 35, 1136-1147.] | |
| [48] | Li YN, Zhao L, Zhao XQ, Zhou HK (2004) Effects of a 5-year mimic temperature increase to the structure and productivity of Kobresia humilis meadow. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 12, 236-239. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李英年, 赵亮, 赵新全, 周华坤 (2004) 5年模拟增温后矮嵩草草甸群落结构及生产量的变化. 草地学报, 12, 236-239.] | |
| [49] | Li ZZ, Du GZ, Hui C, Yue DX (2002) The optimal control model of the stocking farm management of alpine meadow in southern Gansu and research on a strategy for sustained utilization. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 38(4), 85-89. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李自珍, 杜国祯, 惠苍, 岳东霞 (2002) 甘南高寒草地牧场管理的最优控制模型及可持续利用对策研究. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 38(4), 85-89.] | |
| [50] | Liu B, Wu N, Luo P, Tao YP (2007) Characteristics of soil nutrient distribution in high-altitude meadow ecosystems with different management and degradation scenarios. Chi¬nese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 15(4), 45-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘兵, 吴宁, 罗鹏, 陶豫萍 (2007) 草场管理措施及退化程度对土壤养分含量变化的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 15(4), 45-48.] | |
| [51] | Liu JX, Wang J, Hu XL (2010) Regressive analysis of the effect of precipitation on yield of pasture at high and cold area Tongde County. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 31(1), 83-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘剑霞, 王军, 胡小玲 (2010) 降水对青海同德高寒草地牧草产量影响的积分回归分析. 畜牧与饲料科学, 31(1), 83-84.] | |
| [52] | Liu W, Zhou L, Wang X (1999) Responses of plant and rodents to different grazing intensity. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 19, 376-382. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘伟, 周立, 王溪 (1999) 不同放牧强度对植物及啮齿动物作用的研究. 生态学报, 19, 376-382.] | |
| [53] | Liu XQ, Zhang X, Zhang LF, Li YN, Zhao L, Xu SX, Li HQ, Ma RR, Niu B, Gao YB, Gu S (2016) Effects of exclosure duration on the community structure and species diversity of an alpine meadow in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 5150-5162. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘晓琴, 张翔, 张立锋, 李英年, 赵亮, 徐世晓, 李红琴, 马荣荣, 牛犇, 高玉葆, 古松 (2016) 封育年限对高寒草甸群落组分和物种多样性的影响. 生态学报, 36, 5150-5162.] | |
| [54] | Liu Z, Li Q, Chen DD, Zhai WT, Zhao L, Xu SX, Zhao XQ (2015) Patterns of plant species diversity along an altitudinal gradient and its effect on above-ground biomass in alpine meadows in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Biodiversity Science, 23, 451-462. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘哲, 李奇, 陈懂懂, 翟文婷, 赵亮, 徐世晓, 赵新全 (2015) 青藏高原高寒草甸物种多样性的海拔梯度分布格局及对地上生物量的影响. 生物多样性, 23, 451-462.] | |
| [55] | Loreau M, Naeem S, Inchausti P, Bengtsson J, Grime JP, Hector A, Hooper DU, Huston MA, Raffaelli D, Schmid B, Tilman D, Wardle DA(2001) Bio¬diversity and ecosystem functioning: Current knowledge and future challenges. Science, 294, 804-808. |
| [56] | Ma XX, Yan Y, Lu XY, Wang XD (2016) Dynamics of belowground biomass and its relationship with soil mois¬ture in alpine grassland on the North Tibetan Plateau. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 25, 189-195. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马星星, 鄢燕, 鲁旭阳, 王小丹 (2016) 藏北高寒草地地下生物量特征及其与土壤水分的关系. 生态环境学报, 25, 189-195.] | |
| [57] | Niu KC, Choler P, Zhao BB, Du GZ (2009) The allometry of reproductive biomass in response to land use in Tibetan alpine grasslands. Functional Ecology, 23, 274-283. |
| [58] | Niu KC, Zhao ZG, Luo YJ, Du GZ (2006) Fertilization effects on species reproductive allocation in an alpine meadow plant community. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Ver¬sion), 30, 817-826. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [牛克昌, 赵志刚, 罗燕江, 杜国祯 (2006) 施肥对高寒草甸植物群落主要组分种繁殖分配的影响. 植物生态学报, 30, 817-826.] | |
| [59] | Niu SL, Wu MY, Han Y, Xia JY, Li LH, Wan SQ (2008) Water-mediated responses of ecosystem carbon fluxes to climatic change in a temperate steppe. New Phytologist, 177, 209-219. |
| [60] | Pakeman RJ (2004) Consistency of plant species and trait responses to grazing along a productivity gradient: A multi- site analysis. Journal of Ecology, 92, 893-905. |
| [61] | Pan SY, Kong BB, Yao TH, Wei XH, Li YN, Zhu ZH (2015) Effects of clipping and fertilizing on the relationship bet¬ween functional diversity and aboveground net primary productivity in an alpine meadow. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 39, 867-877. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [潘石玉, 孔彬彬, 姚天华, 卫欣华, 李英年, 朱志红 (2015) 刈割和施肥对高寒草甸功能多样性与地上净初级生产力关系的影响. 植物生态学报, 39, 867-877.] | |
| [62] | Peng SS, Piao SL, Wang T, Sun JY, Shen ZH (2009) Temp¬e¬r¬a¬ture sensitivity of soil respiration in different ecosystems in China. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 41, 1008-1014. |
| [63] | Piao SL, Ciais P, Huang Y, Shen ZH, Peng SS, Li JS, Zhou LP, Liu HY, Ma YC, Ding YH, Friedlingstein P, Liu CZ, Tan K, Yu YQ, Zhang TY, Fang JY (2010) The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China. Nature, 467, 43-51. |
| [64] | Qi WW, Niu HS, Wang SP, Liu YJ, Zhang LR (2012) Simula¬tion of effects of warming on carbon budget in alpine meadow ecosystem on the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32, 1713-1722. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [亓伟伟, 牛海山, 汪诗平, 刘艳杰, 张立荣 (2012) 增温对青藏高原高寒草甸生态系统固碳通量影响的模拟研究. 生态学报, 32, 1713-1722.] | |
| [65] | Qin DH (2014) Ecological Protection and Sustainable Development in the Three-River Headwaters Region. Sci-ence Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [秦大河 (2014) 三江源区生态保护与可持续发展. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [66] | Qiu B, Luo YJ, Du GZ (2004) The effect of fertilizer gradients on vegetation characteristics in alpine meadow. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 13(6), 65-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [邱波, 罗燕江, 杜国祯 (2004) 施肥梯度对甘南高寒草甸植被特征的影响. 草业学报, 13(6), 65-68.] | |
| [67] | Quan GL, Shang ZH (2015) A comprehensive review of warming experiments of grassland ecosystem in China. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34, 1166-1173. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [权国玲, 尚占环 (2015) 中国草地生态系统模拟增温实验的综合比较. 生态学杂志, 34, 1166-1173.] | |
| [68] | Ren QJ, Wu GL, Ren GH (2009) Effect of grazing intensity on characteristics of alpine meadow communities in the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 18, 256-261. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [仁青吉, 武高林, 任国华 (2009) 放牧强度对青藏高原东部高寒草甸植物群落特征的影响. 草业学报, 18, 256-261.] | |
| [69] | Rustad LE, Campbell JL, Marion GM, Norby RJ, Mitchell MJ, Hartley AE, Cornelissen JHC, Gurevitch J, GCTE-NEWS (2001) A meta-analysis of the response of soil respiration, net nitrogen mineralization, and aboveground plant growth to experimental ecosystem warming. Oecologia, 126, 543-562. |
| [70] | Sa WJ, An LZ, Wei S (2012) Changes in plant community di¬versity and aboveground biomass along with altitude within an alpine meadow on the Three-River Source region. Chi¬nese Science Bulletin, 57, 3573-3577. |
| [71] | Sala OE, Chapin FS III, Armesto JJ, Berlow E, Bloomfield J, Dirzo R, Huber-Sanwald E, Huenneke LF, Jackson RB, Kinzig A, Leemans R, Lodge DM, Mooney HA, Oesterheld M, Poff NL, Sykes MT, Walker BH, Walker M, Wall DH (2000) Biodiversity: Global biodiversity scenarios for the year 2100. Science, 287, 1770-1774. |
| [72] | Shang ZH, Deng B, Ding LM, Ren GH, Xin GS, Liu ZY, Wang YL, Long RJ (2013) The effect of three years of fencing enclosure on soil seed banks and the relationship with above-ground vegetation of degraded alpine grasslands of the Tibetan Plateau. Plant and Soil, 364, 229-244. |
| [73] | Shen JL, Tan G, Qiao HL, Zhang JH, Meng Y (2000) Study on effect of grassland improvement on alpine degraded grass¬land vegetation. Grassland of China, (5), 49-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [沈景林, 谭刚, 乔海龙, 张娟华, 孟杨 (2000) 草地改良对高寒退化草地植被影响的研究. 中国草地, (5), 49-54.] | |
| [74] | Shen ZX, Zhou XM, Chen ZZ, Zhou HK (2002) Response of plant groups to simulated rainfall and nitrogen supply in alpine Kobresia humilis meadow. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica. 26, 288-294. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [沈振西, 周兴民, 陈佐忠, 周华坤 (2002) 高寒矮嵩草草甸植物类群对模拟降水和施氮的响应. 植物生态学报, 26, 288-294.] | |
| [75] | Shi F, Li YE, Gao QZ, Wan YF, Qin XB, Jin L, Liu YT, Wu YJ (2009) Effects of managements on soil organic carbon of grassland in China. Pratacultural Science, 26(3), 9-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [石锋, 李玉娥, 高清竹, 万运帆, 秦晓波, 金琳, 刘运通, 武艳娟 (2009) 管理措施对我国草地土壤有机碳的影响. 草业科学, 26(3), 9-15.] | |
| [76] | Shi FS, Wu N, Luo P (2008) Effect of temperature enhance¬ment on community structure and biomass of subalpine meadow in northwestern Sichuan. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28, 5286-5293. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [石福孙, 吴宁, 罗鹏 (2008) 川西北亚高山草甸植物群落结构及生物量对温度升高的响应. 生态学报, 28, 5286-5293.] | |
| [77] | Shi GX, Liu YJ, Johnson NC, Olsson PA, Mao L, Cheng G, Jiang SJ, An LZ, Du GZ, Feng HY (2014) Interactive effects of light intensity and soil fertility on root-associated arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Plant and Soil, 378, 173-188. |
| [78] | Srivastava DS, Cadotte MW, MacDonald AA, Marushia RG, Mirotchnick N (2012) Phylogenetic diversity and the func¬tioning of ecosystems. Ecology Letters, 15, 637-648. |
| [79] | Sun G, Wu N, Luo P (2005) Characteristics of soil nitrogen and carbon of pastures under different management in northwestern Sichuan. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 29, 304-310. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙庚, 吴宁, 罗鹏 (2005) 不同管理措施对川西北草地土壤氮和碳特征的影响. 植物生态学报, 29, 304-310.] | |
| [80] | Tian L, Zhang Y, Zhu J (2014) Decreased surface albedo driven by denser vegetation on the Tibetan Plateau. Envi¬ronmental Research Letters, 9, 104001. |
| [81] | Tilman D (2000) Causes, consequences and ethics of biodi¬versity. Nature, 405, 208-211. |
| [82] | Tilman D, Downing JA (1994) Biodiversity and stability in grasslands. Nature, 367, 363-365. |
| [83] | Tilman D, Knops J, Wedin D, Reich P, Ritchie M, Siemann E (1997) The influence of functional diversity and compo¬sition on ecosystem processes. Science, 277, 1300-1302. |
| [84] | Tilman D, Reich PB, Knops J, Wedin D, Mielke T, Lehman C (2001) Diversity and productivity in a long-term grassland experiment. Science, 294, 843-845. |
| [85] | Trenberth KE, Dai A, Rasmussen RM, Parsons DB (2003) The changing character of precipitation. Bulletin of the Ame¬r¬ican Meteorological Society, 84, 1205-1217. |
| [86] | Unlu K, Ozenirler G, Yurteri C (1999) Nitrogen fertilizer leaching from cropped and irrigated sandy soil in Central Turkey. European Journal of Soil Science, 50, 609-620. |
| [87] | van der Heijden MGA, Klironomos JN, Ursic M, Moutoglis P, Streitwolf-Engel R, Boller T, Wiemken A, Sanders IR (1998) Mycorrhizal fungal diversity determines plant biodi¬versity, ecosystem variability and productivity. Nature, 396, 69-72. |
| [88] | Waide RB, Willig MR, Steiner CF, Mittelbach G, Gough L, Dodson SI, Juday GP, Parmenter R (1999) The relationship between productivity and species richness. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 30, 257-300. |
| [89] | Wan SQ, Norby RJ, Ledford J, Weltzin JF (2007) Responses of soil respiration to elevated CO2, air warming, and changing soil water availability in a model old-field grassland. Global Change Biology, 13, 2411-2424. |
| [90] | Wang CS, Meng FD, Li XE, Jiang LL, Wang SP (2014) Factors affecting plant primary productivity of grasslands: A review. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34, 4125-4132. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王常顺, 孟凡栋, 李新娥, 姜丽丽, 汪诗平 (2014) 草地植物生产力主要影响因素研究综述. 生态学报, 34, 4125-4132.] | |
| [91] | Wang CT, Long RJ, Cao GM, Wang QL, Jing ZC, Shi JJ (2008a) The relationship between soil nutrients and species diversity productivity of different type grasslands in alpine meadow. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 39, 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王长庭, 龙瑞军, 曹广民, 王启兰, 景增春, 施建军 (2008a) 高寒草甸不同类型草地土壤养分与物种多样性-生产力关系. 土壤通报, 39, 1-8.] | |
| [92] | Wang CT, Long RJ, Ding LM (2004a) The effects of differences in functional group diversity and composition on plant community productivity in four types of alpine meadow communities. Biodiversity Science, 12, 403-409. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王长庭, 龙瑞军, 丁路明 (2004a) 高寒草甸不同草地类型功能群多样性及组成对植物群落生产力的影响. 生物多样性, 12, 403-409.] | |
| [93] | Wang CT, Long RJ, Ding LM, Lai DZ, Li YF (2005a) Species diversity, community stability and ecosystem function: Extension of the continuous views. Pratacultural Science, 22, 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王长庭, 龙瑞军, 丁路明, 来德珍, 李有福 (2005a) 草地生态系统中物种多样性、群落稳定性和生态系统功能的关系. 草业科学, 22, 1-7.] | |
| [94] | Wang CT, Long RJ, Wang QL, Cao GM, Shi JJ, Du YG (2008b) Response of plant diversity and productivity to soil resources changing under grazing disturbance on an alpine meadow. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28, 4144-4152. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王长庭, 龙瑞军, 王启兰, 曹广民, 施建军, 杜岩功 (2008b) 放牧扰动下高寒草甸植物多样性、生产力对土壤养分条件变化的响应. 生态学报, 28, 4144-4152.] | |
| [95] | Wang CT, Long RJ, Wang QJ, Ding LM, Wang MP (2007) Effects of altitude on plant-species diversity and productiv¬ity in an alpine meadow, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Austra¬lian Journal of Botany, 55, 110-117. |
| [96] | Wang CT, Long RJ, Wang QJ, Jing ZC, Ding LM (2005b) Relationship between species diversity and productivity in four types of alpine meadow plant communities. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 24, 483-487. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王长庭, 龙瑞军, 王启基, 景增春, 丁路明 (2005b) 高寒草甸不同草地群落物种多样性与生产力关系研究. 生态学杂志, 24, 483-487.] | |
| [97] | Wang CT, Long RJ, Wang QJ, Jing ZC, Shi HL (2004b) Changes in plant species diversity and productivity along an elevation gradient in an alpine meadow. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 28, 240-245. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王长庭, 王启基, 龙瑞军, 景增春, 史惠兰 (2004b) 高寒草甸群落植物多样性和初级生产力沿海拔梯度变化的研究. 植物生态学报, 28, 240-245.] | |
| [98] | Wang CT, Wang GX, Liu W, Wang QL (2013) Effects of fertilization gradients on plant community structure and soil characteristics in alpine meadow. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 3103-3113. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王长庭, 王根绪, 刘伟, 王启兰 (2013) 施肥梯度对高寒草甸群落结构、功能和土壤质量的影响. 生态学报, 33, 3103-3113.] | |
| [99] | Wang FG, Wang WY, Chen Z, Wang QJ (2007) Effects of changes in land use on plant community structure and species diversity in alpine meadows. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 43(3), 58-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王发刚, 王文颖, 陈志, 王启基 (2007) 土地利用变化对高寒草甸植物群落结构及物种多样性的影响. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 43(3), 58-63.] | |
| [100] | Wang GX, Li YS, Wang YB (2010) Surface Processes and Environmental Changes in the Region of Yellow River source in the Tibetan Plateau. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [王根绪, 李元寿, 王一博 (2010) 青藏高原河源区地表过程与环境变化. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [101] | Wang M, Li Y, Bai XZ, Huang RQ (2004) The impact of global warming on vegetation resources in the hinterland of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal of Natural Resources, 19, 331-336. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王谋, 李勇, 白宪洲, 黄润秋 (2004) 全球变暖对青藏高原腹地草地资源的影响. 自然资源学报, 19, 331-336.] | |
| [102] | Wang QJ, Wang WY, Deng ZF (1998) The dynamics of biomass and the allocation of energy in alpine Kobresia meadow communities, Haibei region of Qinghai Province. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 22, 222-230. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王启基, 王文颖, 邓自发 (1998) 青海海北地区高山嵩草草甸植物群落生物量动态及能量分配. 植物生态学报, 22, 222-230.] | |
| [103] | Wang SP, Duan JC, Xu GP, Wang YF, Zhang ZH, Rui YC, Luo CY, Xu B, Zhu XX, Chang XF, Cui XY, Niu HS, Zhao XQ, Wang WY (2012) Effects of warming and grazing on soil N availability, species composition and ANPP in alpine meadow. Ecology, 93, 2365-2376. |
| [104] | Wang WY, Wang QJ, Wang G, Jing ZC (2007) Effects of land degradation and rehabilitation on vegetation carbon and nitrogen content of alpine meadow in China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 31, 1073-1078. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王文颖, 王启基, 王刚, 景增春 (2007) 高寒草甸土地退化及其恢复重建对植被碳、氮含量的影响. 植物生态学报, 31, 1073-1078.] | |
| [105] | Wang XX, Dong SK, Yang B, Li YY, Su XK (2014) The effects of grassland degradation on plant diversity, primary productivity and soil fertility in the alpine region of Asia’s headwaters. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186, 6903-6917. |
| [106] | Wang XX, Dong SK, Sherman R, Liu QR, Liu SL, Li YY, Wu Y (2015) A comparison of biodiversity-ecosystem function relationships in alpine grasslands across a degradation gra¬dient on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. The Rangeland Jour¬nal, 37, 45-55. |
| [107] | Wei FW, Nie YG, Miao HX, Lu H, Hu YB (2014) Advan¬cements of the researches on biodiversity loss mechanisms. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59, 430-437. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [魏辅文, 聂永刚, 苗海霞, 路浩, 胡义波 (2014) 生物多样性丧失机制研究进展. 科学通报, 59, 430-437.] | |
| [108] | Wei XH, Yang FY, Sun L (2010) Effects of reseeding and fertilization on the vegetation recovery of degraded grass¬land in North Tibet. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 38, 18155-18156. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [魏学红, 杨富裕, 孙磊 (2010) 补播和施肥对藏北高寒退化草地的改良效果. 安徽农业科学, 38, 18155-18156.] | |
| [109] | Wu GL, Du GZ (2007) Discussion on ecological construction and sustainable development of degraded alpine grassland ecosystem of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Journal of Nature, 29, 160-164. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [武高林, 杜国祯 (2007) 青藏高原退化高寒草地生态系统恢复和可持续发展探讨. 自然杂志, 29, 160-164.] | |
| [110] | Wu JS, Li XJ, Shen ZX, Zhang XZ, Shi PL, Yu CQ, Wang JS, Zhou YT (2012) Species diversity distribution pattern of alpine grasslands communities along a precipitation gradient across Northern Tibet Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 21 17-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [武建双, 李晓佳, 沈振西, 张宪洲, 石培礼, 余成群, 王景升, 周宇庭 (2012) 藏北高寒草地样带物种多样性沿降水梯度的分布格局. 草业学报, 21, 17-25.] | |
| [111] | Wu ZT, Dijkstra P, Koch GW, Peñuelas J, Hungate BA (2011) Responses of terrestrial ecosystems to temperature and precipitation change: A meta-analysis of experimental man¬ipulation. Global Change Biology, 17, 927-942. |
| [112] | Xu MH, Liu M, Zhai DT, Xue X, Peng F, You QG (2016a) Effects of experimental warming on the root biomass of an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 6812-6822. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐满厚, 刘敏, 翟大彤, 薛娴, 彭飞, 尤全刚 (2016a) 模拟增温对青藏高原高寒草甸根系生物量的影响. 生态学报, 36, 6812-6822.] | |
| [113] | Xu MH, Liu M, Zhai DT, Xue X, Peng F, You QG (2016b) Dynamic changes in biomass and its relationship with environmental factors in an alpine meadow on the Qing¬hai- Tib¬etan Plateau, based on simulated warming exper¬iments. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 5759-5767. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐满厚, 刘敏, 翟大彤, 薛娴, 彭飞, 尤全刚 (2016b) 青藏高原高寒草甸生物量动态变化及与环境因子的关系——基于模拟增温实验. 生态学报, 36, 5759-5767.] | |
| [114] | Xu W, Ma ZY, Jing X, He JS (2016) Biodiversity and ecosys¬tem multifunctionality: Advances and perspectives. Biodi¬ver¬sity Science, 24, 55-71. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐炜, 马志远, 井新, 贺金生 (2016) 生物多样性与生态系统多功能性: 进展与展望. 生物多样性, 24, 55-71.] | |
| [115] | Xu ZF, Hu TX, Li XY, Zhang YB, Xian JR, Wang KY (2009) Short-term responses of grass community in clear-cutting land of sub-alpine regions simulated global warming, Western Sichuan. Acta Ecologica Sinica. 29, 2089-2095. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐振峰, 胡庭兴, 李小艳, 张远彬, 鲜骏仁, 王开运 (2009) 川西亚高山采伐迹地草坡群落对模拟增温的短期响应. 生态学报, 29, 2089-2095.] | |
| [116] | Yang YH, Rao S, Hu HF, Chen AP, Ji CJ, Zhu B, Zuo WY, Li XR, Shen HH, Wang ZH, Tang YH, Fang JY (2004) Plant species richness of alpine grasslands in relation to environmental factors and biomass on the Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Biodiversity, 12, 200-205. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨元合, 饶胜, 胡会峰, 陈安平, 吉成均, 朱彪, 左闻韵, 李轩然, 沈海花, 王志恒, 唐艳鸿, 方精云 (2004) 青藏高原高寒草地植物物种丰富度及其与环境因子和生物量的关系. 生物多样性, 12, 200-205.] | |
| [117] | Yang YJ, Zhou HK, Ye X, Yao BQ, Wang WY, Zhao XQ, Zhang H (2014) Short-term responses of plant community structure and function to nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium additions in an alpine meadow of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 34, 2317-2323. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨月娟, 周华坤, 叶鑫, 姚步青, 王文颖, 赵新全, 张灏 (2014) 青藏高原高寒草甸植物群落结构和功能对氮、磷、钾添加的短期响应. 西北植物学报, 34, 2317-2323.] | |
| [118] | Yang YS (2017) The impacts of global environmental changes on typical ecosystem: Status, challenges and trends. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨玉盛 (2017) 全球环境变化对典型生态系统的影响研究: 现状, 挑战与发展趋势. 生态学报, 37, 1-11.] | |
| [119] | Yang YW, Zhou HK, Li XL, Zhao XQ, Ye X (2017) Initial response of species diversity and productivity to nutrient addition on alpine meadow. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occi¬dentalis Sinica, 26, 159-166. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨元武, 周华坤, 李希来, 赵新全, 叶鑫 (2017) 高寒草甸物种多样性和生产力对养分添加的初期响应. 西北农业学报, 26, 159-166.] | |
| [120] | Yang ZL, Yang GH (2000) Potential productivity and livestock carrying capacity of high-frigid grassland in China. Reso¬urces Science, 22, 73-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨正礼, 杨改河 (2000) 中国高寒草地生产潜力与载畜量研究. 资源科学, 22, 73-77.] | |
| [121] | Yang ZL, Powell JR, Zhang CH, Du GZ (2012) The effect of environmental and phylogenetic drivers on community assembly in an alpine meadow community. Ecology, 93, 2321-2328. |
| [122] | Yu XC, Yao BQ, Zhou HK, Jin YX, Yang YJ, Wang WY, Dong SK, Zhao XQ (2015) Variable responses to long-term simulated warming of underground biomass and carbon allocations of two alpine meadows on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Chinese Science Bulletin, 60, 379-388. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [余欣超, 姚步青, 周华坤, 金艳霞, 杨月娟, 王文颖, 董世魁, 赵新全 (2015) 青藏高原两种高寒草甸地下生物量及其碳分配对长期增温的响应差异. 科学通报, 60, 379-388.] | |
| [123] | Zhang CH (2014) Effects of grazing and fertilization on community productivity and species richness in eastern alpine meadow of Tibetan Plateau. Pratacultural Science, 31, 2293-2300. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张春花 (2014) 放牧方式和施肥梯度对高寒草甸群落生产力和物种丰富度的影响. 草业科学, 31, 2293-2300.] | |
| [124] | Zhang J, Zhao H, Zhang T, Zhao X, Drake S (2005) Commu¬nity succession along a chronosequence of vegetation resto¬ration on sand dunes in Horqin sandy land. Journal of Arid Environments, 62, 555-566. |
| [125] | Zhang QG, Zhang DY (2003) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: Recent advances and trends. Biodiversity Science, 11, 351-363. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张全国, 张大勇 (2003) 生物多样性与生态系统功能: 最新的进展与动向. 生物多样性, 11, 351-363.] | |
| [126] | Zhang T, Chen XP, Zhao JX, Wang XM, Zhang R, Bai YF, Li YF, Guo RY, Shang ZH (2015) Effects of carbon and nitrogen additions on species diversity and biomass of alpine meadow plant communities. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 24, 1604-1610. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张涛, 陈晓鹏, 赵景学, 王喜明, 张蕊, 白彦福, 李银风, 郭瑞英, 尚占环 (2015) 碳、氮添加对高寒草甸植物群落物种多样性和生物量的影响. 生态环境学报, 24, 1604-1610.] | |
| [127] | Zhao BB, Niu KC, Du GZ (2009) The effect of grazing on above-ground biomass allocation of 27 plant species in an alpine meadow plant community in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 29, 1596-1606. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵彬彬, 牛克昌, 杜国祯 (2009) 放牧对青藏高原东缘高寒草甸群落27种植物地上生物量分配的影响. 生态学报, 29, 1596-1606.] | |
| [128] | Zhao L, Xu SX, Zhou HK, Dong QM, Zhao XQ (2013) Alpine Grassland Management Manual. Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chendu. (in Chinese) |
| [赵亮, 徐世晓, 周华坤, 董全民, 赵新全 (2013) 高寒草地管理手册. 四川科技出版社, 成都.] | |
| [129] | Zhao L, Li Q, Chen DD, Xu SX, Zhou HK, Wang SP, Zhao XQ (2014) Principles of alpine grassland ecosystems carbon sequestration and management practices on Sanjiangyuan regions, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Quaternary Sciences, 34, 795-802. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵亮, 李奇, 陈懂懂, 徐世晓, 周华坤, 汪诗平, 赵新全 (2014) 三江源区高寒草地碳流失原因、增汇原理及管理实践. 第四纪研究, 34, 795-802.] |
| [1] | Jing Gan Xiangxu Liu Xueming Lu Xing Yue. China's Large Cities in Global Biodiversity Hotspots: Conservation Policies and Optimization Directions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | Zixuan Zeng Rui Yang Yue Huang Luyao Chen. Characteristics of bird diversity and environmental relationships in Tsinghua University campus [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | Mingyue Zang, Li Liu, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feilong Hu, Xiaoqiang Lu, Jiaqi Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. China’s urban biodiversity conservation under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | Xiaoyu Zhu, Chenhao Wang, Zhongjun Wang, Yujun Zhang. Research progress and prospect of urban green space biodiversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | Lin Yuan, Siqi Wang, Jingxuan Hou. “Leaving space for wildness” in metropolitan region: Trends and prospects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | Min Hu, Binbin Li, Coraline Goron. Green is not enough: A management framework for urban biodiversity-friendly parks [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | Xin Wang, Femgyu Bao. Analysis of the ecological restoration effect of South Dianchi National Wetland Park based on the enhancement of bird diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | Yue Ming, Peiyao Hao, Lingqian Tan, Xi Zheng. A study on urban biodiversity conservation and enhancement in china based on the concept of green and high-quality development of cities [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | Gan Xie, Jing Xuan, Qidi Fu, Ze Wei, Kai Xue, Hairui Luo, Jixi Gao, Min Li. Establishing an intelligent identification model for unmanned aerial vehicle surveys of grassland plant diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | Xiaolin Chu, Quanguo Zhang. A review of experimental evidence for the evolutionary speed hypothesis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | Zhiyu Liu, Xin Ji, Guohui Sui, Ding Yang, Xuankun Li. Invertebrate diversity in buffalo grass and weedy lawns at Beijing Capital International Airport [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24456-. |
| [12] | Wei Song, Cai Cheng, Jiawei Wang, Jihua Wu. Soil microbes regulate the relationships between plant diversity and ecosystem functions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [13] | Xiaoqiang Lu, Shanshan Dong, Yue Ma, Xu Xu, Feng Qiu, Mingyue Zang, Yaqiong Wan, Luanxin Li, Cigang Yu, Yan Liu. Current status, challenges, and prospects of frontier technologies in biodiversity conservation applications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [14] | Qiaoyi Nong, Jun Cao, Wenda Cheng, Yanqiong Peng. Comparative study of monitoring methods for Apoidea resources and diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [15] | Guo Yutong, Li Sucui, Wang Zhi, Xie Yan, Yang Xue, Zhou Guangjin, You Chunhe, Zhu Saning, Gao Jixi. Coverage and distribution of national key protected wild species in China’s nature reserves [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()