



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (11): 23214. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023214 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023214
俄广旭1, 白天天2, 朱振宇1, 郭雪峰1,2,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-06-25
接受日期:2023-10-18
出版日期:2023-11-20
发布日期:2023-12-08
通讯作者:
* E-mail: 基金资助:
Guangxu E1, Tiantian Bai2, Zhenyu Zhu1, Xuefeng Guo1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2023-06-25
Accepted:2023-10-18
Online:2023-11-20
Published:2023-12-08
Contact:
* E-mail: 摘要:
动物消化道栖息着复杂的微生物群落, 它们与动物的生理和代谢过程有着密切的联系。现有研究表明消化道微生物的演化与多样性受到动物生存环境、饮食习惯、生活方式等因素影响, 而消化道微生物群落组成和功能也可以影响到动物的进化, 这种寄生与被寄生物种间的相互作用是二者进化过程中微生物多样性的重要驱动力。本文概述了动物与消化道微生物进化关系及不同动物的消化道微生物群的组成, 并探讨了动物与消化道微生物群在适应性进化过程中的联系以及不同动物中消化道优势微生物, 我们发现尽管动物消化道微生物区系组成具有多样性, 但大多数动物消化道70%-90%的微生物群落仍然来自于厚壁菌门和拟杆菌门, 其原因可能是这两个菌门在分解复杂碳水化合物方面有重要作用。同时我们也指出当前研究应考虑到动物和消化道微生物进化趋势的定义、进化速度以及动物与消化道微生物间存在的竞争与合作等因素对于二者进化关系的影响, 以便于验证其准确性。
俄广旭, 白天天, 朱振宇, 郭雪峰 (2023) 动物消化道微生物多样性与宿主协同进化关系的研究进展. 生物多样性, 31, 23214. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023214.
Guangxu E, Tiantian Bai, Zhenyu Zhu, Xuefeng Guo (2023) Advances in research on the relationship between microbial diversity in the animal digestive tract and coevolution with the host. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23214. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023214.
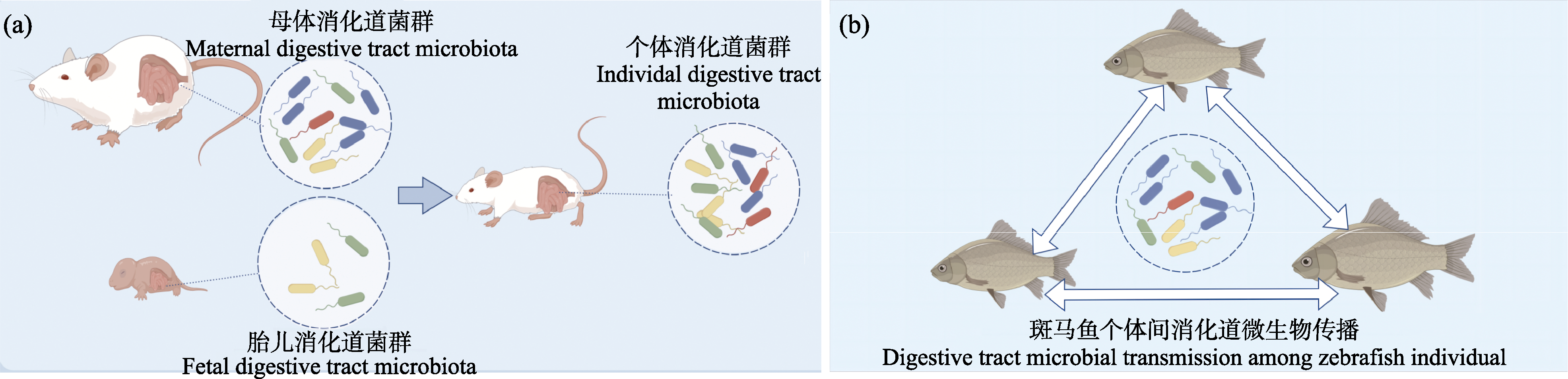
图1 消化道微生物在小鼠世代间的垂直传播(a)以及在斑马鱼个体间的水平传递(b)
Fig. 1 Vertical transmission of digestive tract microorganisms between mouse generations (a) and horizontal transmission between zebrafish individual (b)
| 不同动物消化道 Digestive tract of different animals | 细菌 Bacteria | 真菌 Fungus | 古菌 Archaea | 原生生物 Protozoa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 昆虫 Insect | 沃尔巴克氏菌 Woibachia | 毕赤酵母属 Pichia 酵母菌属 Saccharomyces 曲霉属 Aspergillus 青霉属 Penicillium Herpotrichiellaceae Phanerochaetaceae | 甲烷杆菌属 Methanobacterium 甲烷球菌属 Methanococcus 甲烷微菌属 Methanomicrobium | Oxymonadida Trichomonada Hypermastigida |
| 鱼类 Fish | 肠杆菌属 Enterobacter 气单胞菌属 Aeromonas 不动杆菌属 Acinetobacter 弧菌属 Vibrio 假单胞菌属 Pseudomonas 无色杆菌属 Achromobacter 棒杆菌属 Corynebacterium 黄杆菌属 Flavobacterium 微球菌属 Micrococcus | 假丝酵母菌属 Candida 酵母菌属 Saccharomyces 红酵母属 Rhodotorula 丝孢酵母属 Trichosporon 德巴利酵母属 Debaryomyces | 广古菌门 Euryarchaeota 纳古菌门 Nanoarchaeota 奇古菌门 Thaumarchaeota 初古菌门 Korarchaeota | 纤毛虫属 Balantidium 毛滴虫属 Trichomonas Paracichlidotherus Diplomonadida |
| 禽类 Poultry | 梭菌属 Clostridium 瘤胃球菌属 Ruminococcus 乳杆菌属 Lactobacillus 拟杆菌属 Bacteroides | 小囊菌属 Microascus 毛癣菌属 Trichophyton 曲霉属 Aspergillus 赤霉属 Gibberella 假丝酵母菌属 Candida | ||
| 反刍动物 Ruminant | 普雷沃氏菌属 Prevotella 拟杆菌属 Bacteroides 丁酸弧菌属 Butyrivibrio 梭菌属 Clostridium 颤螺菌属 Oscillospira 瘤胃球菌属 Ruminococcus 琥珀酸菌属 Succiniclasticum 琥珀酸弧菌属 Succinivibrio | 盲肠鞭菌属 Caecomyces 新美鞭菌属 Neocallimastix 梨囊鞭菌属 Piromyces | 嗜甲烷菌科 Methanomethylophilaceae 甲烷球形菌属 Methanosphaera 甲烷短杆菌属 Methanobrevibacter | 内毛虫目 Entodiniomorphida 复毛虫属 Diplodinium 前毛虫属 Epidinium Enoploplastron |
| 植食性单胃哺乳动物 Herbivorous monogastric mammals | 乳杆菌属 Lactobacillus 链球菌属 Streptococcus 放线杆菌属 Actinobacillus 八叠球菌属 Sarcina 拟杆菌属 Bacteroides 普雷沃氏菌属 Prevotella 梭菌属 Clostridium 螺毛菌属 Lachnospiraceae 瘤胃球菌属 Ruminococcus 密螺旋体属 Treponema | 新美鞭菌属 Neocallimastix 根囊鞭菌属 Orpinomyces 厌氧鞭菌属 Anaeromyces | 甲烷粒菌属 Methanocorpusculum 瘤胃甲烷短杆菌 Methanobrevibacter ruminantium | 纤毛虫属 Balantidium 贾第虫属 Giardia 毛滴虫属 Trichomonas |
表1 不同动物消化道中的优势微生物
Table 1 Dominant microorganisms in the digestive tract of different animals
| 不同动物消化道 Digestive tract of different animals | 细菌 Bacteria | 真菌 Fungus | 古菌 Archaea | 原生生物 Protozoa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 昆虫 Insect | 沃尔巴克氏菌 Woibachia | 毕赤酵母属 Pichia 酵母菌属 Saccharomyces 曲霉属 Aspergillus 青霉属 Penicillium Herpotrichiellaceae Phanerochaetaceae | 甲烷杆菌属 Methanobacterium 甲烷球菌属 Methanococcus 甲烷微菌属 Methanomicrobium | Oxymonadida Trichomonada Hypermastigida |
| 鱼类 Fish | 肠杆菌属 Enterobacter 气单胞菌属 Aeromonas 不动杆菌属 Acinetobacter 弧菌属 Vibrio 假单胞菌属 Pseudomonas 无色杆菌属 Achromobacter 棒杆菌属 Corynebacterium 黄杆菌属 Flavobacterium 微球菌属 Micrococcus | 假丝酵母菌属 Candida 酵母菌属 Saccharomyces 红酵母属 Rhodotorula 丝孢酵母属 Trichosporon 德巴利酵母属 Debaryomyces | 广古菌门 Euryarchaeota 纳古菌门 Nanoarchaeota 奇古菌门 Thaumarchaeota 初古菌门 Korarchaeota | 纤毛虫属 Balantidium 毛滴虫属 Trichomonas Paracichlidotherus Diplomonadida |
| 禽类 Poultry | 梭菌属 Clostridium 瘤胃球菌属 Ruminococcus 乳杆菌属 Lactobacillus 拟杆菌属 Bacteroides | 小囊菌属 Microascus 毛癣菌属 Trichophyton 曲霉属 Aspergillus 赤霉属 Gibberella 假丝酵母菌属 Candida | ||
| 反刍动物 Ruminant | 普雷沃氏菌属 Prevotella 拟杆菌属 Bacteroides 丁酸弧菌属 Butyrivibrio 梭菌属 Clostridium 颤螺菌属 Oscillospira 瘤胃球菌属 Ruminococcus 琥珀酸菌属 Succiniclasticum 琥珀酸弧菌属 Succinivibrio | 盲肠鞭菌属 Caecomyces 新美鞭菌属 Neocallimastix 梨囊鞭菌属 Piromyces | 嗜甲烷菌科 Methanomethylophilaceae 甲烷球形菌属 Methanosphaera 甲烷短杆菌属 Methanobrevibacter | 内毛虫目 Entodiniomorphida 复毛虫属 Diplodinium 前毛虫属 Epidinium Enoploplastron |
| 植食性单胃哺乳动物 Herbivorous monogastric mammals | 乳杆菌属 Lactobacillus 链球菌属 Streptococcus 放线杆菌属 Actinobacillus 八叠球菌属 Sarcina 拟杆菌属 Bacteroides 普雷沃氏菌属 Prevotella 梭菌属 Clostridium 螺毛菌属 Lachnospiraceae 瘤胃球菌属 Ruminococcus 密螺旋体属 Treponema | 新美鞭菌属 Neocallimastix 根囊鞭菌属 Orpinomyces 厌氧鞭菌属 Anaeromyces | 甲烷粒菌属 Methanocorpusculum 瘤胃甲烷短杆菌 Methanobrevibacter ruminantium | 纤毛虫属 Balantidium 贾第虫属 Giardia 毛滴虫属 Trichomonas |
| 口腔 Oral | 食道 Esophagus | 胃 Stomach | 小肠 Small intestine | 大肠 Large intestine |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 孪生球菌属 Gemella 韦荣氏球菌属 Veillonella 奈瑟菌属 Neisseria 梭杆菌属 Fusobacterium 链球菌属 Streptococcus 普雷沃氏菌 Prevotella 假单胞菌属 Pseudomonas 放线菌属 Actinomyces | 链球菌属 Streptococcus 普雷沃氏菌 Prevotella 韦荣氏球菌属Veillonella | 芽孢杆菌 Bacillales incertae sedis 链球菌属 Streptococcus 肠杆菌属 Enterobacter 纤毛菌属 Leptotrichia 韦荣氏球菌属 Veillonella 假单胞菌属 Pseudomonas | 链球菌属 Streptococcus 普雷沃氏菌 Prevotella 韦荣氏球菌属 Veillonella 梭杆菌 Fusobacterium 大肠杆菌 Escherichia coli 克雷伯菌 Klebsiella 柠檬酸杆菌 Citrobacter | 梭菌科 Clostridiaceae 螺毛菌科 Lachnospiraceae 拟杆菌科 Bacteroidaceae |
表2 人类消化道不同部位优势微生物
Table 4 Dominant microorganisms in different parts of human digestive tract
| 口腔 Oral | 食道 Esophagus | 胃 Stomach | 小肠 Small intestine | 大肠 Large intestine |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 孪生球菌属 Gemella 韦荣氏球菌属 Veillonella 奈瑟菌属 Neisseria 梭杆菌属 Fusobacterium 链球菌属 Streptococcus 普雷沃氏菌 Prevotella 假单胞菌属 Pseudomonas 放线菌属 Actinomyces | 链球菌属 Streptococcus 普雷沃氏菌 Prevotella 韦荣氏球菌属Veillonella | 芽孢杆菌 Bacillales incertae sedis 链球菌属 Streptococcus 肠杆菌属 Enterobacter 纤毛菌属 Leptotrichia 韦荣氏球菌属 Veillonella 假单胞菌属 Pseudomonas | 链球菌属 Streptococcus 普雷沃氏菌 Prevotella 韦荣氏球菌属 Veillonella 梭杆菌 Fusobacterium 大肠杆菌 Escherichia coli 克雷伯菌 Klebsiella 柠檬酸杆菌 Citrobacter | 梭菌科 Clostridiaceae 螺毛菌科 Lachnospiraceae 拟杆菌科 Bacteroidaceae |
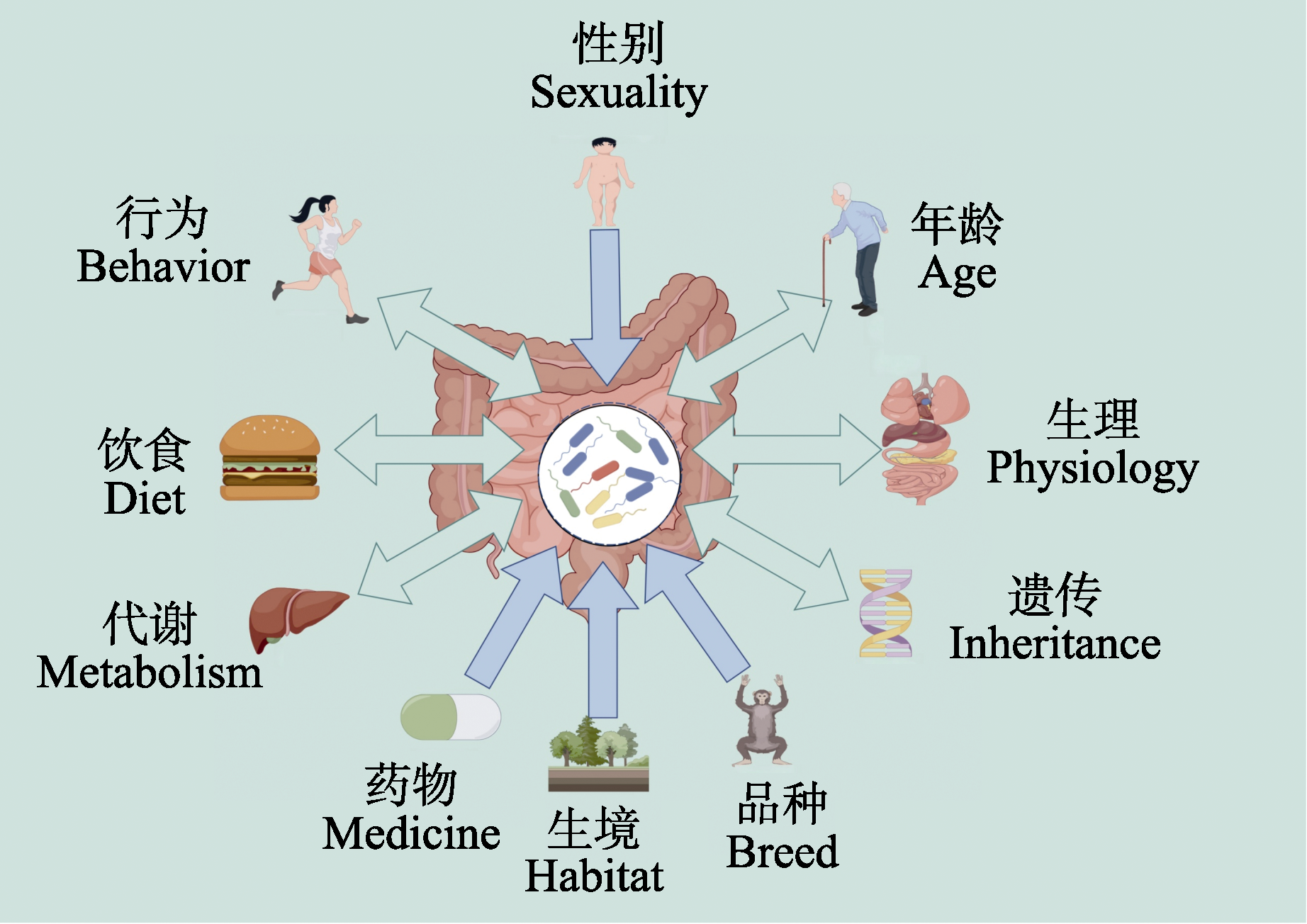
图2 宿主与消化道微生物互作关系及影响消化道微生物组成的因素
Fig. 2 The interaction between host and digestive tract microorganisms and the factors affecting the composition of digestive tract microorganisms
| [1] |
Alberdi A, Andersen SB, Limborg MT, Dunn RR, Gilbert MTP (2022) Disentangling host-microbiota complexity through hologenomics. Nature Reviews Genetics, 23, 281-297.
DOI |
| [2] |
Arumugam M, Members MCA, Raes J, Pelletier E, Le Paslier D, Yamada T, Mende DR, Fernandes GR, Tap J, Bruls T, Batto JM, Bertalan M, Borruel N, Casellas F, Fernandez L, Gautier L, Hansen T, Hattori M, Hayashi T, Kleerebezem M, Kurokawa K, Leclerc M, Levenez F, Manichanh C, Nielsen HB, Nielsen T, Pons N, Poulain J, Qin JJ, Sicheritz-Ponten T, Tims S, Torrents D, Ugarte E, Zoetendal EG, Wang J, Guarner F, Pedersen O, de Vos WM, Brunak S, Doré J, Weissenbach J, Ehrlich SD, Bork P (2011) Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature, 473, 174-180.
DOI |
| [3] |
Basset Y, Cizek L, Cuénoud P, Didham RK, Guilhaumon F, Missa O, Novotny V, Ødegaard F, Roslin T, Schmidl J, Tishechkin AK, Winchester NN, Roubik DW, Aberlenc HP, Bail J, Barrios H, Bridle JR, Castaño-Meneses G, Corbara B, Curletti G, Duarte da Rocha W, De Bakker D, Delabie JHC, Dejean A, Fagan LL, Floren A, Kitching RL, Medianero E, Miller SE, Gama de Oliveira E, Orivel J, Pollet M, Rapp M, Ribeiro SP, Roisin Y, Schmidt JB, Sørensen L, Leponce M (2012) Arthropod diversity in a tropical forest. Science, 338, 1481-1484.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Belkaid Y, Hand TW (2014) Role of the microbiota in immunity and inflammation. Cell, 157, 121-141.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Benson AK, Kelly SA, Legge R, Ma FR, Low SJ, Kim J, Zhang M, Oh PL, Nehrenberg D, Hua KJ, Kachman SD, Moriyama EN, Walter J, Peterson DA, Pomp D (2010) Individuality in gut microbiota composition is a complex polygenic trait shaped by multiple environmental and host genetic factors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 107, 18933-18938. |
| [6] |
Berg G, Rybakova D, Fischer D, Cernava T, Vergès MC C, Charles T, Chen X, Cocolin L, Eversole K, Corral GH, Kazou M, Kinkel L, Lange L, Lima N, Loy A, Macklin JA, Maguin E, Mauchline T, McClure R, Mitter B, Ryan M, Sarand I, Smidt H, Schelkle B, Roume H, Kiran GS, Selvin J, de Souza RSC, van Overbeek L, Singh BK, Wagner M, Walsh A, Sessitsch A, Schloter M (2020) Microbiome definition re-visited: Old concepts and new challenges. Microbiome, 8, 103.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Broderick NA, Lemaitre B (2012) Gut-associated microbes of Drosophila melanogaster. Gut Microbes, 3, 307-321.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Brune A (2014) Symbiotic digestion of lignocellulose in termite guts. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 12, 168-180.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Burns AR, Miller E, Agarwal M, Rolig AS, Milligan-Myhre K, Seredick S, Guillemin K, Bohannan BJM (2017) Interhost dispersal alters microbiome assembly and can overwhelm host innate immunity in an experimental zebrafish model. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 114, 11181-11186. |
| [10] |
Callegari M, Crotti E, Fusi M, Marasco R, Gonella E, De Noni I, Romano D, Borin S, Tsiamis G, Cherif A, Alma A, Daffonchio D (2021) Compartmentalization of bacterial and fungal microbiomes in the gut of adult honeybees. Npj Biofilms and Microbiomes, 7, 42.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | Carroll SB (2005) Endless Forms Most Beautiful:The New Science of Evo Devo and the Making of the Animal Kingdom. WWW Norton & Company, New York. |
| [12] |
Cazemier AE, Hackstein JHP, Op den Camp HJM, Rosenberg J, van der Drift C (1997) Bacteria in the intestinal tract of different species of arthropods. Microbial Ecology, 33, 189-197.
PMID |
| [13] |
Ceja-Navarro JA, Vega FE, Karaoz U, Hao Z, Jenkins S, Lim HC, Kosina P, Infante F, Northen TR, Brodie EL (2015) Gut microbiota mediate caffeine detoxification in the primary insect pest of coffee. Nature Communications, 6, 7618.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Chapagain P, Arivett B, Cleveland BM, Walker DM, Salem M (2019) Analysis of the fecal microbiota of fast- and slow-growing rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). BMC Genomics, 20, 788.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | Cheng SC, Liu CB, Yao XQ, Hu JY, Yin TT, Lim BK, Chen W, Wang GD, Zhang CL, Irwin DM, Zhang ZG, Zhang YP, Yu L (2023) Hologenomic insights into mammalian adaptations to myrmecophagy. National Science Review, 10, nwac174. |
| [16] |
Colston TJ, Jackson CR (2016) Microbiome evolution along divergent branches of the vertebrate tree of life: What is known and unknown. Molecular Ecology, 25, 3776-3800.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Colwell RR (1962) The bacterial flora of puget sound fish. Journal of Applied Bacteriology, 25, 147-158.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Couch CE, Stagaman K, Spaan RS, Combrink HJ, Sharpton TJ, Beechler BR, Jolles AE (2021) Diet and gut microbiome enterotype are associated at the population level in African buffalo. Nature Communications, 12, 2267.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | Cui HR, Bai TT, Zhao LB, Chen YX, Guo XF, Jin W (2022) Comparison and analysis of rumen microflora structure difference between Hu sheep and Karakul sheep. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 34, 1721-1729. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[崔浩然, 白天天, 赵林波, 陈颜旭, 郭雪峰, 金巍 (2022) 湖羊与卡拉库尔羊瘤胃菌群结构差异性比较分析. 动物营养学报, 34, 1721-1729.]
DOI |
|
| [20] | David LA, Maurice CF, Carmody RN, Gootenberg DB, Button JE, Wolfe BE, Ling AV, Devlin AS, Varma Y, Fischbach MA, Biddinger SB, Dutton RJ, Turnbaugh PJ (2014) Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature, 505, 559-563. |
| [21] |
Deshpande NP, Riordan SM, Castaño-Rodríguez N, Wilkins MR, Kaakoush NO (2018) Signatures within the esophageal microbiome are associated with host genetics, age, and disease. Microbiome, 6, 227.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Dewhirst FE, Chen T, Izard J, Paster BJ, Tanner ACR, Yu WH, Lakshmanan A, Wade WG (2010) The human oral microbiome. Journal of Bacteriology, 192, 5002-5017.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
Diaz CJM, Casanova NA, Fernández Miyakawa ME (2019) Microbiota, gut health and chicken productivity: What is the connection? Microorganisms, 7, 374.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Dimitroglou A, Merrifield DL, Carnevali O, Picchietti S, Avella M, Daniels C, Güroy D, Davies SJ (2011) Microbial manipulations to improve fish health and production—A Mediterranean perspective. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 30, 1-16. |
| [25] |
Douglas AE (2015) Multiorganismal insects: Diversity and function of resident microorganisms. Annual Review of Entomology, 60, 17-34.
DOI PMID |
| [26] | Douglas E (2010) The Symbiotic Habit. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [27] |
Duncan SH, Belenguer A, Holtrop G, Johnstone AM, Flint HJ, Lobley GE (2007) Reduced dietary intake of carbohydrates by obese subjects results in decreased concentrations of butyrate and butyrate-producing bacteria in feces. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73, 1073-1078.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
Egerton S, Culloty S, Whooley J, Stanton C, Ross RP (2018) The gut microbiota of marine fish. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9, 873.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
Engel P, Moran NA (2013) The gut microbiota of insects- diversity in structure and function. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 37, 699-735.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Ericsson AC, Johnson PJ, Lopes MA, Perry SC, Lanter HR (2016) A microbiological map of the healthy equine gastrointestinal tract. PLoS ONE, 11, e0166523. |
| [31] |
Fan PX, Bian BL, Teng L, Nelson CD, Driver J, Elzo MA, Jeong KC (2020) Host genetic effects upon the early gut microbiota in a bovine model with graduated spectrum of genetic variation. The ISME Journal, 14, 302-317.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Fan QS, Wanapat M, Yan TH, Hou FJ (2020) Altitude influences microbial diversity and herbage fermentation in the rumen of yaks. BMC Microbiology, 20, 370.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | Flint HJ, Bayer EA (2008) Plant cell wall breakdown by anaerobic microorganisms from the mammalian digestive tract. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1125, 280-288. |
| [34] |
Flint HJ, Scott KP, Duncan SH, Louis P, Forano E (2012) Microbial degradation of complex carbohydrates in the gut. Gut Microbes, 3, 289-306.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Foster JA, Neufeld KAM (2013) Gut-brain axis: How the microbiome influences anxiety and depression. Trends in neurosciences, 36, 305-312.
DOI PMID |
| [36] | Fujisaka S, Watanabe Y, Tobe K (2023) The gut microbiome: A core regulator of metabolism. Journal of Endocrinology, 256, e220111. |
| [37] |
Gajardo K, Rodiles A, Kortner TM, Krogdahl Å, Bakke AM, Merrifield DL, Sørum H (2016) A high-resolution map of the gut microbiota in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar): A basis for comparative gut microbial research. Scientific Reports, 6, 30893.
DOI PMID |
| [38] |
Gatesoupe FJ (2007) Live yeasts in the gut: Natural occurrence, dietary introduction, and their effects on fish health and development. Aquaculture, 267, 20-30.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Gootenberg DB, Turnbaugh PJ (2011) Companion animals symposium: Humanized animal models of the microbiome. Journal of animal science, 89, 1531-1537.
DOI PMID |
| [40] |
Grice EA, Kong HH, Conlan S, Deming CB, Davis J, Young AC, Bouffard GG, Blakesley RW, Murray PR, Green ED, Turner ML, Segre JA, Program NCS (2009) Topographical and temporal diversity of the human skin microbiome. Science, 324, 1190-1192.
DOI PMID |
| [41] | Groussin M, Mazel F, Alm EJ (2020) Co-evolution and co-speciation of host-gut bacteria systems. Cell Host & Microbe, 28, 12-22. |
| [42] |
Guo N, Wu QF, Shi FY, Niu JH, Zhang T, Degen AA, Fang QG, Ding LM, Shang ZH, Zhang ZG, Long RJ (2021) Seasonal dynamics of diet-gut microbiota interaction in adaptation of yaks to life at high altitude. Npj Biofilms and Microbiomes, 7, 38.
DOI PMID |
| [43] | Hackstein JH (2018) (Endo) Symbiotic Methanogenic Archaea. Springer Nature, Switzerland. |
| [44] |
Haindl R, Schick S, Kulozik U (2021) Influence of cultivation pH on composition, diversity, and metabolic production in an in vitro human intestinal microbiota. Fermentation, 7, 156.
DOI URL |
| [45] | Helfman S, Collette B, Facey E, Bowen BW (2009) The Diversity of Fishes: Biology, Evolution, and Ecology, 2nd Edtion. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken. |
| [46] | Henderson G, Cox F, Ganesh S, Jonker A, Young W, Janssen HP (2015) Rumen microbial community composition varies with diet and host, but a core microbiome is found across a wide geographical range. Scientific Reports, 6, 14567. |
| [47] |
Hillman ET, Lu H, Yao TM, Nakatsu CH (2017) Microbial ecology along the gastrointestinal tract. Microbes and Environments, 32, 300-313.
DOI PMID |
| [48] |
Hongoh Y (2010) Diversity and genomes of uncultured microbial symbionts in the termite gut. Bioscience, Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 74, 1145-1151.
DOI URL |
| [49] | Hsiung T (1930) A Monograph on the Protozoa of the Large Intestine of the Horse. PhD dissertation, Iowa State University, Ames. |
| [50] |
Hu JM, Lin SL, Zheng BD, Cheung PCK (2018) Short-chain fatty acids in control of energy metabolism. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 58, 1243-1249.
DOI PMID |
| [51] |
Jewell KA, McCormick CA, Odt CL, Weimer PJ, Suen G (2015) Ruminal bacterial community composition in dairy cows is dynamic over the course of two lactations and correlates with feed efficiency. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 81, 4697-4710.
DOI PMID |
| [52] |
Johnson EL, Heaver SL, Waters JL, Kim BI, Bretin A, Goodman AL, Gewirtz AT, Worgall TS, Ley RE (2020) Sphingolipids produced by gut bacteria enter host metabolic pathways impacting ceramide levels. Nature communications, 11, 2471.
DOI PMID |
| [53] |
Józefiak D, Rutkowski A, Martin SA (2004) Carbohydrate fermentation in the avian ceca: A review. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 113, 1-15.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Khafipour E, Li S, Tun HM, Derakhshani H, Moossavi S, Plaizier JC (2016) Effects of grain feeding on microbiota in the digestive tract of cattle. Animal Frontiers, 6, 13-19.
DOI URL |
| [55] | Kikuchi Y, Hayatsu M, Hosokawa T, Nagayama A, Tago K, Fukatsu T (2012) Symbiont-mediated insecticide resistance. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 109, 8618-8622. |
| [56] |
Kim M, Morrison M, Yu ZT (2011) Status of the phylogenetic diversity census of ruminal microbiomes. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 76, 49-63.
DOI PMID |
| [57] |
Kim PS, Shin NR, Lee JB, Kim MS, Whon TW, Hyun DW, Yun JH, Jung MJ, Kim JY, Bae JW (2021) Host habitat is the major determinant of the gut microbiome of fish. Microbiome, 9, 166.
DOI PMID |
| [58] | Klindworth A, Pruesse E, Schweer T, Peplies J, Quast C, Horn M, Glöckner FO (2013) Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Research, 41, e1. |
| [59] | Koenig JE, Spor A, Scalfone N, Fricker AD, Stombaugh J, Knight R, Angenent LT, Ley RE (2011) Succession of microbial consortia in the developing infant gut microbiome. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 108, 4578-4585. |
| [60] |
Kohl KD, Weiss RB, Cox J, Dale C, Dearing MD (2014) Gut microbes of mammalian herbivores facilitate intake of plant toxins. Ecology Letters, 17, 1238-1246.
DOI PMID |
| [61] | Kokou F, Sasson G, Nitzan T, Doron-Faigenboim A, Harpaz S, Cnaani A, Mizrahi I (2018) Host genetic selection for cold tolerance shapes microbiome composition and modulates its response to temperature. eLife, 7, e36398. |
| [62] |
Krajmalnik-Brown R, Ilhan ZE, Kang DW, DiBaise JK (2012) Effects of gut microbes on nutrient absorption and energy regulation. Nutrition in Clinical Practice, 27, 201-214.
DOI PMID |
| [63] |
Kushmaro A, Rosenberg E, Fine M, Loya Y (1997) Bleaching of the coral Oculina patagonica by Vibrio AK-1. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 147, 159-165.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
Kwong WK, Moran NA (2016) Gut microbial communities of social bees. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 14, 374-384.
DOI PMID |
| [65] |
Le Chatelier E, Nielsen T, Qin JJ, Prifti E, Hildebrand F, Falony G, Almeida M, Arumugam M, Batto JM, Kennedy S, Leonard P, Li JH, Burgdorf K, Grarup N, Jørgensen T, Brandslund I, Nielsen HB, Juncker AS, Bertalan M, Levenez F, Pons N, Rasmussen S, Sunagawa S, Tap J, Tims S, Zoetendal EG, Brunak S, Clément K, Doré J, Kleerebezem M, Kristiansen K, Renault P, Sicheritz-Ponten T, de Vos WM, Zucker JD, Raes J, Hansen T, Guedon E, Delorme C, Layec S, Khaci G, van de Guchte M, Vandemeulebrouck G, Jamet A, Dervyn R, Sanchez N, Maguin E, Haimet F, Winogradski Y, Cultrone A, Leclerc M, Juste C, Blottière H, Pelletier E, LePaslier D, Artiguenave F, Bruls T, Weissenbach J, Turner K, Parkhill J, Antolin M, Manichanh C, Casellas F, Boruel N, Varela E, Torrejon A, Guarner F, Denariaz G, Derrien M, Veiga P, Oozeer R, Knol J, Rescigno M, Brechot C, M’Rini C, Mérieux A, Yamada T, Bork P, Wang J, Ehrlich SD, Pedersen O, Consortium M (2013) Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with metabolic markers. Nature, 500, 541-546.
DOI |
| [66] | Ley RE (2016) Prevotella in the gut: Choose carefully. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 13, 69-70. |
| [67] |
Ley RE, Lozupone CA, Hamady M, Knight R, Gordon JI (2008) Worlds within worlds: Evolution of the vertebrate gut microbiota. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 6, 776-788.
DOI PMID |
| [68] |
Ley RE, Peterson DA, Gordon JI (2006a) Ecological and evolutionary forces shaping microbial diversity in the human intestine. Cell, 124, 837-848.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI (2006b) Microbial ecology: Human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature, 444, 1022-1023.
DOI |
| [70] | Li B, Jia GB, Wen DX, Zhao XX, Zhang JX, Xu Q, Zhao XL, Jiang N, Liu ZJ, Wang YC (2022) Rumen microbiota of indigenous and introduced ruminants and their adaptation to the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13, 1027138. |
| [71] |
Li BB, Zhang K, Li C, Wang XL, Chen YL, Yang YX (2019) Characterization and comparison of microbiota in the gastrointestinal tracts of the goat (Capra hircus) during preweaning development. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10, 2125.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
Li J, Zhao FQ, Wang YD, Chen JR, Tao J, Tian G, Wu SL, Liu WB, Cui QH, Geng B, Zhang WL, Weldon R, Auguste K, Yang L, Liu XY, Chen L, Yang XC, Zhu BL, Cai J (2017) Gut microbiota dysbiosis contributes to the development of hypertension. Microbiome, 5, 14.
DOI PMID |
| [73] | Li JL, Powell JE, Guo J, Evans JD, Wu J, Williams P, Lin QH, Moran NA, Zhang ZG (2015) Two gut community enterotypes recur in diverse bumblebee species. Current Biology, 25, R652-R653. |
| [74] |
Li K, Bihan M, Yooseph S, Methé BA (2012) Analyses of the microbial diversity across the human microbiome. PLoS ONE, 7, e32118.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
Liu YY, de Bruijn I, Jack ALH, Drynan K, van den Berg AH, Thoen E, Sandoval-Sierra V, Skaar I, van West P, Diéguez-Uribeondo J, van der Voort M, Mendes R, Mazzola M, Raaijmakers JM (2014) Deciphering microbial landscapes of fish eggs to mitigate emerging diseases. The ISME Journal, 8, 2002-2014.
DOI URL |
| [76] | Louca S, Polz MF, Mazel F, Albright MBN, Huber JA, O’Connor MI, Ackermann M, Hahn AS, Srivastava DS, Crowe SA, Doebeli M, Parfrey LW (2018) Function and functional redundancy in microbial systems. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2, 936-943. |
| [77] |
Louis P, Flint HJ (2017) Formation of propionate and butyrate by the human colonic microbiota. Environmental Microbiology, 19, 29-41.
DOI PMID |
| [78] |
Ma Y, Ma S, Chang L, Wang HJ, Ga Q, Ma L, Bai ZZ, Shen YY, Ge RL (2019) Gut microbiota adaptation to high altitude in indigenous animals. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 516, 120-126.
DOI PMID |
| [79] |
Mackie RI (2002) Mutualistic fermentative digestion in the gastrointestinal tract: Diversity and evolution. Integrative and Comparative Biology, 42, 319-326.
DOI PMID |
| [80] |
Maier L, Pruteanu M, Kuhn M, Zeller G, Telzerow A, Anderson EE, Brochado AR, Fernandez KC, Dose H, Mori H, Patil KR, Bork P, Typas A (2018) Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria. Nature, 555, 623-628.
DOI URL |
| [81] |
Martens EC, Neumann M, Desai MS (2018) Interactions of commensal and pathogenic microorganisms with the intestinal mucosal barrier. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 16, 457-470.
DOI PMID |
| [82] |
Martínez I, Wallace G, Zhang CM, Legge R, Benson AK, Carr TP, Moriyama EN, Walter J (2009) Diet-induced metabolic improvements in a hamster model of hypercholesterolemia are strongly linked to alterations of the gut microbiota. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75, 4175-4184.
DOI PMID |
| [83] | Mary HC, John RM (1995) The avian cecum: A review. The Wilson Bulletin, 107, 93-121. |
| [84] | McFall-Ngai M, Hadfield MG, Bosch TCG, Carey HV, Domazet-Lošo T, Douglas AE, Dubilier N, Eberl G, Fukami T, Gilbert SF, Hentschel U, King N, Kjelleberg S, Knoll AH, Kremer N, Mazmanian SK, Metcalf JL, Nealson K, Pierce NE, Rawls JF, Reid A, Ruby EG, Rumpho M, Sanders JG, Tautz D, Wernegreen JJ (2013) Animals in a bacterial world, a new imperative for the life sciences. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 110, 3229-3236. |
| [85] |
Moeller AH, Suzuki TA, Phifer-Rixey M, Nachman MW (2018) Transmission modes of the mammalian gut microbiota. Science, 362, 453-457.
DOI PMID |
| [86] |
Mohammed WS, Ziganshina EE, Shagimardanova EI, Gogoleva NE, Ziganshin AM (2018) Comparison of intestinal bacterial and fungal communities across various xylophagous beetle larvae (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Scientific Reports, 8, 10073.
DOI PMID |
| [87] |
Morais LH, Schreiber HL, Mazmanian SK (2021) The gut microbiota-brain axis in behaviour and brain disorders. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 19, 241-255.
DOI PMID |
| [88] | Moran NA, Sloan DB (2015). The hologenome concept: Helpful or hollow? PLOS Biology, 13, e1002311. |
| [89] |
Morrison DJ, Preston T (2016) Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes, 7, 189-200.
DOI PMID |
| [90] |
Muegge BD, Kuczynski J, Knights D, Clemente JC, González A, Fontana L, Henrissat B, Knight R, Gordon JI (2011) Diet drives convergence in gut microbiome functions across mammalian phylogeny and within humans. Science, 332, 970-974.
DOI PMID |
| [91] |
Mueller UG, Linksvayer TA (2022) Microbiome breeding: Conceptual and practical issues. Trends in Microbiology, 30, 997-1011.
DOI URL |
| [92] |
Mulder IE, Schmidt B, Stokes CR, Lewis M, Bailey M, Aminov RI, Prosser JI, Gill BP, Pluske JR, Mayer CD, Musk CC, Kelly D (2009) Environmentally-acquired bacteria influence microbial diversity and natural innate immune responses at gut surfaces. BMC Biology, 7, 79.
DOI PMID |
| [93] |
Mura E, Edwards J, Kittelmann S, Kaerger K, Voigt K, Mrázek J, Moniello G, Fliegerova K (2019) Anaerobic fungal communities differ along the horse digestive tract. Fungal Biology, 123, 240-246.
DOI PMID |
| [94] | Navarrete P, Magne F, Araneda C, Fuentes P, Barros L, Opazo R, Espejo R, Romero J (2012) PCR-TTGE analysis of 16S rRNA from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) gut microbiota reveals host-specific communities of active bacteria. PLoS ONE, 7, e31335. |
| [95] |
Nayak SK (2010) Role of gastrointestinal microbiota in fish. Aquaculture Research, 41, 1553-15573.
DOI URL |
| [96] |
Neis EPJG, Dejong CHC, Rensen SS (2015) The role of microbial amino acid metabolism in host metabolism. Nutrients, 7, 2930-2946.
DOI PMID |
| [97] |
Neisha AS (2009) Microbes in gastrointestinal health and disease. Gastroenterology, 136, 65-80.
DOI PMID |
| [98] | Neufeld KM, Kang N, Bienenstock J, Foster JA (2011) Reduced anxiety-like behavior and central neurochemical change in germ-free mice. Neurogastroenterology and Motility, 23, 255-e119. |
| [99] |
Newman JT, Cosenza BJ, Buck JD (1972) Aerobic microflora of the bluefish (Pomatomus saltatrix) intestine. Journal of the Fisheries Research Board of Canada, 29, 333-336.
DOI URL |
| [100] |
Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Kinross J, Burcelin R, Gibson G, Jia W, Pettersson S (2012) Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science, 336, 1262-1267.
DOI PMID |
| [101] |
Oakley BB, Lillehoj HS, Kogut MH, Kim WK, Maurer JJ, Pedroso A, Lee MD, Collett SR, Johnson TJ, Cox NA (2014) The chicken gastrointestinal microbiome. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 360, 100-112.
DOI PMID |
| [102] | Olav V, Øivind B, François JG, Jorge GV, Victoriano M, Simona P, Peter B (2013) Microbiology and immunology of fish larvae. Reviews in Aquaculture, 5, s1-s25. |
| [103] |
Palma-Hidalgo JM, Jiménez E, Popova M, Morgavi DP, Martín-García AI, Yáñez-Ruiz DR, Belanche A (2021) Inoculation with rumen fluid in early life accelerates the rumen microbial development and favours the weaning process in goats. Animal Microbiome, 3, 11.
DOI PMID |
| [104] | Pan XL, Zhou GL, Wu JH, Bian GW, Lu P, Raikhel AS, Xi ZY (2012) Wolbachia induces reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent activation of the toll pathway to control dengue virus in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 109, E23-E31. |
| [105] |
Poinar JG (2009) Early Cretaceous protist flagellates (Parabasalia: Hypermastigia: Oxymonada) of cockroaches (Insecta: Blattaria) in Burmese amber. Cretaceous Research, 30, 1066-1072.
DOI URL |
| [106] |
Qiu Q, Zhang GJ, Ma T, Qian WB, Wang JY, Ye ZQ, Cao CC, Hu QJ, Kim J, Larkin DM, Auvil L, Capitanu B, Ma J, Lewin HA, Qian XJ, Lang YS, Zhou R, Wang LZ, Wang K, Xia JQ, Liao SG, Pan SK, Lu X, Hou HL, Wang Y, Zang XT, Yin Y, Ma H, Zhang J, Wang ZF, Zhang YM, Zhang DW, Yonezawa T, Hasegawa M, Zhong Y, Liu WB, Zhang Y, Huang ZY, Zhang SX, Long RJ, Yang HM, Wang J, Lenstra JA, Cooper DN, Wu Y, Wang J, Shi P, Wang J, Liu JQ (2012) The yak genome and adaptation to life at high altitude. Nature Genetics, 44, 946-949.
DOI PMID |
| [107] |
Rios-Covian D, Salazar N, Gueimonde M, de los Reyes-Gavilan CG (2017) Shaping the metabolism of intestinal Bacteroides population through diet to improve human health. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8, 376.
DOI PMID |
| [108] | Robinson K, Xiao YP, Johnson TJ, Chen BL, Yang Q, Lyu WT, Wang J, Fansler N, Becker S, Liu J, Yang H, Zhang GL (2020) Chicken intestinal mycobiome: Initial characterization and its response to bacitracin methylene disalicylate. Applied and environmental microbiology, 86, e00304-20. |
| [109] |
Robinson K, Yang Q, Stewart S, Whitmore MA, Zhang GL (2022) Biogeography, succession, and origin of the chicken intestinal mycobiome. Microbiome, 10, 55.
DOI PMID |
| [110] |
Rohwer F, Seguritan V, Azam F, Knowlton N (2002) Diversity and distribution of coral-associated bacteria. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 243, 1-10.
DOI URL |
| [111] |
Rosenberg E, Falkovitz L (2004) The Vibrio shiloi/Oculina patagonica model system of coral bleaching. Annual Review of Microbiology, 58, 143-159.
PMID |
| [112] |
Russell JB, Rychlik JL (2001) Factors that alter rumen microbial ecology. Science, 292, 1119-1122.
DOI PMID |
| [113] |
Rychlik I (2020) Composition and function of chicken gut microbiota. Animals, 10, 103.
DOI URL |
| [114] |
Saborío-Montero A, Gutiérrez-Rivas M, López-García A, García-Rodríguez A, Atxaerandio R, Goiri I, Jiménez-Montero JA, González-Recio O (2021) Holobiont effect accounts for more methane emission variance than the additive and microbiome effects on dairy cattle. Livestock Science, 250, 104538.
DOI URL |
| [115] |
Salyers AA, West SE, Vercellotti JR, Wilkins TD (1977) Fermentation of mucins and plant polysaccharides by anaerobic bacteria from the human colon. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 34, 529-533.
DOI PMID |
| [116] |
Schwiertz A, Taras D, Schäfer K, Beijer S, Bos NA, Donus C, Hardt PD (2010) Microbiota and SCFA in lean and overweight healthy subjects. Obesity, 18, 190-195.
DOI PMID |
| [117] |
Sekirov I, Russell SL, Antunes LC, Finlay BB (2010) Gut microbiota in health and disease. Physiological Reviews, 90, 859-904.
DOI PMID |
| [118] |
Serbus LR, Casper-Lindley C, Landmann F, Sullivan W (2008) The genetics and cell biology of Wolbachia-host interactions. Annual Review of Genetics, 42,683-707.
DOI PMID |
| [119] |
Servin AL (2004) Antagonistic activities of lactobacilli and bifidobacteria against microbial pathogens. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 28, 405-440.
DOI PMID |
| [120] | Sharon G, Segal D, Ringo JM, Hefetz A, Zilber-Rosenberg I, Rosenberg E (2010) Commensal bacteria play a role in mating preference of Drosophila melanogaster. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 107, 20051-20056. |
| [121] |
Slavin JL (2005) Dietary fiber and body weight. Nutrition, 21, 411-418.
DOI PMID |
| [122] |
Smith NW, Shorten PR, Altermann EH, Roy NC, McNabb WC (2019) Hydrogen cross-feeders of the human gastrointestinal tract. Gut Microbes, 10, 270-288.
DOI PMID |
| [123] |
Soares JH, Leffel EC, Larsen RK (1970) Neonatal lambs in a gnotobiotic environment. Journal of Animal Science, 31, 733-740.
PMID |
| [124] |
Soen Y (2014) Environmental disruption of host-microbe co-adaptation as a potential driving force in evolution. Frontiers in Genetics, 5, 168.
DOI PMID |
| [125] |
Sokol H, Leducq V, Aschard H, Pham HP, Jegou S, Landman C, Cohen D, Liguori G, Bourrier A, Nion-Larmurier I, Cosnes J, Seksik P, Langella P, Skurnik D, Richard ML, Beaugerie L (2017) Fungal microbiota dysbiosis in IBD. Gut, 66, 1039-1048.
DOI PMID |
| [126] | Song W, Li LZ, Huang HL, Jiang KJ, Zhang FY, Chen XZ, Zhao M, Ma LB (2016) The gut microbial community of antarctic fish detected by 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis. BioMed Research International, 2016, 3241529. |
| [127] |
Sonnenburg ED, Zheng HJ, Joglekar P, Higginbottom SK, Firbank SJ, Bolam DN, Sonnenburg JL (2010) Specificity of polysaccharide use in intestinal Bacteroides species determines diet-induced microbiota alterations. Cell, 141, 1241-1252.
DOI PMID |
| [128] | Stanley D, Geier MS, Hughes RJ, Denman SE, Moore RJ (2013) Highly variable microbiota development in the chicken gastrointestinal tract. PLoS ONE, 8, e84290. |
| [129] |
Stanley D, Hughes RJ, Moore RJ (2014) Microbiota of the chicken gastrointestinal tract: Influence on health, productivity and disease. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 98, 4301-4310.
DOI PMID |
| [130] |
Suárez-Zamorano N, Fabbiano S, Chevalier C, Stojanović O, Colin DJ, Stevanović A, Veyrat-Durebex C, Tarallo V, Rigo D, Germain S, Ilievska M, Montet X, Seimbille Y, Hapfelmeier S, Trajkovski M (2015) Microbiota depletion promotes browning of white adipose tissue and reduces obesity. Nature Medicine, 21, 1497-1501.
DOI PMID |
| [131] |
Tailford LE, Crost EH, Kavanaugh D, Juge N (2015) Mucin glycan foraging in the human gut microbiome. Frontiers in Genetics, 6, 81.
DOI PMID |
| [132] |
Talwar C, Nagar S, Lal R, Negi RK (2018) Fish gut microbiome: Current approaches and future perspectives. Indian Journal of Microbiology, 58, 397-414.
DOI PMID |
| [133] |
Thomas CM, Desmond-Le Quéméner E, Gribaldo S, Borrel G (2022) Factors shaping the abundance and diversity of the gut archaeome across the animal Kingdom. Nature Communications, 13, 3358.
DOI PMID |
| [134] |
Thong-On A, Suzuki K, Noda S, Inoue JI, Kajiwara S, Ohkuma M (2012) Isolation and characterization of anaerobic bacteria for symbiotic recycling of uric acid nitrogen in the gut of various termites. Microbes and Environments, 27, 186-192.
PMID |
| [135] |
Tran NT, Zhang J, Xiong F, Wang GT, Li WX, Wu SG (2018) Altered gut microbiota associated with intestinal disease in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 34, 71.
DOI |
| [136] | Turnbaugh PJ, Bäckhed F, Fulton L, Gordon JI (2008) Diet-induced obesity is linked to marked but reversible alterations in the mouse distal gut microbiome. Cell Host & Microbe, 3, 213-223. |
| [137] |
Vasapolli R, Schütte K, Schulz C, Vital M, Schomburg D, Pieper DH, Vilchez-Vargas R, Malfertheiner P (2019) Analysis of transcriptionally active bacteria throughout the gastrointestinal tract of healthy individuals. Gastroenterology, 157, 1081-1092.
DOI PMID |
| [138] | Voigt RM, Forsyth CB, Green SJ, Mutlu E, Engen P, Vitaterna MH, Turerk FW, Keshavarzian A (2014) Circadian disorganization alters intestinal microbiota. PLoS ONE, 9, e97500. |
| [139] |
Waclawiková B, Codutti A, Alim K, El Aidy S (2022) Gut microbiota-motility interregulation: insights from in vivo, ex vivo and in silico studies. Gut Microbes, 14, 1997296.
DOI PMID |
| [140] |
Wang SC, Wang LY, Fan X, Yu C, Feng L, Yi L (2020) An insight into diversity and functionalities of gut microbiota in insects. Current Microbiology, 77, 1976-1986.
DOI PMID |
| [141] |
Wang SS, Song F, Gu HY, Shu ZL, Wei XW, Zhang K, Zhou YX, Jiang LR, Wang ZF, Li JN, Luo HB, Liang WB (2022) Assess the diversity of gut microbiota among healthy adults for forensic application. Microbial Cell Factories, 21, 46.
DOI PMID |
| [142] |
Wei S, Morrison M, Yu Z (2013) Bacterial census of poultry intestinal microbiome. Poultry Science, 92, 671-683.
DOI PMID |
| [143] |
Wilck N, Matus MG, Kearney SM, Olesen SW, Forslund K, Bartolomaeus H, Haase S, Mähler A, Balogh A, Markó L, Vvedenskaya O, Kleiner FH, Tsvetkov D, Klug L, Costea PI, Sunagawa S, Maier LS, Rakova N, Schatz V, Neubert P, Frätzer C, Krannich A, Gollasch M, Grohme DA, Côrte-Real BF, Gerlach RG, Basic M, Typas A, Wu C, Titze JM, Jantsch J, Boschmann M, Dechend R, Kleinewietfeld M, Kempa S, Bork P, Linker RA, Alm EJ, Müller DN (2017) Salt-responsive gut commensal modulates TH 17 axis and disease. Nature, 551, 585-589.
DOI URL |
| [144] |
Wu DW, Vinitchaikul P, Deng MY, Zhang GR, Sun LY, Wang HX, Gou X, Mao HM, Yang SL (2021) Exploration of the effects of altitude change on bacteria and fungi in the rumen of yak (Bos grunniens). Archives of Microbiology, 203, 835-846.
DOI PMID |
| [145] |
Wu GD, Chen J, Hoffmann C, Bittinger K, Chen YY, Keilbaugh SA, Bewtra M, Knights D, Walters WA, Knight R, Sinha R, Gilroy E, Gupta K, Baldassano R, Nessel L, Li HZ, Bushman FD, Lewis JD (2011) Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science, 334, 105-108.
DOI PMID |
| [146] |
Xin JW, Chai ZX, Zhang CF, Zhang Q, Zhu Y, Cao HW, Zhong JC, Ji QM (2019) Comparing the microbial community in four stomach of dairy cattle, yellow cattle and three yak herds in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10, 1547.
DOI PMID |
| [147] |
Yadav S, Jha R (2019) Strategies to modulate the intestinal microbiota and their effects on nutrient utilization, performance, and health of poultry. Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology, 10, 2.
DOI PMID |
| [148] |
Yoo JY, Groer M, Dutra SVO, Sarkar A, McSkimming DI (2020) Gut microbiota and immune system interactions. Microorganisms, 8, 1587.
DOI URL |
| [149] |
Yun JH, Roh SW, Whon TW, Jung MJ, Kim MS, Park DS, Yoon C, Nam YD, Kim YJ, Choi JH, Kim JY, Shin NR, Kim SH, Lee WJ, Bae JW (2014) Insect gut bacterial diversity determined by environmental habitat, diet, developmental stage, and phylogeny of host. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 80, 5254-5264.
DOI URL |
| [150] |
Zhang CH, Zhang MH, Pang XY, Zhao YF, Wang LH, Zhao LP (2012) Structural resilience of the gut microbiota in adult mice under high-fat dietary perturbations. The ISME Journal, 6, 1848-1857.
DOI URL |
| [151] |
Zhang ZG, Xu DM, Wang L, Hao JJ, Wang JF, Zhou X, Wang WW, Qiu Q, Huang XD, Zhou JW, Long RJ, Zhao FQ, Shi P (2016) Convergent evolution of rumen microbiomes in high-altitude mammals. Current Biology, 26, 1873-1879.
DOI PMID |
| [152] | Zhou H, Yang LY, Ding JM, Dai RH, He C, Xu K, Luo LX, Xiao L, Zheng YM, Han CX, Akinyemi FT, Honaker CF, Zhang Y, Siegel PB, Meng H (2022) Intestinal microbiota and host cooperate for adaptation as a hologenome. mSystems, 7, e01261-21. |
| [153] |
Zilber-Rosenberg I, Rosenberg E (2008) Role of microorganisms in the evolution of animals and plants: The hologenome theory of evolution. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 32, 723-735.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [3] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [4] | 周昊, 王茗毅, 张楚格, 肖治术, 欧阳芳. 昆虫旅馆在独栖蜂多样性保护中的现状与挑战[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24472-. |
| [5] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [6] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [7] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [8] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [9] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [10] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [11] | 徐欢, 辛凤飞, 施宏亮, 袁琳, 薄顺奇, 赵欣怡, 邓帅涛, 潘婷婷, 余婧, 孙赛赛, 薛程. 生态修复技术集成应用对长江口北支生境与鸟类多样性提升效果评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24478-. |
| [12] | 谢林哲, 彭旻晟, 韩建林, 方美英, 吕锋骅, 陈宁博, 王国栋, 李钢, 尹婷婷. 家养动物及其野生近缘种中文名与拉丁名使用建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24293-. |
| [13] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [14] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [15] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()