



生物多样性 ›› 2010, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (3): 262-274. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.262 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2010.262
收稿日期:2009-10-29
接受日期:2010-01-01
出版日期:2010-05-20
发布日期:2012-02-08
通讯作者:
何舜平
作者简介: E-mail: clad@ihb.ac.cn基金资助:
Xiying Ku1,2, Chuanjiang Zhou1,3, Shunping He1,*( )
)
Received:2009-10-29
Accepted:2010-01-01
Online:2010-05-20
Published:2012-02-08
Contact:
Shunping He
摘要:
基于体侧色斑、背鳍前部形态、吻长及尾柄长的差异, Ng和Kottelat(2007)将分布于中国的黄颡鱼群体划为两个物种: 北方群体为Pseudobagrus sinensis, 南方群体为P. fulvidraco。本研究通过对70个黄颡鱼标本相关形态特征的测量及对线粒体cyt b基因序列的分析, 探讨了P. sinensis物种的有效性问题。结果表明: 依据体侧色斑和背鳍前部形态的差异, 可将黄颡鱼分为对应于P. sinensis和P. fulvidraco的两种形态类型, 但对尾柄长、吻长的测量发现二者没有差异。对70条cyt b基因序列的分析结果为: 两种鱼类有1个共同的单倍型; 两种鱼类的单系性在系统发育分析中都没有得到重现, 而二者聚在一起形成获得100%支持率的单系群; 两种鱼类群体之间存在持续的基因交流(Nm = 4.7); 两种鱼类在单倍型的巢式支系分析(nested clade analysis, NCA)中没有形成各自独立的进化谱系, 所有的单倍型以不超过5步的突变全部被纳入同一个进化网络中。因此我们认为P. sinensis不是有效物种, 而应被视为黄颡鱼的一种形态类型。基于cyt b基因的序列变异, 本研究对黄颡鱼群体的遗传多样性和种群结构作了初步分析。群体的核苷酸不配对分布及Tajima’sD中性检验表明, 约在10.1-14.1万年前, 黄颡鱼在其分布范围内经历过群体扩张, 推测这可能是导致黄颡鱼群体单倍型多样度高(h = 0.857 ± 0.0014)而核苷酸多样度低( π = 0.0023 ± 0.0003)的主要原因。此外, 分析结果显示黄颡鱼群体缺乏明显的地理结构, 推测原因可能是历史上水系的连通促进了不同地理群体之间的基因交流。
库喜英, 周传江, 何舜平 (2010) 中国黄颡鱼的线粒体DNA多样性及其分子系统学. 生物多样性, 18, 262-274. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.262.
Xiying Ku, Chuanjiang Zhou, Shunping He (2010) Validity of Pseudobagrus sinensis and mitochondrial DNA diversity of Pseudobagrus fulvidraco populations in China. Biodiversity Science, 18, 262-274. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.262.
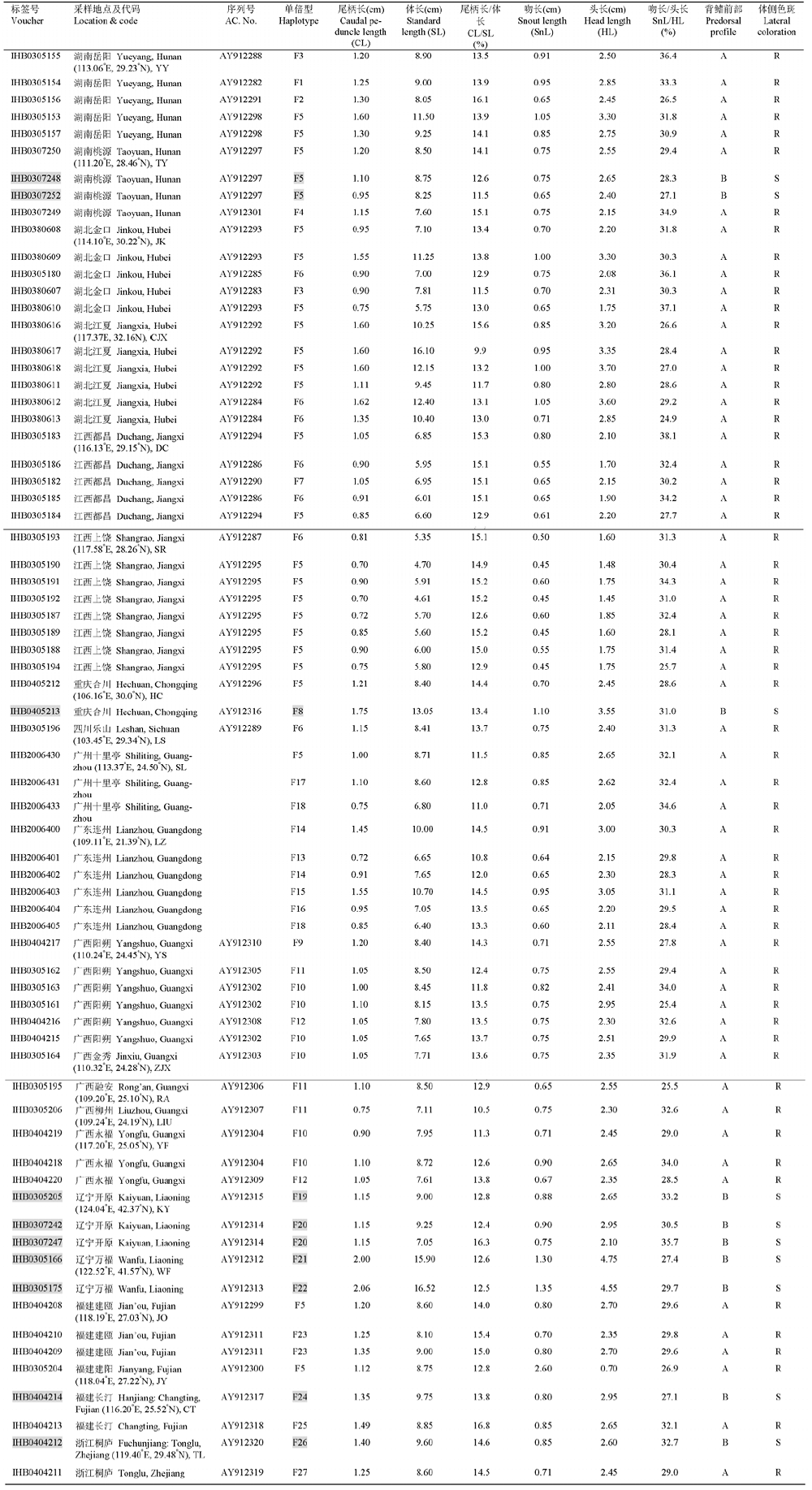 |
表1 实验所用标本的标签号、采集地及相关形态特征的度量值。灰色字体部分代表鉴定为Psendobagrus sinensis的样本。
Table 1 Sampling and morphometric data for fish materials of Pseudobagrus fulvidraco and P. sinensis.Specimens under grey represent those provisionally identified as P. sinensis according to Ng & Kottelat ( 2007).
 |
| 尾柄长/体长比例 Caudal peduncle length / standard length | 吻长与/头长比例 Snout length / head length | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P. sinensis | P. fulvidraco | P. sinensis | P. fulvidraco | ||
| Ng & Kottelat ( | 9.5-10.9% | 7.3-9.6% | 29.8-32.2% | 32.2-37.5% | |
| 本研究测量结果 Measurements in this study | 11.5-16.3% | 9.9-16.8% | 27.1-35.7% | 24.9-38.1% | |
表2 Pseudobagrus fulvidraco与P. sinensis尾柄长及吻长的比较
Table 2 Comparison of caudal peduncle and snout length between Pseudobagrus sinensisand P. fulvidraco
| 尾柄长/体长比例 Caudal peduncle length / standard length | 吻长与/头长比例 Snout length / head length | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P. sinensis | P. fulvidraco | P. sinensis | P. fulvidraco | ||
| Ng & Kottelat ( | 9.5-10.9% | 7.3-9.6% | 29.8-32.2% | 32.2-37.5% | |
| 本研究测量结果 Measurements in this study | 11.5-16.3% | 9.9-16.8% | 27.1-35.7% | 24.9-38.1% | |
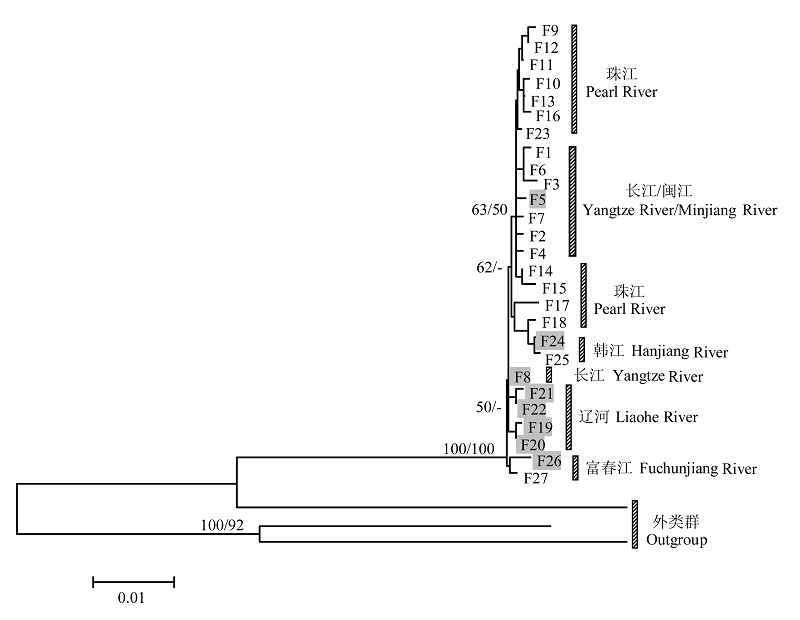
图1 基于cyt b基因得到的单倍型NJ/MP树。节点处的数值依次为NJ/MP分析中1,000次重复抽样所得的自展支持率(仅大于50%的显示)。灰色部分为Pseudobagrus sinensis的单倍型。
Fig. 1 The neighbor-joining (NJ) / maximum parsimony (MP) tree based on cyt bgene sequences. Values above nodes are proportions of 1,000 bootstrap pseudoreplicates in which the node was recovered in NJ/MP analysis (only values above 50% are shown). The grey boxes are haplotypes of Pseudobagrus sinensis.
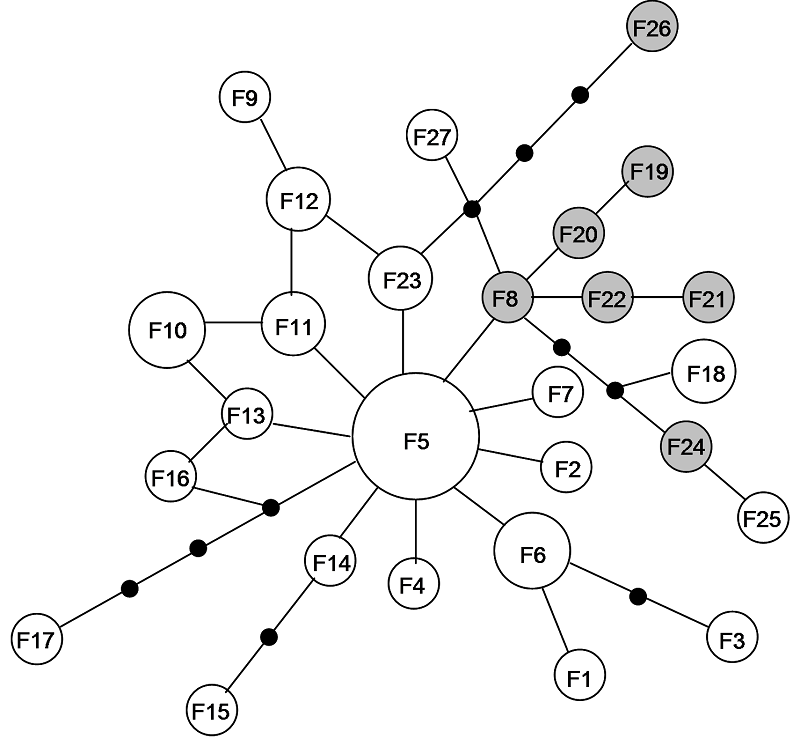
图2 单倍型的进化网络图。圆圈的面积与单倍型包含的样本数成比例; 黑圈表示理论上存在, 但在本研究中没有观测到的单倍型; 单倍型之间的每一连线代表一个突变步骤。灰色部分为Pseudobagrus sinensis的单倍型(F5未标示)。
Fig. 2 Network relationships of haplotypes. Size of circle is proportional to the sample size of haplotypes. Small black circles represent a haplotype which is a necessary intermediate but is not found in the sampled population. Each line connecting haplotypes represent one mutation step. The grey circles are haplotypes of Pseudobagrus sinensis (F5 is not marked).
| 遗传变异来源 Source of variation | ΦST | ΦSC | ΦCT | 组间 Among groups (%) | 群体间 Within populations (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 所有群体 All populations | 0.892 | - | - | 89.15 | 10.85 |
| 水系间 Among drainages | 0.922 | 0.159 | 0.907 | 90.74 | 7.79 |
| 系统树的分支 Among clades | 0.959 | 0.607 | 0.897 | 89.66 | 4.07 |
| 物种间 Between species (P. sinensis/P. fulvidraco) | -0.147 | -0.562 | 0.265 | 26.5 | -41.26 |
表3 本研究对70个样本的AMOVA分析
Table 3 Hierarchical analysis of AMOVA
| 遗传变异来源 Source of variation | ΦST | ΦSC | ΦCT | 组间 Among groups (%) | 群体间 Within populations (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 所有群体 All populations | 0.892 | - | - | 89.15 | 10.85 |
| 水系间 Among drainages | 0.922 | 0.159 | 0.907 | 90.74 | 7.79 |
| 系统树的分支 Among clades | 0.959 | 0.607 | 0.897 | 89.66 | 4.07 |
| 物种间 Between species (P. sinensis/P. fulvidraco) | -0.147 | -0.562 | 0.265 | 26.5 | -41.26 |
| 长江 Yangtze River | 珠江 Pearl River | 闽江 Minjiang | 韩江 Hanjiang | 富春江 Fuchunjiang | 水系内不同群体间 Among groups within drainages | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 长江 Yangtze River | 0.0008 | |||||
| 珠江 Pearl River | 0.0040 | 0.0027 | ||||
| 闽江 Minjiang River | 0.0028 | 0.0050 | 0.0018 | |||
| 韩江 Hanjiang River | 0.0051 | 0.0067 | 0.0058 | 0.0006 | ||
| 富春江 Fuchunjiang River | 0.0035 | 0.0055 | 0.0038 | 0.0042 | 0.0009 | |
| 辽河 Liaohe River | 0.0058 | 0.0070 | 0.0068 | 0.0071 | 0.0059 | 0.0037 |
表4 不同水系的群体间的未校正p距离
Table 4 Uncorrected p distances among groups of different drainages
| 长江 Yangtze River | 珠江 Pearl River | 闽江 Minjiang | 韩江 Hanjiang | 富春江 Fuchunjiang | 水系内不同群体间 Among groups within drainages | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 长江 Yangtze River | 0.0008 | |||||
| 珠江 Pearl River | 0.0040 | 0.0027 | ||||
| 闽江 Minjiang River | 0.0028 | 0.0050 | 0.0018 | |||
| 韩江 Hanjiang River | 0.0051 | 0.0067 | 0.0058 | 0.0006 | ||
| 富春江 Fuchunjiang River | 0.0035 | 0.0055 | 0.0038 | 0.0042 | 0.0009 | |
| 辽河 Liaohe River | 0.0058 | 0.0070 | 0.0068 | 0.0071 | 0.0059 | 0.0037 |
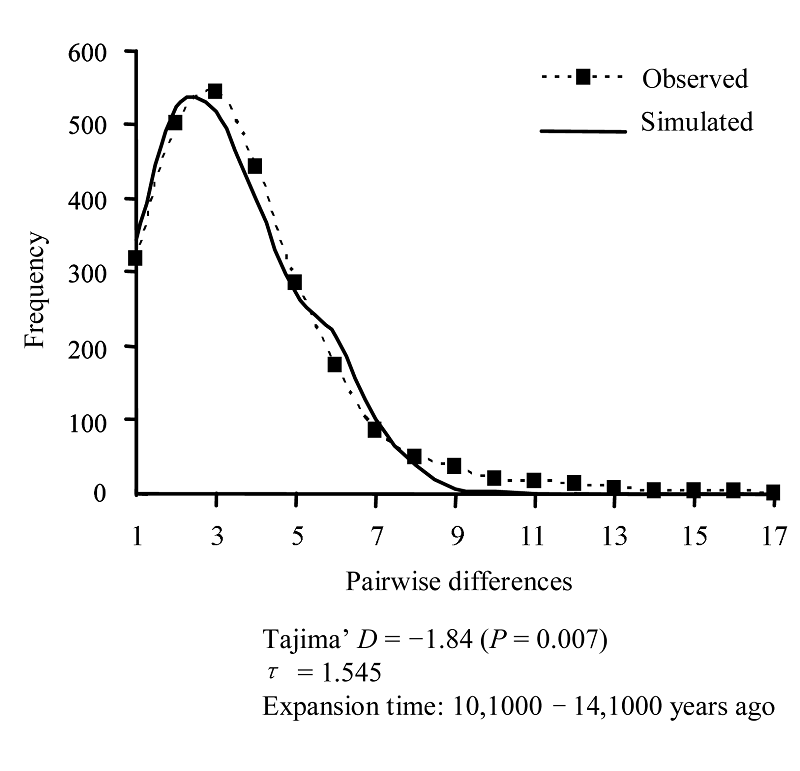
图3 黄颡鱼群体cyt b基因的核苷酸不配对分布。实线为模拟的不配对分布, 虚线为观察到的不配对分布。
Fig. 3 Mismatch distribution for the population of Pseudobagrus fulvidraco. The solid line depicts the simulated mismatch distribution, the dashed line describes the observed distribution.
| [1] | Avise JC (2000) Empirical intraspecific phylogeography. In: Phylogeography, the History and Formation of Species. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts. |
| [2] | Avise JC, Walker D, Johns GC (1998) Speciation durations and Pleistocene effects on vertebrate phylogeography. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series B, Biological Sciences, 265, 1707-1712. |
| [3] | Chu XL (褚新洛), Zheng BS (郑葆珊), Dai DY (戴定远) (1999) Fauna Sinica (Teleostei): Siluriformes (中国动物志: 硬骨鱼纲·鲇形目). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [4] | Clark MK, Schoenbohm LM, Royden LH, Whipple KX, Burchfiel BC, Zhang X, Tang W, Wang E, Chen L (2004) Surface uplift, tectonics, and erosion of eastern Tibet from large-scale drainage patterns. Tectonics, 23, TC1006, doi: 10.1029/2002TC001402. |
| [5] |
Clement M, Posada D, Crandall KA (2000) TCS: a computer program to estimate gene genealogies. Molecular Ecology, 9, 1657-1659.
DOI URL PMID |
| [6] | Compilatory Commission of Physical Geography of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences (中国科学院自然地理编委会) (1980) Physical Geography of China: Physiognomy (中国自然地理: 地貌). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [7] |
Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S (2005) Arlequin (version 3.0): an integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evolutionary Bioinformatics (Online), 1, 47-50.
URL PMID |
| [8] | Fang YL (方耀林), Wang DQ (汪登强), Liu SP (刘绍平), Wu G (伍刚), Liao FC (廖伏初), Chen DQ (陈大庆) (2005) Variation in mitochondrial DNA of Pelteobagrus fulvidraco from three lakes in the Middle Yangtze River. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China (中国水产科学), 12, 56-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Grant WS, Bowen BW (1998) Shallow population histories in deep evolutionary lineages of marine fishes: insights from sardines and anchovies and lessons for conservation. Journal of Heredity, 89, 415-426. |
| [10] |
Hewitt GM (2000) The genetic legacy of the quaternary ice ages. Nature, 405, 907-913.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] |
Hudson RR, Slatkint M, Maddison WP (1992) Estimation of levels of gene flow from DNA sequence data. Genetics, 132, 583-589.
URL PMID |
| [12] | Ku XY, Peng ZG, Diogo R, He SP (2007) MtDNA phylogeny provides evidence of generic polyphyleticism for East Asian bagrid catfishes. Hydrobiologia, 579, 147-159. |
| [13] | Lee CL, Kim IS (1990) A taxonomic revision of the family Bagridae (Pisces, Siluriformes) from Korea. Korean Journal of Ichthyology, 2, 117-137. |
| [14] | Liu HZ (刘焕章) (1998) A preliminary analysis to biogeographical process of the eastern Asian freshwater fishes. Acta Zootaxonomica Sinica (动物分类学报), 23, 49-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [15] | Liu SP (刘世平) (1997) A study on the biology of Pelteobagrus fulvidraco in Poyang Lake. Chinese Journal of Zoology (动物学杂志), 32 (4),10-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] | Lydeard C, Roe KJ (1997) The phylogenetic utility of the mitochondrial cytochrome b gene for inferring relationships among Actinopterygian fishes. In: Molecular Systematics of Fishes (eds Kocher TD, Stepien CA),pp.285-303. Academic Press, San Diego. |
| [17] |
Muse SV, Weir BS (1992) Testing for equality of evolutionary rates. Genetics, 132, 269-276.
URL PMID |
| [18] | Naseka AM, Bogutskaya NG (2004) Contribution to taxonomy and nomenclature of freshwater fishes of the Amur drainage area and the Far East (Pisces, Osteichthyes). Zoosystematica Rossica, 12, 279-290. |
| [19] | Ng HH, Dodson JJ (1999) Morphological and genetic descriptions of a new species of catfish, Hemibagrus chrysops, from Sarawak, East Malaysia, with an assessment of phylogenetic relationships (Teleostei: Bagridae). The Raffles Bulletin of Zoology, 47, 45-57. |
| [20] | Ng HH, Kottelat M (2007) The identity of Tachysurus sinensis (La Cepede, 1803), with the designation of a neotype (Teleostei: Bagridae) and notes on the identity of T. fulvidraco (Richardson, 1845). Electronic Journal of Ichthyology, 2, 35-45. |
| [21] | Peng ZG, He SP, Zhang YG (2002) Mitochondrial cytochrome b sequence variations and phylogeny of East Asian bagrid catfishes. Progress in Natural Science, 12, 421-425. |
| [22] |
Perdices A, Cunha C, Coelho MM (2004) Phylogenetic structure of Zacco platypus (Teleostei, Cyprinidae) populations on the upper and middle Chang Jiang (=Yangtze) drainage inferred from cytochrome b sequences. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 31, 192-203.
DOI URL PMID |
| [23] |
Perdices A, Sayanda D, Coelho MM (2005) Mitochondrial diversity of Opsariichthys bidens (Teleostei, Cyprinidae) in three Chinese drainages. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 37, 920-927.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] |
Raymond M, Rousset F (1995) An exact test for population differentiation. Evolution, 49, 1280-1283.
DOI URL PMID |
| [25] | Ren ME (任美锷), Bao HS (包浩生), Han TC (韩同春) (1959) The Jinsha River valley landforms and river-capture in northwestern Yunnan. Acta Geographica Sinica (地理学报), 25 (2),135-155. (in Chinese) |
| [26] |
Rogers AR, Harpending A (1992) Population growth makes waves in distribution of pairwise genetic differences. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 9, 552-569.
DOI URL PMID |
| [27] | Song P (宋平), Pan YF (潘云风), Xiang Z (向筑), Hu JR (胡珈瑞), Hu YC (胡隐昌), Cai CL (蔡从利) (2001) RAPD markers and genetic diversity in Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. Journal of Wuhan University (Natural Science Edition) (武汉大学学报自然科学版), 47, 233-237. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] | Swofford DL (2002) PAUP*: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (* and other methods). Version 4. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Massachusetts. |
| [29] |
Tajima F (1989) Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics, 123, 585-595.
URL PMID |
| [30] |
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA 4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24, 1596-1599.
DOI URL PMID |
| [31] |
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewnink F (1997) The Clustal_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequences alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 25, 4876-4882.
DOI URL PMID |
| [32] |
Wang JP, Hsu KC, Chiang TY (2000) Mitochondrial DNA phylogeography of Acrossocheilus paradoxus (Cyprinidae) in Taiwan. Molecular Ecology, 9, 1483-1494.
DOI URL PMID |
| [33] |
Wang ZW, Wu QJ, Zhou JF, Ye YZ (2004) Geographic distribution of Pelteobagrus fulvidraco and Pelteobagrus vachelli in the Yangtze River based on mitochondrial DNA markers. Biochemical Genetics, 42, 391-400.
DOI URL PMID |
| [34] | Watanabe K, Nishida M (2003) Genetic population structure of Japanese bagrid catfishes. Ichthyological Research, 50, 140-148. |
| [35] |
Yang L, He SP (2008) Phylogeography of the freshwater catfish Hemibagrus guttatus (Siluriformes, Bagridae): implications for South China biogeography and influence of sea-level changes. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 49, 393-398.
DOI URL PMID |
| [36] |
Yang L, Mayden RL, He SP (2009) Population genetic structure and geographical differentiation of the Chinese catfish Hemibagrus macropterus (Siluriformes, Bagridae): evidence for altered drainages patterns. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 51, 405-411.
DOI URL PMID |
| [37] | Yap SY (2002) On the distributional patterns of Southeast-East Asian freshwater fish and their history. Journal of Biogeography, 29, 1187-1199. |
| [38] | Zhang Y (张燕), Zhang E (张鹗), He SP (何舜平) (2003) Studies on the structure of the control region of the Bagridae in China and its phylogenetic significance. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica (水生生物学报), 27, 463-467. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [39] | Zhao K, Duan ZY, Yang GS, Peng ZG, He SP, Chen YY (2007) Origin of Gymnocypris przewalskii and phylogenetic history of Gymnocypris eckloni (Teleostei: Cyprinidae). Progress in Natural Science, 17, 520-528. |
| [1] | 王嘉陈, 徐汤俊, 许唯, 张高季, 尤艺瑾, 阮宏华, 刘宏毅. 城市景观格局对大蚰蜒种群遗传结构的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [2] | 吕燕文, 王子韵, 肖钰, 何梓晗, 吴超, 胡新生. 谱系分选理论与检测方法的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23400-. |
| [3] | 李庆多, 栗冬梅. 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [4] | 冯晨, 张洁, 黄宏文. 统筹植物就地保护与迁地保护的解决方案: 植物并地保护(parallel situ conservation)[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [5] | 齐海玲, 樊鹏振, 王跃华, 刘杰. 中国北方六省区胡桃的遗传多样性和群体结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [6] | 熊飞, 刘红艳, 翟东东, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 陈大庆. 基于基因组重测序的长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [7] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [8] | 何艺玥, 刘玉莹, 张富斌, 秦强, 曾燏, 吕振宇, 杨坤. 梯级水利工程背景下的嘉陵江干流蛇鮈群体遗传多样性和遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23160-. |
| [9] | 孙维悦, 舒江平, 顾钰峰, 莫日根高娃, 杜夏瑾, 刘保东, 严岳鸿. 基于保护基因组学揭示荷叶铁线蕨的濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21508-. |
| [10] | 陶克涛, 白东义, 图格琴, 赵若阳, 安塔娜, 铁木齐尔·阿尔腾齐米克, 宝音德力格尔, 哈斯, 芒来, 韩海格. 基于基因组SNPs对东亚家马不同群体遗传多样性的评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21031-. |
| [11] | 崔静, 徐明芳, 章群, 李瑶, 曾晓舒, 李莎. 基于3种线粒体标记探讨中日沿海角木叶鲽遗传多样性差异[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21485-. |
| [12] | 孙琼, 王嵘, 陈小勇. 物种形成过程中的分化基因组岛及其形成机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(3): 21383-. |
| [13] | 孙军, 宋煜尧, 施义锋, 翟键, 燕文卓. 近十年中国海洋生物多样性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22526-. |
| [14] | 栗冬梅, 杨卫红, 李庆多, 韩茜, 宋秀平, 潘虹, 冯云. 巴尔通体在滇西南蝙蝠中高度流行并具有丰富的遗传变异特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1245-1255. |
| [15] | 姚志, 郭军, 金晨钟, 刘勇波. 中国纳入一级保护的极小种群野生植物濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(3): 394-408. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()