



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 21473. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021473 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021473
所属专题: 青藏高原生物多样性与生态安全
收稿日期:2021-11-23
接受日期:2022-04-03
出版日期:2022-06-20
发布日期:2022-05-18
通讯作者:
郭小芳
作者简介:* E-mail: gxf005@hotmail.com基金资助:
Wenkai Xue, Huadanshang Meng, Yanhong Wang, Pan Zhu, Ji De, Xiaofang Guo( )
)
Received:2021-11-23
Accepted:2022-04-03
Online:2022-06-20
Published:2022-05-18
Contact:
Xiaofang Guo
摘要:
微生物多样性在评估水体生态环境方面发挥着重要作用。本研究以青藏高原纳木措湖为研究对象, 开展水体可培养丝状真菌多样性及影响因子研究。通过膜过滤平置培养法、经典分类法和rRNA转录间隔区(ITS)序列分析对纳木措湖20个采样点的丝状真菌进行分离、纯化及鉴定, 测定水体理化指标, 综合分析丝状真菌空间分布格局与理化因子的相关性。菌种鉴定结果显示, 从纳木措水体样品中共分离纯化出1,412株丝状真菌, 隶属22属47种, 其中链格孢属(Alternaria)、青霉属(Penicillium)和毛霉属(Mucor)为优势属, 链格孢(Alternaria chlamydosporigena)和冻土毛霉(Mucor hiemalis)为优势种; Pearson相关性分析显示, 丝状真菌总丰度与温度、铵态氮、全磷呈显著正相关; 冗余分析显示, 铵态氮、温度、全磷、全氮、盐度及电导率是影响纳木措湖丝状真菌群落组成与分布的主要理化因子。综上所述, 纳木措水体可培养丝状真菌具有较高的物种多样性和空间异质性, 而且水体环境因子影响其分布。
薛文凯, 孟华旦尚, 王艳红, 朱攀, 德吉, 郭小芳 (2022) 纳木措可培养丝状真菌多样性及其与理化因子关系. 生物多样性, 30, 21473. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021473.
Wenkai Xue, Huadanshang Meng, Yanhong Wang, Pan Zhu, Ji De, Xiaofang Guo (2022) Relationship between culturable filamentous fungal diversity and environmental factors in Nam Co Lake. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21473. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021473.
| 样点 Site | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 出现 频率 OF (%) | 相对 多度 RA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 被孢霉属 Mortierella | 4 | 2 | 7 | 1 | 12 | 10 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 5 | 6 | 3 | 3 | - | 2 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 6 | - | 90 | 6.4 |
| 链格孢属 Alternaria | - | 14 | 22 | 3 | 12 | 12 | 16 | 15 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 15 | 8 | 1 | 6 | 17 | 8 | 6 | 8 | 6 | 95 | 12.8 |
| 青霉属 Penicillium | 4 | 24 | 25 | 17 | 13 | 8 | 11 | 11 | 19 | 20 | 8 | 15 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 19 | 12 | 18 | 41 | 10 | 100 | 20.3 |
| 曲霉属 Aspergillus | - | - | 1 | - | 4 | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | 25 | 0.6 |
| 壳霉属 Stagonosporopsis | 1 | 9 | 4 | - | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 12 | 1 | 80 | 3.4 |
| 小不整球科属 Plectosphaerella | 10 | 22 | 1 | - | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - | 3 | 1 | - | 2 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 80 | 4.5 |
| 蜡蚧菌属 Lecanicillium | 2 | 13 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 100 | 5.2 |
| 镰刀菌属 Fusarium | 3 | 8 | 4 | 5 | 9 | 10 | 19 | 7 | 9 | 2 | 7 | 13 | 5 | - | 3 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 11 | 95 | 9.6 |
| 微座孢属 Microdochium | 1 | 3 | 9 | - | 6 | 5 | 11 | 9 | 3 | 2 | - | 5 | 3 | - | 2 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 85 | 6.3 |
| Parengyodontium | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | 13 | - | 1 | 10 | 5 | - | - | 1 | - | 8 | 40 | 2.8 |
| 棒束孢属 Isaria | - | - | 3 | 6 | 1 | - | 3 | - | 2 | - | - | 2 | 26 | - | - | - | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | 50 | 3.3 |
| 木霉属 Trichoderma | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| 漆斑菌属 Myrothecium | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 10 | 0.1 |
| 枝孢菌属 Cladosporium | 1 | 3 | 30 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 8 | 11 | 2 | 2 | - | 8 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 95 | 7.2 |
| 毛霉属 Mucor | 27 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 12 | 10 | 7 | 6 | 10 | 1 | 20 | 4 | 2 | 12 | 18 | 9 | 2 | 12 | 26 | 7 | 100 | 14.3 |
| 派伦霉属 Peyronellaea | - | 2 | - | 2 | - | - | 1 | 3 | - | 1 | - | 3 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3 | 40 | 1.1 |
| 葡萄孢属 Botrytis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| 刺束梗孢属 Akanthomyces | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| 新丛赤壳属 Neonectria | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 40 | 0.8 |
| 三胞霉属 Tricellula | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| 帚枝霉属 Sarocladium | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 6 | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 15 | 0.6 |
| 附球菌属 Epicoccum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | 15 | 0.2 |
| 总丰度 TA (cfu/L) | 54 | 105 | 118 | 47 | 78 | 65 | 91 | 79 | 78 | 41 | 64 | 76 | 58 | 30 | 49 | 69 | 54 | 69 | 123 | 64 | - | 99.9 |
表1 纳木措水体可培养丝状真菌属水平分布
Table 1 Distribution of culturable filamentous fungal genera in Nam Co Lake
| 样点 Site | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 出现 频率 OF (%) | 相对 多度 RA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 被孢霉属 Mortierella | 4 | 2 | 7 | 1 | 12 | 10 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 5 | 6 | 3 | 3 | - | 2 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 6 | - | 90 | 6.4 |
| 链格孢属 Alternaria | - | 14 | 22 | 3 | 12 | 12 | 16 | 15 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 15 | 8 | 1 | 6 | 17 | 8 | 6 | 8 | 6 | 95 | 12.8 |
| 青霉属 Penicillium | 4 | 24 | 25 | 17 | 13 | 8 | 11 | 11 | 19 | 20 | 8 | 15 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 19 | 12 | 18 | 41 | 10 | 100 | 20.3 |
| 曲霉属 Aspergillus | - | - | 1 | - | 4 | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | 25 | 0.6 |
| 壳霉属 Stagonosporopsis | 1 | 9 | 4 | - | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 12 | 1 | 80 | 3.4 |
| 小不整球科属 Plectosphaerella | 10 | 22 | 1 | - | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - | 3 | 1 | - | 2 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 80 | 4.5 |
| 蜡蚧菌属 Lecanicillium | 2 | 13 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 100 | 5.2 |
| 镰刀菌属 Fusarium | 3 | 8 | 4 | 5 | 9 | 10 | 19 | 7 | 9 | 2 | 7 | 13 | 5 | - | 3 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 11 | 95 | 9.6 |
| 微座孢属 Microdochium | 1 | 3 | 9 | - | 6 | 5 | 11 | 9 | 3 | 2 | - | 5 | 3 | - | 2 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 85 | 6.3 |
| Parengyodontium | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | 13 | - | 1 | 10 | 5 | - | - | 1 | - | 8 | 40 | 2.8 |
| 棒束孢属 Isaria | - | - | 3 | 6 | 1 | - | 3 | - | 2 | - | - | 2 | 26 | - | - | - | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | 50 | 3.3 |
| 木霉属 Trichoderma | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| 漆斑菌属 Myrothecium | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 10 | 0.1 |
| 枝孢菌属 Cladosporium | 1 | 3 | 30 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 8 | 11 | 2 | 2 | - | 8 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 95 | 7.2 |
| 毛霉属 Mucor | 27 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 12 | 10 | 7 | 6 | 10 | 1 | 20 | 4 | 2 | 12 | 18 | 9 | 2 | 12 | 26 | 7 | 100 | 14.3 |
| 派伦霉属 Peyronellaea | - | 2 | - | 2 | - | - | 1 | 3 | - | 1 | - | 3 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3 | 40 | 1.1 |
| 葡萄孢属 Botrytis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| 刺束梗孢属 Akanthomyces | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| 新丛赤壳属 Neonectria | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 40 | 0.8 |
| 三胞霉属 Tricellula | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| 帚枝霉属 Sarocladium | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 6 | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 15 | 0.6 |
| 附球菌属 Epicoccum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | 15 | 0.2 |
| 总丰度 TA (cfu/L) | 54 | 105 | 118 | 47 | 78 | 65 | 91 | 79 | 78 | 41 | 64 | 76 | 58 | 30 | 49 | 69 | 54 | 69 | 123 | 64 | - | 99.9 |
| 样点 Site | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 出现 频率 OF (%) | 相对 多度 RA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高山被孢霉 Mortierella alpina | 4 | 2 | 7 | 1 | 12 | 10 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 5 | 6 | 3 | 3 | - | 2 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 6 | - | 90 | 6.4 |
| Alternaria multiformis | - | - | 10 | - | 4 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 3 | - | - | 1 | 4 | 3 | - | 1 | 65 | 2.6 |
| 链格孢 Alternaria chlamydosporigena | - | 14 | 12 | 3 | 8 | 9 | 15 | 11 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 14 | 5 | 1 | 6 | 16 | 4 | 3 | 8 | 5 | 95 | 10.1 |
| 产黄青霉 Penicillium chrysogenum | - | 4 | 3 | - | - | - | 2 | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 10 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 55 | 1.9 |
| 酒色青霉 Penicillium vinaceum | - | 4 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 6 | - | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | - | 3 | - | - | 75 | 3.2 |
| 波兰青霉 Penicillium polonicum | - | 1 | 2 | - | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 60 | 1.6 |
| Penicillium dipodomyicola | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 12 | - | 60 | 2.0 |
| 桔青霉 Penicillium citrinum | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | 5 | 2 | 6 | - | - | 1 | - | - | 1 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 60 | 2.4 |
| Penicillium halotolerans | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| 普通青霉 Penicillium commune | 3 | 2 | 7 | 6 | - | - | 3 | 1 | 2 | 10 | 1 | 4 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 3 | 5 | - | 5 | 75 | 3.8 |
| 扩展青霉 Penicillium expansum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | 10 | 0.2 |
| 卡门柏青霉 Penicillium camemberti | - | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 20 | 0.3 |
| Penicillium goetzii | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| 纳地青霉 Penicillium nalgiovense | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | 1 | 15 | 0.3 |
| 样点 Site | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 出现频率 OF (%) | 相对多度 RA (%) |
| 灰玫瑰青霉 Penicillium griseoroseum | - | - | 1 | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 10 | 0.1 |
| 青霉菌属一种 Penicillium sp. | - | 9 | 1 | 2 | 3 | - | 3 | 3 | 4 | - | 1 | 6 | - | - | 1 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 15 | - | 70 | 4.3 |
| 黑曲霉 Aspergillus niger | - | - | - | - | 4 | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 15 | 0.4 |
| 黄曲霉 Aspergillus flavus | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | 10 | 0.2 |
| 壳霉菌属一种 Stagonosporopsis sp. | 1 | 9 | 4 | - | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 12 | 1 | 80 | 3.3 |
| Stagonosporopsis astragali | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| Plectosphaerella plurivora | 10 | 22 | 1 | - | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - | 3 | 1 | - | 2 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 80 | 4.5 |
| 两型蜡蚧菌 Lecanicillium dimorphum | 2 | 11 | 7 | 2 | 2 | - | 2 | 3 | 7 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 95 | 4.6 |
| Lecanicillium attenuatum | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 10 | 0.2 |
| 蜡蚧轮枝菌 Lecanicillium lecanii | - | - | - | - | - | 3 | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 15 | 0.4 |
| 三线镰刀菌 Fusarium tricinctum | 2 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 18 | 2 | 9 | 1 | 6 | 12 | 4 | - | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 9 | 95 | 7.2 |
| 镰刀菌属一种 Fusarium sp. | 1 | 6 | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | 4 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | 2 | 1 | - | - | 1 | 2 | 55 | 1.5 |
| 燕麦镰刀菌 Fusarium avenaceum | - | 1 | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | 5 | 1 | - | 50 | 1.0 |
| Microdochium bolleyi | 1 | 3 | 9 | - | 6 | 5 | 11 | 9 | 3 | 2 | - | 5 | 3 | - | 2 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 85 | 6.3 |
| Parengyodontium album | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | 13 | - | 1 | 10 | 5 | - | - | 1 | - | 8 | 40 | 2.8 |
| 玫烟色棒束孢 Isaria fumosorosea | - | - | 3 | 6 | 1 | - | 3 | - | 2 | - | - | 2 | 26 | - | - | - | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | 50 | 3.3 |
| 西蒙斯木霉 Trichoderma simmonsii | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| 露湿漆斑菌 Myrothecium roridum | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 10 | 0.1 |
| 多主枝孢 Cladosporium herbarum | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| Cladosporium asperulatum | - | 1 | 21 | - | - | 1 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 1 | - | 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 75 | 3.5 |
| 芽枝状枝孢 Cladosporium pseudocladosporioides | 1 | 2 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 1 | - | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 95 | 3.1 |
| 分枝杆菌 Cladosporium ramotenellum | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | 2 | - | - | 25 | 0.5 |
| 总状毛霉 Mucor racemosus | 13 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 15 | 1.0 |
| 刺囊毛霉 Mucor spinosus | - | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 2 | 12 | - | 2 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 65 | 2.8 |
| 冻土毛霉 Mucor hiemalis | 14 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 11 | 10 | 7 | 6 | 10 | 1 | 19 | 3 | - | - | 18 | 7 | - | 6 | 24 | 3 | 85 | 10.6 |
| Peyronellaea glomerata | - | 2 | - | 2 | - | - | 1 | 3 | - | 1 | - | 3 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3 | 40 | 1.1 |
| 灰葡萄孢 Botrytis cinerea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| Akanthomyces muscarius | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| Neonectria ramulariae | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| Neonectria lugdunensis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 35 | 0.7 |
| 三胞霉属一种 Tricellula sp. | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| 帚枝霉属一种 Sarocladium sp. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 6 | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 15 | 0.6 |
| 黑附球菌 Epicoccum nigrum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | 15 | 0.2 |
表2 纳木措水体可培养丝状真菌种水平分布
Table 2 Distribution of culturable filamentous fungal species in Nam Co Lake
| 样点 Site | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 出现 频率 OF (%) | 相对 多度 RA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高山被孢霉 Mortierella alpina | 4 | 2 | 7 | 1 | 12 | 10 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 5 | 6 | 3 | 3 | - | 2 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 6 | - | 90 | 6.4 |
| Alternaria multiformis | - | - | 10 | - | 4 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 3 | - | - | 1 | 4 | 3 | - | 1 | 65 | 2.6 |
| 链格孢 Alternaria chlamydosporigena | - | 14 | 12 | 3 | 8 | 9 | 15 | 11 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 14 | 5 | 1 | 6 | 16 | 4 | 3 | 8 | 5 | 95 | 10.1 |
| 产黄青霉 Penicillium chrysogenum | - | 4 | 3 | - | - | - | 2 | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 10 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 55 | 1.9 |
| 酒色青霉 Penicillium vinaceum | - | 4 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 6 | - | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | - | 3 | - | - | 75 | 3.2 |
| 波兰青霉 Penicillium polonicum | - | 1 | 2 | - | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 60 | 1.6 |
| Penicillium dipodomyicola | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 12 | - | 60 | 2.0 |
| 桔青霉 Penicillium citrinum | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | 5 | 2 | 6 | - | - | 1 | - | - | 1 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 60 | 2.4 |
| Penicillium halotolerans | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| 普通青霉 Penicillium commune | 3 | 2 | 7 | 6 | - | - | 3 | 1 | 2 | 10 | 1 | 4 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 3 | 5 | - | 5 | 75 | 3.8 |
| 扩展青霉 Penicillium expansum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | 10 | 0.2 |
| 卡门柏青霉 Penicillium camemberti | - | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 20 | 0.3 |
| Penicillium goetzii | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| 纳地青霉 Penicillium nalgiovense | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | 1 | 15 | 0.3 |
| 样点 Site | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 出现频率 OF (%) | 相对多度 RA (%) |
| 灰玫瑰青霉 Penicillium griseoroseum | - | - | 1 | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 10 | 0.1 |
| 青霉菌属一种 Penicillium sp. | - | 9 | 1 | 2 | 3 | - | 3 | 3 | 4 | - | 1 | 6 | - | - | 1 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 15 | - | 70 | 4.3 |
| 黑曲霉 Aspergillus niger | - | - | - | - | 4 | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 15 | 0.4 |
| 黄曲霉 Aspergillus flavus | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | 10 | 0.2 |
| 壳霉菌属一种 Stagonosporopsis sp. | 1 | 9 | 4 | - | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 12 | 1 | 80 | 3.3 |
| Stagonosporopsis astragali | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| Plectosphaerella plurivora | 10 | 22 | 1 | - | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - | 3 | 1 | - | 2 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 80 | 4.5 |
| 两型蜡蚧菌 Lecanicillium dimorphum | 2 | 11 | 7 | 2 | 2 | - | 2 | 3 | 7 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 95 | 4.6 |
| Lecanicillium attenuatum | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 10 | 0.2 |
| 蜡蚧轮枝菌 Lecanicillium lecanii | - | - | - | - | - | 3 | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 15 | 0.4 |
| 三线镰刀菌 Fusarium tricinctum | 2 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 18 | 2 | 9 | 1 | 6 | 12 | 4 | - | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 9 | 95 | 7.2 |
| 镰刀菌属一种 Fusarium sp. | 1 | 6 | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | 4 | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | 2 | 1 | - | - | 1 | 2 | 55 | 1.5 |
| 燕麦镰刀菌 Fusarium avenaceum | - | 1 | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | 5 | 1 | - | 50 | 1.0 |
| Microdochium bolleyi | 1 | 3 | 9 | - | 6 | 5 | 11 | 9 | 3 | 2 | - | 5 | 3 | - | 2 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 85 | 6.3 |
| Parengyodontium album | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | 13 | - | 1 | 10 | 5 | - | - | 1 | - | 8 | 40 | 2.8 |
| 玫烟色棒束孢 Isaria fumosorosea | - | - | 3 | 6 | 1 | - | 3 | - | 2 | - | - | 2 | 26 | - | - | - | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | 50 | 3.3 |
| 西蒙斯木霉 Trichoderma simmonsii | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| 露湿漆斑菌 Myrothecium roridum | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 10 | 0.1 |
| 多主枝孢 Cladosporium herbarum | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| Cladosporium asperulatum | - | 1 | 21 | - | - | 1 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 1 | - | 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 75 | 3.5 |
| 芽枝状枝孢 Cladosporium pseudocladosporioides | 1 | 2 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 1 | - | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 95 | 3.1 |
| 分枝杆菌 Cladosporium ramotenellum | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | 2 | - | - | 25 | 0.5 |
| 总状毛霉 Mucor racemosus | 13 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 15 | 1.0 |
| 刺囊毛霉 Mucor spinosus | - | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 2 | 12 | - | 2 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 65 | 2.8 |
| 冻土毛霉 Mucor hiemalis | 14 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 11 | 10 | 7 | 6 | 10 | 1 | 19 | 3 | - | - | 18 | 7 | - | 6 | 24 | 3 | 85 | 10.6 |
| Peyronellaea glomerata | - | 2 | - | 2 | - | - | 1 | 3 | - | 1 | - | 3 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3 | 40 | 1.1 |
| 灰葡萄孢 Botrytis cinerea | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| Akanthomyces muscarius | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| Neonectria ramulariae | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| Neonectria lugdunensis | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 35 | 0.7 |
| 三胞霉属一种 Tricellula sp. | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 | 0.1 |
| 帚枝霉属一种 Sarocladium sp. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 6 | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 15 | 0.6 |
| 黑附球菌 Epicoccum nigrum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | 15 | 0.2 |
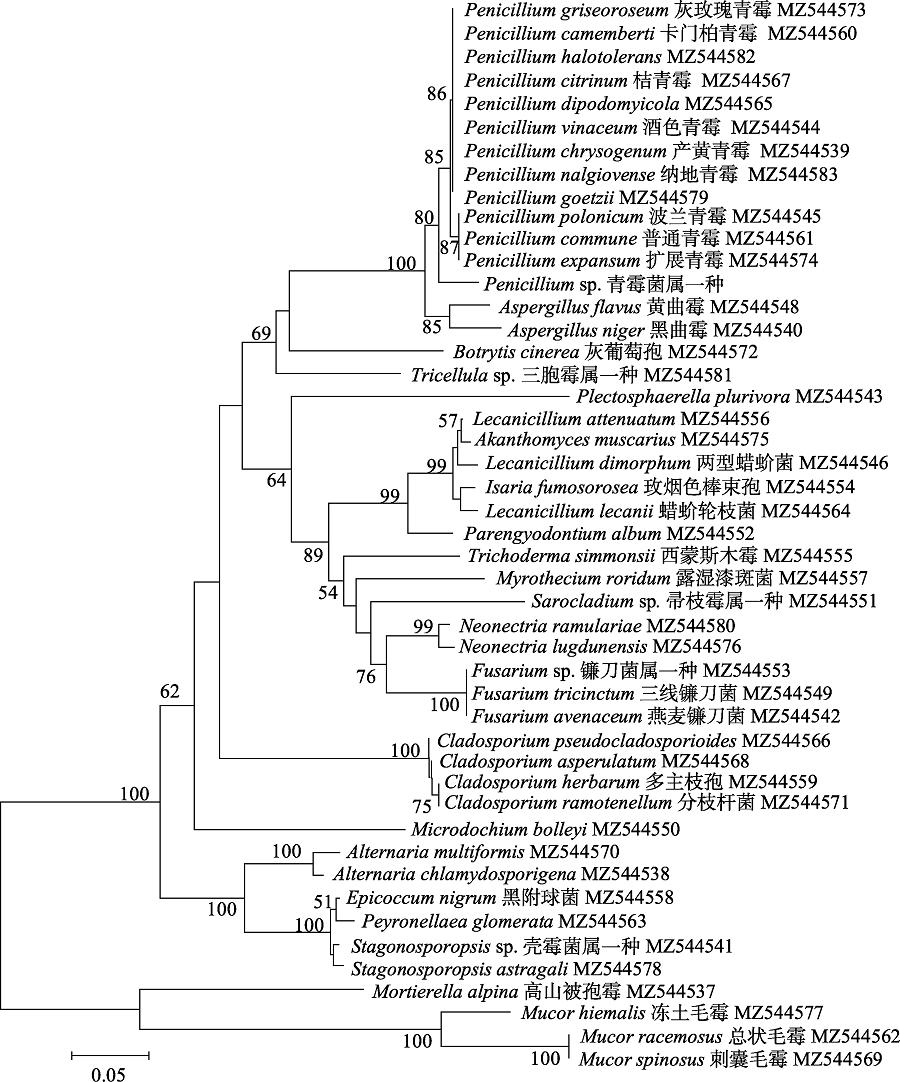
图1 基于ITS序列构建的Neighbor-Joining系统发育树。菌株后数字为GenBank登录号, 分支点数字代表1,000次重复后自展值, 左下角标尺表示5%的序列进化差异。
Fig. 1 Phylogenetic tree constructed through Neighbor-Joining analysis based on ITS sequences. The numbers after the strain are GenBank accession numbers, numbers at the nodes are bootstrap values obtained after 1,000 replicates, the scale at the lower left corner represents 5% sequence evolution difference.
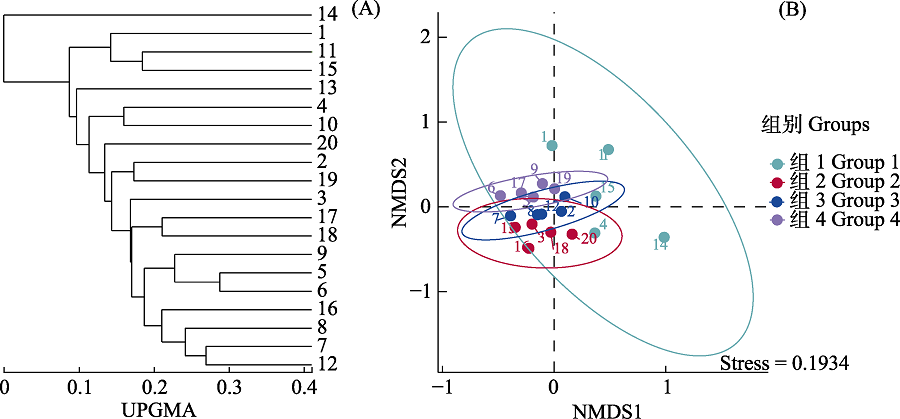
图2 纳木措各样点水体可培养丝状真菌组成的聚类分析。(A)不同样点丝状真菌物种组成的UPGMA聚类分析, 数字代表样点, 分支长度代表不同样点间的距离, 分支靠的越近表示样点间相似度越高。(B)不同样点丝状真菌物种组成的非度量多维尺度分析, 图中颜色代表不同的分组。
Fig. 2 Cluster analysis of culturable filamentous fungal composition in different sites from Nam Co Lake. (A) For UPGMA clustering analysis of filamentous fungi species composition at different points, the number represents sample points, the length of branches represents the distance between different points, and the closer the branches are, the higher the similarity between sample points. (B) Non-metric multidimensional scale analysis of filamentous fungal species composition at different points, with colors representing different groupings.
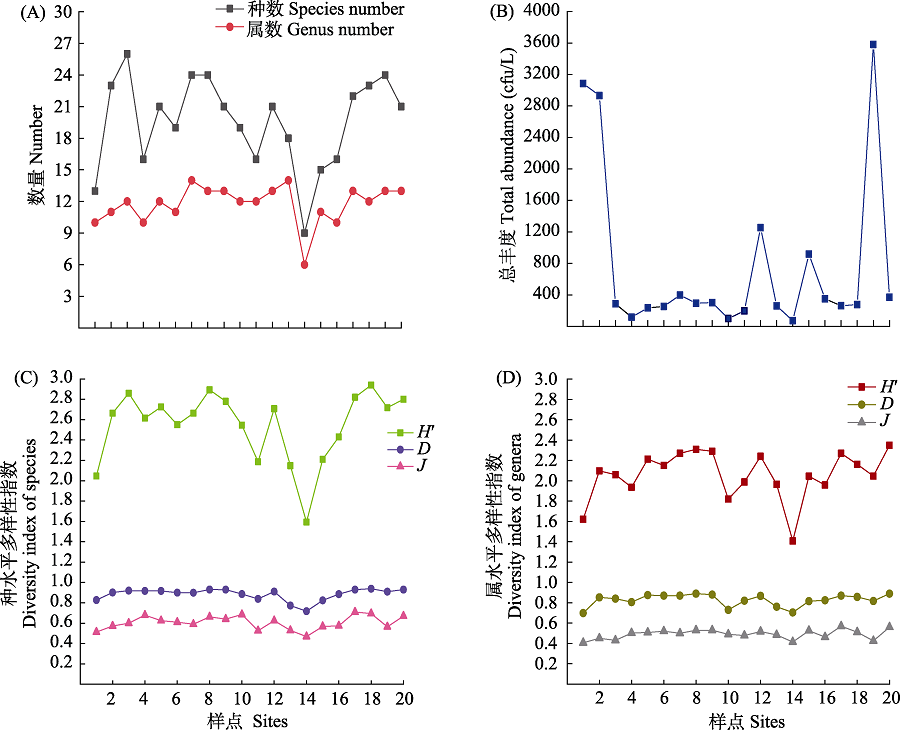
图3 纳木措各样点水体可培养丝状真菌多样性指数。(A)丝状真菌属种数; (B)丝状真菌总丰度; (C)丝状真菌种水平多样性指数; (D)丝状真菌属水平多样性指数; H': Shannon指数; J: Pielou指数; D: Simpson指数。
Fig. 3 Diversity indexes of culturable filamentous fungi in different sites from Nam Co Lake. (A) Number of filamentous fungal species and genera; (B) Total abundance of filamentous fungi; (C) Diversity indexes of filamentous fungal species; (D) Diversity indexes of filamentous fungal genera; H', Shannon index; J, Pielou index; D, Simpson index.
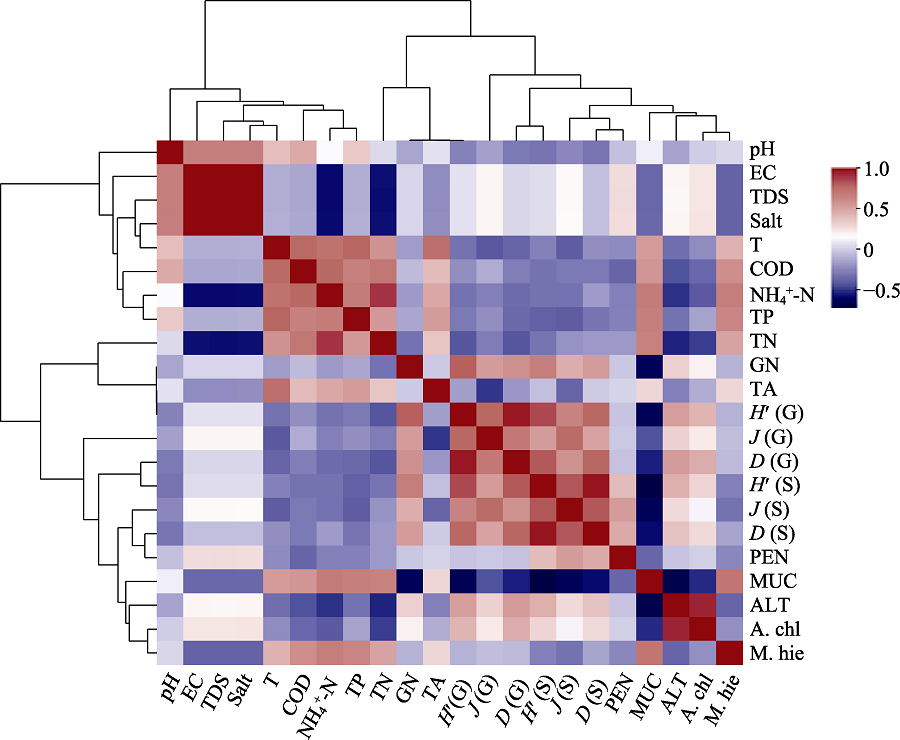
图4 纳木措各样点可培养丝状真菌属种水平多样性指数与水体理化因子Pearson相关性分析。EC: 电导率; TDS: 总溶解固体量; Salt: 盐度; T: 温度; COD: 化学需氧量; NH4+-N: 铵态氮; TP: 全磷; TN: 全氮; GN: 丝状真菌属数; TA: 丝状真菌总丰度; H' (G)、J (G)、D (G): 丝状真菌属水平多样性指数; H' (S)、J (S)、D (S): 丝状真菌种水平多样性指数; PEN: 青霉属; MUC: 毛霉属; ALT: 链格孢属; A. chl: 链格孢; M. hie: 冻土毛霉。
Fig. 4 Pearson correlation coefficient between culturable filamentous fungi genera and species diversity index and environmental factors of different sites in Nam Co Lake. EC, Electric conductivity; TDS, Total dissolved salt; T, Temperature; COD, Chemical oxygen demand; NH4+-N, Ammonia nitrogen; TP, Total phosphorous; TN, Total nitrogen; GN, Number of filamentous fungal genera; TA, Total abundance of filamentous fungi; H' (G), J (G) and D (G) indicates the diversity indexes of filamentous fungal genera; H' (S), J (S) and D (S) indicates the diversity indexes of filamentous fungal species; PEN, Penicillium; MUC, Mucor; ALT, Altermaria; A. chl, A. chlaamydosporigena; M. hie, M. hiemalis.
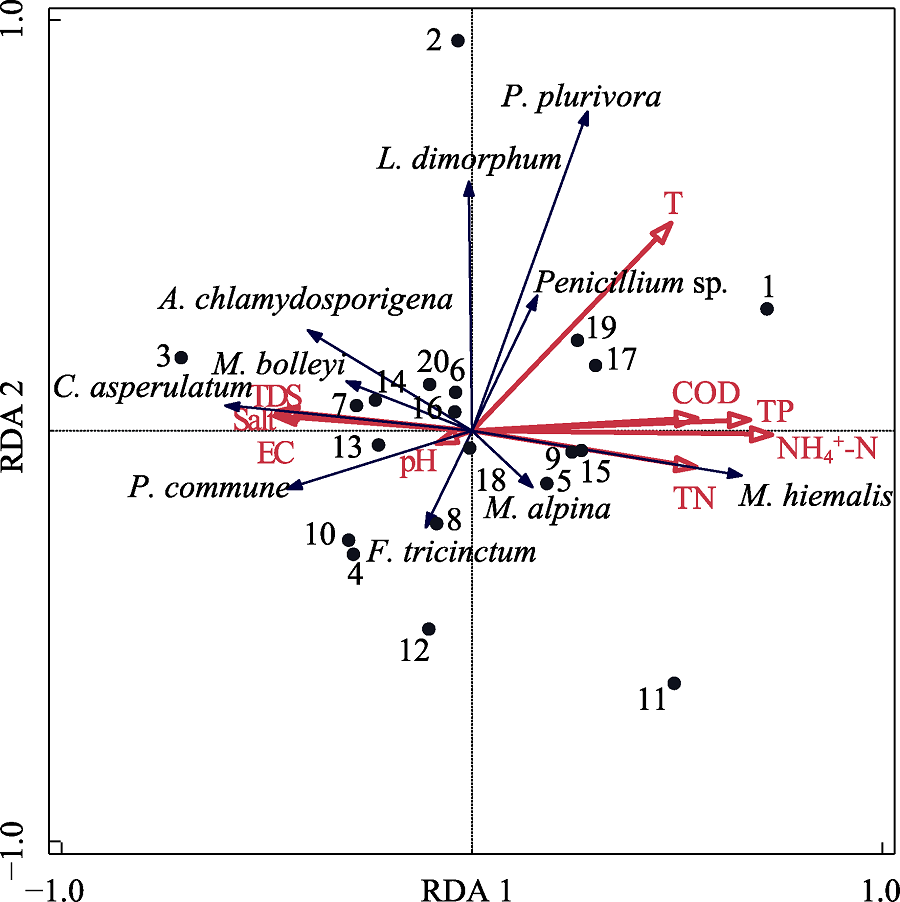
图5 纳木措水体主要丝状真菌与理化因子RDA排序图。数字1-20: 20个样点; EC: 电导率; TDS: 总溶解固体量; Salt: 盐度; T: 温度; COD: 化学需氧量; NH4+-N: 铵态氮; TP: 全磷; TN: 全氮。
Fig. 5 RDA ordination diagram of main filamentous fungi associated with environmental factors in Nam Co Lake. Numbers 1-20, 20 samples; EC, Electric conductivity; TDS, Total dissolved salt; T, Temperature; COD, Chemical oxygen demand; NH4+-N, Ammonia nitrogen; TP, Total phosphorous; TN, Total nitrogen; P. plurivora, Penicillium plurivora; L. dimorphum, Lecanicillium dimorphum; A. chlamydosporigena, Alternaria chlamydosporigena; M. bolleyi, Micro- dochium bolleyi; C. asperulatum, Cladosporium asperulatum; P. commune, Penicillium commune; F. tricinctum, Fusarium tricinctum; M. alpine, Mortierella alpine; M. hiemalis, Mucor hiemalis.
| 区域 Region | 纳木措(夏季) Nam Co Lake (Summer) | 滇池(秋季) Dianchi Lake (Autumn) | 程海湖(冬季) Chenghai Lake (Winter) | 程海湖(春季) Chenghai Lake (Spring) | 洱海(干季) Erhai (Dry season) | 洱海(雨季) Erhai (Rainy season) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Altitude (m) | 4,718 | 1,887.5 | 1,500 | 1,500 | 1,972 | 1,972 |
| pH | 8.72-9.66 | 7.37-8.26 | 9.31-9.44 | - | 7.8-8.2 | 7.7-8.2 |
| 总丰度 Total number of strains (cfu/L) | 1,412 | 788 | 212 | 172 | - | - |
| 属数 Genera number | 22 | 67 | 28 | 20 | 26 | 11 |
| 优势属 Dominant genera | 链格孢属 Alternaria 毛霉属 Mucor 青霉属 Penicillium | 枝孢菌属 Cladosporium 青霉属 Penicillium | 曲霉属 Aspergillus 青霉属 Penicillium | 曲霉属 Aspergillus 青霉属 Penicillium | 细囊霉属 Leptolegnia 根生壶菌属 Rhizophydium 水霉属 Saprolegnia 青霉属 Penicillium | 细囊霉属 Leptolegnia 根生壶菌属 Rhizophydium 拟青霉属 Paecilomyces 青霉属 Penicillium |
| 香农指数 Shannon-Wiener index (H') | 1.41-2.94 | 1.27-2.31 | 2.6429 | 2.2298 | - | - |
| 辛普森指数 (D) Simpson index | 0.70-0.94 | 0.62-0.86 | 0.9027 | 0.8408 | - | - |
| 皮卢指数 Pielou index (J) | 0.41-0.71 | 0.34-0.61 | 0.7931 | 0.7324 | - | - |
| 全氮 TN (mg/L) | 0.15-0.97 | 1.86-4.09 | 0.10-0.70 | - | - | - |
| 全磷 TP (mg/L) | 0.01-0.05 | 0.01-0.121 | 0.016-0.367 | - | - | - |
| 温度 T (℃) | 9.70-20.57 | 11-17 | 16.5-17.5 | - | 15 | 22.2 |
| 培养基 Medium | 酸化PDA培养基, 酸化YM培养基, RBCH培养基Acidified PDA medium, Acidified YM medium, RBCH medium | PDA培养基, YM培养基, 马丁氏培养基 PDA medium, YM medium, Martin medium | 含青霉素的PDA培养基, 马丁氏培养基, 酸化YM培养基, 含青霉素的燕麦培养基诱发真菌孢子培养基 PDA medium with penicillin, Martin medium, Acidified YM medium, Oatmeal agar with penicillin, Induce fungal spore medium | - | - | |
| 参考文献 Reference | - | Ge, 2017①(①戈帆 (2017) 云南高原湖泊滇池的可培养丝状真菌多样性及其活性研究. 硕士学位论文, 云南大学, 昆明.) | Jin et al, | Yang & Ding, | Yang & Ding, | |
表3 四种高原湖泊不同季节水体可培养丝状真菌对比
Table 3 Comparison of culturable filamentous fungi in four highland lakes in different seasons
| 区域 Region | 纳木措(夏季) Nam Co Lake (Summer) | 滇池(秋季) Dianchi Lake (Autumn) | 程海湖(冬季) Chenghai Lake (Winter) | 程海湖(春季) Chenghai Lake (Spring) | 洱海(干季) Erhai (Dry season) | 洱海(雨季) Erhai (Rainy season) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Altitude (m) | 4,718 | 1,887.5 | 1,500 | 1,500 | 1,972 | 1,972 |
| pH | 8.72-9.66 | 7.37-8.26 | 9.31-9.44 | - | 7.8-8.2 | 7.7-8.2 |
| 总丰度 Total number of strains (cfu/L) | 1,412 | 788 | 212 | 172 | - | - |
| 属数 Genera number | 22 | 67 | 28 | 20 | 26 | 11 |
| 优势属 Dominant genera | 链格孢属 Alternaria 毛霉属 Mucor 青霉属 Penicillium | 枝孢菌属 Cladosporium 青霉属 Penicillium | 曲霉属 Aspergillus 青霉属 Penicillium | 曲霉属 Aspergillus 青霉属 Penicillium | 细囊霉属 Leptolegnia 根生壶菌属 Rhizophydium 水霉属 Saprolegnia 青霉属 Penicillium | 细囊霉属 Leptolegnia 根生壶菌属 Rhizophydium 拟青霉属 Paecilomyces 青霉属 Penicillium |
| 香农指数 Shannon-Wiener index (H') | 1.41-2.94 | 1.27-2.31 | 2.6429 | 2.2298 | - | - |
| 辛普森指数 (D) Simpson index | 0.70-0.94 | 0.62-0.86 | 0.9027 | 0.8408 | - | - |
| 皮卢指数 Pielou index (J) | 0.41-0.71 | 0.34-0.61 | 0.7931 | 0.7324 | - | - |
| 全氮 TN (mg/L) | 0.15-0.97 | 1.86-4.09 | 0.10-0.70 | - | - | - |
| 全磷 TP (mg/L) | 0.01-0.05 | 0.01-0.121 | 0.016-0.367 | - | - | - |
| 温度 T (℃) | 9.70-20.57 | 11-17 | 16.5-17.5 | - | 15 | 22.2 |
| 培养基 Medium | 酸化PDA培养基, 酸化YM培养基, RBCH培养基Acidified PDA medium, Acidified YM medium, RBCH medium | PDA培养基, YM培养基, 马丁氏培养基 PDA medium, YM medium, Martin medium | 含青霉素的PDA培养基, 马丁氏培养基, 酸化YM培养基, 含青霉素的燕麦培养基诱发真菌孢子培养基 PDA medium with penicillin, Martin medium, Acidified YM medium, Oatmeal agar with penicillin, Induce fungal spore medium | - | - | |
| 参考文献 Reference | - | Ge, 2017①(①戈帆 (2017) 云南高原湖泊滇池的可培养丝状真菌多样性及其活性研究. 硕士学位论文, 云南大学, 昆明.) | Jin et al, | Yang & Ding, | Yang & Ding, | |
| [1] | Chen YM, Zhang XC, Wu JL (1979) Studies on the dimorphism of Mucor hiemalis. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 19, 393-399. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈聿美, 张雪聪, 吴经纶 (1979) 冻土毛霉两型性的研究. 微生物学报, 19, 393-399.] | |
| [2] | Chen YX, Lou LP, Li WH (2004) Effect of microorganisms on the biogenic matter circulation of lake. China water pollution control and ecological restoration technology advanced seminar, Hangzhou. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈英旭, 楼莉萍, 李文红 (2004) 微生物在湖泊生源要素循环中的作用. 中国水环境污染控制与生态修复技术高级研讨会, 杭州.] | |
| [3] |
Dong SY, Xue X, You QG, Peng F (2014) Remote sensing monitoring of the lake area changes in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in recent 40 years. Journal of Lake Sciences, 26, 535-544. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [董斯扬, 薛娴, 尤全刚, 彭飞 (2014) 近40年青藏高原湖泊面积变化遥感分析. 湖泊科学, 26, 535-544.] | |
| [4] |
Eastwood WJ, Roberts N, Lamb HF, Tibby JC (1999) Holocene environmental change in southwest Turkey: A palaeoecological record of lake and catchment- related changes. Quaternary Science Reviews, 18, 671-695.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Feng ZH, Sun GY (2020) Advances in the classification of Alternaria and related genera. Journal of Fungal Research, 18, 294-303. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [冯中红, 孙广宇 (2020) 链格孢属及相关属分类研究新进展. 菌物研究, 18, 294-303.] | |
| [6] | Fu Q, Lin JJ, Zhuang ZX, Huang HB, Sun EX, Gan MY, Xiao YJ (2020) Identification of the marine protease-producing fungus Parengyodontium album HX2019006 and the optimization of its fermentation conditions. Food and Fermentation Industries, 46(10), 185-190. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [傅奇, 林俊杰, 庄峙厦, 黄华斌, 孙恩贤, 甘美裕, 肖玉娟 (2020) 一株海洋来源蛋白酶产生菌Parengyodontium album HX2019006的鉴定及其发酵条件研究. 食品与发酵工业, 46(10), 185-190.] | |
| [7] | Geng QR, Yang FY, Wang YH, Che YW, Yang KL (2020) Research advance in functional and synthetic regulation of secondary metabolites of filamentous fungi. Mycosystema, 39, 539-547. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [耿青如, 杨飞洋, 王雨荷, 车雨微, 杨坤龙 (2020) 丝状真菌次级代谢产物的功能与合成调控研究进展. 菌物学报, 39, 539-547.] | |
| [8] | Gou P, Ye QH, Wei QF (2015) Lake ice change at the Nam Co Lake on the Tibetan Plateau during 2000-2013 and influencing factors. Progress in Geography, 34, 1241-1249. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[勾鹏, 叶庆华, 魏秋方 (2015) 2000-2013年西藏纳木措湖冰变化及其影响因素. 地理科学进展, 34, 1241-1249.]
DOI |
|
| [9] |
Ho JC, Michalak AM, Pahlevan N (2019) Widespread global increase in intense lake phytoplankton blooms since the 1980s. Nature, 574, 667-670.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Hou LF (2020) Species Diversity and Salt Tolerance of Dark Septate Endophytes in Three Desert Plants. PhD dissertation, Hebei University, Baoding, Hebei. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [侯力峰 (2020) 三种荒漠植物深色有隔内生真菌物种多样性和耐盐性研究. 博士学位文论, 河北大学, 河北保定.] | |
| [11] |
Hu AY, Yao TD, Jiao NZ, Liu YQ, Yang Z, Liu XB (2010) Community structures of ammonia-oxidising archaea and bacteria in high-altitude lakes on the Tibetan Plateau. Freshwater Biology, 55, 2375-2390.
DOI URL |
| [12] | Huang XN, Tang S, Lü XF (2020) Progress and prospect for synthetic biology research of the industrial filamentous fungi Aspergillus terreus. Synthetic Biology Journal, 1, 187-211. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄雪年, 唐慎, 吕雪峰 (2020) 工业丝状真菌土曲霉合成生物技术研究进展及展望. 合成生物学, 1, 187-211.] | |
| [13] | Huang YB, Jiang XD, Liu W, Huang CS, Zhang LP, Zhu HN, Zhang CS, Zhang WJ (2018) Chromanones from Montipora foliosa-derived Parengyodontium album SCSIO 40430. Microbiology China, 45, 1881-1888. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄艳冰, 蒋晓东, 刘威, 黄春帅, 张丽萍, 诸晗宁, 张长生, 张文军 (2018) 叶状蔷薇珊瑚来源真菌Parengyodontium album SCSIO 40430次级代谢产物研究. 微生物学通报, 45, 1881-1888.] | |
| [14] | Jiang JH, Huang Q (2004) Distribution and variation of lakes in Tibetan Plateau and their comparison with lakes in other part of China. Water Resources Protection, (6), 24-27, 70. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [姜加虎, 黄群 (2004) 青藏高原湖泊分布特征及与全国湖泊比较. 水资源保护, (6), 24-27, 70.] | |
| [15] |
Jin FY, Li ZY, Wang YX, Dong MH, Yan YP, Li SL, Yang LY (2013) Diversity of cultivable fungi isolated from the Chenghai Lake in Yunnan Province. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 19, 1025-1030. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [晋方佑, 李治滢, 王永霞, 董明华, 严亚萍, 李绍兰, 杨丽源 (2013) 云南程海湖可培养真菌多样性分析. 应用与环境生物学报, 19, 1025-1030.] | |
| [16] |
Keil A, Berking J, Mügler I, Schütt B, Schwalb A, Steeb P (2010) Hydrological and geomorphological basin and catchment characteristics of lake Nam Co, South- Central Tibet. Quaternary International, 218, 118-130.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Keith S, Gareth MJ, Walter G, Bryce K (2011) The Genera of Hyphomycetes. Fungal Biodiversity Centre Press, Hong Kong. |
| [18] |
Kirchman DL (2002) The ecology of Cytophaga-Flavobacteria in aquatic environments. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 39, 91-100.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | Kirk PM, Cannon PF, Minter DW, Stalpers JA (2008) Ainsworth & Bisby’s Dictionary of the Fungi (10th edition). Oxon Press, Oxford. |
| [20] | Landeweert R, Leeflang P, Kuyper TW, Hoffland E, Rosling A, Wernars K, Smit E (2003) Molecular identification of ectomycorrhizal mycelium in soil horizons. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 69, 327-333. |
| [21] |
Li XB, He HB, Zhang XD, Kazanci C, Li ZA, Necpalova M, Ma QQ (2020) Calculation of fungal and bacterial inorganic nitrogen immobilization rates in soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 153, 108114.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Li ZH, Pubu CR, Lyu ML, Wang M, Liu XY (2018) Species diversity of zygomycotan fungi in the Tibet Autonomous Region. Microbiology China, 45, 1250-1261. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李政宏, 普布次仁, 吕美林, 旺姆, 刘小勇 (2018) 西藏接合菌物种多样性初探. 微生物学通报, 45, 1250-1261.] | |
| [23] |
Liu AR, Yang T, Xu W, Shangguan ZJ, Wang JZ, Liu HY, Shi Y, Chu HY, He JS (2018) Status, issues and prospects of belowground biodiversity on the Tibetan alpine grassland. Biodiversity Science, 26, 972-987. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[刘安榕, 杨腾, 徐炜, 上官子健, 王金洲, 刘慧颖, 时玉, 褚海燕, 贺金生 (2018) 青藏高原高寒草地地下生物多样性: 进展、问题与展望. 生物多样性, 26, 972-987.]
DOI |
|
| [24] | Liu YX, Cao PX, Ma HM, Liu X (2019) Research progress on soil microbial diversity and its influencing factors in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Environmental Ecology, 1(6), 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘怡萱, 曹鹏熙, 马红梅, 刘星 (2019) 青藏高原土壤微生物多样性及其影响因素研究进展. 环境生态学, 1(6), 1-7.] | |
| [25] | Liu ZQ, Pan BZ, Han X, Li G, Wang TY(2022) Water environmental characteristics and water quality assessment of lakes in Tibetan Plateau. Environmental Science. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘智琦, 潘保柱, 韩谞, 李刚, 王韬轶 (2022) 青藏高原湖泊水环境特征及水质评价. 环境科学. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202111079.] | |
| [26] | Lu AX, Yao TD, Wang LH, Liu SY, Guo ZL (2005) Study on the fluctuations of typical glaciers and lakes in the Tibetan Plateau using remote sensing. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 27, 783-792. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [鲁安新, 姚檀栋, 王丽红, 刘时银, 郭治龙 (2005) 青藏高原典型冰川和湖泊变化遥感研究. 冰川冻土, 27, 783-792.] | |
| [27] | Sun LF, Zhang YH, Pei KQ (2009) A rapid extraction of genomic DNA from fungi. Mycosystema, 28, 299-302. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙立夫, 张艳华, 裴克全 (2009) 一种高效提取真菌总DNA的方法. 菌物学报, 28, 299-302.] | |
| [28] | Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research, CAS (1984) Rivers and Lakes in Tibet. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [中国科学院青藏高原综合科学考察队 (1984) 西藏河流与湖泊. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [29] |
Wang JB, Zhu LP, Daut G, Ju JT, Lin X, Wang Y, Zhen XL (2009) Investigation of bathymetry and water quality of Lake Nam Co, the largest lake on the central Tibetan Plateau, China. Limnology, 10, 149-158.
DOI URL |
| [30] | White TJ, Bruns TD, Lee SB, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and Direct Sequencing of Fungal Ribosomal RNA Genes for Phylogenetics. PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications. Academic Press, San Diego. |
| [31] |
Woolway RI, Merchant CJ (2019) Worldwide alteration of lake mixing regimes in response to climate change. Nature Geoscience, 12, 271-276.
DOI |
| [32] | Yan YP, Li ZY, Dong MH, Zhou Q, Jin FY, Yang LY, Li SL (2013) Yeasts from Yangzonghai Lake in Yunnan (China): Diversity and extracellular enzymes. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 53, 1205-1212. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [严亚萍, 李治滢, 董明华, 周巧, 晋方佑, 杨丽源, 李绍兰 (2013) 云南阳宗海酵母菌种群结构及产胞外酶测试. 微生物学报, 53, 1205-1212.] | |
| [33] | Yang FR, Ding HS (1986) A study distribution of the fungi groups in the limnetic body of Er-Hai Lake. Journal of Yunnan University (Natural Sciences Edition), (3), 319-324. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨发蓉, 丁骅孙 (1986) 洱海湖体真菌类群分布的研究. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), (3), 319-324.] | |
| [34] |
Ye XC, Zhang Q, Liu J, Li XH, Xu CY (2013) Distinguishing the relative impacts of climate change and human activities on variation of streamflow in the Poyang Lake catchment, China. Journal of Hydrology, 494, 83-95.
DOI URL |
| [35] | You QL, Kang SC, Li CL, Li MS, Liu JS (2007) Variation features of meteorological elements at Nam Co station, Tibetan Plateau. Meteorological Monthly, (3), 54-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [游庆龙, 康世昌, 李潮流, 李茂善, 刘景时 (2007) 青藏高原纳木措气象要素变化特征. 气象, (3), 54-60.] | |
| [36] | Zhang GZ, Zhang XJ, Chen Q, Li Z, Guo K, Yang HT (2015) Isolation and identification of three Chinese new records in Trichoderma harzianum species complex. Shandong Science, 28(6), 43-46, 51. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张广志, 张新建, 陈泉, 李哲, 郭凯, 杨合同 (2015) 哈茨木霉复合种内3个中国新记录种的分离和鉴定. 山东科学, 28(6), 43-46, 51.] | |
| [37] | Zhang HG, Li L, Zhao Y, Wang X, Xue LG (2013) Seasonal changes of culturable microbes in different altitude lakes in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal of Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine, 32, 49-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张红光, 李琳, 赵燕, 王鑫, 薛林贵 (2013) 青藏高原不同海拔湖水中可培养微生物的季节性变化. 中兽医医药杂志, 32, 49-55.] | |
| [38] | Zhu LP, Zhang GQ, Yang RM, Liu C, Yang K, Qiao BJ, Han BP (2019) Lake variations on Tibetan Plateau of recent 40 years and future changing tendency. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 34, 1254-1263. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱立平, 张国庆, 杨瑞敏, 刘翀, 阳坤, 乔宝晋, 韩博平 (2019) 青藏高原最近40年湖泊变化的主要表现与发展趋势. 中国科学院院刊, 34, 1254- 1263.] | |
| [39] | Zou TW, Ren LW, Zhang YT, Ding R, Zhang H (2015) The overview of the diversity of aquatic fungi. Heilongjiang Science, 6(7), 25, 29. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [邹彤雯, 任立伟, 张玉婷, 丁锐, 张浩 (2015) 水生真菌多样性概述. 黑龙江科学, 6(7), 25, 29.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [3] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [4] | 周昊, 王茗毅, 张楚格, 肖治术, 欧阳芳. 昆虫旅馆在独栖蜂多样性保护中的现状与挑战[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24472-. |
| [5] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [6] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [7] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [8] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [9] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [10] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [11] | 徐欢, 辛凤飞, 施宏亮, 袁琳, 薄顺奇, 赵欣怡, 邓帅涛, 潘婷婷, 余婧, 孙赛赛, 薛程. 生态修复技术集成应用对长江口北支生境与鸟类多样性提升效果评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24478-. |
| [12] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [13] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [14] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [15] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn