



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 21485. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021485 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021485
崔静1, 徐明芳1, 章群1,*( ), 李瑶1, 曾晓舒1, 李莎2,3
), 李瑶1, 曾晓舒1, 李莎2,3
收稿日期:2021-11-27
接受日期:2022-01-18
出版日期:2022-05-20
发布日期:2022-03-13
通讯作者:
章群
作者简介:* E-mail: zhangqunjnu@gmail.com基金资助:
Jing Cui1, Mingfang Xu1, Qun Zhang1,*( ), Yao Li1, Xiaoshu Zeng1, Sha Li2,3
), Yao Li1, Xiaoshu Zeng1, Sha Li2,3
Received:2021-11-27
Accepted:2022-01-18
Online:2022-05-20
Published:2022-03-13
Contact:
Qun Zhang
摘要:
角木叶鲽(Pleuronichthys cornutus)是东亚沿海重要的鲽形目经济鱼类, 为更好地保护和开发利用其种质资源, 有必要全面了解其遗传背景。本研究测定了中国和日本沿海7个群体200尾角木叶鲽线粒体控制区(CR) 5'端、细胞色素b (Cytb)和NADH脱氢酶第二亚基(ND2)基因序列, 比较不同标记在解析遗传多样性和种群结构上的可行性与有效性, 阐明中日沿海角木叶鲽群体间出现遗传分化的分子机制。CR序列分析发现中日沿海7个角木叶鲽群体遗传多样性表现出较高的单倍型多样性(Hd = 0.9699)和较低的核苷酸多样性(π = 0.0061); 各群体间无显著的遗传分化(FST = -0.0197-0.0184, P > 0.05); 单倍型网络未显示出明显的地理聚群和谱系结构; 分子方差分析(AMOVA)表明变异主要发生在群体内部(> 99.17%)。进一步通过Cytb和ND2基因分别与CR序列对比分析, 结果表明群体遗传多样性均表现为高Hd (0.9683-0.9829)低π (0.0050-0.0063)模式, 仅有ND2基因分析FST值(FST = 0.0302, P < 0.05)显示了中国碣石(GDJS)和日本明石(JAP)群体间显著的低水平遗传分化现象。CR、Cytb和ND2的单倍型网络图均无明显的地理聚类和谱系结构, AMOVA分析也显示变异主要来源于群体内(> 98.39%)。种群历史动态分析结果显示, 角木叶鲽可能在第四纪中更新世晚期经历了群体扩张事件, 扩张时间分别为31.93-9.58万年前(CR)、27.53-22.02万年前(Cytb)和26.99-18.75万年前(ND2)。综上所述, 中日沿海的角木叶鲽具有较高遗传多样性, GDJS和JAP群体间存在低度分化; ND2基因比CR和Cytb序列更适于分析角木叶鲽种群遗传结构, 选择多个遗传标记可有效弥补单一标记分析遗传多样性的局限性; 推测冰期两大独立避难所的形成及GDJS和JAP群体距离相隔较远是其发生遗传分化的主要原因。研究结果为中日沿海角木叶鲽渔业资源的种质保护与可持续利用提供了理论依据。
崔静, 徐明芳, 章群, 李瑶, 曾晓舒, 李莎 (2022) 基于3种线粒体标记探讨中日沿海角木叶鲽遗传多样性差异. 生物多样性, 30, 21485. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021485.
Jing Cui, Mingfang Xu, Qun Zhang, Yao Li, Xiaoshu Zeng, Sha Li (2022) Differences in genetic diversity of Pleuronichthys cornutus in the coastal water of China and Japan based on three mitochondrial markers. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21485. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021485.
| 海域 Sea region | 采样地点 Sample site | 样本数量 Sample size | 样本编号 Sample no. | 经纬度 Coordinates | 采样时间 Sampling date | 样本来源 Sample source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中国黄海 Yellow Sea, China | 辽宁丹东 LNDD | 30 | LNDD 01-14 | 39.86° N, 124.16° E | 2008.10 | 朱叶等, |
| LNDD 15-30 | 39.86° N, 124.16° E | 2021.04 | 本研究 This study | |||
| 山东青岛 SDQD | 36 | SDLSh 01-14 | 36.07° N, 120.42° E | 2008.10 | 朱叶等, | |
| SDQD 01-22 | 36.07° N, 120.38° E | 2018.04 | 本研究 This study | |||
| 中国东海 East China Sea | 浙江舟山 ZJZS | 42 | ZJDSh 01-13 | 30.19° N, 122.17° E | 2008.11 | 朱叶等, |
| ZJZS 01-29 | 29.99° N, 122.20° E | 2021.05 | 本研究 This study | |||
| 浙江温州 ZJWZ | 14 | ZJWZ 01-14 | 28.02° N, 120.79° E | 2011.11 | 本研究 This study | |
| 中国南海 South China Sea | 广东饶平 GDRP | 23 | GDRP 01-16 | 23.62° N, 116.94° E | 2008.12 | 朱叶等, |
| GDNA 01-07 | 23.42° N, 117.02° E | 2021.04 | 本研究 This study | |||
| 广东碣石 GDJS | 20 | GDJS 01-20 | 22.81° N, 115.82° E | 2014.08 | 本研究 This study | |
| 日本濑户内海 Seto inland sea, Japan | 日本明石 JAP | 35 | JAP 01-35 | 34.64° N, 134.98° E | 2019.07 | 本研究 This study |
| 合计 Total | - | 200 | - | - | - | - |
表1 本研究角木叶鲽样本采集信息表
Table 1 Sample information of Pleuronichthys corunutus in this study
| 海域 Sea region | 采样地点 Sample site | 样本数量 Sample size | 样本编号 Sample no. | 经纬度 Coordinates | 采样时间 Sampling date | 样本来源 Sample source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中国黄海 Yellow Sea, China | 辽宁丹东 LNDD | 30 | LNDD 01-14 | 39.86° N, 124.16° E | 2008.10 | 朱叶等, |
| LNDD 15-30 | 39.86° N, 124.16° E | 2021.04 | 本研究 This study | |||
| 山东青岛 SDQD | 36 | SDLSh 01-14 | 36.07° N, 120.42° E | 2008.10 | 朱叶等, | |
| SDQD 01-22 | 36.07° N, 120.38° E | 2018.04 | 本研究 This study | |||
| 中国东海 East China Sea | 浙江舟山 ZJZS | 42 | ZJDSh 01-13 | 30.19° N, 122.17° E | 2008.11 | 朱叶等, |
| ZJZS 01-29 | 29.99° N, 122.20° E | 2021.05 | 本研究 This study | |||
| 浙江温州 ZJWZ | 14 | ZJWZ 01-14 | 28.02° N, 120.79° E | 2011.11 | 本研究 This study | |
| 中国南海 South China Sea | 广东饶平 GDRP | 23 | GDRP 01-16 | 23.62° N, 116.94° E | 2008.12 | 朱叶等, |
| GDNA 01-07 | 23.42° N, 117.02° E | 2021.04 | 本研究 This study | |||
| 广东碣石 GDJS | 20 | GDJS 01-20 | 22.81° N, 115.82° E | 2014.08 | 本研究 This study | |
| 日本濑户内海 Seto inland sea, Japan | 日本明石 JAP | 35 | JAP 01-35 | 34.64° N, 134.98° E | 2019.07 | 本研究 This study |
| 合计 Total | - | 200 | - | - | - | - |
| 海域 Sea | 群体 Population | 数量 Sample size | 变异位点数 Variable sites | 单倍型数 Nh Number of haplotypes | 单倍型多样性 Hd Haplotype diversity | 核苷酸多样性 π Nucleotide diversity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中国 China | LNDD | 29 | 23 | 20 | 0.9606 | 0.0064 |
| SDQD | 36 | 21 | 27 | 0.9682 | 0.0063 | |
| ZJZS | 42 | 17 | 31 | 0.9826 | 0.0059 | |
| ZJWZ | 14 | 13 | 12 | 0.9780 | 0.0057 | |
| GDRP | 23 | 10 | 15 | 0.9486 | 0.0055 | |
| GDJS | 20 | 18 | 16 | 0.9632 | 0.0061 | |
| 日本 Japan | JAP | 35 | 20 | 23 | 0.9647 | 0.0064 |
| 总计 Total | - | 199 | 43 | 90 | 0.9699 | 0.0061 |
表2 基于CR序列分析中国和日本沿海角木叶鲽群体的遗传多样性
Table 2 Genetic diversity of Pleuronichthys cornutus in coastal water of China and Japan based on CR sequence analysis
| 海域 Sea | 群体 Population | 数量 Sample size | 变异位点数 Variable sites | 单倍型数 Nh Number of haplotypes | 单倍型多样性 Hd Haplotype diversity | 核苷酸多样性 π Nucleotide diversity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中国 China | LNDD | 29 | 23 | 20 | 0.9606 | 0.0064 |
| SDQD | 36 | 21 | 27 | 0.9682 | 0.0063 | |
| ZJZS | 42 | 17 | 31 | 0.9826 | 0.0059 | |
| ZJWZ | 14 | 13 | 12 | 0.9780 | 0.0057 | |
| GDRP | 23 | 10 | 15 | 0.9486 | 0.0055 | |
| GDJS | 20 | 18 | 16 | 0.9632 | 0.0061 | |
| 日本 Japan | JAP | 35 | 20 | 23 | 0.9647 | 0.0064 |
| 总计 Total | - | 199 | 43 | 90 | 0.9699 | 0.0061 |
| 地点 Sites | JAP | LNDD | SDQD | ZJZS | ZJWZ | GDRP | GDJS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JAP | - | 44.6264 | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | 29.9692 |
| LNDD | 0.0111 | - | 109.1491 | 51.9659 | 26.7628 | 34.0782 | ∞ |
| SDQD | -0.0070 | 0.0046 | - | ∞ | 238.7344 | 229.9147 | 198.7032 |
| ZJZS | -0.0046 | 0.0095 | -0.0082 | - | ∞ | ∞ | 56.3828 |
| ZJWZ | -0.0197 | 0.0184 | 0.0021 | -0.0062 | - | ∞ | 31.4081 |
| GDRP | -0.0130 | 0.0145 | 0.0022 | -0.0188 | -0.0071 | - | 30.4981 |
| GDJS | 0.0164 | -0.0046 | 0.0025 | 0.0088 | 0.0157 | 0.0161 | - |
表3 基于CR分析的角木叶鲽FST值(对角线下方)和Nm值(对角线上方)。* P < 0.05; ∞, Nm数值为负值。
Table 3 Pairwise FST estimates (below diagonal) and Nm (upper diagonal) across sampling sites of Pleuronichthys cornutus based on CR sequences analysis. * P < 0.05; ∞, the value of Nm is negative.
| 地点 Sites | JAP | LNDD | SDQD | ZJZS | ZJWZ | GDRP | GDJS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JAP | - | 44.6264 | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | 29.9692 |
| LNDD | 0.0111 | - | 109.1491 | 51.9659 | 26.7628 | 34.0782 | ∞ |
| SDQD | -0.0070 | 0.0046 | - | ∞ | 238.7344 | 229.9147 | 198.7032 |
| ZJZS | -0.0046 | 0.0095 | -0.0082 | - | ∞ | ∞ | 56.3828 |
| ZJWZ | -0.0197 | 0.0184 | 0.0021 | -0.0062 | - | ∞ | 31.4081 |
| GDRP | -0.0130 | 0.0145 | 0.0022 | -0.0188 | -0.0071 | - | 30.4981 |
| GDJS | 0.0164 | -0.0046 | 0.0025 | 0.0088 | 0.0157 | 0.0161 | - |
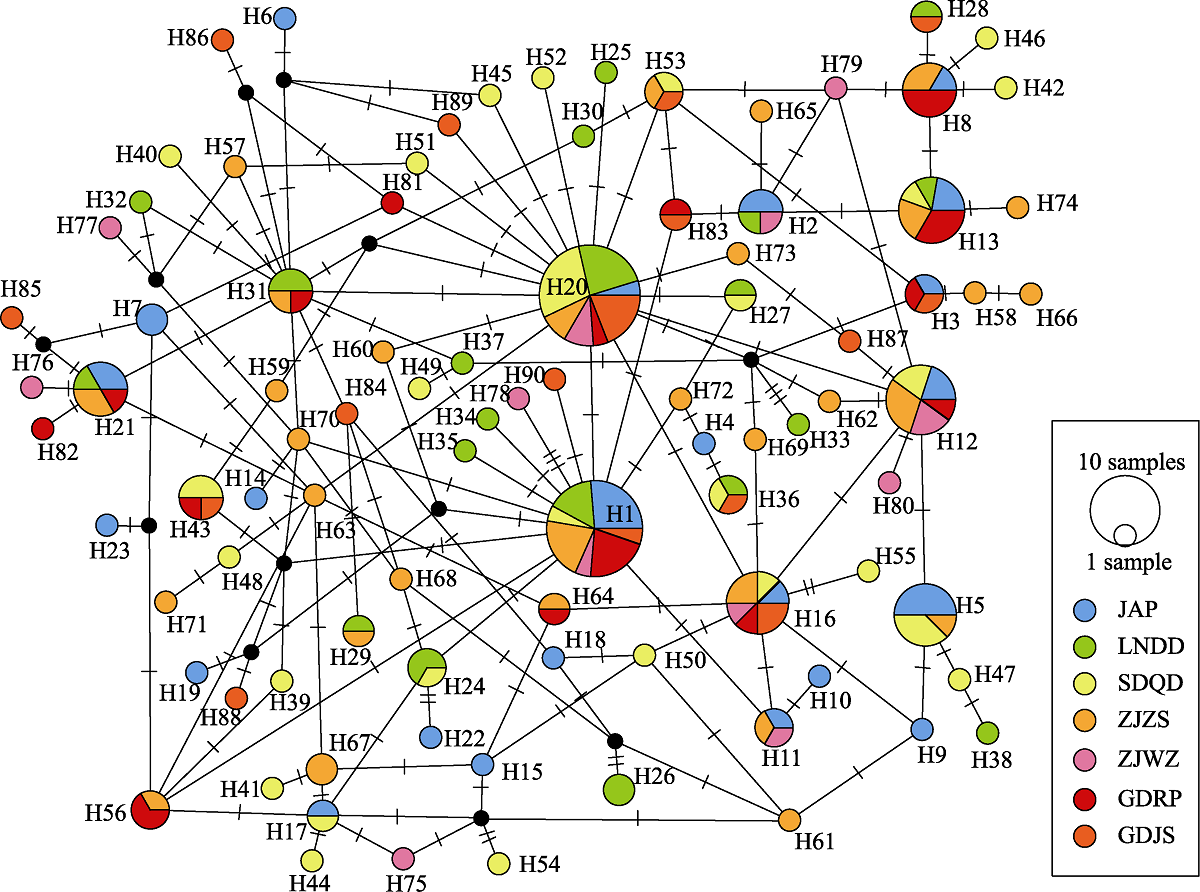
图1 7个角木叶鲽群体的CR序列单倍型网络图。不同的填充颜色代表不同的种群; 节点大小与单倍型频率相对应; “1 sample”的节点大小为1个个体, “10 samples”则为10个个体; 黑点表示理论上存在但未被监测到的单倍型; 圆圈之间的短横线代表突变。地点代号同表1中采样地点代号。
Fig. 1 Median-joining network of mtDNA CR haplotypes from 7 populations of Pleuronichthys cornutus. Different filling traits represent different populations; Node size corresponds to the haplotype frequencies; The node size of “1 sample” is 1 individual, and that of “10 samples” is 10 individuals; Black dots indicate haplotypes that theoretically present but not monitored; Short horizontal line on the line between the circles represents one mutation step. Location codes are the same as the sample sites in Table 1.
| 分组方式 Method of grouping | 变异比例 Percentage of variation (%) | FST 统计值 FST statistics (P-value) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 组群间 Among groups | 组群内群体间 Among populations within groups | 群体内 Within populations | ||
| 7个群体 Seven populations | 0.050 | - | 99.950 | 0.00054 (P > 0.05) |
| 中国6个群体和日本1个群体 Six populations from China and one population from Japan | -0.260 | 0.140 | 100.120 | -0.00118 (P > 0.05) |
| 濑户内海、中国黄海、东海和南海 Seto inland sea, Yellow Sea, East China Sea, and South China Sea | -0.410 | 0.410 | 100.000 | 0.00003 (P > 0.05) |
| 台湾海峡以南和台湾海峡以北 North of Taiwan Strait and south of Taiwan Strait | 0.990 | -0.160 | 99.170 | -0.00168 (P > 0.05) |
表4 基于CR的角木叶鲽群体AMOVA分析
Table 4 AMOVA analysis of Pleuronichthys cornutus populations based on CR sequence
| 分组方式 Method of grouping | 变异比例 Percentage of variation (%) | FST 统计值 FST statistics (P-value) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 组群间 Among groups | 组群内群体间 Among populations within groups | 群体内 Within populations | ||
| 7个群体 Seven populations | 0.050 | - | 99.950 | 0.00054 (P > 0.05) |
| 中国6个群体和日本1个群体 Six populations from China and one population from Japan | -0.260 | 0.140 | 100.120 | -0.00118 (P > 0.05) |
| 濑户内海、中国黄海、东海和南海 Seto inland sea, Yellow Sea, East China Sea, and South China Sea | -0.410 | 0.410 | 100.000 | 0.00003 (P > 0.05) |
| 台湾海峡以南和台湾海峡以北 North of Taiwan Strait and south of Taiwan Strait | 0.990 | -0.160 | 99.170 | -0.00168 (P > 0.05) |
| 群体 Population | 数量 Sample size | CR/Cytb/ND2遗传多样性 CR/Cytb/ND2 genetic diversity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 变异位点 Variable sites | 单倍型数 Nh Number of haplotypes | 单倍型多样性 Hd Haplotype diversity | 核苷酸多样性 π Nucleotide diversity | |||
| 中国 China | LNDD | 30 | 20/41/36 | 20/23/22 | 0.9563/0.9494/0.9678 | 0.0067/0.0048/0.0048 |
| SDQD | 30 | 19/44/47 | 23/27/26 | 0.9494/0.9908/0.9908 | 0.0063/0.0058/0.0053 | |
| ZJZS | 26 | 13/27/45 | 22/22/23 | 0.9877/0.9846/0.9815 | 0.0061/0.0039/0.0055 | |
| GDJS | 20 | 18/46/45 | 16/18/20 | 0.9632/0.9842/1.0000 | 0.0061/0.0063/0.0059 | |
| 日本 Japan | JAP | 34 | 20/40/32 | 22/25/20 | 0.9626/0.9768/0.9412 | 0.0063/0.0050/0.0041 |
| 合计 Total | 140 | 35/103/112 | 74/95/94 | 0.9683/0.9829/0.9811 | 0.0063/0.0051/0.0050 | |
表5 基于CR、Cytb和ND2序列分析角木叶鲽群体的样本信息和遗传多样性
Table 5 Sample information and genetic diversity indices of Pleuronichthys cornutus populations based on CR, Cytb, and ND2 sequences
| 群体 Population | 数量 Sample size | CR/Cytb/ND2遗传多样性 CR/Cytb/ND2 genetic diversity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 变异位点 Variable sites | 单倍型数 Nh Number of haplotypes | 单倍型多样性 Hd Haplotype diversity | 核苷酸多样性 π Nucleotide diversity | |||
| 中国 China | LNDD | 30 | 20/41/36 | 20/23/22 | 0.9563/0.9494/0.9678 | 0.0067/0.0048/0.0048 |
| SDQD | 30 | 19/44/47 | 23/27/26 | 0.9494/0.9908/0.9908 | 0.0063/0.0058/0.0053 | |
| ZJZS | 26 | 13/27/45 | 22/22/23 | 0.9877/0.9846/0.9815 | 0.0061/0.0039/0.0055 | |
| GDJS | 20 | 18/46/45 | 16/18/20 | 0.9632/0.9842/1.0000 | 0.0061/0.0063/0.0059 | |
| 日本 Japan | JAP | 34 | 20/40/32 | 22/25/20 | 0.9626/0.9768/0.9412 | 0.0063/0.0050/0.0041 |
| 合计 Total | 140 | 35/103/112 | 74/95/94 | 0.9683/0.9829/0.9811 | 0.0063/0.0051/0.0050 | |
| 序列 Sequences | 地点 Sites | JAP | LNDD | SDQD | ZJZS | GDJS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR | JAP | - | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | 29.3686 |
| LNDD | -0.0051 | - | 77.9929 | 79.3722 | ∞ | |
| SDQD | -0.0060 | 0.0064 | - | ∞ | ∞ | |
| ZJZS | -0.0302 | 0.0063 | -0.0064 | - | 19.3728 | |
| GDJS | 0.0167 | -0.0036 | -0.0063 | 0.0252 | - | |
| Cytb | JAP | - | ∞ | ∞ | 133.9086 | 49.7008 |
| LNDD | -0.0059 | - | ∞ | ∞ | 53.3793 | |
| SDQD | -0.0001 | -0.0013 | - | 133.1898 | 111.8596 | |
| ZJZS | 0.0037 | -0.0091 | 0.0037 | - | 16.1058 | |
| GDJS | 0.0100 | 0.0093 | 0.0045 | 0.0301 | - | |
| ND2 | JAP | - | 164.5165 | 57.1701 | 369.8704 | 16.0618 |
| LNDD | 0.0030 | - | ∞ | 34.3918 | 26.5856 | |
| SDQD | 0.0087 | -0.0037 | - | 123.8781 | ∞ | |
| ZJZS | 0.0014 | 0.0143 | 0.0040 | - | 27.6373 | |
| GDJS | 0.0302* | 0.0185 | -0.0103 | 0.0178 | - |
表6 基于CR、Cytb和ND2分析角木叶鲽群体间成对FST值(对角线下方)和Nm值(对角线上方)。* P < 0.05; ∞: Nm数值为负值。
Table 6 Pairwise FST estimates (below diagonal) and Nm (upper diagonal) between sampling sites of Pleuronichthys cornutus based on CR, Cytb and ND2 sequences. * P < 0.05; ∞, the value of Nm is negative.
| 序列 Sequences | 地点 Sites | JAP | LNDD | SDQD | ZJZS | GDJS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR | JAP | - | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | 29.3686 |
| LNDD | -0.0051 | - | 77.9929 | 79.3722 | ∞ | |
| SDQD | -0.0060 | 0.0064 | - | ∞ | ∞ | |
| ZJZS | -0.0302 | 0.0063 | -0.0064 | - | 19.3728 | |
| GDJS | 0.0167 | -0.0036 | -0.0063 | 0.0252 | - | |
| Cytb | JAP | - | ∞ | ∞ | 133.9086 | 49.7008 |
| LNDD | -0.0059 | - | ∞ | ∞ | 53.3793 | |
| SDQD | -0.0001 | -0.0013 | - | 133.1898 | 111.8596 | |
| ZJZS | 0.0037 | -0.0091 | 0.0037 | - | 16.1058 | |
| GDJS | 0.0100 | 0.0093 | 0.0045 | 0.0301 | - | |
| ND2 | JAP | - | 164.5165 | 57.1701 | 369.8704 | 16.0618 |
| LNDD | 0.0030 | - | ∞ | 34.3918 | 26.5856 | |
| SDQD | 0.0087 | -0.0037 | - | 123.8781 | ∞ | |
| ZJZS | 0.0014 | 0.0143 | 0.0040 | - | 27.6373 | |
| GDJS | 0.0302* | 0.0185 | -0.0103 | 0.0178 | - |
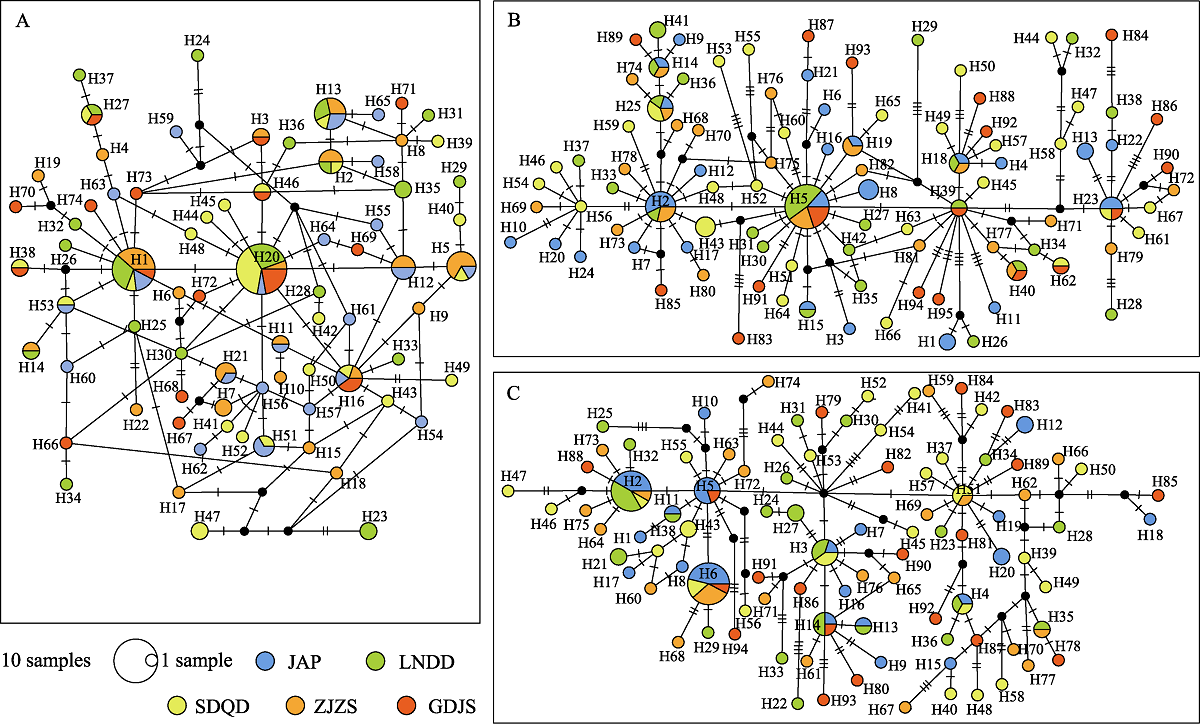
图2 5个角木叶鲽群体的CR (A)、Cytb (B)和ND2 (C)单倍型网络图。不同的填充颜色代表不同的种群; 节点大小与单倍型频率相对应; “1 sample”的节点大小为1个个体; 黑点表示理论上存在但未被监测到的单倍型; 圆圈之间的短横线代表突变。地点代号同表1中采样地点代号。
Fig. 2 Median-joining network of mtDNA CR (A), Cytb (B), and ND2 (C) haplotypes from 5 populations of Pleuronichthys cornutus. Different filling traits represent different populations; Node size corresponds to the haplotype frequencies, and “1 sample” size is one individual. Black dots indicate haplotypes that theoretically present but not monitored; Short horizontal line on the line between the circles represents one mutation step. Location codes are the same as the sample sites in Table 1.
| 分组方式 Method of grouping | Cytb/ND2变异比例 Percentage of Cytb/ND2 variation (%) | Cytb/ND2 FST 统计值 Cytb/ND2 FST statistics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 组群间 Among groups | 组群内群体间 Among populations within groups | 群体内 Within populations | ||
| 7个群体 Seven populations | 0.32/0.85 | -/- | 99.68/99.15 | 0.0032*/0.0085* |
| 中国6个群体和日本1个群体 Six populations from China and one population from Japan | -0.44/0.24 | 0.52/074 | 99.62/99.02 | 0.0008*/0.0098* |
| 濑户内海、中国黄海、东海和南海 Seto inland sea, Yellow Sea, East China Sea, and South China Sea | 0.35/-0.73 | 0/1.50 | 99.64/99.23 | 0.0036*/0.0077* |
| 台湾海峡以南和台湾海峡以北 North of Taiwan Strait and south of Taiwan Strait | 1.87/0.74 | -0.2/0.62 | 98.39/98.64 | 0.0161*/0.0136* |
表7 基于Cytb和ND2基因对5个角木叶鲽群体的AMOVA分析
Table 7 AMOVA analysis of 5 populations from Pleuronichthys cornutus based on Cytb and ND2 sequences. * P < 0.05.
| 分组方式 Method of grouping | Cytb/ND2变异比例 Percentage of Cytb/ND2 variation (%) | Cytb/ND2 FST 统计值 Cytb/ND2 FST statistics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 组群间 Among groups | 组群内群体间 Among populations within groups | 群体内 Within populations | ||
| 7个群体 Seven populations | 0.32/0.85 | -/- | 99.68/99.15 | 0.0032*/0.0085* |
| 中国6个群体和日本1个群体 Six populations from China and one population from Japan | -0.44/0.24 | 0.52/074 | 99.62/99.02 | 0.0008*/0.0098* |
| 濑户内海、中国黄海、东海和南海 Seto inland sea, Yellow Sea, East China Sea, and South China Sea | 0.35/-0.73 | 0/1.50 | 99.64/99.23 | 0.0036*/0.0077* |
| 台湾海峡以南和台湾海峡以北 North of Taiwan Strait and south of Taiwan Strait | 1.87/0.74 | -0.2/0.62 | 98.39/98.64 | 0.0161*/0.0136* |
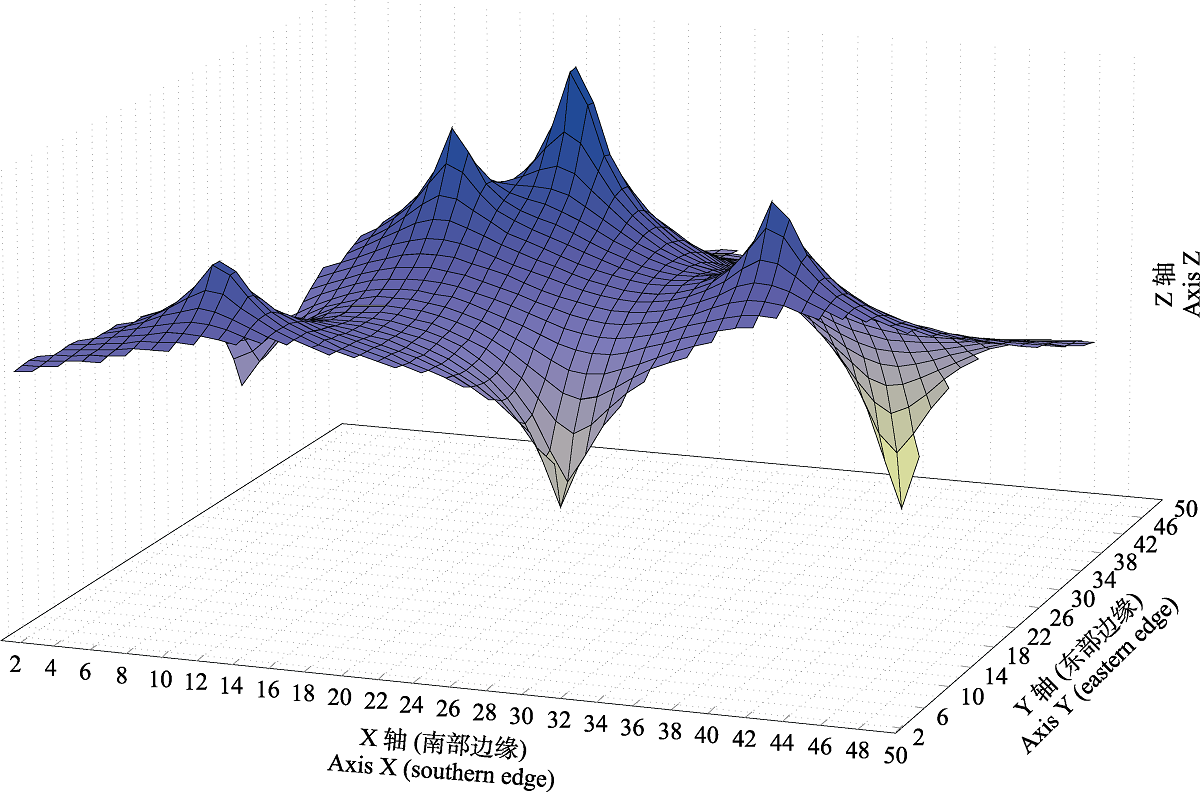
图3 角木叶鲽ND2基因的遗传距离空间分布图。X轴对应经度关系和Y轴对应纬度关系, 为本研究所考察群体的地理位置(表1); Z轴对应遗传距离。
Fig. 3 Genetic landscape shape of Pleuronichthys cornutus based on ND2 gene. X-axis corresponds to longitude and Y-axis corresponds to latitude that for the geographical location of population examined in this study (Table 1); Z-axis corresponds to genetic distance.
| 群体 Population | CR/Cytb/ND2中性检验 CR/Cytb/ND2 neutrality statistics | CR/Cytb/ND2错配分析 CR/Cytb/ND2 mismatch analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tajima’s D | Fu’s FS | SSD | r | τ | |
| JAP | -1.025/-1.751*/-1.624* | -15.980*/-16.752*/-9.805* | 0.011*/0.003/0.003 | 0.044*/0.010/0.019 | 3.3/4.9/5.0 |
| LNDD | -0.961/-1.943*/-1.632* | 13.064*/-15.607*/13.174* | 0.002/0.002/0.014 | 0.017/0.006/0.037 | 3.9/2.4/4.0 |
| SDQD | -0.975/-1.753*/-1.983* | 20.467*/-22.938*/-21.070* | 0.001/0.008/0.006 | 0.019/0.022/0.016 | 3.7/4.0/4.0 |
| ZJZS | -0.105/-1.610*/-1.966* | -21.947*/-19.343*/-17.299* | 0.015*/0.003/0.009 | 0.052*/0.025/0.017 | 3.0/3.1/4.0 |
| GDJS | -1.292/-2.044*/-2.071* | -11.773*/-10.660*/-17.156* | 0.004/0.004/0.016 | 0.032/0.010/0.030 | 3.5/4.0/5.0 |
| 总体 Overall | -0.872/-1.821*/-1.855* | -16.646*/-17.060*/-15.701* | 0.006/0.004/0.010 | 0.033/0.015/0.024 | 3.5/3.7/4.4 |
表8 5个角木叶鲽群体的中性检验和核苷酸错配分析
Table 8 Indices of neutrality statistics and demographic parameter estimates based on CR, Cytb and ND2 sequences in five populations of Pleuronichthys cornutus
| 群体 Population | CR/Cytb/ND2中性检验 CR/Cytb/ND2 neutrality statistics | CR/Cytb/ND2错配分析 CR/Cytb/ND2 mismatch analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tajima’s D | Fu’s FS | SSD | r | τ | |
| JAP | -1.025/-1.751*/-1.624* | -15.980*/-16.752*/-9.805* | 0.011*/0.003/0.003 | 0.044*/0.010/0.019 | 3.3/4.9/5.0 |
| LNDD | -0.961/-1.943*/-1.632* | 13.064*/-15.607*/13.174* | 0.002/0.002/0.014 | 0.017/0.006/0.037 | 3.9/2.4/4.0 |
| SDQD | -0.975/-1.753*/-1.983* | 20.467*/-22.938*/-21.070* | 0.001/0.008/0.006 | 0.019/0.022/0.016 | 3.7/4.0/4.0 |
| ZJZS | -0.105/-1.610*/-1.966* | -21.947*/-19.343*/-17.299* | 0.015*/0.003/0.009 | 0.052*/0.025/0.017 | 3.0/3.1/4.0 |
| GDJS | -1.292/-2.044*/-2.071* | -11.773*/-10.660*/-17.156* | 0.004/0.004/0.016 | 0.032/0.010/0.030 | 3.5/4.0/5.0 |
| 总体 Overall | -0.872/-1.821*/-1.855* | -16.646*/-17.060*/-15.701* | 0.006/0.004/0.010 | 0.033/0.015/0.024 | 3.5/3.7/4.4 |
| [1] |
Ando D, Ikeda M, Sekino M, Sugaya T, Katamachi D, Yoseda K, Kijima A (2016) Improvement of mitochondrial DNA haplotyping in Japanese flounder populations using the sequences of control region and ND2 gene. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi, 82, 712-719.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Bandelt HJ, Forster P, Röhl A (1999) Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 16, 37-48.
PMID |
| [3] | Bao MM, Huo LP, Liu HH (2017) Analysis of the nutritional composition in Pleuronichthys cornutus of Zhoushan. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 45(22), 52-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [包苗苗, 霍利平, 刘慧慧 (2017) 舟山海域角木叶鲽营养成分分析. 安徽农业科学, 45(22), 52-54.] | |
| [4] |
Bradman H, Grewe P, Appleton B (2011) Direct comparison of mitochondrial markers for the analysis of swordfish population structure. Fisheries Research, 109, 95-99.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Chen DG, Liu CG, Dou SZ (1992) The biology of flatfish (Pleuronectinae) in the coastal waters of China. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research, 29, 25-33.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Dai Q, Lu ZH, Xue LJ, Xu HX (2017) Species composition and assessment of the stock study on Peuronectiformes in the East China Sea. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science), 36, 379-388. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [戴乾, 卢占晖, 薛利建, 徐汉祥 (2017) 东海鲽形目种类组成与资源量评估. 浙江海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 36, 379-388.] | |
| [7] |
Donaldson KA, Wilson RR (1999) Amphi-panamic geminates of snook (Percoidei: Centropomidae) provide a calibration of the divergence rate in the mitochondrial DNA control region of fishes. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 13, 208-213.
PMID |
| [8] |
Ely B, Viñas J, Bremer J, Black D, Lucas L, Covello K, Labrie A, Thelen E (2005) Consequences of the historical demography on the global population structure of two highly migratory cosmopolitan marine fishes: The yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares) and the skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis). BMC Evolutionary Biology, 5, 19.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Excoffier L, Lischer H (2010) Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Molecular Ecology Resources, 10, 564-567.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Fiedler PL, Jain SK (1992) Conservation Biology: The Theory and Practice of Nature Conservation, Preservation, and Management, 157-158. Chapman & Hall, New York. |
| [11] | Gao TX, Ren GJ, Liu JX, Xiao YS (2009) Progress in molecular phylogeography of marine fish. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 39, 897-902, 1036. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [高天翔, 任桂静, 刘进贤, 肖永 (2009) 海洋鱼类分子系统地理学研究进展. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 39, 897-902, 1036.] | |
| [12] |
Grant W (1998) Shallow population histories in deep evolutionary lineages of marine fishes: Insights from sardines and anchovies and lessons for conservation. The Journal of Heredity, 89, 415-426.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai Ocean University (1962) The Fishes of South China Sea. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [中国科学院动物研究所, 中国科学院海洋研究所, 上海水产学院 (1962) 南海鱼类志. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [14] | Irwin DM, Kocher TD, Wilson AC (1991) Evolution of the cytochrome b gene of mammals. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 1991, 128-144. |
| [15] |
Kocher TD, Conroy JA, Mckaye KR, Stauffer JR, Lockwood S F (1995) Evolution of NADH dehydrogenase subunit 2 in east African cichlid fish. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 4, 420-432.
PMID |
| [16] | Kong XY, Yu JZ, Zhou LS, Yu ZN (2007) Comparative analysis of 5'-end sequence of the mitochondrial control region of six flatfish species (Pleuronectidae) from the Yellow Sea. Raffles Bulletin of Zoology, 14, 111-120. |
| [17] |
Lee WJ, Conroy J, Howell WH, Kocher TD (1995) Structure and evolution of teleost mitochondrial control regions. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 41, 54-66.
PMID |
| [18] | Li KR (1992) Climate Change and Its Impact in China. China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李克让 (1992) 中国气候变化及其影响. 海洋出版社, 北京.] | |
| [19] | Li MD (2012) The Ecology of Economic Fishes in China. Tianjin Science and Technology Press, Tianjin. (in Chinese) |
| [李明德 (2012) 中国经济鱼类生态学. 天津科学技术出版社, 天津.] | |
| [20] |
Liu Q, Liu L, Song N, Wang XH, Gao TX (2019) Genetic structure in the marbled rockfish (Sebastiscus marmoratus) across most of the distribution in the northwestern Pacific. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 35, 1249-1259.
DOI |
| [21] |
Mane S, Guerin P, Mouillot D, Blanchet S, Velez L, Albouy C, Pellissier L (2020) Global determinants of freshwater and marine fish genetic diversity. Nature Communications, 11, 692.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Miller M (2005) Alleles in space (AIS): Computer software for the joint analysis of interindividual spatial and genetic information. The Journal of Heredity, 96, 722-724.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Ni G, Li Q, Kong LF, Yu H (2014) Comparative phylogeography in marginal seas of the northwestern Pacific. Molecular Ecology, 23, 534-548.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Okello JBA, Nyakaana S, Masembe C, Siegismund HR, Arctander P (2005) Mitochondrial DNA variation of the common hippopotamus: Evidence for a recent population expansion. Heredity, 95, 206-215.
PMID |
| [25] |
Rogers AR, Harpending H (1992) Population growth makes waves in the distribution of pairwise genetic differences. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 9, 552-569.
PMID |
| [26] |
Rozas J, Ferrer-Mata A, Sánchez-DelBarrio JC, Guirao-Rico S, Librado P, Ramos-Onsins SE, Sánchez-Gracia A (2017) DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large datasets. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 34, 3299-3302.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Song N, Jia N, Yanagimoto T, Lin LS, Gao TX (2013) Genetic differentiation of Trachurus japonicus from the northwestern Pacific based on the mitochondrial DNA control region. Mitochondrial DNA, 24, 705-712.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | Song YX, Gao TX, Yang TY, Han ZQ, Song N (2018) Comparative analysis of genetic diversity and morphology of Pleuronichthys cornutus populations. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 48, 49-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宋垚萱, 高天翔, 杨天燕, 韩志强, 宋娜 (2018) 角木叶鲽的群体遗传多样性研究和形态学分析. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 48, 49-55.] | |
| [29] |
Sudhir K, Glen S, Koichiro T (2016) MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33, 1870-1874.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | Sun XP (2006) China’s Offshore Area Ocean. China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [孙湘平 (2006) 中国近海区域海洋. 海洋出版社, 北京.] | |
| [31] |
Tajima F (1983) Evolutionary relationship of DNA sequences in finite populations. Genetics, 105, 437-460.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
Takeshima H, Iguchi K, Nishida M (2005) Unexpected ceiling of genetic differentiation in the control region of the mitochondrial DNA between different subspecies of the Ayu Plecoglossus altivelis. Zoological science, 22, 401-410.
PMID |
| [33] |
Tarallo A, Angelini C, Sanges R, Yagi M, Agnisola C, D’Onofrio G (2016) On the genome base composition of teleosts: The effect of environment and lifestyle. BMC Genomics, 17, 173.
DOI PMID |
| [34] | Verma R, Singh M, Kumar S (2016) Unraveling the limits of mitochondrial control region to estimate the fine scale population genetic differentiation in anadromous fish Tenualosa ilisha. Scientifica, 2016, 2035240. |
| [35] |
Wang L, Shi XF, Su YQ, Meng ZN, Lin HR (2013) Genetic divergence and historical demography in the endangered large yellow croaker revealed by mtDNA. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 46, 137-144.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Wang PX (1999) Response of western Pacific marginal seas to glacial cycles: Paleoceanographic and sedimentological features. Marine Geology, 156, 5-39.
DOI URL |
| [37] | Wright S (1978) Evolution and the Genetics of Population:Variability Within and Among Natural Population. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [38] |
Xiang DG, Li YF, Li XH, Chen WT, Ma XH (2021) Population structure and genetic diversity of Culter recurviceps revealed by multi-loci. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1505-1512. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[向登高, 李跃飞, 李新辉, 陈蔚涛, 马秀慧 (2021) 多基因联合揭示海南鲌的遗传结构与遗传多样性. 生物多样性, 29, 1505-1512.]
DOI |
|
| [39] | Xiao WH, Zhang YP (2000) Genetics and evolution of mitochondrial DNA in fish. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 24, 385- 391. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [肖武汉, 张亚平 (2000) 鱼类线粒体DNA的遗传与进化. 水生生物学报, 24, 385-391.] | |
| [40] |
Yamamoto K, Nagasawa K (2015) Temporal changes in demersal fish assemblage structure in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi, 81, 429-437.
DOI URL |
| [41] | Yang XS, Zhang Q, Yu FY, Lü JL, Di XD, Shao WJ, Huang ZY, Lu LF (2017) MtDNA ND2 sequence-based genetic analysis of Anabas testudineus from South China and Lancang Mekong River. South China Fisheries Science, 13, 43-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨喜书, 章群, 余帆洋, 吕金磊, 底晓丹, 邵伟军, 黄镇宇, 卢丽锋 (2017) 华南6水系与澜沧江-湄公河攀鲈线粒体ND2基因的遗传多样性分析. 南方水产科学, 13, 43-50.] | |
| [42] | Yao YT, Harff J, Meyer M, Zhan WH (2009) Reconstruction of paleocoastlines for the northwestern South China Sea since the Last Glacial Maximum. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 39, 753-762. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [姚衍桃, Harff Jan, 詹文欢 (2009) 南海西北部末次盛冰期以来的古海岸线重建. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), 39, 753-762.] | |
| [43] | Yue XL, Zhang Q, Zhao S, Fan FJ (2010) A fast and efficient method for isolation of genomic DNA from fish specimens. Biotechnology Bulletin, (2), 202-204. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [乐小亮, 章群, 赵爽, 范凤娟 (2010) 一种高效快速的鱼类标本基因组DNA提取方法. 生物技术通报, (2), 202-204.] | |
| [44] |
Zardoya R, Meyer A (1996) Phylogenetic performance of mitochondrial protein-coding genes in resolving relationships among vertebrates. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 13, 933-942.
PMID |
| [45] | Zheng DY, Guo YJ, Yang TY, Gao TX, Zheng Y, Yuan DH, Si SJ (2019) Genetic diversity analysis of Sillago japonica based on mitochondrial DNA ND2 gene. South China Fisheries Science, 15, 84-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郑德育, 郭易佳, 杨天燕, 高天翔, 郑瑶, 袁冬皓, 斯舒谨 (2019) 基于线粒体ND2基因序列的少鳞鱚遗传多样性研究. 南方水产科学, 15, 84-91.] | |
| [46] | Zhu Y, Zhang Q, Li GS, Liu HL, Ma B, Huang XY, Si CL (2012) Genetic diversity of four Pleuronichthys cornutus populations in coastal waters of China. Marine Science Bulletin, 31, 552-556. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱叶, 章群, 李贵生, 刘海林, 马奔, 黄小彧, 司从利 (2012) 中国近海角木叶鲽(Pleuronichthys cornutus)种群遗传多样性研究. 海洋通报, 31, 552-556.] | |
| [47] | Zhu YD, Zhang CL (1963) The Fishes of East China Sea. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [朱元鼎, 张春霖 (1963) 东海鱼类志. 科学出版社, 北京.] |
| [1] | 王嘉陈, 徐汤俊, 许唯, 张高季, 尤艺瑾, 阮宏华, 刘宏毅. 城市景观格局对大蚰蜒种群遗传结构的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [2] | 冯晨, 张洁, 黄宏文. 统筹植物就地保护与迁地保护的解决方案: 植物并地保护(parallel situ conservation)[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [3] | 李庆多, 栗冬梅. 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [4] | 齐海玲, 樊鹏振, 王跃华, 刘杰. 中国北方六省区胡桃的遗传多样性和群体结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [5] | 熊飞, 刘红艳, 翟东东, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 陈大庆. 基于基因组重测序的长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [6] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [7] | 何艺玥, 刘玉莹, 张富斌, 秦强, 曾燏, 吕振宇, 杨坤. 梯级水利工程背景下的嘉陵江干流蛇鮈群体遗传多样性和遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23160-. |
| [8] | 孙维悦, 舒江平, 顾钰峰, 莫日根高娃, 杜夏瑾, 刘保东, 严岳鸿. 基于保护基因组学揭示荷叶铁线蕨的濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21508-. |
| [9] | 陶克涛, 白东义, 图格琴, 赵若阳, 安塔娜, 铁木齐尔·阿尔腾齐米克, 宝音德力格尔, 哈斯, 芒来, 韩海格. 基于基因组SNPs对东亚家马不同群体遗传多样性的评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21031-. |
| [10] | 孙军, 宋煜尧, 施义锋, 翟键, 燕文卓. 近十年中国海洋生物多样性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22526-. |
| [11] | 栗冬梅, 杨卫红, 李庆多, 韩茜, 宋秀平, 潘虹, 冯云. 巴尔通体在滇西南蝙蝠中高度流行并具有丰富的遗传变异特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1245-1255. |
| [12] | 姚志, 郭军, 金晨钟, 刘勇波. 中国纳入一级保护的极小种群野生植物濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(3): 394-408. |
| [13] | 叶俊伟, 田斌. 中国西南地区重要木本油料植物扁核木的遗传结构及成因[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1629-1637. |
| [14] | 向登高, 李跃飞, 李新辉, 陈蔚涛, 马秀慧. 多基因联合揭示海南鲌的遗传结构与遗传多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(11): 1505-1512. |
| [15] | 苏金源, 燕语, 李冲, 李丹, 杜芳. 通过遗传多样性探讨极小种群野生植物的致濒机理及保护策略: 以裸子植物为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(3): 376-384. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()