



生物多样性 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (10): 1386-1395. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021050 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021050
所属专题: 昆虫多样性与生态功能
滕备1,2, 杨海东1,3, 佟一杰1, 梁敏轩4, 张嘉康4, 李英铭4, 白明1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-02-06
接受日期:2021-07-29
出版日期:2021-10-20
发布日期:2021-10-20
通讯作者:
白明
作者简介:* E-mail: baim@ioz.ac.cn基金资助:
Bei Teng1,2, Haidong Yang1,3, Yijie Tong1, Manhin Leung4, Kahong Cheung4, Yingming Lee4, Benoit Guénard5, Ming Bai1,*( )
)
Received:2021-02-06
Accepted:2021-07-29
Online:2021-10-20
Published:2021-10-20
Contact:
Ming Bai
摘要:
标本标准化采集是昆虫多样性研究的根本。昆虫种类繁多、习性复杂、分布广泛, 基于不同的研究目标, 昆虫学家会选用不同的采集方法。由于主动式采集方法存在较多干扰因素和重现性差等问题, 以飞行阻隔器(flight interception trap, FIT)、马氏网(Malaise trap, MT)和罐诱(pitfall trap, PT)为代表的被动式采集方法被广泛应用, 并在昆虫多样性研究中展现独特的优势。然而关于这些被动式采集方法的收集特点和采集效果等还缺乏系统性研究。本研究选取香港城门13个样点, 利用上述3种被动式采集方法共156个采集装备开展为期24天的鞘翅目昆虫采集工作, 并通过多样性指数分析、多度分析、体型与食性相关分析、相似性分析以及物种累积曲线分析评估了不同采集方法对甲虫的收集效果。本研究共采集甲虫6,380头, 涉及40科197种, 分析结果显示: (1)采用不同采集方法获得的物种数量和组成存在差异。从科级和种级的数量来看, FIT (36科, 149种) > MT (24科, 79种) > PT (17科, 60种); 在物种组成方面, FIT与PT之间、MT与PT之间区别较大, FIT与MT对应的物种相似度稍高于前两组。(2)多样性指数和物种多度分布分析显示: 丰富度指数为FIT > MT > PT, 优势度指数为FIT > PT > MT, 多样性指数为MT > FIT > PT, 均匀度指数为MT > PT > FIT。3种方法采集到的甲虫个体数为1头的种较多, 个体数超过1头的种在时间和空间方面的分布较广, 优势科的种类较少, 但其个体数占总个体数的比例较高。(3) FIT和PT均采集到了6类食性的甲虫, 其中藻食性的缨甲科甲虫仅见于FIT和PT采集方法。(4)物种累积曲线的结果表明3种采集方法效果均较好。3种采集方法各有特点, 但FIT采集的综合效果最优。FIT和MT两种方法的结合提升了采集甲虫的种类、食性和体型等方面的覆盖度, 更利于对甲虫多样性及类群与生态环境功能互作的研究。3种方法所收集到的甲虫存在一定差异, 因此可以针对不同研究目的选取适宜的采集方式。
滕备, 杨海东, 佟一杰, 梁敏轩, 张嘉康, 李英铭, 白明 (2021) 三种被动式采集方法对甲虫收集效果的比较研究: 以香港城门样地为例. 生物多样性, 29, 1386-1395. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021050.
Bei Teng, Haidong Yang, Yijie Tong, Manhin Leung, Kahong Cheung, Yingming Lee, Benoit Guénard, Ming Bai (2021) A comparative study on the collection effectiveness of beetles by three passive acquisition methods in Shing Mun (Hong Kong). Biodiversity Science, 29, 1386-1395. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021050.
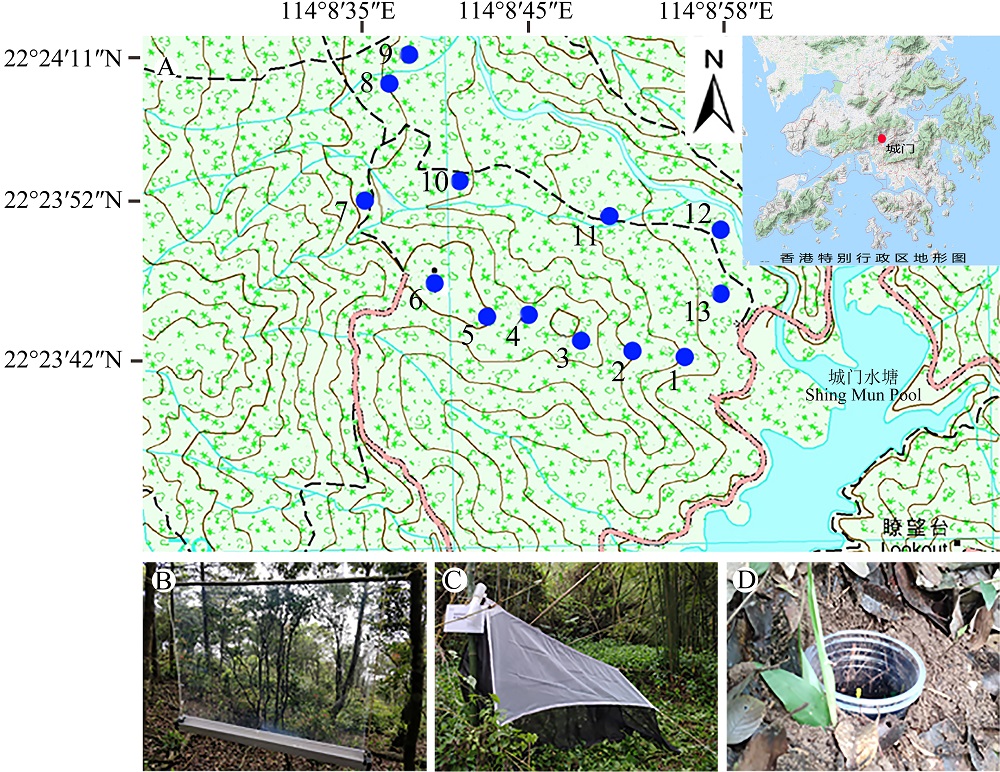
图1 香港城门样地采集样点和3种被动式采集方法。A: 样点位置(圆点标注); B: 飞行阻隔器; C: 马氏网; D: 诱罐。
Fig. 1 The sampling points in Shing Mun, Hong Kong and the three passive acquisition methods. A, Layout of sampling points (dots indicated); B, Flight interception trap; C, Malaise trap; D, Pitfall trap.
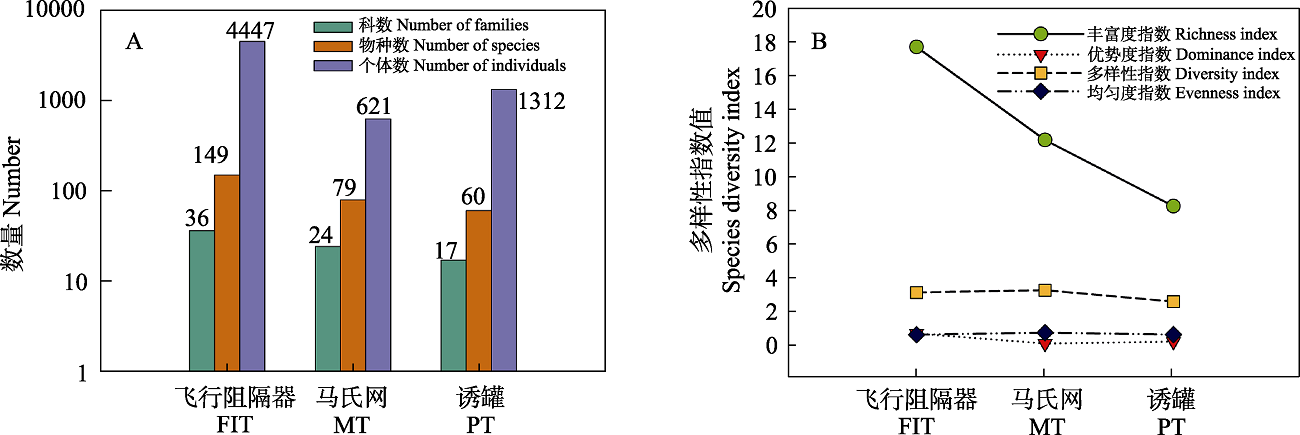
图2 3种采集方法采集的甲虫多样性统计。A:科数、物种数及个体数; B: 多样性指数。
Fig. 2 Diversity statistics of beetles collected by three collection methods. A, Number of beetle families, species and individuals; B, The diversity indices of beetles. FIT, Flight interception trap; MT, Malaise trap; PT, Pitfall trap.
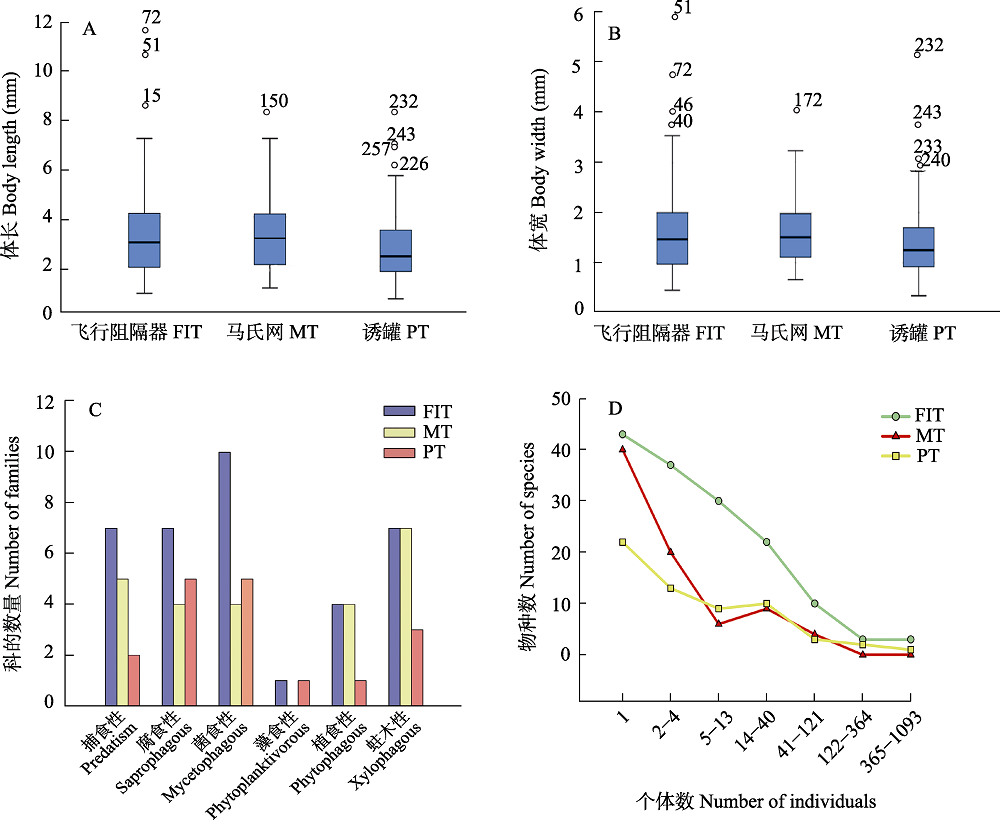
图3 3种采集方法采集的甲虫基于体长(A)、体宽(B)、食性(C)和物种多度(D)的比较研究。A和B图中的数字表示体型异常值对应的标本编号。
Fig. 3 Comparison of the body length (A), body width (B), feeding habit (C) and species abundance (D) among beetles collected by the three methods. The numbers in figures A and B represent specimen numbers corresponding to body size outliers. FIT, Flight interception trap; MT, Malaise trap; PT, Pitfall trap.
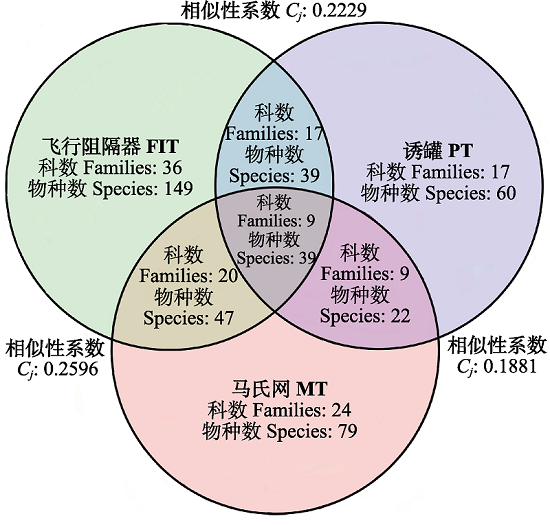
图4 3种方法采集的甲虫科数和种数的相似性
Fig. 4 Similarity of beetle family and species among the three sampling methods. FIT, Flight interception trap; MT, Malaise trap; PT, Pitfall trap.
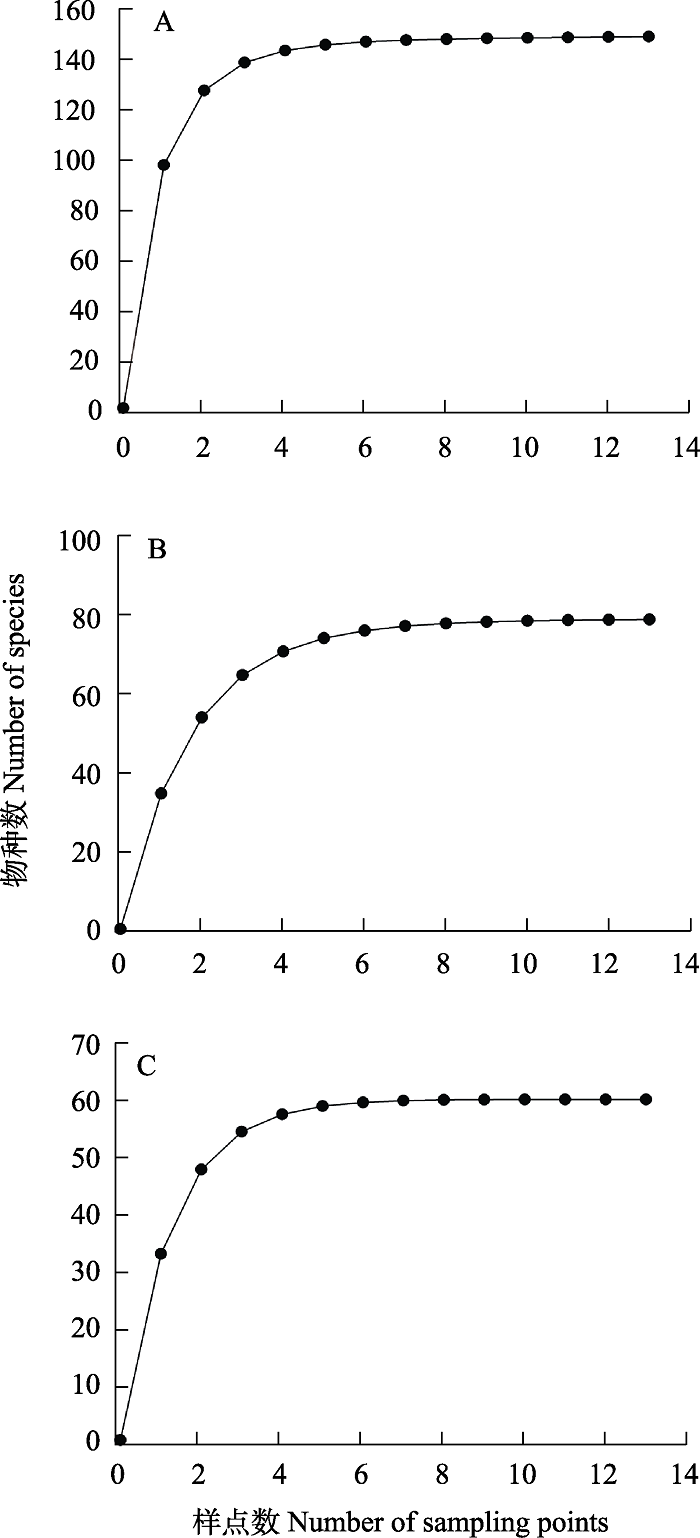
图5 3种方法下基于样点数的物种累积曲线。A: 飞行阻隔器; B:马氏网; C: 诱罐。
Fig. 5 Species accumulation curves based on number of sampling points under three methods. A, Flight interception trap; B, Malaise trap; C, Pitfall trap.
| [1] | Ades GWJ, Dudgeon D (1999) Insect seasonality in Hong Kong: A monsoonal environment in the northern tropics. Memoirs of the Hong Kong Natural History Society, 22, 81-97. |
| [2] |
Campos WG, Pereira D, Schoereder JH (2000) Comparison of the efficiency of flight interception trap models for sampling Hymenoptera and other insects. Anais da Sociedade Entomológica do Brasil, 29, 381-389.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Chao A, Chazdon RL, Colwell RK, Shen TJ (2005) A new statistical approach for assessing similarity of species composition with incidence and abundance data. Ecology Letters, 8, 148-159.
DOI URL |
| [4] | Chung AYC (2004) Vertical stratification of beetles (Coleoptera) using flight interception traps in a lowland rainforest of Sabah, Malaysia. Sepilok Bulletin, 1, 29-41. |
| [5] | Dobony CA, Edwards JW (2001) A new flight interception trap for arthropod sampling. Entomological News, 112, 217-220. |
| [6] | Dong H, Yang GL, Kong LG, Zhang WG (2017) Collection, production and preservation of insect specimen. Laboratory Science, 20(1), 37-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [董会, 杨广玲, 孔令广, 张卫光 (2017) 昆虫标本的采集、制作与保存. 实验室科学, 20(1), 37-39.] | |
| [7] | Fang XS, Li YJ, Huang J (2011) Discussion on the characteristics of cultural resources in Hong Kong's country parks and its protection and utilization. South Architecture, (3), 27-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [方小山, 黎英健, 黄杰 (2011) 浅议香港郊野公园人文资源的特色与保护利用. 南方建筑, (3), 27-32.] | |
| [8] |
Gaston KJ (2000) Global patterns in biodiversity. Nature, 405, 220-227.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Green J, Bohannan BJM (2006) Spatial scaling of microbial biodiversity. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 21, 501- 507.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Guo YY (2003) The current research state and progress of insect biodiversity. Sci-Tech Information Development & Economy, 13(12), 131-132. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭玉永 (2003) 昆虫生物多样性的研究现状与进展. 科技情报开发与经济, 13(12), 131-132.] | |
| [11] | He Z, Yang DD, Tong XW, Wang BL, Gu ZR (2007) Species diversity of insects in Badagongshan National Nature Reserve of Hunan Province. Journal of Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 27(2), 61-65, 82. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [何振, 杨道德, 童新旺, 王帮利, 谷志容 (2007) 湖南八大公山自然保护区昆虫物种的多样性. 中南林业科技大学学报, 27(2), 61-65, 82.] | |
| [12] |
Hill CJ, Cermak M (1997) A new design and some preliminary results for a flight intercept trap to sample forest canopy arthropods. Australian Journal of Entomology, 36, 51-55.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Huang RX (2005) The Fauna of the Desert Insects of Xinjiang and Its Formation and Evolution. Xinjiang Science and Technology Press, Urumqi. (in Chinese) |
| [黄人鑫 (2005) 新疆荒漠昆虫区系及其形成与演变. 新疆科学技术出版社, 乌鲁木齐.] | |
| [14] |
Jaccard P (1912) The distribution of the flora in the alpine zone. The New Phytologist, 11, 37-50.
DOI URL |
| [15] | Kong FZ, Yu RC, Xu ZJ, Zhou MJ (2012) Application of excel in calculation of biodiversity indices. Marine Sciences, 36(4), 57-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孔凡洲, 于仁成, 徐子钧, 周名江 (2012) 应用Excel软件计算生物多样性指数. 海洋科学, 36(4), 57-62.] | |
| [16] |
Lamarre GPA, Molto Q, Fine PVA, Baraloto C (2012) A comparison of two common flight interception traps to survey tropical arthropods. ZooKeys, 216, 43-55.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Li HX, Sui JZ, Zhou SX, Zhou Q, Sun HG (1987) Key to Insects. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李鸿兴, 隋敬之, 周士秀, 周勤, 孙洪国 (1987) 昆虫分类检索. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [18] | Li Q (2011) Species accumulation curves and its application. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 48, 1882-1888. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李巧 (2011) 物种累积曲线及其应用. 应用昆虫学报, 48, 1882-1888.] | |
| [19] | Li Q, Gao TP, Zhou XY, Chen YL, Guo WJ (2008) Initial studies of the insect community of Leucaena leucocephala plantation in Yuanmou Arid-hot Valley, Yunnan. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 28, 109-112. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李巧, 高泰平, 周兴银, 陈彦林, 郭文俊 (2008) 云南元谋干热河谷新银合欢林昆虫群落初探. 中南林业科技大学学报, 28, 109-112.] | |
| [20] | Ma KP, Liu YM (1994) Measurement of biotic community diversity. I. α diversity (Part 2). Chinese Biodiversity, 2, 231-239. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平, 刘玉明 (1994) 生物群落多样性的测度方法. I.α多样性的测度方法(下). 生物多样性, 2, 231-239.] | |
| [21] | Martin JEH (1978) The Insects and Arachnids of Canada, Part 1: Collecting, Preparing and Preserving Insects, Mites, and Spiders. Canada Department of Agriculture, Canada. |
| [22] | Masner L, Goulet H (1981) A new model of flight interception trap for some hymenopterous insects. Entomological News, 92(5), 199-202. |
| [23] |
Moreno CE, Halffter G (2001) On the measure of sampling effort used in species accumulation curves. Journal of Applied Ecology, 38, 487-490.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Mühlenberg M (1989) Freilandöekologie. Quelle & Meyer Verlag, Heidelberg. |
| [25] | Nie RE, Yang MX, Xue HJ, Yang YR, Tong YJ, Qiu TF, Bai M, Yang XK (2017) The application and effectiveness of a flight interception trap for insect collecting. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 54, 530-535. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [聂瑞娥, 杨美霞, 薛怀君, 杨御儒, 佟一杰, 邱腾飞, 白明, 杨星科 (2017) 飞行阻隔器在昆虫采集中的应用探究. 应用昆虫学报, 54, 530-535.] | |
| [26] | Qi DM (2012) Diversity of Coleoptera in the south of Mt. Gongga, Jiulong County. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 33(1), 37-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [亓东明 (2012) 贡嘎山南麓鞘翅目昆虫多样性研究初探: 以九龙县为例. 野生动物, 33(1), 37-41.] | |
| [27] | Ren GD, Yu YZ (1999) The Darkling Beetles from Deserts and Semideserts of China (Coleoptera:Tenebrionidae). Hebei University Press, Baoding. (in Chinese) |
| [任国栋, 于有志 (1999) 中国荒漠半荒漠的拟步甲科昆虫. 河北大学出版社, 保定.] | |
| [28] |
Samways MJ (1993) Insects in biodiversity conservation: Some perspectives and directives. Biodiversity and Conservation, 2, 258-282.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Seibold S, Bässler C, Brandl R, Büche B, Szallies A, Thorn S, Ulyshen MD, Müller J (2016) Microclimate and habitat heterogeneity as the major drivers of beetle diversity in dead wood. Journal of Applied Ecology, 53, 934-943.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Shang SQ, Wu XB, Wang ZL, Peng HN, Zhou HL, Zhang HY, Bai YL (2020) Butterfly community structure and species- abundance distribution in different habitats in the Xinglong Mountains National Nature Reserve. Biodiversity Science, 28, 983-992. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [尚素琴, 吴兴波, 王召龙, 彭鹤年, 周惠丽, 张红勇, 白映禄 (2020) 兴隆山国家级自然保护区不同生境的蝴蝶群落结构与种-多度分布. 生物多样性, 28, 983-992.] | |
| [31] | Shao TY, Wang KQ, Liu XL, Liu SZ, Zhu CD (2015) Current research state and progress of utilizing suction trap for insect biodiversity. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, (12), 170-173. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [邵天玉, 王克勤, 刘兴龙, 刘思竹, 朱朝东 (2015) 利用吸虫塔研究昆虫生物多样性的现状与展望. 黑龙江农业科学, (12), 170-173.] | |
| [32] |
Ugland KI, Gray JS, Ellingsen KE (2003) The species- accumulation curve and estimation of species richness. Journal of Animal Ecology, 72, 888-897.
DOI URL |
| [33] | van Achterberg K (2009) Can Townes type Malaise traps be improved? Some recent developments. Entomologische Berichten, 69(4), 129-135. |
| [34] |
Wang Y, Gao GC, Fu BQ, Wu Z (2009) Composition and spatial distribution pattern of ground-dwelling beetle communities in Yeyahu Wetland, Beijing. Biodiversity Science, 17, 30-42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[王玉, 高光彩, 付必谦, 吴专 (2009) 北京野鸭湖湿地地表甲虫群落组成与空间分布格局. 生物多样性, 17, 30-42.]
DOI |
|
| [35] | Wang ZX, Wang F, Wu SY, Wu H, Zhang LP, Miao W (2021) Community structure and diversity of arthropod in shelterbelt of Laogang Comprehensive Utilization Base of Solid Waste. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry Science and Technology, 41(1), 82-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王章训, 王凤, 吴时英, 吴华, 张丽萍, 缪玮 (2021) 利用马氏网评估老港固废物综合利用基地防护林节肢动物群落结构及多样性. 浙江林业科技, 41(1), 82-87.] | |
| [36] | Yang B, Wang HF, Hao JX (2011) Study on the diversity of moths under laminate in larch plantation. Jilin Agriculture, (9), 85-87. (in Chinese) |
| [杨斌, 王海峰, 郝建秀 (2011) 长白落叶松人工林灯下蛾类昆虫多样性研究. 吉林农业, (9), 85-87.] | |
| [37] | Yang JK (1958) Collection of Insects. Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers, Shanghai. (in Chinese) |
| [杨集昆 (1958) 昆虫的采集. 上海科学技术出版社, 上海.] | |
| [38] | Yang ZW, Ding SX, Zhang AJ, Hua BZ (2009) A new method of insect acquisition: Flight interception trap. Shaanxi Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 55(4), 84-85. (in Chinese) |
| [杨宗武, 丁升选, 张爱娟, 花保祯 (2009) 昆虫采集新方法: 飞行拦截网. 陕西农业科学, 55(4), 84-85.] | |
| [39] | Zha YP, Luo QG, Wang GX, Wu SB, Huang DQ, Deng CS, Wei Q (2006) Community diversity of butterfly in Houhe National Nature Reserve. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 17, 265-268. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [查玉平, 骆启桂, 王国秀, 吴少斌, 黄大钱, 邓长盛, 隗权 (2006) 后河国家级自然保护区蝴蝶群落多样性研究. 应用生态学报, 17, 265-268.] | |
| [40] | Zhang BL, Zhang Y, Liao J, Ades GWJ, Liu SJ, Lu WH (2004) Diversity comparisons of beetles (Insecta: Coleoptera) between impact flight trap and ultraviolet light trap in the secondary forest at Kadoorie Farm, Hong Kong. Biodiversity Science, 12, 301-311. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[张兵兰, 张茵, 廖婕, Ades GWJ, 刘绍基, 卢文华 (2004) 香港嘉道理农场次生林区碰撞诱捕网和黑光灯捕虫器采集所得鞘翅目甲虫多样性比较. 生物多样性, 12, 301-311.]
DOI |
|
| [41] |
Zhang S, Lin F, Yuan ZQ, Kuang X, Jia SH, Wang YY, Suo YY, Fang S, Wang XG, Ye J, Hao ZQ (2015) Herb layer species abundance distribution patterns in different seasons in an old-growth temperate forest in Changbai Mountain, China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 641-648. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张姗, 蔺菲, 原作强, 匡旭, 贾仕宏, 王芸芸, 索炎炎, 房帅, 王绪高, 叶吉, 郝占庆 (2015) 长白山阔叶红松林草本层物种多度分布格局及其季节动态. 生物多样性, 23, 641-648.]
DOI |
|
| [42] | Zhang SY, Guo XG, Gong ZD, Zhang LY, Wu D, Wang ZK (2008) Investigation on community ecology and species- abundance distribution of fleas on small mammals in 21 counties of Yunnan, China. Chinese Journal of Zoonoses, 24, 518-521. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张胜勇, 郭宪国, 龚正达, 张丽云, 吴滇, 王政昆 (2008) 云南省21县市小兽体表蚤类群落生态及种多度分布. 中国人兽共患病学报, 24, 518-521.] | |
| [43] | Zhang Y, Ren GD, Gao ZH (2014) The analyses of the species diversity and fauna distribution of Coleoptera in Beijing- Tianjin-Hebei of China. Journal of Environmental Entomology, 36, 157-165. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张越, 任国栋, 郜振华 (2014) 京津冀地区甲虫物种多样性与区系分布. 环境昆虫学报, 36, 157-165.] | |
| [44] | Zhang Z (2016) A preliminary study on effective collection of plant pest and disease specimens. China Agricultural Information, (24), 81-82. (in Chinese) |
| [张珍 (2016) 有效收集作物病虫害标本初探. 中国农业信息, (24), 81-82.] | |
| [45] | Zheng LY, Gui H (1999) Insect Classification. Nanjing Normal University Press, Nanjing. (in Chinese) |
| [郑乐怡, 归鸿 (1999) 昆虫分类. 南京师范大学出版社, 南京.] | |
| [46] | Zhou HZ, Yu XD, Luo TH, He JJ, Zhou HS, Ye CJ (2000) Insect abundance and environmental effects in Shennongjia Natural Reserve, Hubei Province. Chinese Biodiversity, 8, 262-270. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周红章, 于晓东, 罗天宏, 何君舰, 周海生, 叶婵娟 (2000) 湖北神农架自然保护区昆虫的数量变化与环境关系的初步研究. 生物多样性, 8, 262-270.] | |
| [47] | Zhou HZ, Yu XD, Luo TH, Li XY, Wang FY, Li DE, Zhou YLZ, Zhao CY (2014) Collecting methods and sampling techniques of ground dwelling and predating Carabids and Staphylinids beetles. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 51, 1367-1375. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周红章, 于晓东, 罗天宏, 李晓燕, 王凤艳, 李德娥, 周毓灵子, 赵彩云 (2014) 土壤步甲和隐翅虫的采集与田间调查取样技术. 应用昆虫学报, 51, 1367-1375.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [3] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [4] | 周昊, 王茗毅, 张楚格, 肖治术, 欧阳芳. 昆虫旅馆在独栖蜂多样性保护中的现状与挑战[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24472-. |
| [5] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [6] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [7] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [8] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [9] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [10] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [11] | 徐欢, 辛凤飞, 施宏亮, 袁琳, 薄顺奇, 赵欣怡, 邓帅涛, 潘婷婷, 余婧, 孙赛赛, 薛程. 生态修复技术集成应用对长江口北支生境与鸟类多样性提升效果评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24478-. |
| [12] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [13] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [14] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [15] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()