



生物多样性 ›› 2013, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (5): 582-589. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.08077 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2013.08077
所属专题: 昆虫多样性与生态功能
收稿日期:2013-04-01
接受日期:2013-06-14
出版日期:2013-09-20
发布日期:2013-10-08
通讯作者:
谭敦炎
基金资助:Received:2013-04-01
Accepted:2013-06-14
Online:2013-09-20
Published:2013-10-08
Contact:
Tan Dunyan
摘要:
地下芽地下结实是指由植株地下芽分化形成的具长管状花被的花伸出地表开放、而子房在地下发育成果实的一种特殊结实现象。白番红花(Crocus alatavicus)是生长于天山西部亚高山带、具地下芽地下结实特性的多年生早春短命植物。本文采用野外观测和控制实验方法, 对该物种地下子房和幼果的发育特点与种子扩散特性及其适应意义进行了研究。结果表明: 白番红花从开花到地下果实露出地表的发育时间约需35 d, 地下果实在花梗的伸长生长作用下露出地面开裂并扩散种子, 且种子具有油质体等典型蚁传植物种子的特征。蚁类是白番红花种子的主要传播者。在搬运种子的Formica pressilabris、栗色林蚁和黑褐蚁中, F. pressilabris出现的频率最高, 但栗色林蚁搬运的速度最快、距离最远。3种蚂蚁搬运白番红花种子的平均距离为62.4±1.7 cm。Formica pressilabris将白番红花种子搬运至蚁穴中后取食油质体, 且有超过50%的种子被储藏在蚁穴中。啮齿类和鸟类不传播白番红花种子, 但水媒和风媒对种子的短距离散布具有一定作用。这些结果说明: 白番红花的地下结实及蚁传特性不仅可保护发育中的子房及果实躲避地表草食动物的取食, 避免自然火灾对地上果实的伤害, 以及延长果实和种子的发育时间以保障其安全成熟, 还可避免真菌和其他病原体的侵扰、减少同胞之间以及母株与子代间的竞争, 使种子在适宜环境中萌发并建立新的种群。
付子燕, 谭敦炎 (2013) 地下结实植物白番红花地下果实的生产与种子扩散特性. 生物多样性, 21, 582-589. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.08077.
Ziyan Fu,Dunyan Tan (2013) Characteristics of the production of underground fruits and seed dispersal of Crocus alatavicus, a geophytic-geocarpic species. Biodiversity Science, 21, 582-589. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.08077.
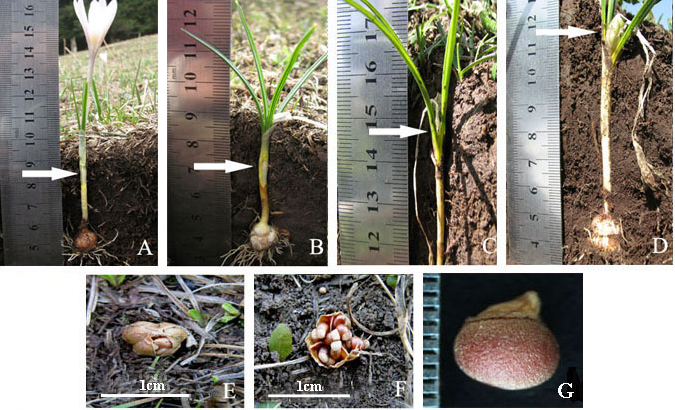

图1 新疆赛里木湖畔森林草原上白番红花开花植株不同发育时期地下子房/果实的位置以及成熟果实与种子的形态。(A)盛花期; (B)花萎蔫期; (C)花凋落期; (D)果实出土期; (E) 露出地表的果实; (F)开裂的果实; (G)成熟种子。箭头指向子房/果实的位置。
Fig. 1 Position of the underground ovary/fruit of flowering plants of Crocus alatavicus at different developmental stages in the forest steppe of the vicinity of Sailimu Lake, Xinjiang, and the morphology of the mature fruit and seed. (A) Full-blooming stage; (B) Wilting stage; (C) Withering stage; (D) Fruit beginning to protrude above the soil level; (E) Fruit above soil surface; (F) Dehisced fruit; (G) Mature seed. The arrow points to the position of ovary/fruit.

图2 新疆赛里木湖畔森林草原上3种蚂蚁对白番红花种子的搬运。(A) Formica pressilabris; (B)黑褐蚁; (C)栗色林蚁。
Fig. 2 Removal of Crocus alatavicus seeds by three ant species in the forest steppe of the vicinity of Sailimu Lake, Xinjiang. (A) Formica pressilabris; (B) F. gagates; (C) F. fusca.
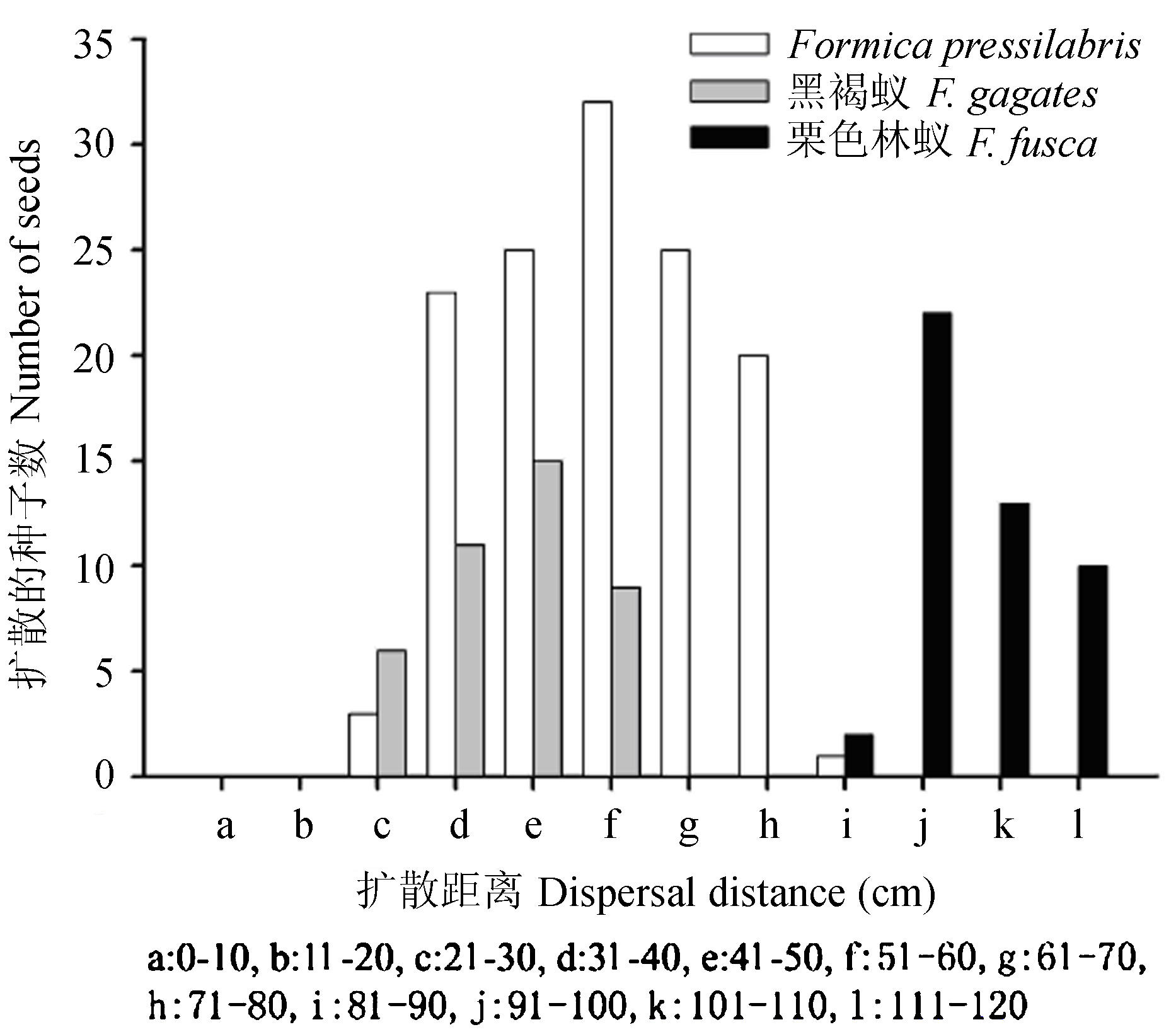
图3 新疆赛里木湖畔森林草原上白番红花种子被3种蚂蚁搬运的距离
Fig. 3 Removal distance of Crocus alatavicus seeds by three ant species in the forest steppe of the vicinity of Sailimu Lake, Xinjiang
| 1 | Barker NP (2005) A review and survey of basicarpy, geocarpy, and amphicarpy in the African and Madagascan flora.Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden, 92, 445-462. |
| 2 | Burtt BL (1970) The evolution and taxonomic significance of a subterranean ovary in certain monocotyledons. Israel Journal of Botany, 19, 77-90. |
| 3 | Cellot B, Mouillot F, Henry CP (1998) Flood drift and propagule bank of aquatic macrophytes in a riverine wetland.Journal of Vegetation Science, 9, 631-640. |
| 4 | Chen F (陈帆), Chen J (陈进), Liu ZQ (刘志秋), Zhang L (张玲), Liu Y (刘勇), Bai ZL (白智林) (2004) The role of ants in seed dispersal of Globba lancangensis and the spatial distribution of its seedlings.Acta Phytoecologica Sinica(植物生态学报), 28, 210-217. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 5 | Cheplick GP (1994) Life history evolution in amphicarpic plants.Plant Species Biology, 9, 119-131. |
| 6 | Culver DC, Beattie AJ (1978) Myrmecochory in Viola: dynamics of seed-ant interactions in some west Virginia species.The Journal of Ecology, 66, 53-72. |
| 7 | Culver DC, Beattie AJ (1983) Effects of ant mounds on soil chemistry and vegetation patterns in a Colorado montane meadow.Ecology, 64, 485-492. |
| 8 | Dafni A, Werker E (1982) Pollination ecology of Sternbergia clusiana (Ker-Gawler) Spreng. (Amaryllidaceae). New Phytologist, 91, 571-577. |
| 9 | Ferguson ME, Jarvis A, Stalker HT, Williams DE, Guarino L, Valls JFM, Pittman RN, Simpson CE, Bramel PJ (2005) Biogeography of wild Arachis (Leguminosae): distribution and environmental characterisation.Biodiversity and Conservation, 14, 1777-1798. |
| 10 | Gómez C, Espadaler X (1998) Myrmecochorous dispersal distances: a world survey.Journal of Biogeography, 25, 573-580. |
| 11 | Gopinathan MC, Babu CR (1987) Breeding systems and pollination in Vigna minima (Leguminosae, Papilionoideae).Plant Systematics and Evolution, 156, 117-126. |
| 12 | Harper JL (1977) Population Biology of Plants. Academic Press, New York. |
| 13 | Hollmann J, Myburgh S, van Wyk B (1995) Aardvark and cucumber—A remarkable relationship.Veld & Flora, 95, 108-109. |
| 14 | Hughes L, Westoby M (1992a) Fate of seeds adapted for dispersal by ants in Australian sclerophyll vegetation.Ecology, 73, 1285-1299. |
| 15 | Hughes L, Westoby M (1992b) Effect of diaspore characteristics on removal of seeds adapted for dispersal by ants.Ecology, 73, 1300-1312. |
| 16 | Kaul V, Koul AK, Sharma MC (2000) The underground flower.Current Science, 78, 39-44. |
| 17 | Keighery GJ (1982) Geocarpy in Tribulopsis R. Br. (Zygophyllaceae). Flora, 172, 329-333. |
| 18 | Kudoh H, Whigham DF (2001) A genetic analysis of hydrologically dispersed seeds of Hibiscus moscheutos (Malvaceae).American Journal of Botany, 88, 588-593. |
| 19 | Lev-Yadun S (2000) Why are underground flowering and fruiting more common in Israel than anywhere else in the world? Current Science, 79, 289. |
| 20 | Li HJ (李宏俊), Zhang ZB (张知彬), Wang YS (王玉山), Wang FS (王福生), Cao XP (曹小平) (2004) Small rodents community composition and seasonal changes of their dominant populations in Dongling Mountain.Acta Ther- iologica Sinica(兽类学报), 24, 215-221. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 21 | Li RH (李儒海), Qiang S (强胜) (2007) Progresses and prospects in research of weed seed dispersal. Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 27, 5361-5370. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 22 | Lu CH (鲁长虎), Chang JC (常家传) (1998) Effect of the fleshy-fruits eating birds on seed dispersal.Chinese Journal of Ecology(生态学杂志), 17, 61-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 23 | Ma DD (马道典), Zhang LP (张莉萍), Wang QJ (王前进), Zeng QJ (曾庆江), Jiang FQ (姜逢清), Wang YJ (王亚俊), Hu RJ (胡汝骥) (2003) Influence of the warm-wet climate on Sailimu Lake.Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology(冰川冻土), 25, 219-223. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 24 | Ma J (马杰), Li QF (李庆芬), Sun RY (孙儒泳), Liu DZ (刘定震) (2004) Influence on seed bank of Quercus liaotungensis by birds and rodents in Dongling Mountain.Chinese Journal of Ecology(生态学杂志), 23, 107-110. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 25 | Ma SB (马绍宾), Li DZ (李德铢) (2002) Dispersal and evolution in higher plants. I. Diaspores, their quantity and life span as well as dispersal mechanisms.Acta Botanica Yunnanica(云南植物研究), 24, 569-582. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 26 | Mao ZM (毛祖美), Zhang DM (张佃民) (1994) The conspectus of ephemeral flora in northern Xinjiang.Arid Zone Research(干旱区研究), 11(3), 1-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 27 | Min HY (闵海燕), Chen G (陈刚), Sun GR (孙国荣), Wang C (王聪), Liu AP (刘爱平), Du K (杜坤), Zhang B (张彪) (2008) Resource allocation and reproductive cost of plants from four types of seedlings of Commelina benghalensis.Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 28, 1802-1809. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 28 | Nathan R, Muller-Landau HC (2000) Spatial patterns of seed dispersal, their determinants and consequences for recruitment.Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 15, 278-285. |
| 29 | Passos L, Oliveira PS (2002) Ants affect the distribution and performance of seedlings of Clusia criuva, a primarily bird-dispersed rain forest tree.Journal of Ecology, 90, 517-528. |
| 30 | Pizo MA, Oliveira PS (1998) Interaction between ants and seeds of a nonmyrmecochorous neotropical tree, Cabralea canjerana (Meliaceae), in the Atlantic forest of southeast Brazil.American Journal of Botany, 85, 669-674. |
| 31 | Price MV, Jenkins SH (1986) Rodents as seed consumers and seed dispersers. In: Seed Dispersal (ed. Murray DR), pp. 191-235. Academic Press, Sydney. |
| 32 | Sernander R (1906) Entwurf einer monographie der europäischen myrmekochoren.Kungliaga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens Handlingar, 41, 1-410. |
| 33 | Talaiti (塔来提), Gong HH (龚红花), Zhou DL (周多林), Daolihong (道里洪) (2003) Experiment on the effects of duck herding in high-altitude meadows of Sailimu Lake to eliminate locusts, an insect.Xinjiang Animal Husbandry(新疆畜牧业), (3), 43-44. (in Chinese) |
| 34 | Tan DY (谭敦炎), Zhang Y (张洋), Wang AB (王爱波) (2010) A review of geocarpy and amphicarpy in angiosperms, with special reference to their ecological adaptive significance.Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology(植物生态学报), 34, 72-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 35 | Totland Ø, Matthews I (1998) Determinants on pollinator activity and flower preference to the early spring blooming Crocus vernus.Acta Oecologica, 19, 155-166. |
| 36 | Wang W (王巍), Ma KP (马克平) (2001) Predation and dispersal of Quercus liaotungensis Koidz. acorns by animals in Dongling Mountain, Northern China .I. Effect of rodents removal on loss of acorns.Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 21, 204-210. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 37 | Willmer PG, Stone GN (1997) How aggressive ant-guards assist seed-set in Acacia flowers.Nature, 388, 165-167. |
| 38 | Wu ZY, Raven PH (2000) Iridaceae. In: Flora of China (eds Wu ZY, Raven PH), pp. 297-313. Science Press, Beijing, and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, St. Louis. |
| 39 | Yao XL (姚晓琳), Piao ZJ (朴正吉), Li BH (李步杭), Zhang J (张健), Wang XG (王绪高), Ye J (叶吉), Hao ZQ (郝占庆) (2008) Pinus koraiensis seed consumption by rodents and birds.Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology(应用生态学报), 19, 1759-1763. (in Chinese) |
| 40 | Zhang S (张霜), Chen J (陈进) (2008) Secondary seed dispersal of Ficus benjamina: new evidence for ant-Nonmyrmeco chorous mutualism.Chinese Journal of Ecology(生态学杂志), 27, 1913-1919. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 41 | Zhang Y (张洋), Tan DY (谭敦炎) (2009) Breeding system and pollination biology of Crocus alatavicus (Iridaceae), a geocarpic subalpine plant of the western Tianshan Mountains.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 17, 468-475. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 42 | Zhang ZY (张智英), Li YH (李玉辉), Zhao ZM (赵志模) (2002) Mutualism between ants and myrmecochores.Zoological Research(动物学研究), 23, 437-443. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 43 | Zhou HP, Chen J, Chen F (2007) Ant-mediated seed dispersal contributes to the local spatial pattern and genetic structure of Globba lancangensis (Zingiberaceae). Journal of Heredity, 98, 317-324. |
| [1] | 施国杉, 刘峰, 曹光宏, 陈典, 夏尚文, 邓云, 王彬, 杨效东, 林露湘. 西双版纳热带季节雨林木本植物的beta多样性: 空间、环境与林分结构的作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24285-. |
| [2] | 王明慧, 陈昭铨, 李帅锋, 黄小波, 郎学东, 胡子涵, 尚瑞广, 刘万德. 云南普洱季风常绿阔叶林不同种子扩散方式的优势种空间点格局分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23147-. |
| [3] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [4] | 曲梦君, 努尔依拉·阿巴拜克, 邹旭阁, 赵航, 朱威霖, 王健铭, 李景文. 地理距离和环境因子对阿拉善戈壁植物群落β多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22029-. |
| [5] | 米湘成, 王绪高, 沈国春, 刘徐兵, 宋晓阳, 乔秀娟, 冯刚, 杨洁, 毛子昆, 徐学红, 马克平. 中国森林生物多样性监测网络: 二十年群落构建机制探索的回顾与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22504-. |
| [6] | 张丹, 马松梅, 魏博, 王春成, 张林, 闫涵. 中国梭梭属植物历史分布格局及其驱动机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(1): 21192-. |
| [7] | 武鹏峰, 崔淑艳, Abid Ali, 郑国. 蜘蛛飞航研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(4): 517-530. |
| [8] | 杨锡福, 张洪茂, 张知彬. 植物大年结实及其与动物贮食行为之间的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(7): 821-832. |
| [9] | 姚志良,温韩东,邓云,曹敏,林露湘. 哀牢山亚热带中山湿性常绿阔叶林树种beta多样性格局形成的驱动力[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(4): 445-454. |
| [10] | 刘翔宇, 赵慈良, 许洺山, 梁启明, 朱晓彤, 李亮, 阎恩荣. 中国东部海岛维管植物的beta多样性及其驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(4): 380-387. |
| [11] | 高梅香, 林琳, 常亮, 孙新, 刘冬, 吴东辉. 土壤动物群落空间格局和构建机制研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(10): 1034-1050. |
| [12] | 郭志文, 郑景明. 用植物生活史性状预测种子扩散方式[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(9): 966-971. |
| [13] | 蒙洋, 邱月, 张亮, 王翠玲, 臧振华, 张学耀, 申国珍, 闫彩凤, 陈全胜. 地理距离、海拔和气候差异对独龙江流域维管植物群落物种空间相异性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(12): 1313-1320. |
| [14] | 赵鸣飞, 王国义, 邢开雄, 王宇航, 薛峰, 康慕谊, 罗开. 秦岭西部森林群落相似性递减格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(1): 3-10. |
| [15] | 李新辉, 刘延虹, 刘晔, 许玥, 杨阳, 沈泽昊. 地理距离及环境差异对云南元江干热河谷植物群落beta多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(4): 399-406. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()
