



生物多样性 ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (12): 1313-1320. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017076 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2017076
蒙洋1,2, 邱月1,2, 张亮1,3, 王翠玲1,2, 臧振华1,4, 张学耀1,2, 申国珍1, 闫彩凤1, 陈全胜1,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2017-11-23
接受日期:2017-11-26
出版日期:2017-12-20
发布日期:2017-12-10
通讯作者:
陈全胜
基金资助:
Yang Meng1,2, Yue Qiu1,2, Liang Zhang1,3, Cuiling Wang1,2, Zhenhua Zang1,4, Xueyao Zhang1,2, Guozhen Shen1, Caifeng Yan1, Quansheng Chen1,3,*( )
)
Received:2017-11-23
Accepted:2017-11-26
Online:2017-12-20
Published:2017-12-10
Contact:
Chen Quansheng
摘要:
物种相异性(species dissimilarity)主要反映了群落物种组成的时空变化, 其与随机和确定性因素之间的关系能揭示群落构建及生物多样性形成和维持的机理。本文以独龙江流域植物群落为研究对象, 以群落间Jaccard物种相异性指数为指标, 分析它同地理距离、气候和海拔差异之间的关系及各类因子影响的权重。结果表明, 群落间Jaccard物种相异性指数变化范围为0.42-1, 且随自然对数转换的地理距离、海拔和气候差异(多年日平均温度, 年平均降水量)的增大而呈显著的线性增加趋势; 地理距离、气候差异和海拔差异可以解释独龙江流域群落物种相异性指数将近30%的变异。地理距离单独解释度为18.80%, 气候差异和海拔差异分别可以解释3.47%和0.10%。研究结果表明, 独龙江流域群落物种在空间上的更替是环境限制和扩散限制综合作用的结果。群落间物种相异性较大, 且影响物种更替的因素中地理距离占有较大的权重, 说明在对该地区进行生物多样性保护时, 在综合考虑环境因素影响的基础上, 还应充分考虑地形的阻隔作用和繁殖体扩散能力的大小。
蒙洋, 邱月, 张亮, 王翠玲, 臧振华, 张学耀, 申国珍, 闫彩凤, 陈全胜 (2017) 地理距离、海拔和气候差异对独龙江流域维管植物群落物种空间相异性的影响. 生物多样性, 25, 1313-1320. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017076.
Yang Meng, Yue Qiu, Liang Zhang, Cuiling Wang, Zhenhua Zang, Xueyao Zhang, Guozhen Shen, Caifeng Yan, Quansheng Chen (2017) Effects of geographical distance and differences in climate and altitude on species dissimilarity of vascular plant communities in the Dulongjiang River Watershed Area. Biodiversity Science, 25, 1313-1320. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017076.
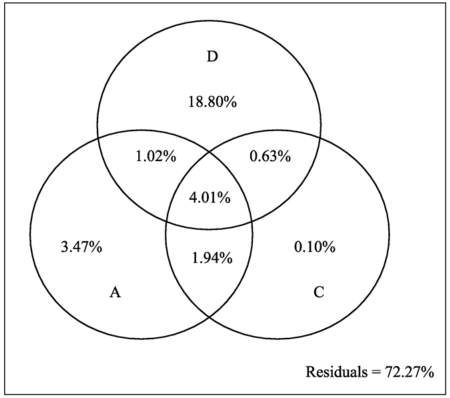
图4 群落之间地理距离(D)、海拔差异(A)以及气候差异(C)对物种更替的解释。
Fig. 4 Partitional effects of Ln-transformed geographic distance (D), altitude difference (A) and climatic difference (C) on species turnover of plants.
| [1] | Aiello-Lammens ME, Slingsby JA, Merow C, Mollmann HK, Euston-Brown D, Jones CS, Silander JA (2016) Processes of community assembly in an environmentally heterogeneous, high biodiversity region. Ecography, 39, 1-16. |
| [2] | Blundo C, Gonzalez-Espinosa M, Malizia LR (2016) Relative contribution of niche and neutral processes on tree species turnover across scales in seasonal forests of NW Argentina. Plant Ecology, 217, 359-368. |
| [3] | Chave J, Muller-Landau HC, Levin SA (2002) Comparing classical community models: theoretical consequences for patterns of diversity. The American Naturalist, 159, 1-23. |
| [4] | Chen SB, Ouyang ZY, Xu WH, Xiao Y (2010) A review of beta diversity studies. Biodiversity Science, 18, 323-335. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈圣宾, 欧阳志云, 徐卫华, 肖燚 (2010) Beta多样性研究进展. 生物多样性, 18, 323-335.] | |
| [5] | Chen Y, Yuan ZL, Li PK, Cao RF, Jia HR, Ye YZ (2016) Effects of environment and space on species turnover of woody plants across multiple forest dynamic plots in East Asia. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7, 1-11. |
| [6] | Cheng JJ, Mi XC, Ma KP, Zhang JT (2011) Responses of species-abundance distribution to varying sampling scales in a subtropical broad-leaved forest. Biodiversity Science, 19, 168-177. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [程佳佳, 米湘成, 马克平, 张金屯 (2011) 亚热带常绿阔叶林群落物种多度分布格局对取样尺度的响应. 生物多样性, 19, 168-177.] | |
| [7] | Dodson R, Marks D (1997) Daily air temperature interpolated at high spatial resolution over a large mountainous region. Climate Research, 8, 1-20. |
| [8] | Fahrig L, Baudry J, Brotons L, Burel FG, Crist TO, Fuller RJ, Sirami C, Siriwardena GM, Martin JL (2011) Functional landscape heterogeneity and animal biodiversity in agricultural landscapes. Ecology Letters, 14, 101-112. |
| [9] | Feng JM, Wang XP, Fang JY (2006) Altitudinal pattern of species richness and test of the Rapoport’s rules in the Drung River Area, Southwest China. Acta Scientiarum Na¬tu¬ralium Universitatis Pekinensis, 42, 515-520. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [冯建孟, 王襄平, 方精云 (2006) 云南独龙江地区种子植物物种多样性垂直分布格局和 Rapoport法则的验证. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 42, 515-520.] | |
| [10] | Freestone AL, Inouye BD (2006) Dispersal limitation and environmental heterogeneity shape scale-dependent diversity patterns in plant communities. Ecology, 87, 2425-2432. |
| [11] | Gueze M, Paneque-Galvez J, Luz AC, Pino J, Orta-Martinez M, Reyes-Garcia V, Macia MJ (2013) Determinants of tree species turnover in a southern Amazonian rain forest. Journal of Vegetation Science, 24, 284-295. |
| [12] | Hager A (2010) The effect of climate and soil conditions on tree species turnover in a tropical montane cloud forest in Costa Rica. Revista De Biologia Tropical, 58, 1489-1506. |
| [13] | Hardy OJ, Couteron P, Munoz F, Ramesh BR, Pelissier R (2012) Phylogenetic turnover in tropical tree communities: impact of environmental filtering, biogeography and mesoclimatic niche conservatism. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 1007-1016. |
| [14] | Hubbell SP (2001) The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography. Princeton University Press, New Jersey. |
| [15] | Jones MM, Gibson N, Yates C, Ferrier S, Mokany K, Williams KJ, Manion G, Svenning JC (2016) Underestimated effects of climate on plant species turnover in the Southwest Australian Floristic Region. Journal of Biogeography, 43, 289-300. |
| [16] | Jones MM, Tuomisto H, Clark DB, Olivas P (2006) Effects of mesoscale environmental heterogeneity and dispersal limitation on floristic variation in rain forest ferns. Journal of Ecology, 94, 181-195. |
| [17] | Leps J, de Bello F, Smilauer P, Dolezal J (2011) Community trait response to environment: disentangling species turnover vs. intraspecific trait variability effects. Ecography, 34, 856-863. |
| [18] | Li H (1996) Investigation on the overwintering of Dulongjiang Plant. Yunnan Geographic Environment Research, 8, 93-96. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李恒 (1996) 独龙江植物越冬考察记实. 云南地理环境研究, 8, 93-96.] | |
| [19] | Li XH, Liu YH, Liu Y, Xu Y, Yang Y, Shen ZH (2016) Impacts of geographical distances and environmental differences on the beta diversity of plant communities in the dry-hot valley of the Yuanjiang River. Biodiversity Science, 24, 399-406. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李新辉, 刘延虹, 刘晔, 许玥, 杨阳, 沈泽昊 (2016) 地理距离及环境差异对云南元江干热河谷植物群落beta多样性的影响. 生物多样性, 24, 399-406.] | |
| [20] | Li XZ (1996) Landforms in Drang River Basin. Yunnan Geographic Environment Research, 8, 59-72. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李先之 (1996) 独龙江流域地貌. 云南地理环境研究, 8, 59-72.] | |
| [21] | Liu WL, Yang J, Sun J, Li XZ (2016) Species turnover of wetland vegetation in northeastern China: disentangling the relative effects of geographic distance, climate, and hydro-geomorphology. Flora, 220, 1-7. |
| [22] | Loke LH, Bouma TJ, Todd PA (2017) The effects of manipulating microhabitat size and variability on tropical seawall biodiversity: field and flume experiments. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 492, 113-120. |
| [23] | Ma KP (2016) Conservation biology, conservation ecology and biodiversity science. Biodiversity Science, 24, 125-126. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平 (2016) 保护生物学, 保护生态学与生物多样性科学. 生物多样性, 24, 125-126.] | |
| [24] | Ma KP, Qian YQ, Wang C (1995) Present state and future of biodiversity studies. Science and Technology Review, 13, 27-30. (in Chinese) |
| [马克平, 钱迎倩, 王晨 (1995) 生物多样性研究的现状与发展趋势. 科技导报, 13, 27-30.] | |
| [25] | Ma KP, Ye WH, Yu SL, Ma KM, Wang W, Guan WB (1997) Studies on plant community diversity in Dongling Mountain, Beijing, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 17, 593-600. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马克平, 叶万辉, 于顺利, 马克明, 王巍, 关文彬 (1997) 北京东灵山地区植物群落多样性研究. 生态学报, 17, 593-600.] | |
| [26] | Marion ZH, Fordyce JA, Fitzpatrick BM (2017) Pairwise beta diversity resolves an underappreciated source of confusion in calculating species turnover. Ecology, 98, 933-939. |
| [27] | McCain CM, Beck J (2016) Species turnover in vertebrate communities along elevational gradients is idiosyncratic and unrelated to species richness. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 25, 299-310. |
| [28] | McGlinn DJ, Palmer MW (2011) Quantifying the influence of environmental texture on the rate of species turnover: evidence from two habitats. Plant Ecology, 212, 495-506. |
| [29] | Mena JL, Vazquez-Dominguez E (2005) Species turnover on elevational gradients in small rodents. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 14, 539-547. |
| [30] | Michel AK, Winter S (2009) Tree microhabitat structures as indicators of biodiversity in Douglas-fir forests of different stand ages and management histories in the Pacific Northwest, USA. Forest Ecology and Management, 257, 1453-1464. |
| [31] | Murphy SJ, Salpeter K, Comita LS (2016) Higher beta-di¬versity observed for herbs over woody plants is driven by stronger habitat filtering in a tropical understory. Ecology, 97, 2074-2084. |
| [32] | Niu KC, Liu YN, Shen ZH, He FL, Fang JY (2009) Community assembly: the relative importance of neutral theory and niche theory. Biodiversity Science, 17, 579-593. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [牛克昌, 刘怿宁, 沈泽昊, 何芳良, 方精云 (2009) 群落构建的中性理论和生态位理论. 生物多样性, 17, 579-593.] | |
| [33] | Oksanen J, Kindt R, Legendre P, O’Hara B, Stevens MHH, Oksanen MJ, Suggests M (2007) The vegan package. Community Ecology Package. R Package version 2.0-4.0.2007) The vegan package. Community Ecology Package. R Package version 2.0-4.0. |
| [34] | Pandit SN, Kolasa J (2012) Opposite effects of environmental variability and species richness on temporal turnover of species in a complex habitat mosaic. Hydrobiologia, 685, 145-154. |
| [35] | Qian H, Badgley C, Fox DL (2009) The latitudinal gradient of beta diversity in relation to climate and topography for mammals in North America. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 18, 111-122. |
| [36] | Qian H, Ricklefs RE (2012) Disentangling the effects of geographic distance and environmental dissimilarity on global patterns of species turnover. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 341-351. |
| [37] | Qian H, Shimono A (2012) Effects of geographic distance and climatic dissimilarity on species turnover in alpine meadow communities across a broad spatial extent on the Tibetan Plateau. Plant Ecology, 213, 1357-1364. |
| [38] | Ruokolainen K, Tuomisto H (2002) Beta-diversity in tropical forests. Science, 297, 1439. |
| [39] | Tian H (1994) The soil type and distribution regular of Dulongjiang River basin. Yunnan Geographic Environment Research, 2, 17-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [田宏 (1994) 独龙江流域土壤类型及分布规律. 云南地理环境研究, 2, 17-26.] | |
| [40] | Tuomisto H, Ruokolainen K, Yli-Halla M (2003) Dispersal, environment, and floristic variation of western Amazonian forests. Science, 299, 241-244. |
| [41] | Ulrich W, Jabot F, Gotelli NJ (2017) Competitive interactions change the pattern of species co-occurrences under neutral dispersal. Oikos, 126, 91-100. |
| [42] | Wang CY, He ZR, Peng MC (2013) Studies on Vegetation and Plants in Dulongjiang (Upper Irrawaddy River) Watershed and Adjacent Area. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [王崇云, 和兆荣, 彭明春 (2013) 独龙江流域及邻近区域植被与植物研究. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [43] | Wang S, Wang X, Guo H, Fan W, Lü H, Duan R (2013) Distinguishing the importance between habitat specialization and dispersal limitation on species turnover. Ecology and Evolution, 3, 3545-3553. |
| [44] | Whittaker RH (1960) Vegetation of the Siskiyou Mountains, Oregon and California. Ecological Monographs, 30, 280-338. |
| [45] | Zemunik G, Turner BL, Lambers H, Laliberte E (2016) Increasing plant species diversity and extreme species turnover accompany declining soil fertility along a long-term chronosequence in a biodiversity hotspot. Journal of Ecology, 104, 792-805. |
| [46] | Zhao MF, Wang GY, Xing KX, Wang GY, Wang YH, Xue F, Kang MY, Luo K (2017) Patterns and determinants of species similarity decay of forest communities in the western Qinling Mountains. Biodiversity Science, 25, 3-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵鸣飞, 王国义, 邢开雄, 王宇航, 薛峰, 康慕谊, 罗开 (2017) 秦岭西部森林群落相似性递减格局及其影响因素. 生物多样性, 25, 3-10.] |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn