



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (1): 21192. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021192 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021192
张丹1, 马松梅2,*( ), 魏博1, 王春成1, 张林2, 闫涵2
), 魏博1, 王春成1, 张林2, 闫涵2
收稿日期:2021-05-13
接受日期:2021-09-14
出版日期:2022-01-20
发布日期:2022-01-29
通讯作者:
马松梅
作者简介:* E-mail: shzmsm@126.com基金资助:
Dan Zhang1, Songmei Ma2,*( ), Bo Wei1, Chuncheng Wang1, Lin Zhang2, Han Yan2
), Bo Wei1, Chuncheng Wang1, Lin Zhang2, Han Yan2
Received:2021-05-13
Accepted:2021-09-14
Online:2022-01-20
Published:2022-01-29
Contact:
Songmei Ma
摘要:
梭梭属(Haloxylon)植物是藜科的古老孑遗物种, 探究末次间冰期(last interglacial period, LIG)和末次盛冰期(last glacial maximum period, LGM)以来中国梭梭属植物的历史地理分布格局及其驱动机制, 对了解气候变化背景下旱生植物区系的发展与演化具有重要意义。本研究利用梭梭属85个自然分布点数据(60条梭梭(Haloxylon ammodendron)分布记录、25条白梭梭(H. persicum)分布记录)和2套环境因子数据, 整合GIS空间分析和9种物种分布模型, 分析了梭梭属末次间冰期以来的地理分布格局变化及其驱动机制。基于62个梭梭属种群的叶绿体基因测序数据, 利用最小成本路径方法, 模拟了末次间冰期以来梭梭属可能的扩散路径。利用R软件prcomp函数对影响梭梭属分布的环境变量进行主成分分析(principal component analysis, PCA), 评价了环境变量对梭梭属适宜分布的贡献, 并分析了关键变量与分布适宜性的相关性。结果表明: (1)集成模型的模拟精度较单一模型显著提升, 且对白梭梭的模拟精度高于梭梭; (2)末次间冰期以来, 梭梭属植物的分布均经历了显著收缩和冰后期扩张, 末次间冰期至末次盛冰期时期, 在准噶尔盆地、塔里木盆地西部广泛分布的梭梭大面积向西退缩至避难所(准噶尔盆地西北缘和塔里木盆地西北缘); 白梭梭从准噶尔盆地、塔里木盆地西端向南退缩至避难所(准噶尔盆地南缘); 末次盛冰期至今, 梭梭向东沿甘肃北部扩张直至内蒙古西部阿拉善荒漠, 白梭梭向东北方向小范围扩张, 占据了准噶尔盆地西部和南缘; (3)末次间冰期以来的气候波动对梭梭属植物的分布存在较大限制, 降水因子主导了梭梭属适宜分布面积的变化, 温度因子影响了梭梭属分布适宜性的高低。
张丹, 马松梅, 魏博, 王春成, 张林, 闫涵 (2022) 中国梭梭属植物历史分布格局及其驱动机制. 生物多样性, 30, 21192. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021192.
Dan Zhang, Songmei Ma, Bo Wei, Chuncheng Wang, Lin Zhang, Han Yan (2022) Historical distribution pattern and driving mechanism of Haloxylon in China. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21192. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021192.
| 气候因子 Climatic factor | 梭梭 Haloxylon ammodendron | 白梭梭 Haloxylon persicum | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 | |
| 平均气温日较差 Mean diurnal range (Bio2) | -0.4010 | -0.023 | -0.4471 | 0.3015 | 0.7218 | -0.0155 | 0.0800 | 0.0560 | 0.6657 | 0.0289 | 0.3137 | 0.5855 |
| 温度季节性 Temperature seasonality (Bio4) | 0.3534 | 0.3672 | 0.3143 | 0.3992 | 0.1067 | -0.2803 | ||||||
| 最热月最高温 Max temperature of warmest month (Bio5) | -0.4205 | -0.3078 | -0.2280 | -0.2558 | 0.3226 | 0.0864 | ||||||
| 最冷月最低温 Min temperature of coldest month (Bio6) | -0.3240 | 0.0336 | -0.5535 | 0.0760 | 0.1049 | 0.4440 | ||||||
| 气温年较差 Annual temperature range (Bio7) | -0.2233 | -0.4475 | 0.2756 | -0.4223 | 0.3220 | -0.3503 | ||||||
| 最湿季平均温 Mean temperature of wettest quarter (Bio8) | -0.0631 | 0.6370 | 0.4028 | -0.0623 | 0.3398 | 0.4079 | ||||||
| 最干季平均温 Mean temperature of driest quarter (Bio9) | -0.3546 | 0.2862 | 0.0772 | 0.6046 | 0.5461 | -0.2837 | ||||||
| 最冷季平均温 Mean temperature of coldest quarter (Bio11) | -0.3831 | 0.2188 | 0.0367 | -0.7455 | 0.0309 | -0.1367 | ||||||
| 年均降水量 Annual precipitation (Bio12) | 0.4753 | -0.1496 | -0.2554 | -0.0359 | 0.4549 | 0.3195 | ||||||
| 最湿月降水量 Precipitation of wettest month (Bio13) | 0.0528 | -0.5800 | 0.6229 | -0.1540 | 0.4640 | -0.1687 | 0.4583 | 0.2152 | -0.2196 | -0.2281 | 0.4103 | -0.2874 |
| 最干月降水量 Precipitation of driest month (Bio14) | 0.4469 | -0.0836 | -0.1889 | -0.2130 | 0.1093 | 0.3556 | ||||||
| 降水季节性变化 Precipitation seasonality (Bio15) | -0.4064 | -0.2396 | 0.2714 | 0.2735 | -0.2429 | 0.6464 | -0.0183 | 0.5997 | -0.0048 | -0.3225 | 0.0936 | -0.1350 |
| 最冷季降水量 Precipitation of coldest season (Bio19) | 0.4426 | -0.1004 | -0.2010 | -0.2152 | 0.2551 | 0.4042 | 0.3162 | -0.4364 | -0.0558 | 0.4762 | 0.0238 | -0.2155 |
表1 影响梭梭和白梭梭分布的气候变量的主成分(PC)特征值
Table 1 Principal component (PC) eigenvalues of climate variables affecting the distribution of Haloxylon ammodendron and H. persicum
| 气候因子 Climatic factor | 梭梭 Haloxylon ammodendron | 白梭梭 Haloxylon persicum | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 | |
| 平均气温日较差 Mean diurnal range (Bio2) | -0.4010 | -0.023 | -0.4471 | 0.3015 | 0.7218 | -0.0155 | 0.0800 | 0.0560 | 0.6657 | 0.0289 | 0.3137 | 0.5855 |
| 温度季节性 Temperature seasonality (Bio4) | 0.3534 | 0.3672 | 0.3143 | 0.3992 | 0.1067 | -0.2803 | ||||||
| 最热月最高温 Max temperature of warmest month (Bio5) | -0.4205 | -0.3078 | -0.2280 | -0.2558 | 0.3226 | 0.0864 | ||||||
| 最冷月最低温 Min temperature of coldest month (Bio6) | -0.3240 | 0.0336 | -0.5535 | 0.0760 | 0.1049 | 0.4440 | ||||||
| 气温年较差 Annual temperature range (Bio7) | -0.2233 | -0.4475 | 0.2756 | -0.4223 | 0.3220 | -0.3503 | ||||||
| 最湿季平均温 Mean temperature of wettest quarter (Bio8) | -0.0631 | 0.6370 | 0.4028 | -0.0623 | 0.3398 | 0.4079 | ||||||
| 最干季平均温 Mean temperature of driest quarter (Bio9) | -0.3546 | 0.2862 | 0.0772 | 0.6046 | 0.5461 | -0.2837 | ||||||
| 最冷季平均温 Mean temperature of coldest quarter (Bio11) | -0.3831 | 0.2188 | 0.0367 | -0.7455 | 0.0309 | -0.1367 | ||||||
| 年均降水量 Annual precipitation (Bio12) | 0.4753 | -0.1496 | -0.2554 | -0.0359 | 0.4549 | 0.3195 | ||||||
| 最湿月降水量 Precipitation of wettest month (Bio13) | 0.0528 | -0.5800 | 0.6229 | -0.1540 | 0.4640 | -0.1687 | 0.4583 | 0.2152 | -0.2196 | -0.2281 | 0.4103 | -0.2874 |
| 最干月降水量 Precipitation of driest month (Bio14) | 0.4469 | -0.0836 | -0.1889 | -0.2130 | 0.1093 | 0.3556 | ||||||
| 降水季节性变化 Precipitation seasonality (Bio15) | -0.4064 | -0.2396 | 0.2714 | 0.2735 | -0.2429 | 0.6464 | -0.0183 | 0.5997 | -0.0048 | -0.3225 | 0.0936 | -0.1350 |
| 最冷季降水量 Precipitation of coldest season (Bio19) | 0.4426 | -0.1004 | -0.2010 | -0.2152 | 0.2551 | 0.4042 | 0.3162 | -0.4364 | -0.0558 | 0.4762 | 0.0238 | -0.2155 |
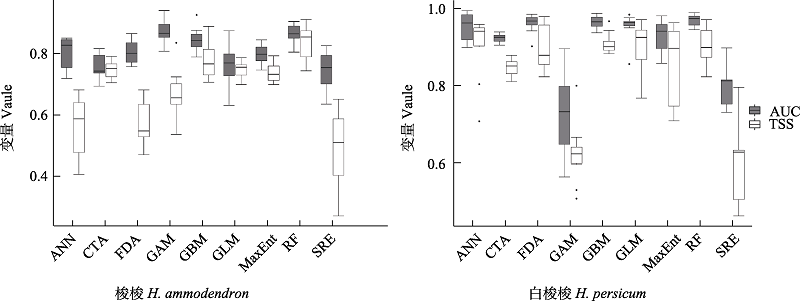
图1 不同模型预测精度评价。ANN: 人工神经网络; CTA: 分类树分析; FDA: 柔性判别分析; GAM: 广义相加模型; GBM: 推进式回归树; GLM: 广义线性模型; MaxEnt: 最大熵模型; RF: 随机森林; SRE: 表面分布区分室模型; AUC: 特征曲线下的面积; TSS: 真实技巧统计值。
Fig. 1 Evaluation of prediction results of different models. ANN, Artificial neural networks; CTA, Classification tree analysis; FDA, Flexible discriminant analysis; GAM, Generalized additive models; GBM, Generalized boosted models; GLM, Generalized linear models; MaxEnt, Maximum entropy; RF, Random forests; SRE, One rectilinear envelope similar to bioclim; AUC, Area under the curve; TSS, True skill statistics.
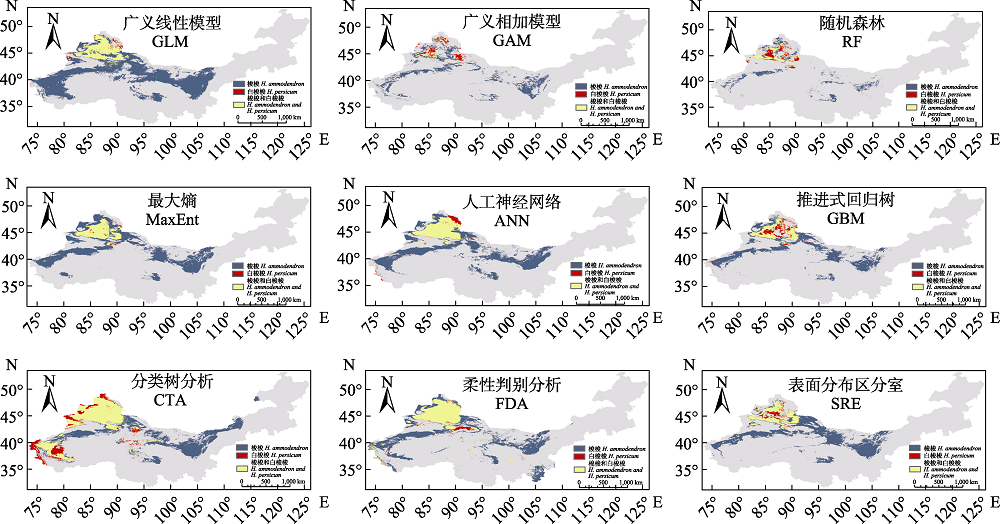
图2 基准气候(1970-2000年)条件下不同模型模拟的中国梭梭属植物的适宜分布
Fig. 2 Suitable distributions of Haloxylon plants in China simulated by different models in the base period (1970-2000). ANN, Artificial neural networks; CTA, Classification tree analysis; FDA, Flexible discriminant analysis; GAM, Generalized additive models; GBM, Generalized boosted models; GLM, Generalized linear models; MaxEnt, Maximum entropy; RF, Random forests; SRE, One rectilinear envelope similar to bioclim.
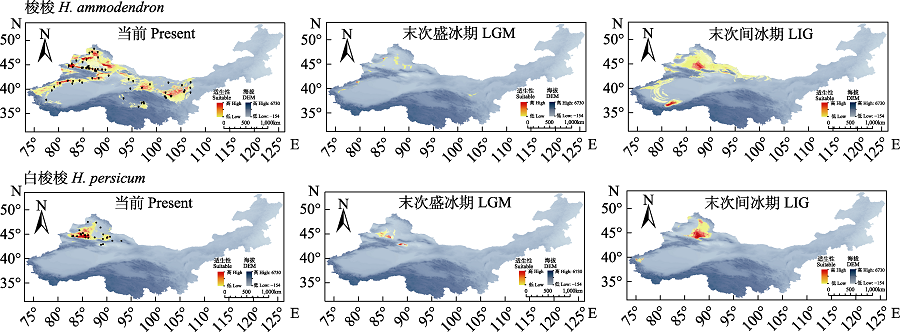
图3 中国梭梭属植物不同时期的适宜分布
Fig. 3 Suitable distribution of Haloxylon in different periods in China. LGM, Last glacial maximum period; LIG, Last interglacial period.
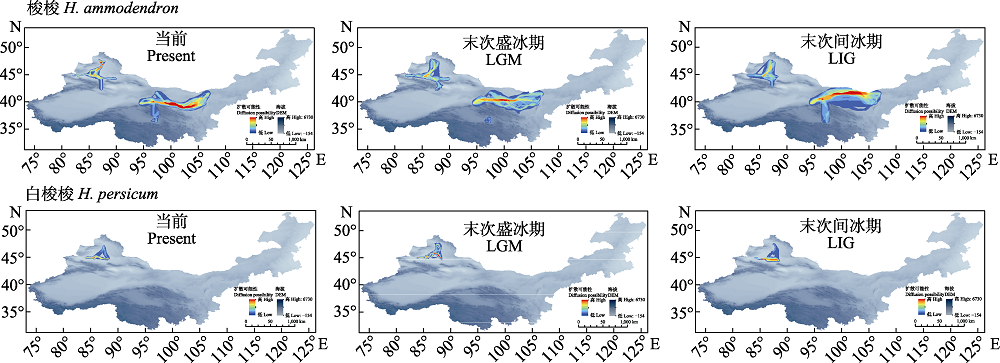
图4 中国梭梭属不同时期可能的迁移扩散路径
Fig. 4 Possible migration and diffusion paths of Haloxylon in different periods in China. LGM, Last glacial maximum period; LIG, Last interglacial period.
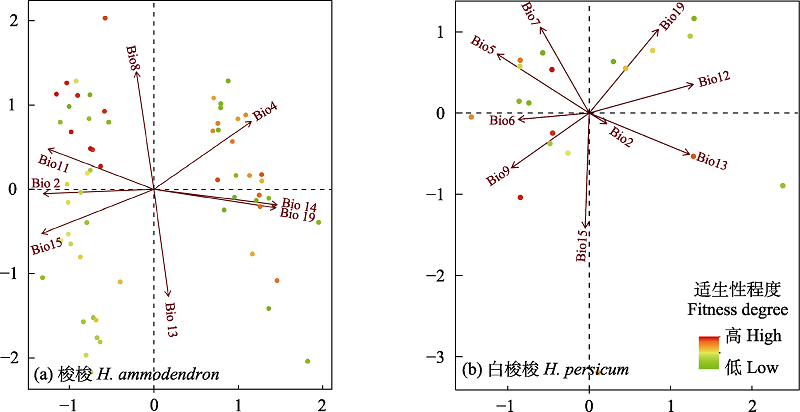
图5 基准气候(1970-2000年)条件下影响梭梭属植物分布的气候因子的主成分分析(PCA)。图中气候变量名称见表1。
Fig. 5 Principal component analysis (PCA) of climatic factors affecting the distribution of Haloxylon under baseline climate (1970-2000). The names of climate variables in the figure are shown in Table 1.
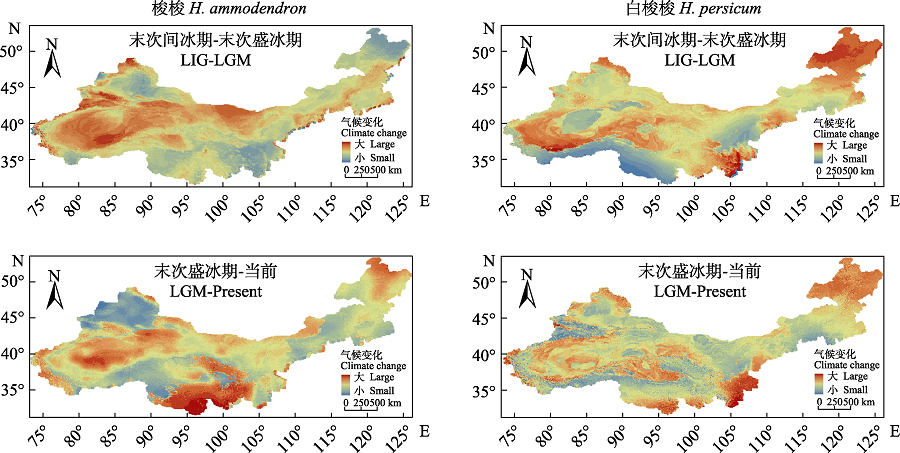
图6 不同时段影响梭梭和白梭梭分布的气候因子的变化程度
Fig. 6 Changes of climatic factors affecting the distribution of Haloxylon ammodendron and H. persicum in different periods. LGM, Last glacial maximum period; LIG, Last interglacial period.
| [1] |
Chan LM, Brown JL, Yoder AD (2011) Integrating statistical genetic and geospatial methods brings new power to phylogeography. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 59, 523-537.
DOI URL |
| [2] | Chang H, Liu T, Liu HF, Du HY (2018) The impacts of climate change on the potential habitat of Haloxylon anmodendron and uncertainty analysis. Journal of Shihezi University (Natural Science), 36, 351-357. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 常红, 刘彤, 刘华峰, 杜皓阳 (2018) 气候变化对我国梭梭潜在分布的影响及不确定性分析. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版), 36, 351-357.] | |
| [3] | Chang J, Pan CD, Shi RF (2006) Analysis on dominant species distribution patterns and relation of Ass. Haloxylon persicum + H. ammodendron. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 29(2), 26-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 常静, 潘存德, 师瑞锋 (2006) 梭梭‐白梭梭群落优势种种群分布格局及其种间关系分析. 新疆农业大学学报, 29(2), 26-29.] | |
| [4] | Fu GQ, Xu XY, Ma JP, Xu MS, Liu J, Ding AQ (2016) Responses of Haloxylon ammodendron potential geographical distribution to the hydrothermal conditions under MaxEnt model. Pratacultural Science, 33, 2173-2179. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 付贵全, 徐先英, 马剑平, 徐梦莎, 刘江, 丁爱强 (2016) 基于MaxEnt下梭梭潜在地理分布对水热条件的响应. 草业科学, 33, 2173- 2179.] | |
| [5] | Gao B, Hu N, Guo YL, Gu W, Zou JY (2017) Comparison of the potential geographical distribution of foxtail millet (Setaria italica) predicted by different models. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28, 3331-3340. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 高蓓, 胡凝, 郭彦龙, 顾蔚, 邹继业 (2017) 中国谷子潜在地理分布的多模型比较. 应用生态学报, 28, 3331-3340.] | |
| [6] | Guo QS, Guo ZH, Yan H, Wang CL, Tan DY, Ma C, He HY (2005a) Study on potential distribution of Haloxylon plants dominated desert vegetation in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 25, 848-853, 946. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郭泉水, 郭志华, 阎洪, 王春玲, 谭德远, 马超, 何红艳 (2005a) 我国以梭梭属植物为优势的潜在荒漠植被分布. 生态学报, 25, 848-853, 946.] | |
| [7] | Guo QS, Wang CL, Guo ZH, Tan DY, Shi ZM (2005b) Geographic distribution of existing Haloxylon desert vegetation and its patch character in China. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 41(5), 2-7, 219. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郭泉水, 王春玲, 郭志华, 谭德远, 史作民 (2005b) 我国现存梭梭荒漠植被地理分布及其斑块特征. 林业科学, 41(5), 2-7, 219.] | |
| [8] |
Jia SW, Zhang ML (2021) Introgression of phylogeography lineages of Convolvulus gortschakovii (Convolvulaceae) in the northwest China. Plant Systematics and Evolution, 307, doi: 10.1007/s00606-020-01734-z.
DOI |
| [9] |
Jiang XL, An M, Zheng SS, Deng M, Su ZH (2019) Geographical isolation and environmental heterogeneity contribute to the spatial genetic patterns of Quercus kerrii (Fagaceae). Heredity, 120, 219-233.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Kozhoridze G, Orlovsky N, Orlovsky L, Blumberg DG, Golan-Goldhirsh A (2015) Geographic distribution and migration pathways of Pistacia-Present, past and future. Ecography, 38, 1141-1154.
DOI URL |
| [11] | Liu Y (2008) Simulations of Climate Changes over China in LGM and Mid-Holocene. PhD dissertation, Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, Nanjing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘煜 (2008) 末次冰期冰盛期和中全新世中国地区气候变化的数值研究. 博士学位论文, 南京信息工程大学, 南京.] | |
| [12] | Liu YD, Qi YT, Qiu YJ, Zhang H, Wang SM (2009) The geographical distribution, origin and evolution of Ephedra. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 23, 120-126. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘运东, 齐妍婷, 邱远金, 张浩, 王绍明 (2009) 麻黄属的地理分布与起源演化. 干旱区资源与环境, 23, 120-126.] | |
| [13] | Lu HY, Guo ZT (2015) Impact of climatic change and human activity on desert and sand field in northern china since the last glacial maximum. China Basic Science, 17(2), 3-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 鹿化煜, 郭正堂 (2015) 末次盛冰期以来气候变化和人类活动对我国沙漠和沙地环境的影响. 中国基础科学, 17(2), 3-8.] | |
| [14] |
Manel S, Schwartz MK, Luikart G, Taberlet P (2003) Landscape genetics: Combining landscape ecology and population genetics. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 18, 189-197.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Manel S, Segelbacher G (2009) Perspectives and challenges in landscape genetics. Molecular Ecology, 18, 1821-1822.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Marmion M, Luoto M, Heikkinen RK, Thuiller W (2009) The performance of state-of-the-art modelling techniques depends on geographical distribution of species. Ecological Modelling, 220, 3512-3520.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Meng LH, Yang R, Abbott RJ, Miehe G, Hu TH, Liu JQ (2007) Mitochondrial and chloroplast phylogeography of Picea crassifolia Kom. (Pinaceae) in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and adjacent highlands. Molecular Ecology, 16, 4128-4137.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Parolo G, Rossi G, Ferrarini A (2008) Toward improved species niche modelling: Arnica montana in the Alps as a case study. Journal of Applied Ecology, 45, 1410-1418.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Richards CL, Carstens BC, Lacey Knowles L (2007) Distribution modelling and statistical phylogeography: An integrative framework for generating and testing alternative biogeographical hypotheses. Journal of Biogeography, 34, 1833-1845.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Schorr G, Holstein N, Pearman PB, Guisan A, Kadereit JW (2012) Integrating species distribution models (SDMs) and phylogeography for two species of alpine Primula. Ecology and Evolution, 2, 1260-1277.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Soltis DE, Morris AB, McLachlan JS., Manos PS, Soltis PS. (2006) Comparative phylogeography of unglaciated eastern North America. Molecular Ecology, 15, 4261-4293.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Song ZC, Wang WM, Mao FY (2008) Palynological implications for relationship between aridification and monsoon climate in the tertiary of NW China. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 47, 265-272. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 宋之琛, 王伟铭, 毛方园 (2008) 依据孢粉资料探讨我国西北地区第三纪时期的干旱化及其与季风的关系. 古生物学报, 47, 265-272.] | |
| [23] |
Street GM (2020) Habitat suitability and distribution models with applications in R. The Journal of Wildlife Management, 84, 1212-1213.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Sun FF, Nie YB, Ma SM, Wei B, Ji WQ (2019) Species differentiation of Haloxylon ammodendron and Haloxylon persicum based on ITS and cpDNA sequences. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 55(3), 43-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙芳芳, 聂迎彬, 马松梅, 魏博, 吉万全 (2019) 基于ITS和cpDNA序列的梭梭和白梭梭物种分化. 林业科学, 55(3), 43-53.] | |
| [25] |
Suo ZL, Jia ZQ, Lu Q, Pan BR, Jin XB, Xu G, Peng XQ, Sun HB, Tao YH (2012) Distinguishing Haloxylon persicum and H. ammodendron (Haloxylon Bunge, Amaranthaceae) using DNA marker. AASRI Procedia, 1, 305-310.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Svenning JC, Normand S, Kageyama M (2008) Glacial refugia of temperate trees in Europe: Insights from species distribution modelling. Journal of Ecology, 96, 1117-1127.
DOI URL |
| [27] | Wang HC, Zhu H, Li YF, Yi XG, Li M, Nan CH, Wang XR (2020) Potential distribution and ecological characteristic of Chinese endemic species Cerasus xueluoensis. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 28, 136-144. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王华辰, 朱弘, 李涌福, 伊贤贵, 李蒙, 南程慧, 王贤荣 (2020) 中国特有植物雪落樱桃潜在分布及其生态特征. 热带亚热带植物学报, 28, 136-144.] | |
| [28] | Wang L, Xu XG, Li Y (2018) Prediction of potential geographical distribution pattern change for Melliodendron xylocarpum Handel-Mazzetti since the Last Glacial Maximum. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 37, 278-286. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王璐, 许晓岗, 李垚 (2018) 末次盛冰期以来陀螺果潜在地理分布格局变迁预测. 生态学杂志, 37, 278-286.] | |
| [29] | Wei B, Ma SM, Song J, He LY, Li XC (2019) Prediction of the potential distribution and ecological suitability of Fritillaria walujewii. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39, 228-234. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 魏博, 马松梅, 宋佳, 贺凌云, 李晓辰 (2019) 新疆贝母潜在分布区域及生态适宜性预测. 生态学报, 39, 228-234.] | |
| [30] | Wei Y, Yin LK, Yan C (2005) Study on the flowering and wind-borne pollination characteristics of Haloxylon persicum. Arid Zone Research, 22, 85-89. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 魏岩, 尹林克, 严成 (2005) 白梭梭开花及风媒传粉特点. 干旱区研究, 22, 85-89.] | |
| [31] | Yin HX, Wang LR, Shi Y, Qian CJ, Zhou HK, Wang WY, Ma XF, Tran LP, Zhang BY (2020) The East Asian winter monsoon scts as a major selective factor in the intraspecific differentiation of drought-tolerant Nitraria tangutorum in Northwest China. Plants (Basel), 9, 1100. |
| [32] | Yu HB, Zhang YL, Li SC, Qi W, Hu ZJ (2014) Predicting the dispersal routes of alpine plant Pedicularis longiflora (Orobanchaceae) based on GIS and species distribution models. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 25, 1669- 1673. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 于海彬, 张镱锂, 李士成, 祁威, 胡忠俊 (2014) 基于GIS和物种分布模型的高山植物长花马先蒿迁移路线模拟. 应用生态学报, 25, 1669-1673.] | |
| [33] | Zhao L, Li WJ, Yang G, Yan K, He XL, Li FD, Gao YL, Tian LJ (2021) Moisture, temperature, and salinity of a typical desert plant (Haloxylon ammodendron) in an arid oasis of Northwest China. In: Sustainability, 13, 1908. |
| [34] | Zhao TB (2006) Studies on Spatial Distribution Pattern, Habitats Selection and Dynamic of Rhombomys opimus Population. PhD dissertation, Inner Mongolia University, Hohhot. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵天飙 (2006) 大沙鼠种群空间分布格局、栖息地选择及种群动态的研究. 博士学位论文, 内蒙古大学, 呼和浩特.] | |
| [35] | Zhao ZF, Wei HY, Guo YL, Gu W (2016) Potential distribution of Panax ginseng and its predicted responses to climate change. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27, 3607- 3615. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵泽芳, 卫海燕, 郭彦龙, 顾蔚 (2016) 人参潜在地理分布以及气候变化对其影响预测. 应用生态学报, 27, 3607-3615.] | |
| [36] | Zhu N (2019) Modelling the suitable habitat distribution of Magnolia officinalis using ensemble model. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 37, 481-489. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱妮 (2019) 基于组合物种分布模型(ensemble model)的厚朴适宜生境分布模拟. 四川农业大学学报, 37, 481-489.] |
| [1] | 李晶晶, 张杰, 胡自民, 段德麟. 加拿大-西北∇大西洋地区掌形藻的种群遗传结构与动态变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(3): 306-314. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn