



生物多样性 ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (9): 966-971. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017019 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2017019
收稿日期:2017-01-17
接受日期:2017-06-09
出版日期:2017-09-20
发布日期:2017-10-04
通讯作者:
郑景明
作者简介:# 共同第一作者
基金资助:Received:2017-01-17
Accepted:2017-06-09
Online:2017-09-20
Published:2017-10-04
Contact:
Zheng Jingming
About author:# Co-first authors
摘要:
种子扩散方式对植物物种分布、种群动态及群落组成都有重要影响, 但目前有关种子扩散方式的数据还很欠缺。植物的生活史性状与种子扩散方式联系密切, 通过植物生活史性状预测种子的扩散方式是一种有效的研究手段。本文基于我国360种植物的生长型、株高、种子质量和果实类型以及种子扩散方式的数据集, 随机抽取288个物种数据(80%)作为训练样本, 采用神经网络、决策树、费舍尔线性判别和支持向量机算法, 分别建立种子扩散方式的预测模型, 将其余72个物种数据(20%)用于模型检验。以1,000次随机抽样后的平均判别正确率作为模型预测效果的评价指标。结果表明: 用生长型、株高、种子质量及果实类型作为主要预测变量, 构建的神经网络、决策树、费希尔线性判别和支持向量机模型均能达到较好的预测效果, 准确率分别为78.90%、77.09%、77.81%和78.14%, 其中以神经网络模型的预测效果最好。进一步研究发现, 神经网络模型对动物扩散、无助力扩散和风扩散的预测效果分别为81.32%、74.90%和81.45%。本研究为植物种子扩散方式预测提供了一种新的思路。
郭志文, 郑景明 (2017) 用植物生活史性状预测种子扩散方式. 生物多样性, 25, 966-971. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017019.
Zhiwen Guo, Jingming Zheng (2017) Predicting modes of seed dispersal using plant life history traits. Biodiversity Science, 25, 966-971. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017019.
| 生活史性状 Life history trait | 分类水平 Class level | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 生长型 Growth form | 草本; 灌木; 藤本; 乔木 Herb; Shrub; Vine; Tree | Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae, 1979 |
| 株高 Plant height | < 0.5 m; 0.5-2.0 m; 2.0-5.0 m; > 5.0 m | Westoby et al, 1990 |
| 果实类型 Fruit type | 裂果; 闭果; 肉质果 Dehisce; Achene; Fruit | Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae, 1979 |
| 种子质量 Seed mass | < 0.1 mg; 0.1-100 mg; > 100 mg | Westoby et al, 1996 |
| 扩散方式 Dispersal mode | 无助力扩散; 风扩散; 动物扩散 Autochory; Anemochory; Zoochory | Baskin & Baskin, 1998,2014 |
表1 5个植物生活史性状的分类水平及划分方法
Table 1 The protocol of classification level in five life history traits of plant
| 生活史性状 Life history trait | 分类水平 Class level | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 生长型 Growth form | 草本; 灌木; 藤本; 乔木 Herb; Shrub; Vine; Tree | Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae, 1979 |
| 株高 Plant height | < 0.5 m; 0.5-2.0 m; 2.0-5.0 m; > 5.0 m | Westoby et al, 1990 |
| 果实类型 Fruit type | 裂果; 闭果; 肉质果 Dehisce; Achene; Fruit | Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae, 1979 |
| 种子质量 Seed mass | < 0.1 mg; 0.1-100 mg; > 100 mg | Westoby et al, 1996 |
| 扩散方式 Dispersal mode | 无助力扩散; 风扩散; 动物扩散 Autochory; Anemochory; Zoochory | Baskin & Baskin, 1998,2014 |
| Gamma 系数 Gamma index | 生长型 Growth form | 株高 Plant height | 果实类型 Fruit type | 种子质量 Seed mass |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height | 0.96** | |||
| 果实类型 Fruit type | 0.55** | 0.47** | ||
| 种子质量 Seed mass | 0.69** | 0.64** | 0.49** | |
| 扩散方式 Dispersal mode | 0.70** | 0.63** | 0.87** | 0.50** |
表2 5个植物生活史性状间的相关性
Table 2 Correlations between five life history traits of plants
| Gamma 系数 Gamma index | 生长型 Growth form | 株高 Plant height | 果实类型 Fruit type | 种子质量 Seed mass |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 Plant height | 0.96** | |||
| 果实类型 Fruit type | 0.55** | 0.47** | ||
| 种子质量 Seed mass | 0.69** | 0.64** | 0.49** | |
| 扩散方式 Dispersal mode | 0.70** | 0.63** | 0.87** | 0.50** |
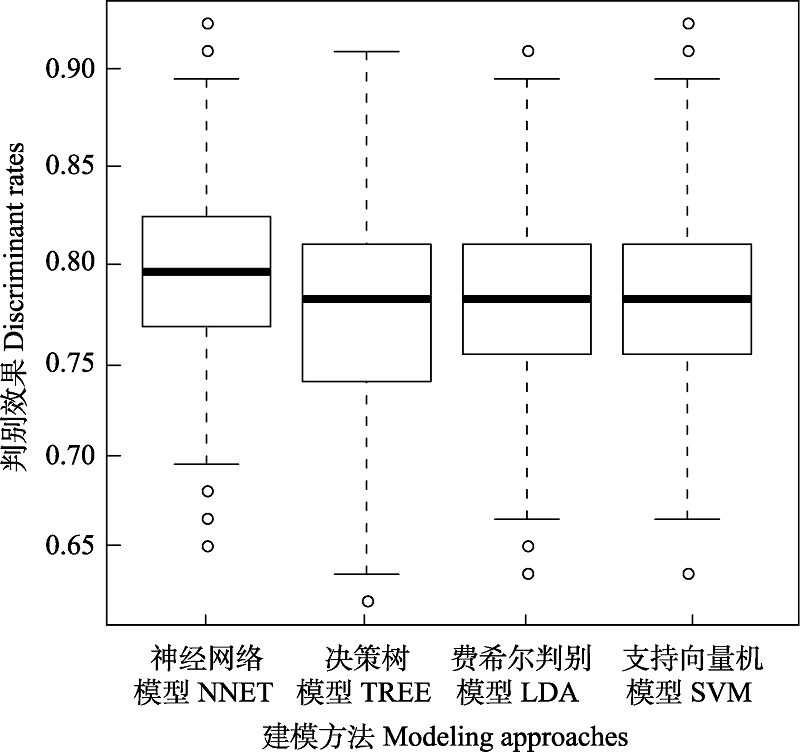
图1 4种模型对种子扩散方式的判别效果
Fig. 1 The discriminant rates of four models to seed dispersal modes. NNET, Neural network model; TREE, Decision tree model; LDA, Fisher linear discriminant model; SVM, Support vector machine model.
| [1] | Baskin C, Baskin J (1998) Seeds: Ecology, Biogeography, and Evolution of Dormancy and Germination. Academic Press, San Diego. |
| [2] | Baskin C, Baskin J (2014) Seeds: Ecology, Biogeography, and Evolution of Dormancy and Germination, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego. |
| [3] |
Cain ML, Damman H, Muir A (1998) Seed dispersal and the Holocene migration of woodland herbs. Ecological Monograph, 68, 325-347.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Cain ML, Milligan BG, Strand AE (2000) Long-distance seed dispersal in plant populations. American Journal of Botany, 87, 1217-1227.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] | Clark JS, Macklin E, Wood L (1998) Stages and spatial scales of recruitment limitation in southern Appalachian forests. Ecological Monographs, 68, 157-166. |
| [6] | Cortes C (1995) Support-vector networks. Machine Learning, 20, 273-297. |
| [7] | Delectis Florae Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae Agendae Academicae Sinicae Edita(1979) Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会(1979) 中国植物志. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [8] |
Hewitt N, Kellman M (2002) Tree seed dispersal among forest fragments. II. Dispersal abilities and biogeographical controls. Journal of Biogeography, 29, 351-363.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Hughes L, Dunlop M, French K, Leishman MR, Rice B, Rodgerson L, Westoby M (1994) Predicting dispersal spectra: a minimal set of hypotheses based on plant attributes. Journal of Ecology, 82, 933-950.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Jordano P, Forget PM, Lambert JE, B?hning-Gaese K, Traveset A, Wright SJ (2011) Frugivores and seed dispersal: mechanisms and consequences for biodiversity of a key ecological interaction. Biology Letters, 7, 321-323.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] |
Lei X, Yang QS, Liu HM, Xing JZ, Wang XH (2015) Character of seed rain of species with different dispersal modes in Tiantong evergreen broad-leaved forest, Zhejiang Province. Journal of East China Normal University, 21, 122-132. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[雷霄, 杨庆松, 刘何铭, 邢九州, 王希华 (2015) 浙江天童常绿阔叶林不同扩散方式物种种子雨的基本特征. 华东师范大学学报, 21, 122-132.]
DOI URL |
|
| [12] |
Leishman MR, Westoby M (1994) Hypotheses on seed size: tests using the semi-arid flora of western New South Wales, Australia. The American Naturalist, 143, 890-906.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Leishman MR, Westoby M, Jurado E (1995) Correlates of seed size variation: a comparison among five temperate floras. Journal of Ecology, 83, 517-529.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Li BH, Hao ZQ, Bin Y, Zhang J, Wang M (2012) Seed rain dynamics reveals strong dispersal limitation, different reproductive strategies and responses to climate in a temperate forest in Northeast China. Journal of Vegetation Science, 23, 271-279.
DOI URL |
| [15] | Li J, Guo C, Xiao ZS (2013) Fruit composition and seed dispersal strategies of woody plants in a Dujiangyan subtropical forest, Southwest China. Biodiversity Science, 21, 572-581. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李娟, 郭聪, 肖治术 (2013) 都江堰亚热带森林常见木本植物果实组成与种子扩散策略. 生物多样性, 21, 572-581.] | |
| [16] | Liu MT (2001) Data Mining Technology and Its Application. National Defense University Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [刘明同 (2001) 数据挖掘技术及其应用. 国防大学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [17] |
Moles AT, Ackerly DD, Webb CO, Tweddle JC, Dickie JB, Pitman AJ, Westoby M (2005) Factors that shape seed mass evolution. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 102, 10540-10544.
DOI URL PMID |
| [18] |
Mori SA, Brown JL (1998) Epizoochorous dispersal by barbs, hooks, and spines in a lowland moist forest in central French Guiana. Brittonia, 50, 165-173.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Neubert MG, Caswell H (2000) Demography and dispersal: calculation and sensitivity analysis of invasion speed for structured populations. Ecology, 81, 1613-1628.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Tang HS, Yao YW (2001) Research on decision tree in data mining. Application Research of Computers, 18(8), 18-19, 22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[唐华松, 姚耀文 (2001) 数据挖掘中决策树算法的探讨. 计算机应用研究, 18(8), 18-19, 22]
DOI URL |
|
| [21] |
Thompson K, Rabinowitz D (1989) Do big plants have big seeds? The American Naturalist, 133, 722-728.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Thomson FJ, Moles A T, Auld TD, Ramp D, Ren S, Kingsford RT (2010) Chasing the unknown: predicting seed dispersal. Journal of Ecology, 98, 1310-1318.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Thomson FJ, Moles AT, Auld TD, Kingsford RT (2011) Seed dispersal distance is more strongly correlated with plant height than with seed mass. Journal of Ecology, 99, 1299-1307.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Thuiller W, Albert C, Araujo MB, Berry PM, Cabeza M, Guisan A, Hickler T, Midgely GF, Paterson J, Schurr FM, Sykes MT, Zimmermann NE (2008) Predicting global change impacts on plant species’ distributions: future challenges. Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 9, 137-152.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Turner IM (2001) The Ecology of Trees in the Tropical Rain Forest. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [26] | van der Pijl L (1982) Principles of Dispersal in Higher Plants. Springer-Verlag, New York. |
| [27] | Wang JH, Du GZ, Cui XL, Zheng XF, Qi W (2009) Germination characteristics of 61 common woody species from the eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau of China and their life history correlates. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 33, 171-179. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王桔红, 杜国祯, 崔现亮, 郑秀芳, 齐威 (2009) 青藏高原东缘61种常见木本植物种子萌发特性及其与生活史的关联. 植物生态学报, 33, 171-179.] | |
| [28] |
Westoby M, Jurado E, Leishman M (1992) Comparative evolutionary ecology of seed size. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 7, 368-372.
DOI URL PMID |
| [29] |
Westoby M, Leishman M, Lord JM (1996) Comparative ecology of seed size and dispersal. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 351, 1309-1318.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Westoby M, Rice B, Howell J (1990) Seed size and plant- growth form as factors in dispersal spectra. Ecology, 71, 1307-1315.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Willson MF (1993) Dispersal mode, seed shadows, and colonization patterns. Plant Ecology, 107/108, 261-280.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Willson MF, Rice BL, Westoby M (1990) Seed dispersal spectra: a comparison of temperate plant-communities. Journal of Vegetation Science, 1, 547-562.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Yao B, Yu JP, Liu XJ, Mi XC, Ma KP (2015) Effect of seed traits on spatial aggregation of trees in a subtropical evergreen. Biodiversity Science, 23, 157-166. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[姚蓓, 余建平, 刘晓娟, 米湘成, 马克平 (2015) 亚热带常绿阔叶林种子性状对木本植物聚集格局的影响. 生物多样性, 23, 157-166.]
DOI URL |
|
| [34] |
Yu SL, Chen HW, Li H (2007) Advances in ecology of mass. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 31, 989-997. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[于顺利, 陈宏伟, 李晖 (2007) 种子重量的生态学研究进展. 植物生态学报, 31, 989-997.]
DOI URL |
|
| [35] | Zhang DY (2004) Plant Life History Evolution and Reproductive Ecology. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张大勇 (2004) 植物生活史进化与繁殖生态学. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [36] | Zheng JM, Sang WG, Ma KP (2004) Advances in model construction of anemochoric seed long distance dispersal. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 28, 414-425. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郑景明, 桑卫国, 马克平 (2004) 种子的长距离风传播模型研究进展. 植物生态学报, 28, 414-425.] | |
| [37] | Zhou HP, Chen GY, Yue H, Cun M (2014) Seed predation and dispersal of Hevea brasiliensis in Xishuangbanna introduction area. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 33, 2025-2030. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周会平, 陈国云, 岳海, 寸明 (2014) 橡胶树在西双版纳引种区的种子捕食与散布. 生态学杂志, 33, 2025-2030.] |
| [1] | 郑博瀚, 陈鑫瑶, 倪健. 中国维管植物生长型和生活型数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23468-. |
| [2] | 王晓凤, 米湘成, 王希华, 江明喜, 杨涛, 张健, 沈泽昊. 中国中亚热带常绿阔叶林群落木本植物多样性比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23296-. |
| [3] | 邵晨, 李耀琪, 罗奥, 王志恒, 席祯翔, 刘建全, 徐晓婷. 不同生活型被子植物功能性状与基因组大小的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 575-585. |
| [4] | 李晶, 周天阳, 鲁雪丽, 李新涛, 孙斌, 孟红杰. 珍稀植物连香树在其中国分布区北缘的种子性状及幼苗更新限制[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(10): 1161-1173. |
| [5] | 王宁, 李卫芳, 周兵, 闫小红. 中国入侵克隆植物入侵性、克隆方式及地理起源[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(1): 12-. |
| [6] | 姚蓓, 余建平, 刘晓娟, 米湘成, 马克平. 亚热带常绿阔叶林种子性状对木本植物聚集格局的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(2): 157-166. |
| [7] | 韩大勇, 杨允菲. 松嫩草地植物群落物种多度–分布关系及其解释[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(3): 348-357. |
| [8] | 汪殷华, 米湘成, 陈声文, 李铭红, 于明坚. 古田山常绿阔叶林主要树种2002-2007年间更新动态[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(2): 178-189. |
| [9] | 孙华之, 谭敦炎, 曲荣明. 短命植物小疮菊异形瘦果特性及其对荒漠环境的适应[J]. 生物多样性, 2008, 16(4): 353-361. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()
