



生物多样性 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (3): 361-372. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020158 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020158
所属专题: 生物入侵
赵阳1,2,3( ), 牛诚祎2, 李雪健2,4, 刘海波2, 孙光3, 罗遵兰3,*(
), 牛诚祎2, 李雪健2,4, 刘海波2, 孙光3, 罗遵兰3,*( ), 赵亚辉2,*(
), 赵亚辉2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-04-20
接受日期:2020-07-04
出版日期:2021-03-20
发布日期:2020-09-12
通讯作者:
罗遵兰,赵亚辉
作者简介:E-mail: zhaoyh@ioz.ac.cn;基金资助:
Yang Zhao1,2,3( ), Chengyi Niu2, Xuejian Li2,4, Haibo Liu2, Guang Sun3, Zunlan Luo3,*(
), Chengyi Niu2, Xuejian Li2,4, Haibo Liu2, Guang Sun3, Zunlan Luo3,*( ), Yahui Zhao2,*(
), Yahui Zhao2,*( )
)
Received:2020-04-20
Accepted:2020-07-04
Online:2021-03-20
Published:2020-09-12
Contact:
Zunlan Luo,Yahui Zhao
About author:luozunlan@163.com摘要:
汉江是南水北调中线工程和引汉济渭等跨流域调水工程重要的水源区, 了解其鱼类多样性的现状及变化对于水生态保护尤为重要。作者于2016-2017年间对汉江洋县段干流与6条主要支流的鱼类多样性组成进行了两次调查, 以Margalef丰富度指数、Shannon-Wiener多样性指数、Pielou均匀度指数和Jaccard相似性系数对洋县境内7条河流进行评估, 同时通过相对重要性指数(index of relative importance,IRI)判定优势种, 利用鱼类丰度生物量(abundance biomass comparison, ABC)曲线分析鱼类受干扰情况。结合历史记录, 调查区域内共分布有土著鱼类76种, 隶属于6目14科57属, 以鲤形目鲤科和鲇形目鲿科鱼类为主, 分别占土著鱼类总数的57.89%和11.84%; 珍稀濒危鱼类共计5种, 包括3种国家级保护水生野生动物。鱼类多样性分析结果显示汉江干流的丰富度指数和多样性指数显著高于6条支流。7条河流的IRI指数显示优势种为宽鳍鱲(Zacco platypus)。ABC曲线显示目前调查区域内鱼类小型化现象明显、鱼类受到较严重干扰。水利水电工程建设对于调查区域鱼类多样性影响最大, 干流大型水库(大坝)通过改变原有流水生境、阻断河流纵向连通性、淹没重要鱼类产卵场等对鱼类多样性和群落组成产生不利影响; 支流引水式的中小型电站造成下游河段减、脱水而使河道发生断流以及生境破碎化, 从而威胁土著鱼类的生存。在跨流域调水过程中, 应重视不同水系鱼类引入的潜在生态风险。对引汉济渭工程的水源区鱼类多样性现状的调查, 有助于未来跨流域调水过程中鱼类变化的动态监测和外来物种的预警。
赵阳, 牛诚祎, 李雪健, 刘海波, 孙光, 罗遵兰, 赵亚辉 (2021) 跨流域调水背景下汉江流域洋县段的鱼类多样性及资源现状. 生物多样性, 29, 361-372. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020158.
Yang Zhao, Chengyi Niu, Xuejian Li, Haibo Liu, Guang Sun, Zunlan Luo, Yahui Zhao (2021) Fish diversity and resource status in the Yangxian Section of the Hanjiang River under the context of inter-basin water transfer. Biodiversity Science, 29, 361-372. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020158.
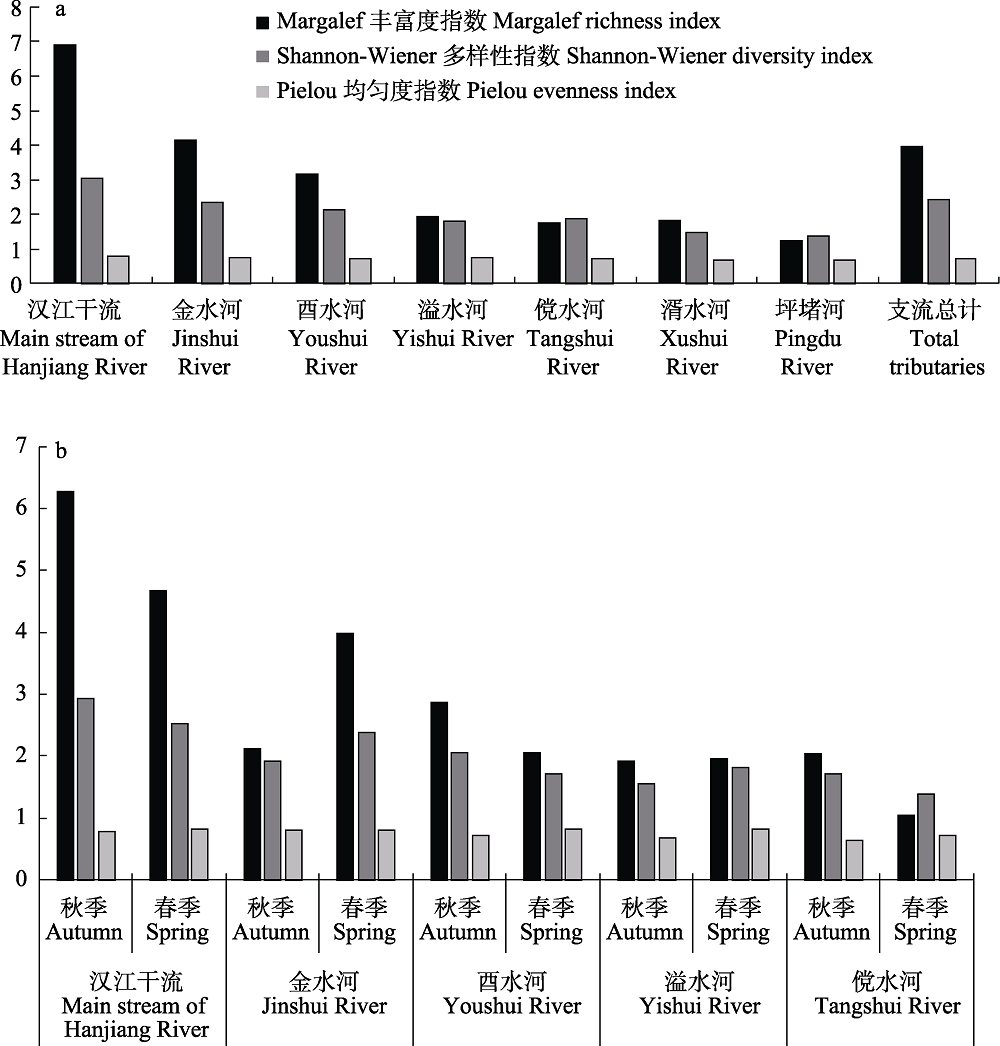
图2 汉江洋县段各河流鱼类群落多样性(a)及鱼类群落多样性的季节变化(b)
Fig. 2 Fish diversity of different rivers (a) and seasonal variation of fish diversity of different rivers (b) in the Yangxian section of the Hanjiang River basin
| 酉水河 Youshui River | 溢水河 Yishui River | 傥水河 Tangshui River | 湑水河 Xushui River | 坪堵河 Pingdu River | 汉江 Hanjiang River | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 金水河 Jinshui River | 0.48 | 0.26 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.25 | 0.41 |
| 酉水河 Youshui River | 0.39 | 0.50 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.32 | |
| 溢水河 Yishui River | 0.71 | 0.33 | 0.29 | 0.19 | ||
| 傥水河 Tangshui River | 0.47 | 0.43 | 0.26 | |||
| 湑水河 Xushui River | 0.60 | 0.15 | ||||
| 坪堵河 Pingdu River | 0.10 |
表1 汉江洋县段各河流鱼类的Jaccard相似性系数
Table 1 The Jaccard similarity coefficient in different rivers in the Yangxian section of the Hanjiang River
| 酉水河 Youshui River | 溢水河 Yishui River | 傥水河 Tangshui River | 湑水河 Xushui River | 坪堵河 Pingdu River | 汉江 Hanjiang River | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 金水河 Jinshui River | 0.48 | 0.26 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.25 | 0.41 |
| 酉水河 Youshui River | 0.39 | 0.50 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.32 | |
| 溢水河 Yishui River | 0.71 | 0.33 | 0.29 | 0.19 | ||
| 傥水河 Tangshui River | 0.47 | 0.43 | 0.26 | |||
| 湑水河 Xushui River | 0.60 | 0.15 | ||||
| 坪堵河 Pingdu River | 0.10 |
| 物种 Species | 相对重要性指数 Index of relative importance (IRI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 总计 Total | 秋季 Autumn | 春季 Spring | |
| 宽鳍鱲 Zacco platypus | 1,031.97 | 1,952.15 | - |
| 短须颌须鮈 Gnathopogon imberbis | 918.31 | 1,279.67 | 383.99 |
| 马口鱼 Opsariicjthys bidens | 761.68 | 632.14 | 1,151.37 |
| 似鮈 Pseudogobio vaillanti vaillant | 588.57 | 968.44 | - |
| 拉氏鱥 Phoxinus lagowskii | 263.62 | 459.69 | - |
| 乐山小鳔鮈 Microphysogobio kiatingensis | 234.78 | 389.86 | - |
| 银鮈 Squalidus argentatus | 148.60 | 340.77 | - |
| 大斑花鳅 Cobitis macrostigma | 239.22 | 236.36 | 270.79 |
| 花? Hemibarbus maculatus | - | 144.64 | - |
| 麦穗鱼 Pseudorasbora parva | - | 122.10 | - |
| 圆吻鲴 Distoechodon tumirostris | - | 117.47 | - |
| 鲫 Carassius auratus | - | 113.58 | - |
| 尖头鲌 Culter oxycephalus | - | - | 172.79 |
| 多鳞白甲鱼 Onychostoma macrolepis | - | - | 169.57 |
| 神农吻虾虎鱼 Rhinogobius shennongensis | - | - | 163.97 |
| 鲇 Silurus asotus | - | - | 103.77 |
表2 汉江洋县段鱼类优势种和重要种的季节变化
Table 2 Seasonal variation of fish dominant species and important species in the Yangxian section of the Hanjiang River basin
| 物种 Species | 相对重要性指数 Index of relative importance (IRI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 总计 Total | 秋季 Autumn | 春季 Spring | |
| 宽鳍鱲 Zacco platypus | 1,031.97 | 1,952.15 | - |
| 短须颌须鮈 Gnathopogon imberbis | 918.31 | 1,279.67 | 383.99 |
| 马口鱼 Opsariicjthys bidens | 761.68 | 632.14 | 1,151.37 |
| 似鮈 Pseudogobio vaillanti vaillant | 588.57 | 968.44 | - |
| 拉氏鱥 Phoxinus lagowskii | 263.62 | 459.69 | - |
| 乐山小鳔鮈 Microphysogobio kiatingensis | 234.78 | 389.86 | - |
| 银鮈 Squalidus argentatus | 148.60 | 340.77 | - |
| 大斑花鳅 Cobitis macrostigma | 239.22 | 236.36 | 270.79 |
| 花? Hemibarbus maculatus | - | 144.64 | - |
| 麦穗鱼 Pseudorasbora parva | - | 122.10 | - |
| 圆吻鲴 Distoechodon tumirostris | - | 117.47 | - |
| 鲫 Carassius auratus | - | 113.58 | - |
| 尖头鲌 Culter oxycephalus | - | - | 172.79 |
| 多鳞白甲鱼 Onychostoma macrolepis | - | - | 169.57 |
| 神农吻虾虎鱼 Rhinogobius shennongensis | - | - | 163.97 |
| 鲇 Silurus asotus | - | - | 103.77 |
| 物种 Species | 相对重要性指数 Index of relative importance (IRI) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 汉江 Hanjiang River | 金水河 Jinshui River | 溢水河 Yishui River | 傥水河 Tangshui River | 酉水河 Youshui River | 湑水河 Xushui River | 坪堵河 Pingdu River | |
| 宽鳍鱲 Zacco platypus | - | 1,775.83 | - | 1,904.29 | 1,312.76 | 7,872.73 | 4,161.01 |
| 马口鱼 Opsariicjthys bidens | - | 1,013.00 | - | 1,237.04 | 5,750.20 | - | - |
| 拉氏鱥 Phoxinus lagowskii | - | - | - | 1,806.22 | - | - | 6,876.49 |
| 银鮈 Squalidus argentatus | 859.67 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 似鮈 Pseudogobio vaillanti vaillant | - | 2,039.71 | - | 1,478.20 | 1,895.42 | - | 5,129.72 |
| 短须颌须鮈 Gnathopogon imberbis | - | - | 1,172.40 | 3,290.10 | 1,303.19 | 6,877.97 | 1,148.46 |
| 红尾荷马条鳅 Homatula variegata | - | - | - | - | - | 1,995.12 | - |
| 大斑花鳅 Cobitis macrostigma | - | - | 6,300.01 | - | - | - | - |
| 稀有花鳅 Cobitis rarus | - | - | 1,488.03 | - | - | - | - |
| 泥鳅 Misgurnus anguillicaudatus | - | - | 1,571.80 | - | - | - | - |
表3 汉江洋县段鱼类优势种的空间变化
Table 3 Spatial variation of dominant fish species in the Yangxian section of the Hanjiang River basin
| 物种 Species | 相对重要性指数 Index of relative importance (IRI) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 汉江 Hanjiang River | 金水河 Jinshui River | 溢水河 Yishui River | 傥水河 Tangshui River | 酉水河 Youshui River | 湑水河 Xushui River | 坪堵河 Pingdu River | |
| 宽鳍鱲 Zacco platypus | - | 1,775.83 | - | 1,904.29 | 1,312.76 | 7,872.73 | 4,161.01 |
| 马口鱼 Opsariicjthys bidens | - | 1,013.00 | - | 1,237.04 | 5,750.20 | - | - |
| 拉氏鱥 Phoxinus lagowskii | - | - | - | 1,806.22 | - | - | 6,876.49 |
| 银鮈 Squalidus argentatus | 859.67 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 似鮈 Pseudogobio vaillanti vaillant | - | 2,039.71 | - | 1,478.20 | 1,895.42 | - | 5,129.72 |
| 短须颌须鮈 Gnathopogon imberbis | - | - | 1,172.40 | 3,290.10 | 1,303.19 | 6,877.97 | 1,148.46 |
| 红尾荷马条鳅 Homatula variegata | - | - | - | - | - | 1,995.12 | - |
| 大斑花鳅 Cobitis macrostigma | - | - | 6,300.01 | - | - | - | - |
| 稀有花鳅 Cobitis rarus | - | - | 1,488.03 | - | - | - | - |
| 泥鳅 Misgurnus anguillicaudatus | - | - | 1,571.80 | - | - | - | - |
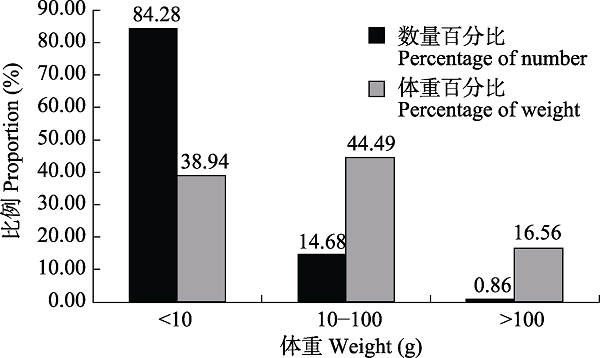
图3 汉江洋县段不同体重范围鱼类的数量和重量占总数量和总体重的比例
Fig. 3 The proportion of fish quantity and weight to total quantity and weight in different weight ranges in the Yangxian section of the Hanjiang River basin
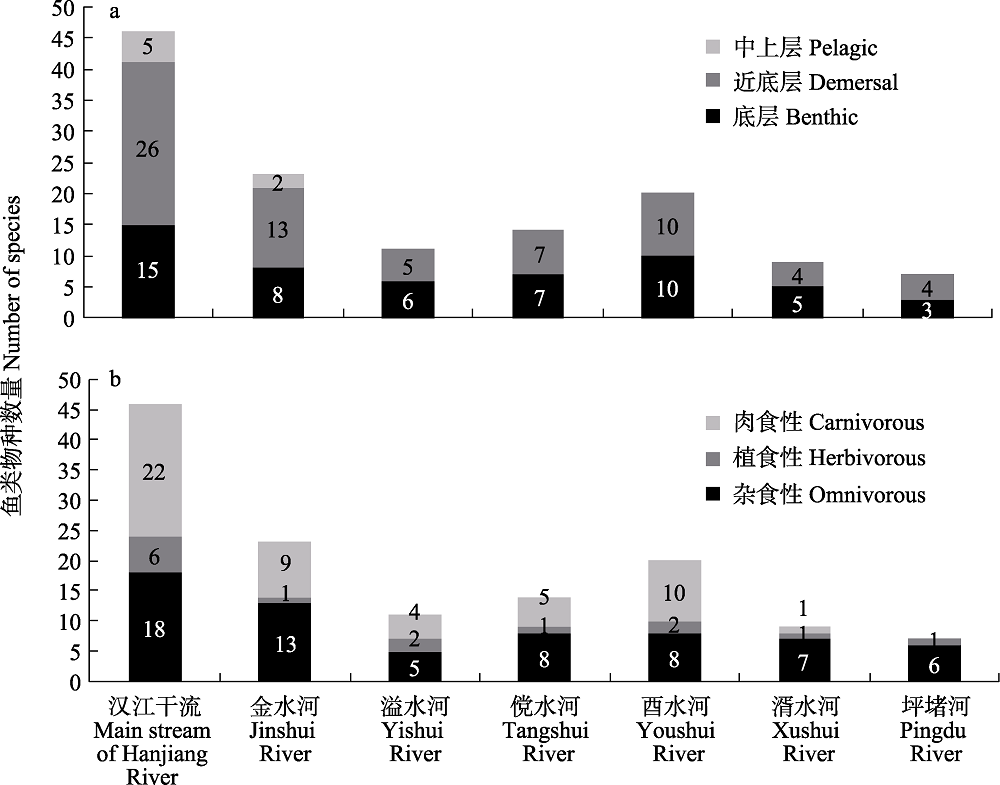
图4 汉江洋县段各河流鱼类按栖息空间以及食性划分的生态习性
Fig. 4 Ecological habits of fish in the Yangxian section of the Hanjiang River basin by habitation space and food preference
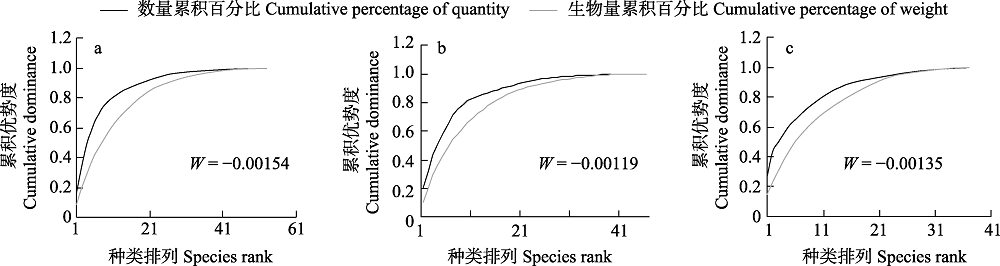
图5 汉江洋县段鱼类丰度生物量曲线。a: 鱼类总体; b: 秋季鱼类; c: 春季鱼类。
Fig. 5 Plot abundance biomass comparison of fish in the Yangxian section of the Hanjiang River basin. A, Fish population; B, Fish in autumn; C, Fish in spring.
| [1] | Blanchard F, Leloc’H F, Hily C, Boucher J (2004) Fishing effects on diversity, size and community structure of the benthic invertebrate and fish megafauna on the Bay of Biscay coast of France. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 280,249-260. |
| [2] | Cao L, Zhang E, Zang CX, Cao WX (2016) Evaluating the status of China’s continental fish and analyzing their causes of endangerment through the red list assessment. Biodiversity Science, 24,598-609. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 曹亮, 张鹗, 臧春鑫, 曹文宣 (2016) 通过红色名录评估研究中国内陆鱼类受威胁现状及其成因. 生物多样性, 24,598-609.]. | |
| [3] | Chen XH, Li XP, Cheng X (2008) Spatial-temporal distribution of fish assemblages in the upstreams of Huangpu River and Suzhou Creek. Biodiversity Science, 16,191-196. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈小华, 李小平, 程曦 (2008) 黄浦江和苏州河上游鱼类多样性组成的时空特征. 生物多样性, 16,191-196.]. | |
| [4] | Chen YY (1998) Fauna of China ∙ Osteichthyes ∙ Cypriniformes (Ⅱ). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 陈宜瑜 (1998) 中国动物志·硬骨鱼纲·鲤形目(中卷). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [5] | Chen ZC, Yuan SL, Gao JZ (1991) Yangxian County Overview. Shaanxi Administration, (16),49. (in Chinese) |
| [ 陈章存, 袁社龄, 高敬智 (1991) 洋县概况. 陕西政报, (16), 49.]. | |
| [6] | Chu XL, Zheng BS, Dai DY (1999) Fauna of China · Osteichthyes · Siluriformes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 褚新洛, 郑葆珊, 戴定远 (1999) 中国动物志·硬骨鱼纲·鲇形目. 科学出版社, 北京.]. | |
| [7] | Dang H, Ma QR, Song XF, Li HW (2019) Analysis and countermeasures of the impact of the Han-to-Weihe River Transfer Project on the water environment of the water-receiving area. Shaanxi Water Resources, (7),73-75. (in Chinese) |
| [ 党辉, 马清瑞, 宋晓峰, 李宏伟 (2019) 引汉济渭工程对受水区水环境的影响分析及对策. 陕西水利, (7),73-75.]. | |
| [8] | Fan WD (1986) The current situation of fishery resources and opinions on development and utilization in the upper reaches of the Hanjiang River. Reservoir Fisheries, (4),33-38. (in Chinese) |
| [ 范维端 (1986) 汉江上游渔业资源的现状和开发利用意见. 水利渔业, (4),33-38.]. | |
| [9] | Jiang ZG, Jiang JP, Wang YZ, Zhang E, Zhang YY, Li LL, Xie F, Cai B, Cao L, Zheng GM, Dong L, Zhang ZW, Ding P, Luo ZH, Ding CQ, Ma ZJ, Tang SH, Cao WX, Li CW, Hu HJ, Ma Y, Wu Y, Wang YX, Zhou KY, Liu SY, Chen YY, Li JT, Feng ZJ, Wang Y, Wang B, Li C, Song XL, Cai L, Zang CX, Zeng Y, Meng ZB, Fang HX, Ping XG (2016) Red List of China’s Vertebrates. Biodiversity Science, 24,500-551. (in Chinese and in English). |
| [ 蒋志刚, 江建平, 王跃招, 张鹗, 张雁云, 李立立, 谢锋, 蔡波, 曹亮, 郑光美, 董路, 张正旺, 丁平, 罗振华, 丁长青, 马志军, 汤宋华, 曹文宣, 李春旺, 胡慧建, 马勇, 吴毅, 王应祥, 周开亚, 刘少英, 陈跃英, 李家堂, 冯祚建, 王燕, 王斌, 李成, 宋雪琳, 蔡蕾, 臧春鑫, 曾岩, 孟智斌, 方红霞, 平晓鸽 (2016) 中国脊椎动物红色名录. 生物多样性, 24,500-551.]. | |
| [10] | Jing ZX, Xia J, Zhang X, Wang Q, Shi W, Ma XY (2019) Spatial and temporal distribution and variation of water quality in the middle and downstream of Hanjiang River. Research of Environmental Sciences, 32,104-115. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 景朝霞, 夏军, 张翔, 王强, 石卫, 马协一 (2019) 汉江中下游干流水质状况时空分布特征及变化规律. 环境科学研究, 32,104-115.]. | |
| [11] | Li SZ (1981) Distribution and Division of Freshwater Fishes in China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李思忠 (1981) 中国淡水鱼类的分布区划. 科学出版社, 北京.]. | |
| [12] | Li XF, Huang DM, Xie WX, Chang XL, Yang HY, Zhang YQ, He JQ (2005) Status of fisher resources in the middle reaches of the Hanjing River. Journal of Lake Sciences, 17,366-372. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李修峰, 黄道明, 谢文星, 常秀岭, 杨汉运, 张友谦, 何家庆 (2005) 汉江中游鱼类资源现状. 湖泊科学, 17,366-372.]. | |
| [13] | Lin XZ, Li DM, Liu HZ, Lin HS, Yang SR, Fan HJ, Wen RS (2016) Fish species diversity and its seasonal variations in the Chaozhou section of Hanjiang River, Guangdong Province. Biodiversity Science, 24,185-194. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 林小植, 李冬梅, 刘焕章, 林鸿生, 杨少荣, 范汉金, 温茹淑 (2016) 广东韩江潮州江段鱼类多样性及季节变化. 生物多样性, 24,185-194.]. | |
| [14] | Liu BT, Li CG (2019) Comprehensive evaluation of ecological environment in water supply area of the middle-route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 35,191-196. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘伯涛, 李崇贵 (2019) 南水北调中线工程水源区生态环境综合评价. 科技通报, 35,191-196.]. | |
| [15] | Lu JY, Lin L (2020) Problems and countermeasures on water eco-environment in Hanjiang River Ecological Economic belt. Research of Environmental Sciences, 33,1179-1186. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 卢金友, 林莉 (2020) 汉江生态经济带水生态环境问题及对策. 环境科学研究, 33,1179-1186.]. | |
| [16] | Luo H, Zhou XX (2017) Analysis on ecological impact identification and evaluation index system of Inter Basin Water Diversion Project. Environmental Science and Management, 42,190-194. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 罗昊, 周雪欣 (2017) 跨流域调水工程的生态影响识别及评价指标体系研究. 环境科学与管理, 42,190-194.]. | |
| [17] | Ma YL, Peng K (2020) Research on optimal operation of cascade reservoirs in Hanjiang River Basin. Water Resources Planning and Design, (2),63-66, 101. (in Chinese) |
| [ 马雅丽, 彭昆 (2020) 汉江流域梯级水库群优化调度研究. 水利规划与设计, (2),63-66, 101.]. | |
| [18] | Mao YZ (2014) Research on general arrangement of Huangjinxia hydro-junction. Shaanxi Water Resources, (2),53-55. (in Chinese) |
| [ 毛拥政 (2014) 黄金峡水利枢纽总布置研究. 陕西水利, (2),53-55.]. | |
| [19] | Margalef R (1958) Information theory in ecology. General System Yearbook, 3,36-71. |
| [20] | State Environmental Protection Administration (1992) Aquatic Monitoring Manual. Southeast University Press, Nanjing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 国家环保总局 (1992) 水生生物监测手册. 东南大学出版社, 南京.]. | |
| [21] | Parry GDR, Johnson MS, Bell RM, Edwards RW, Wathern P (1984) Ecological methodology. In: Planning and Ecology (eds Roberts RD, Roberts TM), pp.37-98. Springer, Dordrecht. |
| [22] | Pinkas L, Oliphant MS, Iverson ILK (1970) Food habits of albacore, bluefin tuna, and bonito in California waters. Fish Bulletin, 152,1-105. |
| [23] | Shaanxi Institute of Zoology, Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Department of Biology, Lanzhou University (1987) Fishes in Qinling Mountains Area. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 陕西省动物研究所, 中国科学院水生生物研究所, 兰州大学生物系 (1987) 秦岭鱼类志. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [24] | Wang DQ, Gao L, Duan XB, Chen DQ, Meng Q, Liu SP (2019) Preliminary analysis of the early resources of fish in the lower reaches of the Hanjiang River and the effect of cascade joint ecological regulation on fish reproduction. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 28,1909-1917. (in Chinese) |
| [ 汪登强, 高雷, 段辛斌, 陈大庆, 孟秋, 刘绍平 (2019) 汉江下游鱼类早期资源及梯级联合生态调度对鱼类繁殖影响的初步分析. 长江流域资源与环境, 28,1909-1917.]. | |
| [25] | Wang KF, Zhang HX, Yang XZ, Wei WK, Zhao Y, Hu WX (2003) Fish resources and diversity in Changqing National Reserve. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 31,5-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王开锋, 张红星, 杨兴中, 魏武科, 赵阳, 胡万兴 (2003) 陕西长青自然保护区鱼类资源及其多样性. 陕西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 31,5-9.]. | |
| [26] | Wang QJ, Zhao H, Luo L, Zhang HX, Wang ZQ, Li JW (2012) Study on the diversity of fish resources in the Xushui River Basin. Journal of Hydroecology, 33,100-103. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王启军, 赵虎, 罗磊, 张红星, 王中乾, 李军文 (2012) 湑水河流域鱼类资源多样性研究. 水生态学杂志, 33,100-103.]. | |
| [27] | Wang XL, Song XX (2019) Study on the change of hydrological regime in the middle and lower reaches of Hanjiang River under the influence of cascade water conservancy projects. Journal of Central China Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 53,685-691. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王学雷, 宋辛辛 (2019) 梯级水库叠加影响下汉江中下游流域水文情势变化研究. 华中师范大学学报(自然科学版), 53,685-691.]. | |
| [28] | Wang Z, Song C, Yan WL, Zhu LF (2019) Biodiversity and spatial pattern of fish in the Pingchuan segment of the upper reaches of Hanjiang River. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 28,1675-1681. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王卓, 宋策, 闫文龙, 朱来福 (2019) 汉江上游平川段鱼类群落多样性及空间格局分析. 长江流域资源与环境, 28,1675-1681.]. | |
| [29] | Wu HL, Zhong JS (2008) Fauna of China ∙ Osteichthyes ∙ Perciformes (V) ∙ Gobioidei. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 伍汉霖, 钟俊生 (2008) 中国动物志·硬骨鱼纲·鲈形目五·虾虎鱼亚目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [30] | Wu XW (1981) Fishes of Cyprinidae in China (I). Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai. (in Chinese) |
| [ 伍献文 (1981) 中国鲤科鱼类志(上卷). 上海科学技术出版社, 上海.] | |
| [31] | Wu XW (1982) Fishes of Cyprinidae in China (II). Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai. (in Chinese) |
| [ 伍献文 (1982) 中国鲤科鱼类志(下卷). 上海科学技术出版社, 上海.] | |
| [32] | Yue PQ (2000) Fauna of China · Osteichthyes · Cypriniformes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 乐佩琦 (2000) 中国动物志·硬骨鱼纲·鲤形目. 科学出版社. 北京.] | |
| [33] | Zhang CG, Zhao YH (2016) Species Diversity and Distribution of Inland Fishes in China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张春光, 赵亚辉 (2016) 中国内陆鱼类物种与分布. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [34] | Zhang HB, Zhong L, Yang JY, Mao ZY, Yang GL, Li Y, Xu TQ (2006) On fish species diversity of Hanjiang River in Shaanxi Province. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 34,60-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张海斌, 钟林, 杨军严, 毛治彦, 杨甘霖, 李云, 许涛清 (2006) 汉江陕西段河流湿地鱼类物种多样性研究. 陕西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 34,60-66.]. | |
| [35] | Zhang PL, Zhu SH, Wan JW, Li XF (2017) Design of high-head fish-pass structure for Huangjinxia Water Control Project. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 48(28),44-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张鹏利, 朱世洪, 万继伟, 黎贤访 (2017) 黄金峡水利枢纽高水头过鱼建筑物设计. 水利水电技术, 48(28),44-48.]. |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 周昊, 王茗毅, 张楚格, 肖治术, 欧阳芳. 昆虫旅馆在独栖蜂多样性保护中的现状与挑战[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24472-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [6] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [7] | 徐欢, 辛凤飞, 施宏亮, 袁琳, 薄顺奇, 赵欣怡, 邓帅涛, 潘婷婷, 余婧, 孙赛赛, 薛程. 生态修复技术集成应用对长江口北支生境与鸟类多样性提升效果评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24478-. |
| [8] | 易木荣, 卢萍, 彭勇, 汤勇, 许久恒, 尹浩萍, 张路杨, 翁晓东, 底明晓, 雷隽, 卢宸祺, 曹如君, 戴年华, 占德洋, 童媚, 楼智明, 丁永刚, 柴静, 车静. 北潦河金家水支流江西大鲵野外种群现状及栖息地评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24145-. |
| [9] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [10] | 李沫潼, 何拓, 李薇, 廖菁, 曾岩. 从CITES的术语看野生动植物国际贸易监管规则[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24545-. |
| [11] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [14] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| [15] | 周志华, 金效华, 罗颖, 李迪强, 岳建兵, 刘芳, 何拓, 李希, 董晖, 罗鹏. 中国林草部门落实《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》的机制、成效分析及建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24487-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn