



生物多样性 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (3): 351-360. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020189 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020189
张菁1, 白煜1, 黄子强1, 张正旺2, 李东来1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-05-07
接受日期:2020-08-15
出版日期:2021-03-20
发布日期:2020-09-20
通讯作者:
李东来
作者简介:E-mail: lidonglai@lnu.edu.cn基金资助:
Jing Zhang1, Yu Bai1, Ziqiang Huang1, Zhengwang Zhang2, Donglai Li1,*( )
)
Received:2020-05-07
Accepted:2020-08-15
Online:2021-03-20
Published:2020-09-20
Contact:
Donglai Li
摘要:
盐地碱蓬(Suaeda salsa)盐沼湿地是黄渤海地区河口区域的重要湿地类型, 是水鸟迁徙停歇期的重要栖息地。本研究以辽河口国家级自然保护区为研究地点, 通过对盐地碱蓬盐沼湿地和相邻泥质滩涂两个固定样区连续三年的水鸟组成调查和行为观察, 分析盐地碱蓬盐沼湿地在鸻鹬类多样性维持和栖息地利用中的作用。共记录到鸻鹬类水鸟28种6,348只次, 其中盐地碱蓬湿地记录到4科13种, 泥质滩涂记录到4科27种, 泥质滩涂的物种多样性显著高于盐地碱蓬盐沼湿地。此外, 盐地碱蓬盐沼湿地与相邻的泥质滩涂的鸻鹬类鸟类群落组成存在较大差异, 盐地碱蓬盐沼湿地的鸟类群落组成以体型较大的大杓鹬(Numenius madagascariensis)、白腰杓鹬(N. arquata)、灰鸻(Pluvialis squatarola)等为主, 而泥质滩涂以环颈鸻(Charadrius alexandrinus)、黑腹滨鹬(Calidris alpina)等小型鸻鹬类为主, 这说明两种生境在鸟类多样性维持中具有不同的功能。行为分析发现, 泥质滩涂中栖息鸟类的主要行为为取食(58.71%-93.26%), 而盐地碱蓬盐沼湿地鸟类的行为既包括较大比例的取食, 也包括休息, 特别是在春季迁徙期。这进一步说明, 两种生境在水鸟的栖息地利用中具有一定的生态功能差异。尽管盐地碱蓬盐沼湿地记录到的鸟类物种数和数量均低于泥质滩涂, 但是, 两种生境中存在较大比例的共同分布物种, 这说明其生态功能具有较强的生态互补性, 二者作为一种独特的湿地景观组合, 在鸻鹬类迁徙停歇期的栖息地利用和物种多样性维持中发挥着不可替代的作用。
张菁, 白煜, 黄子强, 张正旺, 李东来 (2021) 盐地碱蓬盐沼与相邻泥质滩涂湿地迁徙期鸻鹬类的群落组成及行为差异. 生物多样性, 29, 351-360. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020189.
Jing Zhang, Yu Bai, Ziqiang Huang, Zhengwang Zhang, Donglai Li (2021) Community composition and behavioral differences of migrating shorebirds between two habitats within a Suaeda salsa saltmarsh-mudflat wetland mosaics. Biodiversity Science, 29, 351-360. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020189.
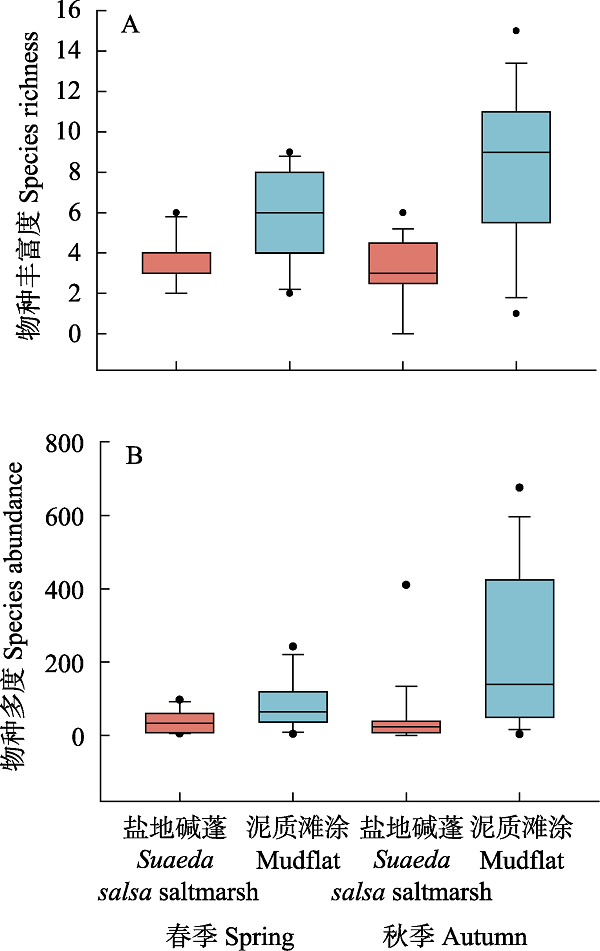
图2 不同生境和季节间鸻鹬鸟类物种丰富度(A)和物种多度(B)差异。春季: n = 11; 秋季: n = 17。箱子上下边界代表上下四分位数, 箱子中间实线为中位数, 上下边缘分别代表除异常值外的最大值和最小值, 实心圆点为离异值。
Fig. 2 The difference in species richness (A) and abundance (B) of shorebirds between two habitats in different migratory seasons. Spring: n = 11; autumn: n = 17. The solid lines in the box denote the median value and box edges show the upper and lower quartiles. The maximum and minimum show the largest and lowest data point excluding any outliers and the solid circles show outliers.
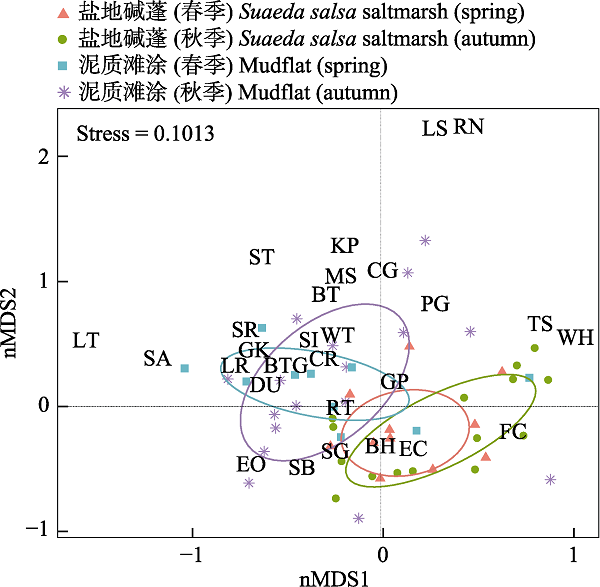
图3 不同生境和季节间鸻鹬类群落结构nMDS分析的权重图。FC: 大杓鹬; EC: 白腰杓鹬; WH: 中杓鹬; CG: 青脚鹬; CR: 红脚鹬; RT: 翻石鹬; TS: 翘嘴鹬; SR: 鹤鹬; DU: 黑腹滨鹬; BTG: 斑尾塍鹬; GK: 大滨鹬; EO: 蛎鹬; MS: 泽鹬; ST: 尖尾滨鹬; SA: 三趾滨鹬; RN: 红颈滨鹬; GP: 灰鸻; KP: 环颈鸻; PG: 金斑鸻; LS: 蒙古沙鸻; LR: 金眶鸻; SG: 黑嘴鸥; BH: 红嘴鸥; SI: 西伯利亚银鸥; SB: 灰背鸥; BT: 黑尾鸥; WT: 白翅浮鸥; LT: 白额燕鸥。
Fig. 3 nMDS plots of shorebird community between two habitats (Suaeda salsa saltmarsh vs. mudflat) in two migratory seasons. FC, Numenius madagascariensis; EC, Numenius arquata; WH, Numenius phaeopus; CG, Tringa nebularia; CR, Tringa totanus; RT, Arenaria interpres; TS, Xenus cinereus; SR, Tringa erythropus; DU, Calidris apoina; BTG, Limosa lapponica; GK, Calidris tenuirostris; EO, Haematopus ostralegus; MS, Tringa stagnatilis; ST, Calidris acuminata; SA, Calidris alba; RN,Calidris ruficollis; GP, Pluvialis squatarola; KP, Charadrius alexandrinus; PG, Pluvialis fulva; LS, Charadrius mongolus; LR, Charadrius dubius; SG, Saundersilarus saundersi; BH, Chroicocephalus ridibundus; SI, Larus vegae; SB, Larus schistisagus; BT, Larus crassirostris; WT, Chlidonias leucopterus; LT, Sternula albifrons.
| 盐地碱蓬 Suaeda salsa saltmarsh | 泥质滩涂 Mudflat | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 Spring | 秋季 Autumn | 春季 Spring | 秋季 Autumn | |
| 盐地碱蓬(春季) Suaeda salsa saltmarsh (Spring) | 8 | 6 (0.46) | 6 (0.40) | 8 (0.32) |
| 盐地碱蓬(秋季) Suaeda salsa saltmarsh (Autumn) | 11 | 7 (0.41) | 11 (0.44) | |
| 泥质滩涂(春季) Mudflat (Spring) | 13 | 11 (0.41) | ||
| 泥质滩涂(秋季) Mudflat (Autumn) | 25 | |||
表1 不同季节和生境间鸻鹬类共有种的数量及其相似度
Table 1 Number of shared species and similarity coefficients of shorebirds among different seasons and habitats
| 盐地碱蓬 Suaeda salsa saltmarsh | 泥质滩涂 Mudflat | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 Spring | 秋季 Autumn | 春季 Spring | 秋季 Autumn | |
| 盐地碱蓬(春季) Suaeda salsa saltmarsh (Spring) | 8 | 6 (0.46) | 6 (0.40) | 8 (0.32) |
| 盐地碱蓬(秋季) Suaeda salsa saltmarsh (Autumn) | 11 | 7 (0.41) | 11 (0.44) | |
| 泥质滩涂(春季) Mudflat (Spring) | 13 | 11 (0.41) | ||
| 泥质滩涂(秋季) Mudflat (Autumn) | 25 | |||
| [1] | Bamford M, Watkins D, Bancroft W, Tischler G, Wahl J (2008) Migratory Shorebirds of the East Asian-Australasian Flyway Population Estimates and Internationally Important Sites. Wetlands International Oceania, Canberra, Australia. |
| [2] |
Battley PF, Warnock N, Tibbitts TL, Gill RE Jr, Piersma T, Hassell CJ, Douglas DC, Mulcahy DM, Gartrell BD, Schuckard R, Melville DS, Riegen AC (2012) Contrasting extreme long-distance migration patterns in bar-tailed godwits Limosa lapponica. Journal of Avian Biology, 43,21-32.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Burger J, Howe MA, Hahn DC, Chase J (1997) Effects of tide cycles on habitat selection and habitat partitioning by migrating shorebirds. The Auk, 94,743-758. |
| [4] | Chen L, Zhang ML, Li FL, Yu WY (2019) Structure and diversity of bird communities in Liaohekou Wetlands in Spring 2017. Wetland Science, 17,146-151. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈龙, 张美玲, 李凤丽, 于文颖 (2019) 2017年春季辽河口湿地鸟类群落结构和多样性. 湿地科学, 17,146-151.]. | |
| [5] |
Chen P, Zhang Y, Zhu XJ, Lu CH (2019) Distribution of crabs along a habitat gradient on the Yellow Sea coast after Spartina alterniflora invasion. PeerJ, 7,e6775.
DOI URL PMID |
| [6] | China Coastal Waterbird Census Group, Bai QQ, Chen JZ, Chen ZH, Dong GT, Dong JT, Dong WX, Fu VWK, Han YX, Lu G, Li J, Liu Y, Lin Z, Meng DR, Martinez J, Ni GH, Shan K, Sun RJ, Tian SX, Wang FQ, Xu ZW, Yu YT, Yang J, Yang ZD, Zhang L, Zhang M, Zeng XW (2015) Identification of coastal wetlands of international importance for waterbirds: A review of China Coastal Waterbird Surveys 2005-2013. Avian Research, 6,12. |
| [7] | Choi CY, Battley PF, Potter MA, Ma ZJ, Melville DS, Sukkaewmanee P (2017) How migratory shorebirds selectively exploit prey at a staging site dominated by a single prey species. The Auk, 134,76-91. |
| [8] | Choi CY, Battley PF, Potter MA, Rogers KG, Ma ZJ (2015) The importance of Yalu Jiang coastal wetland in the north Yellow Sea to bar-tailed godwits Limosa lapponica and great knots Calidris tenuirostris during northward migration. Bird Conservation International, 25,53-70. |
| [9] | Choi CY, Gan XJ, Hua N, Wang Y, Ma ZJ (2014) The habitat use and home range analysis of Dunlin (Calidris alpina) in Chongming Dongtan, China and their conservation implications. Wetlands, 34,255-266. |
| [10] | Darnell TM, Smith EH (2004) Avian use of natural and created salt marsh in Texas, USA. Waterbirds, 27,355-361. |
| [11] | Delectis Florae Reioublicae Popularis Sinicae Agendae Academiae Sinicae Edita (1979) Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 中国科学院中国植物志编委会 (1979) 中国植物志. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [12] | Duan HL, Xia SX, Jackson MV, Zhao N, Liu Y, Teng JK, Meng Z, Yu XB, Shi JB (2020) Identifying new sites of significance to waterbirds conservation and their habitat modification in the Yellow and Bohai seas in China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 22,e01031. |
| [13] | Feng CC, Zhang SD, Liu WL, Zhao TT, Cao YD, Xiangyu JG, Ma ZJ (2019) Food composition of five migratory shorebirds at the Dandong Yalu River coastal wetland in spring migration. Journal of Fudan University (Natural Science), 58,497-505. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 冯晨晨, 张守栋, 刘文亮, 赵天天, 曹一迪, 向余劲攻, 马志军 (2019) 丹东鸭绿江口湿地春季5种迁徙鹬类的食物组成. 复旦学报(自然科学版), 58,497-505.]. | |
| [14] | Gan XJ, Cai YT, Choi CY, Ma ZJ, Chen JK, Li B (2009) Potential impacts of invasive Spartina alterniflora on spring bird communities at Chongming Dongtan, a Chinese wetland of international importance. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 83,211-218. |
| [15] | Gomez-Sapiens MM, Soto-Montoya E, Hinojosa-Huerta O (2013) Shorebird abundance and species diversity in natural intertidal and non-tidal anthropogenic wetlands of the Colorado River delta, Mexico. Ecological Engineering, 59,74-83. |
| [16] | Hou WH, Lu WZ, Zhao KY, Zhang JL, Zhang RJ, Lei W, Liao GX, Liu CA (2019) Research on the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of Helice tientsinensis in red beach of the Liaohe estuary. Marine Environmental Science, 38,272-277. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 侯文昊, 卢伟志, 赵开远, 张家林, 张瑞瑾, 雷威, 廖国祥, 刘长安 (2019) 辽河口红海滩天津厚蟹种群时空分布特征研究. 海洋环境科学, 38,272-277.]. | |
| [17] | Howes J, Bakewell D (1989) Shorebird Studies Manual. AWB Press, Kuala Lumpur. |
| [18] | Hu Y, Li QH, Li Y, He Y, Han MS, Sun RG, Gao TJ (2019) Analysis of structure and dynamics of metazooplankton community in Baihua Reservoir of Guizhou Province based on nMDS and RDA. Research of Environmental Sciences, 32,1510-1518. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 胡艺, 李秋华, 李钥, 何应, 韩孟书, 孙荣国, 高廷进 (2019) 基于nMDS和RDA方法分析贵州百花水库后生浮游动物群落结构动态. 环境科学研究, 32,1510-1518.]. | |
| [19] | Hua N (2014) Fuel Deposition of Shorebirds at Stopping Sites in the Yellow Sea During Spring Migration. PhD dissertation, Fudan University, Shanghai. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 华宁 (2014) 鸻鹬类春季在黄海区域迁徙停歇地的能量积累. 博士学位论文, 复旦大学, 上海.] | |
| [20] | Hua N, Tan K, Chen Y, Ma ZJ (2015) Key research issues concerning the conservation of migratory shorebirds in the Yellow Sea region. Bird Conservation International, 25,38-52. |
| [21] |
Jackson MV, Carrasco LR, Choi CY, Li J, Ma ZJ, Melville DS, Mu T, Peng HB, Woodworth BK, Yang ZY, Zhang L, Fuller RA (2019) Multiple habitat use by declining migratory birds necessitates joined-up conservation. Ecology and Evolution, 9,2505-2515.
URL PMID |
| [22] | Jiang HX, Chu GZ, Qian FW, Lu J (2002) Breeding microhabitat selection of Saunders’ gull (Larus saundersi) in Yancheng of Jiangsu Province, China. Biodiversity Science, 10,170-174. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 江红星, 楚国忠, 钱法文, 陆军 (2002) 江苏盐城黑嘴鸥 ( Larus saundersi)繁殖微生境的选择. 生物多样性, 10,170-174.]. | |
| [23] | Jiang JH, Dai NH, Shao MQ, Huang ZQ, Lu P (2015) Time budget and foraging behavior of wintering common cranes inhabiting rice fields of Poyang Lake. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35,270-279. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蒋剑虹, 戴年华, 邵明勤, 黄志强, 卢萍 (2015) 鄱阳湖区稻田生境中灰鹤越冬行为的时间分配与觅食行为. 生态学报, 35,270-279.]. | |
| [24] | Jiang KY, Wu M, Shao XX, Lü Y (2013) Diversity of bird communities in southern Hangzhou Bay and the Qiantang River estuary and their responses to reclamation of intertidal mudflats. Biodiversity Science, 21,214-223. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蒋科毅, 吴明, 邵学新, 吕咏 (2013) 杭州湾及钱塘江河口南岸滨海湿地鸟类群落多样性及其对滩涂围垦的响应. 生物多样性, 21,214-223.]. | |
| [25] | Jing K, Ma ZJ, Li B, Li JH, Chen JK (2007) Foraging strategies involved in habitat use of shorebirds at the intertidal area of Chongming Dongtan, China. Ecological Research, 22,559-570. |
| [26] | Kong DJ, Yang XJ, Zhong XY, Dao MB, Zhu Y (2008) Diurnal time budget and behavior rhythm of wintering black-necked crane ( Grus nigricollis) at Dashanbao in Yunnan. Zoological Research, 29,195-202. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孔德军, 杨晓君, 钟兴耀, 道美标, 朱勇 (2008) 云南大山包黑颈鹤日间越冬时间分配和活动节律. 动物学研究, 29,195-202.]. | |
| [27] | Kruskal JB (1964) Nonmetric multidimensional scaling: A numerical method. Psychometrika, 29,115-129. |
| [28] |
Lehnen SE, Krementz DG (2013) Use of aquaculture ponds and other habitats by autumn migrating shorebirds along the lower Mississippi River. Environmental Management, 52,417-426.
DOI URL PMID |
| [29] | Lei WP, Masero JA, Piersma T, Zhu BR, Yang HY, Zhang ZW (2018) Alternative habitat: The importance of the Nanpu Saltpans for migratory waterbirds in the Chinese Yellow Sea. Bird Conservation International, 28,549-566. |
| [30] |
Li DL, Chen SH, Guan L, Lloyd H, Liu YL, Lü JZ, Zhang ZW (2011) Patterns of waterbird community composition across a natural and restored wetland landscape mosaic, Yellow River delta, China. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 91,325-332.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Li DL, Chen SH, Lloyd H, Zhu SY, Shan K, Zhang ZW (2013) The importance of artificial habitats to migratory waterbirds within a natural/artificial wetland mosaic, Yellow River delta, China. Bird Conservation International, 23,184-198.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Li DL, Ding YQ, Yuan Y, Lloyd H, Zhang ZW (2014) Female tidal mudflat crabs represent a critical food resource for migratory red-crowned cranes in the Yellow River delta, China. Bird Conservation International, 24,416-428.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Li DL, Liu Y, Sun XH, Lloyd H, Zhu SY, Zhang SY, Wan DM, Zhang ZW (2017) Habitat-dependent changes in vigilance behaviour of red-crowned crane influenced by wildlife tourism. Scientific Reports, 7,16614.
DOI URL PMID |
| [34] | Li DL, Zhang J, Liu Y, Lloyd H, Pagani-Núñez E, Zhang ZW (2020) Differences in dietary specialization, habitat use and susceptibility to human disturbance influence feeding rates and resource partitioning between two migratory Numenius curlew species. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 245,106990. |
| [35] | Lu W, Xiao J, Lei W, Du J, Li Z, Cong P, Hou W, Zhang J, Chen L, Zhang Y, Liao GX (2018) Human activities accelerated the degradation of saline seepweed red beaches by amplifying top-down and bottom-up forces. Ecosphere, 9,e02352. |
| [36] | Ma ZJ, Gan XJ, Cai YT, Chen JK, Li B (2011) Effects of exotic Spartina alterniflora on the habitat patch associations of breeding saltmarsh birds at Chongming Dongtan in the Yangtze River estuary, China. Biological Invasions, 13,1673-1686. |
| [37] | Ma ZJ, Li B, Zhao B, Jing K, Tang S, Chen J (2004) Are artificial wetlands good alternatives to natural wetlands for waterbirds?—A case study on Chongming Island, China. Biodiversity and Conservation, 13,333-350. |
| [38] |
Ma ZJ, Melville DS, Liu JG, Chen L, Yang HY, Ren WW, Zhang ZW, Piersma T, Li B (2014) Rethinking China’s new great wall. Science, 346,912-914.
DOI URL PMID |
| [39] | Masero JA, Pérez-Hurtado A (2001) Importance of the supratidal habitats for maintaining overwintering shorebird populations: How redshanks use tidal mudflats and adjacent saltworks in Southern Europe. The Condor, 103,21-30. |
| [40] | Masero JA, Pérez-Hurtado A, Castro M, Arroyo GM (2000) Complementary use of intertidal mudflats and adjacent salinas by foraging waders. Ardea, 88,177-191. |
| [41] | Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (2005) Ecosystems and Human Well-being: Current State and Trends. Island Press, Washington, DC. |
| [42] | Moreno S, Villafuerte R, Delibes M (1996) Cover is safe during the day but dangerous at night: The use of vegetation by European wild rabbits. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 74,1656-1660. |
| [43] | Mou XJ, Liu XT, Yan BX, Cui BS (2015) Classification system of coastal wetlands in China. Wetland Science, 13 (1),19-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 牟晓杰, 刘兴土, 阎百兴, 崔保山 (2015) 中国滨海湿地分类系统. 湿地科学, 13(1),19-26.]. | |
| [44] |
Murray NJ, Phinn SR, DeWitt M, Ferrari R, Johnston R, Lyons MB, Clinton N, Thau D, Fuller RA (2019) The global distribution and trajectory of tidal flats. Nature, 565,222-225.
DOI URL PMID |
| [45] | Peng HB, Anderson GQA, Chang Q, Choi CY, Chowdhury SU, Clark NA, Gan XJ, Hearn RD, Li J, Lappo EG, Liu WL, Ma ZJ, Melville DS, Phillips JF, Syroechkovskiy EE, Tong MX, Wang SL, Zhang L, Zöckler C (2017) The intertidal wetlands of southern Jiangsu Province, China—Globally important for spoon-billed sandpipers and other threatened waterbirds, but facing multiple serious threats. Bird Conservation International, 27,305-322. |
| [46] |
Studds CE, Kendall BE, Murray NJ, Wilson HB, Rogers DI, Clemens RS, Gosbell K, Hassell CJ, Jessop R, Melville DS, Milton DA, Minton CD, Possingham HP, Riegen AC, Straw P, Woehler EJ, Fuller RA (2017) Rapid population decline in migratory shorebirds relying on Yellow Sea tidal mudflats as stopover sites. Nature Communications, 8,14895.
URL PMID |
| [47] | Tchabovsky AV, Krasnov B, Khokhlova IS, Shenbrot GI (2001) The effect of vegetation cover on vigilance and foraging tactics in the fat sand rat Psammomys obesus. Journal of Ethology, 19,105-113. |
| [48] | Tian Y, Luo L, Mao D, Wang Z, Li L, Liang J (2017) Using Landsat images to quantify different human threats to the Shuangtai Estuary Ramsar site, China. Ocean & Coastal Management, 135,56-64. |
| [49] | Van Gils JA, Battley PF, Piersma T, Drent R (2005) Reinterpretation of gizzard sizes of red knots world-wide emphasises overriding importance of prey quality at migratory stopover sites. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 272,2609-2618. |
| [50] | Wan S, Qin P, Liu J, Zhou H (2009) The positive and negative effects of exotic Spartina alterniflora in China. Ecological Engineering, 35,444-452. |
| [51] | Yang HY, Chen B, Ma ZJ, Hua N, Van Gils JA, Zhang ZW, Piersma T (2013) Economic design in a long-distance migrating molluscivore: How fast-fuelling red knots in Bohai Bay, China, get away with small gizzards. Journal of Experimental Biology, 216,3627-3636. |
| [52] | Yang YX (2002) New knowledge on the progress of international wetland science research and priority field and prospect of Chinese wetland science research. Advance in Earth Sciences, 17,508-514. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨永兴 (2002) 国际湿地科学研究进展和中国湿地科学研究优先领域与展望. 地球科学进展, 17,508-514.]. | |
| [53] | Zhang A, Yuan X, Yang X, Shao S, Li J, Ding D (2016) Temporal and spatial distributions of intertidal macrobenthos in the sand flats of the Shuangtaizi Estuary, Bohai Sea in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36,172-179. |
| [54] | Zhang X, Hua N, Ma Q, Xue WJ, Feng XS, Wu W, Tang CD, Ma ZJ (2011) Diet of great knots (Calidris tenuirostris) during spring stopover at Chongming Dongtan, China. Chinese Birds, 2,27-32. |
| [55] | Zhang X, Hua N, Tang CD, Ma Q, Xue WJ, Wu W, Ma ZJ (2013) Food composition and sources of dunlins ( Calidris alpina) at Chongming Dongtan: Stable isotope analysis. Journal of Fudan University (Natural Science), 52,112-118. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张璇, 华宁, 汤臣栋, 马强, 薛文杰, 吴巍, 马志军 (2013) 崇明东滩黑腹滨鹬(Calidris alpina)食物来源和组成的稳定同位素分析. 复旦学报(自然科学版), 52,112-118.]. | |
| [56] | Zheng GM (2012) Ornithology. Beijing Normal University Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 郑光美 (2012) 鸟类学. 北京师范大学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [57] | Zheng GM (2017) A Checklist on the Classification and Distribution of the Birds of China, 3rd edn. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 郑光美 (2017) 中国鸟类分类与分布名录(第三版). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [58] | Zhou B, Zhou LZ, Chen JY, Cheng YQ, Xu WB (2010) Diurnal time-activity budgets of wintering hooded cranes (Grus monacha) in Shengjin Lake, China. Waterbirds, 33,110-115. |
| [1] | 王双贵, 郭志宏, 顾伯健, 李天醍, 苏玉兵, 马伯丞, 管宏信, 黄巧雯, 王放, 张卓锦. 六盘山华北豹的栖息地利用及保护建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 22342-. |
| [2] | 张淑萍, 郑光美, 徐基良. 城市化对城市麻雀栖息地利用的影响:以北京市为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2006, 14(5): 372-381. |
| [3] | 徐基良, 张晓辉, 张正旺, 郑光美, 阮祥锋, 张可银. 白冠长尾雉雄鸟的冬季活动区与栖息地利用研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2005, 13(5): 416-423. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn