



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (10): 1174-1181. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020018 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020018
所属专题: 青藏高原生物多样性与生态安全; 生物入侵
邓亨宁1, 鞠文彬1,2, 高云东1,2, 张君议1, 李诗琦1,2, 高信芬1,2,*( ), 徐波1,2,*(
), 徐波1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-01-14
接受日期:2020-05-12
出版日期:2020-10-20
发布日期:2020-10-20
通讯作者:
高信芬,徐波
作者简介:E-mail: xfgao@cib.ac.cn;基金资助:
Hengning Deng1, Wenbin Ju1,2, Yundong Gao1,2, Junyi Zhang1, Shiqi Li1,2, Xinfen Gao1,2,*( ), Bo Xu1,2,*(
), Bo Xu1,2,*( )
)
Received:2020-01-14
Accepted:2020-05-12
Online:2020-10-20
Published:2020-10-20
Contact:
Xinfen Gao,Bo Xu
摘要:
横断山区为全球生物多样性热点地区之一, 也是全国生态屏障的重要组成部分。新建川藏铁路雅安至昌都段横跨横断山核心地区, 铁路建设形成的交通网络将沿线生物多样性热点区域与外界相连, 导致生物入侵风险陡增。为获得区域内外来入侵植物的种类及分布特征信息, 为即将开始的铁路工程建设、生态保护及生态修复等工作提供参考, 我们在雅安-昌都段内选择43个位点各进行长度1 km、宽度20 m的样线调查。研究结果显示: 雅安-昌都段共发现外来入侵植物58种, 隶属于18科42属, 其中出现频度最高的种类依次是牛膝菊(Galinsoga parviflora)、秋英(Cosmos bipinnatus)和鬼针草(Bidens pilosa)。从危害等级来看, 其中10种为恶性入侵种, 16种为严重入侵种, 8种为局部入侵种, 15种为一般入侵种, 9种为有待观察种, 超过半数种类具有明显入侵性。原产地分析结果显示美洲是该区域外来入侵植物的主要原产地。基于海拔及主要河流区段的比较研究发现: 入侵植物的种类数量呈现出明显的由东向西、由低海拔向高海拔逐渐递减的趋势, 该分布格局是环境因子和人类活动共同作用的结果。结合铁路沿线入侵现状和生境特征, 本文分析了铁路建设可能造成的外来植物入侵风险, 并针对入侵的防范提出了相应的建议。
邓亨宁, 鞠文彬, 高云东, 张君议, 李诗琦, 高信芬, 徐波 (2020) 新建川藏铁路(雅安-昌都段)沿线外来入侵植物种类及分布特征. 生物多样性, 28, 1174-1181. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020018.
Hengning Deng, Wenbin Ju, Yundong Gao, Junyi Zhang, Shiqi Li, Xinfen Gao, Bo Xu (2020) The species composition and distributional characteristics of invasive alien plants along the new Sichuan-Tibet Railway (Ya’an to Changdu section). Biodiversity Science, 28, 1174-1181. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020018.
| 物种 Species | 产地 Origin | F | TD | 物种 Species | 产地 Origin | F | TD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苋科 Amaranthaceae | 土荆芥 D. ambrosioides | 美洲 America | 4.65 | 1 | |||
| 莲子草属 Alternanthera | 旋花科 Convolvulaceae | ||||||
| 喜旱莲子草 A. philoxeroides | 美洲 America | 18.60 | 1 | 番薯属 Ipomoea | |||
| 刺花莲子草 A. pungens | 美洲 America | 4.65 | 2 | 牵牛 I. nil | 美洲 America | 4.65 | 2 |
| 苋属 Amaranthus | 圆叶牵牛 I. purpurea | 美洲 America | 16.28 | 1 | |||
| 凹头苋 A. blitum | 美洲 America | 9.30 | 2 | 豆科 Fabaceae | |||
| 老鸦谷 A. cruentus | 美洲 America | 6.98 | 3 | 苜蓿属 Medicago | |||
| 绿穗苋 A. hybridus | 美洲 America | 4.65 | 2 | 南苜蓿 M. polymorpha | 跨洲 Cross continent | 4.65 | 4 |
| 千穗谷 A. hypochondriacus | 美洲 America | 2.33 | 3 | 紫苜蓿 M. sativa | 亚洲 Asia | 4.65 | 4 |
| 苋 A. tricolor | 亚洲 Asia | 9.30 | 3 | 草木犀属 Melilotus | |||
| 菊科 Asteraceae | 白花草木犀 M. albus | 跨洲 Cross continent | 11.63 | 4 | |||
| 紫菀属 Aster | 草木犀 M. officinalis | 跨洲 Cross continent | 2.33 | 4 | |||
| 钻叶紫菀 A. subulatus | 美洲 America | 16.28 | 1 | 车轴草属 Trifolium | |||
| 鬼针草属 Bidens | 红车轴草 T. pratense | 跨洲 Cross continent | 6.98 | 2 | |||
| 婆婆针 B. bipinnata | 美洲 America | 2.33 | 3 | 白车轴草 T. repens | 跨洲 Cross continent | 27.91 | 2 |
| 大狼杷草 B. frondosa | 美洲 America | 2.33 | 1 | 野豌豆属 Vicia | |||
| 鬼针草 B. pilosa | 美洲 America | 34.88 | 1 | 长柔毛野豌豆 V. villosa | 跨洲 Cross continent | 2.33 | 4 |
| 金鸡菊属 Coreopsis | 唇形科 Lamiaceae | ||||||
| 剑叶金鸡菊 C. lanceolata | 美洲 America | 2.33 | 3 | 鼠尾草属 Salvia | |||
| 两色金鸡菊 C. tinctoria | 美洲 America | 9.30 | 5 | 一串红 S. splendens | 美洲 America | 4.65 | 5 |
| 秋英属 Cosmos | 锦葵科 Malvaceae | ||||||
| 秋英 C. bipinnatus | 美洲 America | 37.21 | 5 | 木槿属 Hibiscus | |||
| 野茼蒿属 Crassocephalum | 野西瓜苗 H. trionum | 非洲 Asia | 2.33 | 4 | |||
| 野茼蒿 C. crepidioides | 非洲 Africa | 25.58 | 2 | 桑科 Moraceae | |||
| 鳢肠属 Eclipta | 大麻属 Cannabis | ||||||
| 鳢肠 E. prostrata | 美洲 America | 2.33 | 4 | 大麻 C. sativa | 亚洲 Asia | 4.65 | 4 |
| 飞蓬属 Erigeron | 桃金娘科 Myrtaceae | ||||||
| 一年蓬 E. annuus | 美洲 America | 25.58 | 1 | 桉属 Eucalyptus | |||
| 小飞蓬 E. canadensis | 美洲 America | 27.91 | 1 | 桉 E. robusta | 大洋洲 Oceania | 2.33 | 5 |
| 苏门白酒草 E. sumatrensis | 美洲 America | 16.28 | 1 | 紫茉莉科 Nyctaginaceae | |||
| 香丝草 E. bonariensis | 美洲 America | 25.58 | 2 | 紫茉莉属 Mirabilis | |||
| 牛膝菊属 Galinsoga | 紫茉莉 M. jalapa | 美洲 America | 2.33 | 2 | |||
| 牛膝菊 G. parviflora | 美洲 America | 48.84 | 2 | 商陆科 Phytolaccaceae | |||
| 千里光属 Senecio | 商陆属 Phytolacca | ||||||
| 欧洲千里光 S. vulgaris | 欧洲 Europe | 20.93 | 4 | 垂序商陆 P. americana | 美洲 America | 11.63 | 2 |
| 苦苣菜属 Sonchus | 禾本科 Poaceae | ||||||
| 花叶滇苦菜 S. asper | 跨洲 Cross continent | 6.98 | 4 | 燕麦属 Avena | |||
| 苦苣菜 S. oleraceus | 跨洲 Cross continent | 13.95 | 4 | 野燕麦 A. fatua | 跨洲 Cross continent | 16.28 | 2 |
| 万寿菊属 Tagetes | 雀麦属 Bromus | ||||||
| 万寿菊 T. erecta | 美洲 America | 2.33 | 5 | 扁穗雀麦 B. catharticus | 美洲 America | 4.65 | 2 |
| 蒲公英属 Taraxacum | 黑麦草属 Lolium | ||||||
| 药用蒲公英 T. officinale | 欧洲 Europe | 2.33 | 4 | 黑麦草 L. perenne | 欧洲 Europe | 2.33 | 4 |
| 百日菊属 Zinnia | 雀稗属 Paspalum | ||||||
| 百日菊 Z. elegans | 美洲 America | 9.30 | 5 | 毛花雀稗 P. dilatatum | 美洲 America | 4.65 | 3 |
| 落葵科 Basellaceae | 狗尾草属 Setaria | ||||||
| 落葵薯属 Anredera | 棕叶狗尾草 S. palmifolia | 非洲 Africa | 18.60 | 4 | |||
| 落葵薯 A. cordifolia | 美洲 America | 9.30 | 1 | 马齿苋科 Portulacaceae | |||
| 落葵属 Basella | 土人参属 Talinum | ||||||
| 落葵 B. alba | 跨洲 Cross continent | 6.98 | 5 | 土人参 T. paniculatum | 美洲 America | 2.33 | 4 |
| 紫草科 Boraginaceae | 玄参科 Scrophulariaceae | ||||||
| 聚合草属 Symphytum | 婆婆纳属 Veronica | ||||||
| 聚合草 S. officinale | 跨洲 Cross continent | 2.33 | 5 | 阿拉伯婆婆纳 V. persica | 亚洲 Asia | 2.33 | 3 |
| 仙人掌科 Cactaceae | 茄科 Solanaceae | ||||||
| 仙人掌属 Opuntia | 曼陀罗属 Datura | ||||||
| 梨果仙人掌 O. ficus-indica | 美洲 America | 2.33 | 2 | 曼陀罗 D. stramonium | 美洲 America | 16.28 | 2 |
| 藜科 Chenopodiaceae | 假酸浆属 Nicandra | ||||||
| 藜属 Chenopodium | 假酸浆 N. physalodes | 美洲 America | 4.65 | 3 | |||
| 杖藜 C. giganteum | 亚洲 Asia | 2.33 | 5 | 茄属 Solanum | |||
| 刺藜属 Dysphania | 喀西茄 S. aculeatissimum | 美洲 America | 6.98 | 2 |
表1 新建川藏铁路(雅安-昌都段)外来入侵植物种类、原产地、频度(F, %)及危害等级(TD)
Table 1 The species composition, origin, frequency (F, %) and threat grade (TD) of invasive alien plants in the new Sichuan-Tibet Railway (Ya’an to Changdu section)
| 物种 Species | 产地 Origin | F | TD | 物种 Species | 产地 Origin | F | TD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苋科 Amaranthaceae | 土荆芥 D. ambrosioides | 美洲 America | 4.65 | 1 | |||
| 莲子草属 Alternanthera | 旋花科 Convolvulaceae | ||||||
| 喜旱莲子草 A. philoxeroides | 美洲 America | 18.60 | 1 | 番薯属 Ipomoea | |||
| 刺花莲子草 A. pungens | 美洲 America | 4.65 | 2 | 牵牛 I. nil | 美洲 America | 4.65 | 2 |
| 苋属 Amaranthus | 圆叶牵牛 I. purpurea | 美洲 America | 16.28 | 1 | |||
| 凹头苋 A. blitum | 美洲 America | 9.30 | 2 | 豆科 Fabaceae | |||
| 老鸦谷 A. cruentus | 美洲 America | 6.98 | 3 | 苜蓿属 Medicago | |||
| 绿穗苋 A. hybridus | 美洲 America | 4.65 | 2 | 南苜蓿 M. polymorpha | 跨洲 Cross continent | 4.65 | 4 |
| 千穗谷 A. hypochondriacus | 美洲 America | 2.33 | 3 | 紫苜蓿 M. sativa | 亚洲 Asia | 4.65 | 4 |
| 苋 A. tricolor | 亚洲 Asia | 9.30 | 3 | 草木犀属 Melilotus | |||
| 菊科 Asteraceae | 白花草木犀 M. albus | 跨洲 Cross continent | 11.63 | 4 | |||
| 紫菀属 Aster | 草木犀 M. officinalis | 跨洲 Cross continent | 2.33 | 4 | |||
| 钻叶紫菀 A. subulatus | 美洲 America | 16.28 | 1 | 车轴草属 Trifolium | |||
| 鬼针草属 Bidens | 红车轴草 T. pratense | 跨洲 Cross continent | 6.98 | 2 | |||
| 婆婆针 B. bipinnata | 美洲 America | 2.33 | 3 | 白车轴草 T. repens | 跨洲 Cross continent | 27.91 | 2 |
| 大狼杷草 B. frondosa | 美洲 America | 2.33 | 1 | 野豌豆属 Vicia | |||
| 鬼针草 B. pilosa | 美洲 America | 34.88 | 1 | 长柔毛野豌豆 V. villosa | 跨洲 Cross continent | 2.33 | 4 |
| 金鸡菊属 Coreopsis | 唇形科 Lamiaceae | ||||||
| 剑叶金鸡菊 C. lanceolata | 美洲 America | 2.33 | 3 | 鼠尾草属 Salvia | |||
| 两色金鸡菊 C. tinctoria | 美洲 America | 9.30 | 5 | 一串红 S. splendens | 美洲 America | 4.65 | 5 |
| 秋英属 Cosmos | 锦葵科 Malvaceae | ||||||
| 秋英 C. bipinnatus | 美洲 America | 37.21 | 5 | 木槿属 Hibiscus | |||
| 野茼蒿属 Crassocephalum | 野西瓜苗 H. trionum | 非洲 Asia | 2.33 | 4 | |||
| 野茼蒿 C. crepidioides | 非洲 Africa | 25.58 | 2 | 桑科 Moraceae | |||
| 鳢肠属 Eclipta | 大麻属 Cannabis | ||||||
| 鳢肠 E. prostrata | 美洲 America | 2.33 | 4 | 大麻 C. sativa | 亚洲 Asia | 4.65 | 4 |
| 飞蓬属 Erigeron | 桃金娘科 Myrtaceae | ||||||
| 一年蓬 E. annuus | 美洲 America | 25.58 | 1 | 桉属 Eucalyptus | |||
| 小飞蓬 E. canadensis | 美洲 America | 27.91 | 1 | 桉 E. robusta | 大洋洲 Oceania | 2.33 | 5 |
| 苏门白酒草 E. sumatrensis | 美洲 America | 16.28 | 1 | 紫茉莉科 Nyctaginaceae | |||
| 香丝草 E. bonariensis | 美洲 America | 25.58 | 2 | 紫茉莉属 Mirabilis | |||
| 牛膝菊属 Galinsoga | 紫茉莉 M. jalapa | 美洲 America | 2.33 | 2 | |||
| 牛膝菊 G. parviflora | 美洲 America | 48.84 | 2 | 商陆科 Phytolaccaceae | |||
| 千里光属 Senecio | 商陆属 Phytolacca | ||||||
| 欧洲千里光 S. vulgaris | 欧洲 Europe | 20.93 | 4 | 垂序商陆 P. americana | 美洲 America | 11.63 | 2 |
| 苦苣菜属 Sonchus | 禾本科 Poaceae | ||||||
| 花叶滇苦菜 S. asper | 跨洲 Cross continent | 6.98 | 4 | 燕麦属 Avena | |||
| 苦苣菜 S. oleraceus | 跨洲 Cross continent | 13.95 | 4 | 野燕麦 A. fatua | 跨洲 Cross continent | 16.28 | 2 |
| 万寿菊属 Tagetes | 雀麦属 Bromus | ||||||
| 万寿菊 T. erecta | 美洲 America | 2.33 | 5 | 扁穗雀麦 B. catharticus | 美洲 America | 4.65 | 2 |
| 蒲公英属 Taraxacum | 黑麦草属 Lolium | ||||||
| 药用蒲公英 T. officinale | 欧洲 Europe | 2.33 | 4 | 黑麦草 L. perenne | 欧洲 Europe | 2.33 | 4 |
| 百日菊属 Zinnia | 雀稗属 Paspalum | ||||||
| 百日菊 Z. elegans | 美洲 America | 9.30 | 5 | 毛花雀稗 P. dilatatum | 美洲 America | 4.65 | 3 |
| 落葵科 Basellaceae | 狗尾草属 Setaria | ||||||
| 落葵薯属 Anredera | 棕叶狗尾草 S. palmifolia | 非洲 Africa | 18.60 | 4 | |||
| 落葵薯 A. cordifolia | 美洲 America | 9.30 | 1 | 马齿苋科 Portulacaceae | |||
| 落葵属 Basella | 土人参属 Talinum | ||||||
| 落葵 B. alba | 跨洲 Cross continent | 6.98 | 5 | 土人参 T. paniculatum | 美洲 America | 2.33 | 4 |
| 紫草科 Boraginaceae | 玄参科 Scrophulariaceae | ||||||
| 聚合草属 Symphytum | 婆婆纳属 Veronica | ||||||
| 聚合草 S. officinale | 跨洲 Cross continent | 2.33 | 5 | 阿拉伯婆婆纳 V. persica | 亚洲 Asia | 2.33 | 3 |
| 仙人掌科 Cactaceae | 茄科 Solanaceae | ||||||
| 仙人掌属 Opuntia | 曼陀罗属 Datura | ||||||
| 梨果仙人掌 O. ficus-indica | 美洲 America | 2.33 | 2 | 曼陀罗 D. stramonium | 美洲 America | 16.28 | 2 |
| 藜科 Chenopodiaceae | 假酸浆属 Nicandra | ||||||
| 藜属 Chenopodium | 假酸浆 N. physalodes | 美洲 America | 4.65 | 3 | |||
| 杖藜 C. giganteum | 亚洲 Asia | 2.33 | 5 | 茄属 Solanum | |||
| 刺藜属 Dysphania | 喀西茄 S. aculeatissimum | 美洲 America | 6.98 | 2 |
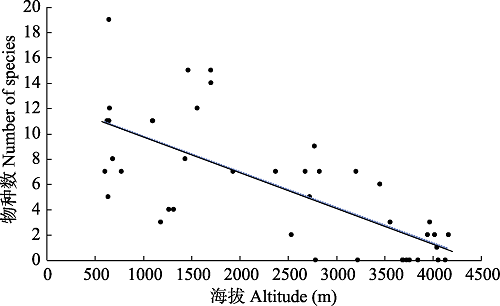
图2 新建川藏铁路(雅安-昌都段)外来入侵植物物种数与海拔相关性分析
Fig. 2 Correlation analysis on the number of invasive alien species and altitude in the new Sichuan-Tibet Railway (Ya’an to Changdu section)
| [1] | Alexander JM, Lembrechts JJ, Cavieres LA, Daehler C, Haider S, Kueffer C, Liu G, McDougall K, Milbau A, Pauchard A, Rew LJ, Seipel T ( 2016) Plant invasions into mountains and alpine ecosystems: Current status and future challenges. Alpine Botany, 126, 89-103. |
| [2] | Geleduoji ( 2019) The construction of the regional central city in the construction of the Sichuan-Tibet Railway. Contemporary County Economy, 8(1), 54-55. (in Chinese) |
| [ 格勒多吉 ( 2019) 以川藏铁路建设培塑区域中心城市. 当代县域经济, 8(1), 54-55.] | |
| [3] | Huang YL, Deng JQ, Zhang HW ( 2015) Schematic study on limiting gradient of Chengdu-Lhasa Railway. High Speed Railway Technology, 6(3), 97-101. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 黄艳磊, 邓军桥, 张红伟 ( 2015) 川藏铁路限制坡度方案研究. 高速铁路技术, 6(3), 97-101.] | |
| [4] | He TP, Li YM, Lu SF, Liu XX, Wen XF, Tang ZG, Chen Y, Luo Q ( 2011) Investigation and study on the alien invasive plants along Nan-You Expressway of Guangxi. Guangxi Forestry Science, 40, 277-280. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 和太平, 李玉梅, 陆山风, 刘晓星, 文祥凤, 唐忠国, 陈燕, 罗清 ( 2011) 广西南友高速公路路域外来入侵植物调查研究. 广西林业科学, 40, 277-280.] | |
| [5] | Jiang AL, Zhu SS, Chen YQ, Guo XM, Wang RJ ( 2018) Alien invasive plants in Hong Kong, China. Guihaia, 38, 289-298. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蒋奥林, 朱双双, 陈雨晴, 郭晓明, 王瑞江 ( 2018) 中国香港外来入侵植物. 广西植物, 38, 289-298.] | |
| [6] | Jiang AL, Zhu SS, Li XY, Chen YQ, Guo XM, Li SY, Wang FG, Wang RJ ( 2017) Dynamic changes in alien invasive plants in Guangzhou during 2008-2016. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 25, 288-298. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蒋奥林, 朱双双, 李晓瑜, 陈雨晴, 郭晓明, 李仕裕, 王发国, 王瑞江 ( 2017) 2008-2016年间广州市外来入侵植物的变化分析. 热带亚热带植物学报, 25, 288-298.] | |
| [7] | Jiang J, Yang X ( 2009) Quantitative segmentation of the three gradient terrain of China based on DEM. Geomatics World, 7(1), 8-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蒋捷, 杨昕 ( 2009) 基于DEM中国地势三大阶梯定量划分. 地理信息世界, 7(1), 8-13.] | |
| [8] | Ju JG, Wang N, Guo YJ, Zhou XJ, Wu XX ( 2011) Current situation analysis of invasive plant in Jiangxi Province. Journal of Jinggangshan University (Natural Science), 32(1), 126-130. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 鞠建文, 王宁, 郭永久, 周小军, 吴星星 ( 2011) 江西省外来入侵植物现状分析. 井冈山大学学报(自然科学版), 32(1), 126-130.] | |
| [9] | Liu ZX, Zeng YP, Zhou S, Yu K ( 2017) Research and implementation of canyon wind characteristics monitoring system along Sichuan-Tibet Railway. High Speed Railway Technology, 8(2), 29-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘孜学, 曾永平, 周帅, 虞凯 ( 2017) 川藏铁路峡谷风特性监测系统的方案研究及实现高速. 高速铁路技术, 8(2), 29-34.] | |
| [10] | Nel JL, Richardson DM, Rouget M, Mgidi TN, Mdzeke N, Le Maitre DC, van Wilgen BW, Schonegevel L, Henderson L, Neser S ( 2004) A proposed classification of invasive alien plant species in South Africa: Towards prioritizing species and areas for management action. South African Journal of Science, 100, 53-64. |
| [11] | Peng SL, Xiang YC ( 1999) The invasion of exotic plants and effects of ecosystems. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 19, 560-568. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 彭少麟, 向言词 ( 1999) 植物外来种入侵及其对生态系统的影响. 生态学报, 19, 560-568.] | |
| [12] | Sellersberg I ( 1998) Ecological effects of roads and traffic: A literature review. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 7, 317-333. |
| [13] | Shi Q, Chen X, Luo XJ, Chen FX, Ren XH ( 2017) Investigation and analysis on alien invasive plants in Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei Province. Journal of Biosafety, 26, 215-223. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 石青, 陈雪, 罗雪晶, 陈凤新, 任晓鸿 ( 2017) 京津冀外来入侵植物的种类调查与分析. 生物安全学报, 26, 215-223.] | |
| [14] | Tu MZ, Zhang ZX, Dai WW ( 2016) The impact of mountain highway construction on forest ecological environment along the route. Journal of Yibin University, 16(6), 108-111. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 涂美珍, 张正雄, 戴伟文 ( 2016) 山区公路建设对沿线森林生态环境的影响. 宜宾学院学报, 16(6), 108-111.] | |
| [15] | Wang CX, Xu S, Zhang TH, Zhang XR, Wu G ( 2020) Relationship analysis on road network expansion and ecological environmental pressure change: Case study of Xiamen. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(2), 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王辰星, 徐舒, 张天海, 张小瑞, 吴钢 ( 2020) 路网扩张与生态环境压力变化的关系研究——以厦门市为例. 生态学报, 40(2), 1-5.] | |
| [16] | Wang ZQ, Gao JZ ( 2012) Investigation on alien invasive plants in Henan Expressway. Soil and Water Conservation in China, ( 12), 47-49. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王增琪, 高均昭 ( 2012) 河南高速公路中的外来入侵植物调查. 中国水土保持, ( 12), 47-49.] | |
| [17] | Wu ZY ( 1991) Areal-types of the Chinese genera seeds plants. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 13(S4), 1-139. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴征镒 ( 1991) 中国种子植物属的分布区类型. 云南植物研究, 13(S4), 1-139.] | |
| [18] | Wu ZY, Sun H, Zhou ZK, Li DZ, Peng H ( 2011) Floristics of Seed Plants from China. Science Press, Bejing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 吴征镒, 孙航, 周浙昆, 李德珠, 彭华 ( 2011) 中国种子植物区系地理. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [19] | Wu ZY, Zhou ZK, Li DZ, Peng H, Sun H ( 2003) The areal- types of the world families of seed plants. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 25, 245-257. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴征镒, 周浙昆, 李德珠, 彭华, 孙航 ( 2003) 世界种子植物科的分布类型系统. 云南植物研究, 25, 245-257.] | |
| [20] | Xing Y, Ree RH ( 2017) Uplift-driven diversification in the Hengduan Mountains, a temperate biodiversity hotspot. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 114, E3444-E3451. |
| [21] | Xu HG, Qiang S, Han ZM, Guo JY, Huang ZG, Sun HY, He SP, Ding H, Wu HR, Wan FH ( 2004) The distribution and introduction pathway of alien invasive species in China. Biodiversity Science, 12, 626-638. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐海根, 强胜, 韩正敏, 郭建英, 黄宗国, 孙红英, 何舜平, 丁晖, 吴海荣, 万方浩 ( 2004) 中国外来入侵物种的分布与传入路径分析. 生物多样性, 12, 626-638.] | |
| [22] | Yan J, Yan XL, Wang ZH, Li HR, Ma JS ( 2017) Distribution pattern and rating of alien invasive plants in Anhui Province. Plant Science Journal, 35, 679-690. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 严靖, 闫小玲, 王樟华, 李惠茹, 马金双 ( 2017) 安徽省外来入侵植物的分布格局及其等级划分. 植物科学学报, 35, 679-690.] | |
| [23] | Yan XL, Liu QR, Shou HY, Zeng XF, Zhang Y, Chen L, Liu Y, Ma HY, Qi SY, Ma JS ( 2014) The categorization and analysis on the geographic distribution patterns of Chinese alien invasive plants. Biodiversity Science, 22, 667-676. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 闫小玲, 刘全儒, 寿海洋, 曾宪锋, 张勇, 陈丽, 刘演, 马海英, 齐淑艳, 马金双 ( 2014) 中国外来入侵植物的等级划分与地理分布格局分析. 生物多样性, 22, 667-676.] | |
| [24] | Yang CL, Luo J, Lan JJ ( 2018) Index system for risk assessment of alien plant invasion in Nyingchi, Tibet Autonomous Region, China. Journal of Plateau Agriculture, ( 2), 167-175. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨春蕾, 罗建, 拦继酒 ( 2018) 西藏林芝市外来植物入侵风险评估指标体系. 高原农业, ( 2), 167-175.] | |
| [25] | Yang L, Li JR, Cao J, Cang-Jue ZM, Li LX ( 2016) A brief analysis of risk of invasive species caused by the Tibetan Plateau railway construction. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 28(3), 61-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨乐, 李继荣, 曹建, 仓决卓玛, 李来兴 ( 2016) 浅析青藏高原铁路建设的外来物种入侵风险. 环境监测管理与技术, 28(3), 61-64.] | |
| [26] | Yang XY, Deng HP, Guo J, Huang LY ( 2017) Risk assessment of alien invasive plants in the Jinyun-Mountain National Nature Reserve and countermeasures for their prevent and control. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 39(7), 57-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨小艳, 邓洪平, 郭金, 黄龙仪 ( 2017) 缙云山国家级自然保护区入侵植物风险评估及防控对策研究. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 39(7), 57-63.] | |
| [27] | Yang YP, Meng JB, Han LW, Li Y, Cai HC, Zhu ZR ( 2018) The response of the permafrost to the global climate change in the Qinghai-Tibet railway project corridor. Chinese Railway Science, 39(1), 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨永鹏, 孟进宝, 韩龙武, 李勇, 蔡汉成, 朱兆荣 ( 2018) 青藏铁路工程走廊多年冻土对全球气候变化的响应. 中国铁道科学, 39(1), 1-7.] | |
| [28] |
Zhang DC, Boufford DE, Ree RH, Sun H ( 2009) The 29° N latitudinal line: An important division in the Hengduan Mountains, a biodiversity hotspot in Southwest China. Nordic Journal of Botany, 27, 405-412.
DOI URL |
| [29] | Zhang L, Qiu XY, Tu YL, Wen XM, Luo J ( 2018) Three alien species and one new record of wild species in Tibet. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 27(4), 113-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张丽, 仇晓玉, 土艳丽, 文雪梅, 罗建 ( 2018) 西藏外来植物3种及野生植物新记录1种. 植物资源与环境学报, 27(4), 113-114.] | |
| [30] | Zheng JM, Xu M, Sun Y, Wan HL, Liang TJ ( 2011) Comparison of roadside alien plant composition inside and outside Lushan Nature Reserve, Jiangxi Province. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 33(3), 51-56. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郑景明, 徐满, 孙燕, 万慧霖, 梁同军 ( 2011) 庐山自然保护区内外公路路缘外来植物组成对比. 北京林业大学学报, 33(3), 51-56. |
| [1] | 马文俊, 刘思嘉, 李柯懋, 简生龙, 薛长安, 韩庆祥, 魏金良, 陈生学, 牛依萌, 崔洲平, 隋瑞臣, 田菲, 赵凯. 青海省长江源区鱼类分布及多样性格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24494-. |
| [2] | 陈丁松, 刘子恺, 贺子洋, 陈伟东. 缓步动物多样性、分布特征和生态功能研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24406-. |
| [3] | 张颂琪, 陆义, 陈炳耀, 杨光, 王彦平, 陈传武. 全球鲸豚类形态、生活史和生态学特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24442-. |
| [4] | 弋维, 艾鷖, 吴萌, 田黎明, 泽让东科. 青藏高原高寒草甸土壤古菌群落对不同放牧强度的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24339-. |
| [5] | 时永强, 栾青杉, 单秀娟, 韦超, 赵永松, 孙策策, 金显仕. 长岛南部海域浮游动物多样性周年变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [6] | 赵勇强, 阎玺羽, 谢加琪, 侯梦婷, 陈丹梅, 臧丽鹏, 刘庆福, 隋明浈, 张广奇. 退化喀斯特森林自然恢复中不同生活史阶段木本植物物种多样性与群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| [7] | 林迪, 陈双林, 杜榷, 宋文龙, 饶固, 闫淑珍. 大别山黏菌的物种多样性调查[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23242-. |
| [8] | 姚嘉, 张聪伶, 李时轩, 林阳, 王震, 张煜涵, 周伟龙, 潘心禾, 朱珊, 吴逸卿, 王丹, 刘金亮, 谭珊珊, 沈国春, 于明坚. 百山祖连续海拔样带植物群落特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24052-. |
| [9] | 陈嘉珈, 蒲真, 黄中鸿, 于凤琴, 张建军, 许东华, 徐俊泉, 尚鹏, 地里木拉提∙帕尔哈提, 李耀江, Jigme Tshering, 郭玉民. 全球黑颈鹤越冬种群分布与数量[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22400-. |
| [10] | 陈晓澄, 张鹏展, 康斌, 刘林山, 赵亮. 基于中国科学院西北高原生物研究所馆藏标本分析青藏高原雀形目鸟类物种和功能多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22638-. |
| [11] | 肖俞, 李宇然, 段禾祥, 任正涛, 冯圣碧, 姜志诚, 李家华, 张品, 胡金明, 耿宇鹏. 高黎贡山外来植物入侵现状及管控建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 23011-. |
| [12] | 陈哲涵, 尹进, 叶吉, 刘冬伟, 毛子昆, 房帅, 蔺菲, 王绪高. 增温对东北温带次生林草本群落季节动态的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 23059-. |
| [13] | 张鹤露, 赵美红, 孙世春, 刘晓收. 西藏那曲市高原盐湖自由生活线虫群落多样性与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22533-. |
| [14] | 龚心语, 黄宝荣. 国家公园全民公益性评估指标体系: 以青藏高原国家公园群为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22571-. |
| [15] | 杨涛, 沈泽昊, 王晓凤, 饶杰生, 刘文聪, 田希, 陈稀, 张秋雨, 刘倩, 钱恒君, 解宇阳, 刘其明, 徐衍潇, 涂梦灵, 单子铭, 张玉坤, 侯波, 李建斌, 欧晓昆. 滇中高原亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林植物群落多样性特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23238-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()