



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (11): 1345-1361. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020110 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020110
收稿日期:2020-03-23
接受日期:2020-05-27
出版日期:2020-11-20
发布日期:2020-06-18
通讯作者:
宋础良
作者简介:* E-mail: clsong.ecology@gmail.comReceived:2020-03-23
Accepted:2020-05-27
Online:2020-11-20
Published:2020-06-18
Contact:
Chuliang Song
摘要:
群落内物种间相互作用的结构是高度组织化的。群落结构对多物种共存的影响机制是群落生态学的核心科学问题之一。目前生态学界在这一问题上存在多种不同的观点。一个可能的原因是, 由于环境因子的复杂性, 大部分研究忽略了环境因子对群落结构和物种共存的重要影响。在这一背景下, 近期发展起来的结构稳定性理论系统地联系了群落结构、环境因子和物种共存, 并在此基础上建立了一个和经验数据紧密结合的理论框架。本文首先简要回顾了当前关于群落结构研究的争鸣, 然后介绍了结构稳定性的理论框架和计算方法, 最后详细介绍了结构稳定性理论在不同生态群落和不同生态学问题中的应用。在全球气候变化的背景下, 结构稳定性理论提供了一种新的视角来理解群落层面的生物多样性维持机制。
宋础良 (2020) 结构稳定性: 概念、方法和应用. 生物多样性, 28, 1345-1361. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020110.
Chuliang Song (2020) Structural stability: Concepts, methods, and applications. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1345-1361. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020110.
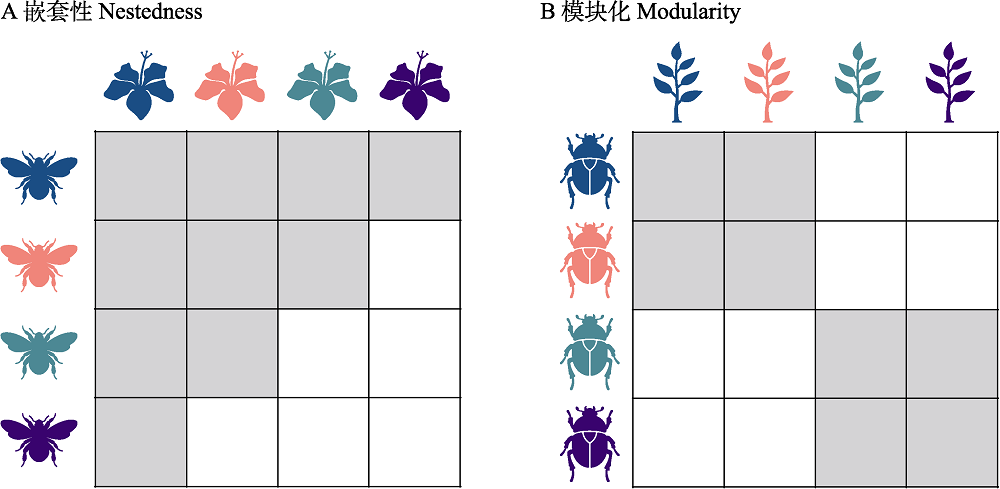
图1 两种经典的群落结构。这里的矩阵展示了群落结构: 每一列代表不同植物, 而每一行代表了不同的授粉种(图A)或者草食动物(图B)。灰色的格子代表两个物种存在种间关系, 而白色的格子则代表不存在。图A展示了嵌套性结构。基于一个物种的种间关系的相对数量, 可以把物种分为泛化种(generalist)和特化种(specialist)。嵌套性结构的特征是认为泛化种会和泛化种以及特化种都相互作用, 而特化种几乎只和泛化种相互作用。嵌套性结构被认为是互利群落的一种普适结构。图B展示了模块化结构。模块化结构的特征是群落分成几个模块, 物种几乎只和同一模块的物种相互作用, 而很少和别的模块的物种相互作用。嵌套性结构被认为是食物网的一种普适结构。
Fig. 1 Two ecological community structures. Here we present an illustration of two hypothetical network structures. The community structure is represented as a matrix. The columns correspond to different plant species while the rows correspond to different pollinators (in Panel A) or herbivores (in Panel B). A species interaction is represented as a gray grid. Panel (A) illustrates the nested structure. The defining feature of a nested structure is that highly connected species interact with both highly connected and poorly connected species, while poorly connected species interact almost exclusively with highly connected species. The nested structure is widely conceived as a universal structure in mutualistic communities. Panel (B) illustrates the modular structure. The defining feature of the modular structure is that in which groups of species have many interactions among them, but few interactions with the rest of the species in the network. The modular structure is widely conceived as a universal structure in food webs.
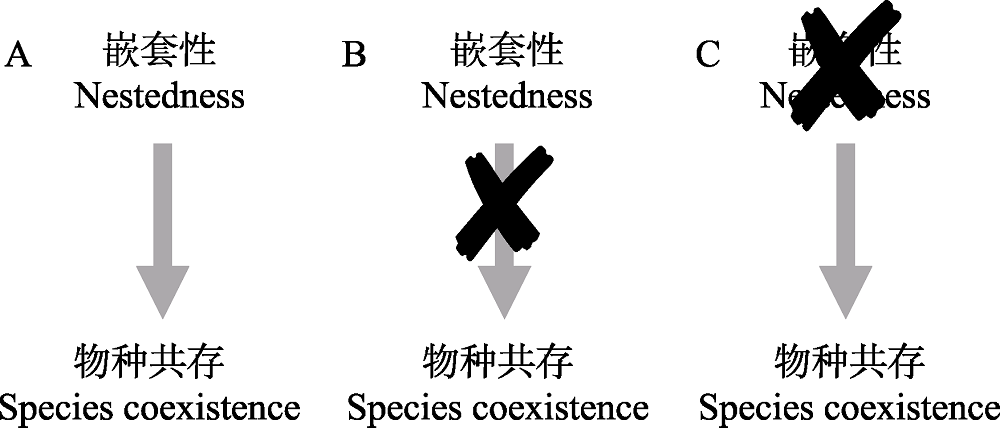
图2 群落结构研究的争鸣。互利群落中关于嵌套性和物种多样性的研究中, 存在三种不同的派系。图A展示了第一种派系, 认为嵌套性是决定互利群落的物种多样性的原因。图B展示了第二种派系, 认为嵌套性并不是决定互利群落的物种多样性的原因。图C展示了第三种派系, 认为嵌套性并不是互利群落的普适结构, 因此嵌套性和物种多样性之间的关系无从谈起。
Fig. 2 The debates in the study of community structures. Three different schools of thought coexist in linking nestedness and species coexistence in mutualistic communities. The first school (Panel A) argues that nestedness is a key factor to support the biodiversity in mutualistic communities, the second school (Panel B) argues there is no causal relationship between the nested pattern and biodiversity, and the third school (Panel C) argues that nested patterns are not universal in observed mutualistic communities, thus makes the whole question a straw man.
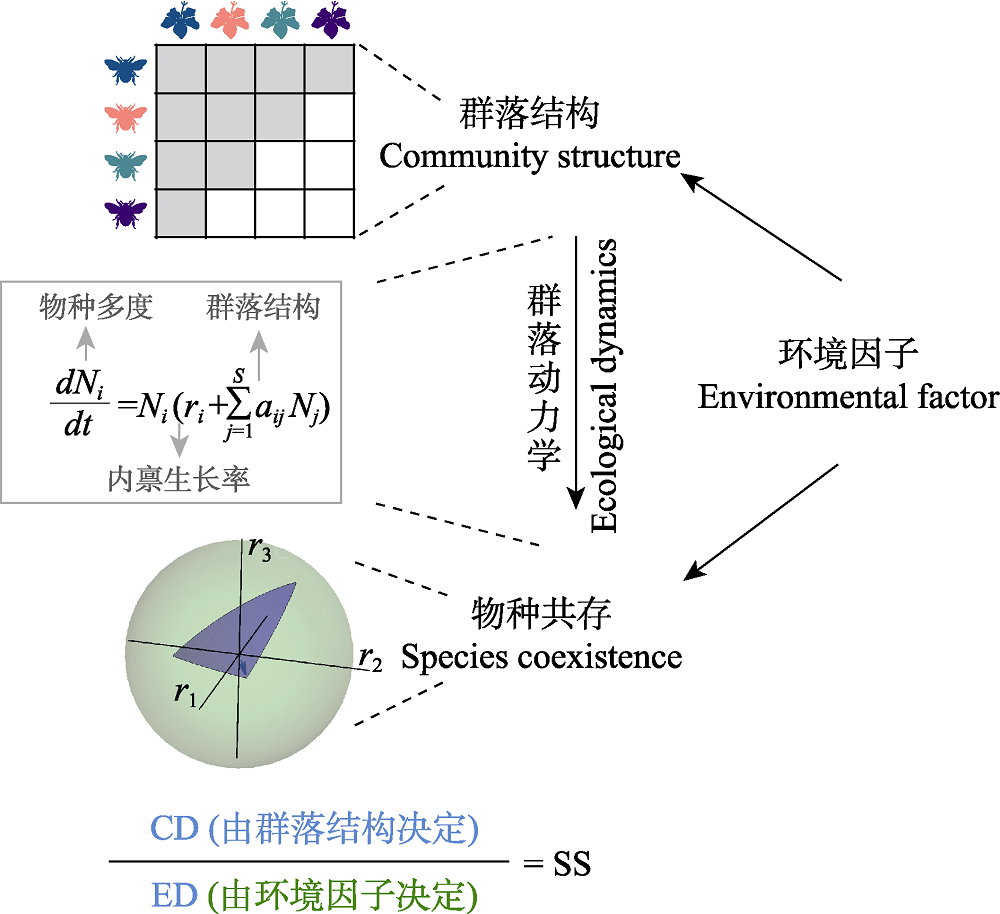
图3 结构稳定性理论的基础数学框架。和经典的群落结构-物种共存理论相比, 结构稳定性理论引入了环境因子。环境因子同时会影响群落结构和物种共存。结构稳定性(SS)的计算需要两部分的信息: 共存域(CD)和环境域(ED)。共存域指的是可以使得物种共存的全部参数的空间, 图中用蓝色区域(图A)指代。共存域是由群落结构通过群落动力学而决定的。环境域指的是这一环境条件下所有可能的参数的空间, 图中用绿色区域(图B)指代。环境域是在给定环境的限制下所有可能的参数的空间。环境域是环境因子决定的。结构稳定性是共存域相对于环境域的大小。结构稳定性越大, 物种在这一环境条件下就有更大可能可以共存。
Fig. 3 The mathematical framework of the structural stability approach. To compute the structural stability (SS) of an ecological community, we need two pieces of information: the coexistence domain (CD) and the environment domain (ED). The coexistence domain (denoted in blue; region A) is the full range of parameters that are compatible with species coexistence. The coexistence domain is determined by the community structure via the ecological dynamics. The environment domain (denoted in green; region B) is the full range of parameters constrained by the given environmentally conditions. The environment domain is determined by the environmental factors. Structural stability is defined as the relative size of the coexistence domain comparing to the environment domain. The larger the structural stability is, the more likely species can coexist under the given environmental conditions.
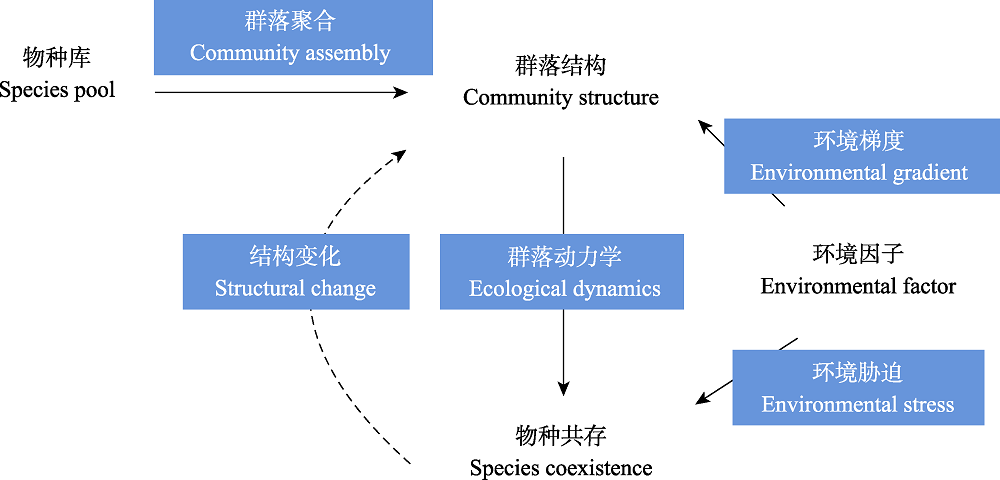
图4 结构稳定性理论的物种共存框架。群落中有4个核心因素: 物种库、群落结构、环境因子和物种共存。这些核心因素之间都有着具体的生态过程(蓝色): 群落聚合、结构变化、群落动力学、环境梯度和环境胁迫。结构稳定性理论试图将这些生态过程整合在一个统一的框架下。对于图中的每一个生态过程, 结构稳定性理论都提出了新的假说和验证方法, 并在实验以及观测数据中得到了验证。
Fig. 4 The structural stability approach for understanding multispecies coexistence. The nodes denote the key elements in ecological dynamics: species pool, community structure, environmental factors, and species coexistence. The links represent the ecological processes (denoted in blue) that connect these elements: community assembly, structural change, ecological dynamics, environmental gradient, and environmental stress. The structural stability approach aims to integrate these ecological processes under a unified framework. For each process, the structural stability approach provides new theoretical predictions, which are validated by experimental and/or observational data.
| [1] |
Adler PB, HilleRisLambers J, Levine JM (2007) A niche for neutrality. Ecology Letters, 10, 95-104.
URL PMID |
| [2] |
AlAdwani M, Saavedra S (2019) Is the addition of higher-order interactions in ecological models increasing the understanding of ecological dynamics? Mathematical Biosciences, 315, 108222.
URL PMID |
| [3] | Alberch P (1989) The logic of monsters: Evidence for internal constraint in development and evolution. Geobios, 22, 21-57. |
| [4] |
Allesina S, Tang S (2012) Stability criteria for complex ecosystems. Nature, 483, 205-208.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] |
Angulo MT, Moog CH, Liu YY (2019) A theoretical framework for controlling complex microbial communities. Nature Communications, 10, 1-12.
DOI URL PMID |
| [6] | Arnoldi JF, Haegeman B (2016) Unifying dynamical and structural stability of equilibria. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 472, 20150874. |
| [7] | Azaele S, Suweis S, Grilli J, Volkov I, Banavar JR, Maritan A (2016) Statistical mechanics of ecological systems: Neutral theory and beyond. Reviews of Modern Physics, 88, 35003. |
| [8] |
Barabás G, D’Andrea R (2016) The effect of intraspecific variation and heritability on community pattern and robustness. Ecology Letters, 19, 977-986.
URL PMID |
| [9] | Barabás G, D’Andrea R, Stump SM (2018) Chesson’s coexistence theory. Ecological Monographs, 88, 277-303. |
| [10] |
Barabás G, Michalska-Smith MJ, Allesina S (2016) The effect of intra- and interspecific competition on coexistence in multispecies communities. The American Naturalist, 188, E1-E12.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] |
Barabás G, Meszéna G, Ostling A (2014a) Fixed point sensitivity analysis of interacting structured populations. Theoretical Population Biology, 92, 97-106.
URL PMID |
| [12] |
Barabás G, Pásztor L, Meszéna G, Ostling A (2014b) Sensitivity analysis of coexistence in ecological communities: Theory and application. Ecology Letters, 17, 1479-1494.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] |
Bascompte J (2010) Structure and dynamics of ecological networks. Science, 329, 765-766.
URL PMID |
| [14] | Bascompte J, Jordano P, Melián CJ, Olesen JM (2003) The nested assembly of plant-animal mutualistic networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 100, 9383-9387. |
| [15] |
Bascompte J, Jordano P, Olesen JM (2006) Asymmetric coevolutionary networks facilitate biodiversity maintenance. Science, 312, 431-433.
DOI URL PMID |
| [16] |
Bastolla U, Fortuna MA, Pascual-García A, Ferrera A, Luque B, Bascompte J (2009) The architecture of mutualistic networks minimizes competition and increases biodiversity. Nature, 458, 1018-1020.
URL PMID |
| [17] |
Bastolla U, Lässig M, Manrubia SC, Valleriani A (2005) Biodiversity in model ecosystems. I. Coexistence conditions for competing species. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 235, 521-530.
DOI URL PMID |
| [18] | Bažant ZP (2000) Structural stability. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 37, 55-67. |
| [19] | Benincà E, Ballantine B, Ellner SP, Huisman J (2015) Species fluctuations sustained by a cyclic succession at the edge of chaos. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 112, 6389-6394. |
| [20] |
Broido AD, Clauset A (2019) Scale-free networks are rare. Nature Communications, 10, 1017.
DOI URL PMID |
| [21] |
Bunin G (2017) Ecological communities with Lotka-Volterra dynamics. Physical Review E, 95, 42414.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Butler S, O’Dwyer JP (2018) Stability criteria for complex microbial communities. Nature Communications, 9, 2970.
URL PMID |
| [23] | Cagua EF, Wootton KL, Stouffer DB (2019) Keystoneness, centrality, and the structural controllability of ecological networks. Journal of Ecology, 107, 1779-1790. |
| [24] |
Callaway RM, Brooker R, Choler P, Kikvidze Z, Lortie CJ, Michalet R, Paolini L, Pugnaire FI, Newingham B, Aschehoug ET, Armas C, Kikodze D, Bradley JC (2002) Positive interactions among alpine plants increase with stress. Nature, 417, 844-848.
DOI URL PMID |
| [25] |
CaraDonna PJ, Petry WK, Brennan RM, Cunningham JL, Bronstein JL, Waser NM, Sanders NJ (2017) Interaction rewiring and the rapid turnover of plant-pollinator networks. Ecology Letters, 20, 385-394.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] | Case TJ (2000) Illustrated Guide to Theoretical Ecology. Oxford University Press, Oxford. |
| [27] | Cenci S, Medeiros LP, Sugihara G, Saavedra S (2020) Assessing the predictability of nonlinear dynamics under smooth parameter changes. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 17, 20190627. |
| [28] |
Cenci S, Montero-Castaño A, Saavedra S (2018a) Estimating the effect of the reorganization of interactions on the adaptability of species to changing environments. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 437, 115-125.
DOI URL PMID |
| [29] | Cenci S, Saavedra S (2018) Structural stability of nonlinear population dynamics. Physical Review E, 97, 12401. |
| [30] |
Cenci S, Saavedra S (2019) Non-parametric estimation of the structural stability of non-equilibrium community dynamics. Nature Ecology and Evolution, 3, 912-918.
DOI URL PMID |
| [31] |
Cenci S, Song C, Saavedra S (2018b) Rethinking the importance of the structure of ecological networks under an environment-dependent framework. Ecology and Evolution, 8, 6852-6859.
DOI URL PMID |
| [32] | Cenci S, Sugihara G, Saavedra S (2019) Regularized S-map for inference and forecasting with noisy ecological time series. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 650-660. |
| [33] |
Chamberlain SA, Bronstein JL, Rudgers JA (2014) How context dependent are species interactions? Ecology Letters, 17, 881-890.
DOI URL PMID |
| [34] |
Chase JM (2003) Community assembly: When should history matter? Oecologia, 136, 489-498.
DOI URL PMID |
| [35] | Chase JM, Leibold MA (2003) Ecological Niches: Linking Classical and Contemporary Approaches. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [36] | Chesson P (2000) Mechanisms of maintenance of species diversity. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 31, 343-366. |
| [37] | Chesson P (2018) Updates on mechanisms of maintenance of species diversity. Journal of Ecology, 106, 1773-1794. |
| [38] | Chu CJ, Wang YS, Liu Y, Jiang L, He FL (2017) Advances in species coexistence theory. Biodiversity Science, 25, 345-354. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 储诚进, 王酉石, 刘宇, 蒋林, 何芳良 (2017) 物种共存理论研究进展. 生物多样性, 25, 345-354.] | |
| [39] |
Clark A, Hillebrand H, Harpole WS (2019) Scale both confounds and informs characterization of species coexistence in empirical systems. The American Naturalist, 194, 794-806.
DOI URL PMID |
| [40] |
Classen A, Eardley CD, Hemp A, Peters MK, Peters RS, Ssymank A, Steffan-Dewenter I (2020) Specialization of plant-pollinator interactions increases with temperature at Mt. Kilimanjaro. Ecology and Evolution, 10, 2182-2195.
DOI URL PMID |
| [41] |
Coulson T, Kendall BE, Barthold J, Plard F, Schindler S, Ozgul A, Gaillard JM (2017) Modeling adaptive and nonadaptive responses of populations to environmental change. The American Naturalist, 190, 313-336.
DOI URL PMID |
| [42] | Currie DJ (2019) Where Newton might have taken ecology. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 28, 18-27. |
| [43] |
D’Andrea R, Ostling A, O’Dwyer JP (2018) Translucent windows: How uncertainty in competitive interactions impacts detection of community pattern. Ecology Letters, 21, 826-835.
DOI URL PMID |
| [44] |
D’Andrea R, Riolo M, Ostling AM (2019) Generalizing clusters of similar species as a signature of coexistence under competition. PLoS Computational Biology, 15, e1006688.
URL PMID |
| [45] | Darwin C (1859) On the Origin of Species, p. 62. John Murray, London. |
| [46] |
Delmas E, Besson M, Brice MH, Burkle LA, Dalla Eiva GV, Fortin MJ, Gravel D, Guimarães PR Jr, Hembry DH, Newman EA, Olesen JM, Pires MM, Yeakel JD, Poisot T (2019) Analysing ecological networks of species interactions. Biological Reviews, 94, 16-36.
DOI URL |
| [47] | Des Roches S, Post DM, Turley NE, Bailey JK, Hendry AP, Kinnison MT, Schweitzer JA, Palkovacs EP (2018) The ecological importance of intraspecific variation. Nature Ecology and Evolution, 2, 57-64. |
| [48] | Deyle ER, Maher MC, Hernandez RD, Basu S, Sugihara G (2016a) Global environmental drivers of influenza. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 113, 13081-13086. |
| [49] | Deyle ER, May RM, Munch SB, Sugihara G (2016b) Tracking and forecasting ecosystem interactions in real time. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 283, 20152258. |
| [50] |
Dougoud M, Vinckenbosch L, Rohr RP, Bersier LF, Mazza C (2018) The feasibility of equilibria in large ecosystems: A primary but neglected concept in the complexity-stability debate. PLoS Computational Biology, 14, e1005988.
DOI URL PMID |
| [51] | Dunne JA, Williams RJ, Martinez ND (2002) Food-web structure and network theory: The role of connectance and size. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 99, 12917-12922. |
| [52] | Egler FE (1986) “Physics Envy” in ecology. Bulletin of the Ecological Society of America, 67, 233-235. |
| [53] | Fontenla JL, Fontenla Y, Cuervo Z, Álvarez de Zayas A (2019) Red de interacción ecológica insectos-plantas en playas del este, la habana, cuba. Acta Botánica Cubana, 218, 129-142. |
| [54] | Forrest JR, Thomson JD (2011) An examination of synchrony between insect emergence and flowering in Rocky Mountain meadows. Ecological Monographs, 81, 469-491. |
| [55] |
Fort H, Vázquez DP, Lan BL (2016) Abundance and generalisation in mutualistic networks: Solving the chicken-and-egg dilemma. Ecology Letters, 19, 4-11.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Frederickson ME (2017) Mutualisms are not on the verge of breakdown. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 32, 727-734.
URL PMID |
| [57] | Fukami T (2015) Historical contingency in community assembly: Integrating niches, species pools, and priority effects. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 46, 1-23. |
| [58] |
Garlaschelli D, Caldarelli G, Pietronero L (2003) Universal scaling relations in food webs. Nature, 423, 165-168.
DOI URL PMID |
| [59] |
Genz A, Bretz F (2002) Comparison of methods for the computation of multivariate t probabilities. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 11, 950-971.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
Gerlach M, Altmann EG (2019) Testing statistical laws in complex systems. Physical Review Letters, 122, 168301.
DOI URL PMID |
| [61] | Godoy O (2019) Coexistence theory as a tool to understand biological invasions in species interaction networks: Implications for the study of novel ecosystems. Functional Ecology, 33, 1190-1201. |
| [62] |
Godoy O, Bartomeus I, Rohr RP, Saavedra S (2018) Towards the integration of niche and network theories. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 33, 287-300.
DOI URL PMID |
| [63] |
Godoy O, Kraft NJ, Levine JM (2014) Phylogenetic relatedness and the determinants of competitive outcomes. Ecology Letters, 17, 836-844.
DOI URL PMID |
| [64] |
Gomes SI, Merckx VS, Saavedra S (2017) Fungal-host diversity among mycoheterotrophic plants increases proportionally to their fungal-host overlap. Ecology and Evolution, 7, 3623-3630.
DOI URL PMID |
| [65] | Grilli J, Adorisio M, Suweis S, Barabás G, Banavar JR, Allesina S, Maritan A (2017) Feasibility and coexistence of large ecological communities. Nature Communications, 8, 14389. |
| [66] | Grilli J, Rogers T, Allesina S (2016) Modularity and stability in ecological communities. Nature Communications, 7, 1-10. |
| [67] |
Guimarães PR, Pires MM, Jordano P, Bascompte J, Thompson JN (2017) Indirect effects drive coevolution in mutualistic networks. Nature, 550, 511-514.
URL PMID |
| [68] |
Guzman LM, Germain RM, Forbes C, Straus S, O’Connor MI, Gravel D, Srivastava DS, Thompson PL (2019) Towards a multi-trophic extension of metacommunity ecology. Ecology Letters, 22, 19-33.
DOI URL PMID |
| [69] |
Hart SP, Schreiber SJ, Levine JM (2016) How variation between individuals affects species coexistence. Ecology Letters, 19, 825-838.
DOI URL PMID |
| [70] | Harte J (2011) Maximum Entropy and Ecology: A Theory of Abundance, Distribution, and Energetics. Oxford University Press, Oxford. |
| [71] |
Harte J, Newman EA (2014) Maximum information entropy: A foundation for ecological theory. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 29, 384-389.
DOI URL PMID |
| [72] |
Hoek TA, Axelrod K, Biancalani T, Yurtsev EA, Liu J, Gore J (2016) Resource availability modulates the cooperative and competitive nature of a microbial cross-feeding mutualism. PLoS Biology, 14, e1002540.
DOI URL PMID |
| [73] | Hofbauer J, Sigmund K (1998) Evolutionary Games and Population Dynamics. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [74] |
Holland JN, Okuyama T, DeAngelis DL (2006) Comment on “asymmetric coevolutionary networks facilitate biodiversity maintenance”. Science, 313, 1887.
DOI URL PMID |
| [75] |
Holme P (2019) Rare and everywhere: Perspectives on scale-free networks. Nature Communications, 10, 1016.
DOI URL PMID |
| [76] | Hubbell SP (1997) A unified theory of biogeography and relative species abundance and its application to tropical rain forests and coral reefs. Coral Reefs, 16, S9-S21. |
| [77] | Hutchinson GE (1978) An Introduction to Population Ecology. Yale University Press, New Haven. |
| [78] | Hutchinson MC, Bramon Mora B, Pilosof S, Barner AK, Kéfi S, Thébault E, Jordano P, Stouffer DB (2019) Seeing the forest for the trees: Putting multilayer networks to work for community ecology. Functional Ecology, 33, 206-217. |
| [79] | Ings TC, Montoya JM, Bascompte J, Blüthgen N, Brown L, Dormann CF, Edwards F, Figueroa D, Jacob U, Jones JI, Lauridsen RB, Ledger ME, Lewis HM, Olesen JM, Van Veen FJ, Warren PH, Woodward G (2009) Ecological networks—Beyond food webs. Journal of Animal Ecology, 78, 253-269. |
| [80] |
James A, Pitchford JW, Plank MJ (2012) Disentangling nestedness from models of ecological complexity. Nature, 487, 227-230.
DOI URL PMID |
| [81] |
James A, Pitchford JW, Plank MJ (2013) James et al reply. Nature, 500, E2-E3.
DOI URL PMID |
| [82] |
Jansen V, Sigmund K (1998) Shaken not stirred: On permanence in ecological communities. Theoretical Population Biology, 54, 195-201.
DOI URL PMID |
| [83] | Kraft NJ, Godoy O, Levine JM (2015) Plant functional traits and the multidimensional nature of species coexistence. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 112, 797-802. |
| [84] | Lawton JH (1999) Are there general laws in ecology? Oikos, 84, 177-192. |
| [85] | Leibold MA, Chase JM (2017) Metacommunity Ecology. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [86] | Letten AD, Ke PJ, Fukami T (2017) Linking modern coexistence theory and contemporary niche theory. Ecological Monographs, 87, 161-177. |
| [87] |
Letten AD, Stouffer DB (2019) The mechanistic basis for higher-order interactions and nonadditivity in competitive communities. Ecology Letters, 22, 423-436.
DOI URL PMID |
| [88] | Levin SA (1992) The problem of pattern and scale in ecology: The Robert H. MacArthur award lecture. Ecology, 73, 1943-1967. |
| [89] |
Levine JM, Bascompte J, Adler PB, Allesina S (2017) Beyond pairwise mechanisms of species coexistence in complex communities. Nature, 546, 56-64.
DOI URL PMID |
| [90] | Levins R (1968) Evolution in Changing Environments: Some Theoretical Explorations. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [91] | Lewontin RC (1969) The meaning of stability. Brookhaven Symposium in Biology, 22, 13-24. |
| [92] |
Li A, Cornelius SP, Liu YY, Wang L, Barabási AL (2017) The fundamental advantages of temporal networks. Science, 358, 1042-1046.
DOI URL PMID |
| [93] |
Li DZ, Liu KY, Zang RG, Wang XP, Sheng LJ, Zhu ZL, Shi Q, Wang CA (2006) Development of the modern niche theory and its main representative genres. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 42(8), 88-94. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 李德志, 刘科轶, 臧润国, 王绪平, 盛丽娟, 朱志玲, 石强, 王长爱 (2006) 现代生态位理论的发展及其主要代表流派. 林业科学, 42(8), 88-94.] | |
| [94] |
Liu YY, Barabási AL (2016) Control principles of complex systems. Reviews of Modern Physics, 88, 035006.
DOI URL |
| [95] |
Liu YY, Slotine JJ, Barabási AL (2011) Controllability of complex networks. Nature, 473, 167-173.
DOI URL PMID |
| [96] |
Loreau M, Hector A (2001) Partitioning selection and complementarity in biodiversity experiments. Nature, 412, 72-76.
DOI URL PMID |
| [97] |
Loreau M, Naeem S, Inchausti P, Bengtsson J, Grime J, Hector A, Hooper D, Huston M, Raffaelli D, Schmid B, Tilman D, Wardle DA (2001) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: Current knowledge and future challenges. Science, 294, 804-808.
DOI URL PMID |
| [98] | Lu PL, Yu Q, He QT (2006) Responses of plant phenology to climatic change. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 26, 923-929. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陆佩玲, 于强, 贺庆棠 (2006) 植物物候对气候变化的响应. 生态学报, 26, 923-929.] | |
| [99] | Margalef R (1968) Perspectives in Ecological Theory. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [100] | Mariani MS, Ren ZM, Bascompte J, Tessone CJ (2019) Nestedness in complex networks: Observation, emergence, and implications. Physics Reports, 813, 1-90. |
| [101] |
May RM (1972) Will a large complex system be stable? Nature, 238, 413-414.
DOI URL PMID |
| [102] | May RM (1975) Stability in ecosystems: Some comments. In: Unifying Concepts in Ecology (eds van Dobben WH, Lowe-McConnell RH), pp. 161-168. Springer, New York. |
| [103] |
May RM (2006) Network structure and the biology of populations. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 21, 394-399.
DOI URL PMID |
| [104] |
Meszéna G, Gyllenberg M, Pásztor L, Metz JA (2006) Competitive exclusion and limiting similarity: A unified theory. Theoretical Population Biology, 69, 68-87.
DOI URL PMID |
| [105] | Michalska-Smith MJ, Allesina S (2019) Telling ecological networks apart by their structure: A computational challenge. PLoS Computational Biology, 15, 1-13. |
| [106] |
Montoya JM, Pimm SL, Solé RV (2006) Ecological networks and their fragility. Nature, 442, 259-264.
DOI URL PMID |
| [107] |
Morgan Ernest S, Brown JH (2001) Homeostasis and compensation: The role of species and resources in ecosystem stability. Ecology, 82, 2118-2132.
DOI URL |
| [108] | Newman MEJ (2010) Networks: An Introduction. Oxford University Press, Oxford. |
| [109] |
Niu KC, Liu YN, Shen ZH, He FL, Fang JY (2009) Community assembly: the relative importance of neutral theory and niche theory. Biodiversity Science, 17, 579-593. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 牛克昌, 刘怿宁, 沈泽昊, 何芳良, 方精云 (2009) 群落构建的中性理论和生态位理论. 生物多样性, 17, 579-593.] | |
| [110] | Nordbotten JM, Levin SA, Szathmáry E, Stenseth NC (2018) Ecological and evolutionary dynamics of interconnectedness and modularity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 115, 750-755. |
| [111] |
Nova N, Deyle ER, Shocket M, MacDonald AJ, Childs M, Rypdal M, Sugihara G, Mordecai EA (2019) Empirical dynamic modeling reveals ecological drivers of dengue dynamics. bioRxiv, doi: 10.1101/2019.12.20.883363.
DOI URL PMID |
| [112] |
Odum EP (1969) The strategy of ecosystem development. Science, 164, 262-270.
DOI URL PMID |
| [113] |
O’Dwyer JP, Rominger A, Xiao X (2017) Reinterpreting maximum entropy in ecology: A null hypothesis constrained by ecological mechanism. Ecology Letters, 20, 832-841.
DOI URL PMID |
| [114] | Pascual M, Dunne JA (2006) Ecological Networks: Linking Structure to Dynamics in Food Webs. Oxford University Press, Oxford. |
| [115] |
Pascual-García A, Bastolla U (2017) Mutualism supports biodiversity when the direct competition is weak. Nature Communications, 8, 14326.
DOI URL PMID |
| [116] | Payrató-Borràs C, Hernández L, Moreno Y (2019) Breaking the spell of nestedness: The entropic origin of nestedness in mutualistic systems. Physical Review X, 9, 31024. |
| [117] | Pearl J (2009) Causality. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [118] |
Pellissier L, Albouy C, Bascompte J, Farwig N, Graham C, Loreau M, Maglianesi MA, Melián CJ, Pitteloud C, Roslin T, Rohr R, Saavedra S, Thuiller W, Woodward G, Zimmermann NE, Gravel D (2018) Comparing species interaction networks along environmental gradients. Biological Reviews, 93, 785-800.
DOI URL PMID |
| [119] | Petry WK, Kandlikar GS, Kraft NJ, Godoy O, Levine JM (2018) A competition-defence trade-off both promotes and weakens coexistence in an annual plant community. Journal of Ecology, 106, 1806-1818. |
| [120] |
Pilosof S, Porter MA, Pascual M, Kéfi S (2017) The multilayer nature of ecological networks. Nature Ecology and Evolution, 1, 1-9.
DOI URL PMID |
| [121] | Pimm SL (1982) Food Webs. Chapman and Hall, London. |
| [122] | Power ME, Tilman D, Estes JA, Menge BA, Bond WJ, Mills LS, Daily G, Castilla JC, Lubchenco J, Paine RT (1996) Challenges in the quest for keystones: Identifying keystone species is difficult—but essential to understanding how loss of species will affect ecosystems. BioScience, 46, 609-620. |
| [123] |
Proulx SR, Promislow DE, Phillips PC (2005) Network thinking in ecology and evolution. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 20, 345-353.
DOI URL PMID |
| [124] | Ribando JM (2006) Measuring solid angles beyond dimension three. Discrete & Computational Geometry, 36, 479-487. |
| [125] | Roberts A (1974) The stability of a feasible random ecosystem. Nature, 251, 607-608. |
| [126] |
Rohr RP, Saavedra S, Bascompte J (2014) On the structural stability of mutualistic systems. Science, 345, 1253497.
DOI URL PMID |
| [127] |
Rohr RP, Saavedra S, Peralta G, Frost CM, Bersier LF, Bascompte J, Tylianakis JM (2016) Persist or produce: A community trade-off tuned by species evenness. The American Naturalist, 188, 411-422.
DOI URL PMID |
| [128] | Rossberg AG (2013) Food Webs and Biodiversity: Foundations, Models, Data. John Wiley & Sons, London. |
| [129] | Roughgarden J (1975) A simple model for population dynamics in stochastic environments. The American Naturalist, 109, 713-736. |
| [130] | Saavedra S, Cenci S, del Val E, Boege K, Rohr RP (2017a) Reorganization of interaction networks modulates the persistence of species in late successional stages. Journal of Animal Ecology, 86, 1136-1146. |
| [131] | Saavedra S, Rohr RP, Bascompte J, Godoy O, Kraft NJ, Levine JM (2017b) A structural approach for understanding multispecies coexistence. Ecological Monographs, 87, 470-486. |
| [132] |
Saavedra S, Rohr RP, Fortuna MA, Selva N, Bascompte J (2016a) Seasonal species interactions minimize the impact of species turnover on the likelihood of community persistence. Ecology, 97, 865-873.
DOI URL PMID |
| [133] |
Saavedra S, Rohr RP, Olesen JM, Bascompte J (2016b) Nested species interactions promote feasibility over stability during the assembly of a pollinator community. Ecology and Evolution, 6, 997-1007.
DOI URL PMID |
| [134] |
Saavedra S, Stouffer DB, Uzzi B, Bascompte J (2011) Strong contributors to network persistence are the most vulnerable to extinction. Nature, 478, 233-235.
DOI URL PMID |
| [135] |
Sales-Pardo M (2017) The importance of being modular. Science, 357, 128-129.
DOI URL PMID |
| [136] |
Scheffers BR, De Meester L, Bridge TC, Hoffmann AA, Pandolfi JM, Corlett RT, Butchart SH, Pearce-Kelly P, Kovacs KM, Dudgeon D, Pacifici M, Rondinini C, Foden WB, Martin TG, Mora C, Bickford D, Watson JEM (2016) The broad footprint of climate change from genes to biomes to people. Science, 354, aaf7671.
DOI URL PMID |
| [137] |
Serván CA, Capitán JA, Grilli J, Morrison KE, Allesina S (2018) Coexistence of many species in random ecosystems. Nature Ecology and Evolution, 2, 1237-1242.
DOI URL PMID |
| [138] |
Simmons BI, Wauchope HS, Amano T, Dicks LV, Sutherland WJ, Dakos V (2019) Vulnerable species interactions are important for the stability of mutualistic networks. BioRxiv, doi: 10.1101/604868.
DOI URL PMID |
| [139] |
Solow AR, Costello C, Beet A (1999) On an early result on stability and complexity. The American Naturalist, 154, 587-588.
DOI URL PMID |
| [140] |
Song C, Altermatt F, Pearse I, Saavedra S (2018a) Structural changes within trophic levels are constrained by within-family assembly rules at lower trophic levels. Ecology Letters, 21, 1221-1228.
DOI URL PMID |
| [141] |
Song C, Barabás G, Saavedra S (2019a) On the consequences of the interdependence of stabilizing and equalizing mechanisms. The American Naturalist, 194, 627-639.
DOI URL PMID |
| [142] |
Song C, Rohr RP, Saavedra S (2017) Why are some plant-pollinator networks more nested than others? Journal of Animal Ecology, 86, 1417-1424.
DOI URL |
| [143] |
Song C, Rohr RP, Saavedra S (2018b) A guideline to study the feasibility domain of multi-trophic and changing ecological communities. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 450, 30-36.
DOI URL PMID |
| [144] |
Song C, Rohr RP, Saavedra S (2019b) Beware z-scores. Journal of Animal Ecology, 88, 808-809.
DOI URL |
| [145] |
Song C, Rohr RP, Vasseur D, Saavedra S (2020a) Disentangling the effects of external perturbations on coexistence and priority effects. Journal of Ecology, 108, 1677-1689.
DOI URL |
| [146] | Song C, Saavedra S (2018a) Structural stability as a consistent predictor of phenological events. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 285, 20180767. |
| [147] |
Song C, Saavedra S (2018b) Will a small randomly assembled community be feasible and stable? Ecology, 99, 743-751.
DOI URL PMID |
| [148] | Song C, Saavedra S (2020a) Bridging parametric and nonparametric measures of species interactions unveils new insights of non-equilibrium dynamics. bioRxiv, doi: 10.1101/2020.03.02.973040. |
| [149] | Song C, Saavedra S (2020b) Telling ecological networks apart by their structure: An environment-dependent approach. PLoS Computational Biology, 16, e1007787. |
| [150] |
Song C, Von Ahn S, Rohr RP, Saavedra S (2020b) Towards a probabilistic understanding about the context-dependency of species interactions. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 35, 384-396.
DOI URL PMID |
| [151] |
Sprockett D, Fukami T, Relman DA (2018) Role of priority effects in the early-life assembly of the gut microbiota. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 15, 197-205.
DOI URL PMID |
| [152] |
Staniczenko PP, Kopp JC, Allesina S (2013) The ghost of nestedness in ecological networks. Nature Communications, 4, 1391.
DOI URL PMID |
| [153] | Stouffer DB, Bascompte J (2011) Compartmentalization increases food-web persistence. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 108, 3648-3652. |
| [154] | Strogatz SH (2014) Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos: With Applications to Physics, Biology, Chemistry, and Engineering. Westview Press, Boulder. |
| [155] | Sugihara G (1994) Nonlinear forecasting for the classification of natural time series. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series A: Physical and Engineering Sciences, 348, 477-495. |
| [156] |
Sugihara G, May R, Ye H, Hsieh CH, Deyle E, Fogarty M, Munch S (2012) Detecting causality in complex ecosystems. Science, 338, 496-500.
DOI URL PMID |
| [157] |
Suweis S, Simini F, Banavar JR, Maritan A (2013) Emergence of structural and dynamical properties of ecological mutualistic networks. Nature, 500, 449-452.
DOI URL PMID |
| [158] |
Thébault E, Fontaine C (2010) Stability of ecological communities and the architecture of mutualistic and trophic networks. Science, 329, 853-856.
DOI URL PMID |
| [159] | Thom R (1972) Stabilité Structurelle et Morphogenèse. InterÉditions, Paris. (in French) |
| [160] | Tilman D (1982) Resource Competition and Community Structure. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [161] | Tylianakis JM, Morris RJ (2017) Ecological networks across environmental gradients. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 48, 25-48. |
| [162] |
Uricchio LH, Daws SC, Spear ER, Mordecai EA (2019) Priority effects and nonhierarchical competition shape species composition in a complex grassland community. The American Naturalist, 193, 213-226.
DOI URL PMID |
| [163] |
Ushio M, Hsieh Ch, Masuda R, Deyle ER, Ye H, Chang CW, Sugihara G, Kondoh M (2018) Fluctuating interaction network and time-varying stability of a natural fish community. Nature, 554, 360-363.
DOI URL PMID |
| [164] |
Valverde S, Piñero J, Corominas-Murtra B, Montoya J, Joppa L, Solé R (2018) The architecture of mutualistic networks as an evolutionary spandrel. Nature Ecology and Evolution, 2, 94-99.
DOI URL PMID |
| [165] | Vellend M (2016) The Theory of Ecological Communities. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [166] | Voitalov I, van der Hoorn P, van der Hofstad R, Krioukov D (2018) Scale-free networks well done. arXiv, 1811. 02071. |
| [167] |
Wang S (2018) Simplicity from complex interactions. Nature Ecology and Evolution, 2, 1201-1202.
DOI URL PMID |
| [168] |
Wang S, Brose U (2018) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in food webs: The vertical diversity hypothesis. Ecology Letters, 21, 9-20.
DOI URL PMID |
| [169] | Wang S, Lamy T, Hallett LM, Loreau M (2019) Stability and synchrony across ecological hierarchies in heterogeneous metacommunities: Linking theory to data. Ecography, 42, 1200-1211. |
| [170] |
Woodward G, Ebenman B, Emmerson M, Montoya JM, Olesen JM, Valido A, Warren PH (2005) Body size in ecological networks. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 20, 402-409.
DOI URL PMID |
| [171] | Wootton JT (1994) The nature and consequences of indirect effects in ecological communities. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 25, 443-466. |
| [172] | Xing DL, Hao ZQ (2011) The principle of maximum entropy and its applications in ecology. Biodiversity Science, 19, 295-302. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 邢丁亮, 郝占庆 (2011) 最大熵原理及其在生态学研究中的应用. 生物多样性, 19, 295-302.] | |
| [173] | Yeakel JD, Pires MM, Rudolf L, Dominy NJ, Koch PL, Guimarães PR, Gross T (2014) Collapse of an ecological network in ancient Egypt. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 111, 14472-14477. |
| [174] | Zhang WP, Sha P, Jia X, Chu CJ, Xiao S, Lin Y, Bai YY, Wang GX (2013) Effects of positive plant interactions on population dynamics and community structures: A review based on individual-based simulation models. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 37, 571-582. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张炜平, 潘莎, 贾昕, 储诚进, 肖洒, 林玥, 白燕远, 王根轩 (2013) 植物间正相互作用对种群动态和群落结构的影响: 基于个体模型的研究进展. 植物生态学报, 37, 571-582.] | |
| [175] | Zhou SR, Zhang DY (2006) Neutral theory in community ecology. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 30, 868-877. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 周淑荣, 张大勇 (2006) 群落生态学的中性理论. 植物生态学报, 30, 868-877.] | |
| [176] | Zhou SR, Zhang DY (2008) A nearly neutral model of biodiversity. Ecology, 89, 248-258. |
| [177] | Zhu BR, Zhang DY (2011) A process-based theoretical framework for community ecology. Biodiversity Science, 19, 389-399. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱璧如, 张大勇 (2011) 基于过程的群落生态学理论框架. 生物多样性, 19, 389-399.] |
| [1] | 张明燡, 王晓梅, 郑言鑫, 吴楠, 李东浩, 樊恩源, 李娜, 单秀娟, 于涛, 赵春暖, 李波, 徐帅, 吴玉萍, 任利群. 黄河口典型牡蛎礁分布区资源状况和栖息地功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [2] | 仝淼, 王欢, 张文双, 王超, 宋建潇. 重金属污染土壤中细菌抗生素抗性基因分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [3] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [4] | 张舒欣, 贾紫璇, 方涛, 刘一凡, 赵微, 王荣, 昌海超, 罗芳丽, 朱耀军, 于飞海. 植物抗逆能力评价方法研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24168-. |
| [5] | 魏诗雨, 宋天骄, 罗佳宜, 张燕, 赵子萱, 茹靖雯, 易华, 林雁冰. 秦岭火地塘针叶林土壤细菌群落的海拔分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [6] | 时永强, 栾青杉, 单秀娟, 韦超, 赵永松, 孙策策, 金显仕. 长岛南部海域浮游动物多样性周年变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [7] | 曲锐, 左振君, 王有鑫, 张良键, 吴志刚, 乔秀娟, 王忠. 基于元素组的生物地球化学生态位及其在不同生态系统中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23378-. |
| [8] | 倪艳梅, 陈莉, 董志远, 孙德斌, 李宝泉, 王绪敏, 陈琳琳. 黄河三角洲湿地生态修复区大型底栖动物群落结构与生态健康评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23303-. |
| [9] | 魏嘉欣, 姜治国, 杨林森, 熊欢欢, 金胶胶, 罗方林, 李杰华, 吴浩, 徐耀粘, 乔秀娟, 魏新增, 姚辉, 余辉亮, 杨敬元, 江明喜. 湖北神农架中亚热带山地落叶阔叶林25 ha动态监测样地群落物种组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23338-. |
| [10] | 吕晓波, 李东海, 杨小波, 张孟文. 红树林群落通过淹水时间及海水盐度的生态位分化实现物种共存[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23302-. |
| [11] | 刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇. 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [12] | 吴芳芳, 刘娜, 何春梅, 原作强, 郝占庆, 尹秋龙. 秦岭山地木本植物群落结构及多样性的海拔梯度格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24239-. |
| [13] | 单航, 雷祖培, 郑方东, 韦博良, 仲磊, 于明坚. 2013-2023年浙江乌岩岭次生常绿阔叶林群落动态变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24372-. |
| [14] | 冯嘉谊, 练琚愉, 冯瑜莙, 张东旭, 曹洪麟, 叶万辉. 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林群落垂直分层对群落结构及功能的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24306-. |
| [15] | 王兴煜, 孟京辉, 任思远, 祝燕. 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林群落生物多样性与地上生物量的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24230-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
