



生物多样性 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (8): 873-879. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019060 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019060
袁海生1,*( ),魏玉莲1,周丽伟1,秦问敏1,崔宝凯2,何双辉2
),魏玉莲1,周丽伟1,秦问敏1,崔宝凯2,何双辉2
收稿日期:2019-02-28
接受日期:2019-04-25
出版日期:2019-08-20
发布日期:2019-09-25
通讯作者:
袁海生
基金资助:
Hai-Sheng Yuan1,*( ),Yulian Wei1,Liwei Zhou1,Wenmin Qin1,Baokai Cui2,Shuanghui He2
),Yulian Wei1,Liwei Zhou1,Wenmin Qin1,Baokai Cui2,Shuanghui He2
Received:2019-02-28
Accepted:2019-04-25
Online:2019-08-20
Published:2019-09-25
Contact:
Yuan Hai-Sheng
摘要:
东北地区木生真菌物种资源丰富, 包括了数十种林木干基腐朽病原真菌。过去对该类真菌曾进行多次调查, 获取了大量物种分布数据, 但对于非重点调查区域是否存在某种真菌物种却不明确。本文选取东北地区具有代表性的4种林木干基腐朽病原真菌, 即红缘拟层孔菌(Fomitopsis pinicola)、落叶松锈迷孔菌(Porodaedalea laricis)、桦剥管孔菌(Piptoporus betulinus)和香栓孔菌(Trametes suaveolens), 根据其地理分布数据和分布地的环境因子数据, 以最大熵模型(MaxEnt)对这些种类在东北地区可能的分布范围进行了模拟预测, 以曲线下面积(area under the receiver operating characteristic curve, AUC)对模型有效性进行评价, 并对各物种的生态位进行了分析。结果显示, 以MaxEnt方法获得的各物种预测模型均获得了较高的AUC值, 分别为0.990, 0.990, 0.989和0.967, 表明4种林木干基腐朽病原真菌预测模型的有效性较高。物种分布模型涉及的环境变量对模型的贡献率显示, 最暖季降水量(Bio18)、温度的年较差(Bio7)、最干季均温(Bio9)等变量对各物种模型贡献率较高。该研究结果为预测4种病原真菌在东北地区的分布范围和科学防治该类病原真菌提供了依据。
袁海生, 魏玉莲, 周丽伟, 秦问敏, 崔宝凯, 何双辉 (2019) 东北4种林木干基腐朽病原真菌潜在分布范围预测及其生态位分析. 生物多样性, 27, 873-879. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019060.
Hai-Sheng Yuan, Yulian Wei, Liwei Zhou, Wenmin Qin, Baokai Cui, Shuanghui He (2019) Potential distribution and ecological niches of four butt-rot pathogenic fungi in Northeast China. Biodiversity Science, 27, 873-879. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019060.
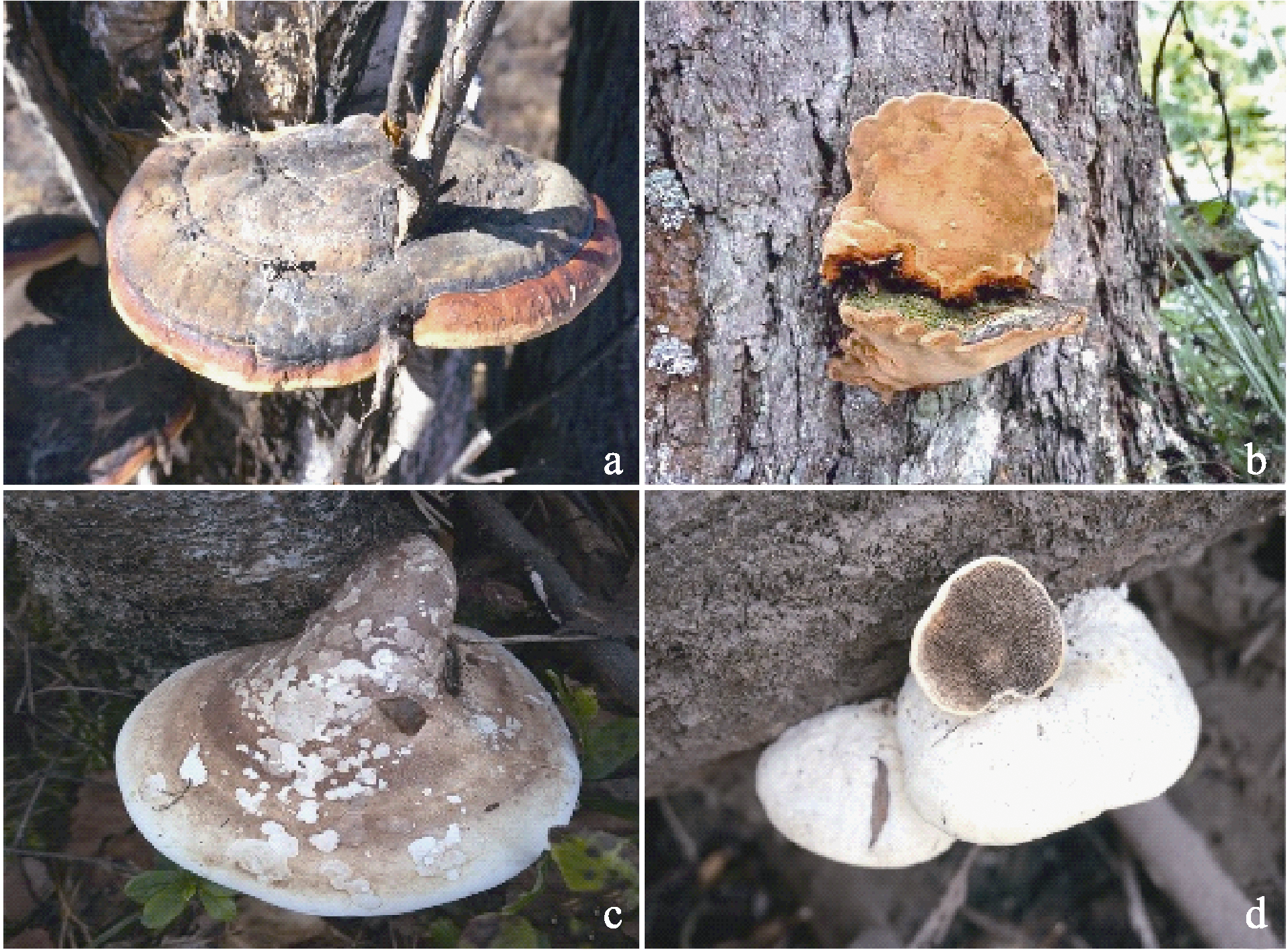

图1 4种病原真菌子实体。(a)红缘拟层孔菌; (b)落叶松锈迷孔菌; (c)桦剥管孔菌; (d)香栓孔菌。
Fig. 1 Basidiocarps of four butt-rot pathogenic fungi. (a) Fomitopsis pinicola; (b) Porodaedalea laricis; (c) Piptoporus betulinus; (d) Trametes suaveolens.
| 物种 Species | 记录点 Registered presence | 训练点数 Number of training points | 训练AUC Training AUC | 测试AUC Test AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 红缘拟层孔菌 Fomitopsis pinicola | 29 | 9 | 0.984 | 0.990 |
| 落叶松锈迷孔菌 Porodaedalea laricis | 9 | 3 | 0.933 | 0.990 |
| 桦剥管孔菌 Piptoporus betulinus | 21 | 7 | 0.984 | 0.989 |
| 香栓孔菌 Trametes suaveolens | 24 | 7 | 0.981 | 0.967 |
表1 4个林木干基腐朽病原真菌分布记录点及曲线下面积值
Table 1 Training and test AUC values obtained in the models for four butt-rot pathogenic fungi
| 物种 Species | 记录点 Registered presence | 训练点数 Number of training points | 训练AUC Training AUC | 测试AUC Test AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 红缘拟层孔菌 Fomitopsis pinicola | 29 | 9 | 0.984 | 0.990 |
| 落叶松锈迷孔菌 Porodaedalea laricis | 9 | 3 | 0.933 | 0.990 |
| 桦剥管孔菌 Piptoporus betulinus | 21 | 7 | 0.984 | 0.989 |
| 香栓孔菌 Trametes suaveolens | 24 | 7 | 0.981 | 0.967 |
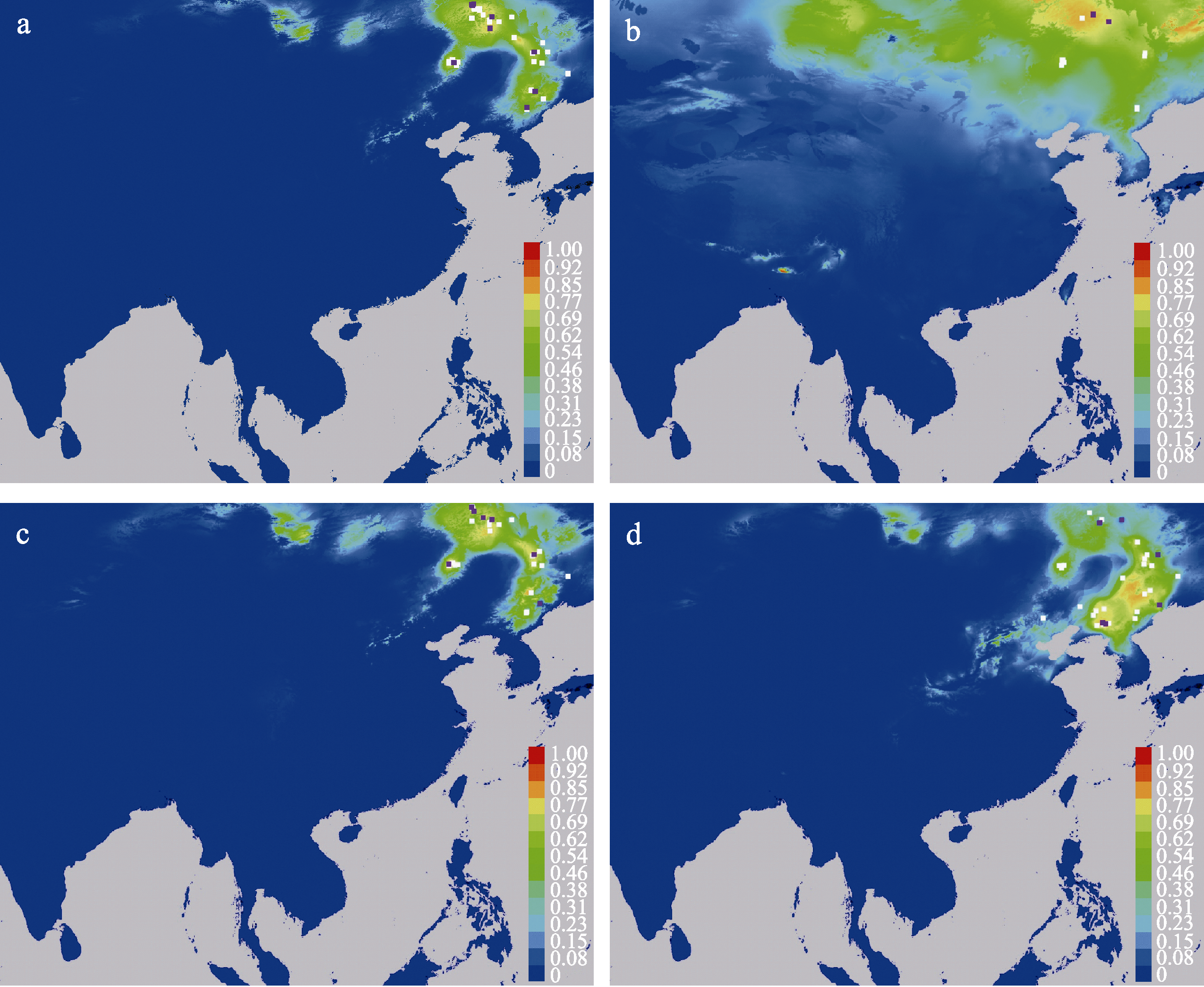
图3 模型预测的4种干基腐朽病原真菌的潜在分布区域。(a)红缘拟层孔菌; (b)落叶松锈迷孔菌; (c)桦剥管孔菌; (d)香栓孔菌。图中白色方块为训练点, 紫色方块为测试点。
Fig. 3 Potential distributions of four butt-rot pathogenic fungi. (a) Fomitopsis pinicola; (b) Porodaedalea laricis; (c) Piptoporus betulinus; (d) Trametes suaveolens. White squares are training points, purple squares are testing points.
| 编号 Code | 环境变量 Environmental variable | 贡献率 Contribution (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 红缘拟层孔菌 Fomitopsis pinicola | 落叶松锈迷孔菌 Porodaedalea laricis | 桦剥管孔菌 Piptoporus betulinus | 香栓孔菌 Trametes suaveolens | |||
| Bio1 | 年均温 Annual mean temperature (℃) | 6.1 | 0 | 11.8 | 2.9 | |
| Bio2 | 昼夜温差月均值 Mean diurnal range (mean of monthly (max - min temp)) (℃) | 0 | 0.9 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio3 | 等温性 Isothermality ((Bio2/Bio7) × 100) | 5.2 | 0 | 5.6 | 4.1 | |
| Bio4 | 温度季节性变化标准差 Temperature seasonality (standard deviation × 100) (C of V) | 16.6 | 0 | 6.6 | 34.9 | |
| Bio5 | 最暖月最高温 Maximum temperature of warmest month (℃) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio6 | 最冷月最低温 Minimum temperature of coldest month (℃) | 0.5 | 0 | 2.9 | 1.7 | |
| Bio7 | 温度的年较差 Temperature annual range (Bio5 - Bio6) (℃) | 29.9 | 4.3 | 17.6 | 4.2 | |
| Bio8 | 最湿季均温 Mean temperature of wettest quarter (℃) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 | |
| Bio9 | 最干季均温 Mean temperature of driest quarter (℃) | 7 | 78.8 | 18.1 | 0 | |
| Bio10 | 最暖季均温 Mean temperature of warmest quarter (℃) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio11 | 最冷季均温 Mean temperature of coldest quarter (℃) | 1.5 | 0 | 6.7 | 2.1 | |
| Bio12 | 年降水量 Annual precipitation (mm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio13 | 最湿月降水量 Precipitation of wettest month (mm) | 0 | 0 | 0.6 | 0 | |
| Bio14 | 最干月降水量 Precipitation of driest month (mm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio15 | 降水量季节性变异系数 Precipitation seasonality (coefficient of variation) (C of V) | 0.5 | 1.7 | 0 | 4.4 | |
| Bio16 | 最湿季降水量 Precipitation of wettest quarter (mm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio17 | 最干季降水量 Precipitation of driest quarter (mm) | 5.5 | 0 | 4.9 | 6.9 | |
| Bio18 | 最暖季降水量 Precipitation of warmest quarter (mm) | 25 | 6.2 | 23.5 | 36.3 | |
| Bio19 | 最冷季降水量 Precipitation of coldest quarter (mm) | 0.8 | 0 | 0.4 | 0.2 | |
| ELE | 海拔 Elevation (m) | 1.4 | 8.1 | 1.2 | 1.8 | |
表2 物种分布模型涉及的环境变量及其对模型的贡献率
Table 2 Environmental variables used to create the species distribution model and their percentage contribution to model performance
| 编号 Code | 环境变量 Environmental variable | 贡献率 Contribution (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 红缘拟层孔菌 Fomitopsis pinicola | 落叶松锈迷孔菌 Porodaedalea laricis | 桦剥管孔菌 Piptoporus betulinus | 香栓孔菌 Trametes suaveolens | |||
| Bio1 | 年均温 Annual mean temperature (℃) | 6.1 | 0 | 11.8 | 2.9 | |
| Bio2 | 昼夜温差月均值 Mean diurnal range (mean of monthly (max - min temp)) (℃) | 0 | 0.9 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio3 | 等温性 Isothermality ((Bio2/Bio7) × 100) | 5.2 | 0 | 5.6 | 4.1 | |
| Bio4 | 温度季节性变化标准差 Temperature seasonality (standard deviation × 100) (C of V) | 16.6 | 0 | 6.6 | 34.9 | |
| Bio5 | 最暖月最高温 Maximum temperature of warmest month (℃) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio6 | 最冷月最低温 Minimum temperature of coldest month (℃) | 0.5 | 0 | 2.9 | 1.7 | |
| Bio7 | 温度的年较差 Temperature annual range (Bio5 - Bio6) (℃) | 29.9 | 4.3 | 17.6 | 4.2 | |
| Bio8 | 最湿季均温 Mean temperature of wettest quarter (℃) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 | |
| Bio9 | 最干季均温 Mean temperature of driest quarter (℃) | 7 | 78.8 | 18.1 | 0 | |
| Bio10 | 最暖季均温 Mean temperature of warmest quarter (℃) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio11 | 最冷季均温 Mean temperature of coldest quarter (℃) | 1.5 | 0 | 6.7 | 2.1 | |
| Bio12 | 年降水量 Annual precipitation (mm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio13 | 最湿月降水量 Precipitation of wettest month (mm) | 0 | 0 | 0.6 | 0 | |
| Bio14 | 最干月降水量 Precipitation of driest month (mm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio15 | 降水量季节性变异系数 Precipitation seasonality (coefficient of variation) (C of V) | 0.5 | 1.7 | 0 | 4.4 | |
| Bio16 | 最湿季降水量 Precipitation of wettest quarter (mm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio17 | 最干季降水量 Precipitation of driest quarter (mm) | 5.5 | 0 | 4.9 | 6.9 | |
| Bio18 | 最暖季降水量 Precipitation of warmest quarter (mm) | 25 | 6.2 | 23.5 | 36.3 | |
| Bio19 | 最冷季降水量 Precipitation of coldest quarter (mm) | 0.8 | 0 | 0.4 | 0.2 | |
| ELE | 海拔 Elevation (m) | 1.4 | 8.1 | 1.2 | 1.8 | |
| 1 | Bao QZ, Wei YL, Yuan HS, Li YR (2006) A new butt-rot disease in tropical area from Yunnan Province. Forest Research, 19, 246-247.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 包晴忠, 魏玉莲, 袁海生, 李永儒 ( 2006) 中国云南一种新的阔叶树干基腐朽病. 林业科学研究, 19, 246-247.] | |
| 2 | Dai YC (2005) Illustrations of Pathogenic Wood-decaying Fungi in China. Science Press, Beijing.(in Chinese) |
| [ 戴玉成 ( 2005) 中国林木病原腐朽菌图志. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 3 | Dai YC (2010) Species diversity of wood-decaying fungi in Northeast China. Mycosystema, 29, 801-818.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 戴玉成 ( 2010) 中国东北地区木材腐朽菌的多样性. 菌物学报, 29, 801-818.] | |
| 4 | Dai YC (2012) Pathogenic wood-decaying fungi on woody plants in China. Mycosystema, 31, 493-509.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 戴玉成 (2012) 中国木本植物病原木材腐朽菌研究. 菌物学报, 31, 493-509.] | |
| 5 | Dai YC, Cui BK, Yuan HS, Li BD ( 2007) Pathogenic wood- decaying fungi in China. Forest Pathology, 37, 105-120. |
| 6 | Dai YC, Qin GF, Xu MQ ( 2000) The forest pathogens of root and butt rot in northeast China. Forest Research, 13, 15-22.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 戴玉成, 秦国夫, 徐梅卿 ( 2000) 中国东北地区的立木腐朽菌. 林业科学研究, 13, 15-22.] | |
| 7 | Jiang JQ, Yuan HS ( 2005) Two newly described polypores on Populus in Northeast China. Forest Research, 18, 280-283.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 姜俊清, 袁海生 (2005) 中国东北杨树上多孔菌二新记录. 林业科学研究, 18, 280-283.] | |
| 8 | Marchioro CA, Krechemer FS ( 2018) Potential global distribution of Diabrotica species and the risks for agricultural production. Pest Management Science, 74, 2100-2109. |
| 9 | Pearce JL, Boyce MS ( 2006) Modelling distribution and abundance with presence-only data. Journal of Applied Ecology, 43, 405-412. |
| 10 | Pearce J, Ferrier S (2000) An evaluation of alternative algorithms for fitting species distribution models using logistic regression. Ecological Modelling, 128, 127-147. |
| 11 | Pearson RG, Raxworthy CJ, Nakamura M, Peterson AT ( 2007) Predicting species distributions from small numbers of occurrence records: A test case using cryptic geckos in Madagascar. Journal of Biogeography, 34, 102-117. |
| 12 | Phillips SJ, Dudík M (2008) Modeling of species distributions with MaxEnt: New extensions and a comprehensive evaluation. Ecography, 31, 161-175. |
| 13 | Phillips SJ, Anderson RP, Schapire RE (2006) Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecological Modelling, 190, 231-259. |
| 14 | Shcheglovitova M, Anderson RP (2013) Estimating optimal complexity for ecological niche models: A Jackknife approach for species with small sample sizes. Ecological Modelling, 269, 9-17. |
| 15 | Wei YL, Dai YC ( 2004) The ecological function of wood- inhabiting fungi in forest ecosystem. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 15, 1935-1938.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 魏玉莲, 戴玉成 ( 2004) 木材腐朽菌在森林生态系统中的功能. 应用生态学报, 15, 1935-1938.] | |
| 16 | Wisz MS, Hijmans RJ, Li J, Peterson AT, Graham CH, Guisan A, Elith J, Dudik M, Ferrier S, Huettman F, Leathwick JR, Lehmann A, Lohamnn L, Loiselle BA, Manion G, Moritz C, Nakamura M, Nakazawa Y, Overton JMcC, Phillips SJ, Richardson KS, Scachetti-Pereira R, Schapire RE, Soberón J, Williams SE, Zimmermann NE ( 2008) Effects of sample size on the performance of species distribution models. Diversity and Distributions, 14, 763-773. |
| 17 | Yuan HS, Wang L, Yu CJ, Dai YC (2008) Two new butt-rot pathogens on broad leaved tree in China. Forest Research, 21, 248-252.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 袁海生, 王琳, 余长军, 戴玉成 ( 2008) 中国阔叶树干基腐朽两种新病原菌. 林业科学研究, 21, 248-252.] | |
| 18 | Yuan HS, Wei YL, Qin WM, Zhou LW (2009) Lignicolous fungi of eastern Less Hinggan Mts. of Heilongjiang Province. Mycosystema, 28, 36-43. |
| 19 | Yuan HS, Wei YL, Wang XG ( 2015) Maxent modeling for predicting potential distribution of Sanghuang, an important group of medicinal fungi in China. Fungal Ecology, 17, 140-145. |
| [1] | 龚翠凤, 韦伟, 罗概, 韩一敏, 吴鹏程, 何梦楠, 闵清悦, 付强, 陈鹏. 大熊猫国家公园崇州片区有蹄类动物空间分布及共存关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24260-. |
| [2] | 卢佳玉, 石小亿, 多立安, 王天明, 李治霖. 基于红外相机技术的天津城市地栖哺乳动物昼夜活动节律评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23369-. |
| [3] | 王艳丽, 张英, 戚春林, 张昌达, 史佑海, 杜彦君, 丁琼. 海南热带雨林国家公园生物多样性热点与保护空缺区域识别: 基于大型真菌与植物视角[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24081-. |
| [4] | 曲锐, 左振君, 王有鑫, 张良键, 吴志刚, 乔秀娟, 王忠. 基于元素组的生物地球化学生态位及其在不同生态系统中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23378-. |
| [5] | 吕晓波, 李东海, 杨小波, 张孟文. 红树林群落通过淹水时间及海水盐度的生态位分化实现物种共存[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23302-. |
| [6] | 杜聪聪, 冯学宇, 陈志林. 桥头堡效应中气候生态位差异的缩小促进了红火蚁的入侵[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24276-. |
| [7] | 原雪姣, 张渊媛, 张衍亮, 胡璐祎, 桑卫国, 杨峥, 陈颀. 基于飞机草历史分布数据拟合的物种分布模型及其预测能力[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24288-. |
| [8] | 谢将剑, 沈忱, 张飞宇, 肖治术. 融合音频及生态位信息的跨地域鸟类物种识别方法[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24259-. |
| [9] | 韩丽霞, 王永健, 刘宣. 外来物种入侵与本土物种分布区扩张的异同[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23396-. |
| [10] | 董廷玮, 黄美玲, 韦旭, 马硕, 岳衢, 刘文丽, 郑佳鑫, 王刚, 马蕊, 丁由中, 薄顺奇, 王正寰. 上海地区金线侧褶蛙种群的潜在空间分布格局及其景观连通性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 22692-. |
| [11] | 刘志发, 王新财, 龚粤宁, 陈道剑, 张强. 基于红外相机监测的广东南岭国家级自然保护区鸟兽多样性及其垂直分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 22689-. |
| [12] | 公欣桐, 陈飞, 高欢欢, 习新强. 两种果蝇成虫与幼虫期的竞争及其对二者共存的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 22603-. |
| [13] | 刘伟, 王濡格, 范天巧, 娜依曼·阿不都力江, 宋新航, 肖书平, 郭宁, 帅凌鹰. 福建省明溪县黑冠鹃隼生境适宜性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22660-. |
| [14] | 赵坤明, 陈圣宾, 杨锡福. 基于红外相机技术调查四川都江堰破碎化森林鸟兽多样性及优势种活动节律[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22529-. |
| [15] | 鲍虞园, 李银康, 林吴颖, 周志琴, 肖晓波, 颉晓勇. 中国南海北部近海鲎资源调查及北部湾潮间带中华鲎幼鲎潜在栖息地评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22407-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn