



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (4): 21385. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021385 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021385
所属专题: 青藏高原生物多样性与生态安全
赵仁生1, 许诗嘉1, 宋鹏飞1,2, 周翔1,2, 张亚洲2,*( ), 袁燕1,*(
), 袁燕1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-09-22
接受日期:2021-12-23
出版日期:2022-04-20
发布日期:2022-03-11
通讯作者:
张亚洲,袁燕
作者简介:54988363@qq.com基金资助:
Rensheng Zhao1, Shijia Xu1, Pengfei Song1,2, Xiang Zhou1,2, Yazhou Zhang2,*( ), Yan Yuan1,*(
), Yan Yuan1,*( )
)
Received:2021-09-22
Accepted:2021-12-23
Online:2022-04-20
Published:2022-03-11
Contact:
Yazhou Zhang,Yan Yuan
About author:First author contact:#Co-first authors
摘要:
青藏高原拥有丰富的药用植物资源, 但目前人们缺乏对其多样性分布格局的清晰认识以及人类活动对药用植物资源影响的评估。本研究收集整理了青藏高原地区254种药用植物分布及人类活动的数据, 分析了当前青藏高原地区药用植物分布格局及其面临的威胁, 并划定出当前需要保护的优先区域。研究结果显示, 青藏高原药用植物的多样性和特有性主要集中在东部和东南部地区, 且较强的人类活动影响力与较高的药用植物多样性和特有性重叠, 这表明人类活动对药用植物多样性和特有性有着显著的影响。进一步结合生物和人类活动两方面因素的算法, 划定了保护优先区, 包括云南西北部、四川西南部和西部、青海东部及西藏中部, 这表明青藏高原现有的保护区存在大量保护空缺。基于此, 本研究提出了包括完善法律法规及政策监管, 增设保护区, 补充和完善保护植物名录, 加强科普宣传, 加强药用植物种质资源的收集、保存与开发的保护青藏高原药用植物资源的建议, 为今后保护政策的制定和保护区划定提供依据, 也借此宣传青藏高原生态保护问题, 唤起民众的保护关注。
赵仁生, 许诗嘉, 宋鹏飞, 周翔, 张亚洲, 袁燕 (2022) 青藏高原药用植物分布格局及保护优先区. 生物多样性, 30, 21385. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021385.
Rensheng Zhao, Shijia Xu, Pengfei Song, Xiang Zhou, Yazhou Zhang, Yan Yuan (2022) Distribution patterns of medicinal plant diversity and their conservation priorities in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21385. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021385.
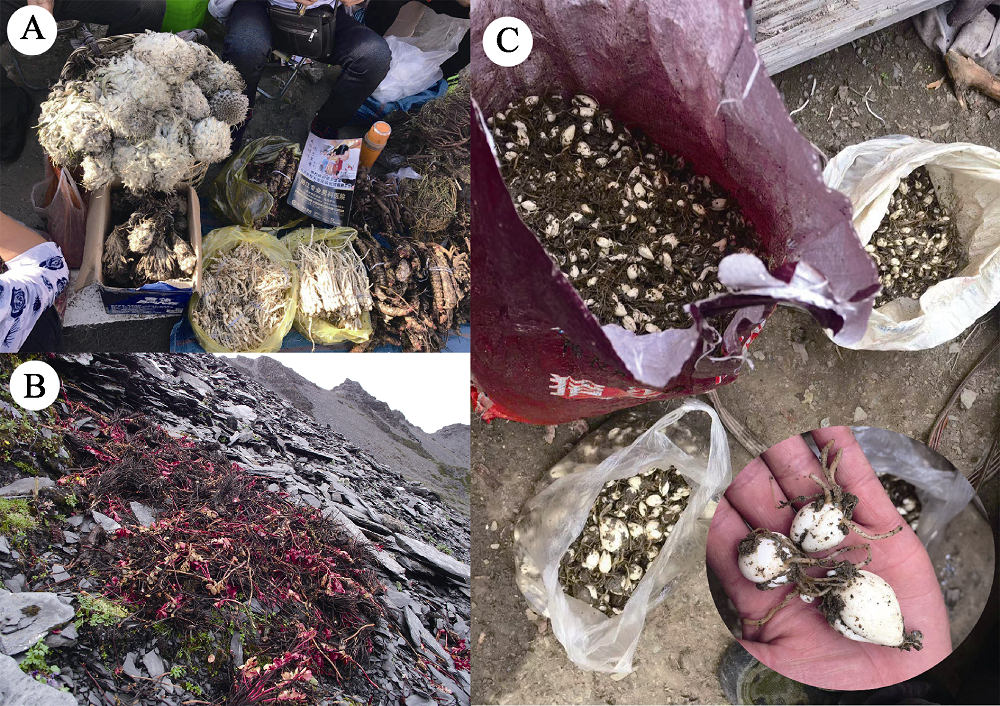

图1 青藏高原地区采挖和售卖的部分野生植物。(A)售卖的绵头雪兔子、党参等药用植物; (B)高山冰缘带上大花红景天被采挖后遗留的破坏现场; (C)当地居民采挖的贝母鳞茎。A、B和C分别由李树荣、宋波和邱天拍摄。
Fig. 1 Some wild plants harvested and sold in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. (A) Selling some medicinal plants, for example Saussurea laniceps and Codonopsis sp.; (B) The damaged site of Rhodiola crenulata after excavation in the alpine subnival belts; (C) Bulbs of Fritillaria sp. were harvested by residents. Photos in A, B and C taken by Li Shurong, Song Bo and Qiu Tian, respectively.
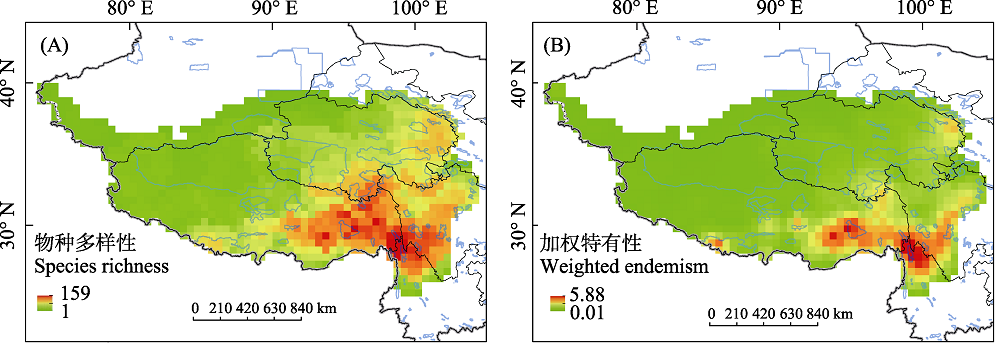
图2 青藏高原药用植物物种多样性和加权特有性分布格局。(A)物种多样性, (B)加权特有性。图中蓝色线表示国家级保护区范围。
Fig. 2 The distribution patterns of species diversity and weighted endemism in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. (A) Species richness, (B) Weighted endemism. Blue lines indicate the national-level protected areas.
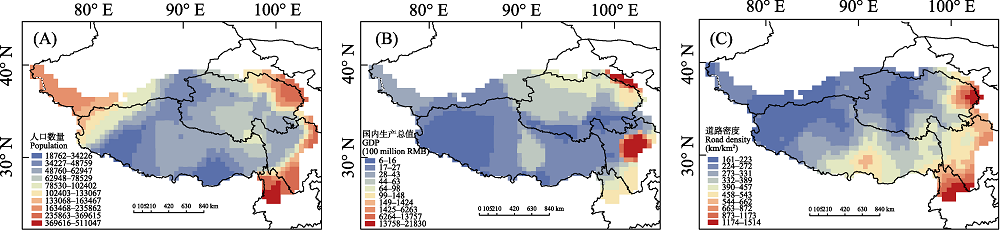
图3 青藏高原人类活动强度分布格局。(A)人口; (B)国内生产总值; (C)道路密度。
Fig. 3 The distribution pattern of human effects in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. (A) Population; (B) Gross domestic product (GDP); (C) Road density.
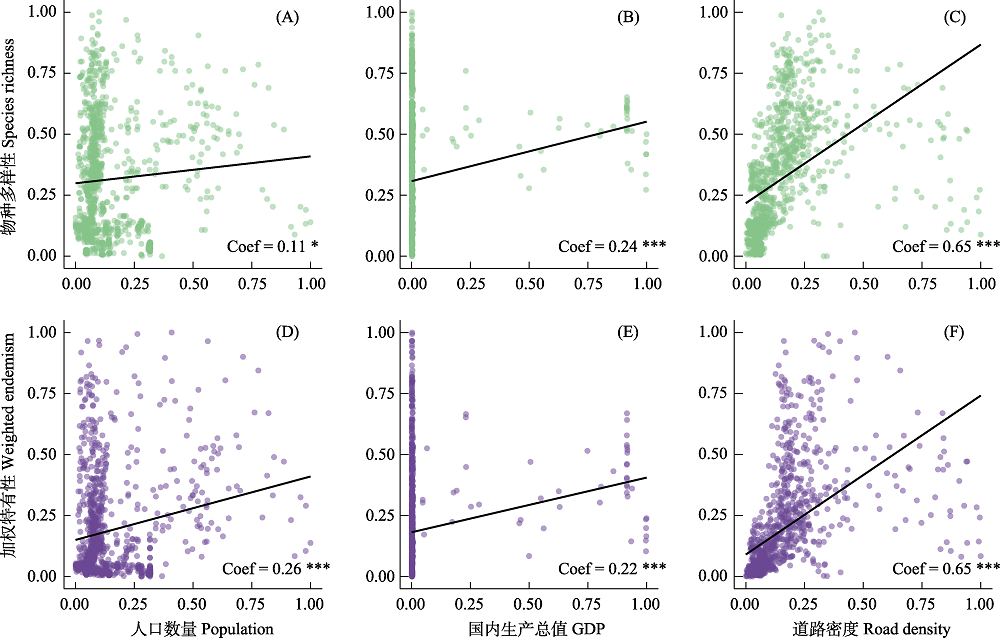
图4 生物指标与人类活动的关系。A-C: 物种多样性指标; D-F: 加权特有性指标。拟合线使用一般线性模型绘制, Coef: 模型拟合系数。* P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001。所有因子被标准化至0-1之间。
Fig. 4 The relationships between biotic factors and human effects. A-C, Species richness; D-F, Weighted endemism. Fitted lines were drawn using linear model. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001. All factors were standardized between 0-1.
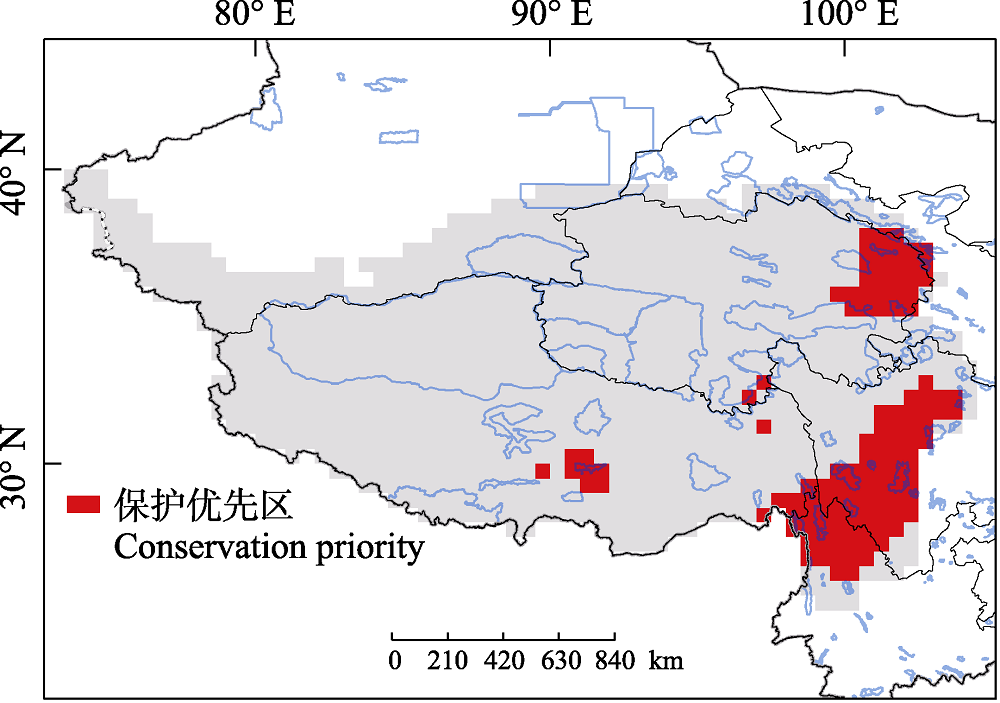
图5 青藏高原药用植物保护优先区。红色栅格为保护优先区; 蓝色线为国家级保护区。
Fig. 5 The conservation priority of medicinal plants in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Red grid cells indicate the priority areas, blue lines indicate the national-level protected areas.
| [1] | Cardillo M, Purvis A, Sechrest W, Gittleman JL, Bielby J, Mace GM (2004) Human population density and extinction risk in the world’s carnivores. PLoS Biology, 2, 909-914. |
| [2] |
Ceballos G, Ehrlich PR, Barnosky AD, García A, Pringle RM, Palmer TM (2015) Accelerated modern human-induced species losses: Entering the sixth mass extinction. Science Advances, 1, e1400253.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Chinese Materia Medica Editorial Committee (2002) Chinese Materia Medica Zang Medicine Volume. Shaghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai. (in Chinese) |
| [中华本草编委会 (2002) 中华本草:藏药卷. 上海科学技术出版社, 上海.] | |
| [4] |
Cincotta RP, Wisnewski J, Engelman R (2000) Human population in the biodiversity hotspots. Nature, 404, 990- 992.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Comprehensive Scientific Expedition Team of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (1993) Vascular Plants in Hengduan Mountain. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [中国科学院青藏高原综合科学考察队 (1993) 横断山维管植物. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [6] |
Ding WN, Ree RH, Spicer RA, Xing YW (2020) Ancient orogenic and monsoon-driven assembly of the world’s richest temperate alpine flora. Science, 369, 578-581.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Editorial Committee of Flora of China (1961-2002) Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae (Flora of China). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [中国植物志编委会 (1961-2002) 中国植物志. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [8] |
Faith DP (1992) Conservation evaluation and phylogenetic diversity. Biological Conservation, 61(1), 1-10.
DOI URL |
| [9] | Gansu Flora Editorial Committee (2005) Flora of Gansu. Gansu Science and Technology Press, Lanzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [甘肃植物志编辑委员会 (2005) 甘肃植物志. 甘肃科学技术出版社, 兰州.] | |
| [10] | Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences (1983) Flora of Tibet. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [中国科学院昆明植物研究所 (1983) 西藏植物志. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [11] | Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences (2006) Flora of Yunnan. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [中国科学院昆明植物研究所 (2006) 云南植物志. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [12] |
Laffan SW, Lubarsky E, Rosauer DF (2010) Biodiverse, a tool for the spatial analysis of biological and related diversity. Ecography, 33, 643-647.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Law W, Salick J (2005) Human-induced dwarfing of Himalayan snow lotus, Saussurea laniceps (Asteraceae). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 102, 10218-10220. |
| [14] | Li XW, Li J (1993) A preliminary floristic study on the feed plants from the region of Hengduan Mountains. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 15, 217-231. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李锡文, 李捷 (1993) 横断山脉地区种子植物区系的初步研究. 云南植物研究, 15, 217-231.] | |
| [15] |
Linder HP (2001) On areas of endemism, with an example from the African Restionaceae. Systematic Biology, 50, 892-912.
PMID |
| [16] |
Liu J, Milne RI, Cadotte MW, Wu ZY, Provan J, Zhu GF, Gao LM, Li DZ (2018) Protect third pole’s fragile ecosystem. Science, 362, 1368-1368.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Luck GW (2007) A review of the relationships between human population density and biodiversity. Biological Reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 82, 607-645.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Myers N, Mittermeier RA, Mittermeier CG, da Fonseca GAB, Kent J (2000) Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature, 403, 853-858.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Niu Y, Stevens M, Sun H (2021) Commercial harvesting has driven the evolution of camouflage in an alpine plant. Current Biology, 31, 446-449.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Peng DL, Sun L, Pritchard HW, Yang J, Sun H, Li ZM (2019) Species distribution modelling and seed germination of four threatened snow lotus (Saussurea), and their implication for conservation. Global Ecology and Conservation, 17, e00565.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Qian LS, Chen JH, Deng T, Sun H (2020) Plant diversity in Yunnan: Current status and future directions. Plant Diversity, 42, 281-291.
DOI URL |
| [22] | R Core Team (2019) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. |
| [23] |
Rana SK, Rana HK, Ranjitkar S, Ghimire SK, Gurmachhan CM, O’Neill AR, Sun H (2020) Climate-change threats to distribution, habitats, sustainability and conservation of highly traded medicinal and aromatic plants in Nepal. Ecological Indicators, 115, 106435.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Sebastien L, Julie J, Francois H (2008) Factominer: An R package for multivariate analysis. Journal of Statistical Software, 25(1), 1-18. |
| [25] | Sichuan Flora Editorial Committee (1981-2007) Flora of Sichuan. Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [四川植物志编委会 (1981-2007) 四川植物志. 四川科学技术出版社, 成都.] | |
| [26] |
Sun H, Niu Y, Chen YS, Song B, Liu CQ, Peng DL, Chen JG, Yang Y (2014) Survival and reproduction of plant species in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 52, 378-396.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Sun H, Zhang JW, Deng T, Boufford DE (2017) Origins and evolution of plant diversity in the Hengduan Mountains, China. Plant Diversity, 39, 161-166.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Wang B, Bao Q, Hoskins B, Wu GX, Liu YM (2008) Tibetan Plateau warming and precipitation changes in East Asia. Geophysical Research Letters, 35, L14702.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Wang SW, Zhou YD, Musili PM, Mwachala G, Hu GW, Wang QF (2020) Inventory incompleteness and collecting priority on the plant diversity in tropical East Africa. Biological Conservation, 241, 108313.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Wang ZH, Fang JY, Tang ZY, Lin X (2011) Patterns, determinants and models of woody plant diversity in China. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 278, 2122-2132. |
| [31] | Wu ZY, Raven P, Hong DY (2013) Flora of China, Vol. 2-3 (Pteridophytes). Science Press, Beijing & Missouri Botanical Garden Press, St. Louis. |
| [32] | Xing YW, Ree RH (2017) Uplift-driven diversification in the Hengduan Mountains, a temperate biodiversity hotspot. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 114, E3444-E3451. |
| [33] | Xinjiang Flora Editorial Committee (1993- 1996) Flora of Xinjiang. Xinjiang Science, Technology and Healthy Press, Urumqi. (in Chinese) |
| [新疆植物志编委会 (1993- 1996) 新疆植物志. 新疆科技卫生出版社, 乌鲁木齐.] | |
| [34] |
Xu Y, Huang JH, Lu XH, Ding Y, Zang RG (2019) Priorities and conservation gaps across three biodiversity dimensions of rare and endangered plant species in China. Biological Conservation, 229, 30-37.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Yu HB, Deane DC, Sui XH, Fang SQ, Chu CJ, Liu Y, He FL (2019a) Testing multiple hypotheses for the high endemic plant diversity of the Tibetan Plateau. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 28, 131-144.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Yu HB, Favre A, Sui XH, Chen Z, Qi W, Xie GW (2019b) Mapping the genetic patterns of plants in the region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Implications for conservation strategies. Diversity and Distributions, 25, 310-324.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Yu HB, Zhang YL, Liu LS, Chen C, Qi W (2018) Floristic characteristics and diversity patterns of seed plants endemic to the Tibetan Plateau. Biodiversity Science, 26, 130-137. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 于海彬, 张镱锂, 刘林山, 陈朝, 祁威 (2018) 青藏高原特有种子植物区系特征及多样性分布格局. 生物多样性, 26, 130-137.]
DOI |
|
| [38] | Yunnan Vegetation Writing Group (1987) Yunnan Vegetation. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [云南植被编写组 (1987) 云南植被. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [39] |
Zhang DC, Ye JX, Sun H (2016) Quantitative approaches to identify floristic units and centres of species endemism in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, south-western China. Journal of Biogeography, 43, 2465-2476.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Zhang YZ (2021) Plant Diversity Patterns and Formation Mechanisms of the Alpine Subnival in the Hengduan Mountains. PhD dissertation, Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张亚洲 (2021) 横断山区高山冰缘带植物多样性格局及形成机制研究. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院昆明植物研究所, 昆明.] | |
| [41] | Zhang YZ, Chen JG, Sun H (2021a) Alpine speciation and morphological innovations: Revelations from a species-rich genus in the northern hemisphere. AoB PLANTS, 13, plab018. |
| [42] |
Zhang YZ, Qian L, Spalink D, Sun L, Chen J, Sun H (2021b) Spatial phylogenetics of two topographic extremes of the Hengduan Mountains in southwestern China and its implications for biodiversity conservation. Plant Diversity 43, 181-191.
DOI URL |
| [43] | Zhang YZ, Qian LS, Chen XF, Sun L, Sun H, Chen JG (2021c) Diversity patterns of cushion plants on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: A basic study for future conservation efforts on alpine ecosystems. Plant Diversity (Online). http://:doi.org/10.1016/j.pld.2021.09.001. |
| [44] |
Zhang YZ, Qian LS, Spalink D, Sun L, Chen JG, Sun H (2020) Spatial phylogenetics of two topographic extremes of the Hengduan Mountains in southwestern China and its implications for biodiversity conservation. Plant Diversity, 43, 181-191.
DOI URL |
| [45] | Zhang YZ, Tang R, Huang XH, Sun WG, Ma XG, Sun H (2019) Saussurea balangshanensis sp. nov. (Asteraceae), from the Hengduan Mountains region, SW China. Nordic Journal of Botany, 37, njb.02078. |
| [46] |
Zhang ZJ, He JS, Li JS, Tang ZY (2015) Distribution and conservation of threatened plants in China. Biological Conservation, 192, 454-460.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Zhao ZX, Yang L, Long JK, Chang ZM, Zhou ZX, Zhi Y, Yang LJ, Li HX, Sui YJ, Gong N, Wang XY, Chen XS (2020) Testing seven hypotheses to determine what explains the current planthopper (Fulgoridae) geographical and species richness patterns in China. Insects, 11, 892.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 罗敏, 杨永川, 靳程, 周礼华, 龙宇潇. 城市森林兽类组成特征及人类活动的影响——以重庆中心城区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24402-. |
| [2] | 弋维, 艾鷖, 吴萌, 田黎明, 泽让东科. 青藏高原高寒草甸土壤古菌群落对不同放牧强度的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24339-. |
| [3] | 钟超, 廖亚琴, 刘伟杰, 隋昊志, 陈清华. 广东沿海海草床的现状、面临的威胁与保护建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23201-. |
| [4] | 陈嘉珈, 蒲真, 黄中鸿, 于凤琴, 张建军, 许东华, 徐俊泉, 尚鹏, 地里木拉提∙帕尔哈提, 李耀江, Jigme Tshering, 郭玉民. 全球黑颈鹤越冬种群分布与数量[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22400-. |
| [5] | 董庆栋, 陈超男, 李艳红, 赵体侠, 孙梓欣, 张哲, 朱连奇. 基于NPP和人类扰动指数评估河南伏牛山地区国家级自然保护区群保护成效与溢出/泄漏效应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22503-. |
| [6] | 陈晓澄, 张鹏展, 康斌, 刘林山, 赵亮. 基于中国科学院西北高原生物研究所馆藏标本分析青藏高原雀形目鸟类物种和功能多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22638-. |
| [7] | 张鹤露, 赵美红, 孙世春, 刘晓收. 西藏那曲市高原盐湖自由生活线虫群落多样性与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22533-. |
| [8] | 江艺欣, 时莹莹, 高朔, 王苏盆. 人为噪音、夜间人造光和路杀对两栖动物的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22427-. |
| [9] | 龚心语, 黄宝荣. 国家公园全民公益性评估指标体系: 以青藏高原国家公园群为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22571-. |
| [10] | 王健铭, 曲梦君, 王寅, 冯益明, 吴波, 卢琦, 何念鹏, 李景文. 青藏高原北部戈壁植物群落物种、功能与系统发育β多样性分布格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 21503-. |
| [11] | 沈国平, 韩睿, 缪增强, 邢江娃, 李永臻, 王嵘, 朱德锐. 青藏高原4类典型水化学特征湖泊的细菌多样性差异及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21420-. |
| [12] | 秦乐, 朱彦鹏, 任月恒, 李博炎, 付梦娣, 李俊生. 青藏高原国家级自然保护区管理能力差异及其对保护成效的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22419-. |
| [13] | 傅声雷, 刘满强, 张卫信, 邵元虎. 土壤动物多样性的地理分布及其生态功能研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22435-. |
| [14] | 戴尊, 陈星, 张建行, 朱毛洁, 宋坤, 邢诗晨, 涂淑雯, 邹璐, 雷祖培, 李宏庆, 王健. 浙江乌岩岭国家级自然保护区叶附生苔类及附主植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(1): 21229-. |
| [15] | 张超, 陈敏豪, 杨立, 庄鸿飞, 武曙红, 湛振杰, 王嘉栋, 栾晓峰. 东北地区水獭分布格局与保护优先区识别[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(1): 21157-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn