



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (4): 21420. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021420 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021420
所属专题: 青藏高原生物多样性与生态安全
沈国平1, 韩睿2, 缪增强1, 邢江娃1, 李永臻1, 王嵘1, 朱德锐1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-10-22
接受日期:2022-02-18
出版日期:2022-04-20
发布日期:2022-03-13
通讯作者:
朱德锐
作者简介:*E-mail: zhuderui2005@126.com基金资助:
Guoping Shen1, Rui Han2, Zengqiang Miao1, Jiangwa Xing1, Yongzhen Li1, Rong Wang1, Derui Zhu1,*( )
)
Received:2021-10-22
Accepted:2022-02-18
Online:2022-04-20
Published:2022-03-13
Contact:
Derui Zhu
摘要:
青藏高原分布着我国最密集的极端环境湖泊群, 湖泊类型和水化学特征多样, 而不同类型湖泊的细菌群落组成与多样性差异的系统研究相对较少。本文以青藏高原4类典型水化学特征湖泊(即氯化物型、MgSO4亚型、Na2SO4亚型、碳酸盐型)为研究对象, 借助Illumina测序16S rRNA基因(V3‒V4区)分析细菌多样性、群落组成差异及其优势属与环境因素的制约关系。结果表明: MgSO4亚型与氯化物型湖泊多属于超盐环境, 而大多数Na2SO4亚型与碳酸盐型湖泊属于咸水、微咸水或淡水环境。4类湖泊获得分类地位明确的细菌共计45门81纲1,148属(52,031个OTUs), 细菌Shannon指数为碳酸盐型(5.27 ± 0.57) > Na2SO4亚型(4.96 ± 0.51) > 氯化物型(4.12 ± 0.80) > MgSO4亚型(3.64 ± 1.04)。优势细菌门是变形菌门、厚壁菌门和拟杆菌门。变形菌门的相对多度总体较高, 优势纲是γ-、α-和β-变形菌纲; 厚壁菌门多分布于MgSO4亚型和氯化物型湖泊, 优势纲是芽孢杆菌纲; 拟杆菌门主要分布于碳酸盐型和Na2SO4亚型湖泊, 优势纲是黄杆菌纲。全部氯化物型和少数MgSO4亚型湖泊的细菌组成相似, 优势属是假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas)、乳球菌属(Lactococcus)和不动杆菌属(Acinetobacter), 其聚集分布与总盐度、主要离子(Mg2+、Cl-、Na+与K+)和温度相关; MgSO4亚型湖泊独有的常见属是芽孢杆菌属(Bacillus)、气单胞菌属(Aeromonas)、大洋芽孢杆菌属(Oceanobacillus)等, 其聚集分布与SO4 2-浓度正相关; Na2SO4亚型与碳酸盐型湖泊的细菌组成相似, 优势属是水弯曲菌属(Aquiflexum)、海仙菌属(Haliea)与苍黄杆菌属(Luteolibacter), 其聚集分布与HCO3 -浓度、pH值和海拔高度呈显著正相关。与世界上其他湖泊组/群相比, 青藏高原湖泊具有独特的细菌优势属和常见属, 不同类型湖泊的细菌群落组成存在显著差异, 可能与水化学类型或地理位置有关。
沈国平, 韩睿, 缪增强, 邢江娃, 李永臻, 王嵘, 朱德锐 (2022) 青藏高原4类典型水化学特征湖泊的细菌多样性差异及影响因素. 生物多样性, 30, 21420. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021420.
Guoping Shen, Rui Han, Zengqiang Miao, Jiangwa Xing, Yongzhen Li, Rong Wang, Derui Zhu (2022) Bacterial diversity differences and influence factors of four types of hydrochemical characteristic lakes in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21420. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021420.
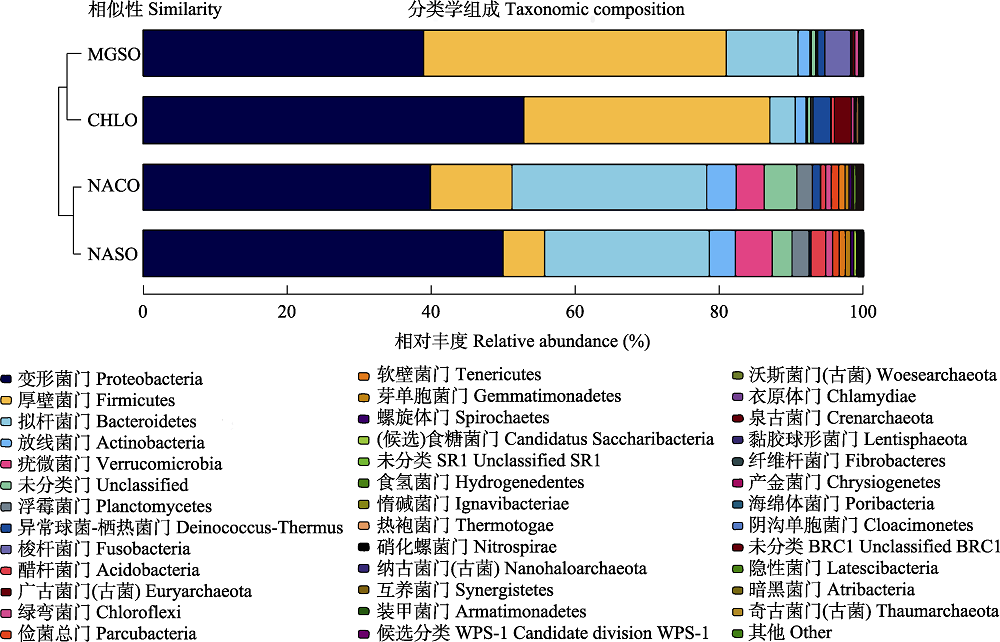
图1 4类典型水化学特征湖泊组的细菌门水平群落组成。CHLO: 氯化物型组; MGSO: MgSO4亚型组; NASO: Na2SO4亚型组; NACO: Na2CO3/NaHCO3型组。
Fig. 1 Community composition of bacteria at phylum level in four typically hydrochemical characteristic lake groups. CHLO, Chloride type group; MGSO, MgSO4 subtype group; NASO, Na2SO4 subtype group; NACO, Na2CO3/NaHCO3 type group.
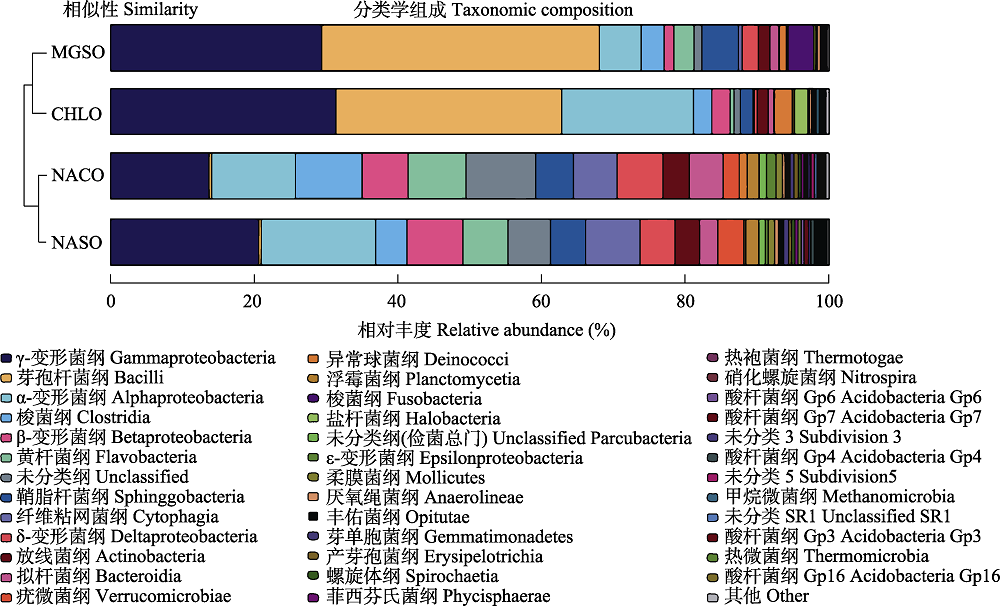
图2 4类典型水化学特征湖泊的细菌纲水平群落组成。CHLO: 氯化物型组; MGSO: MgSO4亚型组; NASO: Na2SO4亚型组; NACO: Na2CO3/NaHCO3型组。
Fig. 2 Community composition of bacteria at class level in four typically hydrochemical characteristic lake groups. CHLO, Chloride type group; MGSO, MgSO4 subtype group; NASO, Na2SO4 subtype group; NACO, Na2CO3/NaHCO3 type group.
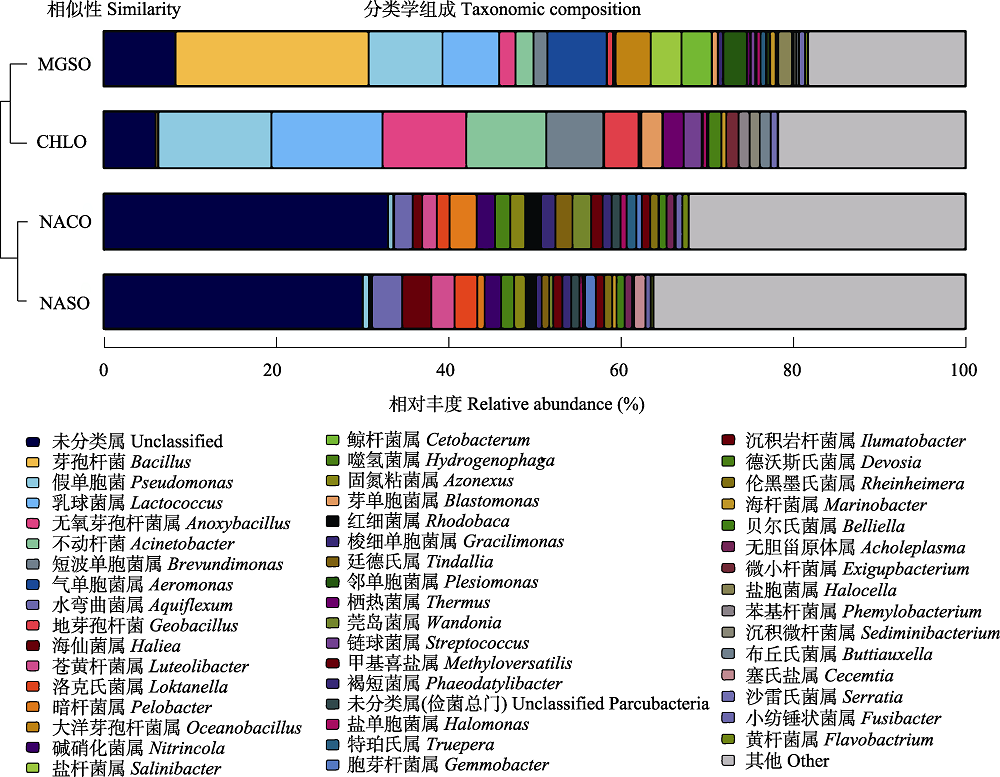
图3 4类典型水化学特征湖泊组的细菌属水平群落组成。CHLO: 氯化物型组; MGSO: MgSO4亚型组; NASO: Na2SO4亚型组; NACO: Na2CO3/NaHCO3型组。
Fig. 3 Community composition of bacteria at genus level in four typically hydrochemical characteristic lake groups. CHLO, Chloride type group; MGSO, MgSO4 subtype group; NASO, Na2SO4 subtype group; NACO, Na2CO3/NaHCO3 type group.
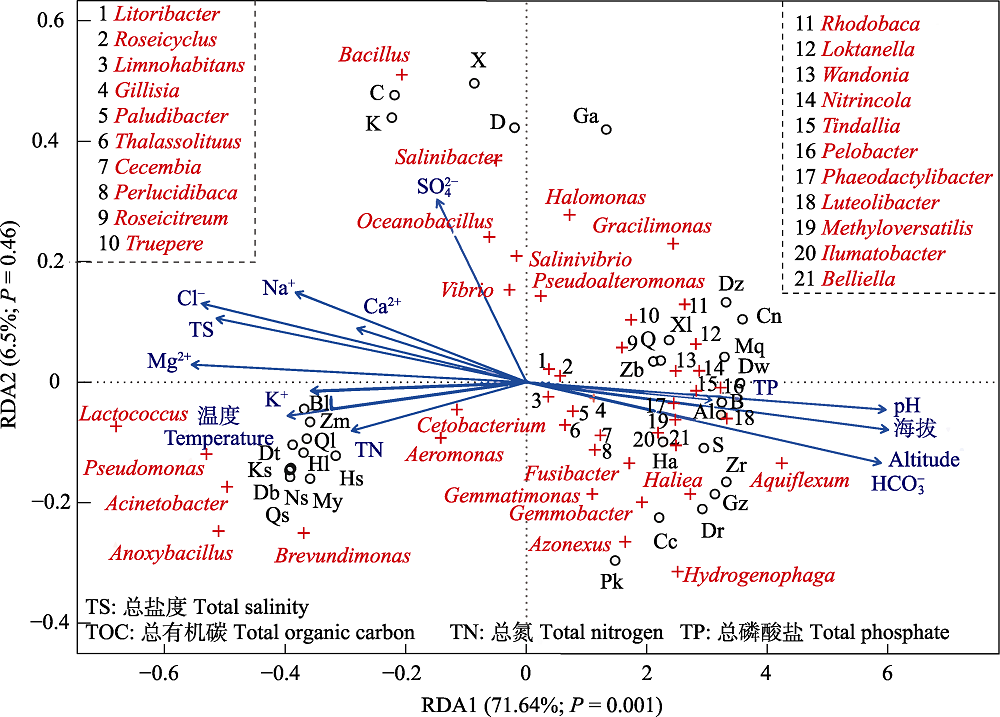
图4 环境因子与样本、优势细菌属的相关性RDA分析。空心圆圈(○)、加号(+)和箭头(↑)分别表示样本、优势细菌属和环境因子; Hs: 霍布逊盐场; Hl: 霍布逊湖; Qs: 察尔汗盐场; Ql: 察尔汗湖; Ks: 昆特依盐场; Bl: 巴伦马海湖; Ns: 牛郎织女湖盐场; Db: (东)达布逊湖; Dt: 东台吉乃尔湖; Zm: (德)宗马海湖; My: 茫崖翡翠湖; C: 茶卡盐湖; K: 柯柯盐湖; D: 大柴旦盐湖; X: 小柴旦盐湖; Q: 青海湖; Pk: 佩枯措; Cc: 措戳龙; Dw: 达瓦措; Zr: 扎日南木措; Ga: 尕海; Ha: 哈拉湖; Xl: 希里沟湖; Zb: 扎布耶湖; B: 巴木措; Mq: 麦穷措; Dz: 达则措; Gz: 公珠措; Cn: 错纳措; Al: 昂拉仁措; S: 色林措; Dr: 当惹雍措。
Fig. 4 Redundancy analysis (RDA) of dominant bacterial genera, samples and environment factors. The hollow circles (○), plus signs (+) and arrows (↑) were shown for different samples, bacterial dominant genus and environmental factors, respectively. Hs, Hulsan Saltern; Hl, Hulsan Lake; Ql, Qarhan Lake; Qs, Qarhan Saltern; Ks, Kunteyi Saltern; Bl, Baluan Mahai Lake; Ns, Niulang Zhinü Saltern; Db, Dabsan Lake; Dt, Dong Taijnar Lake; Zm, Dezongmahai Lake; My, Mangnai Lake; C, Caka Lake; K, Keke Lake; D, Da Qaidam Lake; X, Xiao Qaidam Lake; Pk, Peikü Co; Cc, Cocholong Lake; Dw, Dawa Co; Zr, Zhari Nam Co; Ga, Gahai Lake; Xl, Xiligou Lake; Q, Qinghai Lake; Ha, Hala Lake; Zb, Zabuye Lake; B, Bam Co; Mq, Mêrqung Co; Dz, Dagzê Co; Gz, Gongzhu Co; Cn, Chani Co; Al, Ngangla Ring Co; S, Siling Co; Dr, DangraYum Co.
| [1] |
Abdallah MB, Karray F, Kallel N, Armougom F, Mhiri N, Quéméneur M, Cayol JL, Erauso G, Sayadi S (2018) Abundance and diversity of prokaryotes in ephemeral hypersaline Lake Chott El Jerid using Illumina Miseq sequencing, DGGE and qPCR assays. Extremophiles, 22, 811-823.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Adhikari NP, Adhikari S, Liu XB, Shen L, Gu ZQ (2019) Bacterial diversity in alpine lakes: A review from the third pole region. Journal of Earth Science, 30, 387-396.
DOI |
| [3] |
Çınar S, Mutlu MB (2016) Comparative analysis of prokaryotic diversity in solar salterns in Eastern Anatolia (Turkey). Extremophiles, 20, 589-601.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Couto-Rodríguez RL, Montalvo-Rodríguez R (2019) Temporal analysis of the microbial community from the crystallizer ponds in Cabo Rojo, Puerto Rico, using metagenomics. Genes, 10, 422.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics, 26, 2460-2461.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Edwardson CF, Hollibaugh JT (2018) Composition and activity of microbial communities along the redox gradient of an alkaline, hypersaline lake. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9, 14.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Fazi S, Butturini A, Tass F, Amalfitano S, Ventur S, Vazquez E, Clokie M, Wanjala SW, Pacini N, Harper DM (2018) Biogeochemistry and biodiversity in a network of saline- alkaline lakes: Implications of ecohydrological connectivity in the Kenyan Rift Valley. Ecohydrology & Hydrobiology, 18, 96-106. |
| [8] |
García-Maldonado JQ, Escobar-Zepeda A, Raggi L, Brad MB, Sanchez-Flores A, López-Cortés A (2018) Bacterial and archaeal profiling of hypersaline microbial mats and endoevaporites, under natural conditions and methanogenic microcosm experiments. Extremophiles, 22, 903-916.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Han R, Zhang X, Liu J, Long Q, Chen L, Liu D, Zhu D (2017) Microbial community structure and diversity within hypersaline Keke Salt Lake environments. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 63, 895-908.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Hu A, Yao T, Jiao N, Liu Y, Yang Z, Liu X (2010) Community structures of ammonia-oxidising archaea and bacteria in high-altitude lakes on the Tibetan Plateau. Freshwater Biology, 55, 2375-2390.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Jacob JH, Hussein E, Shakhatreh M, Cornelison CT (2017) Microbial community analysis of the hypersaline water of the Dead Sea using high-throughput amplicon sequencing. Microbiologyopen, 6, e00500.
DOI URL |
| [12] | Jiang H, Huang J, Yang J (2018) Halotolerant and halophilic microbes and their environmental implications in saline and hypersaline lakes in Qinghai Province, China. In: Extremophiles in Eurasian Ecosystems: Ecology, Diversity, and Applications (eds. Egamberdieva D, Birkeland NK, Panosyan H, Li WJ), pp. 299-316. Springer, Singapore. |
| [13] | Kalff J, Gu BH, Li KY (2011) Limnology:Inland Water Ecosystems. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ Kalff J, 古滨河, 李宽意 (2011) 湖沼学:内陆水生态系统. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [14] |
Kilmer BR, Eberl TC, Cunderla B, Chen F, Clark BC, Schneegurt MA (2014) Molecular and phenetic characterization of the bacterial assemblage of Hot Lake, an environment with high concentrations of magnesium sulphate, and its relevance to Mars. International Journal of Astrobiology, 13, 69-80.
PMID |
| [15] |
Kong WD (2013) A review of microbial diversity in polar terrestrial environments. Biodiversity Science, 21, 456-467. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 孔维栋 (2013) 极地陆域微生物多样性研究进展. 生物多样性, 21, 456-467.]
DOI |
|
| [16] |
Lei Z, Yanan C, Miao J, Jing D, Guo X, Li W, Li Y (2020) The levels of microbial diversity in different water layers of saline Chagan Lake, China. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 38, 395-407.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Li KJ, Long J (2015) Biodiversity of halophilic bacteria in Yuncheng Salt Lake of Shanxi Province. Guizhou Agricultural Science, 43, 95-101. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李坤珺, 龙健 (2015) 山西运城盐湖嗜盐细菌的系统发育与种群多样性. 贵州农业科学, 43, 95-101.] | |
| [18] | Liu J, Zhang X, Shen GP, Feng XY, Long QF, Zhu DR (2017) Microbial community structure and diversity of Xiaochaidan Salt Lake in the Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Hydroecology, 38, 55-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘静, 张欣, 沈国平, 封希媛, 龙启福, 朱德锐 (2017) 青藏高原小柴旦盐湖微生物群落结构及多样性. 水生态学杂志, 38, 55-64.] | |
| [19] |
Liu K, Liu Y, Jiao N, Zhu L, Wang J, Hu A, Liu X (2016) Vertical variation of bacterial community in Nam Co, a large stratified lake in central Tibetan Plateau. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 109, 1323-1335.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Liu K, Yao T, Pearce DA, Jiao N, Liu Y (2021) Bacteria in the lakes of the Tibetan Plateau and polar regions. Science of the Total Environment, 754, 142248.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Liu X, Yao T, Kang S, Jiao N, Zeng Y, Liu Y (2010) Salinity affects the composition of the aerobic methanotroph bacterial community of the largest oligosaline lake, Nam Co on the Tibetan Plateau. Geomicrobiology Journal, 27, 669-682.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Liu Y, Priscu JC, Yao T, Vick-Majors TJ, Michaud AB, Jiao N, Hou J, Tian L, Hu A, Chen ZQ (2014) A comparison of pelagic, littoral, and riverine bacterial assemblages in Lake Bangongco, Tibetan Plateau. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 89, 211-221.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Liu Y, Yao T, Jiao N, Zhu L, Hu A, Liu X, Gao J, Chen ZQ (2013) Salinity impact on bacterial community composition in five high-altitude lakes from the Tibetan Plateau, Western China. Geomicrobiology Journal, 30, 462-469.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Naghoni A, Emtiazi G, Amoozegar MA, Cretoiu MS, Stal LJ, Etemadifar Z, Fazeli SA, Bolhuis H (2017) Microbial diversity in the hypersaline Lake Meyghan, Iran. Scientific Reports, 7, 11522.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Oren A (2015) Halophilic microbial communities and their environments. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 33, 119- 124.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Pontefract A, Zhu TF, Walker V, Hepburn H, Lui C, Zuber MT, Ruvkun G, Carr CE (2017) Microbial diversity in a hypersaline sulfate lake: A terrestrial analog of ancient Mars. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8, 1819.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Qin H, Wang S, Feng K, He Z, Virta MJ, Hou W, Dong H, Deng Y (2019) Unraveling the diversity of sedimentary sulfate-reducing prokaryotes (SRP) across Tibetan saline lakes using epicPCR. Microbiome, 7, 71.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Ren LJ, He D, Xing P, Wang YJ, Wu QL (2013) Bacterial diversity and ecological function in lake water bodies. Biodiversity Science, 21, 421-432. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 任丽娟, 何聃, 邢鹏, 王毓菁, 吴庆龙 (2013) 湖泊水体细菌多样性及其生态功能研究进展. 生物多样性, 21, 421-432.]
DOI |
|
| [29] |
Ren Z, Wang F, Qu X, Elser JJ, Liu Y, Chu L (2017) Taxonomic and functional differences between microbial communities in Qinghai Lake and its input streams. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8, 2319.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Salazar RN, Aguirre C, Soto J, Salinas P, Salinas C, Prieto H, Paneque M (2020) Physicochemical parameters affecting the distribution and diversity of the water column microbial community in the high-altitude Andean Lake system of La Brava and La Punta. Microorganisms, 8, 1181.
DOI URL |
| [31] | Shen S (2017) Community structure and diversity of culturable moderate halophilic bacteria isolated from Qrhan Salt Lake on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 57, 490-499. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 沈硕 (2017) 青藏高原察尔汗盐湖地区可培养中度嗜盐菌的群落结构与多样性. 微生物学报, 57, 490-499.] | |
| [32] | Shi Q, Han R, Xing JW, Li YZ, Shen GP, Yong S, Zhu DR (2019) The co-occurrence patterns of microbial community in Qinghai Lake. Chinese High Altitude Medicine and Biology, 40, 85-93. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 石晴, 韩睿, 邢江娃, 李永臻, 沈国平, 永胜, 朱德锐 (2019) 青海湖微生物群落的共生模式. 中国高原医学与生物学杂志, 40, 85-93.] | |
| [33] |
Sirisena KA, Ramirez S, Steele A, Glamoclija M (2018) Microbial diversity of hypersaline sediments from Lake Lucero playa in white sands national monument, New Mexico, USA. Microbial Ecology, 76, 404-418.
DOI PMID |
| [34] | Tian K, Huang YS, Xie J, Ge YX (2018) Half of China’s lakes are on the Tibetan Plateau. Forest & Humankind, 12, 76-91. (in Chinese) |
| [ 田坤, 黄勇士, 谢俊, 葛玉修 (2018) 中国湖泊, 一半在青藏高原. 森林与人类, 12, 76-91.] | |
| [35] |
Vavourakis CD, Ghai R, Rodriguez-Valera F, Sorokin DY, Tringe SG, Hugenholtz P, Muyzer G (2016) Metagenomic insights into the uncultured diversity and physiology of microbes in four hypersaline soda lake brines. Frontiers in Microbiology, 7, 211.
DOI PMID |
| [36] | Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 73, 5261-5267. |
| [37] |
Wang R, Han R, Long Q, Gao X, Xing G, Shen G, Zhu D (2020) Bacterial and archaeal communities within an ultraoligotrophic, high-altitude lake in the pre-Himalayas of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Indian Journal of Microbiology, 60, 363-373.
DOI URL |
| [38] | Wang SM, Dou HS, Chen KZ (1998) A Chronicle of Lakes in China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王苏民, 窦鸿身, 陈克造 (1998) 中国湖泊志. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [39] |
Xiong J, Liu Y, Lin X, Zhang H, Zeng J, Hou J, Yang Y, Yao T, Knight R, Chu H (2012) Geographic distance and pH drive bacterial distribution in alkaline lake sediments across Tibetan Plateau. Environmental Microbiology, 14, 2457- 2466.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Xu LJ, Hu ZY, Zhao YN, Hong XY (2019) Climate change characteristics in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau during 1961-2010. Plateau Meteorology, 38, 911-919. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐丽娇, 胡泽勇, 赵亚楠, 洪潇宇 (2019) 1961-2010年青藏高原气候变化特征分析. 高原气象, 38, 911-919.] | |
| [41] |
Yang J, Jiang H, Dong H, Liu Y (2019) A comprehensive census of lake microbial diversity on a global scale. Science China: Life Sciences, 62, 1320-1331.
DOI URL |
| [42] | Yang J, Jiang H, Sun X, Huang J, Han M, Wang B (2020) Distinct co-occurrence patterns of prokaryotic community between the waters and sediments in lakes with different salinity. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 96, fiaa234. |
| [43] |
Yang J, Ma L, Jiang H, Wu G, Dong H (2016) Salinity shapes microbial diversity and community structure in surface sediments of the Qinghai-Tibetan lakes. Scientific Reports, 6, 25078.
DOI PMID |
| [44] | Zhang J, Yang Y, Zhao L, Liu Y, Xie S, Liu Y (2015) Distribution of sediment bacterial and archaeal communities in plateau freshwater lakes. Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology, 99, 3291-3302. |
| [45] | Zhang X, Liu J, Shen GP, Long QF, Han R, Zhu DR (2017) Illumina-based sequencing analysis of microbial community composition in Chaka Salt Lake in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Microbiology China, 44, 1834-1846. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张欣, 刘静, 沈国平, 龙启福, 韩睿, 朱德锐 (2017) 基于高通量测序研究青藏高原茶卡盐湖微生物多样性. 微生物学通报, 44, 1834-1846.] | |
| [46] | Zhao WY, Yang J, Dong HL, Wu G, Wang S, Sun YJ, Lai ZP, Jiang HC (2013) Microbial diversity in the hypersaline Dabuxun Lake in Qaidam Basin, China. Earth and Environment, 41, 398-405. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵婉雨, 杨渐, 董海良, 吴耿, 王尚, 孙永娟, 赖忠平, 蒋宏忱 (2013) 柴达木盆地达布逊盐湖微生物多样性研究. 地球与环境, 41, 398-405.] | |
| [47] |
Zhe M, Zhang X, Wang B, Sun R, Zheng D (2017) Hydrochemical regime and its mechanism in Yamzhog Yumco Basin, South Tibet. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 27, 1111-1122.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Zheng M, Liu X (2009) Hydrochemistry of salt lakes of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Aquatic Geochemistry, 15, 293-320.
DOI URL |
| [49] | Zheng MP (2014) An Introduction to Saline Lakes on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Kluwer Academic Publishers, London. |
| [50] | Zheng MP, Xiang J, Wei XJ (1989) Salt Lakes of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 郑绵平, 向军, 魏新俊 (1989) 青藏高原盐湖. 科学技术出版社, 北京.] | |
| [51] | Zheng R, Li DL (2016) Decadal changes of the wet and dry climate zone boundaries in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau during 1971-2011. Journal of Desert Research, 36, 1106-1115. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郑然, 李栋梁 (2016) 1971-2011年青藏高原干湿气候区界线的年代际变化. 中国沙漠, 36, 1106-1115.] | |
| [52] | Zhong ZP, Liu Y, Miao LL, Wang F, Chu LM, Wang JL, Liu ZP (2016) Prokaryotic community structure driven by salinity and ionic concentrations in plateau lakes of the Tibetan Plateau. Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology, 82, 1846-1858. |
| [53] |
Zhu D, Han R, Long Q, Gao X, Xing J, Shen G, Li Y, Wang R (2020) An evaluation of the core bacterial communities associated with hypersaline environments in the Qaidam Basin, China. Archives of Microbiology, 202, 2093-2103.
DOI URL |
| [54] | Zhu DR, Han R, Shi Q, Shen GP, Long QF, Shuang J (2017) Correlation analysis of bacterial community and hypersaline environmental factors in extreme salt lakes on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. China Environmental Science, 37, 4657-4666. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱德锐, 韩睿, 石晴, 沈国平, 龙启福, 双杰 (2017) 青藏高原盐湖细菌群落与超盐环境因素的相关性. 中国环境科学, 37, 4657-4666.] | |
| [55] | Zhu LP, Ju JT, Qiao BJ, Yang RM, Liu C, Han BP (2019) Recent lake changes of the Asia Water Tower and their climate response: Progress, problems and prospects. Chinese Science Bulletin, 64, 2796-2806. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 朱立平, 鞠建廷, 乔宝晋, 杨瑞敏, 刘翀, 韩博平 (2019) “亚洲水塔”的近期湖泊变化及气候响应: 进展、问题与展望. 科学通报, 64, 2796-2806.] | |
| [56] |
Zorz JK, Sharp C, Kleiner M, Gordon PMK, Pon RT, Dong X, Strous M (2019) A shared core microbiome in soda lakes separated by large distances. Nature Communications, 10, 4230.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 仝淼, 王欢, 张文双, 王超, 宋建潇. 重金属污染土壤中细菌抗生素抗性基因分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [15] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()