



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (4): 485-495. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019351 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019351
收稿日期:2019-11-06
接受日期:2020-03-11
出版日期:2020-04-20
发布日期:2020-06-15
通讯作者:
陈浒
基金资助:
Cunlu Wang,Hu Chen( ),Hua Xiao,Hongmei Zhang,Linzhi Li,Cheng Guo,Jing Chen,Qiang Wei
),Hua Xiao,Hongmei Zhang,Linzhi Li,Cheng Guo,Jing Chen,Qiang Wei
Received:2019-11-06
Accepted:2020-03-11
Online:2020-04-20
Published:2020-06-15
Contact:
Hu Chen
摘要:
对两栖动物多样性及其生境选择的调查, 可为两栖动物的保护提供基础性资料。我们于2018年9-10月、2019年3-8月对贵州省毕节市撒拉溪石漠化综合治理示范区30个研究样方的两栖动物进行了调查, 共观察到两栖动物5,688只, 隶属2目6科9属10种。采用Shannon-Wiener多样性指数、Margalef丰富度指数、Pielou均匀度指数等分析了不同等级石漠化区域中的两栖动物物种多样性, 采用Sorenson相似性系数、聚类分析等方法分析了群落的相似性与差异性。结果显示: (1)云南小狭口蛙(Glyphoglossus yunnanensis)为优势种, 贵州疣螈(Tylototriton kweichowensis)、红点齿蟾(Oreolalax rhodostigmatus)、中华蟾蜍(Bufo gargarizans)、华西雨蛙(Hyla annectans)和昭觉林蛙(Rana chaochiaoensis)为常见种, 粗皮姬蛙(Microhyla butleri)、沼水蛙(Hylarana guentheri)、筠连臭蛙(Odorrana junlianensis)和威宁蛙(Rana weiningensis)为稀有种。(2)无石漠化区域与潜在石漠化区域两栖动物物种数、个体数以及生境类型较之其他3个等级石漠化区域更为丰富, 多样性指数、丰富度指数以无石漠化区域为最大。(3)无石漠化区域和潜在石漠化区域之间、无石漠化区域和潜在石漠化区域分别与其他3个等级石漠化区域之间表现出较强的差异性。研究表明, 喀斯特地区石漠化导致的生境差异是两栖动物分布差异的重要原因, 加强石漠化的生态治理是喀斯特地区保护两栖动物的重要途径。
王存璐,陈浒,肖华,张红梅,李林芝,郭城,陈静,魏强 (2020) 黔西北石漠化地区两栖动物多样性及其生境选择. 生物多样性, 28, 485-495. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019351.
Cunlu Wang,Hu Chen,Hua Xiao,Hongmei Zhang,Linzhi Li,Cheng Guo,Jing Chen,Qiang Wei (2020) Diversity and habitat selection of amphibians in rocky desertification area in northwestern Guizhou. Biodiversity Science, 28, 485-495. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019351.
| 石漠化等级 Grade of rocky | Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index | Margalef丰富度指数 Margalef richness index | Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index |
|---|---|---|---|
| 无石漠化 No rocky desertification | 1.645 | 0.982 | 0.791 |
| 潜在石漠化 Potential desertification | 0.414 | 0.954 | 0.199 |
| 轻度石漠化 Mild rocky desertification | 0.974 | 0.721 | 0.887 |
| 中度石漠化 Moderate rocky desertification | 0.688 | 0.334 | 0.993 |
| 强度石漠化 Intense rocky desertification | 0.673 | 0.621 | 0.971 |
表1 毕节市撒拉溪石漠化综合治理示范区不同等级石漠化区域两栖动物多样性指数
Table 1 Diversity index of amphibians in rocky desertification areas with different grades in Bijie Salaxi rocky desertification comprehensive control area
| 石漠化等级 Grade of rocky | Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index | Margalef丰富度指数 Margalef richness index | Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou evenness index |
|---|---|---|---|
| 无石漠化 No rocky desertification | 1.645 | 0.982 | 0.791 |
| 潜在石漠化 Potential desertification | 0.414 | 0.954 | 0.199 |
| 轻度石漠化 Mild rocky desertification | 0.974 | 0.721 | 0.887 |
| 中度石漠化 Moderate rocky desertification | 0.688 | 0.334 | 0.993 |
| 强度石漠化 Intense rocky desertification | 0.673 | 0.621 | 0.971 |
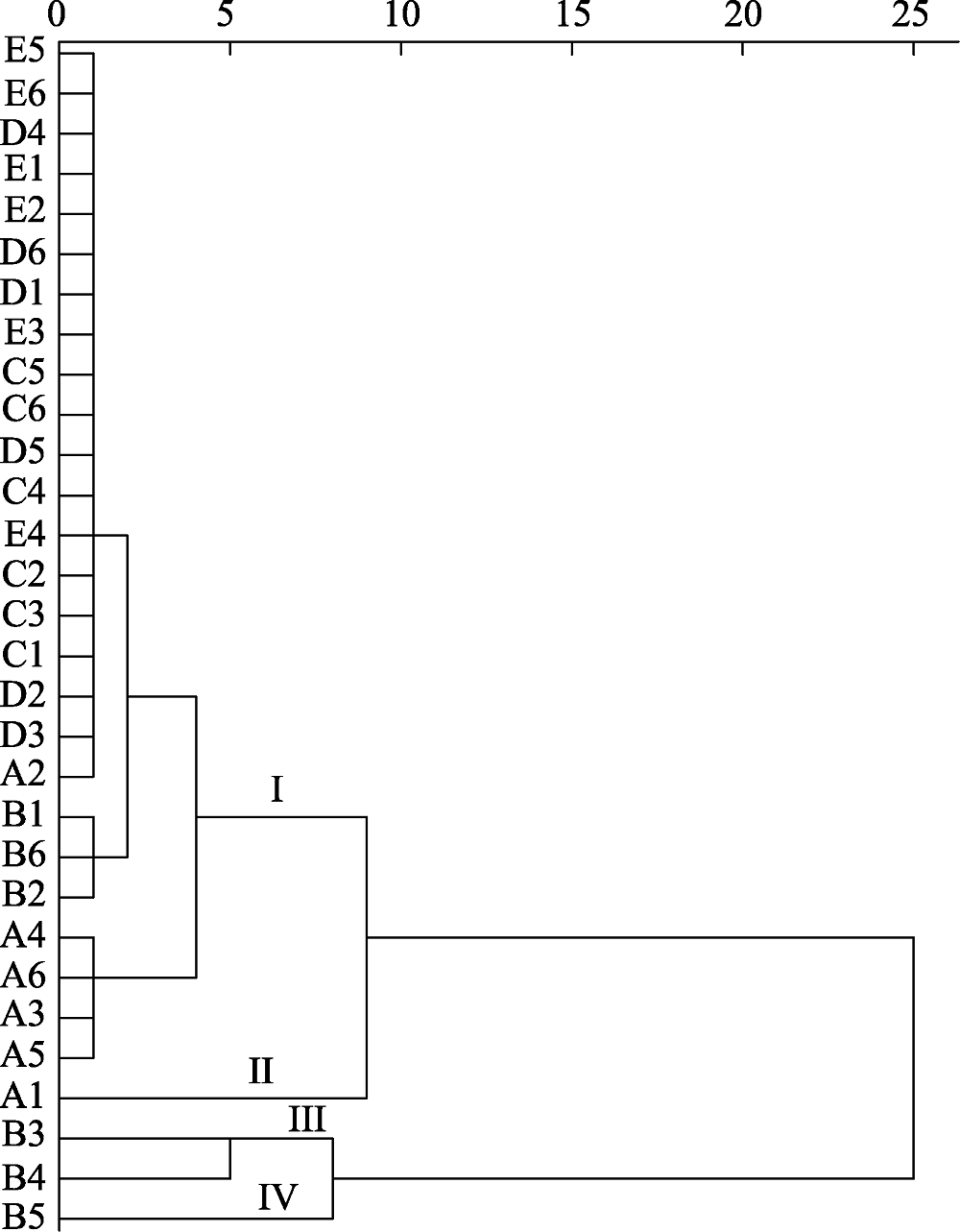
图2 毕节市撒拉溪石漠化综合治理示范区30个样方两栖群落聚类结果。A: 无石漠化; B: 潜在石漠化; C: 轻度石漠化; D: 中度石漠化; E: 强度石漠化。
Fig. 2 Clustering results of amphibian communities in 30 quadrats in Bijie Salaxi rocky desertification comprehensive control area. A, No rocky desertification; B, Potential rocky desertification; C, Mild rocky desertification; D, Moderate rocky desertification; E, Intense rocky desertification.
 |
表2 毕节市萨拉溪石漠化综合治理示范区30个样方两栖动物群落相似性指数
Table 2 Similarity index of amphibian communities in 30 quadrats in Bijie Salaxi rocky desertification comprehensive control area
 |
 |
表3 毕节市撒拉溪石漠化综合治理示范区两栖动物在不同等级石漠化区域分布的生境类型
Table 3 Habitat types of amphibians in different rocky desertification zones in Bijie Salaxi rocky desertification comprehensive control area
 |
 |
表4 毕节市撒拉溪石漠化综合治理示范区两栖动物在不同生境中的分布
Table 4 Distribution of amphibians in different habitats in Bijie Salaxi rocky desertification comprehensive control area
 |
| [1] | An JP, Wang J, Cai XF, Duan ZB, Yan MM (2017) Research progress of soil loss under the dual structure of southwest karst. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 56, 1605-1610. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 安吉平, 王济, 蔡雄飞, 段志斌, 颜蒙蒙 (2017) 西南喀斯特二元结构下土壤流失研究进展. 湖北农业科学, 56, 1605-1610.] | |
| [2] | Chen H, Xiong KN, Liu ZB, Qiu J, Chen YB, Xiao SZ, Yang H (2011) Exploration of land consolidation based on biodiversity protection in the Hetou karst area. Earth and Environment, 39, 450-455. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈浒, 熊康宁, 刘忠斌, 邱杰, 陈永毕, 肖时珍, 杨洪 (2011) 基于生物多样性保护的河头喀斯特土地整理探索. 地球与环境, 39, 450-455.] | |
| [3] | Chen JJ, Zhang X, Yang SJ, Xie ZG, Pan CK, Chen JH (2007) Survey on amphibian in Leigongshan Nature Reserve. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 26, 826-830. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈继军, 张旋, 杨绍军, 谢镇国, 潘成坤, 陈继红 (2007) 贵州雷公山自然保护区两栖动物调查报告. 四川动物, 26, 826-830.] | |
| [4] | Dai SG, Zhang JZ, Jiang YM, Xu N (2010) Diversity of amphibian sand reptiles in Baiqing Karst Nature Reserve of Guizhou. Guizhou Science, 28(1), 72-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 戴诗贵, 张景涿, 江亚猛, 徐宁 (2010) 贵州柏箐喀斯特森林自然保护区两栖爬行动物多样性研究. 贵州科学, 28(1), 72-75.] | |
| [5] | Fei L, Hu SQ, Ye CY, Huang YZ (2006) Fauna Sinica · Amphibia (Vol. 1): General Accounts of Amphibia, Gymnophiona and Urodela. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 费梁, 胡淑琴, 叶昌媛, 黄永昭 (2006) 中国动物志·两栖纲(第一卷): 总论, 蚓螈目, 有尾目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [6] | Fei L, Hu SQ, Ye CY, Huang YZ (2009a) Fauna Sinica · Amphibia (Vol. 2): Anura. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 费梁, 胡淑琴, 叶昌媛, 黄永昭 (2009a) 中国动物志·两栖纲(第二卷): 无尾目. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [7] | Fei L, Hu SQ, Ye CY, Huang YZ (2009b) Fauna Sinica · Amphibia (Vol. 3): Anura, Ranidae. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 费梁, 胡淑琴, 叶昌媛, 黄永昭 (2009b) 中国动物志: 两栖纲(第三卷): 无尾目, 蛙科. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [8] | Fei L, Ye CY, Jiang JP (2012) Colored Atlas of Chinese Amphibians and Their Distributions. Sichuan Publishing House of Science and Technology, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [ 费梁, 叶昌媛, 江建平 (2012) 中国两栖动物及其分布彩色图鉴. 四川科学技术出版社, 成都.] | |
| [9] | Feng XJ, Mi XC, Xiao ZS, Cao L, Wu H, Ma KP (2019) Overview of Chinese Biodiversity Observation Network (Sino BON). Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 34, 1389-1398. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 冯晓娟, 米湘成, 肖治术, 曹垒, 吴慧, 马克平 (2019) 中国生物多样性监测与研究网络建设及进展. 中国科学院院刊, 34, 1389-1398.] | |
| [10] | Huang J, Liang S, Yin XM, Zhu HM, Wu YJ, Gan XP, Wang ZJ (2016) On amphibian resources of Chishui National Nature Reserve for Alsophila spinulosa. Journal of Southwest China Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 41(4), 64-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 黄静, 梁盛, 印显明, 朱汉墨, 吴羿锦, 甘小平, 王志坚 (2016) 赤水桫椤国家级自然保护区两栖动物资源现状. 西南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 41(4), 64-68.] | |
| [11] | Jiang JP, Xie F, Zang CX, Cai L, Li C, Wang B, Li JT, Wang J, Hu JH, Wang Y, Liu JY (2016) Assessing the threat status of amphibians in China. Biodiversity Science, 24, 588-597. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 江建平, 谢锋, 臧春鑫, 蔡蕾, 李成, 王斌, 李家堂, 王杰, 胡军华, 王燕, 刘炯宇 (2016) 中国两栖动物受威胁现状评估. 生物多样性, 24, 588-597.] | |
| [12] | Li B, Zhang W, Shu XX, Mo YM, Pei EL, Yuan X, Wang TH (2017) Distribution characteristic of amphibian in three typical habitats of rural Shanghai. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 26, 824-831. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李贲, 张伟, 束潇潇, 莫英敏, 裴恩乐, 袁晓, 王天厚 (2017) 上海郊区三类典型生境的两栖类分布特征. 长江流域资源与环境, 26, 824-831.] | |
| [13] | Li SZ, Lü JC, Li C, Wei G, Xu N (2015) Investigation of herpetological resources in Mayanghe National Nature Reserve, Guizhou, China. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 50, 59-67. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李仕泽, 吕敬才, 李灿, 魏刚, 徐宁 (2015) 麻阳河国家级自然保护区两栖爬行动物资源调查. 动物学杂志, 50, 59-67.] | |
| [14] | Li SZ, Lü JC, Xu N, Wei G (2017) Field survey on amphibians resources in Nangan Nature Reserve of Guizhou, China. Journal of Guiyang University (Natural Sciences), 12(3), 65-69. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李仕泽, 吕敬才, 徐宁, 魏刚 (2017) 德江楠杆自然保护区两栖动物资源调查. 贵阳学院学报(自然科学版), 12(3), 65-69.] | |
| [15] | Luo ZK (2000) Discussion on desertification control and ecological environment construction in karst area of Guizhou Province. Guizhou Environmental Protection Science and Technology, 6(1), 7-10. (in Chinese) |
| [ 罗中康 (2000) 贵州喀斯特地区荒漠化防治与生态环境建设浅议. 贵州环保科技, 6(1), 7-10.] | |
| [16] | Lü JC, Li SZ, Niu KF, Chen J, Jiang S, Tian Y, Wei G, Xu N (2017a) Amphibian diversity and faunal analysis in Fanjingshan Aational Nature Reserve. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 45, 148-152. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吕敬才, 李仕泽, 牛克锋, 陈靖, 姜森, 田宇, 魏刚, 徐宁 (2017a) 梵净山国家级自然保护区两栖动物多样性及区系组成. 贵州农业科学, 45, 148-152.] | |
| [17] | Lü JC, Zhang HB, Yuan G, Long HW, Guo X, Yu ZG (2017b) Diversity and fauna of amphibians and reptiles in Aha National Wetland Park. Guizhou Science, 35(6), 14-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吕敬才, 张海波, 袁果, 龙汉武, 郭轩, 余志刚 (2017b) 阿哈湖国家湿地公园两栖爬行动物多样性及区系. 贵州科学, 35(6), 14-18.] | |
| [18] | Ma KP, Liu CR, Liu YM (1995) Measurement of biotic community diversity. Ⅱ. β diversity. Chinese Biodiversity, 3, 38-43. (in Chinese) |
| [ 马克平, 刘灿然, 刘玉明 (1995) 生物群落多样性的测度方法Ⅱ. β多样性的测度方法. 生物多样性, 3, 38-43.] | |
| [19] | Ma KP, Liu YM (1994) Measurement of biotic community diversity. I. α diversity (part 2). Chinese Biodiversity, 2, 231-239. (in Chinese) |
| [ 马克平, 刘玉明 (1994) 生物群落多样性的测度方法I. α多样性的测度方法(下). 生物多样性, 2, 231-239.] | |
| [20] |
Mouchet F, Cren S, Cunienq C, Deydier E, Guilet R, Gauthier L (2007) Assessment of lead ecotoxicity in water using the amphibian larvae (Xenopus laevis) and preliminary study of its immobilization in meat and bone meal combustion residues. Biometals, 20, 113-127.
DOI URL |
| [21] | Peng WX, Wang KL, Song TQ, Zeng FP, Wang JR (2008) Controlling and restoration models of complex degradation of vulnerable karst ecosystem. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28, 811-820. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 彭晚霞, 王克林, 宋同清, 曾馥平, 王久荣 (2008) 喀斯特脆弱生态系统复合退化控制与重建模式. 生态学报, 28, 811-820.] | |
| [22] | Ren H, Peng SL, Lu HF (2004) The restoration of degraded ecosystems and restoration ecology. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24, 1760-1768. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 任海, 彭少麟, 陆宏芳 (2004) 退化生态系统恢复与恢复生态学. 生态学报, 24, 1760-1768.] | |
| [23] | Song TQ, Peng WX, Du H, Wang KL, Zeng FP (2014) Occurrence, spatial-temporal dynamics and regulation strategies of karst rocky desertification in Southwest China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34, 5328-5341. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 宋同清, 彭晚霞, 杜虎, 王克林, 曾馥平 (2014) 中国西南喀斯特石漠化时空演变特征、发生机制与调控对策. 生态学报, 34, 5328-5341.] | |
| [24] | Wang J, Li YL, Li Y, Chen HH, Zeng YJ, Shen JM, Wang YY (2019) Morphology, molecular genetics, and acoustics reveal two new species of the genus Leptobrachella from northwestern Guizhou Province, China (Anura, Megophryidae). ZooKeys, 848, 119-154. |
| [25] | Wang JY, Li JF, Zhang LQ, Zou LL (2012) Prediction of land use structure based on biodiversity conservation. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 28, 221-226. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王建英, 李江风, 张丽琴, 邹利林 (2012) 基于生物多样性保护的土地利用结构预测. 农业工程学报, 28, 221-226.] | |
| [26] | Wang YB (2005) Investigation on amphibians in Fokienia hodginsii Nature Reserve, Jinsha and Dafang County, Guizhou. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 24, 401-402. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王延斌 (2005) 贵州金沙县、大方县福建柏自然保护区两栖动物调查. 四川动物, 24, 401-402.] | |
| [27] | Wang YB (2010) Survey of amphibians in Lengshuihe Nature Reserve in Guizhou. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 38, 191-193. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王延斌 (2010) 贵州金沙冷水河自然保护区两栖动物调查. 贵州农业科学, 38, 191-193.] | |
| [28] | Wei G, Chen FG, Li DJ (1989) Preliminary studies on geographical distribution and faunal regions of amphibians of Guizhou Province. Zoological Research, 10, 241-249. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 魏刚, 陈服官, 李德俊 (1989) 贵州两栖动物区系及地理区划的初步研究. 动物学研究, 10, 241-249.] | |
| [29] | Wei G, Xu N, Zhang GF, Tan YM (2007) A survey of amphibians and reptiles in Dashahe Nature Reserve in Guizhou. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 26, 347-350. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 魏刚, 徐宁, 张国防, 谭杨梅 (2007) 贵州大沙河自然保护区两栖爬行动物多样性研究. 四川动物, 26, 347-350.] | |
| [30] | Wu L, Dong Q, Xu RH (1987) Amphibians of Guizhou. Guizhou People’s Publishing House, Guiyang. (in Chinese) |
| [ 伍律, 董谦, 须润华 (1987) 贵州两栖类志. 贵州人民出版社, 贵阳.] | |
| [31] | Xiong KN, Li P, Zhou ZF, An YL, Lü T, Lan AJ (2002) Remote Sensing of Karst Rocky Desertification-GIS Typical Research—Take Guizhou Province as An Example. Geological Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 熊康宁, 黎平, 周忠发, 安裕伦, 吕涛, 蓝安军 (2002) 喀斯特石漠化的遥感-GIS典型研究——以贵州省为例. 地质出版社, 北京.] | |
| [32] | Xu N, Dai SG, Zhang JZ (2008) A survey of amphibians in Qingshuihe Nature Reserve of Guizhou. Journal of Guiyang University (Natural Sciences), 3(4), 6-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐宁, 戴诗贵, 张景涿 (2008) 贵州省清水河风景自然保护区两栖动物调查. 贵阳学院学报(自然科学版), 3(4), 6-8.] | |
| [33] | Yang WK, Zhong WQ, Gao XY (2000) A review of studies on avian habitat selection. Arid Zone Research, 17(3), 71-78. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨维康, 钟文勤, 高行宜 (2000) 鸟类栖息地选择研究进展. 干旱区研究, 17(3), 71-78.] | |
| [34] | Yao ZM, Qin LJ, Tan CJ, Deng HQ (2018) Research on amphibians’ species in Maolan National Nature Reserve, Guizhou. Journal of Guizhou Normal University (Natural Sciences), 36(2), 33-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 姚正明, 覃龙江, 谭成江, 邓怀庆 (2018) 茂兰国家级自然保护区两栖类物种多样性研究. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 36(2), 33-38.] | |
| [35] | Yuan DX (2003) Geological environment and hydroecological problems in karst area. Southern Land Resources, (1), 22-25. (in Chinese) |
| [ 袁道先 (2003) 岩溶地区的地质环境和水文生态问题. 南方国土资源, (1), 22-25.] | |
| [36] | Yuan DX (2001) World correlation of karst ecosystem: Objectives and implementation plan. Advances in Earth Science, 16, 461-466. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 袁道先 (2001) 全球岩溶生态系统对比: 科学目标和执行计划. 地球科学进展, 16, 461-466.] | |
| [37] | Zhang YH, Gong DJ, Yan L, Tian G (2012) Study on amphibious reptiles in Taiyang Mountain of Congjiang County in Guizhou Province. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 40, 194-195. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张永宏, 龚大洁, 闫礼, 田果 (2012) 贵州省从江县太阳山两栖爬行动物研究. 安徽农业科学, 40, 194-195.] | |
| [38] | Zhou SC, Meng GT, Yin YX, Yang J, Yu HW, Ren MF, Liu H (2016) Effect of habitat characteristics on the reproductive effort of dybowsky’s frogs (Rana Dybowskii) in eastern Wanda Mountains, Heilongjiang Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 2521-2527. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 周绍春, 孟根同, 尹远新, 杨娇, 于洪伟, 任梦飞, 刘浩 (2016) 完达山东部林区生境特征对东北林蛙产卵的影响. 生态学报, 36, 2521-2527.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [3] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [4] | 周昊, 王茗毅, 张楚格, 肖治术, 欧阳芳. 昆虫旅馆在独栖蜂多样性保护中的现状与挑战[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24472-. |
| [5] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [6] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [7] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [8] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [9] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [10] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [11] | 徐欢, 辛凤飞, 施宏亮, 袁琳, 薄顺奇, 赵欣怡, 邓帅涛, 潘婷婷, 余婧, 孙赛赛, 薛程. 生态修复技术集成应用对长江口北支生境与鸟类多样性提升效果评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24478-. |
| [12] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [13] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [14] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [15] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn