



生物多样性 ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (2): 195-203. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016001 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2016001
所属专题: 物种形成与系统进化
收稿日期:2016-01-03
接受日期:2016-03-28
出版日期:2017-02-20
发布日期:2017-03-06
基金资助:Received:2016-01-03
Accepted:2016-03-28
Online:2017-02-20
Published:2017-03-06
摘要:
传统植物区系地理学研究主要以植物区系的分类群组成及其分布区类型的分析为主, 忽视了进化历史的分析。本文根据前期云南植物区系的分区研究, 基于云南种子植物1,983个属的系统发育关系, 结合其地理分布, 从进化历史的角度分析不同地理单元的分类群组成、系统发育组成及其相似性, 探讨各个地理单元的系统发育结构及地理单元间的系统发育相似性。结果表明: 云南植物区系不同地理单元的系统发育多样性与科或属的丰富度显著相关, 其系统发育结构为非随机型; 不同地理单元间的系统发育组成相似性与分类群组成相似性显著相关, 二者的聚类分析均表明具有热带植物区系性质的地理单元与具有温带植物区系性质的地理单元各自聚为一类。由此可见, 融合进化历史信息的植物区系分析有助于更加深入地理解植物区系的性质和来源。
李嵘, 孙航 (2017) 植物系统发育区系地理学研究: 以云南植物区系为例. 生物多样性, 25, 195-203. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016001.
Rong Li, Hang Sun (2017) Phylofloristics: a case study from Yunnan, China. Biodiversity Science, 25, 195-203. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016001.
| 地理单元 Geographic regions | 科丰富度 Family richness | 属丰富度 Genus richness | 系统发育多样性 Phylogenetic diversity |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | 180 | 1,226 | 134,237.26 |
| II | 149 | 725 | 82,676.45 |
| III | 176 | 990 | 112,736.74 |
| IV | 165 | 902 | 103,039.67 |
| V | 160 | 875 | 97,805.24 |
| VI | 126 | 520 | 63,362.67 |
| VII | 204 | 1,405 | 154,165.33 |
| VIII | 205 | 1,429 | 156,662.31 |
表1 云南种子植物区系不同地理单元的分类群多样性与系统发育多样性比较
Table 1 Comparison of taxonomic diversity and phylogenetic diversity of different geographic regions for the seed plants in Yunnan
| 地理单元 Geographic regions | 科丰富度 Family richness | 属丰富度 Genus richness | 系统发育多样性 Phylogenetic diversity |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | 180 | 1,226 | 134,237.26 |
| II | 149 | 725 | 82,676.45 |
| III | 176 | 990 | 112,736.74 |
| IV | 165 | 902 | 103,039.67 |
| V | 160 | 875 | 97,805.24 |
| VI | 126 | 520 | 63,362.67 |
| VII | 204 | 1,405 | 154,165.33 |
| VIII | 205 | 1,429 | 156,662.31 |
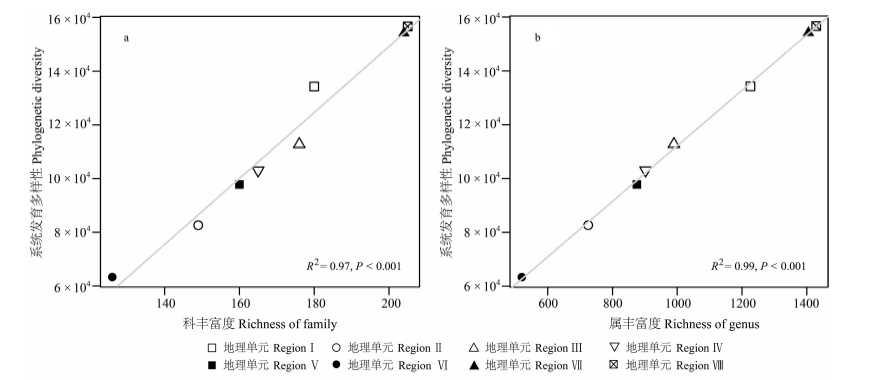
图3 云南植物区系不同地理单元系统发育多样性与科丰富度(a)和属丰富度(b)的关系(I-VIII代表的地理单元同图1)
Fig. 3 Relationships between phylogenetic diversity and family richness (a) or genus richness (b) among the floristic regions in Yunnan. I-VIII indicate different floristic regions as in Fig. 1.
| 地理单元 Geographic regions | 净相关指数 Net relatedness index | 系统发育结构 Phylogenetic structure |
|---|---|---|
| I | 0.60 | 聚集型 Underdispersed |
| II | 0.05 | 聚集型 Underdispersed |
| III | -1.20 | 离散型 Overdispersed |
| IV | 0.81 | 聚集型 Underdispersed |
| V | 0.02 | 聚集型 Underdispersed |
| VI | 1.01 | 聚集型 Underdispersed |
| VII | 1.35 | 聚集型 Underdispersed |
| VIII | 1.00 | 聚集型 Underdispersed |
表2 云南种子植物区系不同地理单元的系统发育结构
Table 2 Phylogenetic structure of different geographic regions for the seed plants in Yunnan
| 地理单元 Geographic regions | 净相关指数 Net relatedness index | 系统发育结构 Phylogenetic structure |
|---|---|---|
| I | 0.60 | 聚集型 Underdispersed |
| II | 0.05 | 聚集型 Underdispersed |
| III | -1.20 | 离散型 Overdispersed |
| IV | 0.81 | 聚集型 Underdispersed |
| V | 0.02 | 聚集型 Underdispersed |
| VI | 1.01 | 聚集型 Underdispersed |
| VII | 1.35 | 聚集型 Underdispersed |
| VIII | 1.00 | 聚集型 Underdispersed |
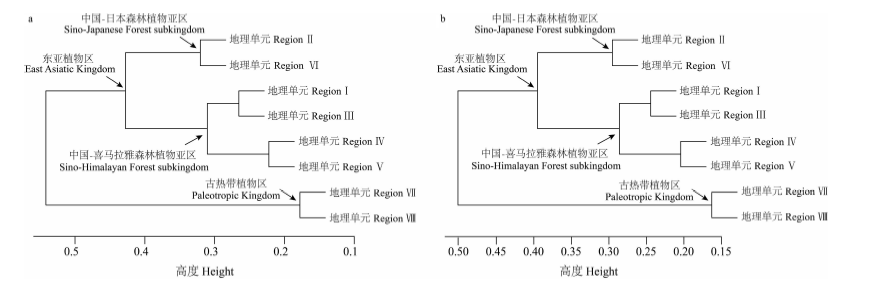
图4 云南植物区系不同地理单元间分类学组成(a)与系统发育组成(b)的相似性聚类
Fig. 4 A cluster dendrogram representing the taxonomic floristic similarity (a) and the phylofloristic similarity (b) between the geographic regions of Yunnan. I-VIII indicate different floristic regions as in Fig. 1.
| 8 | Ge XJ (2015) Application of DNA barcoding in phylofloristics study. Biodiversity Science, 23, 295-296. |
| (in Chinese) [葛学军 (2015) DNA条形码在植物系统发育区系学研究中的应用. 生物多样性, 23, 295-296.] | |
| 9 | Hardy OJ, Couteron P, Munoz F, Ramesh BR, Pélissier R (2012) Phylogenetic turnover in tropical tree communities: impact of environmental filtering, biogeography and mesoclimatic niche conservatism. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 1007-1016. |
| 10 | Harrison TM, Copeland P, Kidd WSF, Yin A (1992) Raising Tibet. Science, 255, 1663-1670. |
| 11 | Kembel SW, Cowan PD, Helmus MR, Cornwell WK, Morlon H, Ackerly DD, Blomberg SP, Webb CO (2010) Picante: R tools for integrating phylogenies and ecology. Bioinformatics, 26, 1463-1464. |
| 12 | Kooyman R, Rossetto M, Cornwell W, Westoby M (2011) Phylogenetic tests of community assembly across regional to continental scales in tropical and subtropical rain forests. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 20, 707-716. |
| 13 | Kreft H, Jetz W (2010) A framework for delineating biogeographical regions based on species distributions. Journal of Biogeography, 37, 2029-2053. |
| 14 | Legendre P, Fortin MJ (2010) Comparison of the Mantel test and alternative approaches for detecting complex multivariate relationships in the spatial analysis of genetic data. Molecular Ecology Resources, 10, 831-844. |
| 15 | Li R, Dao ZL, Ji YH, Li H (2007) A floristic study on the seed plants of the northern Gaoligong Mountains in western Yunnan, China. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 29, 601-615. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [李嵘, 刀志灵, 纪运恒, 李恒 (2007) 高黎贡山北段种子植物区系研究. 云南植物研究, 29, 601-615.] | |
| 16 | Li R, Kraft NJB, Yang J, Wang YH (2015a) A phylogenetically informed delineation of floristic regions within a biodiversity hotspot in Yunnan, China. Scientific Reports, 5, 9396. |
| 17 | Li R, Kraft NJB, Yu HY, Li H (2015b) Seed plant phylogenetic diversity and species richness in conservation planning within a global biodiversity hotspot in eastern Asia. Conservation Biology, 29, 1552-1562. |
| 18 | Li XH, Zhu XX, Niu Y, Sun H (2014) Phylogenetic clustering and overdispersion for alpine plants along elevational gradient in the Hengduan Mountains region, Southwest China. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 52, 280-288. |
| 19 | Li XW (1985) Floristic study of Yunnan Province. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 7, 361-382. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [李锡文 (1985) 云南植物区系. 云南植物研究, 7, 361-382.] | |
| 20 | Li XW (1994) Two big biodiversity centers of Chinese endemic genera of seed plants and their characteristics in Yunnan Province. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 16, 221-227. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [李锡文 (1994) 中国特有属在云南的两大生物多样性中心及其特征. 云南植物研究, 16, 221-227.] | |
| 21 | Li XW (1995a) A floristic study on the seed plants from tropical Yunnan. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 17, 115-128. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [李锡文 (1995a) 云南热带种子植物区系. 云南植物研究, 17, 115-128.] | |
| 22 | Li XW (1995b) A floristic study on the seed plants from the region of Yunnan Plateau. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 17, 1-14. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [李锡文 (1995b) 云南高原地区种子植物区系. 云南植物研究, 17, 1-14.] | |
| 23 | Li XW, Li J (1992) On the validity of Tanaka line and its significance viewed from the distribution of eastern Asiatic genera in Yunnan. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 14, 1-12. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [李锡文, 李捷 (1992) 从滇产东亚属的分布论述“田中线”的真实性和意义. 云南植物研究, 14, 1-12.] | |
| 24 | Li XW, Li J (1993) A preliminary floristic study of the seed plants from the region of the Hengduan Mountains. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 15, 217-231. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [李锡文, 李捷 (1993) 横断山脉地区种子植物区系的初步研究. 云南植物研究, 15, 217-231.] | |
| 25 | Li XW, Li J (1997) The Tanaka-Kaiyong line—an important floristic line for the study of the flora of East Asia. Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden, 84, 888-892. |
| 26 | Li XW, Walker D (1986) The plant geography of Yunnan Province, Southwest China. Journal of Biogeography, 13, 367-397. |
| 27 | Liu JQ, Duan YW, Hao G, Ge XJ, Sun H (2014) Evolutionary history and underlying adaptation of alpine plants on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 52, 241-249. |
| 28 | López-Pujol J, Zhang FM, Sun HQ, Ying TS, Ge S (2011) Centres of plant endemism in China: places for survival or for speciation? Journal of Biogeography, 38, 1267-1280. |
| 29 | Luo D, Yue JP, Sun WG, Xu B, Li ZM, Comes HP, Sun H (2016) Evolutionary history of the subnival flora of the Himalaya-Hengduan Mountains: first insights from comparative phylogeography of four perennial herbs. Journal of Biogeography, 43, 31-43. |
| 1 | An ZS, Kutzbach JE, Prell WL, Porter SC (2001) Evolution of Asian monsoons and phased uplift of the Himalaya-Tibetan Plateau since late Miocene times. Nature, 411, 62-66. |
| 2 | APG III (2009) An update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG III. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 161, 105-121. |
| 30 | Maechler M, Rousseeuw P, Struyf A, Hubert M, Hornik K (2015) Cluster: Cluster Analysis Basics and Extensions. R package version 2.0.3. |
| 31 | Mittermeier RA, Robles PG, Hoffmann M, Pilgrim J, Brooks T, Mittermeier CG, da Fonseca GAB (2004) Hotspots Revisited: Earth’s Biologically Richest and Most Endangered Terrestrial Ecoregions. CEMEX/Agrupaciaon Sierra Madre, Mexico City. |
| 3 | Bryant JA, Lamanna C, Morlon H, Kerkhoff AJ, Enquist BJ, Green JL (2008) Microbes on mountainsides: contrasting elevational patterns of bacterial and plant diversity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 105, 11505-11511. |
| 4 | Elton C (1946) Competition and the structure of ecological communities. Journal of Animal Ecology, 15, 54-68. |
| 32 | Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P, Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Wagner H (2015) Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package version 2.0.3. |
| 33 | Peng H (1996) The floristic equilibrium point of seed plants in Mt. Wuliangshan. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 18, 385-397. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [彭华 (1996) 无量山种子植物的区系平衡点. 云南植物研究, 18, 385-397.] | |
| 34 | Qian H, Richard F, Zhang JL, Zhang J, Chen SB (2016) Phylogenetic structure and ecological and evolutionary determinants of species richness for angiosperm trees in forest communities in China. Journal of Biogeography, 43, 603-615. |
| 5 | Emerson BC, Gillespie RG (2008) Phylogenetic analysis of community assembly and structure over space and time. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 23, 619-630. |
| 6 | Faith DP (1992) Conservation evaluation and phylogenetic diversity. Biological Conservation, 61, 1-10. |
| 7 | Forest F, Grenyer R, Rouget M, Davies TJ, Cowling RM, Faith DP, Balmford A, Manning JC, Proches S, van der Bank M, Reeves G, Hedderson TAJ, Savolainen V (2007) Preserving the evolutionary potential of floras in biodiversity hotspots. Nature, 445, 757-760. |
| 35 | Qian H, Swenson NG, Zhang JL (2013a) Phylogenetic beta diversity of angiosperms in North America. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 22, 1152-1161. |
| 36 | Qian H, Wiens JJ, Zhang J, Zhang YJ (2015) Evolutionary and ecological causes of species richness patterns in North American angiosperm trees. Ecography, 38, 241-250. |
| 37 | Qian H, Zhang YJ, Zhang J, Wang XL (2013b) Latitudinal gradients in phylogenetic relatedness of angiosperm trees in North America. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 22, 1183-1191. |
| 38 | Qiao XJ, Jabot F, Tang ZY, Jiang MX, Fang JY (2015) A latitudinal gradient in tree community assembly processes evidence in Chinese forests. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 24, 314-323. |
| 39 | R Core Team (2014) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. |
| 40 | Ricklefs RE (1987) Community diversity: relative roles of local and regional processes. Science, 235, 161-171. |
| 41 | Sørensen T (1948) A method of establishing groups of equal amplitude in plant sociology based on similarity of species, and its application to analyses of the vegetation on Danish commons. Biologiske Skrifter, 5, 1-34. |
| 42 | Spicer RA, Harris NBW, Widdowson M, Herman AB, Guo S, Valdes PJ, Wolfe JA, Kelley SP (2003) Constant elevation of southern Tibet over the past 15 million years. Nature, 421, 622-624. |
| 43 | Sun H (2002) Evolution of Arctic-Tertiary flora in Himalayan-Hengduan Mountains. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 24, 671-688. |
| (in Chinese with English abstract) [孙航 (2002) 北极-第三纪成分在喜马拉雅-横断山的发展及演化. 云南植物研究, 24, 671-688.] | |
| 44 | Swenson NG, Umaña MN (2014) Phylofloristics: an example from the Lesser Antilles. Journal of Plant Ecology, 7, 166-175. |
| 45 | Tucker CM, Cadotte MW, Davies TJ, Rebelo AG (2012) Incorporating geographical and evolutionary rarity into conservation prioritization. Conservation Biology, 26, 593-601. |
| 46 | Wang Y (2006) Yunnan Mountain Climate. Yunnan Science and Technology Press, Kunming. |
| (in Chinese) [王宇 (2006) 云南山地气候. 云南科技出版社, 昆明.] | |
| 47 | Wang ZH, Fang JY, Tang ZY, Lin X (2012) Relative role of contemporary environment versus history in shaping diversity patterns of China’s woody plants. Ecography, 35, 1124-1133. |
| 48 | Webb CO (2000) Exploring the phylogenetic structure of ecological communities: an example for rain forest trees. The American Naturalist, 156, 145-155. |
| 49 | Webb CO, Ackerly DD, McPeek MA, Donoghue MJ (2002) Phylogenies and community ecology. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 33, 475-505. |
| 50 | Webb CO, Donoghue MJ (2005) Phylomatic: tree assembly for applied phylogenetics. Molecular Ecology Notes, 5, 181-183. |
| 51 | Wu ZY (1977-2006) Flora Yunnanica. Science Press, Beijing. |
| (in Chinese) [吴征镒 (1977-2006) 云南植物志. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 52 | Wu ZY (1987) Vegetation of Yunnan. Science Press, Beijing. |
| (in Chinese) [吴征镒 (1987) 云南植被. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 53 | Wu ZY, Sun H, Zhou ZK, Li DZ, Peng H (2010) Floristics of Seed Plants from China. Science Press, Beijing. |
| (in Chinese) [吴征镒, 孙航, 周浙昆, 李德铢, 彭华 (2010) 中国种子植物区系地理. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 54 | Wu ZY, Wu SG (1996) A proposal for a new floristic kingdom (realm)—the E. Asiatic Kingdom, its delineation and characteristics. In: Floristic Characteristics and Diversity of East Asian Plants (eds Zhang AL, Wu SG), pp. 3-42. China Higher Education Press, Beijing; Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg. |
| 55 | Wu ZY, Zhou ZK, Sun H, Li DZ, Peng H (2006) The Areal-Types of Seed Plants and Their Origin and Differentiation. Yunnan Science and Technology Press, Kunming. |
| (in Chinese) [吴征镒, 周浙昆, 孙航, 李德铢, 彭华 (2006) 种子植物分布区类型及其起源和分化. 云南科技出版社, 昆明.] | |
| 56 | Yang YG (1990) Comprehensive Physical Regionalization in Yunnan. China Higher Education Press, Beijing. |
| (in Chinese) [杨一光 (1990) 云南省综合自然区划. 中国高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| 57 | Zanne AE, Tank DC, Cornwell WK, Eastman JM, Smith SA, FitzJohn RG, McGlinn DJ, O’Meara BC, Moles AT, Reich PB, Royer DL, Soltis DE, Stevens PF, Westoby M, Wright IJ, Aarssen L, Bertin RL, Calaminus A, Govaerts R, Hemmings F, Leishman MR, Oleksyn J, Soltis PS, Swenson NG, Warman L, Beaulieu JM (2014) Three keys to the radiation of angiosperms into freezing environments. Nature, 506, 89-92. |
| 58 | Zhu H (2008) The tropical flora of southern Yunnan, China, and its biogeographical affinities. Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden, 95, 661-680. |
| 59 | Zhu H (2012) Biogeographical divergence of the flora of Yunnan, southwestern China initiated by the uplift of Himalaya and extrusion of Indochina block. PLoS ONE, 7, e45601. |
| 60 | Zhu H (2013) The floras of southern and tropical southeastern Yunnan have been shaped by divergent geological histories. PLoS ONE, 8, e64213. |
| 61 | Zhu H, Cao M, Hu H (2006) Geological history, flora, and vegetation of Xishuangbanna, southern Yunnan, China. Biotropica, 38, 310-317. |
| [1] | 董云伟, 鲍梦幻, 程娇, 陈义永, 杜建国, 高养春, 胡利莎, 李心诚, 刘春龙, 秦耿, 孙进, 王信, 杨光, 张崇良, 张雄, 张宇洋, 张志新, 战爱斌, 贺强, 孙军, 陈彬, 沙忠利, 林强. 中国海洋生物地理学研究进展和热点: 物种分布模型及其应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23453-. |
| [2] | 曹可欣, 王敬雯, 郑国, 武鹏峰, 李英滨, 崔淑艳. 降水格局改变及氮沉降对北方典型草原土壤线虫多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23491-. |
| [3] | 何林君, 杨文静, 石宇豪, 阿说克者莫, 范钰, 王国严, 李景吉, 石松林, 易桂花, 彭培好. 火烧干扰下植物群落系统发育和功能多样性对紫茎泽兰入侵的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24269-. |
| [4] | 杨向林, 赵彩云, 李俊生, 种方方, 李文金. 植物入侵导致群落谱系结构更加聚集: 以广西国家级自然保护区草本植物为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24175-. |
| [5] | 谢艳秋, 黄晖, 王春晓, 何雅琴, 江怡萱, 刘子琳, 邓传远, 郑郁善. 福建海岛滨海特有植物种-面积关系及物种丰富度决定因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22345-. |
| [6] | 高德, 王彦平. 小岛屿效应检测方法研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23299-. |
| [7] | 王彦平, 张敏楚, 詹成修. 嵌套分布格局研究进展: 分析方法、影响机制及保护应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23314-. |
| [8] | 商晓凡, 张健, 高浩杰, 库伟鹏, 毕玉科, 李修鹏, 阎恩荣. 岛屿面积与气候共同影响舟山群岛种子植物丰富度格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23392-. |
| [9] | 孙亚君. 为何要信达尔文的演化论——论《物种起源》的二十五重简约美[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 22243-. |
| [10] | 姜晓燕, 高圣杰, 蒋燕, 田赟, 贾昕, 查天山. 毛乌素沙地植被不同恢复阶段植物群落物种多样性、功能多样性和系统发育多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21387-. |
| [11] | 付飞, 魏慧玉, 常育腾, 王备新, 陈凯. 澜沧江中游水生昆虫生活史和生态学性状多样性的海拔格局: 气候和土地利用的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21332-. |
| [12] | 陈博, 江蓝, 谢子扬, 李阳娣, 李佳萱, 李梦佳, 魏晨思, 邢聪, 刘金福, 何中声. 格氏栲天然林林窗植物物种多样性与系统发育多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(4): 439-448. |
| [13] | 魏慧玉,陈凯,王备新. 澜沧江流域水生昆虫群落分类多样性和功能多样性海拔格局的空间尺度依赖性[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(4): 504-514. |
| [14] | 王波, 黄勇, 李家堂, 戴强, 王跃招, 杨道德. 西南喀斯特地貌区两栖动物丰富度分布格局与环境因子的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(9): 941-950. |
| [15] | 孙德鑫, 刘向, 周淑荣. 停止人为去除植物功能群后的高寒草甸多样性恢复过程与群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(7): 655-666. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()
