



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (12): 23314. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023314 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023314
收稿日期:2023-09-04
接受日期:2023-12-08
出版日期:2023-12-20
发布日期:2023-12-20
通讯作者:
E-mail: 基金资助:
Yanping Wang*( )(
)( ), Minchu Zhang, Chengxiu Zhan
), Minchu Zhang, Chengxiu Zhan
Received:2023-09-04
Accepted:2023-12-08
Online:2023-12-20
Published:2023-12-20
Contact:
E-mail: 摘要:
基于物种分布或群落组成的嵌套格局(嵌套分布格局)是岛屿生物地理学和群落生态学的重要前沿研究领域和核心问题之一。嵌套分布格局最初起源于岛屿物种组成的研究, 是指物种较贫乏岛屿中的物种是物种较丰富岛屿中的物种的一个适当子集的分布模式。深入了解嵌套分布格局及其影响机制对生物多样性保护具有重要意义, 并可用于指导管理工作。近40年来, 嵌套分布格局备受生态学家和保护生物学家的关注, 并且在分析方法、影响机制、生物多样性保护应用等方面都取得了一系列重要进展。本文通过对文献的系统检索和归纳总结, 从4个方面对嵌套分布格局的最新研究进展进行了综述: (1)发展历史及其研究现状; (2)分析方法, 包括各个嵌套指数和零模型的优点与局限; (3)影响机制及其检验方法; (4)在生物多样性保护与管理中的应用。最后, 我们对该领域进行了归纳总结并对以后的发展方向提出了针对性建议, 包括选择最适合的嵌套指数和零模型进行嵌套分析、同时对多种嵌套理论假说进行验证、开展更多关于功能嵌套和谱系嵌套的研究、推动嵌套分布格局与其他相关领域的融合。本文对于深入了解嵌套分布格局的前沿进展, 以及推动国内该领域的快速发展将有重要意义。
王彦平, 张敏楚, 詹成修 (2023) 嵌套分布格局研究进展: 分析方法、影响机制及保护应用. 生物多样性, 31, 23314. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023314.
Yanping Wang, Minchu Zhang, Chengxiu Zhan (2023) A review on the nested distribution pattern (nestedness): Analysis methods, mechanisms and conservation implications. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23314. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023314.
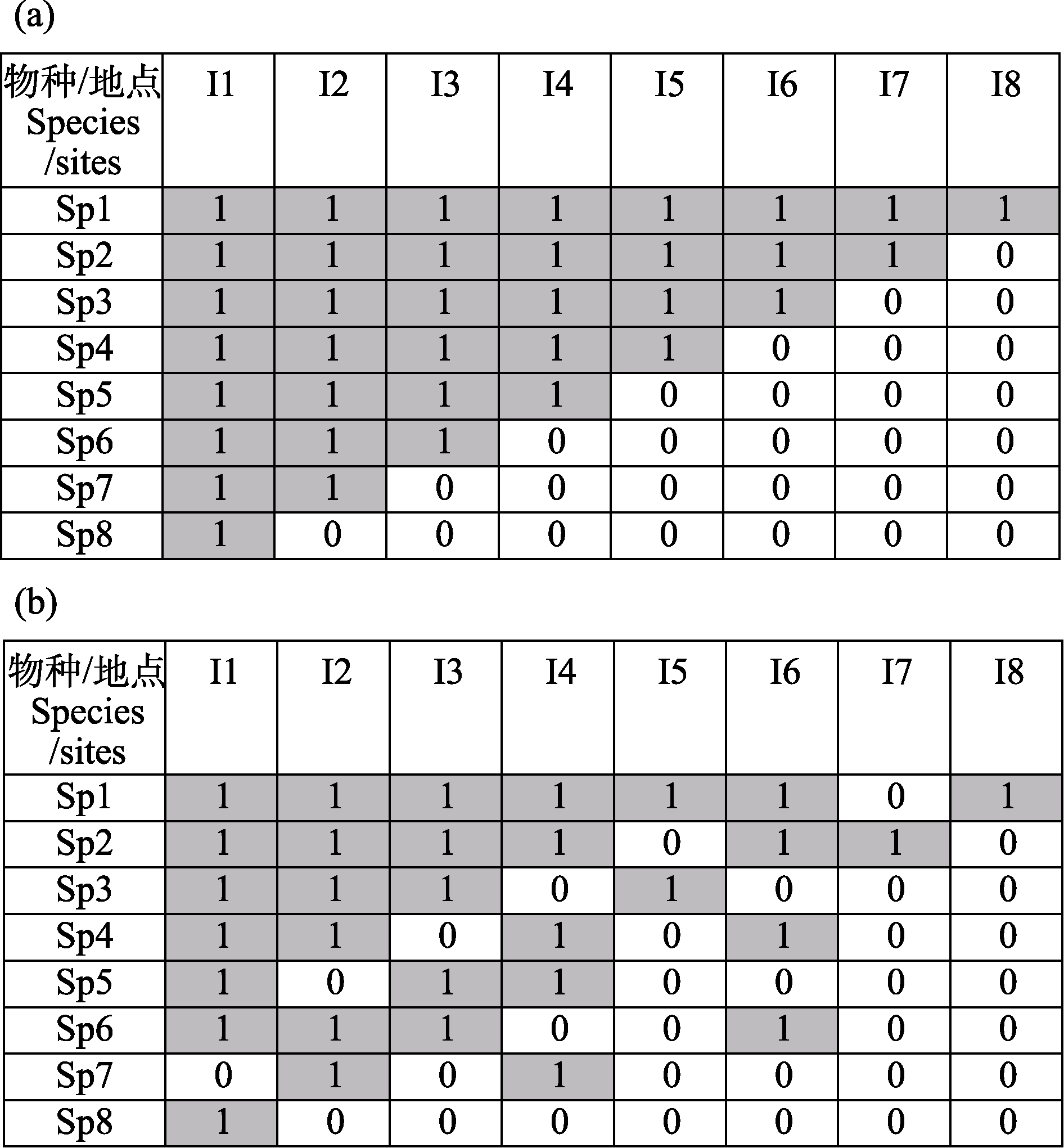
图1 嵌套分布格局示意图。(a)完全嵌套(从物种数最少的岛屿I8到物种最丰富的岛屿I1, 其物种组成依次属于完全嵌套关系); (b)不完全嵌套或显著嵌套。Sp代表物种, I代表岛屿或生境斑块; 1代表物种出现, 0代表物种不出现。
Fig. 1 Sketch maps showing the nested distribution pattern (nestedness). (a) Perfect nestedness (from the most species-poor island I8 to the most species-rich island I1, the species assemblages on them are perfectly nested in turn); (b) Not perfect but significant nestdness. Sp stands for species, I for islands or fragmented patches. 1 indicates the occurrence of species on an island or fragmented patch, while 0 indicates a species does not occur on an island or fragmented patch.
| 简称Abbreviation | 全称 Full names | 术语解释 Explanations |
|---|---|---|
| NODF | 基于重叠和减少填充的嵌套测量 Nestedness metric based on overlap and decreasing fill | 由Almeida-Neto等( |
| WNODF | 基于重叠和减少填充的加权嵌套测量Weighted nestedness metric based on overlap and decreasing fill | 由Almeida-Neto和Ulrich ( |
| N0 | 物种缺失数量 No. of absences | 由Patterson和Atmar ( |
| N1 | 物种出现数量 No. of presences | 由Cutler ( |
| Ua | 非预期缺失数量 No. of unexpected absences | 由Cutler ( |
| Up | 非预期出现数量 No. of unexpected presences | 由Cutler ( |
| Ut | 非预期转换数量 No. of unexpected transformations | 由Cutler ( |
| Nc | - | 由Wright和Reeves ( |
| D | 偏离数量 No. of departures | 由Lomolino ( |
| BR | 差异测量 Discrepancy measure | 由Brualdi和Sanderson ( |
| T | 矩阵温度 Matrix temperature | 由Atmar和Patterson ( |
| BINMATNEST | 二元矩阵温度嵌套计算器 Binary matrix nestedness temperature calculator | 由Rodríguez-Gironés和Santamaría ( |
| HH | 超集数量 No. of supersets | 由Hausdorf和Hennig ( |
表1 本文出现的嵌套指数缩写及其解释
Table 1 Abbreviated nestedness metrics used in the article and their explanations
| 简称Abbreviation | 全称 Full names | 术语解释 Explanations |
|---|---|---|
| NODF | 基于重叠和减少填充的嵌套测量 Nestedness metric based on overlap and decreasing fill | 由Almeida-Neto等( |
| WNODF | 基于重叠和减少填充的加权嵌套测量Weighted nestedness metric based on overlap and decreasing fill | 由Almeida-Neto和Ulrich ( |
| N0 | 物种缺失数量 No. of absences | 由Patterson和Atmar ( |
| N1 | 物种出现数量 No. of presences | 由Cutler ( |
| Ua | 非预期缺失数量 No. of unexpected absences | 由Cutler ( |
| Up | 非预期出现数量 No. of unexpected presences | 由Cutler ( |
| Ut | 非预期转换数量 No. of unexpected transformations | 由Cutler ( |
| Nc | - | 由Wright和Reeves ( |
| D | 偏离数量 No. of departures | 由Lomolino ( |
| BR | 差异测量 Discrepancy measure | 由Brualdi和Sanderson ( |
| T | 矩阵温度 Matrix temperature | 由Atmar和Patterson ( |
| BINMATNEST | 二元矩阵温度嵌套计算器 Binary matrix nestedness temperature calculator | 由Rodríguez-Gironés和Santamaría ( |
| HH | 超集数量 No. of supersets | 由Hausdorf和Hennig ( |
| 嵌套指数分类Classification of nestedness metrics | 嵌套指数 Nestedness metrics | 属性 Characteristics | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 间隙嵌套指数 Gap metrics | N0、N1、Ua、Up、Ut、Nc、D、BR | 受矩阵转换、矩阵大小、形状和填充度的影响(Nc和BR除外); 样本量较小时, 计算的统计检验率较低 Gap metrics are affected by matrix transformation, matrix size, shape and fill (except for Nc and BR). They have low power at small sample size (small matrix size) | Patterson & Atmar, |
| 温度嵌套指数 Temperature metrics | T、BINMATNEST | 不受矩阵转换的影响, 但会受矩阵大小和填充度的影响; 在矩阵中添加非嵌套的特有物种后, T指数会错误地识别出嵌套格局 Temperature metrics are affected by matrix size and fill, but not by matrix transformation. T metric incorrectly indicates an increase in nestedness with the addition of nonnested endemics to matrices | Atmar & Patterson, |
| 重叠嵌套指数 Overlap metrics | HH | 会受到异常值的过度影响, 且没有被标准化 HH is excessively affected by outliers and is not standardized | Hausdorf & Hennig, |
| NODF | 基于行和列填充的标准化差异, 并且可以将总嵌套分解为由列和行分别进行计算; 不受矩阵大小、形状和填充度的影响 NODF is based on standardized differences in row and column fills. It can decompose total nestedness into a sum of the nestedness introduced by columns and by rows separately. NODF is not affected by matrix size, shape and fill | Almeida-Neto et al, | |
| WNODF | 基于NODF的一种简单修改, 用于计算物种分布的多度矩阵数据是否嵌套; 不受矩阵大小、形状和填充度的影响 WNODF is a simple modification of NODF and used to determine the nestedness of the species-by-sites abundance matrix. It is not affected by matrix size, shape and fill | Almeida-Neto & Ulrich, | |
| 功能和谱系嵌套指数 Functional and phylogenetic metrics | phyloNODF | 用物种的系统发育建树解释谱系多样性; 不受矩阵大小、填充度以及树拓扑的影响 phyloNODF can be calculated if a phylogeny is used to account for differences in phylogenetic diversity. It is robust for matrix size, matrix fill, and tree topology | Melo et al, |
| traitNODF | 用功能性状建树解释功能多样性; 不受矩阵大小、填充度以及树拓扑的影响 traitNODF can be calculated if a functional dendrogram constructed from species ecological traits is used to account for the functional diversity. It is robust for matrix size, matrix fill, and tree topology | Melo et al, |
表2 现有嵌套指数及其特点
Table 2 An overview of existing nestedness metrics
| 嵌套指数分类Classification of nestedness metrics | 嵌套指数 Nestedness metrics | 属性 Characteristics | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 间隙嵌套指数 Gap metrics | N0、N1、Ua、Up、Ut、Nc、D、BR | 受矩阵转换、矩阵大小、形状和填充度的影响(Nc和BR除外); 样本量较小时, 计算的统计检验率较低 Gap metrics are affected by matrix transformation, matrix size, shape and fill (except for Nc and BR). They have low power at small sample size (small matrix size) | Patterson & Atmar, |
| 温度嵌套指数 Temperature metrics | T、BINMATNEST | 不受矩阵转换的影响, 但会受矩阵大小和填充度的影响; 在矩阵中添加非嵌套的特有物种后, T指数会错误地识别出嵌套格局 Temperature metrics are affected by matrix size and fill, but not by matrix transformation. T metric incorrectly indicates an increase in nestedness with the addition of nonnested endemics to matrices | Atmar & Patterson, |
| 重叠嵌套指数 Overlap metrics | HH | 会受到异常值的过度影响, 且没有被标准化 HH is excessively affected by outliers and is not standardized | Hausdorf & Hennig, |
| NODF | 基于行和列填充的标准化差异, 并且可以将总嵌套分解为由列和行分别进行计算; 不受矩阵大小、形状和填充度的影响 NODF is based on standardized differences in row and column fills. It can decompose total nestedness into a sum of the nestedness introduced by columns and by rows separately. NODF is not affected by matrix size, shape and fill | Almeida-Neto et al, | |
| WNODF | 基于NODF的一种简单修改, 用于计算物种分布的多度矩阵数据是否嵌套; 不受矩阵大小、形状和填充度的影响 WNODF is a simple modification of NODF and used to determine the nestedness of the species-by-sites abundance matrix. It is not affected by matrix size, shape and fill | Almeida-Neto & Ulrich, | |
| 功能和谱系嵌套指数 Functional and phylogenetic metrics | phyloNODF | 用物种的系统发育建树解释谱系多样性; 不受矩阵大小、填充度以及树拓扑的影响 phyloNODF can be calculated if a phylogeny is used to account for differences in phylogenetic diversity. It is robust for matrix size, matrix fill, and tree topology | Melo et al, |
| traitNODF | 用功能性状建树解释功能多样性; 不受矩阵大小、填充度以及树拓扑的影响 traitNODF can be calculated if a functional dendrogram constructed from species ecological traits is used to account for the functional diversity. It is robust for matrix size, matrix fill, and tree topology | Melo et al, |
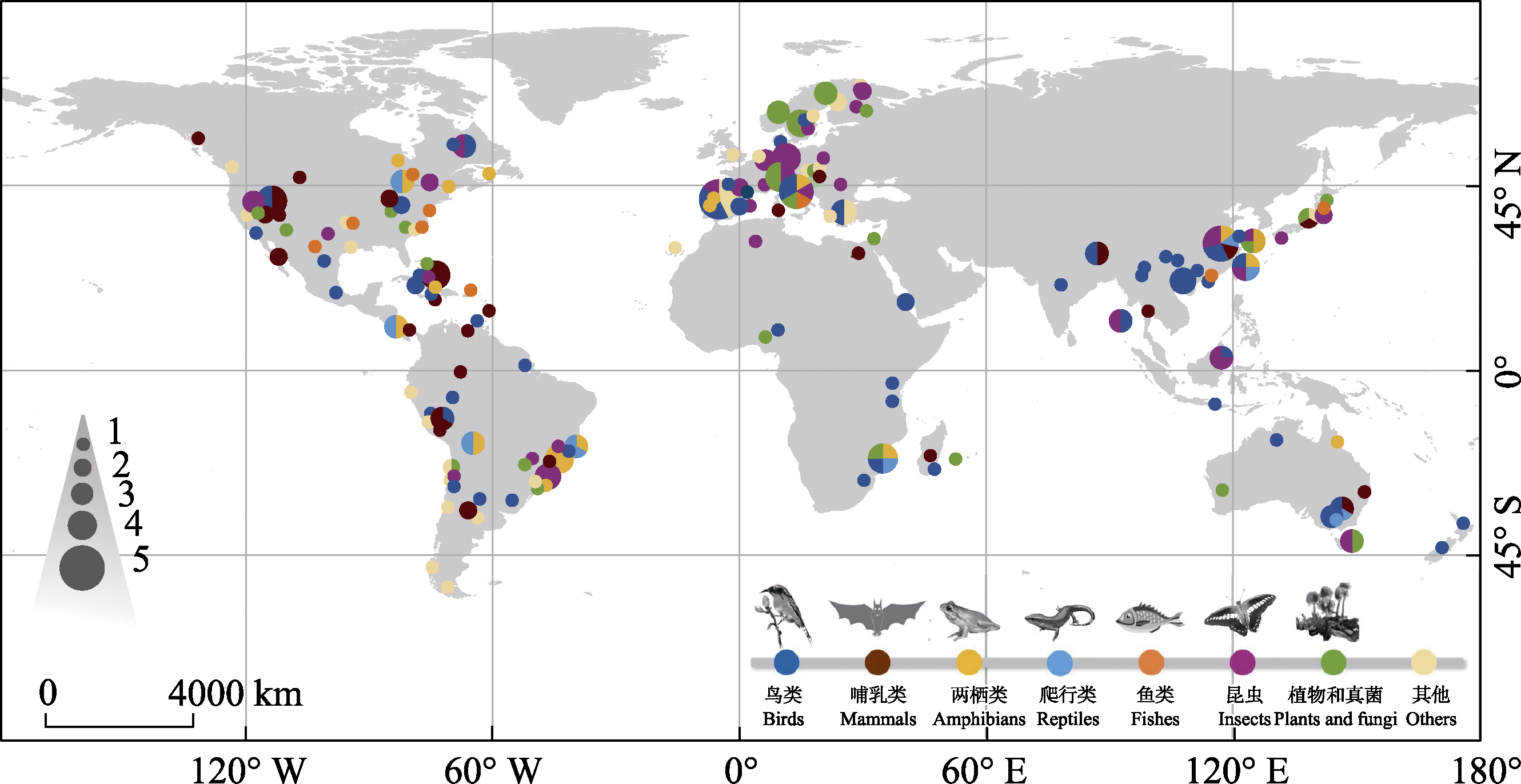
图2 全球嵌套分布格局研究的分布图。该图是截至2023年10月31日以nestedness、nested subset、nested pattern、nested assemblage、嵌套、嵌套格局、嵌套结构、子集套为关键词在Web of Science和中国知网等数据库中检索到的269篇文献(删除了纯粹描述嵌套方法的研究论文和综述论文)的结果。图例中1-5代表嵌套分布格局的研究数量依次递增。
Fig. 2 The distribution of nestedness studies across the world. The figure is based on the results of 269 nestedness studies (excluding articles purely describing nestedness methods and review articles) originated from databases such as Web of Science and CNKI based on the keywords “nestedness” “nested subset” “nested pattern” and “nested assemblage” as of October 31, 2023. Number 1-5 indicates the increasing number of nestedness studies.
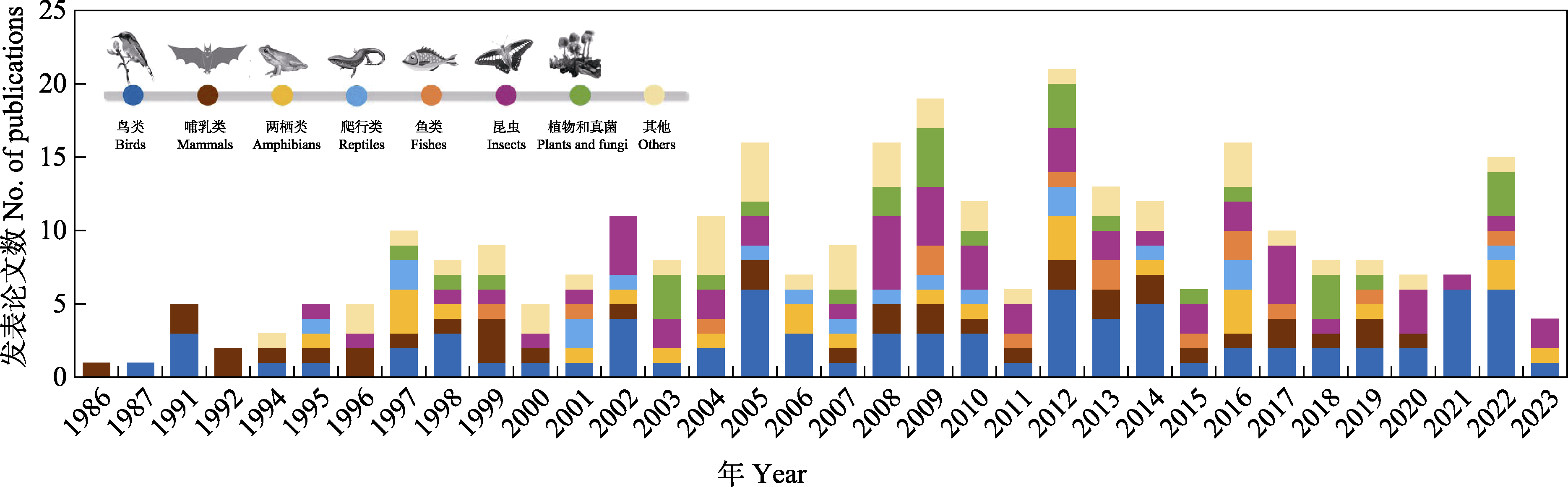
图3 嵌套分布格局在1986-2023年期间的研究趋势。该图是截至2023年10月31日以nestedness、nested subset、nested pattern、nested assemblage、嵌套、嵌套格局、嵌套结构、子集套为关键词在Web of Science和中国知网等数据库中检索到的269篇文献(删除了纯粹描述嵌套方法的研究论文和综述论文)的结果。
Fig. 3 The number of nestedness studies published from 1986 to 2023. The figure is based on the results of 269 nestedness studies (excluding articles purely describing nestedness methods and review articles) originated from databases such as Web of Science and CNKI based on the keywords “nestedness” “nested subset” “nested pattern” and “nested assemblage” as of October 31, 2023.
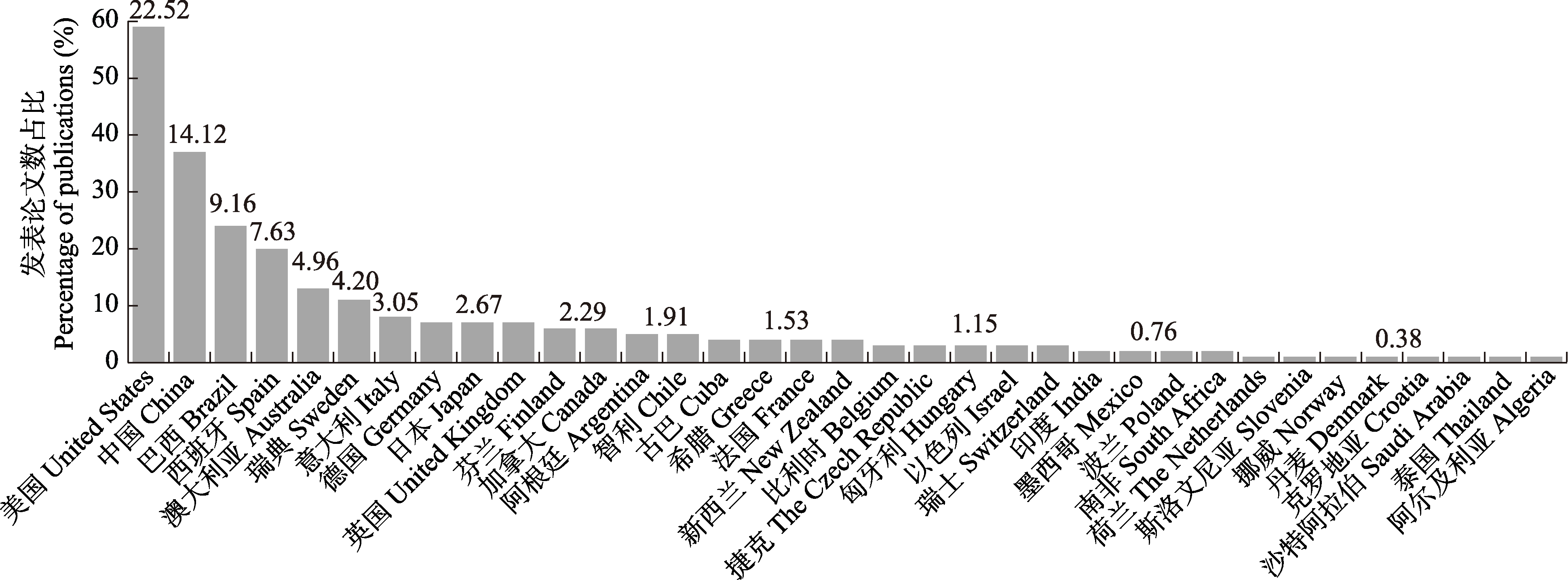
图4 嵌套分布格局研究按照研究人员所在国家的分布图(图中数字代表发表论文占比)。该图是截至2023年10月31日以nestedness、nested subset、nested pattern、nested assemblage、嵌套、嵌套格局、嵌套结构、子集套为关键词在Web of Science和中国知网等数据库中检索到的269篇文献(删除了纯粹描述嵌套方法的研究论文和综述论文)的结果。
Fig. 4 The distribution of nestedness studies based on the countries of researchers (the numbers in the figure represent the percentage of publications). The figure is based on the results of 269 nestedness studies (excluding articles purely describing nestedness methods and review articles) originated from databases such as Web of Science and CNKI based on the keywords “nestedness” “nested subset” “nested pattern” and “nested assemblage” as of October 31, 2023.
| 名称 Names | 简称 Abbreviation | 特点 Characteristics | 参考文献 References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 行限制方式 Row constraint | 列限制方式 Column constraint | 其他名称 Other names | |||
| Fixed-Fixed | FF | 固定 Fixed | 固定 Fixed | SIM9 | Connor & Simberloff, |
| Fixed-Equiprobable | FE | 固定 Fixed | 允许列总数自由变化 Equiprobable | SIM2, R0, Random0 | Patterson & Atmar, |
| Equiprobable-Fixed | EF | 允许行总数自由变化 Equiprobable | 固定 Fixed | SIM3 | Gotelli, |
| Equiprobable-Equiprobable | EE | 允许行总数自由变化 Equiprobable | 允许列总数自由变化 Equiprobable | SIM1, R00 | Atmar & Patterson, |
| Fixedincidence-Proportional | FP | 固定 Fixed | 与物种出现成比例变化 Proportional to species incidences | SIM5, R1, Random1 | Patterson & Atmar, |
| Lognormal-Fixed | LF | 与物种多度取对数成比例变化 Following a lognormal species abundance distribution | 固定 Fixed | - | Ulrich & Gotelli, |
| Incidence-Proportional | IP | 与物种出现成比例变化 Proportional to species incidences | 与物种出现成比例变化 Proportional to species incidences | SIM8, Model 2 | Gotelli, Bascompte et al, |
| Abundance-Proportional | AP | - | 与物种相对多度成比例变化 Proportional to species relative abundances | Randnest | Jonsson, |
| Equiprobable-Proportional | EP | 允许行总数自由变化 Equiprobable | 与物种出现成比例变化 Proportional to species incidences | - | Fischer & Lindenmayer, |
| Proportional | P | 与物种相对多度成比例变化 Proportional to species relative abundances | 与承载能力成比例变化 Proportional to carrying capacities | Recol | Moore & Swihart, |
| Proportional-Proportional | PP | 与行和列的总数成比例变化, 而且行和列的总平均数与原始矩阵相同 Proportional to row and column totals, but the mean values of marginal totals match those of the original matrix | 与行和列的总数成比例变化, 而且行和列的总平均数与原始矩阵相同 Proportional to row and column totals, but the mean values of marginal totals match those of the original matrix | - | Ulrich & Gotelli, |
| tipLabels | - | 不改变物种矩阵组成, 但会随机改变群落谱系构成的枝端结构 It shuffles the tip labels of the tree representation, but the site- by-species matrix is maintained intact | 不改变物种矩阵组成, 但会随机改变群落谱系构成的枝端结构 It shuffles the tip labels of the tree representation, but the site-by-species matrix is maintained intact | - | Melo et al, |
| permRows | - | 随机改变矩阵的行(物种) Randomly reorders rows of the matrix | - | Melo et al, | |
| permColumns | - | - | 随机改变矩阵的列(地点) Randomly reorders columns of the matrix | - | Melo et al, |
表3 用来推断嵌套分布格局是否显著的常用零模型
Table 3 Null models commonly used to infer the significance of nestedness
| 名称 Names | 简称 Abbreviation | 特点 Characteristics | 参考文献 References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 行限制方式 Row constraint | 列限制方式 Column constraint | 其他名称 Other names | |||
| Fixed-Fixed | FF | 固定 Fixed | 固定 Fixed | SIM9 | Connor & Simberloff, |
| Fixed-Equiprobable | FE | 固定 Fixed | 允许列总数自由变化 Equiprobable | SIM2, R0, Random0 | Patterson & Atmar, |
| Equiprobable-Fixed | EF | 允许行总数自由变化 Equiprobable | 固定 Fixed | SIM3 | Gotelli, |
| Equiprobable-Equiprobable | EE | 允许行总数自由变化 Equiprobable | 允许列总数自由变化 Equiprobable | SIM1, R00 | Atmar & Patterson, |
| Fixedincidence-Proportional | FP | 固定 Fixed | 与物种出现成比例变化 Proportional to species incidences | SIM5, R1, Random1 | Patterson & Atmar, |
| Lognormal-Fixed | LF | 与物种多度取对数成比例变化 Following a lognormal species abundance distribution | 固定 Fixed | - | Ulrich & Gotelli, |
| Incidence-Proportional | IP | 与物种出现成比例变化 Proportional to species incidences | 与物种出现成比例变化 Proportional to species incidences | SIM8, Model 2 | Gotelli, Bascompte et al, |
| Abundance-Proportional | AP | - | 与物种相对多度成比例变化 Proportional to species relative abundances | Randnest | Jonsson, |
| Equiprobable-Proportional | EP | 允许行总数自由变化 Equiprobable | 与物种出现成比例变化 Proportional to species incidences | - | Fischer & Lindenmayer, |
| Proportional | P | 与物种相对多度成比例变化 Proportional to species relative abundances | 与承载能力成比例变化 Proportional to carrying capacities | Recol | Moore & Swihart, |
| Proportional-Proportional | PP | 与行和列的总数成比例变化, 而且行和列的总平均数与原始矩阵相同 Proportional to row and column totals, but the mean values of marginal totals match those of the original matrix | 与行和列的总数成比例变化, 而且行和列的总平均数与原始矩阵相同 Proportional to row and column totals, but the mean values of marginal totals match those of the original matrix | - | Ulrich & Gotelli, |
| tipLabels | - | 不改变物种矩阵组成, 但会随机改变群落谱系构成的枝端结构 It shuffles the tip labels of the tree representation, but the site- by-species matrix is maintained intact | 不改变物种矩阵组成, 但会随机改变群落谱系构成的枝端结构 It shuffles the tip labels of the tree representation, but the site-by-species matrix is maintained intact | - | Melo et al, |
| permRows | - | 随机改变矩阵的行(物种) Randomly reorders rows of the matrix | - | Melo et al, | |
| permColumns | - | - | 随机改变矩阵的列(地点) Randomly reorders columns of the matrix | - | Melo et al, |
| 假说Hypothesis | 前提或假设 Assumption | 预测 Prediction | 例子 Examples | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地点特征 Site properties | 物种特征 Species properties | |||
| 被动取样 Passive sampling | 容纳力 Carrying capacities | 地区多度(常见种/偶见种) Regional abundance (common/rare species) | 地区的物种多度决定了岛屿占有情况, 因为常见种与偶见种相比更容易被调查到 Regional abundance predicts island occupancy because rare species are less likely to be sampled in a given area than common species | Andrén, |
| 选择性灭绝 Selective extinction | 容纳力 Carrying capacities | 灭绝敏感性(最小面积需求、体型大小、地理分布范围等) Extinction sensitivity (e.g., minimum area requirement, body size, and geographic range size) | 研究地点的面积决定了物种在生境中的选择性出现, 因为最小面积需求大或具有其他易灭绝特征的物种更容易发生灭绝 Area is the main factor explaining species nestedness because species with large minimum area requirements and other extinction-prone traits have greater extinction risk | Patterson & Atmar, |
| 选择性迁移 Selective colonization | 隔离度 Isolation | 扩散能力 Dispersal ability | 研究地点的隔离度和物种的扩散能力(如身体大小、游泳能力)决定了物种在生境中的选择性出现 Selective occupancy of islands according to island isolation and species traits related to dispersal capacity (e.g., body size, swimming ability) | Darlington, |
| 栖息地嵌套 Habitat nestedness | 栖息地异质性 Habitat heterogeneity | 栖息地专属性 Degree of specialization | 与栖息地特化种相比, 栖息地通才在面积小或资源少的斑块中具有较高的出现率 Compared with specialist species, generalist species can occupy higher proportion of smaller and/or resource poor patches | Wright & Reeves, |
| 人为干扰 Human disturbance | 干扰大小 Degree of disturbance | 干扰容忍性 Disturbance tolerances | 物种在栖息地中的出现由人为干扰决定, 因为对干扰敏感性高的物种更容易发生灭绝 Human disturbance predicts island occupancy because species vulnerable to disturbance are more likely to extinct | Fernández-Juricic, |
表4 嵌套分布格局的形成机制
Table 4 Common hypotheses for explaining the nested subset pattern (nestedness)
| 假说Hypothesis | 前提或假设 Assumption | 预测 Prediction | 例子 Examples | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地点特征 Site properties | 物种特征 Species properties | |||
| 被动取样 Passive sampling | 容纳力 Carrying capacities | 地区多度(常见种/偶见种) Regional abundance (common/rare species) | 地区的物种多度决定了岛屿占有情况, 因为常见种与偶见种相比更容易被调查到 Regional abundance predicts island occupancy because rare species are less likely to be sampled in a given area than common species | Andrén, |
| 选择性灭绝 Selective extinction | 容纳力 Carrying capacities | 灭绝敏感性(最小面积需求、体型大小、地理分布范围等) Extinction sensitivity (e.g., minimum area requirement, body size, and geographic range size) | 研究地点的面积决定了物种在生境中的选择性出现, 因为最小面积需求大或具有其他易灭绝特征的物种更容易发生灭绝 Area is the main factor explaining species nestedness because species with large minimum area requirements and other extinction-prone traits have greater extinction risk | Patterson & Atmar, |
| 选择性迁移 Selective colonization | 隔离度 Isolation | 扩散能力 Dispersal ability | 研究地点的隔离度和物种的扩散能力(如身体大小、游泳能力)决定了物种在生境中的选择性出现 Selective occupancy of islands according to island isolation and species traits related to dispersal capacity (e.g., body size, swimming ability) | Darlington, |
| 栖息地嵌套 Habitat nestedness | 栖息地异质性 Habitat heterogeneity | 栖息地专属性 Degree of specialization | 与栖息地特化种相比, 栖息地通才在面积小或资源少的斑块中具有较高的出现率 Compared with specialist species, generalist species can occupy higher proportion of smaller and/or resource poor patches | Wright & Reeves, |
| 人为干扰 Human disturbance | 干扰大小 Degree of disturbance | 干扰容忍性 Disturbance tolerances | 物种在栖息地中的出现由人为干扰决定, 因为对干扰敏感性高的物种更容易发生灭绝 Human disturbance predicts island occupancy because species vulnerable to disturbance are more likely to extinct | Fernández-Juricic, |
| [1] |
Almeida-Gomes M, Vieira MV, Rocha CFD, Melo AS (2019) Habitat amount drives the functional diversity and nestedness of anuran communities in an Atlantic forest fragmented landscape. Biotropica, 51, 874-884.
DOI |
| [2] |
Almeida-Neto M, Frensel DMB, Ulrich W (2012) Rethinking the relationship between nestedness and beta diversity: A comment on Baselga (2010). Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 772-777.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Almeida-Neto M, Guimarães P, Guimarães PR Jr, Loyola RD, Ulrich W (2008) A consistent metric for nestedness analysis in ecological systems: Reconciling concept and measurement. Oikos, 117, 1227-1239.
DOI URL |
| [4] | Almeida-Neto M, Ulrich W (2011) A straightforward computational approach for measuring nestedness using quantitative matrices. Environmental Modelling & Software, 26, 173-178. |
| [5] |
Andrén H (1994) Can one use nested subset pattern to reject the random sample hypothesis? Examples from boreal bird communities. Oikos, 70, 489-491.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Atmar W, Patterson BD (1993) The measure of order and disorder in the distribution of species in fragmented habitat. Oecologia, 96, 373-382.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | Bascompte J, Jordano P, Melián CJ, Olesen JM (2003) The nested assembly of plant-animal mutualistic networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 100, 9383-9387. |
| [8] |
Baselga A (2010) Partitioning the turnover and nestedness components of beta diversity. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 19, 134-143.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Baselga A (2012) The relationship between species replacement, dissimilarity derived from nestedness, and nestedness. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 21, 1223-1232.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Bender MG, Leprieur F, Mouillot D, Kulbicki M, Parravicini V, Pie MR, Barneche DR, Oliveira-Santos LGR, Floeter SR (2017) Isolation drives taxonomic and functional nestedness in tropical reef fish faunas. Ecography, 40, 425-435.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Blake JG (1991) Nested subsets and the distribution of birds on isolated woodlots. Conservation Biology, 5, 58-66.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Boecklen WJ (1997) Nestedness, biogeographic theory, and the design of nature reserves. Oecologia, 112, 123-142.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Bolger DT, Alberts AC, Soule ME (1991) Occurrence patterns of bird species in habitat fragments: Sampling, extinction, and nested species subsets. The American Naturalist, 137, 155-166.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Brown JH (1986) Two decades of interaction between the MacArthur-Wilson model and the complexities of mammalian distributions. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 28, 231-251.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Brualdi RA, Sanderson JG (1999) Nested species subsets, gaps, and discrepancy. Oecologia, 119, 256-264.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Bruun HH, Moen J (2003) Nested communities of alpine plants on isolated mountains: Relative importance of colonization and extinction. Journal of Biogeography, 30, 297-303.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Burgos E, Ceva H, Perazzo RPJ, Devoto M, Medan D, Zimmermann M, María Delbue A(2007) Why nestedness in mutualistic networks? Journal of Theoretical Biology, 249, 307-313. |
| [18] |
Cai C, Zhang X, Zhu C, Zhao YH, Qiao GX, Ding P (2023) Nested assemblages of aphid species in the Thousand Island Lake: The importance of island area and host plant diversity. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23183. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[蔡畅, 张雪, 朱晨, 赵郁豪, 乔格侠, 丁平 (2023) 千岛湖片段化生境中蚜虫群落嵌套格局的形成: 岛屿面积和寄主植物多样性的作用. 生物多样性, 31, 23183.]
DOI |
|
| [19] |
Calmé S, Desrochers A (1999) Nested bird and micro-habitat assemblages in a peatland archipelago. Oecologia, 118, 361-370.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Chen CW, Xu AC, Ding P, Wang YP (2019) The small-island effect and nestedness in assemblages of medium- and large-bodied mammals on Chinese reservoir land-bridge islands. Basic and Applied Ecology, 38, 47-57.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Chen CW, Zhan CX, Wang YP (2022) Do functional and phylogenetic nestedness follow the same mechanisms as taxonomic nestedness? Evidence from amphibians in the largest archipelago of China. Journal of Animal Ecology, 91, 2424-2436.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Chen SH, Wang YJ (2004) Nestedness pattern of insular community assemblages and its applications. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 23(3), 81-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈水华, 王玉军 (2004) 岛屿群落组成的嵌套格局及其应用. 生态学杂志, 23(3), 81-87.] | |
| [23] |
Coleman BD (1981) On random placement and species-area relations. Mathematical Biosciences, 54, 191-215.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Coleman BD, Mares MA, Willig MR, Hsieh Y (1982) Randomness, area, and species richness. Ecology, 63, 1121-1133.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Connor EF, Simberloff D (1979) The assembly of species communities: Chance or competition? Ecology, 60, 1132-1140. |
| [26] |
Cook RR (1995) The relationship between nested subsets, habitat subdivision, and species diversity. Oecologia, 101, 204-210.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Cook RR, Quinn JF (1995) The influence of colonization in nested species subsets. Oecologia, 102, 413-424.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
Cutler A (1991) Nested faunas and extinction in fragmented habitats. Conservation Biology, 5, 496-505.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Cutler AH (1994) Nested biotas and biological conservation: Metrics, mechanisms, and meaning of nestedness. Landscape and Urban Planning, 28, 73-82.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Darlington PJ (1957) Zoogeography:The Geographical Distribution of Animals. John Wiley & Sons, New York. |
| [31] |
Davidar P, Yogananad K, Ganesh T, Devy S (2002) Distributions of forest birds and butterflies in the Andaman Islands, Bay of Bengal: Nested patterns and processes. Ecography, 25, 5-16.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Diamond JM, Gilpin ME (1982) Examination of the “null” model of connor and simberloff for species co-occurrences on islands. Oecologia, 52, 64-74.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Driscoll DA (2008) The frequency of metapopulations, metacommunities and nestedness in a fragmented landscape. Oikos, 117, 297-309.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Feeley KJ, Gillespie TW, Lebbin DJ, Walter HS (2007) Species characteristics associated with extinction vulnerability and nestedness rankings of birds in tropical forest fragments. Animal Conservation, 10, 493-501.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Fernández-Juricic E (2002) Can human disturbance promote nestedness? A case study with breeding birds in urban habitat fragments. Oecologia, 131, 269-278.
DOI PMID |
| [36] | Fischer J, Lindenmayer DB (2002) Treating the nestedness temperature calculator as a “black box” can lead to false conclusions. Oikos, 99, 193-199. |
| [37] | Fischer J, Lindenmayer DB (2005) Perfectly nested or significantly nested—An important difference for conservation management. Oikos, 109, 485-494. |
| [38] |
Fleishman E, Betrus CJ, Blair RB, Mac Nally R, Murphy DD (2002) Nestedness analysis and conservation planning: The importance of place, environment, and life history across taxonomic groups. Oecologia, 133, 78-89.
DOI PMID |
| [39] |
Fleishman E, Donnelly R, Fay JP, Reeves R (2007) Applications of nestedness analyses to biodiversity conservation in developing landscapes. Landscape and Urban Planning, 81, 271-281.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Frick WF, Hayes JP, Heady PA III (2009) Nestedness of desert bat assemblages: Species composition patterns in insular and terrestrial landscapes. Oecologia, 158, 687-697.
DOI PMID |
| [41] |
Ganzhorn JU, Eisenbeiß B (2001) The concept of nested species assemblages and its utility for understanding effects of habitat fragmentation. Basic and Applied Ecology, 2, 87-99.
DOI URL |
| [42] | Gaston KJ, Blackburn TM (2000) Pattern and Process in Macroecology. Blackwell Science, Oxford. |
| [43] |
González-Oreja JA, De La Fuente-Díaz-Ordaz AA, Hernández-Santín L, Bonache-Regidor C, Buzo-Franco D (2012) Can human disturbance promote nestedness? Songbirds and noise in urban parks as a case study. Landscape and Urban Planning, 104, 9-18.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Gotelli NJ (2000) Null model analysis of species co-occurrence patterns. Ecology, 81, 2606-2621.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Greve M, Chown SL (2006) Endemicity biases nestedness metrics: A demonstration, explanation and solution. Ecography, 29, 347-356.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Greve M, Gremmen NJM, Gaston KJ, Chown SL (2005) Nestedness of Southern Ocean Island biotas: Ecological perspectives on a biogeographical conundrum. Journal of Biogeography, 32, 155-168.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Hausdorf B, Hennig C (2003) Nestedness of north-west European land snail ranges as a consequence of differential immigration from Pleistocene glacial refuges. Oecologia, 135, 102-109.
PMID |
| [48] |
Henle K, Davies KF, Kleyer M, Margules C, Settele J (2004) Predictors of species sensitivity to fragmentation. Biodiversity and Conservation, 13, 207-251.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Higgins CL, Willig MR, Strauss RE (2006) The role of stochastic processes in producing nested patterns of species distributions. Oikos, 114, 159-167.
DOI URL |
| [50] | Honnay O, Hermy M, Coppin P (1999) Nested plant communities in deciduous forest fragments: Species relaxation or nested habitats? Oikos, 84, 119-129. |
| [51] |
Hylander K, Nilsson C, Jonsson BG, Göthner T (2005) Differences in habitat quality explain nestedness in a land snail meta-community. Oikos, 108, 351-361.
DOI URL |
| [52] | Jacoboski LI, Debastiani VJ, de Mendonça-Lima A, Hartz SM (2016) How do diversity and functional nestedness of bird communities respond to changes in the landscape caused by eucalyptus plantations? Community Ecology, 17, 107-113. |
| [53] |
James A, Pitchford JW, Plank MJ (2012) Disentangling nestedness from models of ecological complexity. Nature, 487, 227-230.
DOI |
| [54] |
Jonsson BG (2001) A null model for randomization tests of nestedness in species assemblages. Oecologia, 127, 309-313.
DOI PMID |
| [55] | Joppa LN, Montoya JM, Solé R, Sanderson J, Pimm SL (2010) On nestedness in ecological networks. Evolutionary Ecology Research, 12, 35-46. |
| [56] |
Kadmon R (1995) Nested species subsets and geographic isolation: A case study. Ecology, 76, 458-465.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Li CL, Zhao BB, Wang YP (2019) Nestedness of waterbird assemblages in the subsidence wetlands recently created by underground coal mining. Current Zoology, 65, 155-163.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Li YM, Niemelä J, Li DM (1998) Nested distribution of amphibians in the Zhoushan Archipelago, China: Can selective extinction cause nested subsets of species? Oecologia, 113, 557-564.
DOI PMID |
| [59] | Lomolino MV (1996) Investigating causality of nestedness of insular communities: Selective immigrations or extinctions? Journal of Biogeography, 23, 699-703. |
| [60] |
Loo SE, Mac Nally R, Quinn G (2002) An experimental examination of colonization as a generator of biotic nestedness. Oecologia, 132, 118-124.
DOI PMID |
| [61] |
Martínez-Morales MA (2005) Nested species assemblages as a tool to detect sensitivity to forest fragmentation: The case of cloud forest birds. Oikos, 108, 634-642.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
Matthews TJ, Cottee-Jones HEW, Whittaker RJ (2015a) Quantifying and interpreting nestedness in habitat islands: A synthetic analysis of multiple datasets. Diversity and Distributions, 21, 392-404.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
Matthews TJ, Sheard C, Cottee-Jones HEW, Bregman TP, Tobias JA, Whittaker RJ (2015b) Ecological traits reveal functional nestedness of bird communities in habitat islands: A global survey. Oikos, 124, 817-826.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
McAbendroth L, Foggo A, Rundle SD, Bilton DT (2005) Unravelling nestedness and spatial pattern in pond assemblages. Journal of Animal Ecology, 74, 41-49.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
McKinney ML (1997) Extinction vulnerability and selectivity: Combining ecological and paleontological views. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 28, 495-516.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
Melo AS, Cianciaruso MV, Almeida-Neto M (2014) tree NODF: Nestedness to phylogenetic, functional and other tree-based diversity metrics. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 5, 563-572.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
Meyer CFJ, Kalko EKV (2008) Bat assemblages on Neotropical land-bridge islands: Nested subsets and null model analyses of species co-occurrence patterns. Diversity and Distributions, 14, 644-654.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
Moore JE, Swihart RK (2007) Toward ecologically explicit null models of nestedness. Oecologia, 152, 763-777.
PMID |
| [69] |
Patterson BD (1987) The principle of nested subsets and its implications for biological conservation. Conservation Biology, 1, 323-334.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Patterson BD (1990) On the temporal development of nested subset patterns of species composition. Oikos, 59, 330-342.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
Patterson BD, Atmar W (1986) Nested subsets and the structure of insular mammalian faunas and archipelagos. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 28, 65-82.
DOI URL |
| [72] | Patterson BD, Atmar W (2000) Analyzing species composition in fragments. In: Isolated Vertebrate Communities in the Tropics (ed. Rheinwald G), pp. 9-24. Alexander Koening Zoological Research Institute and Zoological Museum, Bonn. |
| [73] |
Patterson BD, Pacheco V, Solari S (1996) Distribution of bats along an elevational gradient in the Andes of south-eastern Peru. Journal of Zoology, 240, 637-658.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
Petchey OL, Gaston KJ (2002) Functional diversity (FD), species richness and community composition. Ecology Letters, 5, 402-411.
DOI URL |
| [75] | Purvis A, Gittleman JL, Cowlishaw G, Mace GM (2000) Predicting extinction risk in declining species. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 267, 1947-1952. |
| [76] |
Rodríguez-Gironés MA, Santamaría L (2006) A new algorithm to calculate the nestedness temperature of presence-absence matrices. Journal of Biogeography, 33, 924-935.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
Schouten MA, Verweij PA, Barendregt A, Kleukers RJM, de Ruiter PC (2007) Nested assemblages of Orthoptera species in the Netherlands: The importance of habitat features and life-history traits. Journal of Biogeography, 34, 1938-1946.
DOI URL |
| [78] | Shipley B (2000) Cause and Correlation in Biology: A User’s Guide to Path Analysis, Structrual Equations, and Causal Inference. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [79] |
Si XF, Zhao YH, Chen CW, Ren P, Zeng D, Wu LB, Ding P (2017) Beta-diversity partitioning: Methods, applications and perspectives. Biodiversity Science, 25, 464-480. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[斯幸峰, 赵郁豪, 陈传武, 任鹏, 曾頔, 吴玲兵, 丁平 (2017) Beta多样性分解: 方法、应用与展望. 生物多样性, 25, 464-480.]
DOI |
|
| [80] | Simberloff D, Levin B (1985) Predictable sequences of species loss with decreasing island area—Land birds in two archipelagoes. New Zealand Journal of Ecology, 8, 11-20. |
| [81] |
Soga M, Koike S (2012) Life-history traits affect vulnerability of butterflies to habitat fragmentation in urban remnant forests. Écoscience, 19, 11-20.
DOI URL |
| [82] |
Tan XW, Yang XR, Chen CW, Wang YP (2021) Nestedness and underlying processes of bird assemblages in Nanjing urban parks. Current Zoology, 67, 383-392.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
Ulrich W, Almeida-Neto M, Gotelli NJ (2009) A consumer’s guide to nestedness analysis. Oikos, 118, 3-17.
DOI URL |
| [84] |
Ulrich W, Gotelli NJ (2007) Null model analysis of species nestedness patterns. Ecology, 88, 1824-1831.
DOI PMID |
| [85] |
Ulrich W, Gotelli NJ (2012) A null model algorithm for presence-absence matrices based on proportional resampling. Ecological Modelling, 244, 20-27.
DOI URL |
| [86] | Valverde S, Vidiella B, Montañez R, Fraile A, Sacristán S, García-Arenal F (2020) Coexistence of nestedness and modularity in host-pathogen infection networks. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 4, 568-577. |
| [87] |
Wang YP, Bao YX, Yu MJ, Xu GF, Ding P (2010) Nestedness for different reasons: The distributions of birds, lizards and small mammals on islands of an inundated lake. Diversity and Distributions, 16, 862-873.
DOI URL |
| [88] |
Wang YP, Chen CW, Millien V (2023) The integration of the small-island effect and nestedness pattern. Journal of Biogeography, 50, 1234-1243.
DOI URL |
| [89] |
Wang YP, Chen SH, Ding P (2011) Testing multiple assembly rule models in avian communities on islands of an inundated lake, Zhejiang Province, China. Journal of Biogeography, 38, 1330-1344.
DOI URL |
| [90] |
Wang YP, Ding P, Chen SH, Zheng GM (2013) Nestedness of bird assemblages on urban woodlots: Implications for conservation. Landscape and Urban Planning, 111, 59-67.
DOI URL |
| [91] |
Wang YP, Wang X, Ding P (2012) Nestedness of snake assemblages on islands of an inundated lake. Current Zoology, 58, 828-836.
DOI URL |
| [92] |
Watling JI, Donnelly MA (2006) Fragments as islands: A synthesis of faunal responses to habitat patchiness. Conservation Biology, 20, 1016-1025.
PMID |
| [93] |
Webb CO, Ackerly DD, McPeek MA, Donoghue MJ (2002) Phylogenies and community ecology. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 33, 475-505.
DOI URL |
| [94] | Weiher E, Keddy P (1999) Ecological Assembly Rules: Perspectives, Advances, Retreats Advances, Retreats. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [95] |
Wethered R, Lawes MJ (2005) Nestedness of bird assemblages in fragmented Afromontane forest: The effect of plantation forestry in the matrix. Biological Conservation, 123, 125-137.
DOI URL |
| [96] | Whittaker RJ, Fernandez-Palacios JM (2007) Island Biogeography: Ecology, Evolution, and Conservation, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford. |
| [97] |
Worthen WB, Carswell ML, Kelly KA (1996) Nested subset structure of larval mycophagous fly assemblages: Nestedness in a non-island system. Oecologia, 107, 257-264.
DOI PMID |
| [98] |
Worthen WB, Jones MT, Jetton RM (1998) Community structure and environmental stress: Desiccation promotes nestedness in mycophagous fly communities. Oikos, 81, 45-54.
DOI URL |
| [99] |
Wright DH, Patterson BD, Mikkelson GM, Cutler A, Atmar W (1998) A comparative analysis of nested subset patterns of species composition. Oecologia, 113, 1-20.
DOI URL |
| [100] |
Wright DH, Reeves JH (1992) On the meaning and measurement of nestedness of species assemblages. Oecologia, 92, 416-428.
DOI PMID |
| [101] |
Xu AC, Han XF, Zhang XM, Millien V, Wang YP (2017) Nestedness of butterfly assemblages in the Zhoushan Archipelago, China: Area effects, life-history traits and conservation implications. Biodiversity and Conservation, 26, 1375-1392.
DOI URL |
| [102] | Zhang MC, Tang CN, Zhang Q, Zhan CX, Chen CW, Wang YP (2023) Selective extinction and habitat nestedness are the main drivers of lizard nestedness in the Zhoushan Archipelago. Current Zoology, doi: 10.1093/cz/zoac103. |
| [1] | 彭昀月, 罗永梅, 徐泽楠, 靳彤. 集中式大型光伏及风电电场生态影响: 进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23212-. |
| [2] | 谢艳秋, 黄晖, 王春晓, 何雅琴, 江怡萱, 刘子琳, 邓传远, 郑郁善. 福建海岛滨海特有植物种-面积关系及物种丰富度决定因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22345-. |
| [3] | 高德, 王彦平. 小岛屿效应检测方法研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23299-. |
| [4] | 蔡畅, 张雪, 朱晨, 赵郁豪, 乔格侠, 丁平. 千岛湖片段化生境中蚜虫群落嵌套格局的形成: 岛屿面积和寄主植物多样性的作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23183-. |
| [5] | 商晓凡, 张健, 高浩杰, 库伟鹏, 毕玉科, 李修鹏, 阎恩荣. 岛屿面积与气候共同影响舟山群岛种子植物丰富度格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23392-. |
| [6] | 田璐嘉, 杨小波, 李东海, 李龙, 陈琳, 梁彩群, 张培春, 李晨笛. 海口和三亚两城市破碎化林地中鸟类群落多样性与嵌套分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 21424-. |
| [7] | 付裕, 黄康祥, 蔡锦枫, 陈慧敏, 任久生, 万松泽, 张扬, 任珩, 毛瑢, 石福习. 三江平原沼泽湿地4种优势植物空间格局对不同水位环境的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(3): 21392-. |
| [8] | 张健, 孔宏智, 黄晓磊, 傅声雷, 郭良栋, 郭庆华, 雷富民, 吕植, 周玉荣, 马克平. 中国生物多样性研究的30个核心问题[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22609-. |
| [9] | 邹怡. 样本量不一致时的β多样性计算[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(6): 790-797. |
| [10] | 郑进凤, 唐蓉, 贺霜, 陈月红, 伍素, 张凯, 徐雨, 邹晓. 贵州花溪大学城破碎化林地鸟类多样性与嵌套分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 661-667. |
| [11] | 斯幸峰, 赵郁豪, 陈传武, 任鹏, 曾頔, 吴玲兵, 丁平. Beta多样性分解: 方法、应用与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(5): 464-480. |
| [12] | 齐月, 李俊生, 闫冰, 邓贞贞, 付刚. 化学除草剂对农田生态系统野生植物多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(2): 228-236. |
| [13] | 徐爱春, 斯幸峰, 王彦平, 丁平. 千岛湖片段化栖息地地栖哺乳动物的红外相机监测及最小监测时长[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(6): 764-772. |
| [14] | 裴男才, 张金龙, 米湘成, 葛学军. 植物DNA条形码促进系统发育群落生态学发展[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(3): 284-294. |
| [15] | 牛红玉, 王峥峰, 练琚愉, 叶万辉, 沈浩. 群落构建研究的新进展: 进化和生态 相结合的群落谱系结构研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(3): 275-283. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn