



生物多样性 ›› 2014, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (2): 208-215. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13160 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2014.13160
收稿日期:2013-07-12
接受日期:2014-02-20
出版日期:2014-03-20
发布日期:2014-04-03
通讯作者:
李巧
基金资助:
Yanyan Ma1, Zizhong Yang2, Ping Feng1, Qiao Li1,*( )
)
Received:2013-07-12
Accepted:2014-02-20
Online:2014-03-20
Published:2014-04-03
Contact:
Li Qiao
摘要:
为揭示不同蜘蛛类群对火干扰的敏感程度及蜘蛛群落外貌对环境变化产生的响应, 本文选取苍山针阔混交林2007年火烧迹地作为调查样地, 以无火烧记录的样地为对照, 运用陷阱法调查地表蜘蛛群落生活型及季节动态。研究结果显示: (1)火烧迹地中朱氏狂蛛(Zelotes zhui)(相对优势度 DV' =33.03)、晨豹蛛(Pardosa chionophila) (DV'=22.53)和西菱头蛛一种(Sibianor sp.1)(DV'=8.75)占明显优势; 而对照样地中龙隙蛛一种(Draconarius sp.2) (DV'=63.50)占绝对优势; (2)火烧迹地的定居型蜘蛛相对多度为25.82%, 显著少于游猎蜘蛛(P<0.001); 而对照样地的定居型蜘蛛相对多度为92.07%, 显著高于游猎蜘蛛(P<0.001); (3)火烧迹地地表蜘蛛优势类群随季节更替明显, 在夏季和冬季多度为低谷期; 对照样地优势类群稳定, 为漏斗蛛科蜘蛛。研究表明, 火干扰改变了苍山针阔混交林地表蜘蛛群落生活型组成, 降低了定居型蜘蛛的相对多度和地表蜘蛛群落的季节稳定性。
马艳滟, 杨自忠, 冯萍, 李巧 (2014) 火干扰对云南苍山地表蜘蛛群落生活型组成及季节动态的影响. 生物多样性, 22, 208-215. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13160.
Yanyan Ma,Zizhong Yang,Ping Feng,Qiao Li (2014) The influence of fire disturbance on the biotype structure and seasonal dynamics of ground-dwelling spider on Cangshan Mountain, Yunnan Province. Biodiversity Science, 22, 208-215. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13160.
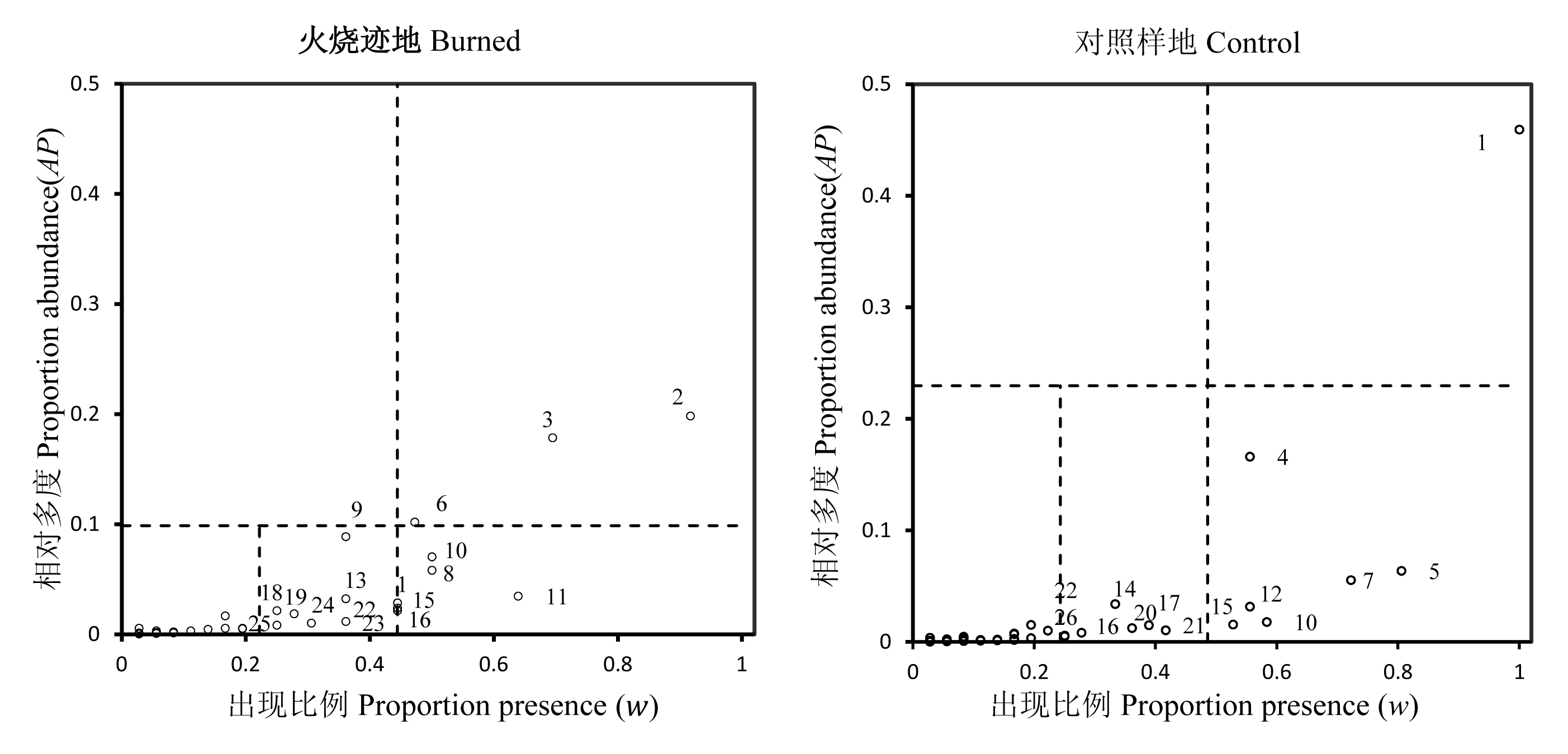
图1 苍山火烧迹地和对照样地地表蜘蛛群落物种组成。图中数字所代表的物种名见表1。
Fig. 1 Composition of ground-dwelling spider community in burned and control forest, Cangshan Mountain, Yunnan. The species identifier number see Table1.
| 科名 Family | 物种名 Species | 生活型 Biotype | 物种编号 Species identifier | 相对优势度 Relative dominance values (DV') | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 火烧迹地 Burned | 对照样地 Control | ||||
| 巨蟹蛛科 Sparassidae | 苍山伪遁蛛 Pseudopoda cangshana | H | 22 | 0.77C | 0.18C |
| 狼蛛科 Lycosidae | 晨豹蛛 Pardosa chionophila | H | 3 | 22.53D | 0.41C |
| 漏斗蛛科 Agelenidae | 龙隙蛛一种 Draconarius sp.2 | W | 1 | 2.31C | 63.50D |
| 不定龙隙蛛 Draconarius incertus | W | 10 | 5.29S | 1.45S | |
| 隙蛛一种 Coelotes sp.3 | W | 20 | 0.62C | ||
| 光先隙蛛 Coelotes guangxian | W | 18 | 0.98C | ||
| 龙隙蛛一种 Draconarius sp.1 | W | 19 | 0.95C | ||
| 隙蛛一种 Coelotes sp.1 | W | 24 | 0.57C | ||
| 船形新漏斗蛛 Neagelena cymbiforma | W | 25 | 0.38C | ||
| 卵形蛛科 Oonopidae | 卵形蛛一种 Oonops sp.1 | H | 17 | 0.81C | |
| 伽马蛛一种 Gamasomorpha sp.1 | H | 21 | 0.61C | ||
| 皿蛛科 Linyphiidae | 中指蛛一种 Centromerus sp.1 | W | 7 | 5.54S | |
| 皿蛛一种 Linyphia sp.5 | W | 12 | 2.44S | ||
| 皿蛛一种 Linyphia sp.9 | W | 13 | 2.13C | ||
| 拟平腹蛛科 Zodariidae | 马利蛛一种 Mallinella sp.2 | H | 9 | 5.83C | |
| 平腹蛛科 Gnaphosidae | 朱氏狂蛛 Zelotes zhui | H | 2 | 33.03D | |
| 大理掠蛛 Drassodes daliensis | H | 11 | 4.04S | ||
| 弱蛛科 Leptonetidae | 弱蛛一种 Leptoneta sp.1 | W | 4 | 12.76S | |
| 跳蛛科 Salticidae | 卡氏方胸蛛 Thiania cavaleriei | H | 26 | 0.20C | |
| 西菱头蛛一种 Sibianor sp.1 | H | 6 | 8.75D | ||
| 兰戈纳蛛一种 Langona sp.1 | H | 8 | 6.40S | ||
| 肖蛸科 Tetragnathidae | 柔弱粗螯蛛 Pachygnatha tenera | W | 5 | 7.11S | |
| 逍遥蛛科 Philodromidae | 逍遥蛛一种 Philodromus sp.2 | H | 23 | 0.77C | |
| 异纺蛛科 Hexathelidae | 大疣蛛一种 Macrothele sp.1 | W | 16 | 1.75C | 0.32C |
| 圆颚蛛科 Corinnidae | 大理刺足蛛 Phrurolithus daliensis | H | 15 | 1.94C | 1.15S |
| 栅蛛科 Hahniidae | 栅蛛一种 Hahnia sp.2 | W | 14 | 1.57C | |
表1 苍山火烧迹地和对照样地地表蜘蛛优势种(D)、亚优势种(S)和常见种(C)组成及其相对优势度
Table 1 Relative dominance values (DV') for the dominant (D), sub-dominant (S) and common (C) ground-dwelling species in the burned and control forest of Cangshan Mountain, Yunnan
| 科名 Family | 物种名 Species | 生活型 Biotype | 物种编号 Species identifier | 相对优势度 Relative dominance values (DV') | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 火烧迹地 Burned | 对照样地 Control | ||||
| 巨蟹蛛科 Sparassidae | 苍山伪遁蛛 Pseudopoda cangshana | H | 22 | 0.77C | 0.18C |
| 狼蛛科 Lycosidae | 晨豹蛛 Pardosa chionophila | H | 3 | 22.53D | 0.41C |
| 漏斗蛛科 Agelenidae | 龙隙蛛一种 Draconarius sp.2 | W | 1 | 2.31C | 63.50D |
| 不定龙隙蛛 Draconarius incertus | W | 10 | 5.29S | 1.45S | |
| 隙蛛一种 Coelotes sp.3 | W | 20 | 0.62C | ||
| 光先隙蛛 Coelotes guangxian | W | 18 | 0.98C | ||
| 龙隙蛛一种 Draconarius sp.1 | W | 19 | 0.95C | ||
| 隙蛛一种 Coelotes sp.1 | W | 24 | 0.57C | ||
| 船形新漏斗蛛 Neagelena cymbiforma | W | 25 | 0.38C | ||
| 卵形蛛科 Oonopidae | 卵形蛛一种 Oonops sp.1 | H | 17 | 0.81C | |
| 伽马蛛一种 Gamasomorpha sp.1 | H | 21 | 0.61C | ||
| 皿蛛科 Linyphiidae | 中指蛛一种 Centromerus sp.1 | W | 7 | 5.54S | |
| 皿蛛一种 Linyphia sp.5 | W | 12 | 2.44S | ||
| 皿蛛一种 Linyphia sp.9 | W | 13 | 2.13C | ||
| 拟平腹蛛科 Zodariidae | 马利蛛一种 Mallinella sp.2 | H | 9 | 5.83C | |
| 平腹蛛科 Gnaphosidae | 朱氏狂蛛 Zelotes zhui | H | 2 | 33.03D | |
| 大理掠蛛 Drassodes daliensis | H | 11 | 4.04S | ||
| 弱蛛科 Leptonetidae | 弱蛛一种 Leptoneta sp.1 | W | 4 | 12.76S | |
| 跳蛛科 Salticidae | 卡氏方胸蛛 Thiania cavaleriei | H | 26 | 0.20C | |
| 西菱头蛛一种 Sibianor sp.1 | H | 6 | 8.75D | ||
| 兰戈纳蛛一种 Langona sp.1 | H | 8 | 6.40S | ||
| 肖蛸科 Tetragnathidae | 柔弱粗螯蛛 Pachygnatha tenera | W | 5 | 7.11S | |
| 逍遥蛛科 Philodromidae | 逍遥蛛一种 Philodromus sp.2 | H | 23 | 0.77C | |
| 异纺蛛科 Hexathelidae | 大疣蛛一种 Macrothele sp.1 | W | 16 | 1.75C | 0.32C |
| 圆颚蛛科 Corinnidae | 大理刺足蛛 Phrurolithus daliensis | H | 15 | 1.94C | 1.15S |
| 栅蛛科 Hahniidae | 栅蛛一种 Hahnia sp.2 | W | 14 | 1.57C | |
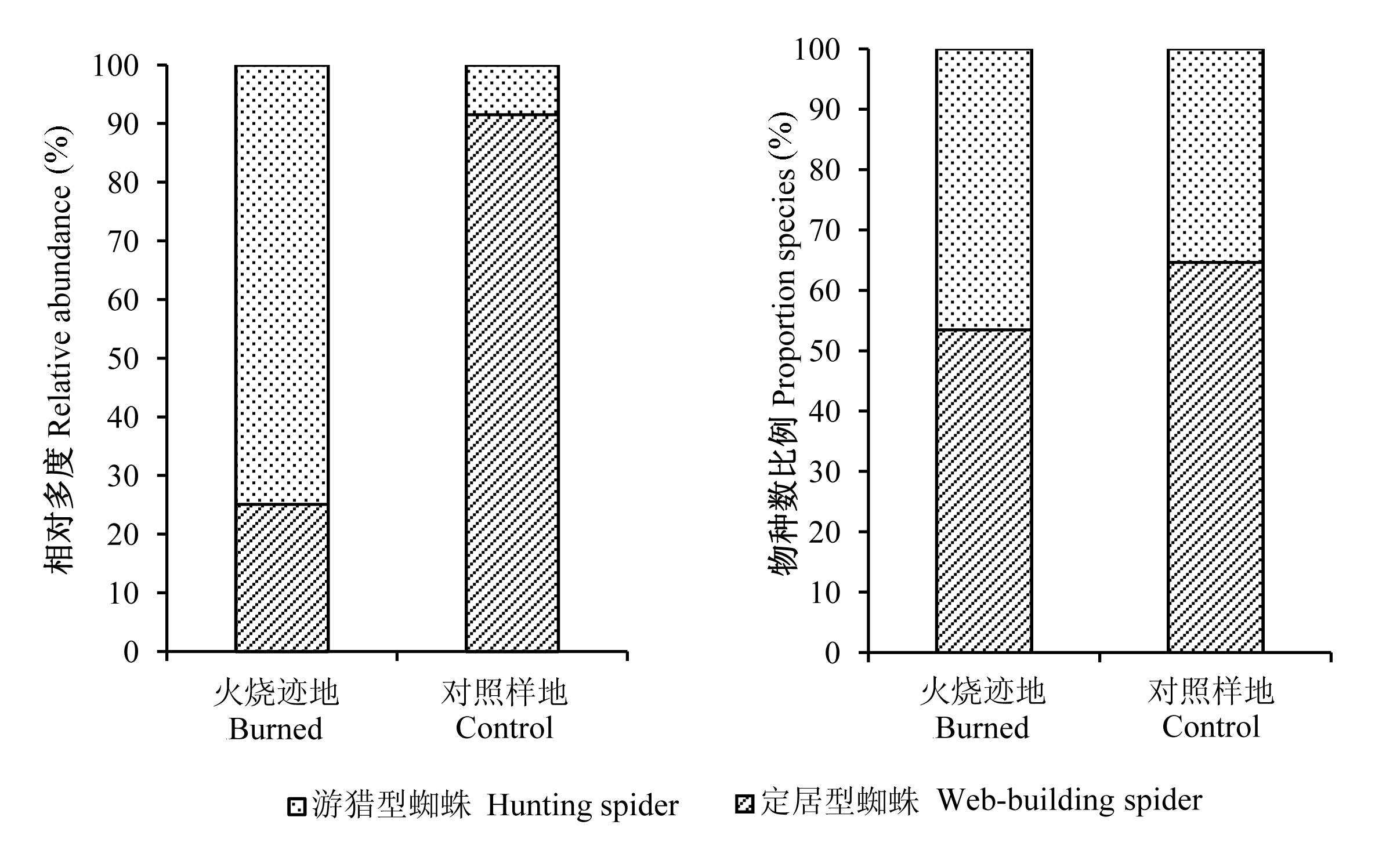
图2 苍山火烧迹地和对照样地地表蜘蛛群落生活型组成
Fig. 2 Biotype (web-building spider vs hunting spider) of ground-dwelling spider community in burned and control forest, Cangshan Mountain, Yunnan
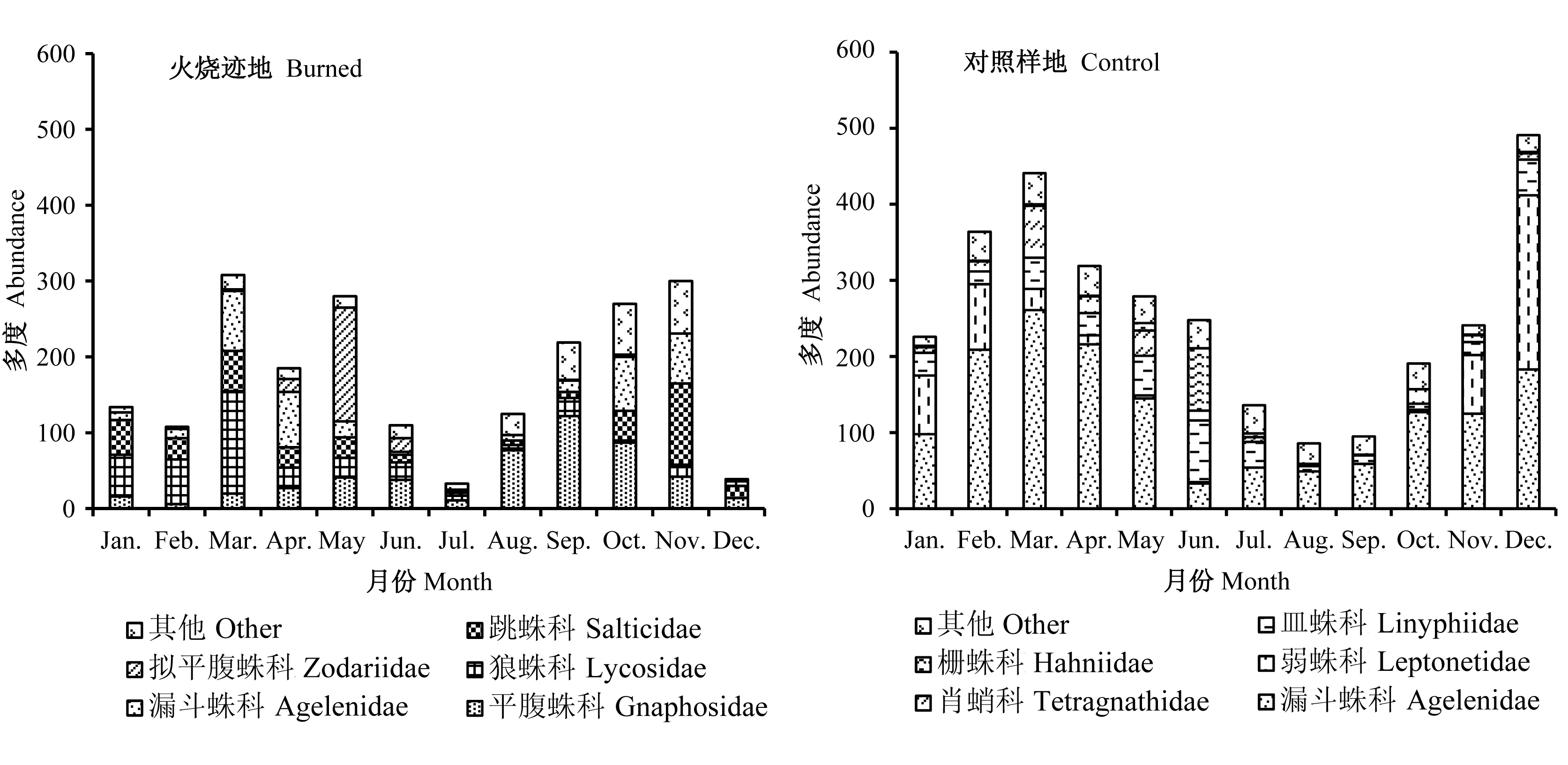
图3 苍山火烧迹地和对照样地地表蜘蛛优势类群季节变化
Fig. 3 Seasonal variation of the dominant group of the ground-dwelling spider in burned and control sites, Cangshan Mountain, Yunnan
| [1] | Balfour RA, Buddle CM, Rypstra AL, Walker SE, Marshall SD (2003) Ontogenetic shifts in competitive interactions and intra-guild predation between two wolf spider species. Ecological Entomology, 28, 25–30. |
| [2] | Brierton BM, Allen DC, Jennings DT (2003) Spider fauna of sugar maple and white ash in northern and central New York State. Journal of Arachnology, 31, 350–362. |
| [3] | Cardoso P, Pekár S, Jocqué R, Coddington JA (2011) Global patterns of guild composition and functional diversity of spiders. PLoS ONE, 6, e21710. |
| [4] | Chatzaki M, Trichas A, Markakis G, Mylonas M (1998) Seasonal activity of the ground spider fauna in a Mediterranean ecosystem (Mt. Youchtas, Crete, Greece). In: Proceedings of the 17th European Colloquium of Arachnology (ed. Beeches B), pp. 235–243. British Arachnological Society, Buckinghamshire. |
| [5] | Chen LD (陈利顶), Fu BJ (傅伯杰) (2000) Ecological significance, characteristics and types of disturbance. Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 20, 581–586. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [6] | Chen LS (陈连水), Yuan FH (袁凤辉), Rao J (饶军), Yan HM (颜亨梅) (2008) An analysis of spider diversity in Shuijiang Nature Reserve in Jiangxi Province, China. Acta Arachnologica Sinica(蛛形学报), 17, 117–120. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [7] | Chen YL (陈彦林), Wang B (王彬), Li HX (李洪鲜), Yan LB (晏利波), Li Q (李巧) (2007) Impact of fire disturbance on arthropod communities in forests of Pinus yunnanensis and Pinus yunnanensis var. pygamaea. Journal of Southwest Foresty College(西南林学院学报), 27(6), 57–61. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [8] | Curtis DJ (1980) Pitfalls in spider community studies (Arachnida, Araneae). Journal of Arachnology, 8, 271–280. |
| [9] | Denno RF, Mitter MS, Langellotto GA, Gratton C, Finke DL (2004) Interactions between a hunting spider and a web-builder: consequences of intraguild predation and cannibalism for prey suppression. Ecological Entomology, 29, 566–577. |
| [10] | Downie IS, Wilson WL, Abernethy VJ, Mccracken DI, Foster GN, Ribers I, Murphy KJ, Waterhouse A (1999) The impact of different agricultural land use on epigeal spider diversity in Scotland. Journal of Insect Conservation, 3, 273–286. |
| [11] | Finke DL, Denno RF (2003) Intraguild predation relaxes natural enemy impacts on herbivore populations. Ecological Entomology, 28, 67–73. |
| [12] | Halaj J, Ross DW, Moldenke AR (1998) Habitat structure and prey availability as predictors of the abundance and community organization of spiders in western Oregon forest canopies. Journal of Arachnology, 26, 203–220. |
| [13] | Hawkins CP, MacMahon JA (1989) Guilds: the multiple meanings of a concept. Annual Review of Entomology, 34, 423–451. |
| [14] | Hore U, Uniyal VP (2008) Effect of prescribed fire on spider assemblage in Terai grasslands, India. Turk Journal Arachnology, 1(1), 15–36. |
| [15] | Horváth R, Lengyel S, Szinetár C, Jakab L (2005) The effect of prey availability on spider assemblages on European black pine (Pinus nigra) bark: spatial patterns and guild structure. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 83, 324–335. |
| [16] | Humphreys WF (1987) Behavioural temperature regulation. In: Ecophysiology of Spiders (ed. Nentwig W), pp. 56–65. Springer-Verlag, Berlin. |
| [17] | Hurd LE, Fagan WF (1992) Cursorial spiders and succession: age or habitat structure?Oecologia, 92, 215–221. |
| [18] | Kato M, Inoue T, Hamid AA, Nagamitsu T, Merdek MB, Nona AR, Hino T, Yamane S, Yumoto T (1995) Seasonality and vertical structure of light attracted insect communities in a dipterocarp forest in Sarawak. Researches on Population Ecology, 37, 59–79. |
| [19] | Kaynas BY, Gurkan B (2008) Species richness and abundance of insects during post-fire succession of Pinus brutia forest in Mediterranean region. Polish Journal of Ecology, 56, 165–172. |
| [20] | Koponen S (2005) Early succession of a boreal spider community after forest fire. Journal of Arachnology, 33, 230–235. |
| [21] | Kuang MS (况明生), Xie SY (谢世友), Zeng Y (曾艳), Li LL (李林立), Feng SG (冯绍国), Zhang YZ (张远瞩) (2002) Study on the Palaeovegation and Palaeoclimate since late Pleistocene in the Dianchang Mountain area in Dali of Yunnan Province. Journal of Southwest China Normal University (Natural Science) (西南师范大学学报(自然科学版)), 27, 759–765. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [22] | Land MF (1985) The morphology and optics of spider eyes. In: Neurobiology of Arachnids (ed. Barth FG), pp. 53–78. Springer-Verlag, Berlin. |
| [23] | Langellotto GA, Denno RF (2004) Responses of invertebrate natural enemies to complex-structured habitats: a meta-analytical synthesis. Oecologia, 139, 1–10. |
| [24] | Li H (李恒), Yang ZZ (杨自忠), Li JH (李继红), Dong XD (董晓东), Wang HB (王浩波), Feng JM (冯建孟) (2009) Effects of successions of communities on plant species diversity in post-fire area in Cangshan Mountain. Journal of Chuxiong Normal University(楚雄师范学院学报), 24, 70–73. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [25] | Lie WL (劣旺禄), Zhu MS (朱明生), Song DX (宋大祥) (1999) Studies on the structure and diversity of soil spider communities in Zhangjiakou area, Hebei Province, China. Acta Arachnologica Sinica(蛛形学报), 8, 49–54. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [26] | Ma YY (马艳滟), Li Q (李巧), Feng P (冯萍), Yang ZZ (杨自忠) (2013) Diversity of ground-dwelling spider community in different restoring times of post-fire forest, Cangshan Mountain, Yunnan Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报), 33, 964–974. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [27] | New TR (1999) Untangling the web: spiders and the challenges of invertebrate conservation. Journal of Insect Conservation, 3, 251–256. |
| [28] | Niwa CG, Peck RW (2002) Influence of prescribed fire on Carabid beetle (Carabidae) and spider (Araneae) assem- blages in forest litter in Southwestern Oregon. Environ- mental Entomology, 31, 785–796. |
| [29] | Nyffeler M (2000) Ecological impact of spider predation: a critical assessment of Bristowe’s and Turnbull’s estimates. Bulletin of the British Arachnological Society, 11, 367–373. |
| [30] | Persons MH, Uetz GW (1996) The influence of sensory information on patch residence time in wolf spiders (Araneae: Lycosidae). Animal Behaviour, 51, 1285–1293. |
| [31] | Pinzón J, Spence JR (2010) Bark-dwelling spider assemblages (Araneae) in the boreal forest: dominance, diversity, composition and life-histories. Journal of Insect Conserva- tion, 14, 439–458. |
| [32] | Platnick NI (2012) The World Spider Catalog, version 13.0. Museum of Natural History. . |
| [33] | Pullin AS (translated by Jia JB (贾竞波)) (2001) Conservation Biology. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [34] | Pyne SJ, Andrews PL, Laven RD (1996) Introduction to Wildland Fire. John Wiley and Sons. New York. |
| [35] | Qin L (覃林) (2009) Statistical Ecology (统计生态学). China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [36] | Qiu D (邱丹), Yang CM (杨春梅) (2005) A preliminary study on the spider’s community in rapefield in Xining. Plant Protection(植物保护), 31, 52–55. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [37] | Ricklefs RE (2001) The Economy of Nature, 5th edn. WH Freeman, New York. |
| [38] | Root RB (1973) Organization of a plant–arthropod association in simple and diverse habitats: the fauna of collards (Brassica oleracea). Ecological Monographs, 50, 81–105. |
| [39] | Russell-Smith A (2002) A comparison of the diversity and composition of ground-active spiders in Mkomazi Game Reserve, Tanzania and Etosha National Park, Namibia. Journal of Arachnology, 30, 383–388. |
| [40] | Rypstra AL (1983) The importance of food and space in limiting web-spider densities: a test using field enclosures. Oecologia, 59, 312–316. |
| [41] | Solow AR (1993) A simple test for change in community structure. Journal of Animal Ecology, 62, 191–193. |
| [42] | Song DX (宋大祥), Zhu MS (朱明生), Chen J (陈军) (2001) The Fauna of Hebei, China (Araneae) (河北动物志: 蜘蛛类). Hebei Science and Technology Publishing House, Shijiazhuang. (in Chinese) |
| [43] | Sudhikumar AV, Mathew MJ, Sunish E, Sebastian PA (2005) Seasonal variation in spider abundance in Kuttanad rice agroecosystem, Kerala, India (Araneae). European Arachnology(Suppl. 1), 181–190. |
| [44] | Sun M (孙明) (2008) Cangshan Annals (苍山志). The Nation- alities Publishing House of Yunnan, Kunming. (in Chinese) |
| [45] | Turnbull AL (1973) Ecology of the true spiders (Arane- omorphae). Annual Review of Entomology, 18, 305–348. |
| [46] | Uetz GW (1975) Temporal and spatial variation in species diversity of wandering spiders (Araneae) in deciduous forest litter. Environmental Entomology, 4, 719–724. |
| [47] | Uetz GW (1991) Habitat Structure: the Physical Arrangement of Objects in Space. Chapman and Hall, London. |
| [48] | Uetz GW (1992) Foraging strategies of spiders. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 7, 155–159. |
| [49] | Uetz GW, Unzicker JD (1976) Pitfall trapping in ecological studies of wandering spiders. Journal of Arachnology, 3, 101–111. |
| [50] | Wagner JD, Toft S, Wise DH (2003) Spatial stratification in litter depth by forest-floor spider. The Journal of Arachnology, 31, 28–39. |
| [51] | Yang C (杨持) (2008) Ecology (生态学). Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [52] | Yang WQ (杨万勤), Zhang J (张健), Hu TX (胡庭兴), Sun H (孙辉) (2006) Forest Soil Ecology (森林土壤生态学). Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [53] | Yang ZZ (杨自忠), Feng JM (冯建孟), Ma YY (马艳滟), Feng P (冯萍), Zhang YG (张耀光) (2012) Quantitative analysis of spider community and diversity after fire in Cangshan Mountain. Acta Arachnologica Sinica(蛛形学报), 21, 122–128. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [54] | Yu GH (喻国辉), Chen J (陈建) (2001) Sampling using pitfall traps in ecological research on spider. Acta Arachnologica Sinica(蛛形学报), 10, 52–56. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [55] | Zhang F (张锋), Zhu LM (朱立敏) (2008) Community structure and diversity of spider in Zhangshiyan scenic area of Hebei Province, China. Chinese Journal of Ecology(生态学杂志), 27, 1937–1940. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [56] | Zhang ZS (张志升), Wei G (魏国), Liu ZH (刘钟华), Zhang YF (张玉富), Zhang YG (张耀光) (2010) Study on the diversity of the spider community of the Changning National Nature Reserve for the Bamboo Forest Sea of Sichuan, China. Sichuan Journal of Zoology(四川动物), 29, 492–495. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [2] | 何泽嵘, 叶鹏, 王舒婷, 关永鑫, 闫淑君, 洪心茹. 中国城市草坪的杂草优势种组成及空间分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24133-. |
| [3] | 李雪萌, 蒋际宝, 张曾鲁, 刘晓静, 王亚利, 吴宜钊, 李银生, 邱江平, 赵琦. 宝天曼国家级自然保护区蚯蚓物种多样性及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23352-. |
| [4] | 王启蕃, 刘小慧, 朱紫薇, 刘磊, 王鑫雪, 汲旭阳, 周绍春, 张子栋, 董红雨, 张明海. 黑龙江北极村国家级自然保护区鸟类与兽类多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 24024-. |
| [5] | 所翟, 俞渃茜, 李媛辉, 徐基良. 基于实证分析中国自然保护区地方立法问题检视和优化路径[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23287-. |
| [6] | 刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇. 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [7] | 黄小龙, 蒙秉顺, 李海波, 冉伟, 杨伟, 王丞, 谢波, 张旭, 冉景丞, 张明明. 基于红外相机的黔金丝猴及其同域分布物种种间关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23402-. |
| [8] | 姚嘉, 张聪伶, 李时轩, 林阳, 王震, 张煜涵, 周伟龙, 潘心禾, 朱珊, 吴逸卿, 王丹, 刘金亮, 谭珊珊, 沈国春, 于明坚. 百山祖连续海拔样带植物群落特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24052-. |
| [9] | 杨向林, 赵彩云, 李俊生, 种方方, 李文金. 植物入侵导致群落谱系结构更加聚集: 以广西国家级自然保护区草本植物为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24175-. |
| [10] | 毛锐锐, 沈拓, 李慧, 田琳楚, 谭海蓉, 卢李荣, 吴小刚, 范宗骥, 伍国仪, 李杰, 吴勇, 朱弼成, 肖治术. 广东车八岭国家级自然保护区无尾两栖类动物鸣声特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24356-. |
| [11] | 崔国发. 关于自然保护地整合优化工作中几个关键问题的讨论与建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 22447-. |
| [12] | 邢超, 林依, 周智强, 赵联军, 蒋仕伟, 林蓁蓁, 徐基良, 詹祥江. 基于DNA条形码技术构建王朗国家级自然保护区陆生脊椎动物遗传资源数据库及物种鉴定[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22661-. |
| [13] | 陈本平, 陈建武, 凌征文, 杨旭, 陈鑫, 李生强, 杨彪. 四川老君山国家级自然保护区林下鸟兽多样性及动态变化数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22566-. |
| [14] | 陈哲涵, 尹进, 叶吉, 刘冬伟, 毛子昆, 房帅, 蔺菲, 王绪高. 增温对东北温带次生林草本群落季节动态的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 23059-. |
| [15] | 姚雪, 陈星, 戴尊, 宋坤, 邢诗晨, 曹宏彧, 邹璐, 王健. 采集策略对叶附生苔类植物发现概率及物种多样性的重要性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22685-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn