



生物多样性 ›› 2013, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (3): 269-277. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.09008 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2013.09008
所属专题: 生物多样性与生态系统功能
童跃伟1,3, 项文化1,2,*( ), 王正文3,*(
), 王正文3,*( ), Walter Durka4, Markus Fischer5
), Walter Durka4, Markus Fischer5
收稿日期:2013-01-07
接受日期:2013-04-11
出版日期:2013-05-20
发布日期:2013-06-05
通讯作者:
项文化,王正文
基金资助:
Yuewei Tong1,3, Wenhua Xiang1,2,*( ), Zhengwen Wang3,*(
), Zhengwen Wang3,*( ), Walter Durka4, Markus Fischer5
), Walter Durka4, Markus Fischer5
Received:2013-01-07
Accepted:2013-04-11
Online:2013-05-20
Published:2013-06-05
Contact:
Xiang Wenhua,Wang Zhengwen
摘要:
在山地森林中, 树木生长不仅受地形的影响, 也与邻株植物存在各种相互作用, 而且具有个体大小依赖性。然而这些影响都具有物种特异性, 即不同物种即使在同类地形或与同种植物相邻也会受到不同乃至相反的影响。此外, 不同物种个体生长的自身大小依赖性也存在差异。作者利用中欧合作项目“中国亚热带森林生物多样性与生态系统功能实验研究(BEF)”实验样地, 以渐危的常绿阔叶木本植物红楠(Machilus thunbergii)为研究对象, 连续两年观测了存活的1,452株红楠幼树基径和树高, 分析坡向和坡度等地形、邻株植物丰富度及其功能群组成、红楠自身大小对红楠幼树生长和存活率的影响。结果表明: (1)红楠幼树位于阴坡时比位于阳坡具有更高的生长速率和存活率, 而坡度只对树高生长量有显著影响; (2)邻株植物物种丰富度对红楠幼树的基径、树高和存活率影响不显著; (3)邻株植物功能类型对红楠幼树生长具有极显著的影响, 影响程度大小依次为落叶阔叶型>落叶阔叶与常绿阔叶的混交型>常绿阔叶型>常绿针叶型, 而对存活率无显著影响; (4)红楠幼树的生长与自身大小呈正相关幂函数关系, 即基径和树高的生长速率都会随着其自身大小的增加而增加。可见, 构建树木生长模型, 不仅要考虑地形等环境因子差异, 而且要充分考虑邻株植物的功能类群差异、邻株植物相互作用的性质和程度, 以及自身个体大小等因素, 为渐危和濒危树种的保护提供更为可靠的理论依据。
童跃伟, 项文化, 王正文, Walter Durka, Markus Fischer (2013) 地形、邻株植物及自身大小对红楠幼树生长与存活的影响. 生物多样性, 21, 269-277. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.09008.
Yuewei Tong,Wenhua Xiang,Zhengwen Wang,Walter Durka,Markus Fischer (2013) Effects of topography, neighboring plants and size-dependence of Machillus thunbergii on sapling growth and survivorship. Biodiversity Science, 21, 269-277. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.09008.
图1 中国亚热带森林生物多样性与生态系统功能实验研究B样地单个样方内的16棵红楠幼树和400株邻株植物幼苗分布图。空心圆点代表400株幼苗, 实心三角形代表16株红楠。
Fig. 1 Planting scheme in a single plot of the study site. Open circles represent 400 tree seedlings, solid triangles represent 16 Machilus thunbergii saplings.
| 序号 Number | 物种 Species | 功能类型 Functional group |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 马尾松 Pinus massoniana | 常绿针叶型 EN |
| 2 | 杉木 Cunninghamia lanceolata | 常绿针叶型 EN |
| 3 | 华东楠 Machilus leptophylla | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 4 | 红楠 Machilus thunbergii | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 5 | 黄绒润楠 Machilus grijsii | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 6 | 苦槠 Castanopsis sclerophylla | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 7 | 闽楠 Phoebe bournei | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 8 | 青冈 Cyclobalanopsis glauca | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 9 | 乳源木莲 Manglietia yuyuanensis | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 10 | 石栎 Lithocarpus glaber | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 11 | 薯豆 Elaeocarpus japonicus | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 12 | 丝栗栲 Castanopsis fargesii | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 13 | 甜槠 Castanopsis eyrei | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 14 | 秃瓣杜英 Elaeocarpus glabripetalus | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 15 | 乌冈栎 Quercus phillyraeoides | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 16 | 香樟 Cinnamomum camphora | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 17 | 中华杜英 Elaeocarpus chinensis | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 18 | 臭椿 Ailanthus altissima | 落叶阔叶型 DB |
| 19 | 垂枝泡花树 Meliosma flexuosa | 落叶阔叶型 DB |
| 20 | 光皮桦 Betula luminifera | 落叶阔叶型 DB |
| 21 | 黄果朴 Celtis biondi | 落叶阔叶型 DB |
| 22 | 拟赤杨 Alniphyllum fortunei | 落叶阔叶型 DB |
| 23 | 山桐子 Idesia polycarpa | 落叶阔叶型 DB |
| 24 | 浙江柿 Diospyros glaucifolia | 落叶阔叶型 DB |
表1 红楠24种邻株植物的物种名称及其功能类型
Table 1 The 24 neighboring plant species of Machilus thunbergii and their functional groups
| 序号 Number | 物种 Species | 功能类型 Functional group |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 马尾松 Pinus massoniana | 常绿针叶型 EN |
| 2 | 杉木 Cunninghamia lanceolata | 常绿针叶型 EN |
| 3 | 华东楠 Machilus leptophylla | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 4 | 红楠 Machilus thunbergii | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 5 | 黄绒润楠 Machilus grijsii | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 6 | 苦槠 Castanopsis sclerophylla | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 7 | 闽楠 Phoebe bournei | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 8 | 青冈 Cyclobalanopsis glauca | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 9 | 乳源木莲 Manglietia yuyuanensis | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 10 | 石栎 Lithocarpus glaber | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 11 | 薯豆 Elaeocarpus japonicus | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 12 | 丝栗栲 Castanopsis fargesii | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 13 | 甜槠 Castanopsis eyrei | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 14 | 秃瓣杜英 Elaeocarpus glabripetalus | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 15 | 乌冈栎 Quercus phillyraeoides | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 16 | 香樟 Cinnamomum camphora | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 17 | 中华杜英 Elaeocarpus chinensis | 常绿阔叶型 EB |
| 18 | 臭椿 Ailanthus altissima | 落叶阔叶型 DB |
| 19 | 垂枝泡花树 Meliosma flexuosa | 落叶阔叶型 DB |
| 20 | 光皮桦 Betula luminifera | 落叶阔叶型 DB |
| 21 | 黄果朴 Celtis biondi | 落叶阔叶型 DB |
| 22 | 拟赤杨 Alniphyllum fortunei | 落叶阔叶型 DB |
| 23 | 山桐子 Idesia polycarpa | 落叶阔叶型 DB |
| 24 | 浙江柿 Diospyros glaucifolia | 落叶阔叶型 DB |
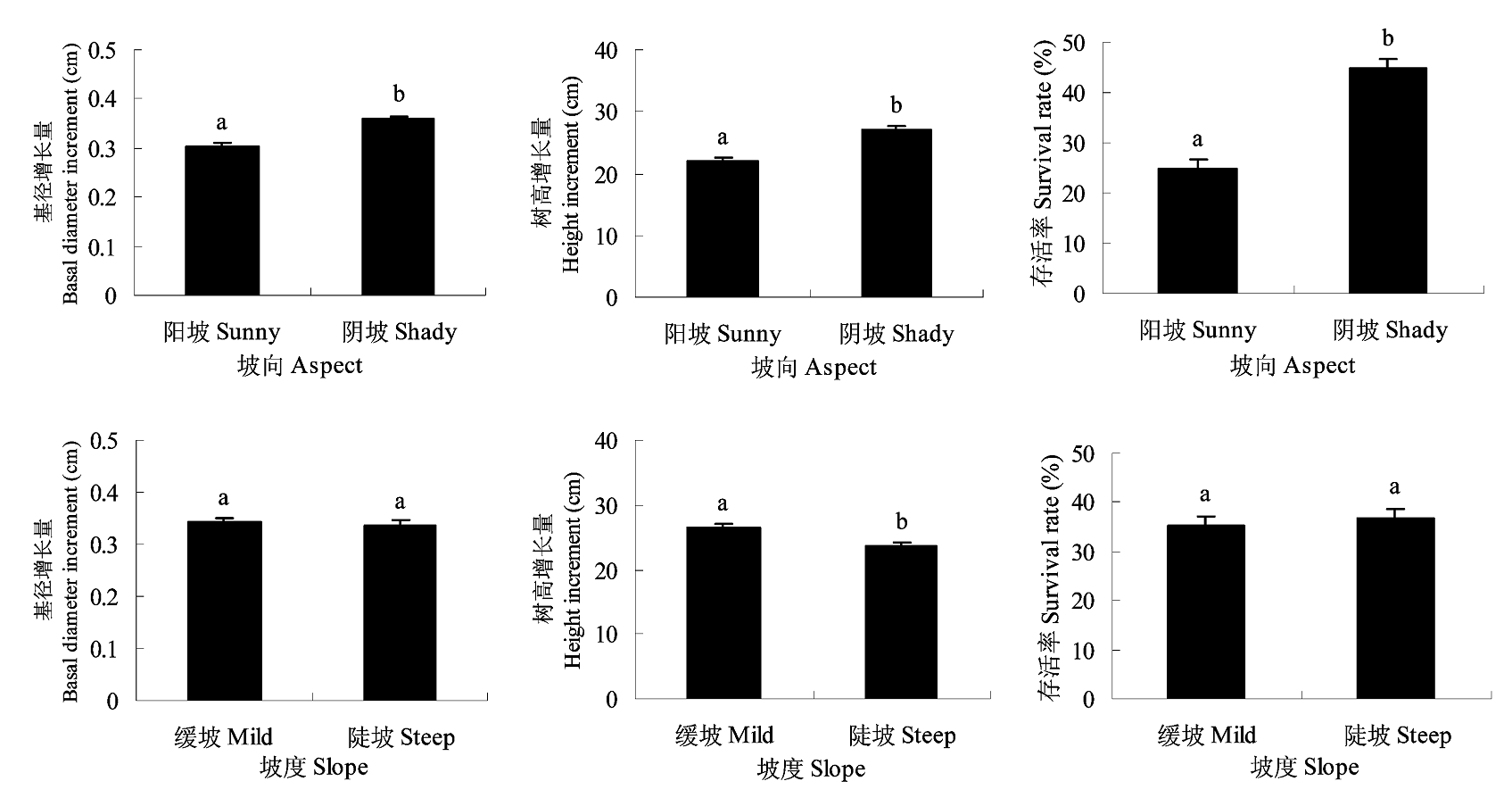
图2 不同坡向和坡度下红楠幼树基径和树高增长量以及存活率的差异(平均值±标准误差)。 不同字母标记的值(a和b)具有显著差异。
Fig. 2 Effects of slope aspect and slope steepness on basal diameter increment, height increment and survival rate of Machilus thunbergii saplings (mean ± SE). Different letters (a and b) represent the significant value.
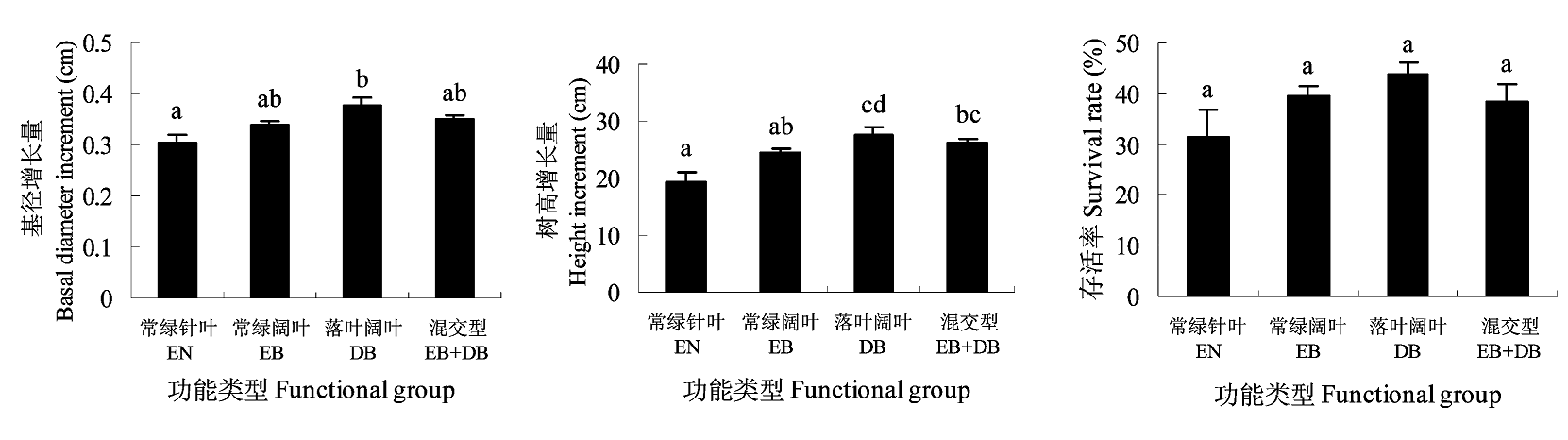
图3 不同邻株植物功能类型下红楠基径和树高增长量及存活率的状况(平均值±标准误差)。不同字母标记的值(a, b, c和d)具有显著差异。
Fig. 3 Basal diameter increment, height increment and survival rate of Machilus thunbergii saplings under different neighbouring plant species functional group (mean ± SE). Different letters (a, b, c and d) represent the significant value. EN = evergreen needle; EB = evergreen broadleaf; DB = deciduous broadleaf.
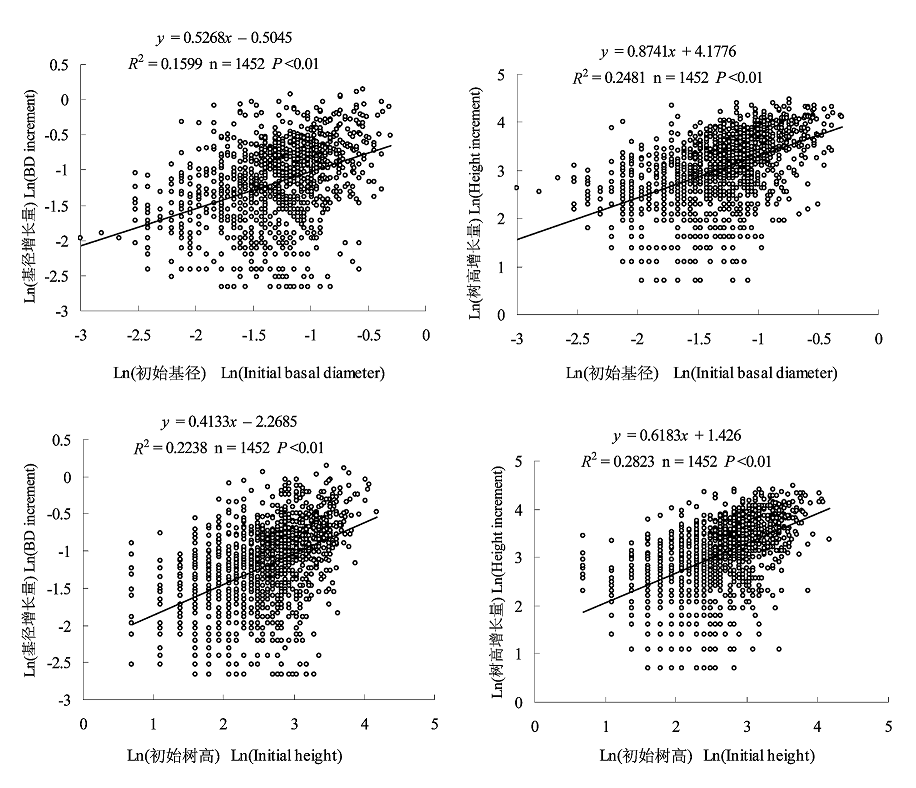
图4 基径和树高增长量的对数与初始基径和树高的对数之间的线性关系
Fig. 4 The linear relationship between the Ln(Basal diameter (BD) increment), Ln(Height increment) and the Ln(Initial basal diameter) and Ln(Initial height) of Machilus thunbergii saplings
| 1 | Bellingham PJ, Tanner EVJ (2000) The influence of topography on tree growth, mortality, and recruitment in a tropical montane forest.Biotropica, 32, 378-384. |
| 2 | Berntson GM, Wayne PM (2000) Characterizing the size dependence of resource acquisition within crowded plant populations.Ecology, 81, 1072-1085. |
| 3 | Bin Y, Lin GJ, Li BH, Wu LF, Shen Y, Ye WH (2012) Seedling recruitment patterns in a 20-ha subtropical forest plot: hints for niche-based processes and negative density dependence.European Journal of Forest Research, 131, 453-463. |
| 4 | Brown JH, Gillooly JF, Allen AP, Savage VM, West GB (2004) Toward a metabolic theory of ecology.Ecology, 85, 1771-1789. |
| 5 | Bruelheide H, Bohnke M, Both S, Fang T, Assmann T, Baruffol M, Bauhus J, Buscot F, Chen XY, Ding BY, Durka W, Erfmeier A, Fischer M, Geissler C, Guo DL, Guo LD, Hardtle W, He JS, Hector A, Krober W, Kuhn P, Lang AC, Nadrowski K, Pei KQ, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Shi XZ, Scholten T, Schuldt A, Trogisch S, von Oheimb G, Welk E, Wirth C, Wu YT, Yang XF, Zeng XQ, Zhang SR, Zhou HZ, Ma KP, Schmid B (2011) Community assembly during secondary forest succession in a Chinese subtropical forest.Ecological Monographs, 81, 25-41. |
| 6 | Callaway RM, Walker LR (1997) Competition and facilition: a synthetic approach to interactions in plant communities.Ecology, 78, 1958-1965. |
| 7 | Choler P, Michalet R, Callaway RM (2001) Facilitation and competition on gradients in alpine plant communities.Ecology, 82, 3295-3308. |
| 8 | Coomes DA, Allen RB (2007) Effects of size, competition and altitude on tree growth.Journal of Ecology, 95, 1084-1097. |
| 9 | Cornelissen JHC, Diez PC, Hunt R (1996) Sapling growth, allocation and leaf attributes in a wide range of woody plant species and types.Journal of Ecology, 84, 755-765. |
| 10 | Ding J (丁佳),Wu Q (吴茜), Yan H (闫慧), Zhang SR (张守仁) (2011) Effects of topographic variations and soil characteristics on plant functional traits in a subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest. Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 19, 158-167. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 11 | Dordel J, Seely B, Simard SW (2011) Relationships between simulated water stress and mortality and growth rates in underplanted Toona ciliate Roem. in subtropical Argentinean plantations.Ecological Modelling, 222, 3226-3235. |
| 12 | Fekedulegn D, Hicks RR Jr, Colbert JJ (2002) Influence of topographic aspect, precipitation and drought on radial growth of four major tree species in an Appalachian watershed. Forest Ecology and Management, 6094, 1-17. |
| 13 | Gale N (2000) The relationship between canopy gaps and topography in a western Ecuadorian rain forest.Biotropica, 32, 653-661. |
| 14 | Herwitz SR, Young SS (1994) Mortality, recruitment, and growth rates of montane tropical rain forest canopy trees on mount Bellenden-Ker, northeast Queensland, Australia.Biotropica, 26, 350-361. |
| 15 | Jiang XM (江香梅) (2001) An introduction to the research progress on Machilus thunbergii.Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis(江西农业大学学报), 23, 231-235. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 16 | Kariuki M, Rolfe M, Smith RGB, Vanclay JK, Kooyman RM (2006) Diameter growth performance varies with species functional-group and habitat characteristics in subtropical rainforests.Forest Ecology and Management, 225, 1-14. |
| 17 | Koorem K, Price JN, Moora M (2011) Species-specific effects of woody litter on sapling emergence and growth of herbaceous plants.PLoS ONE, 6, e26505. |
| 18 | Lai JS, Mi XC, Ren HB, Ma KP (2009) Species-habitat associations change in a subtropical forest of China.Journal of Vegetation Science, 20, 415-423. |
| 19 | Massey FP, Massey K, Press MC, Hartley SE (2006) Neighbourhood composition determines growth, architecture and herbivory in tropical rain forest tree saplings. Journal of Ecology, 94, 646-655. |
| 20 | Miriti MN, Wright SJ, Howe HF (2001) The effects of neighbors on the demography of a dominant desert shrub (Ambrosia dumosa).Ecological Monographs, 71, 491-509. |
| 21 | Mukhtar E, Koike F (2009) Juvenile height growth rate of seven major tree species in a tropical rain forest of west Sumatra. Tropics, 18, 1-6. |
| 22 | Olivero AM, Hix DM (1998) Influence of aspect and stand age on ground flora of southeastern Ohio forest ecosystems.Plant Ecology, 139, 177-187. |
| 23 | Ou YD (区余端), Su ZY (苏志尧), Li ZK (李镇魁), Lin YH (林义辉) (2011) Effects of topographic factors on the distribution patterns of ground plants with different growth forms in montane forests in North Guangdong, China.Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology(应用生态学报), 22, 1107-1113. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 24 | Potvin C, Gotelli NJ (2008) Biodiversity enhances individual performance but does not affect survivorship in tropical trees. Ecology Letters, 11, 217-223. |
| 25 | Riyou T, Hino T, Naoki A, Takakazu Y (2006) Variation in tree growth, mortality and recruitment among topographic positions in a warm temperate forest.Journal of Vegetation Science, 17, 281-290. |
| 26 | Sariyildiz T, Anderson JM, Kucuk M (2005) Effects of tree species and topography on soil chemistry, litter quality, and decomposition in Northeast Turkey.Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 37, 1695-1706. |
| 27 | Schmitt J, Eccleston J, Ehrhardt DW (1987) Dominance and suppression, size-dependent growth and self-thinning in a natural Impatiens capensis population.Journal of Ecology, 75, 651-665. |
| 28 | Soliz-Gamboa CC, Sandbrink A, Zuidema PA (2012) Diameter growth of juvenile trees after gap formation in a Bolivian rain forest: responses are strongly species-specific and size-dependent.Biotropica, 44, 312-320. |
| 29 | Tilman D (1996) Biodiversity: population versus ecosystem stability.Ecology, 77, 350-363. |
| 30 | Wang M (王梅), Zhang WH (张文辉) (2009) Growth and species diversity of Pinus tabulaeformis artificial forest on different slope aspects.Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica(西北植物学报), 29, 1678-1683. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 31 | Wu Q (吴茜), Ding J (丁佳), Yan H (闫慧), Zhang SR (张守仁), Fang T (方腾), Ma KP (马克平) (2011) Effects of simulated precipitation and nitrogen addition on seedling growth and biomass in five tree species in Gutian Mountain, Zhejiang Province, China.Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology(植物生态学报), 35, 256-267. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 32 | Wu ZY, Raven PH, Hong DY (2008) Flora of China, Vol. 7 (Menispermaceae through Capparaceae). Science Press and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Beijing and St. Louis. |
| 33 | Xiao SG (肖宋高), Zhang ZW (张卓文), Liu Q (刘琪) (2009) Effect of site conditions on the growth of Cotinus coggygria in Yiling district of Yichang municipality.Journal of Southwest Forestry University(西南林学院学报), 29, 31-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 34 | Yan XF (闫兴富), Cao M (曹敏) (2007) Impacts of environmental factors on growth and survival of Dipterocarpaceae seedlings: recent advances.Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany(热带亚热带植物学报), 15, 86-92. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 35 | Zhang CY (张春雨), Gao LS (高露双), Zhao YZ (赵亚洲), Jia YZ (贾玉珍), Li JX (李金鑫), Zhao XH (赵秀海) (2009) Response of radial growth to neighboring competition and climate factors inTaxus cuspidata. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology(植物生态学报), 33, 1177-1183. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 36 | Zhang ZP (张泽浦), Fang JY (方精云), Kan M (菅诚) (2000) Effects of competition on growth rate and probability of death of plant individuals: a study based on nursery experiments of Larix leptolepis populations.Acta Phytoecologica Sinica(植物生态学报), 24, 340-345. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 37 | Zhao YZ (赵亚洲), Gao LS (高露双), Zhang CY (张春雨), Ma QY (马钦彦) (2010) Factors affecting radial growth of female and male Pistacia chinensis trees.Chinese Journal of Ecology(生态学杂志), 29, 1937-1943. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 贾贞妮, 张意岑, 杜彦君, 任海保. 干扰对中亚热带森林群落物种多样性演替动态的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24078-. |
| [2] | 孟敬慈, 王国栋, 曹光兰, 胡楠林, 赵美玲, 赵延彤, 薛振山, 刘波, 朴文华, 姜明. 中国芦苇沼泽植物物种丰富度分布格局及其驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23194-. |
| [3] | 施国杉, 刘峰, 曹光宏, 陈典, 夏尚文, 邓云, 王彬, 杨效东, 林露湘. 西双版纳热带季节雨林木本植物的beta多样性: 空间、环境与林分结构的作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24285-. |
| [4] | 陈明苗, 张楚然, 邓云, 李生发, 李逢昌, 唐志忠, 魏兆喆, 张彩彩, 林露湘. 地形因子对亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林木本植物萌生特征的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24282-. |
| [5] | 熊松, 淦江, 谢彦军, 邓晰朝, 覃国乐, 彭晚霞, 曾馥平, 占志立, 谭卫宁, 黄国勤, 杜虎. 喀斯特常绿落叶阔叶林凋落物产量动态及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24248-. |
| [6] | 王丽媛, 胡慧建, 姜杰, 胡一鸣. 南岭哺乳类和鸟类物种丰富度空间分布格局及其影响因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23026-. |
| [7] | 刘志发, 王新财, 龚粤宁, 陈道剑, 张强. 基于红外相机监测的广东南岭国家级自然保护区鸟兽多样性及其垂直分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 22689-. |
| [8] | 邓婷婷, 魏岩, 任思远, 祝燕. 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林地形和林分结构对林下草本植物物种多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22671-. |
| [9] | 陈声文, 任海保, 童光蓉, 王宁宁, 蓝文超, 薛建华, 米湘成. 钱江源国家公园木本植物物种多样性空间分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22587-. |
| [10] | 谢艳秋, 黄晖, 王春晓, 何雅琴, 江怡萱, 刘子琳, 邓传远, 郑郁善. 福建海岛滨海特有植物种-面积关系及物种丰富度决定因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22345-. |
| [11] | 杨科, 丁城志, 陈小勇, 丁刘勇, 黄敏睿, 陈晋南, 陶捐. 怒江流域鱼类多样性及空间分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21334-. |
| [12] | 田璐嘉, 杨小波, 李东海, 李龙, 陈琳, 梁彩群, 张培春, 李晨笛. 海口和三亚两城市破碎化林地中鸟类群落多样性与嵌套分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 21424-. |
| [13] | 王爱霞, 马婧婧, 龚会蝶, 范国安, 王茂, 赵红梅, 程军回. 北疆一年生早春短命植物物种丰富度分布格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(6): 735-745. |
| [14] | 郑进凤, 唐蓉, 贺霜, 陈月红, 伍素, 张凯, 徐雨, 邹晓. 贵州花溪大学城破碎化林地鸟类多样性与嵌套分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 661-667. |
| [15] | 黄小波, 郎学东, 李帅锋, 刘万德, 苏建荣. 生态系统多功能性的指标选择与驱动因子: 研究现状与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1673-1686. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn