



生物多样性 ›› 2013, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (6): 750-757. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.08138 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2013.08138
所属专题: 粮食安全
于燕波1, 王群亮4, ShelaghKell2, NigelMaxted2, Brian V. Ford-Lloyd2, 魏伟3,*( ), 康定明1,*(
), 康定明1,*( ), 马克平3
), 马克平3
收稿日期:2013-06-13
接受日期:2013-09-01
出版日期:2013-11-20
发布日期:2013-12-02
通讯作者:
魏伟,康定明
基金资助:
Yanbo Yu1, Qunliang Wang4, Shelagh Kell2, Nigel Maxted2, Brian V. Ford-Lloyd2, Wei Wei3,*( ), Dingming Kang1,*(
), Dingming Kang1,*( ), Keping Ma3
), Keping Ma3
Received:2013-06-13
Accepted:2013-09-01
Online:2013-11-20
Published:2013-12-02
Contact:
Wei Wei,Kang Dingming
摘要:
栽培植物野生近缘种资源是植物遗传资源的重要组成部分, 拥有独特的生物学特性, 在应对气候变化和保证粮食安全方面具有极大潜力和价值。根据我们的初步调查, 我国拥有24,000多种栽培植物野生近缘种, 其中大多数能够为栽培植物的品种改良提供支持。迁地保护(如种质库)能够收集和保存丰富的遗传资源, 但却无法替代能够包含自然进化信息的原生境保护。我国已经建立了169个栽培植物野生近缘种原生境保护区(点), 迫切需要制定国家栽培植物野生近缘种保护策略和行动计划, 鉴别国家和地区水平上需要优先保护的物种, 以及采取步骤, 整合迁地和原生境保护方法, 达到保护这些优先物种的目的。本文总结了我国栽培植物野生近缘种及其保护所取得的进展, 介绍了国内外在植物遗传资源保护利用方面的成功经验, 并提出了我国栽培植物野生近缘种的保护策略: 建议首先开展栽培植物野生近缘种资源编目工作, 并结合国家和地区的环境与资源状况的国际标准, 确定优先保护种类; 针对不同种类, 采取迁地保护和原生境保护相结合的方法保护栽培植物野生近缘种资源。
于燕波, 王群亮, ShelaghKell, NigelMaxted, Brian V. Ford-Lloyd, 魏伟, 康定明, 马克平 (2013) 中国栽培植物野生近缘种及其保护对策. 生物多样性, 21, 750-757. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.08138.
Yanbo Yu,Qunliang Wang,Shelagh Kell,Nigel Maxted,Brian V. Ford-Lloyd,Wei Wei,Dingming Kang,Keping Ma (2013) Crop wild relatives and their conservation strategies in China. Biodiversity Science, 21, 750-757. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2013.08138.
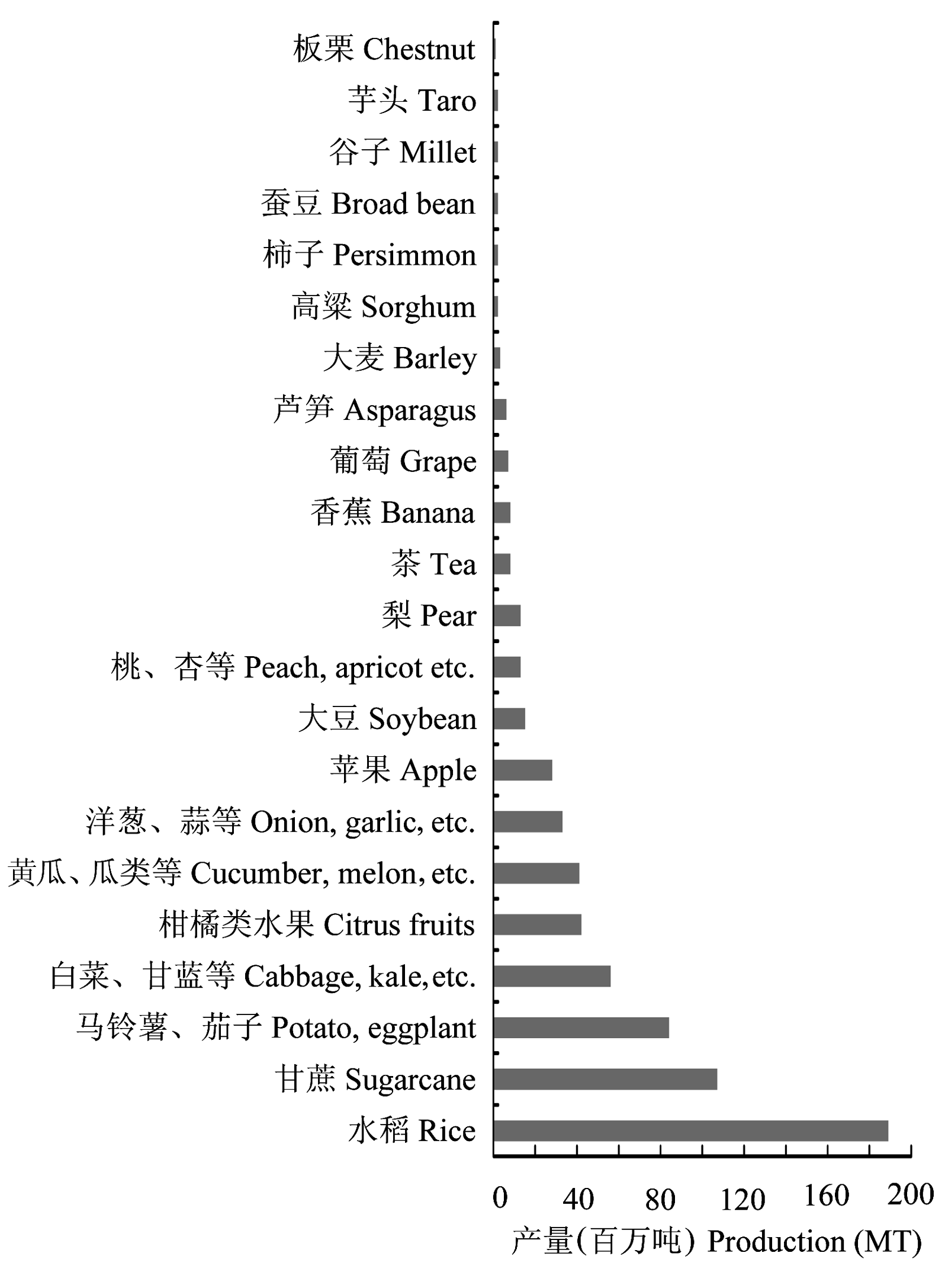
图1 2005-2009年中国平均年产大于100万吨的栽培植物, 其野生近缘种原产于中国, 并可用于品种改良(FAO, 2010)。
Fig. 1 Crops of which China produced an average of >1MT in five years between 2005 and 2009 that have CWR native to China which may be important for crop improvement (FAO, 2010)
| 且 目录 Category | 物种数量 Number of species |
|---|---|
| 植物物种总数 Total number of plant species | 35,342 |
| 栽培植物野生近缘种 Crop wild relatives | 24,538 |
| 粮食栽培植物野生近缘种 Wild relatives of food crops | 1,229 |
| 高经济价值栽培植物的野生近缘种 Wild relatives of crops of high economic importance | 629 |
| 某省特有的粮食栽培植物野生近缘种 Wild relatives of food crops endemic to only one province | 485 |
表1 中国栽培植物野生近缘种物种数统计
Table 1 The statistical summary of crop wild relatives (CWR) in China
| 且 目录 Category | 物种数量 Number of species |
|---|---|
| 植物物种总数 Total number of plant species | 35,342 |
| 栽培植物野生近缘种 Crop wild relatives | 24,538 |
| 粮食栽培植物野生近缘种 Wild relatives of food crops | 1,229 |
| 高经济价值栽培植物的野生近缘种 Wild relatives of crops of high economic importance | 629 |
| 某省特有的粮食栽培植物野生近缘种 Wild relatives of food crops endemic to only one province | 485 |
| 1 | Barazani O, Perevolotsky A, Hadas R (2008) A problem of the rich: prioritizing local plant genetic resources for ex situ conservation in Israel.Biological Conservation, 141, 596-600. |
| 2 | Cook FEM (1995) Economic botany data collection standard. In: Prepared for the International Working Group on Taxonomic Databases for Plant Sciences (TDWG). Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. |
| 3 | Dong YC (董玉琛), Liu X (刘旭) (2005) Crops and Their Wild Relatives in China (中国作物及其野生近缘种植物). China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 4 | Farnsworth E, Klionsky S, Brumback W, Havens K (2006) A set of simple decision matrices for prioritizing collection of rare plant species for ex situ conservation.Biological Conservation, 128, 1-12. |
| 5 | FAO (2010) FAOSTAT. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome, Italy. |
| 6 | Ford-Lloyd BV, Schmidt M, Armstrong SJ, Barazani O, Engels J, Hadas R, Hammer K, Kell S, Kang DM, Khoshbakht K, Li YH, Long CL, Lu BR, Ma KP, Nguyen Viet T, Qiu LJ, Ge S, Wei W, Zhang ZW, Maxted N (2011) Crop wild relatives―undervalued, underutilized and under threat? BioScience, 61, 559-565. |
| 7 | Gepts P (2006) Plant genetic resources conservation and utilization: the accomplishments and future of a societal insurance policy.Crop Science, 46, 2278-2292. |
| 8 | Harley CDG (2011) Climate change, keystone predation, and biodiversity loss.Science, 334, 1124-1127. |
| 9 | Hou XY (侯向阳), Gao WD (高卫东) (1999) Conservation and utilization of wild relatives of crops.Chinese Biodiversity(生物多样性), 7, 327-331. (in Chinese with English absract) |
| 10 | IPCC (2007) Fourth Assessment Report Climate Change 2007: Synthesis Report. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), Geneva, Switzerland. |
| 11 | IUCN (2001) IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria: Version 3.1. IUCN Species Survival Commission, IUCN, Gland, Switzerland and Cambridge, UK. |
| 12 | Jarvis A, Lane A, Hijmans RJ (2008) The effect of climate change on crop wild relatives. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 126, 13-23. |
| 13 | Kell SP, Knüpffer H, Jury SL, Ford-Lloyd BV, Maxted N (2008) Crops and wild relatives of the Euro-Mediterranean region: making and using a conservation catalogue. In: Crop Wild Relative Conservation and Use (eds Maxted N, Ford-Lloyd BV, Kell SP, Iriondo J, Dulloo E, Turok J), pp. 69-109. CAB International, Wallingford, UK. |
| 14 | Liu X (刘旭), Zheng DS (郑殿升), Dong YC (董玉琛), Zhu DW (朱德蔚), Fang JH (方嘉禾), Fei YL (费砚良), Jia JX (贾敬贤), Jiang YQ (蒋尤泉), Yang QW (杨庆文), Wang SM (王述民), Li Y (黎裕), Cao YS (曹永生) (2008) Diversity assessment of crops and their wild relatives in China.Journal of Plant Genetic Resources(植物遗传资源学报), 9, 411-416. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 15 | Ladizinsky G (1998) Plant Evolution Under Domestication. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, the Netherlands. |
| 16 | Laikre L, Larsson LC, Palmé A, Charlier J, Josefsson M, Ryman N (2008) Potentials for monitoring gene level biodiversity: using Sweden as an example.Biodiversity and Conservation, 17, 893-910. |
| 17 | Lu QS (卢庆善), Zhu K (朱凯), Zhang ZP (张志鹏), Wang YQ (王艳秋), Duan YH (段有厚) (2006) Sorghum wild relatives and their useful value.Rain Fed Crops(杂粮作物), 26(5), 322-325. (in Chinese) |
| 18 | Ma KP (马克平) (2012) Studies and conservation of crop wild relatives should be promoted.Biodiversity Science(生物多样性), 20, 641-642. (in Chinese) |
| 19 | Maxted N, Ford-Lloyd BV, Hawkes JG (1997) Plant Genetic Conservation: the in situ Approach. Chapman & Hall, London. |
| 20 | Maxted N, Ford-Lloyd BV, Kell SP, Iriondo JM, Dulloo ME, Turok J (2008a) Crop Wild Relative Conservation and Use. CABI Press, Wallingford, UK. |
| 21 | Maxted N, Dulloo E, Ford-Lloyd BV, Iriondo J, Jarvis A (2008b) Genetic gap analysis: a tool for more effective genetic conservation assessment.Diversity and Distributions, 14, 1018-1030. |
| 22 | Maxted N (2009) Use it or lose it: improving the conservation/use link as a tool to sustain agrobiodiversity.Acta Horticulturae, 806, 549-561. |
| 23 | Maxted N, Kell S (2009) Establishment of a Global Network for the in situ Conservation of Crop Wild Relatives: Status and Needs. FAO Commission on Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture, Rome, Italy. |
| 24 | Maxted N, Kell S, Toledo A, Dulloo E, Heywood V, Hodgkin T, Hunter D, Guarino L, Jarvis A, Ford-Lloyd BV (2010) A global approach to crop wild relative conservation: securing the gene pool for food and agriculture.Kew Bulletin, 65, 561-576. |
| 25 | Maxted N, Kell S, Ford-Lloyd BV, Dulloob E, Toledo A (2012) Toward the systematic conservation of global crop wild relative diversity.Crop Science, 52, 774-785. |
| 26 | Meilleur BA, Hodgkin T (2004) In situ conservation of crop wild relatives: status and trends.Biodiversity and Conservation, 13, 663-684. |
| 27 | Perevolotsky A (2005) Integrating landscape ecology in the conservation of Mediterranean ecosystems: the Israeli experience.Israel Journal of Plant Sciences, 53, 203-213. |
| 28 | Primack RB (2008) A Primer of Conservation Biology, 4th edn. Sinauer Associates Inc., Sunderland, MA. |
| 29 | Scholten M, Maxted N, Kell SP, Ford-Lloyd BV (2008) Creation of a national crop wild relative strategy: a case study for the United Kingdom. In: Crop Wild Relative Conservation and Use (eds Maxted N, Ford-Lloyd BV, Kell SP, Iriondo J, Dulloo E, Turok J), pp. 120-142. CAB International, Wallingford, UK. |
| 30 | Tanksley SD, McCouch SR (1997) Seed banks and molecular maps: unlocking genetic potential from the wild.Science, 277, 1063-1066. |
| 31 | Thuiller T, Lavorel S, Araújo MB, Sykes MT, Prentice IC (2005) Climate change threats to plant diversity in Europe.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 102, 8245-8250. |
| 32 | Van Slageren M (2003) The millennium seed bank: building partnerships in arid regions for the conservation of wild species.Journal of Arid Environments, 54, 195-201. |
| 33 | Wang SM (王述民), Li LH (李立会), Li Y (黎裕), Lu XX (卢新雄), Yang QW (杨庆文), Cao YS (曹永生), Zhang ZW (张宗文), Gao WD (高卫东), Qiu LJ (邱丽娟), Wan JM (万建民), Liu X (刘旭) (2011) Report of plant genetic resources status of China food and agriculture.Journal of Plant Genetic Resources(植物遗传资源学报), 12, 1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 34 | Wei W (魏伟), Qiu LJ (邱丽娟), Zhang ZY (张增艳), Zhou HF (周海飞), Li YH (李英慧) (2008) Neglected and underutilized plant species: first recommendation list for China.Journal of Plant Genetic Resources(植物遗传资源学报), 9, 406-410. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 35 | Zheng DS (郑殿升) (2005) Use of cereal crop wild relatives in crop breeding in China.Journal of Plant Genetic Resources(植物遗传资源学报), 6, 354-358. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 36 | Zheng DS (郑殿升) (2006) General situation of wild relatives of food crop and their conservation in China.Chinese Wild Plant Resources(中国野生植物资源), 25(5), 5-7. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 顾婧婧, 刘宜卓, 苏杨. 基层地方政府在完成《昆蒙框架》中的作用和难点: 基于《联合国气候变化框架公约》任务的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24585-. |
| [2] | 赵富伟, 李颖硕, 陈慧. 新时期我国生物多样性法制建设思考[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 24027-. |
| [3] | 吴琪, 张晓青, 杨雨婷, 周艺博, 马毅, 许大明, 斯幸峰, 王健. 浙江钱江源-百山祖国家公园庆元片区叶附生苔多样性及其时空变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 24010-. |
| [4] | 曹可欣, 王敬雯, 郑国, 武鹏峰, 李英滨, 崔淑艳. 降水格局改变及氮沉降对北方典型草原土壤线虫多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23491-. |
| [5] | 张文斐, 江知禾. 育种产业化背景下生物遗传资源安全: 趋势研判、现实困境及实现机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24274-. |
| [6] | 贾韶琦, 张巨保. 生物遗传资源获取与惠益分享专门立法的重启必要与现实回应[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24383-. |
| [7] | 钟欣艺, 赵凡, 姚雪, 吴雨茹, 许银, 鱼舜尧, 林静芸, 郝建锋. 三星堆遗址城墙不同维护措施下草本植物物种多样性与土壤抗冲性的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23169-. |
| [8] | 冯莉. 国际法视野下生物多样性和气候变化的协同治理[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23110-. |
| [9] | 姚雪, 陈星, 戴尊, 宋坤, 邢诗晨, 曹宏彧, 邹璐, 王健. 采集策略对叶附生苔类植物发现概率及物种多样性的重要性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22685-. |
| [10] | 邵雯雯, 范国祯, 何知舟, 宋志平. 多地同质园实验揭示普通野生稻的表型可塑性与本地适应性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22311-. |
| [11] | 桑佳文, 宋创业, 贾宁霞, 贾元, 刘长成, 乔鲜果, 张琳, 袁伟影, 吴冬秀, 李凌浩, 郭柯. 青藏高原植被调查与制图评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22430-. |
| [12] | 王金洲, 徐靖. “基于自然的解决方案”应对生物多样性丧失和气候变化: 进展、挑战和建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22496-. |
| [13] | 李季蔓, 靳楠, 胥毛刚, 霍举颂, 陈小云, 胡锋, 刘满强. 不同干旱水平下蚯蚓对番茄抗旱能力的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21488-. |
| [14] | 朱瑞良, 马晓英, 曹畅, 曹子寅. 中国苔藓植物多样性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 22378-. |
| [15] | 祖奎玲, 王志恒. 山地物种海拔分布对气候变化响应的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21451-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn