



生物多样性 ›› 2012, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (4): 482-494. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.13056 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2012.13056
叶建飞1,3, 陈之端1, 刘冰2,3, 覃海宁1, 杨永1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2012-02-14
接受日期:2012-04-01
出版日期:2012-07-20
发布日期:2012-09-12
通讯作者:
杨永
作者简介:*E-mail: ephedra@ibcas.ac.cn基金资助:
Jianfei Ye1,3, Zhiduan Chen1, Bing Liu2,3, Haining Qin1, Yong Yang1,*( )
)
Received:2012-02-14
Accepted:2012-04-01
Online:2012-07-20
Published:2012-09-12
Contact:
Yong Yang
摘要:
植物的间断分布格局及其形成机制是植物地理学研究的重要问题之一。本文在对中国大陆与台湾名录整理比较的基础上, 对中国西南与台湾地区的植物间断分布格局及形成机制进行了分析。结果表明, 两地同种型间断分布的维管植物有198种(包括变种和亚种), 隶属于56科129属, 其中蕨类植物86种, 裸子植物3种, 双子叶植物56种, 单子叶植物53种; 两地异种型间断分布的维管植物有22属, 隶属于15科, 其中蕨类植物6属, 裸子植物1属, 双子叶植物7属, 单子叶植物兰科8属。间断分布类群以草本植物为主, 主要是蕨类和兰科植物。间断分布类群在台湾地区主要分布在中部到东北部, 在大陆的分布主要集中在川东-鄂西地区、川西-滇西北地区-藏东南地区和滇东南-桂西-黔西南地区。在垂直高度上, 海拔1,550-2,350 m是间断分布类群最集中分布的海拔范围。我们推测中国西南与台湾地区的间断分布类群有3种来源: 北半球温带、中国西南和热带亚洲来源。
叶建飞, 陈之端, 刘冰, 覃海宁, 杨永 (2012) 中国西南与台湾地区维管植物的间断分布格局及形成机制. 生物多样性, 20, 482-494. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.13056.
Jianfei Ye, Zhiduan Chen, Bing Liu, Haining Qin, Yong Yang (2012) Disjunct distribution of vascular plants between southwestern area and Taiwan area in China. Biodiversity Science, 20, 482-494. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.13056.
| 序号 No. | 属的分布区类型 Distributional patterns of genera | 属数 No. of genera |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 世界广布 Widespread | 9 |
| 热带属 Tropical | 43 | |
| 2 | 热带广布 Pantropic | 11 |
| 3 | 东亚及热带南美间断 Trop. & Subtr. E. Asia & (S.) Trop. Amer. disjuncted | 3 |
| 4 | 旧世界热带 Old World Tropics | 5 |
| 5 | 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲 Trop. Asia to Trop. Australasia Oceania | 10 |
| 6 | 热带亚洲至热带非洲 Trop. Asia to Trop. Africa | 3 |
| 7 | 热带亚洲 Trop. Asia | 11 |
| 温带属 Temperate | 46 | |
| 8 | 北温带 N. Temp. | 20 |
| 9 | 东亚及北美间断 E. Asia & N. Amer. disjuncted | 5 |
| 10 | 旧世界温带 Old World Temp. | 4 |
| 11 | 温带亚洲 Temp. Asia | - |
| 12 | 地中海区、西亚至中亚 Medit., W. to C. Asia | - |
| 13 | 中亚 C. Asia | - |
| 14 | 东亚 E. Asia | 14 |
| 15 | 中国特有 Endemic to China | 3 |
| 总计 Total | 98 |
表1 中国西南与台湾地区间断分布的种子植物属的分布区类型统计
Table 1 Disjunct distributional patterns of genera of seed plants between southwestern area and Taiwan area in China
| 序号 No. | 属的分布区类型 Distributional patterns of genera | 属数 No. of genera |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 世界广布 Widespread | 9 |
| 热带属 Tropical | 43 | |
| 2 | 热带广布 Pantropic | 11 |
| 3 | 东亚及热带南美间断 Trop. & Subtr. E. Asia & (S.) Trop. Amer. disjuncted | 3 |
| 4 | 旧世界热带 Old World Tropics | 5 |
| 5 | 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲 Trop. Asia to Trop. Australasia Oceania | 10 |
| 6 | 热带亚洲至热带非洲 Trop. Asia to Trop. Africa | 3 |
| 7 | 热带亚洲 Trop. Asia | 11 |
| 温带属 Temperate | 46 | |
| 8 | 北温带 N. Temp. | 20 |
| 9 | 东亚及北美间断 E. Asia & N. Amer. disjuncted | 5 |
| 10 | 旧世界温带 Old World Temp. | 4 |
| 11 | 温带亚洲 Temp. Asia | - |
| 12 | 地中海区、西亚至中亚 Medit., W. to C. Asia | - |
| 13 | 中亚 C. Asia | - |
| 14 | 东亚 E. Asia | 14 |
| 15 | 中国特有 Endemic to China | 3 |
| 总计 Total | 98 |
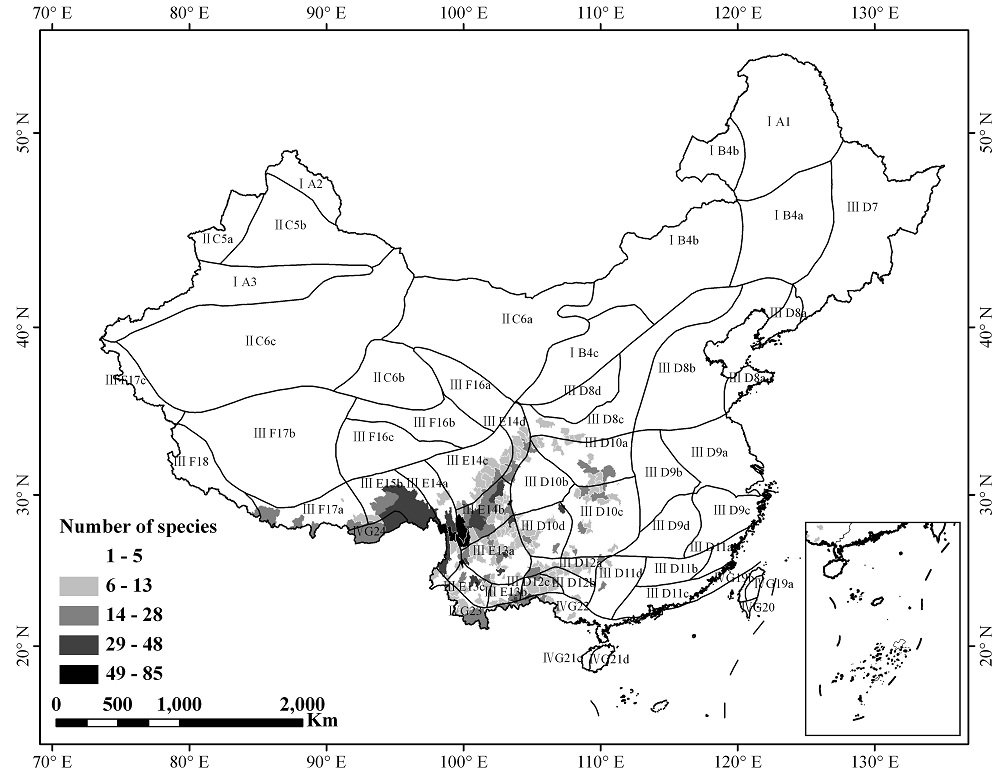
图2 间断分布类群物种丰富度在中国大陆植物区系分区中的地理分布格局
Fig. 2 Geographic pattern of species richness of disjunct taxa between southwestern area and Taiwan area in China according to the floristic region of the mainland China
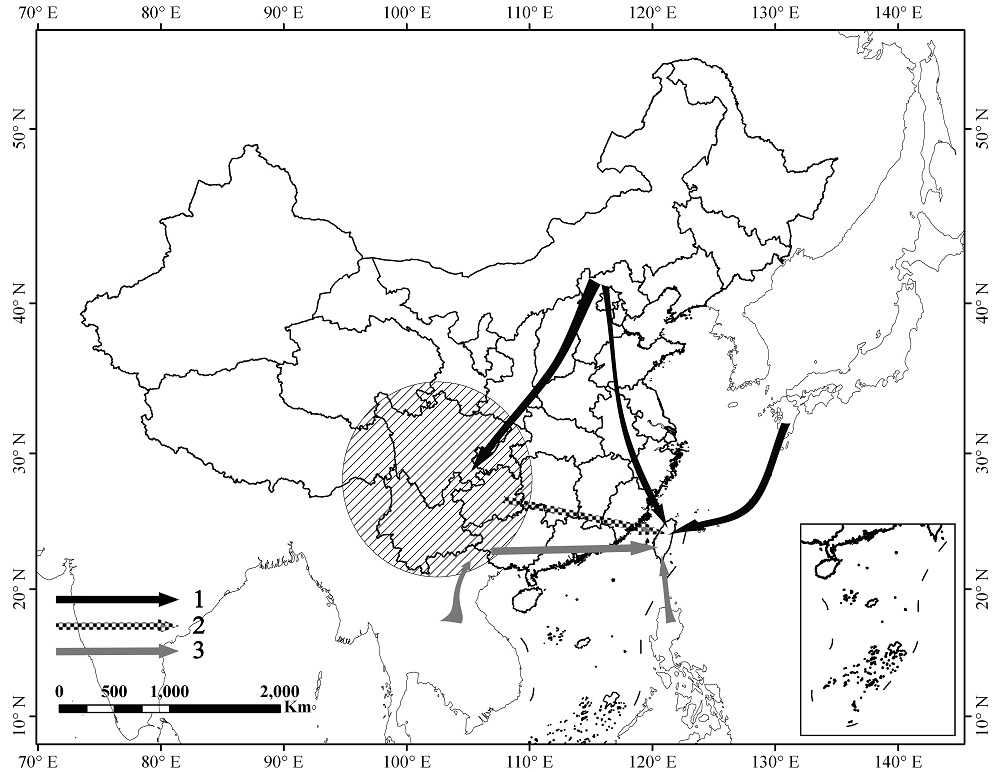
图4 间断分布类群的来源。1. 北温带来源; 2. 中国西南来源; 3. 热带亚洲来源
Fig. 4 Origins of the disjunct taxa between southwestern area and Taiwan area in China. 1. Northern temperate origin; 2. Southwestern China origin; 3. Tropical Asia origin.
| [1] | Chen SC, Liu ZJ, Zhu GH, Lang KY, Ji ZH, Luo YB, Jin XH, Philip JC, Wood JJ, Gale SW, Ormerod P, Vermeulen JJ, Wood HP, Clayton D, Bell A (2009) Orchidaceae. In: Flora of China (eds Wu CY, Raven PH, Hong DY), 25, pp. 1-506. Science Press, Beijing, and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, St. Louis. |
| [2] | Cheng WC (郑万钧), Fu LK (傅立国) (1978) Taxodiaceae. In: Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae (中国植物志) (ed. Editorial Committee of Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae (中国植物志编辑委员会)), 7, pp. 289-293. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [3] | Chiang TY, Schaal BA (2006) Phylogeography of plants in Taiwan and the Ryukyu Archipelago. Taxon, 55, 31-41. |
| [4] | Chou YW, Thomas PI, Ge XJ, LePage BA, Wang CN (2011) Refugia and phylogeography of Taiwania in East Asia. Journal of Biogeography, 38, 1992-2005. |
| [5] | Comes HP, Kadereit JW (1998) The effect of Quaternary climatic changes on plant distribution and evolution. Trends in Plant Science, 3, 432-438. |
| [6] | Dan T, Ikeda H, Mitsui Y, Tsagi Y, Setoguchi H (2009b) Genetic structure of refugial populations of the temperate plant Shortia rotundifolia (Diapensiaceae) on a subtropical island. Conservation Genetics, 10, 859-867. |
| [7] | Dan T, Mitsui Y, Ikeda H, Tsagi Y, Setoguchi H (2009a) Isolation and characterization of microsatellite loci in Shortia rotundifolia (Diapensiaceae), an endangered relict plant on the Ryukyu Islands and Taiwan. Conservation Genetics, 10, 507-509. |
| [8] | Editorial Committee of Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae (中国植物志编辑委员会) (1959-2004) Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae (中国植物志), Tomus 1-80. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [9] | Editorial Committee of the Flora of Taiwan (1993-2003) Flora of Taiwan, 2nd edn. Vols. 1-6. Department of Botany, Taiwan University, Taipei. |
| [10] | Fan J, Qin HN, Li DZ, Jin XH (2009) Molecular phylogeny and biogeography of Holcoglossum (Orchidaceae: Aeridinae) based on nuclear ITS, and chloroplast trnL-F and matK. Taxon, 58, 849-861. |
| [11] | Fang BZ (方碧真), Zhuo ZD (卓正大) (1995) Basic features of seed plant flora in Taiwan area. Tropical Geography (热带地理), 15, 263-271. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] | Gaussen H (1939) Une nouvelle espèce Taiwania, T. flousiana. Travaux du Laboratoire Forestier Toulouse (tome) 1, (Vol.) 3, (art.) 2, 1-9. |
| [13] |
Ge XJ, Zhou XL, Li ZC, Hsu TW, Schaal BA, Chiang TY (2005) Low genetic diversity and significant population structuring in the relict Amentotaxus argotaenia complex (Taxaceae) based on ISSR fingerprinting. Journal of Plant Research, 118, 415-422.
DOI URL PMID |
| [14] | Gray J, Sohma K (1964) Fossil Pachysandra from western America with a comparative study of pollen in Pachysandra and Sarcococca. American Journal of Science, 262, 1159-1197. |
| [15] | Hayata B (1906) On Taiwania, a new genus of Coniferae from the island of Formosa. Journal of the Linnean Society of London, Botany, 37, 330-331. |
| [16] |
Hewitt GM (2000) The genetic legacy of the Quaternary ice ages. Nature, 405, 907-913.
URL PMID |
| [17] | He TN (何廷农), Xue CY (薛春迎), Wang W (王伟) (1994) The origin, dispersal and formation of the distribution pattern of Swertia L. (Gentianaceae). Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica (植物分类学报), 32, 525-537. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Hou XY (侯学煜) (1982) Vegetation Map of China 中国植被图. SinoMaps Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [19] | Hsieh CF (2003) Composition, endemism and phytogeo- graphical affinities of the Taiwan flora. In: Flora of Taiwan, 2nd edn. (ed. Editorial Committee of the Flora of Taiwan), 6, pp. 1-14. Department of Botany, Taiwan University, Taipei. |
| [20] | Hsu R, Wolf JHD (2009) Diversity and phytogeography of vascular epiphytes in a tropical-subtropical transition island, Taiwan. Flora―Morphology, Distribution, Functional Ecology of Plants, 204, 612-627. |
| [21] | Hu HH (1926) A preliminary survey of the forest flora of southeastern China. Contributions from the Biological Laboratory of the Science Society of China, 2(5), 1-20. |
| [22] | Huang TC, Hsiao A (1998) Notes on the Flora of Taiwan (31)—Shortia (Diapensiaceae). Taiwania, 43, 33-37. |
| [23] | Jin XH (2005) Generic delimitation and a new infrageneric system in the genus Holcoglossum (Orchidaceae: Aeridinae). Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 149, 465-468. |
| [24] | Kuo CM (1985) Taxonomy and phytogeography of Taiwanese pteridophytes. Taiwania, 30, 5-100. |
| [25] | Kuo CM (郭城孟) (1998) Floristic of ferns in Taiwan. In: Proceedings of the Cross-Strait Symposium on Floristic Diversity and Conservation (海峡两岸植物多样性与保育) (eds Chiu ST (邱少婷), Peng CI (彭镜毅)), pp. 9-19. Taiwan Museum of Natural Science, Taichung. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [26] | Lai MJ (赖明洲) (2003) The Flora and Vegetation of Taiwan (台湾的植物) (ed. Lai MJ (赖明洲)), pp. 15-23. Morning Star Publishing Inc., Taichung. (in Chinese) |
| [27] | Li HL (1957) The genetic affinities of the Formosan flora. Proceedings of the Eighth Pacific Science Congress, 4, 189-195. |
| [28] | Li HL (1982a) Eastern Asia-eastern North America species-pairs in wide-ranging genera. In: Contributions to Botany, pp. 190-203. Epoch Publishing Co., Taipei. |
| [29] | Li HL (1982b) The relict genera of conifers and taxads of eastern Asia and their geographical distribution. In: Contributions to Botany (ed. Li HL), pp. 216-235. Epoch Publishing Co., Taipei. |
| [30] | Li LQ (李良千) (1995) The geographical distribution of Subfam. Helleboroideae (Ranunculaceae). Acta Phytotaxon- omica Sinica (植物分类学报), 33, 537-555. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [31] | Liao WB (廖文波), Jin JH (金建华), Wang BS (王伯荪), Wu ZH (吴兆洪) (2003) Biodiversities and their continental features of the fern floras in Hainan and Taiwan islands, China. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica (西北植物学报), 23, 1237-1245. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] | Liao WB, Boufford DE (2002) Vascular plant disjunctions and their significance between Taiwan, the Asian mainland and the Himalayan region. In: Abstracts of the Papers Presented at the 7th National Symposium on Systematic and Evolution- ary Botany of Youth (第七届全国系统与进化植物学青年学术研讨会论文摘要集) (ed. Botanical Society of China (中国植物学会)), pp. 61-62. Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [33] | Lin CC (林朝棨) (1963) Quaternary in Taiwan. Taiwan Documents (台湾文献), 14, 1-91. (in Chinese) |
| [34] | Liu RS (刘如笋), Xu YG (徐延恭) (2000) A primary probe into the relationship of Chinese Timaliid birds in Taiwan and on mainland China. Acta Zootaxonomica Sinica (动物分类学报), 25, 106-113. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [35] | Liu TN (刘慎谔) (1985) In: Selected Works of Liou Tchenngo (刘慎谔文集) (ed. Liu TN (刘慎谔)), pp. 229-294. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [36] | Liu TS, Su HJ (1983) Biosystematic studies on Taiwania and numerical evaluations on the systematics of Taxodiaceae. Taiwan Museum Special Publication, ser. No. 2, 1-113. |
| [37] | Manchester SR, Chen ZD, Lu AM, Uemura K (2009) Eastern Asian endemic seed plant genera and their paleogeographic history throughout the Northern Hemisphere. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 47, 1-42. |
| [38] |
Milne RI (2006) Northern Hemisphere plant disjunctions: a window on tertiary land bridges and climate change? Annals of Botany, 98, 465-472.
DOI URL PMID |
| [39] | Nesom GL (2009) Diapensiaceae. In: Flora of North America, Vol. 8, Magnoliophyta: Paeoniaceae to Ericaceae (ed. Editorial Committee of Flora of North America). Oxford University Press, New York. |
| [40] |
Nie ZL, Sun H, Li H, Wen J (2006) Intercontinental biogeography of subfamily Orontioideae (Symplocarpus, Lysichiton, and Orontium) of Araceae in eastern Asia and North America. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 40, 155-165.
DOI URL PMID |
| [41] | Ota H (1998) Geographic patterns of endemism and speciation in amphibians and reptiles of the Ryukyu Archipelago, Japan, with special reference to their paleogeographical implications. Researches on Population Ecology, 40, 189-204. |
| [42] | Peng CI, Kuo CM, Yang YP (1994) Botanical diversity and inventory of Taiwan. In: Biodiversity and Terrestrial Ecosystems (eds Peng CI, Chou CH), pp. 75-85. Institute of Botany, Academia Sinica, Taipei. |
| [43] |
Qian H (2002) Floristic relationships between eastern Asia and North America: test of Gray’s hypothesis. The American Naturalist, 160, 317-332.
DOI URL PMID |
| [44] |
Qian H, Ricklefs RE (2004) Geographical distribution and ecological conservatism of disjunct genera of vascular plants in eastern Asia and eastern North America. Journal of Ecology, 92, 253-265.
DOI URL PMID |
| [45] | Qin HN, Bartholomew B (2005) Diapensiaceae. In: Flora of China (eds Wu CY, Raven PH, Hong DY), 14, pp. 235-237. Science Press, Beijing, and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, St. Louis. |
| [46] | Rönblom K, Anderberg AA (2002) Phylogeny of Diapensi- aceae based on molecular data and morphology. Systematic Botany, 27, 383-395. |
| [47] | Shao KT (邵广昭), Peng CI (彭镜毅), Wu WJ (吴文哲) (2010) Taiwan Species Checklist 2010 (台湾物种名录2010). Forestry Bureau, Council of Agriculture, Executive Yuan, Taipei.(in Chinese) |
| [48] | Sibuet JC, Hsu SK (1997) Geodynamics of the Taiwan arc-arc collision. Tectonophysics, 274, 221-251. |
| [49] | Sibuet JC, Hsu SK (2004) How was Taiwan created? Tectonophysics, 379, 159-181. |
| [50] | Sohma K (1983) Fossil pollen grains of Pachysandra from Japan. Science Reports of the Thoku University, Series 4: Biology, 38, 183-189. |
| [51] |
Suzuki H, Tsuchiya K, Takezaki N (2000) A molecular phylogenetic framework for the Ryukyu endemic rodents Tokudaia osimensis and Diplothrix legata. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 15, 15-24.
DOI URL PMID |
| [52] | The Biodiversity Committee of Chinese Academy of Sciences (中国科学院生物多样性委员会) (2011) Catalogue of Life China 2011 Annual Checklist. CD-ROM. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [53] | Thorne RF (1972) Major disjunctions in the geographic ranges of seed plants. Quarterly Review of Biology, 36, 365-411. |
| [54] | Wang PX, Sun XJ (1994) Last glacial maximum in China: comparison between land and sea. Catena, 23, 341-353. |
| [55] | Wang WC, Fu DZ, Li LQ, Bartholomew B, Brach AR, Dutton BE, Gilbert MG, Kadota Y, Robinson OR, Tamura M, Warnock MJ, Zhu GH, Ziman SN (2001) Ranunculaceae. In: Flora of China (eds Wu CY, Raven PH, Hong DY), 6, pp. 133-438. Science Press, Beijing, and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, St. Louis. |
| [56] | Wang WT (王文采) (1989) Notes on disjunction in the flora of China. Bulletin of Botanical Research (植物研究), 9, 1-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [57] | Wang WT (王文采) (1992a) On some disjunction patterns and some migration routes found in the east Asiatic region. Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica (植物分类学报), 30, 1-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [58] | Wang WT (王文采) (1992b) On some disjunction patterns and some migration routes found in the east Asiatic region (Cont.). Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica (植物分类学报), 30, 97-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [59] | Wang WT (王文采) (1993, 1994) Vascular Plants of the Hengduan Mountains (横断山区维管植物上、下卷). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [60] | Wang WT (王文采) (1996) Notulae de Ranunculaceis sinensibus (XIX). Bulletin of Botanical Research (植物研究), 16, 155-166. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [61] | Wang ZR (王中仁) (2001) A biogeographic comparison on Athyrium Roth in Taiwan and mainland of China. Bulletin of Botanical Research (植物研究), 21, 231-238. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [62] | Wen J (2001) Evolution of eastern Asian-eastern North American biogeographic disjunctions: a few additional issues. International Journal of Plant Sciences, 162, 117-122. |
| [63] | Wilson EH (1920) A phytogeographical sketch of the ligneous flora of Formosa. Journal of the Arnold Arboretum, 2, 25-24. |
| [64] | Wu PC (吴鹏程), Wang MZ (汪楣芝) (2001) Relationship of the tropical elements of bryophytes between Mts Hengduan, Southwest China and Taiwan Province, Southeast China. Guizhou Science (贵州科学), 19, 6-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [65] | Wu YH (吴玉虎) (2008) The Vascular Plants and Their Eco-Geographical Distribution of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau (青藏高原维管植物及其生态地理分布). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [66] | Wu ZY (吴征镒) (1979) The regionalization of Chinese flora. Acta Botanica Yunnanica (云南植物研究), (1), 1-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [67] | Wu ZY (吴征镒) (1998) On the status of the Taiwan flora in reference to a newly proposed Eastern Asiatic Kingdom, with special reference to the unique characteristics and origin of forest ecosystem zonation. In: Proceedings of the Cross-Strait Symposium on Floristic Diversity and Conservation (海峡两岸植物多样性与保育) (eds Chiu ST (邱少婷), Peng CI (彭镜毅)), pp. 1-8. Taiwan Museum of Natural Science, Taichung. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [68] | Wu ZY (吴征镒), Lu AM (路安民), Tang YC (汤彦承), Chen ZD (陈之端), Li DZ (李德铢) (2003) The Families and Genera of Angiosperms in China: A Comprehensive Analysis (中国被子植物科属综论). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [69] | Wu ZY (吴征镒), Sun H (孙航), Zhou ZK (周浙昆), Li DZ (李德铢), Peng H (彭华) (2011) Floristics of Seed Plants from China 中国种子植物区系地理. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [70] | Wu ZY (吴征镒), Zhou ZK (周浙昆), Sun H (孙航), Li DZ (李德铢), Peng H (彭华) (2006) The Areal-Types of Seed Plants and Their Origin and Differentiation 种子植物分布区类型及其起源与分化. Yunnan Science and Technology Press, Kunming. (in Chinese) |
| [71] | Wu ZY, Raven PH, Hong DY (1994-2011) Flora of China, Vols. 4-25. Science Press, Beijing and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, St. Louis. |
| [72] | Wulff EV (translated by Zhong CX (仲崇信), Zhang MZ (张梦庄)) (1960) An Introduction to Historical Plant Geography (历史植物地理学引论), ⅲ-ⅴ, pp. 1-163. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [73] |
Xiang QY, Soltis DE, Soltis PS (1998) The eastern Asian and eastern and western North American floristic disjunction: congruent phylogenetic patterns in seven diverse genera. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 10, 178-190.
DOI URL PMID |
| [74] |
Xiang XG, Hu H, Wang W, Jin XH (2011) DNA barcoding of the recently evolved genus Holcoglossum (Orchidaceae: Aeridinae): a test of DNA barcode candidates. Molecular Ecology Resources, 11, 1012-1021.
URL PMID |
| [75] | Ying TS (应俊生) (2001) Species diversity and distribution pattern of seed plants in China. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 9, 393-398. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [76] | Ying TS (应俊生), Chen ML (陈梦玲) (2011) Plant Geography of China 中国植物地理. Shanghai Scientific and Technical Press, Shanghai. (in Chinese) |
| [77] | Ying TS (应俊生), Hsu KS (徐国士) (2002) An analysis of the flora of seed plants of Taiwan, China: its nature, character-istics, and relations with the flora of the mainland. Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica (植物分类学报), 40, 1-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [78] | Ying TS (应俊生), Zhang YL (张玉龙) (1994) The Endemic Genera of Seed Plants of China 中国种子植物特有属. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [79] | Yu YF (于永福) (1994) Taxonomic studies on the family Taxodiaceae. Bulletin of Botanical Research (植物研究), 14, 369-382. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [80] | Yu YF (于永福) (1995) Origin, evolution and distribution of the Taxodiaceae. Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica (植物分类学报), 33, 362-389. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [81] | Zeng WB (曾文彬) (1994) The passageway of the flora migration on both sides of the Taiwan Strait in Pleistocene Epoch. Acta Botanica Yunnanica (云南植物研究), 16, 107-110. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [82] | Zhang XC (张宪春), Liu QR (刘全儒), Xu J (徐静) 2003 Systematics of Platygyria Ching & S. K. Wu (Polypodia-ceae). Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica (植物分类学报), 41, 410-415. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [83] | Zhou ZZ (周忠泽), Jiang GH (江光怀), Lu RL (鲁润龙) (1999) Study on palyno-geography of Polygonaceae in China. Journal of China University of Science and Technology (中国科技大学学报), 29, 464-470. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [84] | Zhu GL, Harald R, Rudolf K (1995) Rudolf K (1995) Boraginaceae. In: Flora of China (eds Wu CY, Raven PH, Hong DY), 16, pp. 329-427. Science Press, Beijing, and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, St. Louis. |
| [85] | Zhu H (2002) A revision of the genus Lasianthus (Rubiaceae) from China. Systematics and Geography of Plants, 72, 63-110. |
| [86] | Zhu H (朱华) (2008) Distribution patterns of Lasianthus (Rubiaceae) species from eastern Asia and their biogeographical implications. Acta Botanica Yunnanica (云南植物研究), 30, 308-314. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 郑博瀚, 陈鑫瑶, 倪健. 中国维管植物生长型和生活型数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23468-. |
| [2] | 魏嘉欣, 姜治国, 杨林森, 熊欢欢, 金胶胶, 罗方林, 李杰华, 吴浩, 徐耀粘, 乔秀娟, 魏新增, 姚辉, 余辉亮, 杨敬元, 江明喜. 湖北神农架中亚热带山地落叶阔叶林25 ha动态监测样地群落物种组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23338-. |
| [3] | 刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇. 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [4] | 万霞, 张丽兵. 世界维管植物新分类群2023年度报告[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24322-. |
| [5] | 张楚然, 李生发, 李逢昌, 唐志忠, 刘辉燕, 王丽红, 顾荣, 邓云, 张志明, 林露湘. 云南鸡足山亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林20 ha动态监测样地木本植物生境关联与群落数量分类[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23393-. |
| [6] | 李勇, 李三青, 王欢. 天津野生维管植物编目及分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23128-. |
| [7] | 陈慧妹, 李文军, 邱娟, 马占仓, 李波, 杨宗宗, 闻志彬, 孟岩, 曹秋梅, 邱东, 刘丹辉, 金光照. 新疆野生维管植物名录[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23124-. |
| [8] | 陈又生, 宋柱秋, 卫然, 罗艳, 陈文俐, 杨福生, 高连明, 徐源, 张卓欣, 付鹏程, 向春雷, 王焕冲, 郝加琛, 孟世勇, 吴磊, 李波, 于胜祥, 张树仁, 何理, 郭信强, 王文广, 童毅华, 高乞, 费文群, 曾佑派, 白琳, 金梓超, 钟星杰, 张步云, 杜思怡. 西藏维管植物多样性编目和分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23188-. |
| [9] | 韩赟, 迟晓峰, 余静雅, 丁旭洁, 陈世龙, 张发起. 青海野生维管植物名录[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23280-. |
| [10] | 安昌, 庄怡雪, 郑平, 林彦翔, 杨成梓, 秦源. 福建省维管植物名录[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22537-. |
| [11] | 杜诚, 汪远, 闫小玲, 严靖, 李惠茹, 张庆费, 胡永红. 上海市植物物种多样性组成和历史变化暨上海维管植物名录更新(2022版)[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 23093-. |
| [12] | 梁彩群, 陈玉凯, 杨小波, 张凯, 李东海, 江悦馨, 李婧涵, 王重阳, 张顺卫, 朱子丞. 海南省野生维管植物编目和分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 23067-. |
| [13] | 韦毅刚, 温放, 辛子兵, 符龙飞. 广西野生维管植物名录[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 23078-. |
| [14] | 丁炳扬, 金孝锋, 张永华, 李根有, 陈征海, 张方钢. 浙江野生种子植物的分布格局与区系分区[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22515-. |
| [15] | 朱华. 地质事件和季风气候影响了云南植物区系和植被的演化[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23262-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn