



生物多样性 ›› 2011, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (2): 190-196. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.07030 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2011.07030
所属专题: 中国的森林生物多样性监测
宋凯1,2, 米湘成1,*( ), 贾琪1,3, 任海保1, DanBebber4, 马克平1
), 贾琪1,3, 任海保1, DanBebber4, 马克平1
收稿日期:2011-02-22
接受日期:2011-03-04
出版日期:2011-03-20
发布日期:2011-06-01
通讯作者:
米湘成
作者简介:*E-mail: mixiangcheng@ibcas.ac.cn
Kai Song1,2, Xiangcheng Mi1,*( ), Qi Jia1,3, Haibao Ren1, Dan Bebber4, Keping Ma1
), Qi Jia1,3, Haibao Ren1, Dan Bebber4, Keping Ma1
Received:2011-02-22
Accepted:2011-03-04
Online:2011-03-20
Published:2011-06-01
Contact:
Xiangcheng Mi
Supported by:摘要:
群落谱系结构包含群落发育的历史信息, 能从新的角度反映群落形成的生态过程。作者在浙江古田山自然保护区亚热带常绿阔叶林中选择了人为干扰强度不同的4种群落类型, 以20 m×20 m为研究尺度探讨了不同干扰程度对群落谱系结构的影响。结果表明, 人工林(类型I)谱系结构发散; 但间伐林(类型II)、自然恢复林(类型III)以及自然老龄林(类型IV)谱系结构聚集, 且以类型II和IV聚集度最高。进一步分析不同径级谱系结构发现, 在中小径级(DBH≤5 cm和5 cm<DBH≤10 cm), 类型II、III、IV群落谱系结构聚集, 而类型I群落谱系结构发散; 但DBH>10 cm时, 除了类型IV, 其他3种群落都是谱系结构发散, 这反映了在恢复早期种子扩散对这些林型群落构建影响较大; 而皆伐后的演替和间伐增加了群落生境异质性, 生境过滤作用增强, 使类型II、III群落中小径级谱系结构表现为聚集; 类型IV群落不同径级谱系结构均表现为聚集, 可能与其稳定的生境过滤作用有关。
宋凯, 米湘成, 贾琪, 任海保, DanBebber, 马克平 (2011) 不同程度人为干扰对古田山森林群落谱系结构的影响. 生物多样性, 19, 190-196. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.07030.
Kai Song, Xiangcheng Mi, Qi Jia, Haibao Ren, Dan Bebber, Keping Ma (2011) Variation in phylogenetic structure of forest communities along a human disturbance gradient in Gutianshan forest, China. Biodiversity Science, 19, 190-196. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.07030.
| 样地 Plot | 群落类型 Community type | 物种数 Species richness | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总数 Total | DBH≤5 cm | 5 cm <DBH≤ 10 cm | DBH> 10 cm | ||
| 1 | I | 81 | 77 | 31 | 22 |
| 2 | IV | 114 | 96 | 56 | 73 |
| 3 | II | 100 | 100 | 66 | 25 |
| 4 | IV | 89 | 83 | 50 | 39 |
| 5 | III | 105 | 96 | 53 | 43 |
| 6 | III | 123 | 113 | 68 | 46 |
| 7 | I | 90 | 86 | 32 | 18 |
| 8 | II | 95 | 89 | 58 | 25 |
| 9 | II | 85 | 76 | 53 | 19 |
| 10 | IV | 118 | 96 | 68 | 72 |
| 11 | I | 98 | 90 | 40 | 16 |
| 12 | III | 87 | 80 | 45 | 34 |
表1 12个1 ha样地群落类型及不同径级的物种数
Table 1 Community types and species richness of 12 1-ha plots
| 样地 Plot | 群落类型 Community type | 物种数 Species richness | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总数 Total | DBH≤5 cm | 5 cm <DBH≤ 10 cm | DBH> 10 cm | ||
| 1 | I | 81 | 77 | 31 | 22 |
| 2 | IV | 114 | 96 | 56 | 73 |
| 3 | II | 100 | 100 | 66 | 25 |
| 4 | IV | 89 | 83 | 50 | 39 |
| 5 | III | 105 | 96 | 53 | 43 |
| 6 | III | 123 | 113 | 68 | 46 |
| 7 | I | 90 | 86 | 32 | 18 |
| 8 | II | 95 | 89 | 58 | 25 |
| 9 | II | 85 | 76 | 53 | 19 |
| 10 | IV | 118 | 96 | 68 | 72 |
| 11 | I | 98 | 90 | 40 | 16 |
| 12 | III | 87 | 80 | 45 | 34 |
| 群落类型 Community type | I | II | III |
|---|---|---|---|
| II | 0.2146 | ||
| III | 0.2239 | 0.1910 | |
| IV | 0.2920 | 0.2161 | 0.2177 |
表2 不同类型群落间相似性系数(S?rensen指数)
Table 2 The S?rensen index between different community types
| 群落类型 Community type | I | II | III |
|---|---|---|---|
| II | 0.2146 | ||
| III | 0.2239 | 0.1910 | |
| IV | 0.2920 | 0.2161 | 0.2177 |
| 变异来源 Source | df | SS | s2 | F | Pr>F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干扰类型 Disturbance type | 3 | 64.5689 | 21.5230 | 19.09 | <0.0001 |
| 误差 Error | 296 | 333.7407 | 1.1275 | ||
| 总变异 Corrected total | 299 | 398.3096 |
表3 不同程度干扰群落净谱系亲缘关系指数NRI的LSD单因素方差分析表
Table 3 LSD’s one-way ANOVA for Net Relatedness Index of communities with different disturbance types
| 变异来源 Source | df | SS | s2 | F | Pr>F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干扰类型 Disturbance type | 3 | 64.5689 | 21.5230 | 19.09 | <0.0001 |
| 误差 Error | 296 | 333.7407 | 1.1275 | ||
| 总变异 Corrected total | 299 | 398.3096 |
| 变异来源 Source | df | SS | S2 | F | Pr>F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干扰类型 Disturbance type (DT) | 3 | 210.0901 | 70.03 | 42.76 | <.0001 |
| 径级结构 DBH | 2 | 489.0633 | 244.5317 | 149.31 | <.0001 |
| 干扰类型× 径级结构 DT× DBH | 6 | 69.703 | 11.6172 | 7.09 | <.0001 |
| 误差 Error | 859 | 1406.8081 | 1.6377 | ||
| 总变异 Corrected total | 870 | 2175.6645 |
表4 不同干扰类型及径级结构的群落净谱系亲缘关系指数NRI方差分析表
Table 4 Two-way ANOVA for Net Relatedness Index of communities with different disturbance types and DBH classes
| 变异来源 Source | df | SS | S2 | F | Pr>F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干扰类型 Disturbance type (DT) | 3 | 210.0901 | 70.03 | 42.76 | <.0001 |
| 径级结构 DBH | 2 | 489.0633 | 244.5317 | 149.31 | <.0001 |
| 干扰类型× 径级结构 DT× DBH | 6 | 69.703 | 11.6172 | 7.09 | <.0001 |
| 误差 Error | 859 | 1406.8081 | 1.6377 | ||
| 总变异 Corrected total | 870 | 2175.6645 |
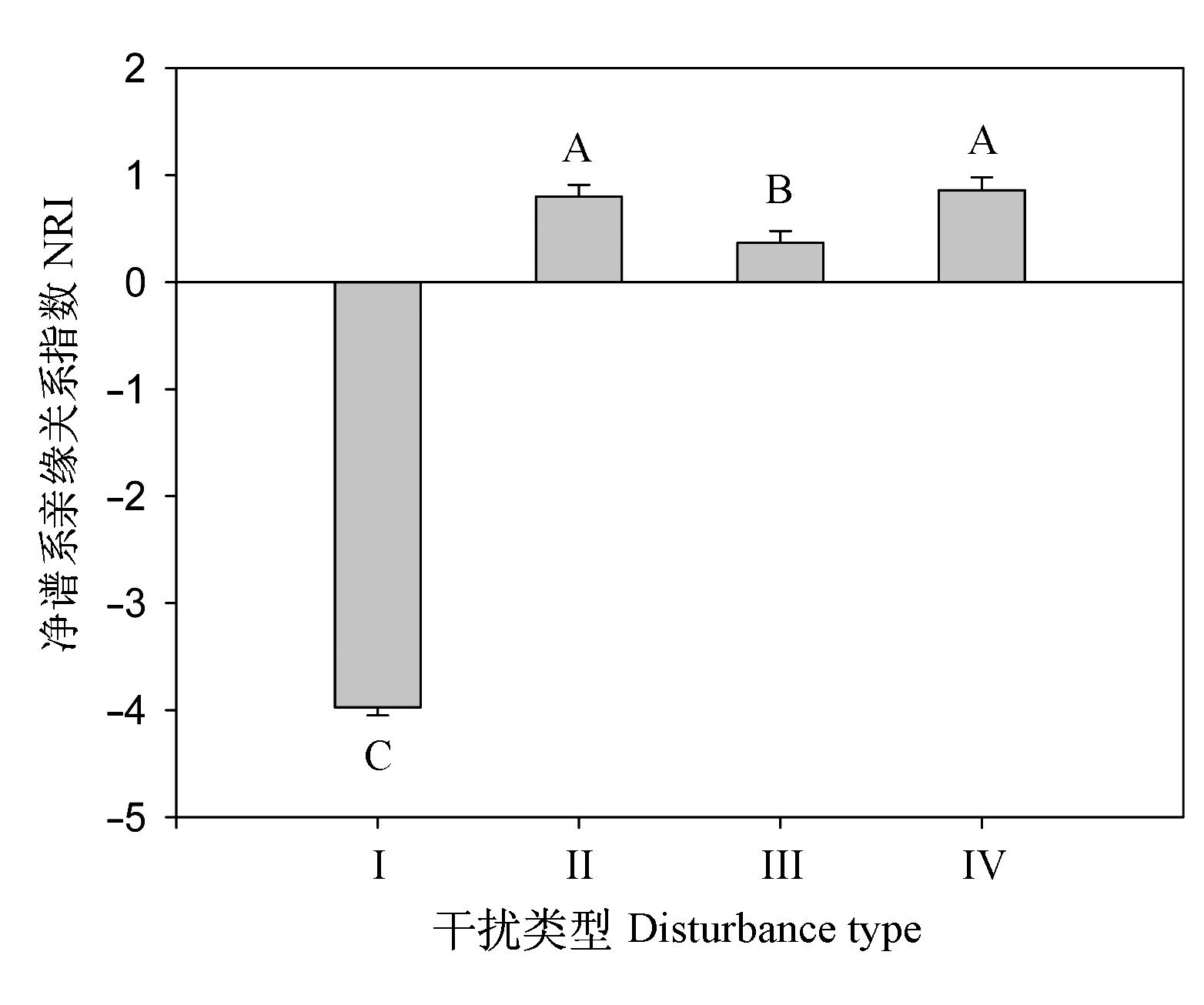
图1 不同干扰类型群落内样方的净谱系亲缘关系NRI平均值。 I、II、III、IV, 同表1。
Fig. 1 The mean value of Net Relatedness Index of communities of different human disturbance types. I, II, III, IV, see Table 1. The letters on bars are the results of multiple comparison for different community types.
| 地形因子 Topographical factor | 海拔 Elevation | 坡向 Aspect | 坡度 Slope | 凹凸度 Convexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | 0.3916 | 0.1153 | 0.3711 | 0.043* |
| R2 | 0.0025 | 0.0083 | 0.0027 | 0.0137 |
表5 不同地形因子对群落谱系结构净谱系亲缘关系指数NRI的影响
Table 5 Effects of different topographical factors on Net Relatedness Index of communities
| 地形因子 Topographical factor | 海拔 Elevation | 坡向 Aspect | 坡度 Slope | 凹凸度 Convexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | 0.3916 | 0.1153 | 0.3711 | 0.043* |
| R2 | 0.0025 | 0.0083 | 0.0027 | 0.0137 |
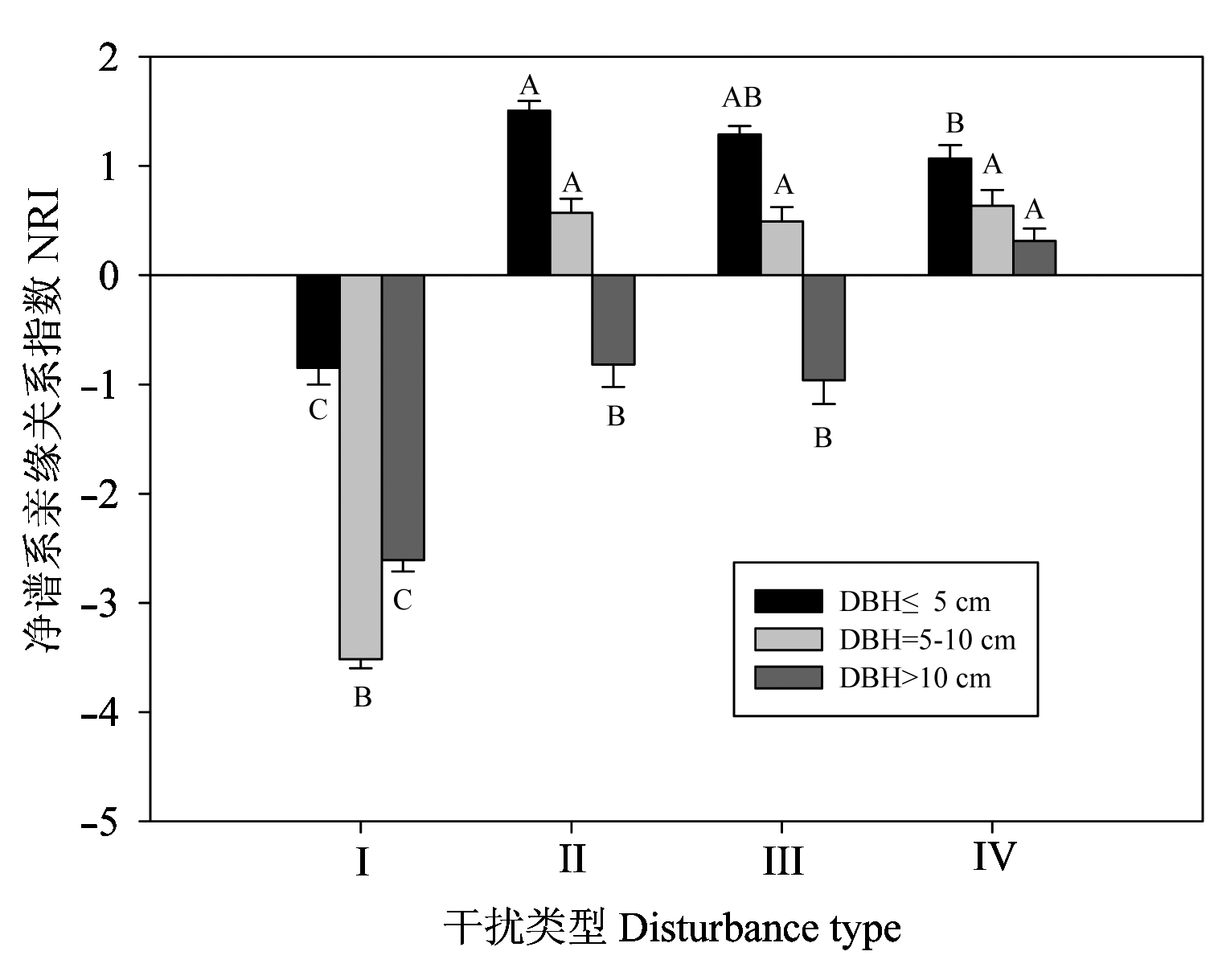
图2 不同径级范围内, 不同干扰类型群落净谱系亲缘关系NRI平均值。 图中字母为同一径级内不同类型群落间的多重比较结果。I、II、III、IV, 同表1。
Fig. 2 The mean value Net Relatedness Index of communities of different DBH classes. The letters on bars are the results of multiple comparison for different community types for the same DBH class. I, II, III, IV, see Table 1.
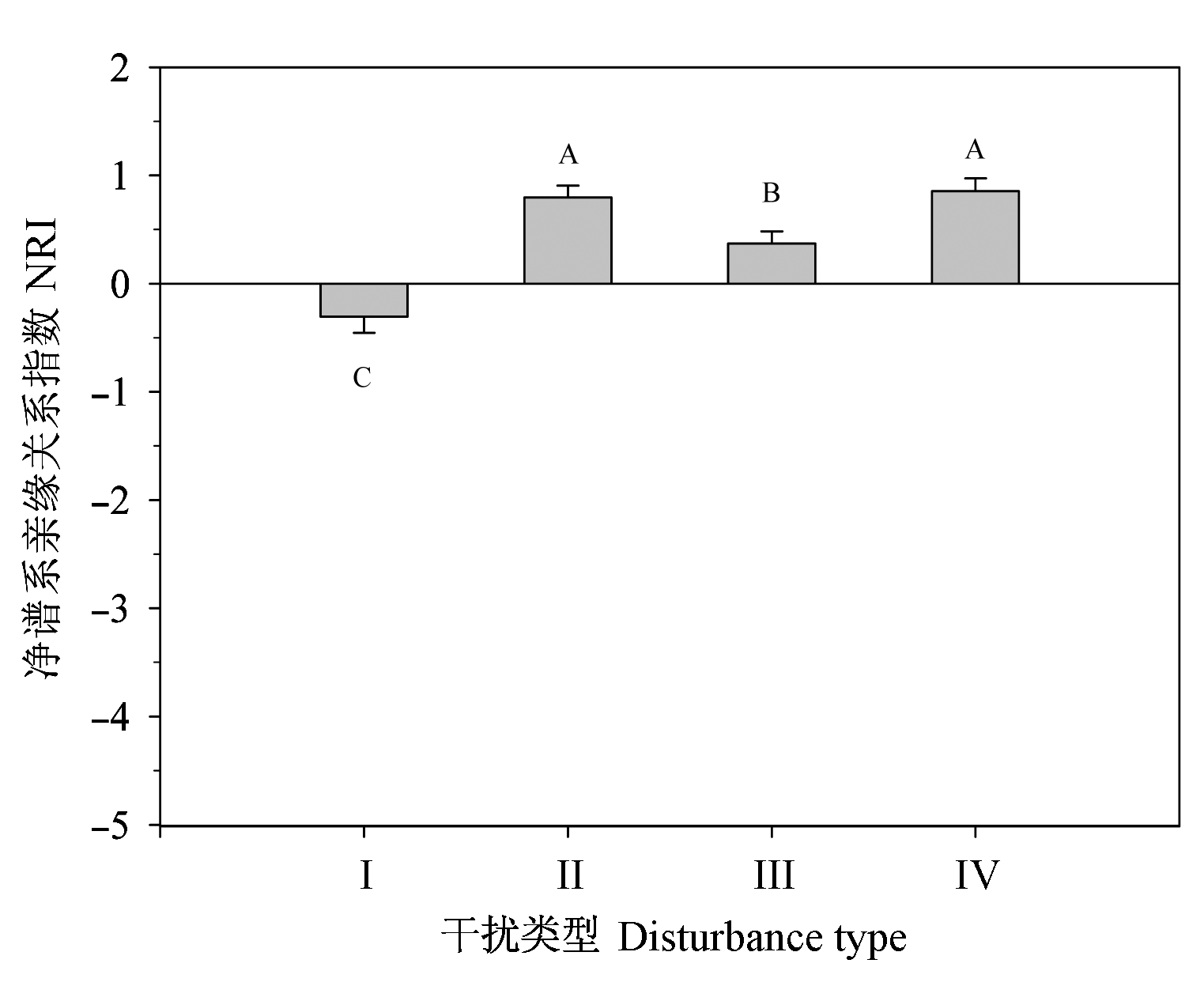
图3 I型人工林去除杉木后, 不同干扰类型群落内样方的净谱系亲缘关系NRI平均值。 图中直方图上方字母为方差分析多重比较结果。I、II、III、IV, 同表1。
Fig. 3 The mean value of Net Relatedness Index of communities with different human disturbance after excluding Cunninghamia lanceolata from plantation forest. The letters on bars are the results of multiple comparison for different community types. I, II, III, IV, see Table 1.
| [1] | Belsky AJ (1986) Regeneration of artificial disturbance in grasslands of the Serengeti National Park, Tanzania: II. Five years of successional change. Journal of Ecology, 74, 937-952. |
| [2] | Brown KA, Gurevitch J (2004) Long-term impacts of logging on forest diversity in Madagascar. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 101, 6045-6049. |
| [3] | Buckley DS, Crow TR, Nauertz EA (2003) Influence of skid trails and haul roads on understory plant richness and composition in managed forest landscapes in Upper Michigan, USA. Forest Ecology and Management, 175, 509-520. |
| [4] |
Cannon CH, Peart DR, Leighton M (1998) Tree species diversity in commercially logged Bornean rainforest. Science, 281, 1366-1368.
URL PMID |
| [5] |
Cavender-Bares J, Ackerly DD, Baum DA, Bazzaz FA (2004) Phylogenetic overdispersion in Floridian oak communities. The American Naturalist, 163, 823-843.
URL PMID |
| [6] |
Cavender-Bares J, Adrienne K, Brianna M (2006) Phylogenetic structure of Floridian plant communities depends on taxonomic and spatial scale. Ecology, 87, S109-S122.
URL PMID |
| [7] | Chazdon RL (2003) Tropical forest recovery: legacies of human impact and natural disturbances. Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 6, 51-71. |
| [8] | Collins SL, Barber SC (1985) Effects of disturbance on diversity on mixed grass prairie. Vegetatio, 64, 87-94. |
| [9] | Gong GQ (宫贵权), Cheng JM (程积民), Mi XC (米湘成), Chen SW (陈声文), Fang T (方腾) (2007) Habitat association of wood species in the Gutianshan subtropical broad-leaved evergreen forest. Science of Soil and Water Conservation (中国水土保持科学), 5(3), 79-83. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [10] |
Helmus MR, Keller W, Paterson MJ (2009) Communities contain closely related species during ecosystem disturbance. Ecology Letters, 13, 162-174.
URL PMID |
| [11] | Huang JX (黄建雄), Zheng FY (郑凤英), Mi XC (米湘成) (2010) Influence of environmental factors on phylogenetic structure at multiple spatial scales in an evergreen broad- leaved forest of China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology (植物生态学报), 34, 309-315. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] | Hubbell SP (2001) The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [13] |
Kembel SW, Hubbell SP (2006) The phylogenetic structure of a neotropical forest tree community. Ecology, 87, S86-S99.
URL PMID |
| [14] | Koleff P, Gaston KJ, Lennon JJ (2003) Measuring beta diversity for presence-absence data. Journal of Animal Ecology, 72, 367-382. |
| [15] |
Letcher SG (2009) Phylogenetic structure of angiosperm communities during tropical forest succession. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 277, 97-104.
URL PMID |
| [16] | Liu ZM (刘志民), Zhao XY (赵晓英), Liu XM (刘新民) (2002) Relationship between disturbance and vegetation. Acta Prataculturae Sinica (草业学报), 11(4), 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] |
Losos JB (2008) Phylogenetic niche conservatism, phylogenetic signal and the relationship between phylogenetic relatedness and ecological similarity among species. Ecology Letters, 11, 995-1007.
DOI URL PMID |
| [18] | Lou LH (楼炉焕), Jin SH (金水虎) (2000) Spermatophyta flora of Gutianshan Nature Reserve in Zhejiang. Journal of Beijing Forestry University (北京林业大学学报), 22(5), 33-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Pickett S TA, White PS (1985) The Ecology of Natural Disturbance and Patch Dynamics. Academic Press, London. |
| [20] | R Development Core Team (2009) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org. (accessed 2010-09) |
| [21] |
Swenson NG, Enquist BJ, Pither J, Thompson J, Zimmerman JK (2006) The problem and promise of scale dependence in community phylogenetics. Ecology, 87, 2418-2424.
URL PMID |
| [22] |
Swenson NG, Enquist BJ, Thompson J, Zimmerman JK (2007) The influence of spatial and size scale on phylogenetic relatedness in tropical forest communities. Ecology, 88, 1770-1780.
URL PMID |
| [23] | Verdu M, Rey PJ, Alcantara JM, Siles G, Valiente-Banuet A (2009) Phylogenetic signatures of facilitation and competition in successional communities. Journal of Ecology, 97, 1171-1180. |
| [24] | Webb CO, Ackerly DD, Kembel S (2008a) Phylocom: software for the analysis of phylogenetic community structure and character evolution. Version 4.0. http://phylodiversity.net/ phylocom. (accessed 2010-09) |
| [25] | Webb CO, Ackerly DD, McPeek MA, Donoghue MJ (2002) Phylogenies and community ecology. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 33, 475-505. |
| [26] | Webb CO, Cannon CH, Davies SJ (2008b) Ecological organization, biogeography, and the phylogenetic structure of tropical forest tree communities. In: Tropical Forest Community Ecology (eds Carson WP, Schnizer SA). Wiley Blackwell, Oxford. |
| [27] | Webb CO, Donoghue MJ (2005) Phylomatic: tree assembly for applied phylogenetics. Molecular Ecology Notes, 5, 181-183. |
| [28] | Wiens JJ, Graham CH (2005) Niche conservatism: integrating evolution, ecology and conservation biology. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 36, 519-539. |
| [29] |
Wikstrom N, Savolainen V, Chase MW (2001) Evolution of the angiosperms: calibrating the family tree. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 268, 2211-2220.
DOI URL PMID |
| [30] | Ye LQ (叶林奇) (2000) The relationship between disturbance and biodiversity. Journal of Guizhou University (Natural Science)(贵州大学学报自然科学版), 17(2), 129-134. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 张明燡, 王晓梅, 郑言鑫, 吴楠, 李东浩, 樊恩源, 李娜, 单秀娟, 于涛, 赵春暖, 李波, 徐帅, 吴玉萍, 任利群. 黄河口典型牡蛎礁分布区资源状况和栖息地功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [2] | 仝淼, 王欢, 张文双, 王超, 宋建潇. 重金属污染土壤中细菌抗生素抗性基因分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [3] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [4] | 魏诗雨, 宋天骄, 罗佳宜, 张燕, 赵子萱, 茹靖雯, 易华, 林雁冰. 秦岭火地塘针叶林土壤细菌群落的海拔分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [5] | 时永强, 栾青杉, 单秀娟, 韦超, 赵永松, 孙策策, 金显仕. 长岛南部海域浮游动物多样性周年变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [6] | 倪艳梅, 陈莉, 董志远, 孙德斌, 李宝泉, 王绪敏, 陈琳琳. 黄河三角洲湿地生态修复区大型底栖动物群落结构与生态健康评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23303-. |
| [7] | 魏嘉欣, 姜治国, 杨林森, 熊欢欢, 金胶胶, 罗方林, 李杰华, 吴浩, 徐耀粘, 乔秀娟, 魏新增, 姚辉, 余辉亮, 杨敬元, 江明喜. 湖北神农架中亚热带山地落叶阔叶林25 ha动态监测样地群落物种组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23338-. |
| [8] | 刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇. 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [9] | 吴芳芳, 刘娜, 何春梅, 原作强, 郝占庆, 尹秋龙. 秦岭山地木本植物群落结构及多样性的海拔梯度格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24239-. |
| [10] | 单航, 雷祖培, 郑方东, 韦博良, 仲磊, 于明坚. 2013-2023年浙江乌岩岭次生常绿阔叶林群落动态变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24372-. |
| [11] | 冯嘉谊, 练琚愉, 冯瑜莙, 张东旭, 曹洪麟, 叶万辉. 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林群落垂直分层对群落结构及功能的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24306-. |
| [12] | 王兴煜, 孟京辉, 任思远, 祝燕. 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林群落生物多样性与地上生物量的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24230-. |
| [13] | 杜晴晴, 任思远, Nicole Tsz Shun Yuan, 祝燕. 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林幼树及成树生产力的影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24284-. |
| [14] | 黄骏涵, 余梵冬, 王裕祥, 黄哲, 张铭斯, 房苗, 舒璐, 徐猛, 韦慧, 汪学杰, 顾党恩, 罗思. 花地河中下游外来鱼类入侵现状及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24249-. |
| [15] | 杨舒涵, 王贺, 陈磊, 廖蓥飞, 严光, 伍一宁, 邹红菲. 松嫩平原异质生境对土壤线虫群落特征的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23295-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn