



生物多样性 ›› 2011, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (6): 696-701. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.06145 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2011.06145
所属专题: 中国的海洋生物多样性
收稿日期:2011-08-19
接受日期:2011-11-04
出版日期:2011-11-20
发布日期:2011-12-19
通讯作者:
黄良民
作者简介:*E-mail: hlm@scsio.ac.cn基金资助:
Zhixin Ke, Liangmin Huang*( ), Yehui Tan, Jianqiang Yin
), Yehui Tan, Jianqiang Yin
Received:2011-08-19
Accepted:2011-11-04
Online:2011-11-20
Published:2011-12-19
Contact:
Liangmin Huang
摘要:
为了更好地了解珊瑚礁区生物群落应对环境变化的生态响应机制, 以及浮游生物群落结构与珊瑚礁发展发育的关系, 我们于2006年10月26日至11月10日对三亚珊瑚礁保护区9个有珊瑚礁分布的站点进行了浮游生物群落结构的调查。共鉴定出浮游植物种类61属130种(包括变种、变型), 其中硅藻门48属101种, 甲藻门10属25种, 蓝藻门2属3种, 金藻门1属1种。硅藻门的角毛藻属(Chaetoceros)种类最多, 根管藻属(Rhizosolenia)的种类次之。调查海区浮游植物的细胞丰度范围为348-11,320个/L, 平均为3,247个/L。在浮游植物群落中硅藻占绝对优势, 平均丰度为3,230个/L, 占总密度的99.5%。调查海区共鉴定出浮游动物76种, 其中桡足类29种, 水母类17种, 浮游幼虫10种, 毛颚类7种, 被囊类6种, 浮游腹足类4种, 十足类、多毛类和介形类各1种。调查海区浮游动物的密度范围为43-190个/m3, 平均为114个/m3。优势类群为桡足类、各类幼虫和毛颚类, 平均分别占浮游动物总密度的28.5%, 27.7%和13.6%。各站位浮游植物的多样性指数和均匀度平均分别为3.98和0.70, 浮游动物的多样性指数和均匀度平均分别为4.37和0.87。鹿回头和大东海海域的浮游植物密度大, 而生物多样性指数低。活的造礁石珊瑚种数和覆盖率高的站点的浮游生物多样性也较高。
柯志新, 黄良民, 谭烨辉, 尹健强 (2011) 三亚珊瑚礁分布海区浮游生物的群落结构. 生物多样性, 19, 696-701. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.06145.
Zhixin Ke, Liangmin Huang, Yehui Tan, Jianqiang Yin (2011) Plankton community structure and diversity in coral reefs area of Sanya Bay, Hainan Province, China. Biodiversity Science, 19, 696-701. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.06145.
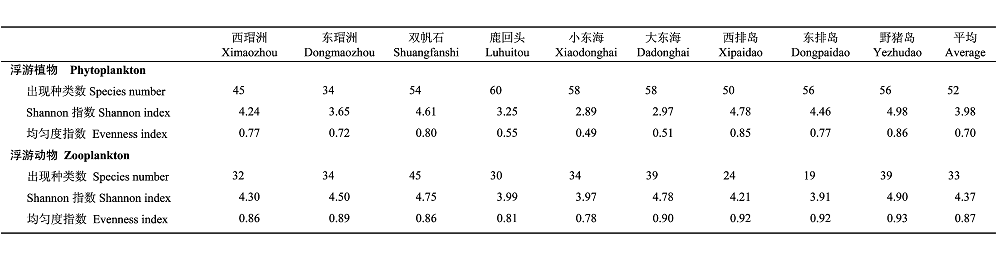 |
表1 调查区域浮游植物和浮游动物的种类数、Shannon多样性指数和Pielou均匀度
Table 1 Species number, Shannon diversity index and Pielou evenness of phytoplankton and zooplankton in the survey regions near Sanya city
 |
| [1] | Guo YJ (郭玉洁), Qian SB (钱树本) (2003) Bacillariophyta in Flora Algarum Marinarum Sinicarum (中国海藻志硅藻门中心纲). 447 pp. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [2] |
Huang LM, Tan YH, Song XY, Huang XP, Wang HK, Zhang S, Dong JD, Chen RY (2003) The status of the ecological environment and a proposed protection strategy in Sanya Bay, Hainan Island, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 47, 180-186.
URL PMID |
| [3] | Huang LM (黄良民), Zhang S (张偲), Wang HK (王汉奎), Wen WY (温伟英), Zhang QM (张乔民) (2007) Ecological Environmental and Bio-resources for Sanya Bay, Hainan Island, China (三亚湾生态环境与生物资源), pp.105-117. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [4] | Jin DX (金德祥), Chen JH (陈金环), Huang KG (黄凯歌) (1965) Marine Planktonic Diatoms in China Sea (中国海洋浮游硅藻类). Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers, Shanghai. (in Chinese) |
| [5] | Lian JS (练健生), Huang H (黄晖), Huang LM (黄良民), Wang DR (王道儒) (2010) Coral Reefs and Their Biodiversity in Sanya Bay (三亚珊瑚礁及其生物多样性), pp.36-37. Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [6] |
Pielou EC (1966) The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 13, 131-144.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Shannon CE, Weaver W (1949) The Mathematical Theory of Communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana. |
| [8] | Sun J (孙军), Liu DY (刘东艳) (2002) The preliminary notion on nomenclature of common phytoplankton in China sea waters. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (海洋与湖沼), 33, 271-286. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Sun J (孙军), Liu DY (刘东艳) (2003) Notes on the nomenclature of the red tide organism Eucampia zodiacus Ehrenberg. Marine Sciences (海洋科学), 27(6), 45-46. (in Chinese) |
| [10] | Sun J (孙军), Liu DY (刘东艳), Ning XR (宁修仁), Liu CG (刘诚刚) (2003) Phytoplankton in the Prydz bay and the adjacent Indian sector of the southern ocean during the austral summer 2001/2002. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (海洋与湖沼), 34, 519-531. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] | Sun J (孙军), Liu DY (刘东艳) (2004) The application of diversity indices in marine phytoplankton studies. Acta Oceanologica Sinica (海洋学报), 26(1), 62-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] | Sun J (孙军), Song SQ (宋书群), Le FF (乐凤凤), Wang D (王丹), Dai MH (戴民汉), Ning XR (宁修仁) (2007) Phytoplankton in northern South China Sea in the winter of 2004. Acta Oceanologica Sinica (海洋学报), 29(5), 132-145 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] | Wang HK (王汉奎), Dong JD (董俊德), Zhang S (张偲), Huang LM (黄良民) (2002) Distribution of N/P ratio and its limitation to growth of phytoplankton in Sanya Bay. Journal of Tropical Oceanography (热带海洋学报), 21(1), 33-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Xu ZL (徐兆礼), Chen YQ (陈亚瞿) (1989) Aggregated intensity of dominant species of zooplankton in autumn in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea. Chinese Journal of Ecology (生态学杂志), 8(4), 13-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [15] | Yin JQ (尹健强), Huang H (黄晖), Huang LM (黄良民), Lin YS (林永水), Li KZ (李开枝), Lian JS (练健生) (2006) Phytoplankton of the coral reef at Dengloujiao, Leizhou Peninsula, Guangdong Province, China. Marine Science Bulletin (海洋通报), 25(2), 8-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] |
Yin JQ (尹健强), Huang H (黄晖), Huang LM (黄良民), Li KZ (李开枝), Lian JS (练健生) (2008) Summer zooplankton in coral reef area of Leizhou Peninsula, China. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (海洋与湖沼), 39(2), 131-138. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [17] | Yin JQ (尹健强), Zhang GX (张谷贤), Tan YH (谭烨辉), Huang LM (黄良民), Li KZ (李开枝) (2004) Species composition and quantitative distribution of zooplankton in Sanya Bay, Hainan Province, China. Journal of Tropical Oceanography (热带海洋学报), 23(5), 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Zhang CX (张才学), Sun SL (孙省利), Xie WL (谢伟良), Xie SY (谢少英), Zhan DL (詹冬玲), Zhang YB (张瑜斌), Zhang JB (张际标), Chen CL (陈春亮) (2009) Seasonal changes of the phytoplankton in Xuwen coral reef area. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (海洋与湖沼), 40, 159-165. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Zhao MX (赵美霞), Yu KF (余克服), Zhang QM (张乔民), Shi Q (施琪) (2009) Evolution and its environmental significance of coral diversity on Luhuitou fringing reef, Sanya. Marine Environmental Science (海洋环境科学), 28(2), 125-130. |
| [20] | Zou RL (邹仁林) (1995) Destruction and Conservation Countermeasures of Coral Reef in China (中国珊瑚礁的现状与保护对策), pp.281-290. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn