



生物多样性 ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (10): 25234. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025234 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2025234
张奕涵1,2, 杨光1,2, 周青松1( ), 牛泽清1(
), 牛泽清1( ), 朱朝东1(
), 朱朝东1( ), 罗阿蓉1,*(
), 罗阿蓉1,*( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2025-06-18
接受日期:2025-09-20
出版日期:2025-10-20
发布日期:2025-11-21
通讯作者:
* E-mail: luoar@ioz.ac.cn基金资助:
Yihan Zhang1,2, Guang Yang1,2, Qingsong Zhou1( ), Zeqing Niu1(
), Zeqing Niu1( ), Chaodong Zhu1(
), Chaodong Zhu1( ), Arong Luo1,*(
), Arong Luo1,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2025-06-18
Accepted:2025-09-20
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-11-21
Contact:
* E-mail: luoar@ioz.ac.cnSupported by:摘要:
蜜蜂类昆虫是全球陆地生物群落的重要组成部分, 是许多农作物和野生植物的重要传粉者, 具有重要的生态和经济价值。解析蜜蜂类的系统发生关系对于揭示其起源与多样化历程具有重要意义。随着分子生物学技术与方法的发展, 利用日益丰富的基因组学数据和系统发生分析方法, 已经对蜜蜂类的谱系关系开展了较为深入的探索。尽管主要分类单元间的关系逐步明朗, 但部分关键类群的系统位置仍存在争议, 这限制了我们对蜜蜂类演化历史、生物地理格局以及功能性状演化机制的全面理解。本文概述了近年基于基因组学数据的蜜蜂类系统发生研究进展, 梳理了当前广泛应用的分子数据类型与分析方法, 并对未来蜜蜂类系统发生基因组学研究领域亟待解决的科学问题进行了展望。此外, 本文配套构建了若干可检索补充资源, 包括代表性文献概览、方法参数与支持度信息、化石证据索引等, 以提升蜜蜂类昆虫系统发生基因组学相关研究进展的透明度与信息价值。
张奕涵, 杨光, 周青松, 牛泽清, 朱朝东, 罗阿蓉 (2025) 蜜蜂类昆虫系统发生基因组学研究概况. 生物多样性, 33, 25234. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025234.
Yihan Zhang, Guang Yang, Qingsong Zhou, Zeqing Niu, Chaodong Zhu, Arong Luo (2025) A review of phylogenomic research on bees. Biodiversity Science, 33, 25234. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025234.
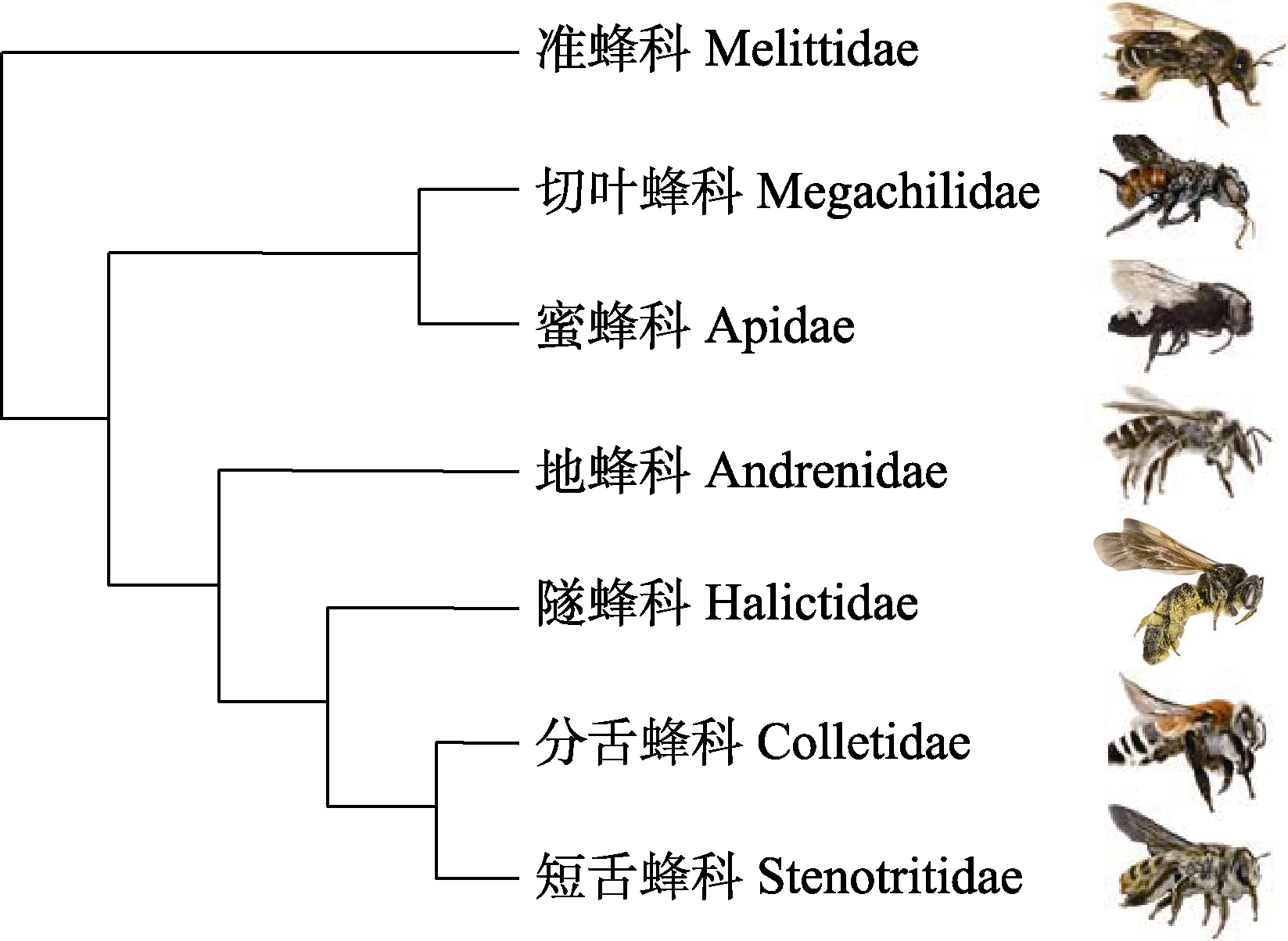
图1 蜜蜂类系统发生关系。基于Branstetter等(2017)。蜜蜂图片从上至下为Macropis europaea、Ashmeadiella xenomastax、Isepeolus wagenknechti、Alocandrena sp.、Dieunomia heteropoda、Caupolicana fulvicollis和Stenotritus pubescens, 均来自维基共享资源。
Fig. 1 Relationship between bee systems. Based on Branstetter et al (2017). Bee image from top to bottom: Macropis europaea, Ashmeadiella xenomastax, Isepeolus wagenknechti, Alocandrena sp., Dieunomia heteropoda, Caupolicana fulvicollis, Stenotritus pubescens. All from Wikimedia commons.
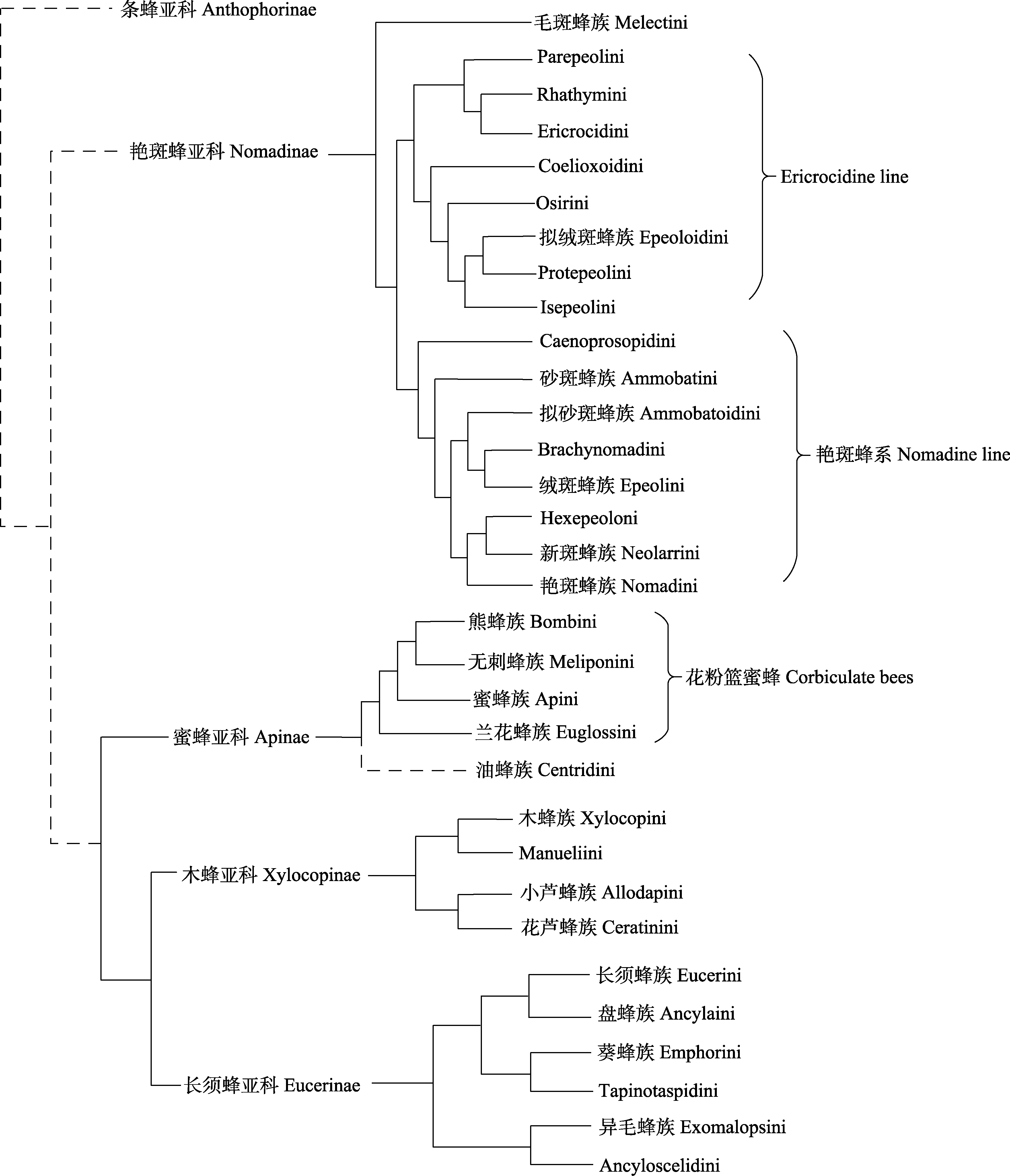
图2 基于当前研究共识的蜜蜂科主要谱系系统发生关系。其中虚线为争议类群, 详细信息见附录2。
Fig. 2 The main phylogenetic relationships of Apidae based on current research consensus. The dashed line represents the disputed relationship, detailed information can be found in Appendix 2.

图4 隧蜂科主要谱系系统发生关系。基于Henríquez- Piskulich等(2024)。※表示低支持度节点。
Fig. 4 The main phylogenetic relationships of Halictidae. Based on Henríquez-Piskulich et al (2024). The asterisk (※) indicates a low support node.
| [1] |
Aberer AJ, Kobert K, Stamatakis A (2014) ExaBayes: Massively parallel Bayesian tree inference for the whole-genome era. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 31, 2553-2556.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Almeida EAB, Bossert S, Danforth BN, Porto DS, Freitas FV, Davis CC, Murray EA, Blaimer BB, Spasojevic T, Ströher PR, Orr MC, Packer L, Brady SG, Kuhlmann M, Branstetter MG, Pie MR (2023) The evolutionary history of bees in time and space. Current Biology, 33, 3409-3422.e6.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Almeida EAB, Danforth BN (2009) Phylogeny of colletid bees (Hymenoptera: Colletidae) inferred from four nuclear genes. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 50, 290-309.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Almeida EAB, Pie MR, Brady SG, Danforth BN (2012) Biogeography and diversification of colletid bees (Hymenoptera: Colletidae): Emerging patterns from the southern end of the world. Journal of Biogeography, 39, 526-544.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Bejerano G, Pheasant M, Makunin I, Stephen S, Kent WJ, Mattick JS, Haussler D (2004) Ultraconserved elements in the human genome. Science, 304, 1321-1325.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Blaimer BB, Lloyd MW, Guillory WX, Brady SG (2016) Sequence capture and phylogenetic utility of genomic ultraconserved elements obtained from pinned insect specimens. PLoS ONE, 11, e0161531.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Bossert S, Copeland RS, Sless TJL, Branstetter MG, Gillung JP, Brady SG, Danforth BN, Policarová J, Straka J (2020) Phylogenomic and morphological reevaluation of the bee tribes Biastini, Neolarrini, and Townsendiellini (Hymenoptera: Apidae) with description of three new species of Schwarzia. Insect Systematics and Diversity, 4(6), 1-29. |
| [8] |
Bossert S, Murray EA, Almeida EAB, Brady SG, Blaimer BB, Danforth BN (2019) Combining transcriptomes and ultraconserved elements to illuminate the phylogeny of Apidae. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 130, 121-131.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Bossert S, Murray EA, Pauly A, Chernyshov K, Brady SG, Danforth BN (2021) Gene tree estimation error with ultraconserved elements: An empirical study on Pseudapis bees. Systematic Biology, 70, 803-821.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Bossert S, Wood TJ, Patiny S, Michez D, Almeida EAB, Minckley RL, Packer L, Neff JL, Copeland RS, Straka J, Pauly A, Griswold T, Brady SG, Danforth BN, Murray EA (2022) Phylogeny, biogeography and diversification of the mining bee family Andrenidae. Systematic Entomology, 47, 283-302.
DOI |
| [11] |
Bouckaert R, Heled J, Kühnert D, Vaughan T, Wu CH, Xie D, Suchard MA, Rambaut A, Drummond AJ (2014) BEAST 2: A software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Computational Biology, 10, e1003537.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Branstetter MG, Danforth BN, Pitts JP, Faircloth BC, Ward PS, Buffington ML, Gates MW, Kula RR, Brady SG (2017) Phylogenomic insights into the evolution of stinging wasps and the origins of ants and bees. Current Biology, 27, 1019-1025.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Branstetter MG, Müller A, Griswold TL, Orr MC, Zhu CD (2021) Ultraconserved element phylogenomics and biogeography of the agriculturally important mason bee subgenus Osmia (Osmia). Systematic Entomology, 46, 453-472.
DOI |
| [14] |
Cardinal S, Danforth BN (2011) The antiquity and evolutionary history of social behavior in bees. PLoS ONE, 6, e21086.
DOI URL |
| [15] | Cardinal S, Straka J, Danforth BN (2010) Comprehensive phylogeny of apid bees reveals the evolutionary origins and antiquity of cleptoparasitism. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 107, 16207-16211. |
| [16] |
Danforth BN, Brady SG, Sipes SD, Pearson A (2004) Single-copy nuclear genes recover Cretaceous-Age divergences in bees. Systematic Biology, 53, 309-326.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Danforth BN, Cardinal S, Praz C, Almeida EAB, Michez D (2013) The impact of molecular data on our understanding of bee phylogeny and evolution. Annual Review of Entomology, 58, 57-78.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Danforth BN, Eardley C, Packer L, Walker K, Pauly A, Randrianambinintsoa FJ (2008) Phylogeny of Halictidae with an emphasis on endemic African Halictinae. Apidologie, 39, 86-101.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Danforth BN, Fang J, Sipes S (2006a) Analysis of family-level relationships in bees (Hymenoptera: Apiformes) using 28S and two previously unexplored nuclear genes: CAD and RNA polymerase II. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 39, 358-372.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Danforth BN, Minckley RL, Neff JL (2019) The Solitary Bees: Biology, Evolution, Conservation. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [21] | Danforth BN, Sipes S, Fang J, Brady SG (2006b) The history of early bee diversification based on five genes plus morphology. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 103, 15118-15123. |
| [22] |
de Oliveira Andrade T, dos Santos Ramos K, López-Uribe MM, Branstetter MG, Brandão CRF, (2022) Integrative approach resolves the taxonomy of Eulaema cingulata (Hymenoptera, Apidae), an important pollinator in the Neotropics. Journal of Hymenoptera Research, 94, 247-269.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Discover Life (2024) Apoidea Species Guide. https://www.discoverlife.org/mp/20q?guide=Apoidea_species&flags=HAS. (accessed on 2024-01-07) |
| [24] |
Dodsworth S (2015) Genome skimming for next-generation biodiversity analysis. Trends in Plant Science, 20, 525-527.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Freitas FV, Branstetter MG, Casali DM, Aguiar AJC, Griswold T, Almeida EAB (2022) Phylogenomic dating and Bayesian biogeography illuminate an antitropical pattern for eucerine bees. Journal of Biogeography, 49, 1034-1047.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Freitas FV, Branstetter MG, Franceschini-Santos VH, Dorchin A, Wright KW, López-Uribe MM, Griswold T, Silveira FA, Almeida EAB (2023) UCE phylogenomics, biogeography, and classification of long-horned bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae: Eucerini), with insights on using specimens with extremely degraded DNA. Insect Systematics and Diversity, 7(4), 1-21. |
| [27] |
Freitas FV, Branstetter MG, Griswold T, Almeida EAB (2021) Partitioned gene-tree analyses and gene-based topology testing help resolve incongruence in a phylogenomic study of host-specialist bees (Apidae: Eucerinae). Molecular Biology and Evolution, 38, 1090-1100.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
Gibbs J, Brady SG, Kanda K, Danforth BN (2012) Phylogeny of halictine bees supports a shared origin of eusociality for Halictus and Lasioglossum (Apoidea: Anthophila: Halictidae). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 65, 926-939.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Gonzalez VH, Griswold T, Praz CJ, Danforth BN (2012) Phylogeny of the bee family Megachilidae (Hymenoptera: Apoidea) based on adult morphology. Systematic Entomology, 37, 261-286.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Grozinger CM, Flenniken ML (2019) Bee viruses: Ecology, pathogenicity, and impacts. Annual Review of Entomology, 64, 205-226.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
Gupta PK (2008) Single-molecule DNA sequencing technologies for future genomics research. Trends in Biotechnology, 26, 602-611.
DOI PMID |
| [32] | Haas J, Hayward A, Buer B, Maiwald F, Nebelsiek B, Glaubitz J, Bass C, Nauen R (2022) Phylogenomic and functional characterization of an evolutionary conserved cytochrome P450-based insecticide detoxification mechanism in bees. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 119, e2205850119. |
| [33] |
Hamilton CA, Lemmon AR, Lemmon EM, Bond JE (2016) Expanding anchored hybrid enrichment to resolve both deep and shallow relationships within the spider tree of life. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 16, 212.
PMID |
| [34] | Heath TA, Huelsenbeck JP, Stadler T (2014) The fossilized birth-death process for coherent calibration of divergence-time estimates. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 111, E2957-E2966. |
| [35] |
Hedtke SM, Patiny S, Danforth BN (2013) The bee tree of life: A supermatrix approach to apoid phylogeny and biogeography. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 13, 138.
DOI PMID |
| [36] |
Henríquez-Piskulich P, Hugall AF, Stuart-Fox D (2024) A supermatrix phylogeny of the world’s bees (Hymenoptera: Anthophila). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 190, 107963.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Inoue J, Donoghue PCJ, Yang ZH (2010) The impact of the representation of fossil calibrations on Bayesian estimation of species divergence times. Systematic Biology, 59, 74-89.
DOI PMID |
| [38] |
Johnson BR, Borowiec ML, Chiu JC, Lee EK, Atallah J, Ward PS (2013) Phylogenomics resolves evolutionary relationships among ants, bees, and wasps. Current Biology, 23, 2058-2062.
DOI PMID |
| [39] |
Johnson RM, Ellis MD, Mullin CA, Frazier M (2010) Pesticides and honey bee toxicity—USA. Apidologie, 41, 312-331.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Johnson RM, Mao WF, Pollock HS, Niu GD, Schuler MA, Berenbaum MR (2012) Ecologically appropriate xenobiotics induce cytochrome P450s in Apis mellifera. PLoS ONE, 7, e31051.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Kawakita A, Ascher JS, Sota T, Kato M, Roubik DW (2008) Phylogenetic analysis of the corbiculate bee tribes based on 12 nuclear protein-coding genes (Hymenoptera: Apoidea: Apidae). Apidologie, 39, 163-175.
DOI URL |
| [42] | Klein AM, Vaissière BE, Cane JH, Steffan-Dewenter I, Cunningham SA, Kremen C, Tscharntke T (2007) Importance of pollinators in changing landscapes for world crops. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 274, 303-313. |
| [43] |
Lamm KS, Redelings BD (2009) Reconstructing ancestral ranges in historical biogeography: Properties and prospects. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 47, 369-382.
DOI |
| [44] |
Landis MJ, Matzke NJ, Moore BR, Huelsenbeck JP (2013) Bayesian analysis of biogeography when the number of areas is large. Systematic Biology, 62, 789-804.
DOI PMID |
| [45] |
Lartillot N, Lepage T, Blanquart S (2009) PhyloBayes 3: A Bayesian software package for phylogenetic reconstruction and molecular dating. Bioinformatics, 25, 2286-2288.
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
Lemmon AR, Emme SA, Lemmon EM (2012) Anchored hybrid enrichment for massively high-throughput phylogenomics. Systematic Biology, 61, 727-744.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
Lepeco A, Branstetter MG, Melo GAR, Freitas FV, Tobin KB, Gan J, Jensen J, Almeida EAB (2024) Phylogenomic insights into the worldwide evolutionary relationships of the stingless bees (Apidae, Meliponini). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 201, 108219.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Lindberg J, Lundeberg J (2010) The plasticity of the mammalian transcriptome. Genomics, 95, 1-6.
DOI PMID |
| [49] | Litman JR, Danforth BN, Eardley CD, Praz CJ (2011) Why do leafcutter bees cut leaves? New insights into the early evolution of bees. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 278, 3593-3600. |
| [50] | Liu YJ, Hu HY (2021) The third generation sequencing technology and its innovation in the field of biology. Science and Technology & Innovation, (5), 34-39. (in Chinese) |
| [刘玉洁, 胡海洋 (2021) 第三代测序技术及其在生物学领域的革新. 科技与创新, (5), 34-39.] | |
| [51] |
Lukoschek V, Scott Keogh J, Avise JC (2012) Evaluating fossil calibrations for dating phylogenies in light of rates of molecular evolution: A comparison of three approaches. Systematic Biology, 61, 22-43.
DOI PMID |
| [52] |
Manjon C, Troczka BJ, Zaworra M, Beadle K, Randall E, Hertlein G, Singh KS, Zimmer CT, Homem RA, Lueke B, Reid R, Kor L, Kohler M, Benting J, Williamson MS, Davies Emyr TG, Field LM, Bass C, Nauen R (2018) Unravelling the molecular determinants of bee sensitivity to neonicotinoid insecticides. Current Biology, 28, 1137-1143.e5.
DOI PMID |
| [53] | Matzke NJ (2018) BioGeoBEARS: BioGeography with Bayesian (and likelihood) Evolutionary Analysis with R Scripts (v1.1.1). https://zenodo.org/record/1478250. (accessed on 2025-09-09) |
| [54] |
Michener CD (1979) Biogeography of the bees. Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden, 66, 277-347.
DOI URL |
| [55] | Michener CD (2007) The Bees of the World, 2nd edn. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore. |
| [56] |
Michez D, Patiny S, Danforth BN (2009) Phylogeny of the bee family Melittidae (Hymenoptera: Anthophila) based on combined molecular and morphological data. Systematic Entomology, 34, 574-597.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Miller DL, Smith EA, Newton ILG (2021) A bacterial symbiont protects honey bees from fungal disease. mBio, 12, e0050321.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Minckley RL, Danforth BN (2019) Sources and frequency of brood loss in solitary bees. Apidologie, 50, 515-525.
DOI |
| [59] |
Minh BQ, Schmidt HA, Chernomor O, Schrempf D, Woodhams MD, von Haeseler A, Lanfear R (2020) IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 37, 1530-1534.
DOI PMID |
| [60] |
Near TJ, Sanderson MJ (2004) Assessing the quality of molecular divergence time estimates by fossil calibrations and fossil-based model selection. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 359, 1477-1483.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
Odanaka KA, Branstetter MG, Tobin KB, Rehan SM (2022) Phylogenomics and historical biogeography of the cleptoparasitic bee genus Nomada (Hymenoptera: Apidae) using ultraconserved elements. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 170, 107453.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
Ohl M, Bleidorn C (2006) The phylogenetic position of the enigmatic wasp family Heterogynaidae based on molecular data, with description of a new, nocturnal species (Hymenoptera: Apoidea). Systematic Entomology, 31, 321-337.
DOI URL |
| [63] | Orr MC, Branstetter MG, Straka J, Yuan F, Leijs R, Zhang D, Zhou Q, Zhu CD (2022) Phylogenomic interrogation revives an overlooked hypothesis for the early evolution of the bee family Apidae (Hymenoptera: Apoidea), with a focus on the subfamily Anthophorinae. Insect Systematics and Diversity, 6(4), 1-15. |
| [64] |
Ozsolak F, Milos PM (2011) RNA sequencing: Advances, challenges and opportunities. Nature Reviews Genetics, 12, 87-98.
DOI PMID |
| [65] |
Parham JF, Donoghue PCJ, Bell CJ, Calway TD, Head JJ, Holroyd PA, Inoue JG, Irmis RB, Joyce WG, Ksepka DT, Patané JSL, Smith ND, Tarver JE, van Tuinen M, Yang ZH, Angielczyk KD, Greenwood JM, Hipsley CA, Jacobs L, Makovicky PJ, Müller J, Smith KT, Theodor JM, Warnock RCM, Benton MJ (2012) Best practices for justifying fossil calibrations. Systematic Biology, 61, 346-359.
DOI PMID |
| [66] | Pesenko YA (1999) Phylogeny and classification of the family Halictidae revised (Hymenoptera: Apoidea). Journal of the Kansas Entomological Society, 72, 104-123. |
| [67] |
Peters RS, Krogmann L, Mayer C, Donath A, Gunkel S, Meusemann K, Kozlov A, Podsiadlowski L, Petersen M, Lanfear R, Diez PA, Heraty J, Kjer KM, Klopfstein S, Meier R, Polidori C, Schmitt T, Liu SL, Zhou X, Wappler T, Rust J, Misof B, Niehuis O (2017) Evolutionary history of the Hymenoptera. Current Biology, 27, 1013-1018.
DOI PMID |
| [68] |
Pisanty G, Richter R, Martin T, Dettman J, Cardinal S (2022) Molecular phylogeny, historical biogeography and revised classification of andrenine bees (Hymenoptera: Andrenidae). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 170, 107151.
DOI URL |
| [69] | Porto DS, Almeida EAB (2021) Corbiculate bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae): Exploring the limits of morphological data to solve a hard phylogenetic problem. Insect Systematics and Diversity, 5, 1-40. |
| [70] |
Potts SG, Imperatriz-Fonseca V, Ngo HT, Aizen MA, Biesmeijer JC, Breeze TD, Dicks LV, Garibaldi LA, Hill R, Settele J, Vanbergen AJ (2016) Safeguarding pollinators and their values to human well-being. Nature, 540, 220-229.
DOI |
| [71] |
Prum RO, Berv JS, Dornburg A, Field DJ, Townsend JP, Lemmon EM, Lemmon AR (2015) A comprehensive phylogeny of birds (Aves) using targeted next-generation DNA sequencing. Nature, 526, 569-573.
DOI |
| [72] |
Ree RH, Smith SA (2008) Maximum likelihood inference of geographic range evolution by dispersal, local extinction, and cladogenesis. Systematic Biology, 57, 4-14.
DOI PMID |
| [73] |
Riddle BR, Dawson MN, Hadly EA, Hafner DJ, Hickerson MJ, Mantooth SJ, Yoder AD (2008) The role of molecular genetics in sculpting the future of integrative biogeography. Progress in Physical Geography: Earth and Environment, 32, 173-202.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
Roig-Alsina A, Michener CD (1993) Studies of the phylogeny and classification of long-tongued bees (Hymenoptera: Apoidea). University of Kansas Science Bulletin, 55, 123-162.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
Romiguier J, Cameron SA, Woodard SH, Fischman BJ, Keller L, Praz CJ (2016) Phylogenomics controlling for base compositional bias reveals a single origin of eusociality in corbiculate bees. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33, 670-678.
DOI PMID |
| [76] |
Ronquist F (1997) Dispersal-vicariance analysis: A new approach to the quantification of historical biogeography. Systematic Biology, 46, 195-203.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
Rozen JG (2003) Eggs, ovariole numbers, and modes of parasitism of cleptoparasitic bees, with emphasis on neotropical species (Hymenoptera: Apoidea). American Museum Novitates, 3413, 1-36.
DOI URL |
| [78] | Sandoval-Arango S, Branstetter MG, Cardoso CF, López-Uribe MM (2023) Phylogenomics reveals within species diversification but incongruence with color phenotypes in widespread orchid bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae: Euglossini). Insect Systematics and Diversity, 7, 1. |
| [79] | Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 74, 5463-5467. |
| [80] |
Sann M, Niehuis O, Peters RS, Mayer C, Kozlov A, Podsiadlowski L, Bank S, Meusemann K, Misof B, Bleidorn C, Ohl M (2018) Phylogenomic analysis of Apoidea sheds new light on the sister group of bees. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 18, 71.
DOI PMID |
| [81] |
Sless TJL, Branstetter MG, Gillung JP, Krichilsky EA, Tobin KB, Straka J, Rozen JG Jr, Freitas FV, Martins AC, Bossert S, Searle JB, Danforth BN (2022) Phylogenetic relationships and the evolution of host preferences in the largest clade of brood parasitic bees (Apidae: Nomadinae). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 166, 107326.
DOI URL |
| [82] |
Stamatakis A (2014) RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics, 30, 1312-1313.
DOI PMID |
| [83] | Torto B, Boucias DG, Arbogast RT, Tumlinson JH, Teal PEA (2007) Multitrophic interaction facilitates parasite-host relationship between an invasive beetle and the honey bee. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 104, 8374-8378. |
| [84] | Wen J, Egan AN, Dikow RB, Zimmer EA (2015) Utility of transcriptome sequencing for phylogenetic inference and character evolution. In: Next-Generation Sequencing in Plant Systematics (eds Hörandl E, Appelhans MS), p. 2. Koeltz Scientific Books, Deutchland. |
| [85] | Wilson EO, Hölldobler B (2005) Eusociality: Origin and consequences. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 102, 13367-13371. |
| [86] |
Wood TJ, Patiny S, Bossert S (2022) An unexpected new genus of panurgine bees (Hymenoptera, Andrenidae) from Europe discovered after phylogenomic analysis. Journal of Hymenoptera Research, 89, 183-210.
DOI URL |
| [87] | Wu YR (2000) Fauna of China∙Insecta (Vol. 20): Hymenoptera∙Melittidae, Apidae. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [吴燕如 (2000) 中国动物志∙昆虫纲(第二十卷): 膜翅目∙准蜂科, 蜜蜂科. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [88] | Wu YR (2006) Fauna of China∙Insecta (Vol. 44): Hymenoptera∙Megachilidae. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [吴燕如 (2006) 中国动物志∙昆虫纲(第四十四卷): 膜翅目∙切叶蜂科. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [89] |
Yang ZH (2007) PAML 4: Phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24, 1586-1591.
DOI PMID |
| [90] |
Yu Y, Harris AJ, Blair C, He XJ (2020) RASP 4: Ancestral state reconstruction tool for multiple genes and characters. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 37, 604-606.
DOI PMID |
| [91] |
Zhang C, Rabiee M, Sayyari E, Mirarab S (2018) ASTRAL-III: Polynomial time species tree reconstruction from partially resolved gene trees. BMC Bioinformatics, 19, 153.
DOI PMID |
| [92] |
Zhang D, Niu ZQ, Luo AR, Orr MC, Ferrari RR, Jin JF, Wu QT, Zhang F, Zhu CD (2022) Testing the systematic status of Homalictus and Rostrohalictus with weakened cross-vein groups within Halictini (Hymenoptera: Halictidae) using low-coverage whole-genome sequencing. Insect Science, 29, 1819-1833.
DOI URL |
| [93] | Zhang DF, Ma QY, Yin TM, Xia T (2013) The third generation sequencing technology and its application. China Biotechnology, 33(5), 125-131. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张得芳, 马秋月, 尹佟明, 夏涛 (2013) 第三代测序技术及其应用. 中国生物工程杂志, 33(5), 125-131.] | |
| [94] |
Zhang YM, Bossert S, Spasojevic T (2025) Evolving perspectives in Hymenoptera systematics: Bridging fossils and genomes across time. Systematic Entomology, 50, 1-31.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 余德菊, 何云雲, 曹敏, 王刚, 杨洁. 基于代谢组学与转录组学技术的热带森林树种共存机制研究——以榕属植物为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(7): 24475-. |
| [2] | 罗敏, 杨永川, 靳程, 周礼华, 龙宇潇. 重庆中心城区城市森林兽类组成特征及其对人类活动的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24402-. |
| [3] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [4] | 靳川, 张子嘉, 底凯, 张卫荣, 乔栋, 程思源, 胡中民. 海南热带雨林植物光合荧光气体交换和叶功能性状数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24139-. |
| [5] | 李艳朋, 盘李军, 陈洁, 许涵, 杨立新. 亚热带人工混交林叶功能性状对森林演替的响应规律及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24049-. |
| [6] | 任嘉隆, 王永珍, 冯怡琳, 赵文智, 严祺涵, 秦畅, 方静, 辛未冬, 刘继亮. 基于陷阱法采集的河西走廊戈壁荒漠甲虫数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23375-. |
| [7] | 冯嘉谊, 练琚愉, 冯瑜莙, 张东旭, 曹洪麟, 叶万辉. 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林群落垂直分层对群落结构及功能的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24306-. |
| [8] | 薛玉洁, 程安鹏, 李珊, 刘晓娟, 李景文. 亚热带森林中环境和物种多样性对灌木存活的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22443-. |
| [9] | 罗彩访, 杨涛, 张秋雨, 王馨培, 沈泽昊. 滇中半湿润常绿阔叶林木本植物的功能特征和功能多样性及其影响因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23215-. |
| [10] | 王健铭, 曲梦君, 王寅, 冯益明, 吴波, 卢琦, 何念鹏, 李景文. 青藏高原北部戈壁植物群落物种、功能与系统发育β多样性分布格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 21503-. |
| [11] | 罗恬, 俞方圆, 练琚愉, 王俊杰, 申健, 吴志峰, 叶万辉. 冠层垂直高度对植物叶片功能性状的影响: 以鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21414-. |
| [12] | 付飞, 魏慧玉, 常育腾, 王备新, 陈凯. 澜沧江中游水生昆虫生活史和生态学性状多样性的海拔格局: 气候和土地利用的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21332-. |
| [13] | 林永一, 王永珍, 冯怡琳, 赵文智, 高俊伟, 刘继亮. 河西走廊中部戈壁地表甲虫群落动态变化及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22343-. |
| [14] | 雍青措姆, 习新强, 牛克昌. 高寒草甸植物物种丧失对草原毛虫的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22069-. |
| [15] | 高程, 郭良栋. 微生物物种多样性、群落构建与功能性状研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22429-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn